Dynamical Analysis of Time Fractional Radial Groundwater Flow Equation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Preliminaries
2.1. Caputo Fractional Derivative
2.2. Atangana–Baleanu Fractional Derivative in Caputo Sense
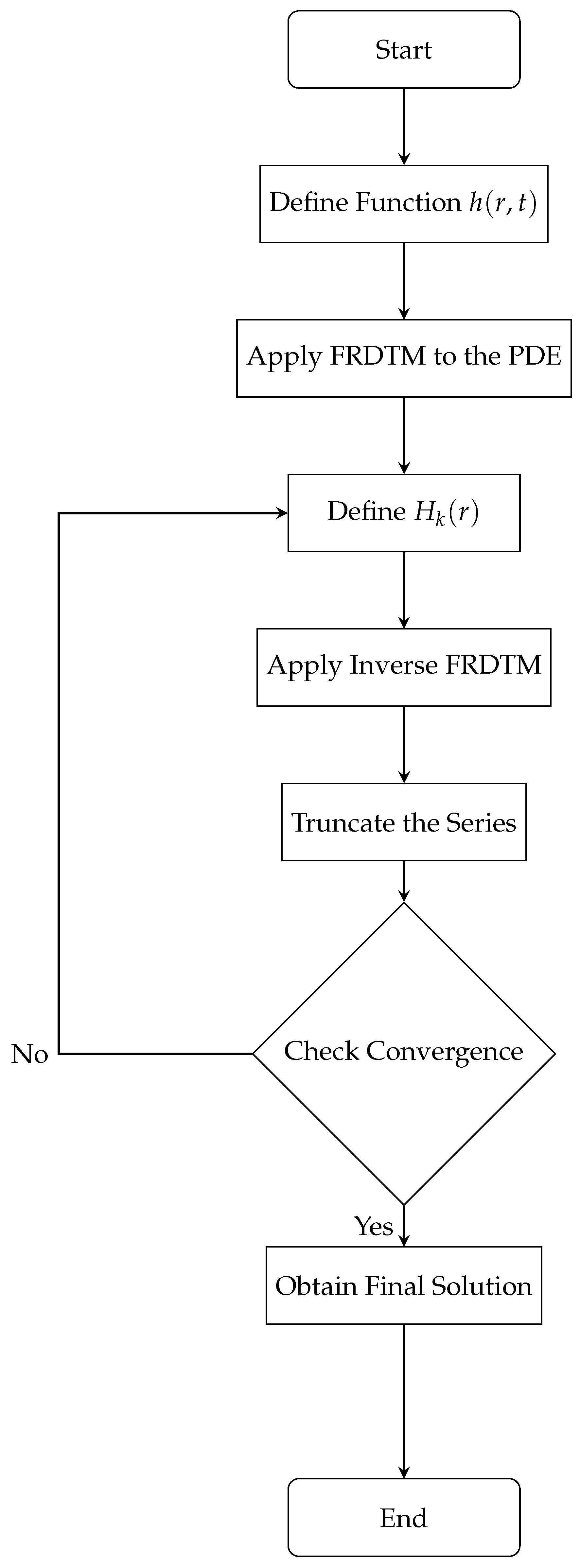
3. Description of the Fractional Reduced Differential Transform Method (FRDTM)
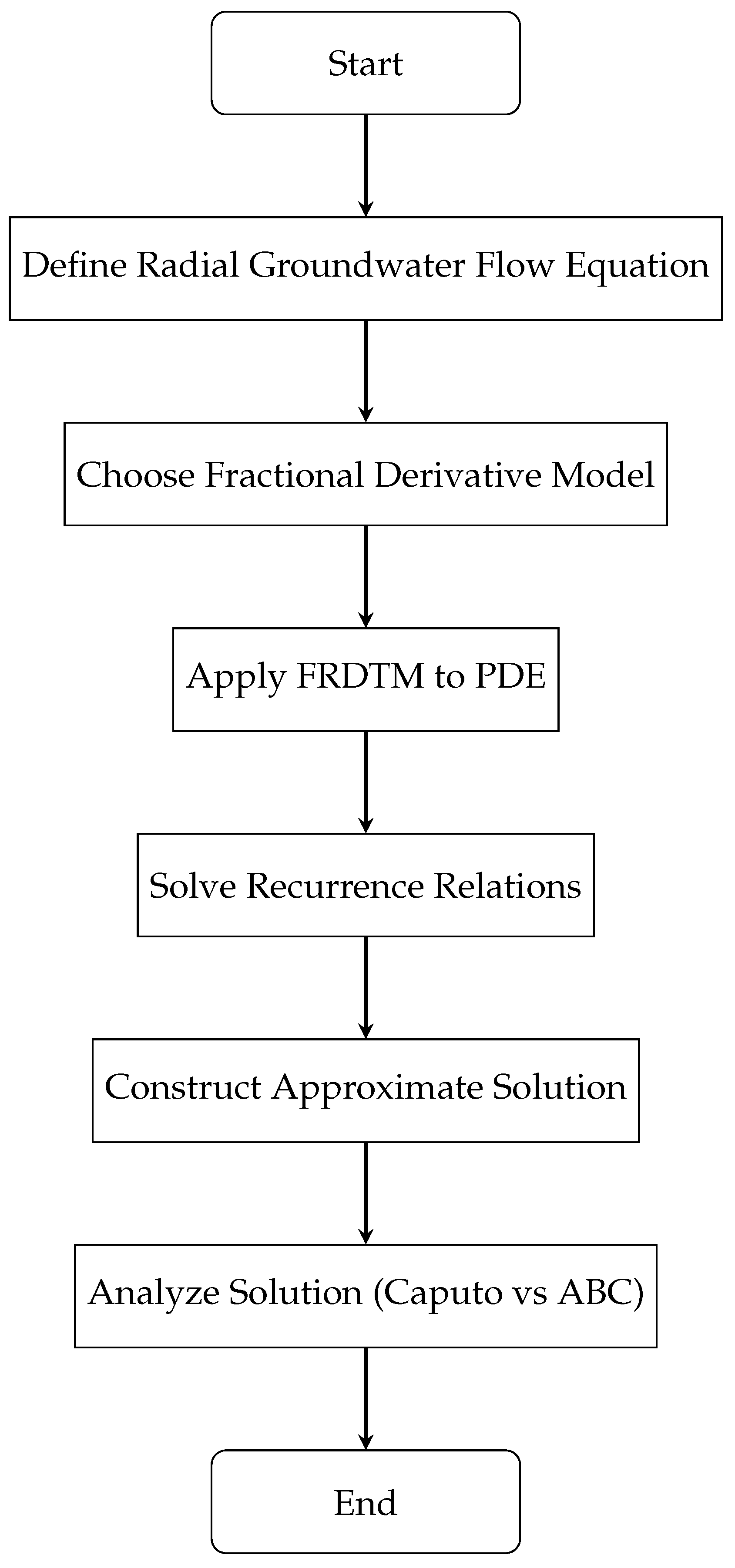
4. Application of FRDTM to Time-Fractional Radial Groundwater Flow Equation with Caputo and Atangana–Baleanu Derivatives
4.1. Caputo Case
4.2. Atangana–Baleanu Caputo Case
5. Convergence and Stability Analysis
5.1. Convergence and Stability Analysis in the Caputo Case
5.1.1. Convergence in the Caputo Case
5.1.2. Generalized Stability Analysis for FRDTM in Caputo Case
Stability Under Perturbations in Initial Conditions
Stability Under Perturbations in Boundary Conditions and External Forces
Stability Under Model Inaccuracies and Numerical Errors
5.1.3. Convergence in the ABC Case
Generalized Stability Under the ABC Fractional Derivative
Stability Under Perturbations in Initial Conditions
Recurrence Relation for ABC Derivative
Norm-Based Energy Analysis
5.1.4. Stability Under Perturbations in Boundary Conditions
Stability Under External Forcing Disturbances
Stability Under Model Inaccuracies and Numerical Errors
6. Error Analysis
6.1. Error Bound Estimate
- The initial condition implies , setting a zero baseline.
- The source term is smooth, spatially bounded, and rapidly decaying, preventing unbounded growth.
- The recurrence relations for contain the factor , which decays super-exponentially with k, dominating any polynomial growth of spatial derivatives or .
- The spatial domain is bounded (), and the spatial derivatives of the functions are controlled since involve polynomials multiplied by decaying exponentials .
6.2. Numerical Estimates of Error Bound for Various Fractional Orders and Radial Distances
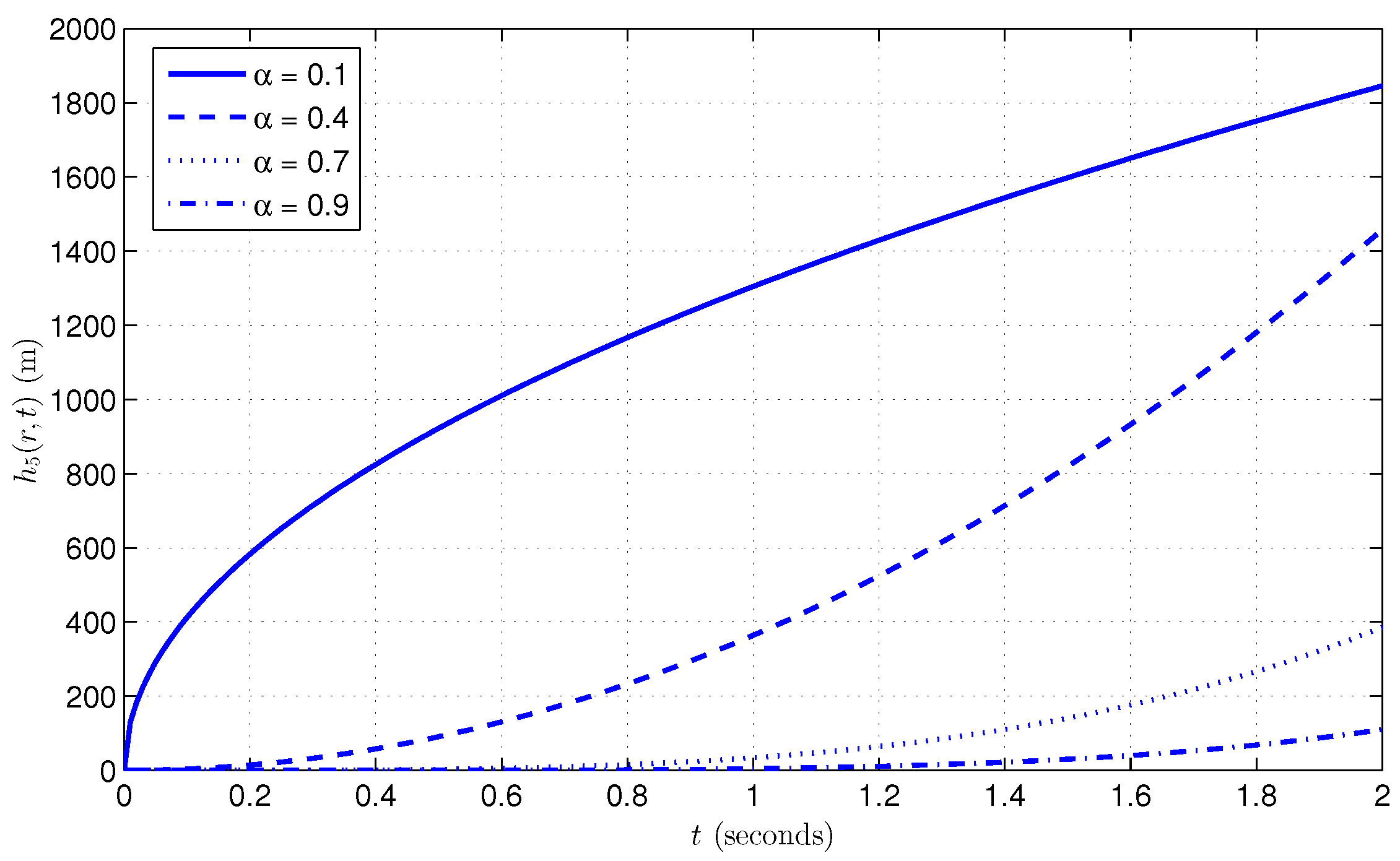
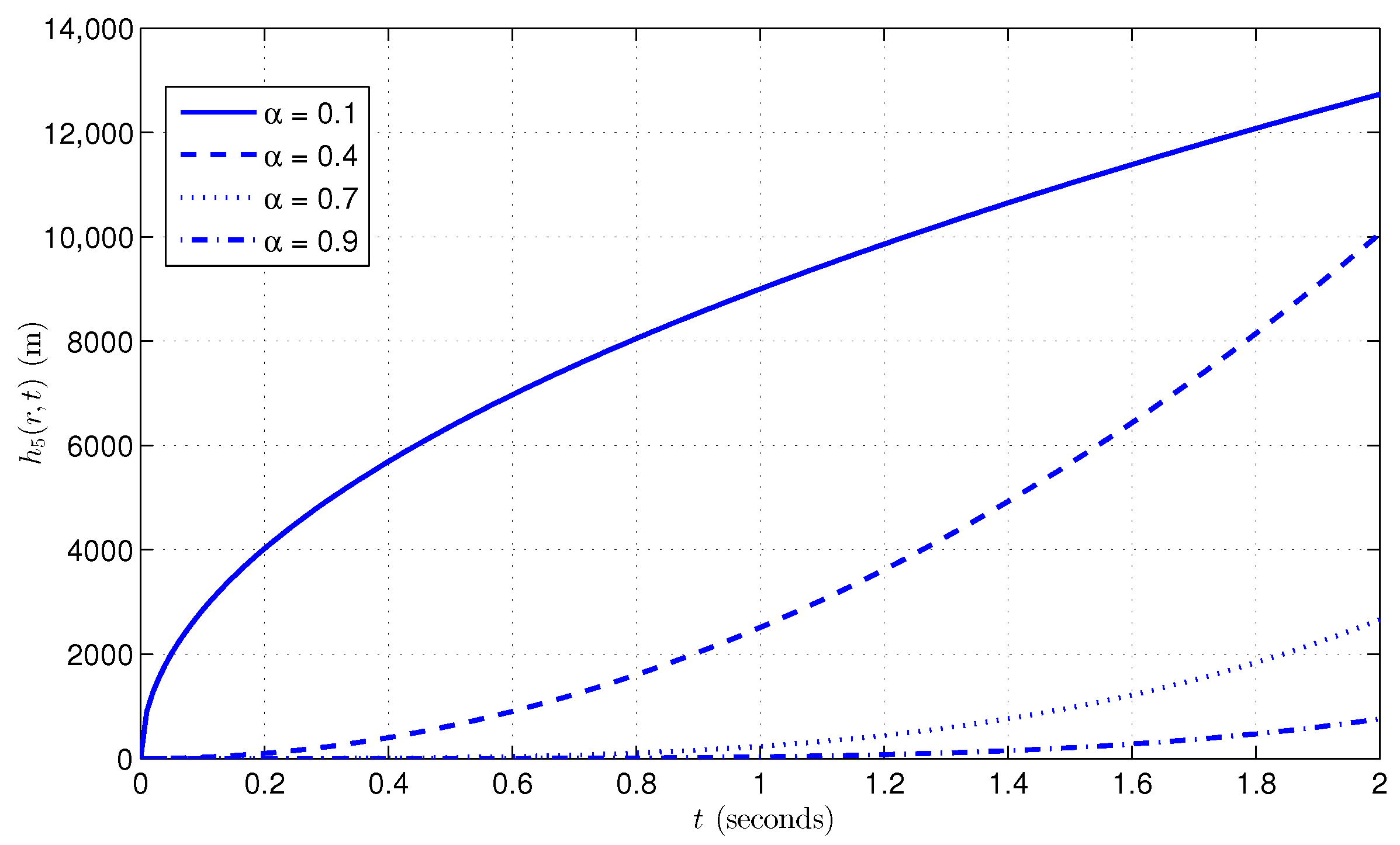
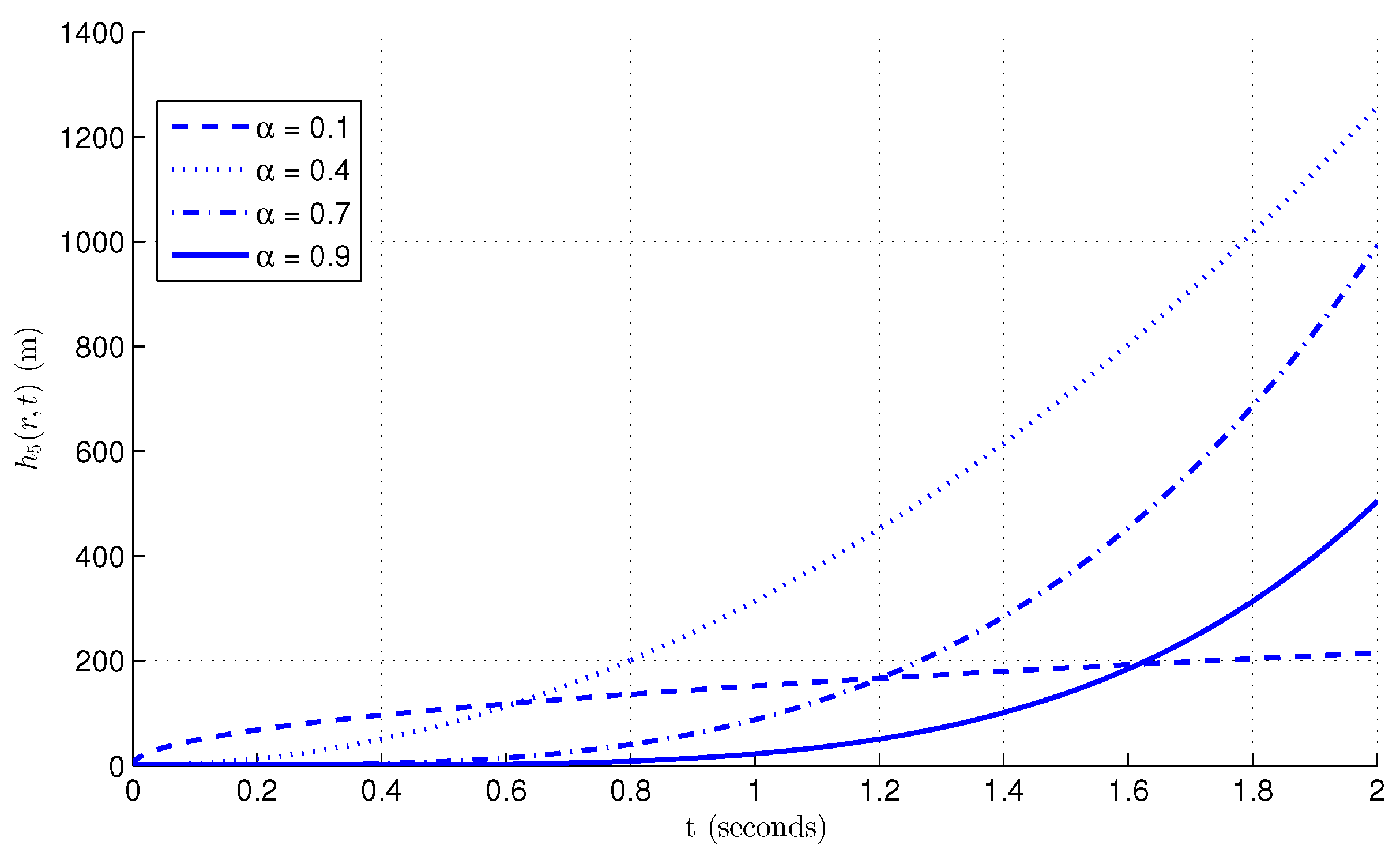
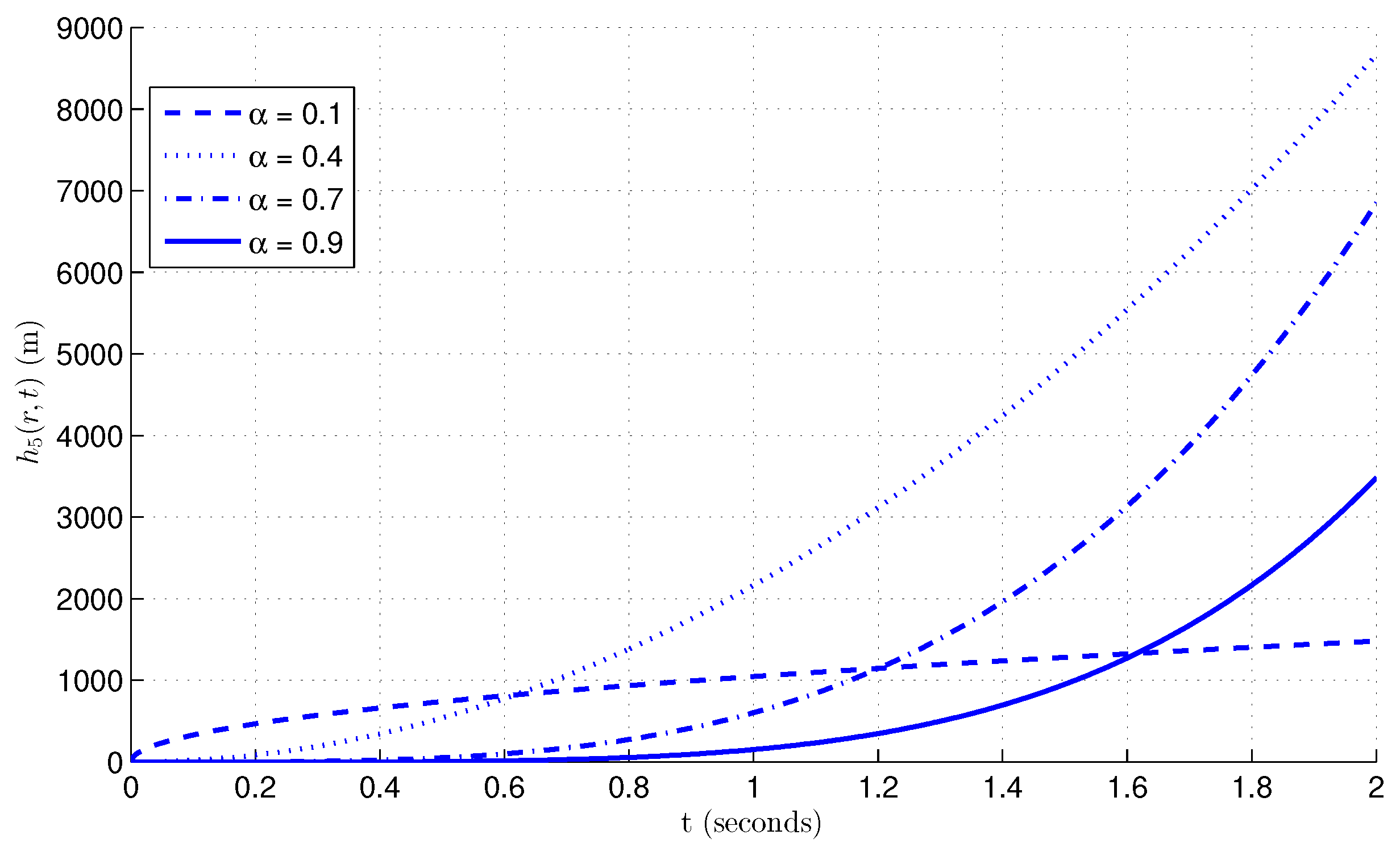
7. Illustration and Discussion
Discussion on Truncation and Boundedness of the Series Solution
- Decay of Higher-Order Terms: The series contains the factor for each term, where . For smaller values of t (as those used in the numerical example), the factor decays quickly as k grows. Because of this, the contribution of higher-order terms is reduced, and there is only a slight inaccuracy introduced when the series is truncated at a finite term (like the fifth term).
- Error Bound for Truncation: The inaccuracy resulting from truncation can be constrained by the summation of the residual terms in the series. The series converges swiftly because of the decay of , resulting in limited contributions from higher-order terms, hence keeping the truncated series within an acceptable error margin. The truncation error is primarily influenced by the subsequent term in the series, which diminishes rapidly for increasing k.
- Stability and Convergence of the Truncated Solution: Despite the truncation, the solution remains stable owing to the limited characteristics of each term in the series. The regularity of the physical system, along with the decay of the fractional time term , ensures that the series converges to a definitive solution. The constrained and fast decaying truncated terms ensure that the truncated solution is stable and effectively reflects the system’s behavior.
- Numerical Approximation and Practical Relevance: The series truncation at the fifth term yields a practical approximation that is precise for standard values of t and r employed in the numerical example. The truncation error is minimal and does not influence the overall performance of the solution. This renders the strategy computationally efficient while guaranteeing that the answer is stable and bounded.
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konikow, L.F.; Mercer, J.W. Groundwater flow and transport modeling. J. Hydrol. 1988, 100, 379–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, T.; Zhang, D. Water flow and solute spreading in heterogeneous soils with spatially variable water content. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.M.; Yeh, H.D. Investigation of solute transport in nonstationary unsaturated flow fields. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 4049–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J. Hydraulics of Groundwater; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Marsily, G.D. Quantitative Hydrogeology: Groundwater Hydrology for Engineers; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Knochenmus, L.A.; Robinson, J.L. Descriptions of Anisotropy and Heterogeneity and Their Effect on Ground-Water Flow and Areas of Contribution to Public Supply Wells in a Karst Carbonate Aquifer System; US Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1996.
- Hubbert, M.K. Darcy’s law and the field equations of the flow of underground fluids. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1957, 2, 23–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igboekwe, M.U.; Amos-Uhegbu, C. Fundamental approach in groundwater flow and solute transport modelling using the finite difference method. Earth Environ. Sci. 2011, 556, 301–328. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.F.; Anderson, M.P. Introduction to Groundwater Modeling: Finite Difference and Finite Element Methods; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.W.; Fan, C.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Ku, C.Y. Generalized finite difference method for numerical solutions of density-driven groundwater flows. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2014, 101, 319–350. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez-Negrete, C.; Domínguez-Mota, F.J.; Román-Gutiérrez, R. Interface formulation for generalized finite difference method for solving groundwater flow. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 166, 105990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyakorn, P.S.; Lester, B.H.; Faust, C.R. Finite element techniques for modeling groundwater flow in fractured aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1983, 19, 1019–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, M.; Hooshyarfarzin, B.; Abbaszadeh, M. Numerical simulation based on a combination of finite-element method and proper orthogonal decomposition to prevent the groundwater contamination. Eng. Comput. 2022, 38 (Suppl. 4), 3445–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Eldho, T.I. A meshless weak strong form method for the groundwater flow simulation in an unconfined aquifer. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2022, 137, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaveni, S.P.; Nair, I.S.; Brindha, K.; Elango, L. Finite element modelling to assess the submarine groundwater discharge in an over exploited multilayered coastal aquifer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 67456–67471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, B. The development of fractional calculus. Hist. Math. 1977, 4, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, S.F. Traité du Calcul Différentiel et du Calcul Intégral, 2nd ed.; Courcier: Paris, France, 1819; pp. 409–410. [Google Scholar]
- Abel, N.H. Solution de quelques problèmes à l’aide d’intégrales définies. Oeuvres Complètes 1823, 1, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fourier, J.B.J. Théorie analytique de la chaleur. Oeuvres Fourier 1822, 1, 508. [Google Scholar]
- Liouville, J. Mémoire sur quelques questions de géométrie et de mécanique, et sur un nouveau genre de calcul pour résoudre ces questions. J. l’École Polytech. 1832, 13, 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Yadav, M.P.; Dubey, R.S. Dual permeability fractional model for flow in the karstic aquifer. Comput. Math. Model. 2025, 36, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Yadav, M.P.; Agarwal, R.P.; Goyal, R. Analytic solution of fractional advection dispersion equation with decay for contaminant transport in porous media. Matematicki Vesnik 2019, 71, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Yadav, M.P.; Agarwal, R.P.; Baleanu, D. Analytic solution of space time fractional advection dispersion equation with retardation for contaminant transport in porous media. Prog. Fract. Differ. Appl. 2019, 5, 283–295. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Yadav, M.P.; Agarwal, R.P. Analytic solution of time fractional Boussinesq equation for groundwater flow in unconfined aquifer. J. Discontinuity Nonlinearity Complex. 2019, 8, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Yadav, M.P.; Agarwal, R.P. Collation analysis of fractional moisture content based model in unsaturated zone using q-homotopy analysis method. In Methods of Mathematical Modelling: Fractional Differential Equations; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2019; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Yadav, M.P.; Baleanu, D.; Purohit, S.D. Existence and uniqueness of miscible flow equation through porous media with a non singular fractional derivative. AIMS Math. 2020, 5, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturi, D.A. Variational Iteration Method and Analytic Solution for Laplace Equation for Steady Groundwater Flow. GEOMATE J. 2024, 26, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.P.; Agarwal, R. Numerical investigation of fractional-fractal Boussinesq equation. Chaos 2019, 29, 013109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzon, G. Fractional variational iteration method for higher-order fractional differential equations. J. Fract. Calc. Appl. 2024, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.H. Approximate analytical solution for seepage flow with fractional derivatives in porous media. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1998, 167, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Yadav, M.P. Numerical approximations of groundwater flow problem using fractional variational iteration method with fractional derivative of singular and nonsingular kernel. Int. J. Math. Ind. 2024, 16, 2450008-1–2450008-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İbiş, B.; Bayram, M. Approximate solution of time-fractional advection-dispersion equation via fractional variational iteration method. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 769713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomian, G. Nonlinear Stochastic Systems: Theory and Applications to Physics; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Adomian, G. Solving Frontier Problems of Physics: The Decomposition Method; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- You, X.; Li, S.; Kang, L.; Cheng, L. A study of the non-linear seepage problem in porous media via the homotopy analysis method. Energies 2023, 16, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, A.; Joshi, M.S. Homotopy Analysis Method for One-Dimensional Burger’s Equation in Longitudinal Dispersion Phenomena via Porous Media. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 2025, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, A.P.; Joshi, M.S. Application of Homotopy Analysis Method for Solving Fingero-Imbibition Equations in Enhanced Oil Recovery. Improv. Oil Gas Recovery 2025, 9, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Şengül, S.; Bekiryazici, Z.; Merdan, M. Approximate solutions of fractional differential equations using optimal q-homotopy analysis method: A case study of Abel differential equations. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyejekwe, O.N. An inverse problem for a time-fractional heat equation: Determination of a time-dependent coefficient via the Laplace homotopy analysis method. Int. J. Appl. 2025, 14, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Delgado, V.F.; Gómez-Aguilar, J.F.; Yépez-Martínez, H.; Baleanu, D.; Escobar-Jimenez, R.F.; Olivares-Peregrino, V.H. Laplace homotopy analysis method for solving linear partial differential equations using a fractional derivative with and without kernel singularity. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016, 2016, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Singh, B.K. Two-dimensional time fractional-order biological population model and its analytical solution. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2014, 1, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K. Fractional reduced differential transform method for numerical computation of a system of linear and nonlinear fractional partial differential equations. Int. J. Open Probl. Comput. Sci. Math. 2016, 9, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawashdeh, M.S. A reliable method for the space-time fractional Burgers and time-fractional Cahn-Allen equations via the FRDTM. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017, 2017, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, C.V. The relation between the lowering of the piezometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a well using ground-water storage. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1935, 16, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, M. Linear models of dissipation whose Q is almost frequency independent—II. Geophys. J. Int. 1967, 13, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A.; Baleanu, D. New fractional derivatives with nonlocal and nonsingular kernel: Theory and application to heat transfer model. Therm. Sci. 2016, 20, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| r | Caputo Case | ABC Case | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error Bound | Error Bound | |||||
| 0.1 | 0.1 | |||||
| 0.5 | ||||||
| 1.0 | ||||||
| 0.3 | 0.1 | |||||
| 0.5 | ||||||
| 1.0 | ||||||
| 0.5 | 0.1 | |||||
| 0.5 | ||||||
| 1.0 | ||||||
| 0.7 | 0.1 | |||||
| 0.5 | ||||||
| 1.0 | ||||||
| 0.9 | 0.1 | |||||
| 0.5 | ||||||
| 1.0 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhamzi, G.; Kumar, P.; Yadav, M.P.; Dubey, R.S. Dynamical Analysis of Time Fractional Radial Groundwater Flow Equation. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9120797
Alhamzi G, Kumar P, Yadav MP, Dubey RS. Dynamical Analysis of Time Fractional Radial Groundwater Flow Equation. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(12):797. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9120797
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhamzi, Ghaliah, Pravindra Kumar, Mahaveer Prasad Yadav, and Ravi Shanker Dubey. 2025. "Dynamical Analysis of Time Fractional Radial Groundwater Flow Equation" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 12: 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9120797
APA StyleAlhamzi, G., Kumar, P., Yadav, M. P., & Dubey, R. S. (2025). Dynamical Analysis of Time Fractional Radial Groundwater Flow Equation. Fractal and Fractional, 9(12), 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9120797







