On-Chip Platform for Slack-Free Carbon Nanotube Resonators †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
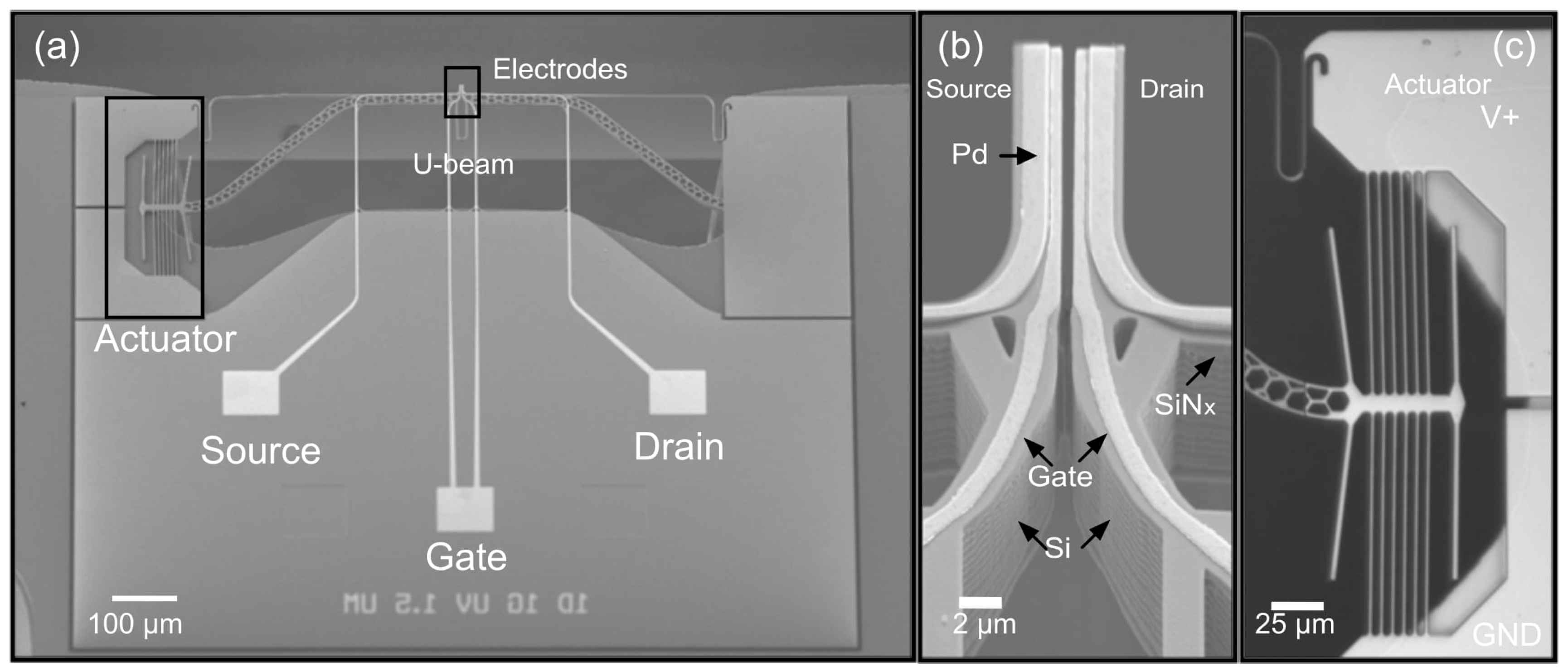
2. Modeling and Fabrication
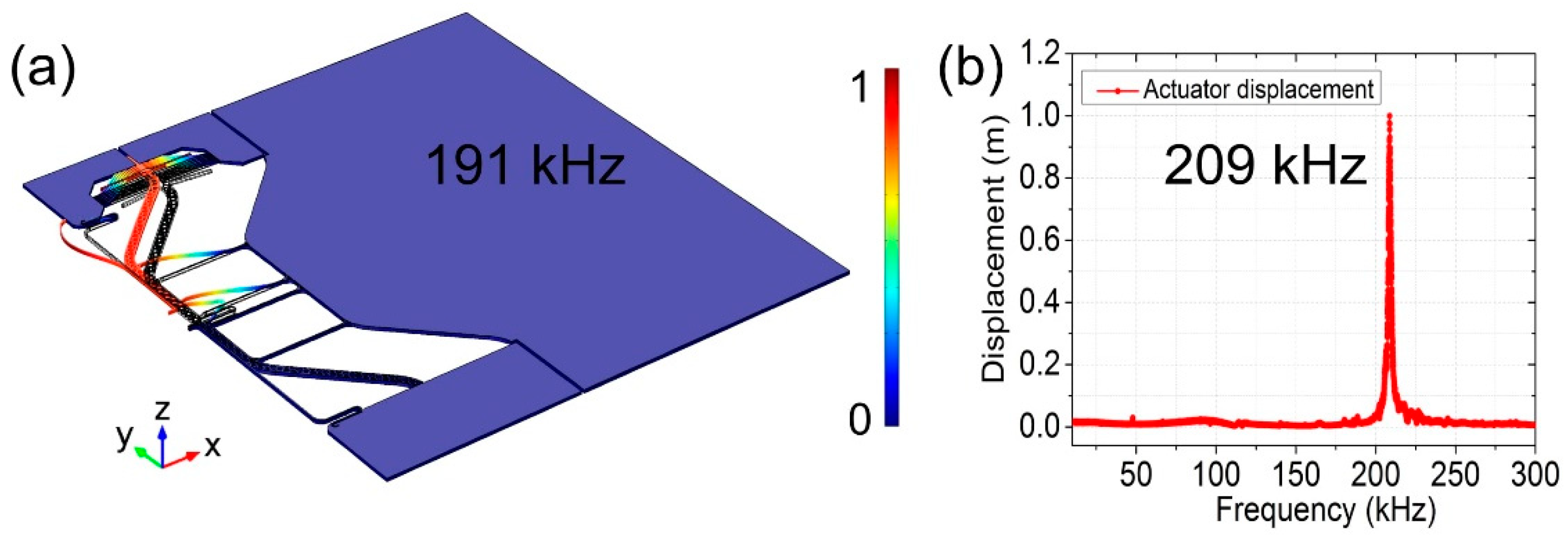
3. Measurement and Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moser, J.; Güttinger, J.; Eichler, A.; Esplandiu, M.J.; Liu, D.E.; Dykman, M.I.; Bachtold, A. Ultrasensitive force detection with a nanotube mechanical resonator. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaste, J.; Eichler, A.; Moser, J.; Ceballos, G.; Rurali, R.; Bachtold, A. A nanomechanical mass sensor with yoctogram resolution. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truax, S.; Lee, S.W.; Muoth, M.; Hierold, C. Axially tunable carbon nanotube resonators using co-integrated microactuators. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6092–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouakad, H.M.; Younis, M.I. Dynamic response of slacked single-walled carbon nanotube resonators. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 67, 1419–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Fu, M.Q.; Wu, G.; Qiu, C.; Shu, J.; Guo, Y.; Wei, X.; Gao, S.; Chen, Q. Remarkable influence of slack on the vibration of a single-walled carbon nanotube resonator. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8658–8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Z.; Fu, M.Q.; Shi, T.W.; Guo, Y.; Wei, X.; Gao, S.; Chen, Q. Transversally and axially tunable carbon nanotube resonators in Situ fabricated and studied inside a scanning electron microscope. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muoth, M.; Hierold, C. Transfer of carbon nanotubes onto micro actuators for hysteresis-free transistors at low thermal budget. In Proceedings of the IEEE 25th International Conference on MEMS, Paris, France, 29 January–2 February 2012; pp. 1352–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, D.A.; Ericson, L.M.; Casavant, M.J.; Liu, J.; Colbert, D.T.; Smith, K.A.; Smalley, R.E. Elastic strain of freely suspended single-wall carbon nanotube ropes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 3803–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Espinosa, H.D. An electromechanical material testing system for in situ electron microscopy and applications. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14503–14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Chen, Q.; Xu, S.; Peng, L.; Zuo, J. Beam to string transition of vibrating carbon nanotubes under axial tension. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ref. | Design | CNT Placement | Power @ 100 nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | PC controlled piezo-SEM stage | 3 probe pick-up-drop | - |
| [10] | AFM cantilever | 3 nanoprobe system | - |
| [9] | On-chip thermal actuator | Probe nanomanipulation | ~28 mW |
| [3] | On-chip thermal actuator | As grown and dry transfer | ~10 mW |
| This work | On-chip thermal actuator | Dry-transfer | 2.7 mW |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, L.; Jenni, L.V.; Roman, C.I.; Hierold, C. On-Chip Platform for Slack-Free Carbon Nanotube Resonators. Proceedings 2017, 1, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040374
Kumar L, Jenni LV, Roman CI, Hierold C. On-Chip Platform for Slack-Free Carbon Nanotube Resonators. Proceedings. 2017; 1(4):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040374
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Lalit, Laura Vera Jenni, Cosmin Ioan Roman, and Christofer Hierold. 2017. "On-Chip Platform for Slack-Free Carbon Nanotube Resonators" Proceedings 1, no. 4: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040374
APA StyleKumar, L., Jenni, L. V., Roman, C. I., & Hierold, C. (2017). On-Chip Platform for Slack-Free Carbon Nanotube Resonators. Proceedings, 1(4), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040374




