Development of Thin Shear Force Sensor Aimed at Improving QOL for Persons with Disabilities †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
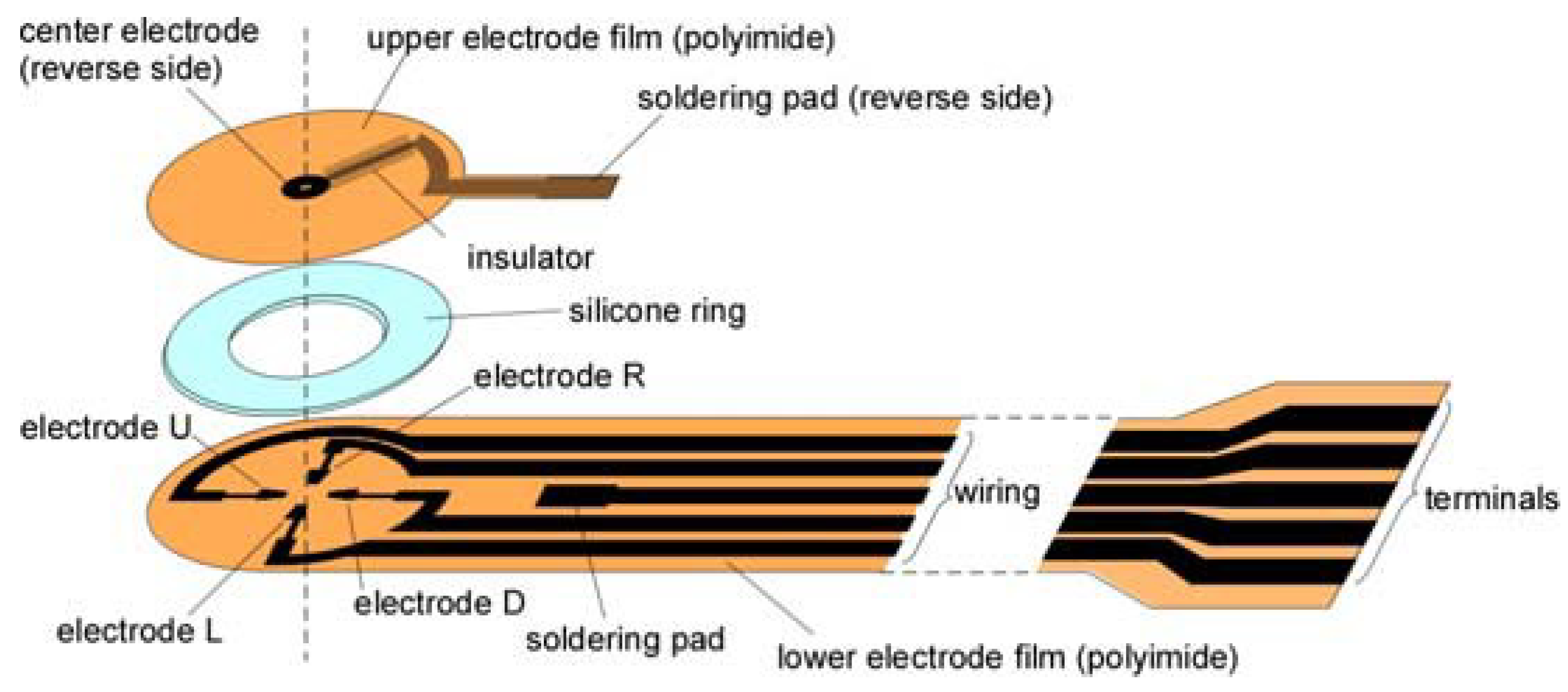
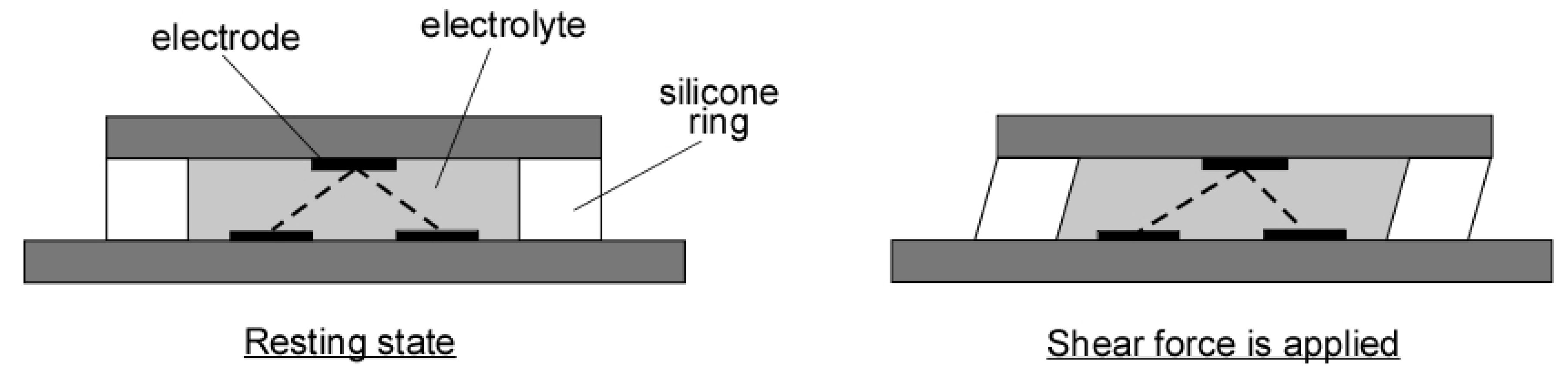
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
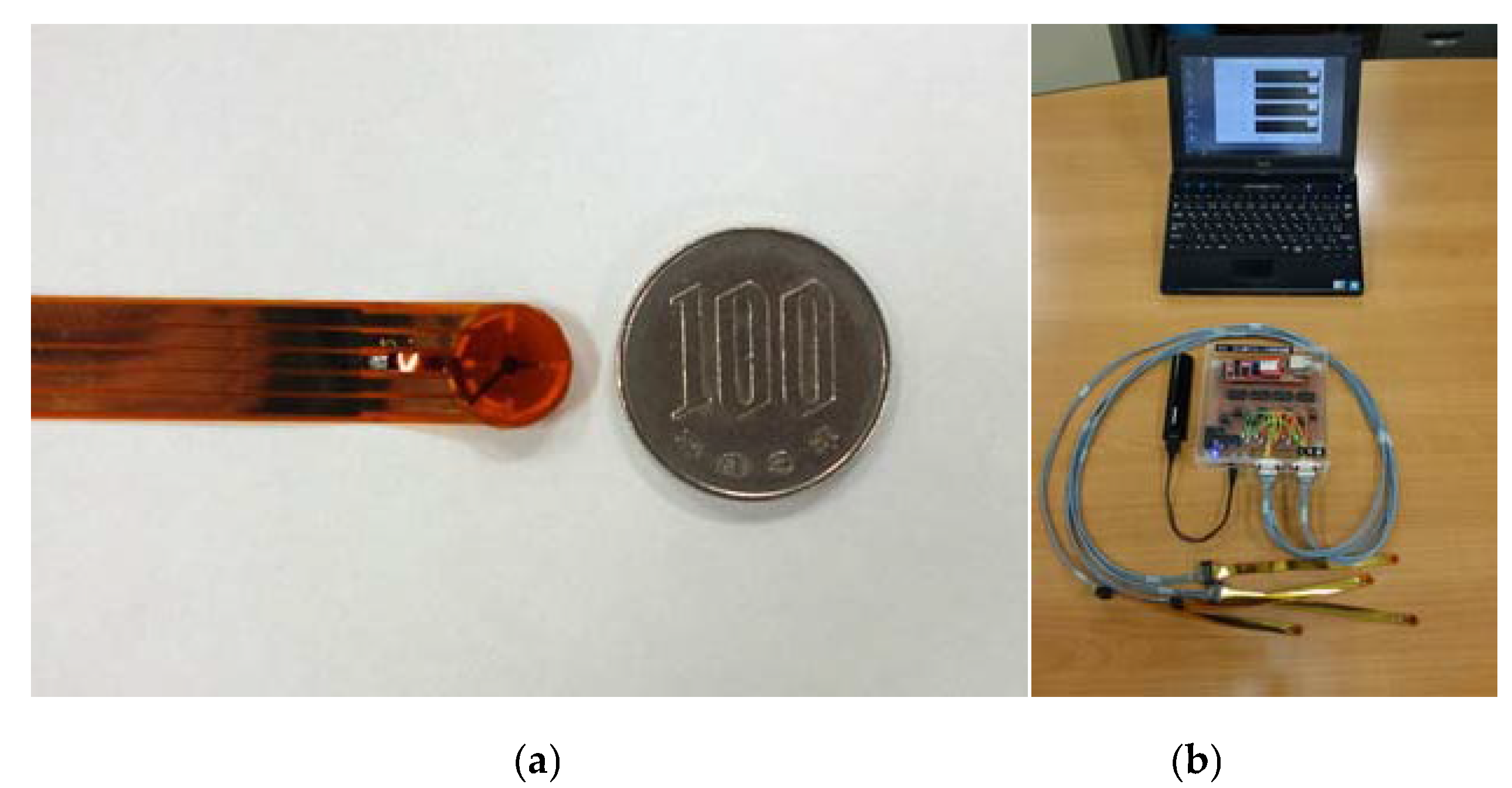
3.1. Sensor and Its Performance
3.2. Application Example
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanders, J.E.; Daly, C.H. Normal and shear stresses on a residual limb in a prosthetic socket during ambulation: Comparison of finite element results with experimental measurements. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1993, 30, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinsdale, S. Decubitus ulcers: Role of pressure and friction in causation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1974, 55, 147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bennett, L.; Kavner, D.; Lee, B.; Trainor, F. Shear vs. pressure as causative factors in skin blood flow occlusion. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1979, 60, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reichel, S.M. Shearing force as a factor in decubitus ulcers in paraplegics. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1958, 166, 762–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyama, S.; Utsumi, S.; Nakamura, T.; Noguchi, T.; Yoshida, Y. A novel thin shear-stress sensor using electrolyte as a conductive element. Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Shirogane, S.; Nakamura, T.; Umino, T.; Uehara, R.; Okamoto, T.; Igarashi, H. Development of wearable sheet-type shear force sensor and measurement system that is insusceptible to temperature and pressure. Sensors 2017, 17, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; Hara, K. Simple fabrication method to produce flexible electrode capable of soldering. Sens. Mater. 2013, 28, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toyama, S.; Shirogane, S.; Nakamura, T.; Watanabe, K.; Hara, K. Development of Thin Shear Force Sensor Aimed at Improving QOL for Persons with Disabilities. Proceedings 2018, 2, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130704
Toyama S, Shirogane S, Nakamura T, Watanabe K, Hara K. Development of Thin Shear Force Sensor Aimed at Improving QOL for Persons with Disabilities. Proceedings. 2018; 2(13):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130704
Chicago/Turabian StyleToyama, Shigeru, Satoshi Shirogane, Takashi Nakamura, Kenta Watanabe, and Kazuhiro Hara. 2018. "Development of Thin Shear Force Sensor Aimed at Improving QOL for Persons with Disabilities" Proceedings 2, no. 13: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130704
APA StyleToyama, S., Shirogane, S., Nakamura, T., Watanabe, K., & Hara, K. (2018). Development of Thin Shear Force Sensor Aimed at Improving QOL for Persons with Disabilities. Proceedings, 2(13), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130704



