Flow Injection Analysis with Microdialysis Probes Enable Minimally Invasive and Dynamic H2O2 Measurements †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
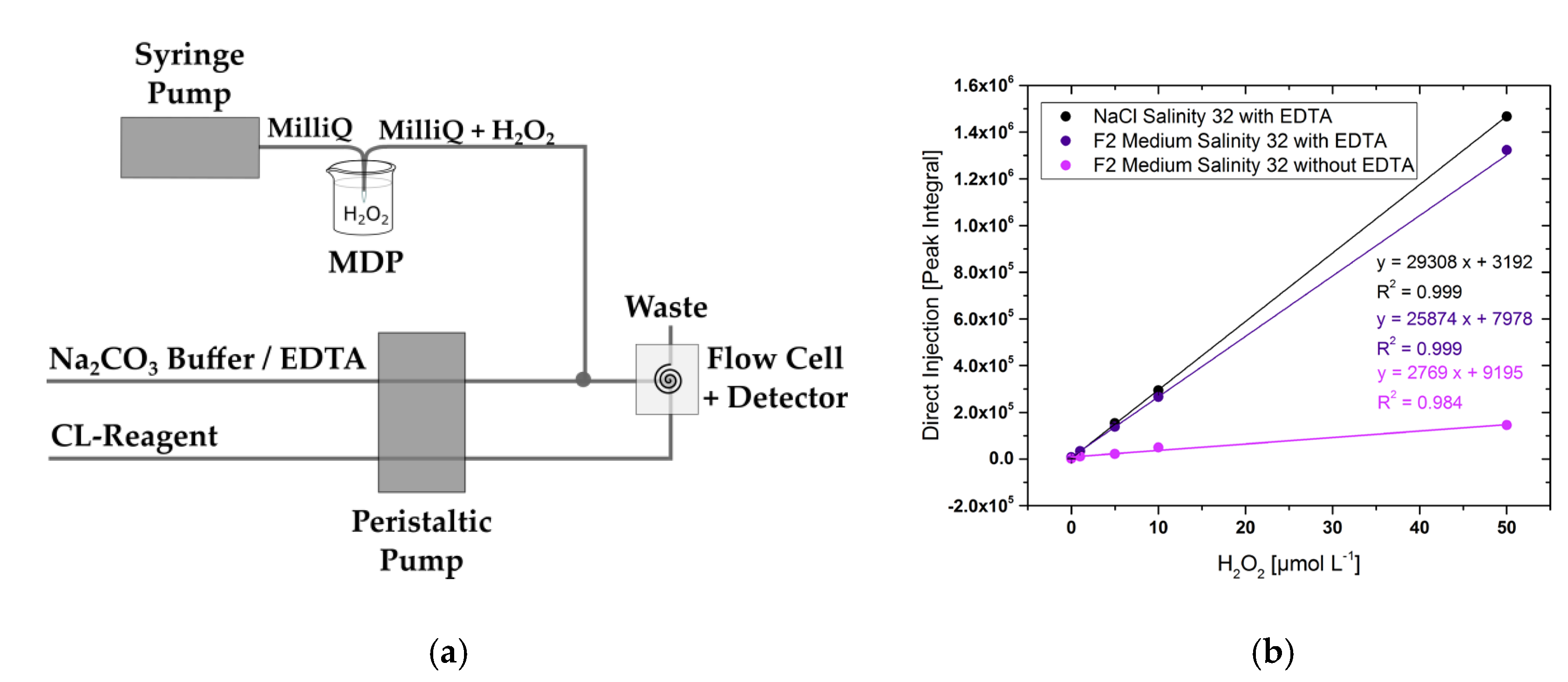
3.1. Set-Up and Calibration with and without EDTA
3.2. Microwave and Agar Effects on H2O2 Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moßhammer, M.; Kühl, M.; Koren, K. Possibilities and Challenges for Quantitative Optical Sensing of Hydrogen Peroxide. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moßhammer, M.; Schrameyer, V.; Peter, Ø.; Koren, K.; Kühl, M. Extracellular Hydrogen Peroxide Measurements Using a Flow Injection System in Combination with Microdialysis Probes—Potential and Challenges. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.W.; Cooper, W.J.; Rusak, S.A.; Peake, B.M.; Kiddle, J.J.; Sullivan, D.W.O.; Melamed, M.L.; Morgan, C.R.; Theberge, S.M. Flow Injection Analysis of H2O2 in Natural Waters Using Acridinium Ester Chemiluminescence: Method Development and Optimization Using a Kinetic Model. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4169–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.W.; Morgan, C.A.; Kieber, D.J.; King, D.W.; Snow, J.A.; Heikes, B.G.; Mopper, K.; Kiddle, J.J. Hydrogen peroxide method intercomparison study in seawater. Mar. Chem. 2005, 97, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Kawasaki, K.; Daimon, S.; Kitagawa, W.; Yamamoto, K.; Tamaki, H.; Tanaka, M.; Nakatsu, C.H.; Kamagata, Y. A hidden pitfall in the preparation of agar media undermines microorganism cultivability. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7659–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moßhammer, M.; Koren, K.; Kühl, M. Flow Injection Analysis with Microdialysis Probes Enable Minimally Invasive and Dynamic H2O2 Measurements. Proceedings 2018, 2, 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130992
Moßhammer M, Koren K, Kühl M. Flow Injection Analysis with Microdialysis Probes Enable Minimally Invasive and Dynamic H2O2 Measurements. Proceedings. 2018; 2(13):992. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130992
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoßhammer, Maria, Klaus Koren, and Michael Kühl. 2018. "Flow Injection Analysis with Microdialysis Probes Enable Minimally Invasive and Dynamic H2O2 Measurements" Proceedings 2, no. 13: 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130992
APA StyleMoßhammer, M., Koren, K., & Kühl, M. (2018). Flow Injection Analysis with Microdialysis Probes Enable Minimally Invasive and Dynamic H2O2 Measurements. Proceedings, 2(13), 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130992



