Abstract
The localization of bad odors is a long standing issue with high relevance for affected people because of the health and safety implications. In order to enable the detection and localization of bad odors we propose a wireless, low-power consuming sensor network. The sensor nodes are designed to wake-up upon initial detection of a bad odor to then start to measure the strength of the odor. Taking into account the spatial variation of the bad odor as well as environmental parameters the odor source may be identified. After the odor vanishes the sensor nodes return to sleep mode.
1. Introduction
The occurrence of bad odors is not only unpleasant for affected persons but also poses a threat to their health and safety. Possible sources of unpleasant smells include landfills, sewers, industrial processes, biogas fermenters, or miscellaneous sources in private homes. From a technological point of view the classification of a smell is challenging since the human olfactory system is able to distinguish between highly complex gas compositions, which are made up of up to 10,000 different molecules [1]. Because of the lack of cost-efficient sensing technologies to provide an objective assessment on the strength and origin of odors it is currently difficult to localize smells and subsequently establish accountability for the culprit. In the past, odor quantification has been approached using electronic noses [2,3], which have used e.g., semiconducting metal oxides, conductive polymers, or piezoelectric materials as gas sensitive transducer [4]. Because of the poor selectivity of the basic gas sensing methods used in electronic noses, the use of pattern recognition schemes is necessary for many scenarios [5]. However, due to the poor reproducibility, long term drifts, high calibration and computational expenditure for most of these approaches a large scale deployment of e-nose systems is difficult [6].
Therefore in this contribution we explore a different approach and try to exploit the fact that bad odors and the hydrogen sulfide concentration are highly correlated [7,8]. This opens up the possibility to employ a highly specific trace gas detection scheme to gauge the H2S concentration using a percolation phase transition in copper (II) oxide [9,10] thus evaluating the odor level. Figure 1 depicts a possible deployment outdoor scenario for the bad odor sensor network. The distributed gas sensor network uses well-localized odor nodes to infer strength and origin of the odor. This way, the origin of an odor may be identified and measures against future disturbances may be taken.
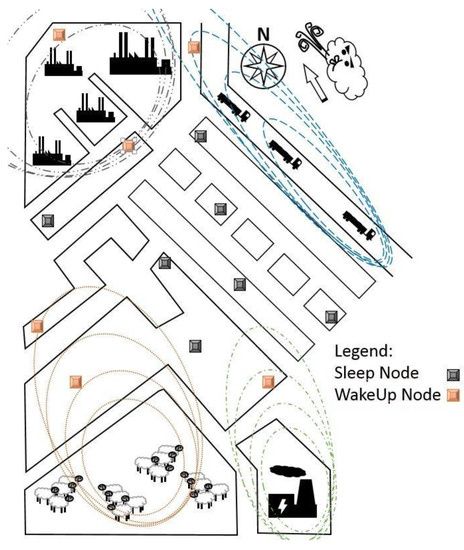
Figure 1.
Schematic drawing of a possible deployment of the odor sensor network: Upon waking up the respective sensor node starts to determine the hydrogen sulphide concentration, which is a very good indicator for the odor level. Taking into account ambient weather conditions and information from the distributed sensor network it is possible to infer the source of the bad odor.
2. Experimental
The system design relies on the high correlation between bad odors and the appearance of hydrogen sulfide. To detect H2S we employ copper(II) oxide (CuO) nanosphere-based functional layers [11] deposited onto micro-machined hotplates [12] via inkjet printing [13]. CuO is known to feature a highly specific reaction towards H2S even at room temperature [14], which ultimately leads to a break-down in electrical resistivity via a percolation phase transition [9,10]. In a low temperature regime below 200 °C the substitution reaction:
dominates. In order to save energy we employ a wake up approach that relies on this reaction: In the sleep mode, the hotplate is not powered permanently and the system checks the layer’s resistivity once a minute using a time-to-digital read-out technique [15]. As soon as an odor event triggers the phase transition and a conductive path of copper sulfide (CuS) appears, the sensor node wakes up and switches into measurement mode. The H2S concentration measurement scheme relies on the reversibility of Reaction (1) and at temperatures exceeding 300 °C the following reaction prevails:
The thermal modulation scheme to determine the H2S concentration has been demonstrated in [16] and is used here. The protocol allows for determining the hydrogen sulfide concentration in the range between 100 ppb and 20 ppm, i.e., over more than two orders of magnitude [9]. These values are used as an indicator for the strength of the bad odor and transmitted via a Wi-Fi protocol. The wireless communication between localized sensor nodes allows for time and spatially resolved H2S concentration information, which enables identifying odor sources. Figure 2 shows a schematic diagram of the components of the odor sensing node as well as their functionality. The node design includes a temperature and humidity sensor to provide a basic assessment of the environmental conditions.
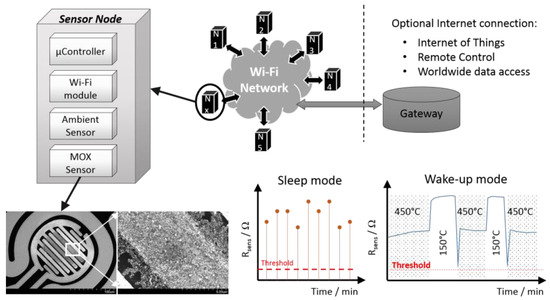
Figure 2.
Concept of the wireless odor sensing network: A CuO based MEMS chip is used as central building block to enable the highly selective detection of H2S, which is used as indicator for the amount of bad odor. In the sleep mode the system checks periodically whether or not a bad odor event has occurred. Once this has happened, the sensor node switches into measurement mode and determines the H2S concentration based on the percolation time. All sensor node data are transmitted to the internet where data regarding spatial and temporal distribution of bad odors may be analyzed.
3. Results
So far the sensor node has been tested in a laboratory environment using an apparatus to simulate real-world conditions [17] and a sample measurement is shown in Figure 3. During three days the system has been kept in an environment of synthetic air with varying levels of humidity and subject to the ambient temperature. Then low levels of hydrogen sulfide were introduced and upon breach of the pre-defined resistivity threshold of 500 MΩ the measurement protocol started automatically.
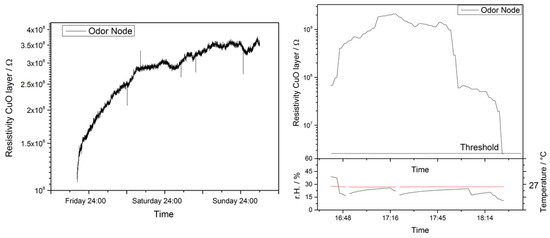
Figure 3.
Sample measurement of a single odor sensing node in the sleep mode, i.e., at ambient temperature: The state of the gas sensitive layer has been checked every minute for several days and no odor event has been detected. The resistivity value varies due to ambient temperature and humidity changes. To simulate an odor event occurring we did expose the device to low levels of hydrogen sulphide of about 1 ppm. The steep decline of the resistivity below a threshold value triggers the odor detection mode.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dymerski, T.M.; Chmiel, T.M.; Wardencki, W. Invited Review Article: An odor-sensing system-powerful technique for foodstuff studies. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.D.; Baietto, M. Applications and Advances in electronic-nose technologies developed for biomedical applications. Sensors 2009, 11, 1105–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, F.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U.; Röck, F.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Electronic nose: Current status and future trends. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.; Scott, S.M.; Ali, Z.; O’Hare, W.T. Chemical sensors for electronic nose systems. Microchim. Acta 2005, 149, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, A.; Llobet, E. Sensor Selection and Chemo-Sensory Optimization: Toward an Adaptable Chemo-Sensory System. Front. Neuroeng. 2012, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonollosa, J.; Fernández, L.; Gutiérrez-Gálvez, A.; Huerta, R.; Marco, S. Calibration transfer and drift counteraction in chemical sensor arrays using Direct Standardization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, M.A.; McGinley, C.M. Comparison of field olfactometers in a controlled chamber using hydrogen sulfide as the test odorant. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gostelow, P.; Parsons, S.A.; Stuetz, R.M. Odour measurements for sewage treatment works. Water Res. 2001, 35, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneer, J.; Knobelspies, S.; Bierer, B.; Wöllenstein, J.; Palzer, S. New method to selectively determine hydrogen sulfide concentrations using CuO layers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneer, J.; Wöllenstein, J.; Palzer, S. Specific, trace gas induced phase transition in copper(II)oxide for highly selective gas sensing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 073509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henzler, K.; Heilemann, A.; Kneer, J.; Guttmann, P.; Jia, H.; Bartsch, E.; Lu, Y.; Palzer, S. Investigation of reactions between trace gases and functional CuO nanospheres and octahedrons using NEXAFS-TXM imaging. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walden, P.; Kneer, J.; Knobelspies, S.; Kronast, W.; Mescheder, U.; Palzer, S. Micromachined Hotplate Platform for the Investigation of Ink-Jet Printed, Functionalized Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2015, 24, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Jia, H.; Bierer, B.; Wöllenstein, J.; Lu, Y.; Palzer, S. Scalable gas sensors fabrication to integrate metal oxide nanoparticles with well-defined shape and size. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramgir, N.S.; Ganapathi, S.K.; Kaur, M.; Datta, N.; Muthe, K.P.; Aswal, D.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Yakhmi, J.V. Sub-ppm H2S sensing at room temperature using CuO thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 151, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, F. The Art of Directly Interfacing Sensors to Microcontrollers. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2012, 2, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobelspies, S.; Bierer, B.; Ortiz Perez, A.; Wöllenstein, J.; Kneer, J.; Palzer, S. Low-cost gas sensing system for the reliable and precise measurement of methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide in natural gas and biomethane. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneer, J.; Eberhardt, A.; Walden, P.; Ortiz Pérez, A.; Wöllenstein, J.; Palzer, S. Apparatus to characterize gas sensor response under real-world conditions in the lab. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 055006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).