Detecting Discontinuities in the Distribution of Earnings Around Zero as an Indication of Earnings Management †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Earnings Management in Healthcare
2.2. The Greek Healthcare Sector
3. Conceptual Framework and Hypothesis Development
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample
4.2. Method
5. Empirical Findings
5.1. Descriptives
5.2. Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caperchione, E.; Cohen, S.; Rossi, F.; Brusca, I. Benefits of Accrual Accounting in the Public Sector; Centre for Financial Reporting Reform (CFRR): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Arnaboldi, M.; Lapsley, I. On the implementation of accrual accounting: A study of conflict and ambiguity. Eur. Account. Rev. 2009, 18, 809–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Mayes, S. Transition to accrual accounting. Tech. Notes Man. 2009, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, V.; Torres, L.; Yetano, A. Accrual accounting in EU local governments: One method, several approaches. Eur. Account. Rev. 2009, 18, 765–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, C.; Hyndman, N. The actual implementation of accruals accounting. Account. Audit. Account. J. 2006, 19, 272–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caperchione, E.; Mussari, R. Comparative Issues in Local Government Accounting; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pilcher, R.; Van Der Zahn, M. Local governments, unexpected depreciation and financial performance adjustment. Financ. Account. Manag. 2010, 26, 299–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, M.; Donatella, P. Earnings management in public-sector organizations: A structured literature review. J. Public Budg. Account. Financ. Manag. 2021, 34, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Carvalho, J.; Pinho, F. Political competition as a motivation for earnings management close to zero: The case of Portuguese municipalities. J. Public Budg. Account. Financ. Manag. 2020, 32, 461–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Carvalho, J.; Pinho, F. Earnings management around zero: A motivation to local politician signalling competence. Public Manag. Rev. 2013, 15, 657–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.W. Opportunistic financial reporting around municipal bond issues. Rev. Account. Stud. 2018, 23, 785–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Bisogno, M.; Malkogianni, I. Earnings management in local governments: The role of political factors. J. Appl. Account. Res. 2019, 20, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Malkogianni, I. Sustainability measures and earnings management: Evidence from Greek municipalities. J. Public Budg. Account. Financ. Manag. 2021, 33, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkogianni, I. Earnings management detection through budget execution. Insights from Greek municipalities. J. Public Budg. Account. Financ. Manag. 2024, 36, 320–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.J.; Van Horn, R.L. How do nonprofit hospitals manage earnings? J. Health Econ. 2005, 24, 815–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballantine, J.; Forker, J.; Greenwood, M. Earnings management in English NHS hospital trusts. Financ. Account. Manag. 2007, 23, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldenburg, L.G.; Gunny, K.A.; Hee, K.W.; Soderstrom, N. Earnings management using real activities: Evidence from nonprofit hospitals. Account. Rev. 2011, 86, 1605–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansant, B. Institutional pressures to provide social benefits and the earnings management behavior of nonprofits: Evidence from the U.S. hospital industry. Contemp. Account. Res. 2015, 33, 1576–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heese, J. The role of overbilling in hospitals’ earnings management decisions. Eur. Account. Rev. 2018, 27, 875–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Noikokyris, E.; Fabiano, G.; Favato, G. Manipulation of profits in Italian publicly-funded healthcare trusts. Public Money Manag. 2019, 39, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulou, S.C.; Stavropoulou, C. Earnings management in public healthcare organizations: The case of the English NHS hospitals. Public Money Manag. 2021, 43, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkogianni, I.; Cohen, S. Earnings management in public hospitals: The case of Greek state-owned hospitals. Public Money Manag. 2022, 42, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahr, H. An improved test for earnings management using kernel density estimation. Eur. Account. Rev. 2014, 23, 559–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, P.M.; Wahlen, J.M. A review of the earnings management literature and its implications for standard setting. Account. Horiz. 1999, 13, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgstahler, D.; Dichev, I. Earnings management to avoid earnings decreases and losses. J. Account. Econ. 1997, 24, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechow, P.M.; Dichev, I.D. The quality of accruals and earnings: The role of accrual estimation errors. Account. Rev. 2002, 77, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, C.; Kaitelidou, D.; Karanikolos, M.; Maresso, A.; World Health Organization. Greece: Health System Review; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- OECD; European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies. Greece: Country Health Profile 2023; OECD: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- PD 146/2003; Defining the Content and the Time of Implementing the Sectoral Accounting in the Public Health Units. WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- Lazari, E. Benchmarking the financial figures and results of public hospitals for the period 2013–2015, based on their published financial statements. Bim. Sci. Inf. J. HHSMA 2017, 28. (in Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Economou, C.; Kaitelidou, D.; Kentikelenis, A.; Maresso, A.; Sissouras, A. The impact of the crisis on the health system and health in Greece. In Economic Crisis, Health Systems and Health in Europe: Country Experience [Internet]; European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kalavrezou, N.; Jin, H. Health Care Reform in Greece: Progress and Reform Priorities; International Monetary Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Health at a Glance 2023; OECD: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M.C.; Meckling, W.H. Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. J. Financ. Econ. 1976, 3, 305–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, J.; Dietrich, M.; Laughlin, R. The development of principal–agent, contracting and accountability relationships in the public sector: Conceptual and cultural problems. Crit. Perspect. Account. 1996, 7, 259–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B. Kernel density estimation technique for statistics and data analysis. In Monographs on Statistics and Applied Probability; Routledge: London, UK, 1986; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Burgstahler, D.; Chuk, E. What have we learned about earnings management? Integrating discontinuity evidence. Contemp. Account. Res. 2017, 34, 726–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNichols, M.F. Research design issues in earnings management studies. J. Account. Public Policy 2000, 19, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
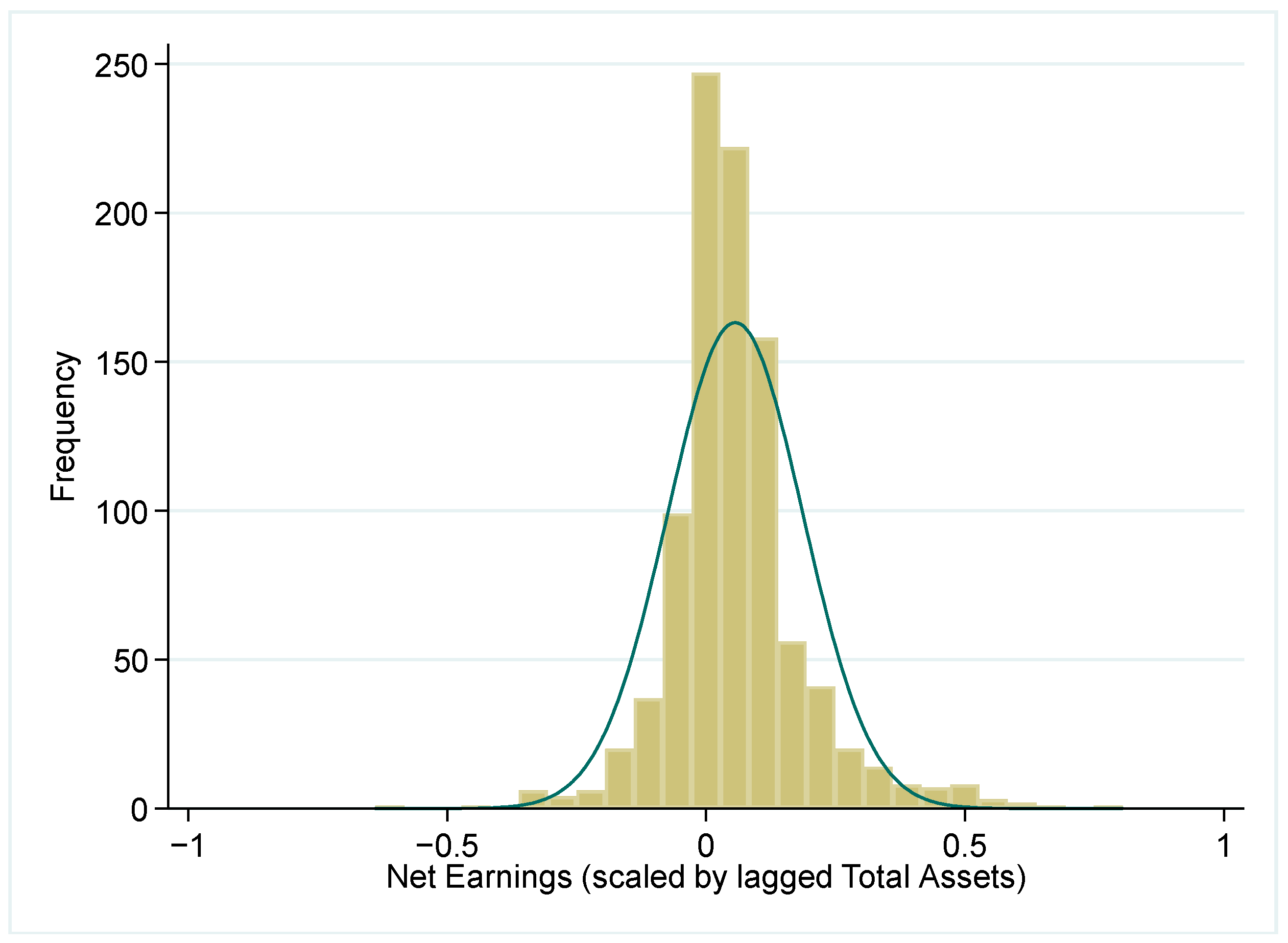
| Mean | p50 | sd | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net earnings (scaled by lagged Total assets) | 0.0617 | 0.0558 | 0.1084 | −0.2736 | 0.5090 |
| Total assets | 92,000,000 | 61,700,000 | 98,600,000 | 793,024 | 612,000,000 |
| Operating income | 43,200,000 | 32,400,000 | 40,400,000 | 1,689,688 | 182,000,000 |
| Operating cost | 59,900,000 | 47,500,000 | 53,100,000 | 2,393,554 | 241,000,000 |
| Intervals | Std. Diff. | Observed | Expected | p-Values | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −0.1110 | −1.3323 | 0.0322 | 0.0407 | 0.1828 | |
| 2 | −0.0555 | −3.2418 | 0.0603 | 0.0902 | 0.0012 | *** |
| 3 | 0.0000 | 0.9303 | 0.1726 | 0.1615 | 0.3522 | |
| 4 | 0.0555 | 3.1264 | 0.2464 | 0.2056 | 0.0018 | *** |
| 5 | 0.1110 | 3.5265 | 0.2287 | 0.1846 | 0.0004 | *** |
| 6 | 0.1665 | −1.4565 | 0.1060 | 0.1214 | 0.1453 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malkogianni, I.; Kourtidis, D. Detecting Discontinuities in the Distribution of Earnings Around Zero as an Indication of Earnings Management. Proceedings 2024, 111, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024111012
Malkogianni I, Kourtidis D. Detecting Discontinuities in the Distribution of Earnings Around Zero as an Indication of Earnings Management. Proceedings. 2024; 111(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024111012
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalkogianni, Ioanna, and Dimitrios Kourtidis. 2024. "Detecting Discontinuities in the Distribution of Earnings Around Zero as an Indication of Earnings Management" Proceedings 111, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024111012
APA StyleMalkogianni, I., & Kourtidis, D. (2024). Detecting Discontinuities in the Distribution of Earnings Around Zero as an Indication of Earnings Management. Proceedings, 111(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024111012






