Oxygen Sensors Based on Screen Printed Platinum and Palladium Doped Indium Oxides †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Sensor Fabrication
2.2. Data Acquisition System
3. Results and Discussion
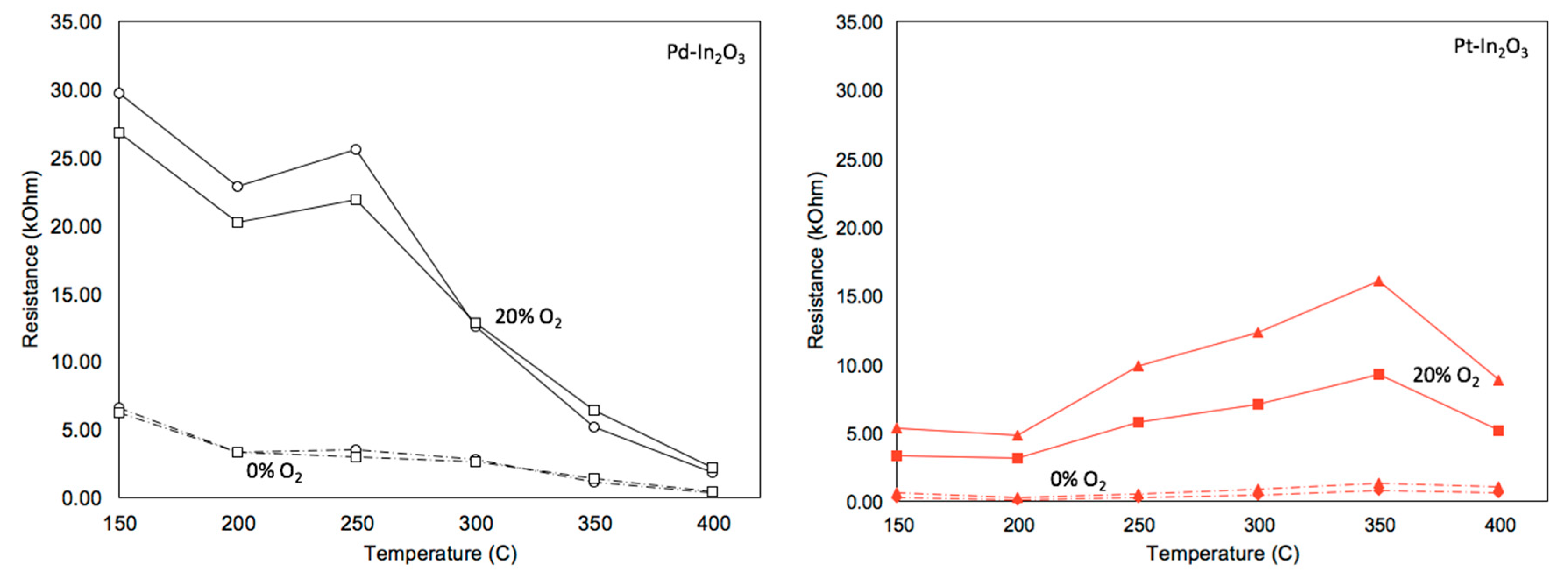
3.1. Material Charaterisation
3.2. Gas Testing
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gas Sensors Market will Grow to Worth $2512.4 Million by 2020: Grand View Research, Inc. abnewsire.com. 2015. Available online: http://www.grandviewresearch.com/press-release/global-gas-sensors-market.
- Alphasense. FAQs. Available online: http://www.alphasense.com/index.php/air/faqs/ (accessed on 13 November).
- Baban, C.; Toyoda, Y.; Ogita, M. Oxygen sensing at high temperatures using Ga2O3 films. Thin Solid Films 2005, 484, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.; Cranny, A.; Simonis de Cloke, C. A low-cost oxygen sensor fabricated as a screen-printed semiconductor device suitable for unheated operation at ambient temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 47, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Bhatnagar, M.C.; Sharma, A.L. Mechanism in Nb doped titania oxygen gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 4, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabouni, F.; Abaab, M.; Rezig, B. Metrological characteristics of ZNO oxygen sensor at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 100, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, G.; Bonavita, A.; Micali, G.; Rizzo, G.; Galvagno, S.; Niederberger, M.; Pinna, N. A highly sensitive oxygen sensor operating at room temperature based on platinum-doped In2O3 nanocrystals. Chem. Commun. 2005, 6032–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, G.; Bonavita, A.; Micali, G.; Rizzo, G.; Pinna, N.; Niederberger, M. In2O3 and Pt-In2O3 nanopowders for low temperature oxygen sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 127, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, D.; Dharmaraj, N.; Kumar, N.S.; Padaki, V.C. Oxygen Sensing Properties of Platinum Doped Indium Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared by Hydrothermal Method. Synth. React. Inorg. Metal Organ. Nano-Metal Chem. 2014, 45, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sari, W.; Smith, P.; Leigh, S.; Covington, J. Oxygen Sensors Based on Screen Printed Platinum and Palladium Doped Indium Oxides. Proceedings 2017, 1, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040401
Sari W, Smith P, Leigh S, Covington J. Oxygen Sensors Based on Screen Printed Platinum and Palladium Doped Indium Oxides. Proceedings. 2017; 1(4):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040401
Chicago/Turabian StyleSari, Wangi, Peter Smith, Simon Leigh, and James Covington. 2017. "Oxygen Sensors Based on Screen Printed Platinum and Palladium Doped Indium Oxides" Proceedings 1, no. 4: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040401
APA StyleSari, W., Smith, P., Leigh, S., & Covington, J. (2017). Oxygen Sensors Based on Screen Printed Platinum and Palladium Doped Indium Oxides. Proceedings, 1(4), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040401





