Abstract
The impact of agricultural land use on the composition of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and its effects on the aquatic carbon cycle are still largely unknown. A sensor for dissolved DOM in stream ecosystems based on fluorescence measurement was developed. It’s an easy to use handheld optical system for online monitoring of DOM under field-conditions. For the determination of DOM two indices are used, namely the freshness index (BIX) and the fluorescence index (FIX).
Keywords:
DOM; fluorescence sensor; BIX; FIX; freshness index; fluorescence index; stream ecosystems; agriculture 1. Introduction
Agriculture is the dominant land use form in Lower Austria, covering more than 46% of the total area. Agriculture delivers significant amounts of dissolved organic matter (DOM) to stream ecosystems, changing basic metabolic processes at the water-sediment interface and affecting the ecological state and the health of the aquatic systems [1,2]. The amount and composition of terrestrial DOM influence benthic microbial growth and respiration as well as CO2 outgassing from streams. However, the impact of agricultural land use on the composition of DOM and its effects on the aquatic carbon cycle are still largely unknown [3]. The current study focuses on the DOM composition of various water sources (surface runoff, soil pore water, drainage water) in response to different types of agricultural land use and practices (e.g., fertilization, tillage) and its effects on benthic microbial processes in stream ecosystems. DOM is a mixture of various compounds of different molecular weights, ranging from simple carbohydrates to complex aromatic molecules [4]. Due to light absorbing chromophores and fluorescent fluorophores, DOM has distinctive spectrophotometric properties in terms of both absorption and fluorescence [5,6]. UV-visible (200–800 nm) optical properties of DOM have been used successfully to determine DOM characteristics such as aromaticity (SUVA254—specific ultraviolet absorbance at 254 nm) and molecular size. Recent advances in fluorescent spectrophotometry have provided a new tool for rapidly identifying DOM fluorophores via excitation–emission matrices (EEM; wavelengths 200—500 nm [7]). An EEM reveals fluorescence centers that are attributed to various DOM components, such as humic-, fulvic- or protein-like fluorophores [5]. Thus, fluorescence can be used to identify anthropogenic DOM sources in streams [6] and to distinguish bioavailable from refractory DOM components, which determine microbial activity and organic matter processing [7].
So far, real-time fluorescence data have mostly been obtained from seawater, while stream studies have been based on DOM analyses in the lab [7]. However, DOM quality can change rapidly due to microbial processing of labile compounds or exposition to sunlight during transport and handling [2], which affects data quality. Real-time fluorescence sensors deliver DOM data in high spatial and temporal resolution without such interferences [8] and, thus, allow for tracing changes in DOM composition over time in response to diurnal patterns in bacterial and algal production, fluctuations in DOM input, or storm events. Besides, real-time monitoring will enable scientists to continuously monitor DOM changes in response to microbial degradation during incubation experiments.
2. Sensor for Dissolved Organic Matter
The lab devices for measuring DOM are unhandy, heavy and cannot be used in open field. The sensor principle is based on fluorescence spectroscopy. To avoid scanning the full spectrum of the sample, different spectroscopic indices for determining DOM in aquatic systems were analyzed. Two prominent indices were considered, namely the freshness index (BIX) and the fluorescence index (FIX). These indices are ratios and, therefore, the main interfering parameter (amount of dissolved organic carbon DOC) can be compensated. Additionally, the chosen indices are robust against different concentration levels of DOM and both have similar tendencies. The BIX shows much more clearly whether it comes to a microbial burden than the FIX. However, the FIX is more robust against wrong handling.
The measurement system consists of several LEDs, which excite fluorescence emission from the water probe. The fluorescence light is filtered at the peak emission wavelength using different optical filters which are fixed on a filter wheel for easy switching. The excitation light for the BIX index is generated by a 310 nm UV LED and spectrally narrowband filtered. For the calculation of the BIX index, the fluorescence emission was measured at wavelength 380 nm and 430 nm by adjusting the filter wheel on the right position and subsequent amplification by a high gain photo multiplier (PMT). To avoid any influence of surrounding stray light on the detector signal, the light source is pulsed and the photomultiplier output signal is phase synchronously amplified by a lock-in amplifier. The measurement of the FIX index is based on the same principle. For this purpose, a 370 nm UV LED and two optical filters at 450 nm and 500 nm are used. Figure 1 shows the 3D printed prototype of the measurement chamber and the filter wheel.
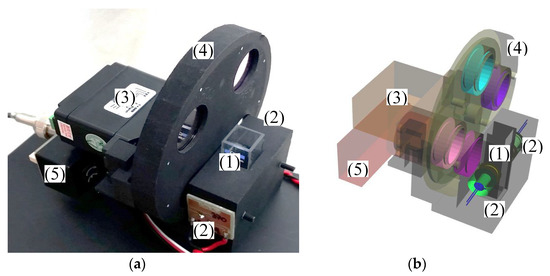
Figure 1.
(a) 3D printed prototype of the measurement chamber with cuvette (1), LED’s (2), servo (3) for rotating the optical filter wheel (4) and the photomultiplier (5). (b) CAD view of the measurement chamber.
Figure 2 shows the complete sensor system. For outdoor use the sensor is placed in a water-proof suitcase. A rechargeable battery powers the system. To perform a measurement, the sample has to be placed into the measurement chamber and the “Measure” Button on the touch screen has to be pressed. For online monitoring a flow cuvette in combination with an external pumping system can be used. An integrated GPS-module gives the opportunity to save the location of the measurement. The measured data will be saved on a SD Card and can be read out via the display, Bluetooth or WIFI.
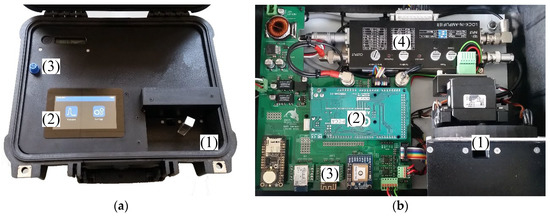
Figure 2.
(a) Hardware of the sensor prototype with measurement chamber (1), processor board (2), wireless modules (GPS, WIFI, BT) (3) and the lock-in amplifier (4). (b) Sensor system ready to use with measurement chamber (1), Touch Display (2) and external power connector (3).
Different concentrations of the fluorophore DPH (1,6-Diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene; ranging from nM to 10 nM) dissolved in cyclohexane were measured with the presented sensor. The results show the good sensitivity and functionality of our system (Figure 3). The next step is the installation of the sensor at the Hydrological Open Air Laboratory (HOAL) in Petzenkirchen (Austria) [9] for online measurements.
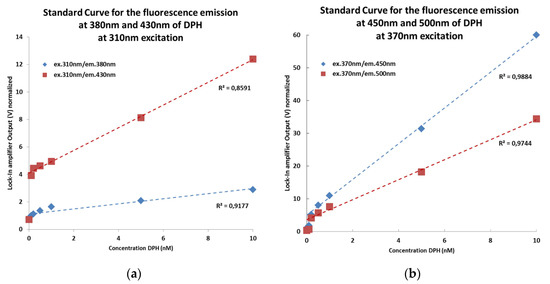
Figure 3.
(a) Standard Curve of the sensor system with DPH in cyclohexane for the fluorescence emission at 380 nm and 430 nm at 310 nm excitation (BIX analysis). (b) Standard Curve of the sensor system with DPH solved in cyclohexane for the fluorescence emission at 450 nm and 500 nm at 370 nm excitation (FIX analysis).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the NÖ Forschungs- und Bildungsges.m.b.H. (NFB) for financially supporting the project (SC15-002).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Eder, A.; Blöschl, G.; Feichtinger, F. Indirect nitrogen losses of managed soils contributing to greenhouse emissions of agricultural areas in Austria: Results from lysimeter studies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2015, 101, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasching, Ch.; Battin, T.J. Exposure of dissolved organic matter to UV-radiation increases bacterial growth efficiency in a clear-water Alpine stream and its adjacent groundwater. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 74, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.F.; Xenopoulos, M.A. Effects of agricultural land use on the composition of fluvial dissolved organic matter. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, D.; Gelbert, J.; Pusch, M.T. Agriculture has changed the amount and composition of dissolved organic matter in Central European headwater streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.; Inverarity, R.; Charlton, M. Detecting river pollution using fluorescence spectrophotometry: Case studies from the Ouseburn, NE England. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 124, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, N.; Baker, A.; Reynolds, D. Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural, waste, and polluted waters-a review. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobble, P.G.; Lead, J.; Baker, A. Aquatic Organic Matter Fluorescence; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brandl, M.; Kellner, K.; Posnicek, T.; Bado, I.; Falkenhagen, D. Spectroscopic Hemoglobin and Bilirubin Measurement on Optically Opaque Particulate Fluids. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Blaschke, A.P.; Broer, M.; Bucher, C.; Carr, G.; Chen, X.; Eder, A.; Exner-Kittridge, M.; Farnleitner, A.; Flores-Orozco, A.; et al. The Hydrological Open Air laboratory (HOAL) in Petzenkirchen: A hypothesis-driven observatory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).