The Impact of Elastoplastic Deformation Behavior on the Apparent Gas Permeability of Deep Fractal Shale Rocks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
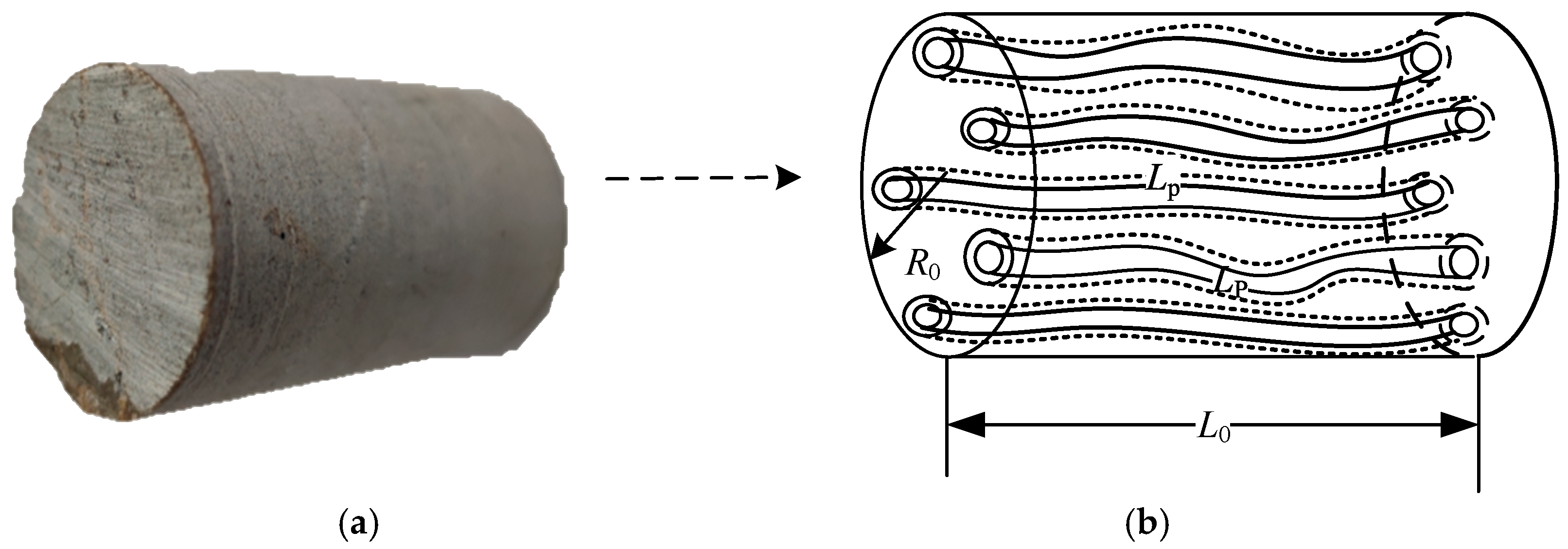
2.1. Capillary and Rock Sample Radius
2.2. Fractal Dimension of Capillary
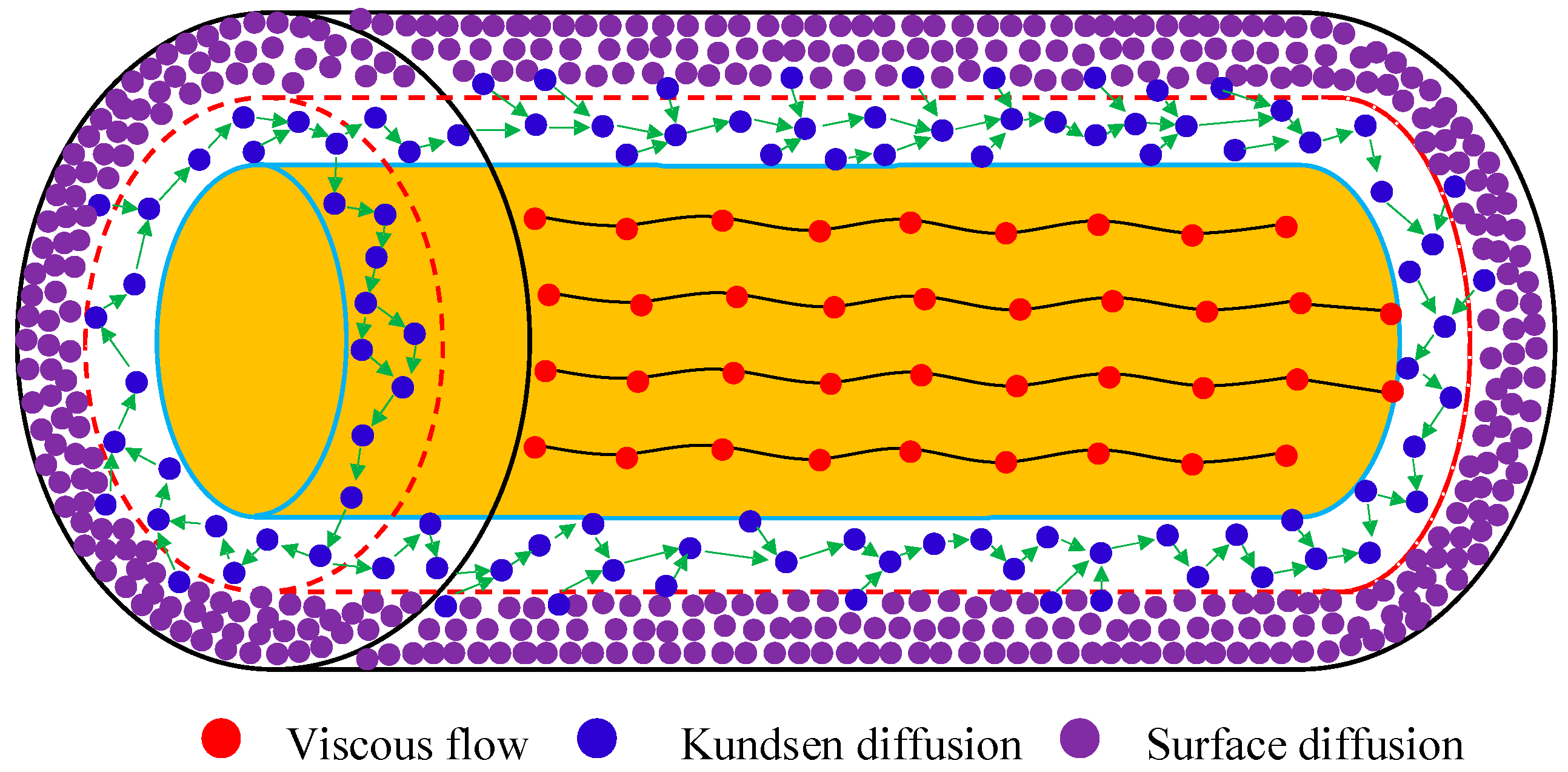
3. The Fractal Descriptions of Shale Gas Reservoirs
4. Results and Discussion
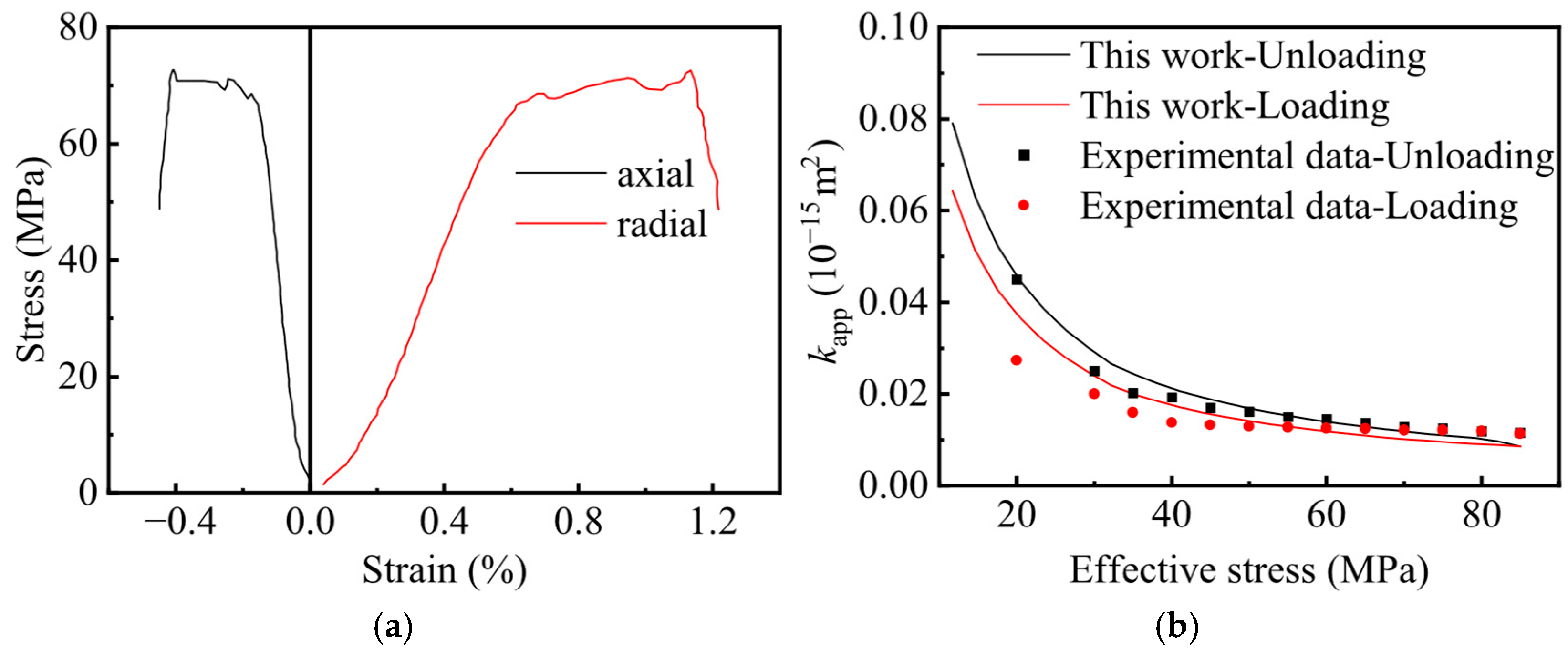
4.1. Model Validation
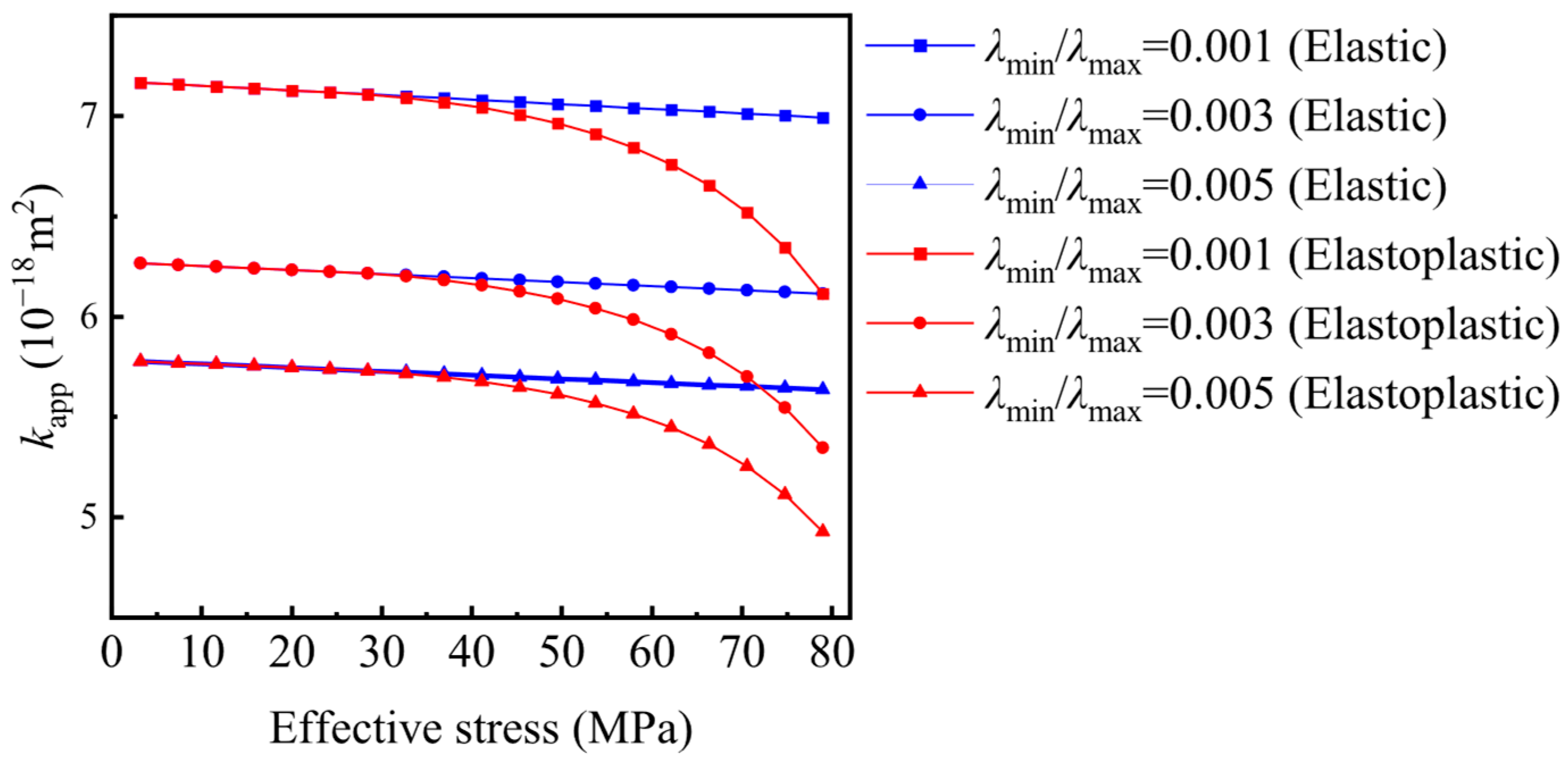
4.2. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
- (1)
- For λmin/λmax = 0.001, the proportion of pore volume attributed to viscous flow decreases from 12.41% to 12.09%, transition flow increases from 47.54% to 47.71%, and Knudsen diffusion increases from 40.05% to 40.19% for elastic shale porous media. Similarly, the proportion of viscous flow pore volume decreases from 12.41% to 10.78%, transition flow increases from 47.54% to 48.43%, and Knudsen diffusion increases from 40.05% to 40.79% for elastoplastic shale porous media.
- (2)
- As for Figure 11b with λmin/λmax = 0.00, the pore volume proportion of viscous flow decreases from 15.08% to 14.71%, transition flow increases from 52.58% to 52.82% when shale porous media is considered as an elastic body. For the elastoplastic body, the proportion of viscous flow decreases from 15.08% to 13.13%, while the proportion of transition flow increases from 52.58% to 53.8%. The pore volume proportion of Knudsen diffusion increases from 32.34% to 32.48% for the elastic body and from 32.34% to 33.08% for the elastoplastic body.
- (3)
- For λmin/λmax = 0.005, for the elastic body, the proportion of the viscous flow region decreases from 16.66% to 16.24%, the transition flow region increases from 54.93% to 55.21%, and the Knudsen diffusion region increases from 28.41% to 28.55%, for elastoplastic body, the proportion of the viscous flow region decreases from 16.66% to 14.52%, the transition flow region increases from 54.93% to 56.35%, and the Knudsen diffusion region increases from 28.41% to 29.14%.
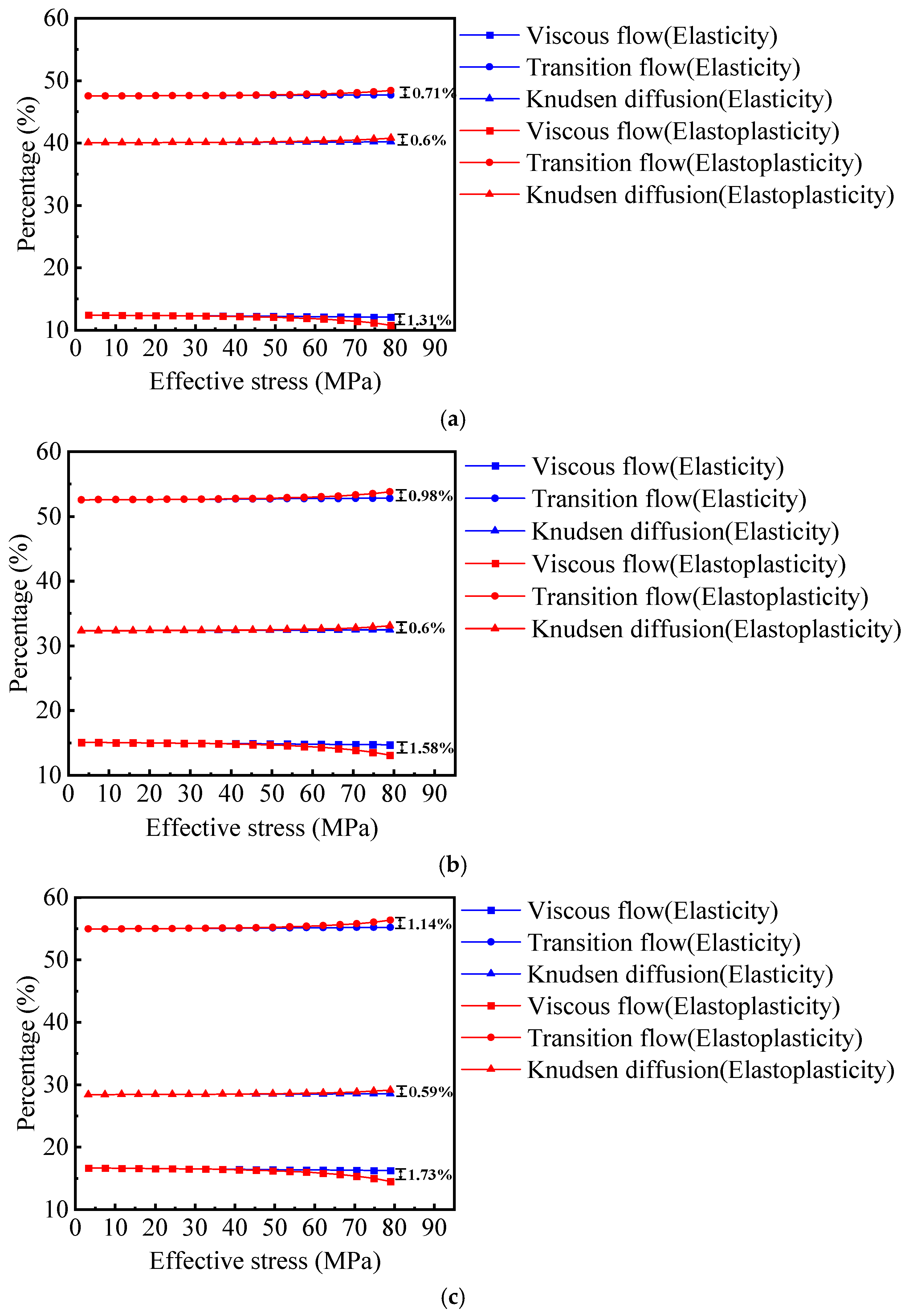
- (1)
- For DT = 1.08, for the elastic porous media: the proportions of the viscous flow, transition flow, and Knudsen diffusion regions change slightly, from 16.74% to 16.33%, 55.05% to 55.32%, and 28.21% to 28.35%, respectively, for the elastoplastic porous media: the changes are more pronounced, the viscous flow region decreases from 16.74% to 14.59%, the transitional flow region increases from 55.05% to 56.47%, and the Knudsen diffusion region rises from 28.21% to 28.94%.
- (2)
- When DT increases to 1.15, for the elastic body, the proportions of the viscous flow, transition flow, and Knudsen diffusion regions change from 14.44% to 14.08%, 51.5% to 51.72%, and 34.06% to 34.21%, respectively. For the elastoplastic media, the viscous flow region decreases from 14.44% to 12.56%, the transitional flow region increases from 51.5% to 52.63%, and the Knudsen diffusion region increases from 34.06% to 34.81%.
- (3)
- When DT further increases to 1.2, for elastic media, the proportions of the viscous flow, transition flow, and Knudsen diffusion regions change from 12.75% to 12.43%, 48.28% to 48.45%, and 38.97% to 39.12%, respectively. However, for the elastoplastic porous media, the viscous flow region decreases more significantly, from 12.75% to 11.08%, the transition flow region increases from 48.28% to 49.2%, and the Knudsen diffusion region rises from 38.97% to 39.72%.
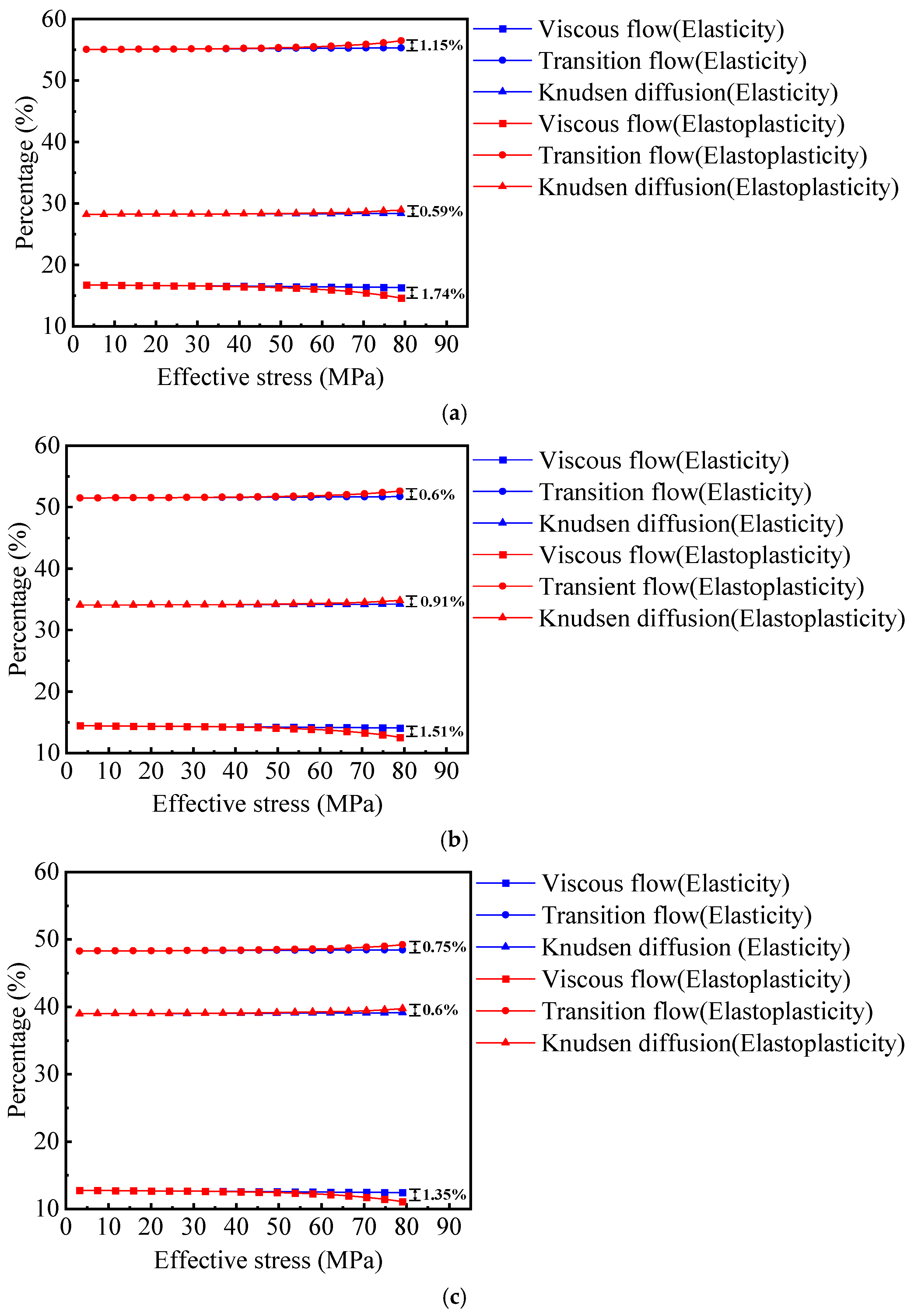
- (1)
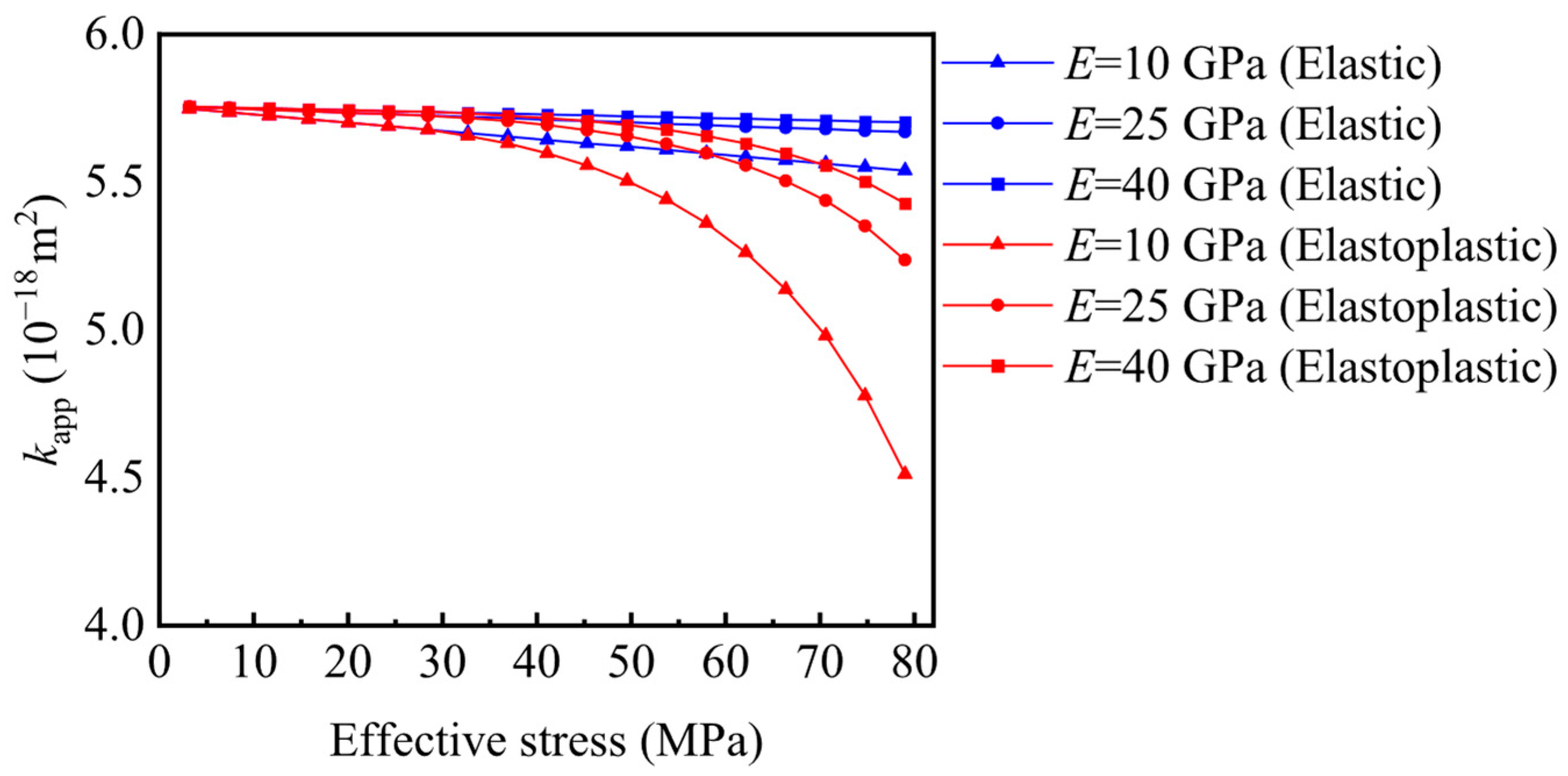
- For E = 10 GPa, Elastic media: viscous flow, transition flow, and Knudsen diffusion regions decrease from 16.73% to 16.11%, increase from 55.05% to 55.48%, and increase from 28.21% to 28.43%, respectively. In contrast, for the elastoplastic shale porous media, the viscous flow region decreases from 16.73% to 13.44%. In comparison, the transition flow region increases from 55.05% to 57.23%, and the Knudsen diffusion region increases from 28.22% to 29.33%.
- (2)
- When E = 25 GPa, for the elastic media, the viscous flow, transition flow region, and Knudsen diffusion regions change from 16.75% to 16.5%, 55.04% to 55.21%, and 28.21% to 28.29%, respectively. For the elastoplastic porous media, the viscous flow region decreases from 16.75% to 15.48%, the transition flow region increases from 55.04% to 55.88%, and the Knudsen diffusion region increases from 28.21% to 28.64%.
- (3)
- When Young’s modulus increases to E = 40 GPa, for the elastic media, the proportions of the viscous flow region, transition flow region, and Knudsen diffusion region decreases from 16.75% to 16.60%, increase from 55.04% to 55.14%, and increase from 28.21% to 28.26%, respectively. For the elastoplastic porous media, the viscous flow region decreases from 16.75% to 15.97%, the transition flow region increases from 55.04% to 55.56%, and the Knudsen diffusion region rises from 28.21% to 28.47%.
- (1)
- At 300 K, as stress increases, the proportions of flow mechanisms vary depending on whether the shale is considered an elastic or elastoplastic material. During elastic deformation, the proportion of viscous flow decreases from 16.74% to 16.33%, transition flow increases from 55.05% to 55.32%, and Knudsen diffusion increases from 28.21% to 28.35%. For elastoplastic deformation, viscous flow decreases to 14.59%, transition flow increases to 56.47%, and Knudsen diffusion increases to 28.94%.
- (2)
- At 353 K, for the elastic body, the proportion of viscous flow decreases from 10.13% to 9.68%, transition flow increases from 59.42% to 59.72%, and Knudsen diffusion increases from 30.45% to 30.61%. For the elastoplastic body, viscous flow decreases from 10.13% to 7.8%, transition flow increases from 59.42% to 60.96%, and Knudsen diffusion increases from 30.45% to 31.24%.
- (3)
- At 403 K, for the elastic body, the proportion of viscous flow decreases from 4.35% to 3.86%, transition flow increases from 63.24% to 63.54%, and Knudsen diffusion increases from 32.41% to 32.57%. For the elastoplastic body, viscous flow decreases dramatically, from 4.35% to 1.89%, while transition flow increases, from 63.24% to 64.87%, and Knudsen diffusion increases, from 30.41% to 33.25%.
5. Conclusions
- At constant effective stress, shale gas apparent permeability increases with pore radius fractal dimension, temperature, and Young’s modulus, but decreases with capillary tortuosity fractal dimension.
- During plastic deformation, plastic strain surpasses elastic strain, leading to more pronounced permeability variations and more significant shifts in pore volume contributions among flow mechanisms compared to purely elastic deformation.
- When the shale core sample is subjected to external circumferential pressure, the internal capillaries experience a uniform force.
- The total number of internal capillaries remains constant even after the core sample is deformed by the applied force.
- During the unloading process of a core sample subjected to peripheral pressure, the capillaries that have undergone plastic deformation do not recover.
- The stress-strain relationship and gas transport properties of the core sample remain in a steady state.
- The shale core sample ideally exhibits elastic-plastic behavior and does not undergo brittle changes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| As | Surface diffusion cross-sectional area |
| b | Slip factor |
| ΔC | Concentration difference |
| Cs | Maximum adsorption capacity at constant temperature and infinite high pressure |
| Cλ, Ceλ, Cpλ | The variation of the inner radius of capillary |
| Ds, | Effective surface diffusion coefficient and surface diffusion coefficient with “0” gas coverage |
| Df, Df0, Dfσ, DT | Fractal dimension, Fractal dimension without stress, Fractal dimension with stress, and fractal dimension of capillary tortuosity |
| E | Young’s modulus |
| ΔH | Isosteric adsorption heat |
| KB, Kn | Boltzmann constant and Knudsen number |
| lg | The free path length of gas molecules |
| L | Characteristic length of the shale gas rock sample |
| Lpσ, L0 | Length of capillary with stress and length of capillary without stress |
| N, N0, Nσ | Cumulative number of capillaries, Cumulative number of capillaries without stress, and Cumulative number of capillaries with stress |
| Pr | The dimensionless pseudo-pressure |
| Δp | Pressure differential |
| pi, po, pL, p | The pressure of the fluid inside the capillary and the external pressure, Langmuir pressure, and shale gas reservoir pressure |
| R | Gas constant |
| Rσ, R0 | The radius of the rock sample changes with stress, and the initial radius without stress |
| T, Tr | Absolute temperature and the dimensionless pseudo-temperature |
| t | The ratio of the outer radius of the capillary to the inner radius |
| tλ | Capillary outer radius |
| Z | Gas dimensionless compressibility factor |
| σe, σp, σλ | Elastic limit stress, plastic limit stress, and effective stress |
| λ | Capillary inner radius |
| λ0, λσ | The inner radius of the capillary without stress and with stress |
| λK, λP | Characteristic pore radius |
| λe | Effective capillary pore radius |
| λmax, λmin | Maximum effective pore radius and minimum pore radius |
| λmaxσ, λminσ | Maximum effective pore radius and minimum pore radius with stress |
| ν | Poisson’s ratio |
| μg | Gas viscosity |
| ρg | Gas density |
| ρ | Ratio of the radius at the junction of the elastic zone and the plastic zones to the inner radius of the capillary |
| δg | Molecular collision diameter of gas molecules |
| α | Rarefaction coefficient |
| θ | Surface coverage of the adsorption gas under the equilibrium condition |
| κb, κm | The blocking coefficient of surface gas molecules and the rate constant for forward migration |
Appendix A
Appendix B
| ppore = 0.4 MPa | ppore = 1.2 MPa | ppore = 1.6 MPa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effective Stress (MPa) | Kapp (10−18 m2) | Effective Stress (MPa) | Kapp (10−18 m2) | Effective Stress (MPa) | Kapp (10−18 m2) |
| 8.79 | 6.63 | 8.12 | 5.62 | 8.67 | 4.9 |
| 10.43 | 6.45 | 10.95 | 5.37 | 10.47 | 4.76 |
| 12.61 | 6.22 | 12.91 | 5.19 | 12.25 | 4.62 |
| 15.22 | 5.96 | 15.52 | 4.96 | 14.03 | 4.49 |
| 17.74 | 5.72 | 18.15 | 4.74 | 16.12 | 4.34 |
| 20.11 | 5.51 | 22.76 | 4.38 | 19.25 | 4.13 |
| 23.56 | 5.21 | 25.59 | 4.17 | 22.75 | 3.9 |
| 26.66 | 4.94 | 27.35 | 4.04 | 25.34 | 3.74 |
| 28.84 | 4.76 | 28.95 | 3.95 | 27.1 | 3.61 |
| ppore = 0.4 MPa | ppore = 1.2 MPa | ppore = 1.6 MPa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effective Stress (MPa) | Kapp (10−18 m2) | Effective Stress (MPa) | Kapp (10−18 m2) | Effective Stress (MPa) | Kapp (10−18 m2) |
| 1.58 | 7.48 | 1.58 | 6.22 | 1.58 | 5.52 |
| 3.16 | 7.28 | 3.16 | 6.06 | 3.16 | 5.37 |
| 4.74 | 7.09 | 4.74 | 5.90 | 4.74 | 5.23 |
| 6.32 | 6.91 | 6.32 | 5.74 | 6.32 | 5.10 |
| 7.89 | 6.73 | 7.89 | 5.59 | 7.89 | 4.96 |
| 9.47 | 6.55 | 9.47 | 5.45 | 9.47 | 4.83 |
| 11.05 | 6.38 | 11.05 | 5.30 | 11.05 | 4.70 |
| 12.63 | 6.21 | 12.63 | 5.16 | 12.63 | 4.58 |
| 14.21 | 6.04 | 14.21 | 5.02 | 14.21 | 4.46 |
| 15.79 | 5.88 | 15.79 | 4.89 | 15.79 | 4.34 |
| 17.37 | 5.72 | 17.37 | 4.76 | 17.37 | 4.22 |
| 18.95 | 5.57 | 18.95 | 4.63 | 18.95 | 4.11 |
| 20.53 | 5.41 | 20.53 | 4.50 | 20.53 | 4.00 |
| 22.11 | 5.27 | 22.11 | 4.38 | 22.11 | 3.89 |
| 23.68 | 5.12 | 23.68 | 4.26 | 23.68 | 3.78 |
| 25.26 | 4.98 | 25.26 | 4.14 | 25.26 | 3.67 |
| 26.84 | 4.84 | 26.84 | 4.03 | 26.84 | 3.57 |
| 28.42 | 4.71 | 28.42 | 3.91 | 28.42 | 3.47 |
| 30 | 4.58 | 30 | 3.80 | 30 | 3.38 |
| Experimental Data | Simulation Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effective Stress (MPa) | Unloading Kapp (10−18 m2) | Loading Kapp (10−18 m2) | Effective Stress (MPa) | Unloading Kapp (10−18 m2) | Loading Kapp (10−18 m2) |
| 25 | 0.0541 | 0.0368 | 15 | 0.0951 | 0.0700 |
| 30 | 0.04525 | 0.0304 | 18 | 0.0792 | 0.0585 |
| 35 | 0.0352 | 0.0289 | 21 | 0.0678 | 0.0503 |
| 40 | 0.03178 | 0.0246 | 23 | 0.0593 | 0.0442 |
| 45 | 0.03046 | 0.0239 | 26 | 0.0526 | 0.0394 |
| 50 | 0.02733 | 0.0205 | 29 | 0.0473 | 0.0356 |
| 55 | 0.02545 | 0.0199 | 32 | 0.0430 | 0.0325 |
| 60 | 0.02386 | 0.0187 | 35 | 0.0394 | 0.0299 |
| 65 | 0.0215 | 0.0183 | 38 | 0.0364 | 0.0277 |
| 70 | 0.0213 | 0.0178 | 41 | 0.0338 | 0.0259 |
| 75 | 0.0189 | 0.0172 | 44 | 0.0315 | 0.0243 |
| 80 | 0.0185 | 0.0168 | 47 | 0.0295 | 0.0229 |
| 85 | 0.0173 | 0.0173 | 50 | 0.0278 | 0.0217 |
| - | - | - | 53 | 0.0262 | 0.0206 |
| - | - | - | 56 | 0.0248 | 0.0196 |
| - | - | - | 59 | 0.0236 | 0.0188 |
| - | - | - | 62 | 0.0225 | 0.0180 |
| - | - | - | 64 | 0.0214 | 0.0173 |
| - | - | - | 67 | 0.0205 | 0.0167 |
| - | - | - | 70 | 0.0196 | 0.0162 |
| - | - | - | 73 | 0.0189 | 0.0158 |
| - | - | - | 76 | 0.0181 | 0.0154 |
| - | - | - | 79 | 0.0175 | 0.0152 |
| - | - | - | 82 | 0.0163 | 0.0151 |
| - | - | - | 85 | 0.0150 | 0.0150 |
| Experimental Data | Simulation Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effective Stress (MPa) | Unloading Kapp (10−18 m2) | Loading Kapp (10−18 m2) | Effective Stress (MPa) | Unloading Kapp (10−18 m2) | Loading Kapp (10−18 m2) |
| 20 | 0.0450 | 0.0273 | 12 | 0.0790 | 0.0642 |
| 30 | 0.0251 | 0.0201 | 15 | 0.0629 | 0.0513 |
| 35 | 0.0203 | 0.0160 | 18 | 0.0522 | 0.0426 |
| 40 | 0.0193 | 0.0137 | 21 | 0.0444 | 0.0364 |
| 45 | 0.0170 | 0.0132 | 23 | 0.0386 | 0.0317 |
| 50 | 0.0161 | 0.0129 | 26 | 0.0340 | 0.0279 |
| 55 | 0.0150 | 0.0127 | 29 | 0.0301 | 0.0248 |
| 60 | 0.0146 | 0.0125 | 32 | 0.0266 | 0.0218 |
| 65 | 0.0138 | 0.0124 | 35 | 0.0243 | 0.0200 |
| 70 | 0.0129 | 0.0121 | 38 | 0.0224 | 0.0184 |
| 75 | 0.0125 | 0.0121 | 41 | 0.0207 | 0.0171 |
| 80 | 0.0119 | 0.0119 | 44 | 0.0193 | 0.0160 |
| 85 | 0.0116 | 0.0116 | 47 | 0.0180 | 0.0150 |
| - | - | - | 50 | 0.0169 | 0.0142 |
| - | - | - | 53 | 0.0160 | 0.0134 |
| - | - | - | 56 | 0.0151 | 0.0127 |
| - | - | - | 59 | 0.0143 | 0.0121 |
| - | - | - | 62 | 0.0136 | 0.0115 |
| - | - | - | 64 | 0.0130 | 0.0110 |
| - | - | - | 67 | 0.0124 | 0.0106 |
| - | - | - | 70 | 0.0118 | 0.0102 |
| - | - | - | 73 | 0.0113 | 0.0098 |
| - | - | - | 76 | 0.0109 | 0.0094 |
| - | - | - | 79 | 0.0104 | 0.0091 |
| - | - | - | 82 | 0.0097 | 0.0088 |
References
- Longde, S.; Caineng, Z.; Rukai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.; Guangyou, Z.; Zhiyong, G. Formation, Distribution and Potential of Deep Hydrocarbon Resources in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, M.; Bayless, D.; Sarvestani, A. A Model for Stress-dependence of Apparent Permeability in Nanopores of Shale Gas Reservoirs. AIChE J. 2020, 66, e16541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, S.; Lyu, S. Nanoindentation Characterization of Shale Micromechanics and Fracturing Ability Evaluation of Reservoir. J. China Coal Soc. 2025, 50, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, S.; Sunwen, J.; Liu, L. Experimental Study on the Stress Sensitivity and Influence Factors of Shale under Varying Stress. Shock Vib. 2018, 2018, 3616942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Liu, S. Evaluation of Permeability Damage for Stressed Coal with Cyclic Loading: An Experimental Study. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 216, 103338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Guo, X.; Peng, S.; Zhao, J.; Yan, F. Experimental Investigation on the Permeability and Damage Characteristics of Raw Coal under Tiered Cyclic Unloading and Loading Confining Pressure. Powder Technol. 2021, 389, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, D.; Amann, F.; Bayer, P.; Elsworth, D. Permeability Evolution in Natural Fractures Subject to Cyclic Loading and Gouge Formation. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2016, 49, 3463–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.-J.; Hsu, J.-Y.; Wu, W.-J.; Shimamoto, T.; Hung, J.-H.; Yeh, E.-C.; Wu, Y.-H.; Sone, H. Stress-Dependence of the Permeability and Porosity of Sandstone and Shale from TCDP Hole-A. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2010, 47, 1141–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Su, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yao, J. Stress sensitivity analysis of fractal porous media based on the Elasto-plastic Thick-walled Cylinder Model. Fractals 2021, 29, 2150162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanizadeh, A.; Gasparik, M.; Amann-Hildenbrand, A.; Gensterblum, Y.; Krooss, B.M. Experimental Study of Fluid Transport Processes in the Matrix System of the European Organic-Rich Shales: I. Scandinavian Alum Shale. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 51, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, K.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, S. Experimental Investigation on the Stress Sensitivity of Permeability in Naturally Fractured Shale. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.-Y.; Shen, Y.-H.; Gao, Y.; Lin, H.; Wan, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Ai, F. Laboratory Study of Stress Sensitivity Characterization and Reservoir Quality Evaluation of Yingxiongling Shale in Qaidam Basin. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 5822–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Chen, Z. Apparent Permeability for Gas Flow in Shale Reservoirs Coupling Effects of Gas Diffusion and Desorption. In Proceedings of the 2nd Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 25–27 August 2014; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Denver, CO, USA, 2014; pp. 2328–2345. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, R.B. Transport Phenomena. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2002, 55, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.K.; Webb, S.W. Gas Transport in Porous Media; Theory and Applications of Transport in Porous Media; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 20, ISBN 978-1-4020-3961-4. [Google Scholar]
- Beskok, A.; Karniadakis, G.E. REPORT: A Model for Flows in Channels, Pipes, and Ducts at Micro and Nano Scales. Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 1999, 3, 43–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civan, F.; Rai, C.S.; Sondergeld, C.H. Shale-Gas Permeability and Diffusivity Inferred by Improved Formulation of Relevant Retention and Transport Mechanisms. Transp. Porous Med. 2011, 86, 925–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanian, M.R.; Aguilera, R.; Kantzas, A. A New Unified Diffusion-Viscous Flow Model Based on Pore Level Studies of Tight Gas Formations. In Proceedings of the SPE Canada Unconventional Resources Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–17 November 2011. SPE-149223-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Lu, D.; Zhang, T. A New Formulation of Apparent Permeability for Gas Transport in Shale. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 23, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Pan, Z.; Ye, Z. Dependence of Gas Shale Fracture Permeability on Effective Stress and Reservoir Pressure: Model Match and Insights. Fuel 2015, 139, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Liu, G.; Xue, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. How Pore Structure Evolves in Shale Gas Extraction: A New Fractal Model. Gas Sci. Eng. 2023, 117, 205061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Elastic–Brittle–Plastic Analysis of Double-Layered Combined Thick-Walled Cylinder Under Internal Pressure. J. Press. Vessel Technol. 2016, 138, 011201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudian, M.S.; Hashemi, M.A.; Tasalloti, A.; Marshall, A.M. Elastic–Brittle–Plastic Behaviour of Shale Reservoirs and Its Implications on Fracture Permeability Variation: An Analytical Approach. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2018, 51, 1565–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yao, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.-S. An Efficient Numerical Simulation of Coupled Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Processes in Deep Shale Gas Reservoirs. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 123112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Li, B.; Ren, C.; Song, H.; Fu, J.; Wu, X. Investigation on Damage-Permeability Model of Dual-Porosity Coal under Thermal-Mechanical Coupling Effect. Gas Sci. Eng. 2024, 123, 205229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Cheng, P. A Fractal Permeability Model for Bi-Dispersed Porous Media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 2983–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Guo, J.; Zeng, F.; Zeng, J.; Lu, C.; Zhao, Z. Gas Mass Transfer Characteristics in Shales: Insights from Multiple Flow Mechanisms, Effective Viscosity, and Poromechanics. Gas Sci. Eng. 2024, 125, 205319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B. Analysis of Flow in Fractal Porous Media. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2008, 61, 050801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadpour, F.; Fisher, D.; Unsworth, M. Nanoscale Gas Flow in Shale Gas Sediments. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2007, 46, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, D. Modeling Two-Phase Flow Behaviour in a Shale Gas Reservoir with Complex Fracture Networks and Flow Dynamics. Gas Sci. Eng. 2023, 119, 205112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letham, E.A. Matrix Permeability Measurements of Gas Shales: Gas Slippage and Adsorption as Sources of Systematic Error. Bachelor’s Thesis, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Li, G.; Tian, S.; Sheng, M.; Fan, X. An Analytical Model for Real Gas Flow in Shale Nanopores with Non-circular Cross-section. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 2893–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M. Development of a New Correlation of Gas Compressibility Factor (Z-Factor) for High Pressure Gas Reservoirs. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2014, 136, 012903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.L.; Gonzalez, M.H.; Eakin, B.E. The Viscosity of Natural Gases. J. Pet. Technol. 1966, 18, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, S.; Xi, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhao, N.; Tang, H.; Zhao, S. Estimation of Shale Adsorption Gas Content Based on Machine Learning Algorithms. Gas Sci. Eng. 2024, 127, 205349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, S. A Fractal Permeability Model for Real Gas in Shale Reservoirs Coupled with Knudsen Diffusion and Surface Diffusion Effects. Fractals 2020, 28, 2050017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yao, B.; Yao, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L. Methane Surface Diffusion Capacity in Carbon-Based Capillary with Application to Organic-Rich Shale Gas Reservoir. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameters | Symbol | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas molar mass | M | kg/mol | 16 × 10−3 |
| Gas molecule diameter | d | m | 0.38 × 10−9 |
| Maximum effective pore radius | λmax | m | 1 × 10−7 |
| Temperature | T | K | 300 |
| Gas constant | R | J/(mol·K) | 8.314 |
| Poisson’s ratio | ν | dimensionless | 0.018 |
| Young’s modulus | E | Pa | 0.5 × 109 |
| Langmuir Pressure | PL | Pa | 16.97 × 106 |
| Maximum adsorption capacity | CL | mol/m3 | 328.7 |
| Isosteric adsorption heat | ΔH | J/mol | 16,000 |
| The ratio of the rate constant for blockage to the rate constant for forward migration | κ | dimensionless | 0.5 |
| The ratio of the outer radius of the capillary to the inner radius | t | dimensionless | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, A.; Yao, J.; Zhang, X. The Impact of Elastoplastic Deformation Behavior on the Apparent Gas Permeability of Deep Fractal Shale Rocks. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9080526
Zhou X, Huang Z, Li A, Yao J, Zhang X. The Impact of Elastoplastic Deformation Behavior on the Apparent Gas Permeability of Deep Fractal Shale Rocks. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(8):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9080526
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xu, Zhaoqin Huang, Aifen Li, Jun Yao, and Xu Zhang. 2025. "The Impact of Elastoplastic Deformation Behavior on the Apparent Gas Permeability of Deep Fractal Shale Rocks" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 8: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9080526
APA StyleZhou, X., Huang, Z., Li, A., Yao, J., & Zhang, X. (2025). The Impact of Elastoplastic Deformation Behavior on the Apparent Gas Permeability of Deep Fractal Shale Rocks. Fractal and Fractional, 9(8), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9080526





