An Image-Denoising Framework Using ℓq Norm-Based Higher Order Variation and Fractional Variation with Overlapping Group Sparsity
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A hybrid model of both fractional total variation with overlapping group sparsity and higher order total variation with ℓq norm is presented, which is able to alleviate staircase artifacts sufficiently by exploiting the sparsity characteristics of images and the superiority of fractional calculus;
- The alternating direction method of multipliers is generalized, and a parallel linear ADMM framework is developed. By imposing different weights onto each operator and applying relaxed steps, fast convergence speed is achieved;
- The proposed method can be applied to image deblurring and other image processes, which is preferable in a broad spectrum of practical applications.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Fractional Calculus
2.2. Proximity Operator
2.3. OGS-FTV
3. The Proposed Algorithm
3.1. Derivation of Parallel Linear ADMM
| Algorithm 1 Parallel linear alternating direction method of multipliers |
| 1. Initialization: 2. Iteration: while the stopping criterion is not satisfied, do 3. update by (24); 4. update by (25); 5. update by (26); 6. update by (27); 7. ; 8. end while and return . |
3.2. Application to the Proposed Model
| Algorithm 2 PLADMM for denoising model (31) |
| 1. Initialization: 2. Iteration: while the stopping criterion is not satisfied, do 3. update by (33); 4. update by (34); 5. update by (35); 6. update by (36); 7. ; 8. end while and return . |
4. Numerical Experiments and Analysis
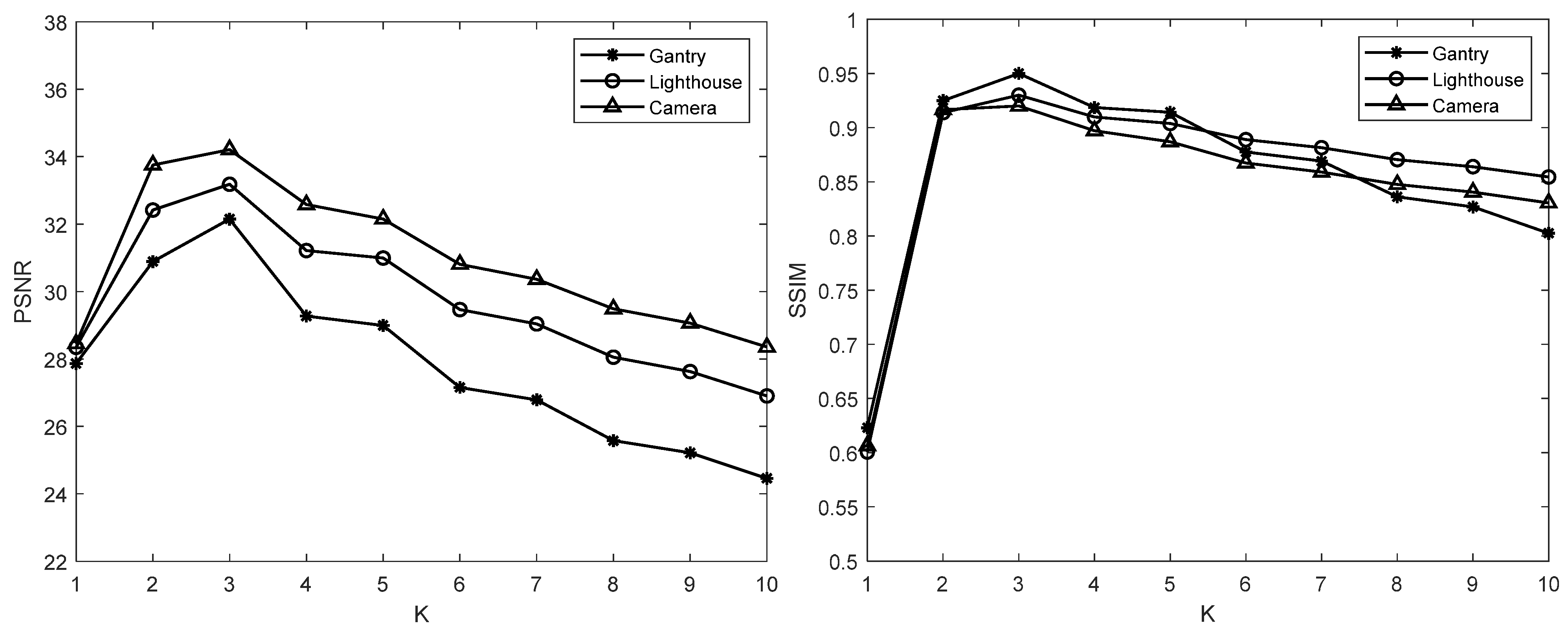
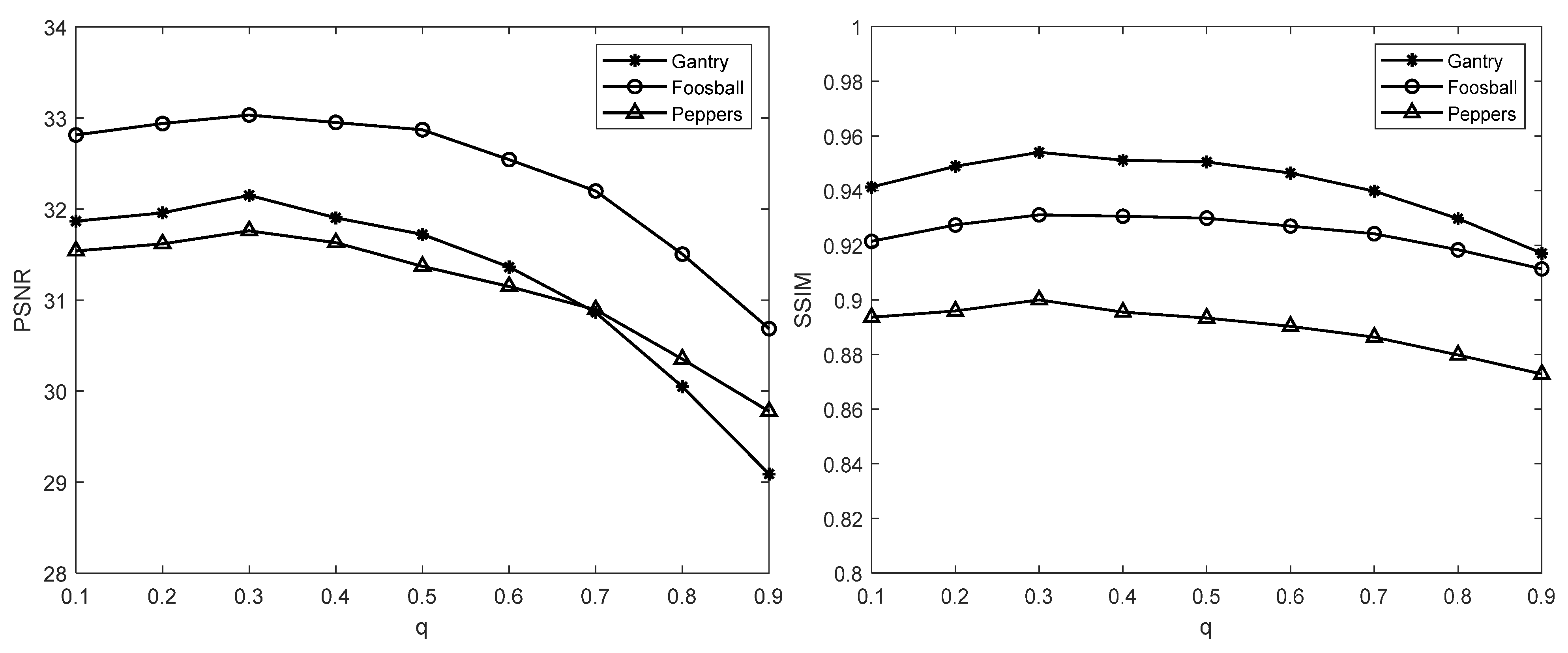
4.1. Parameter Selection
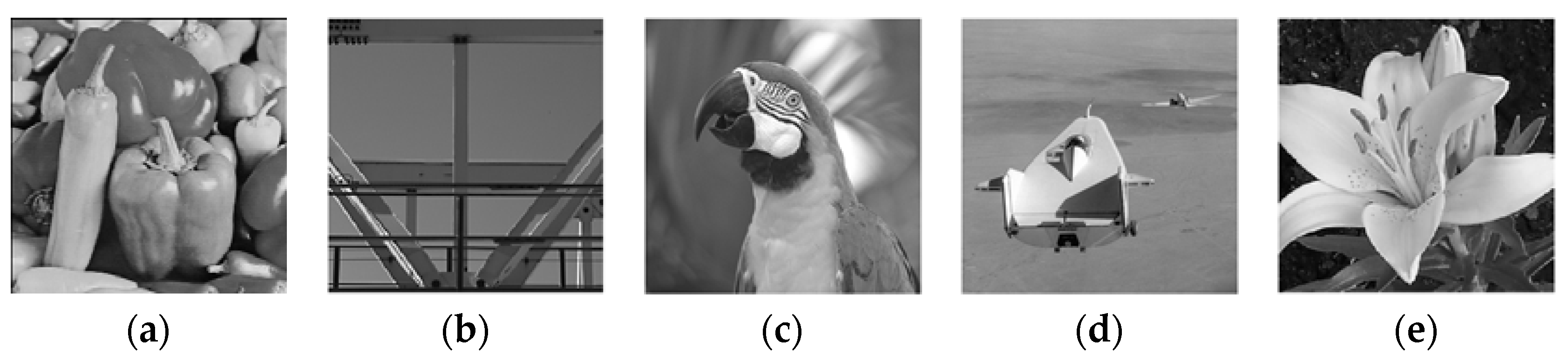
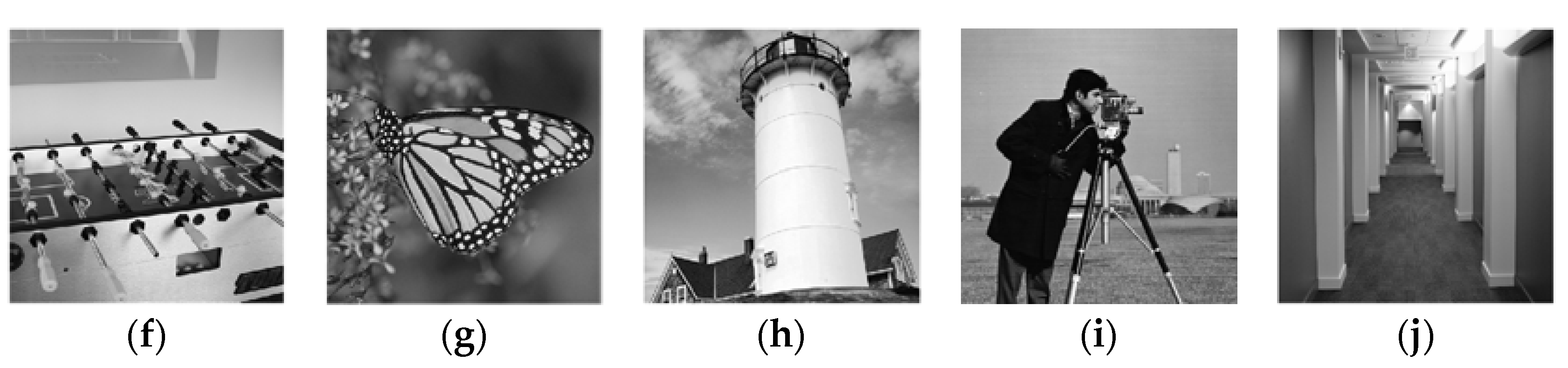
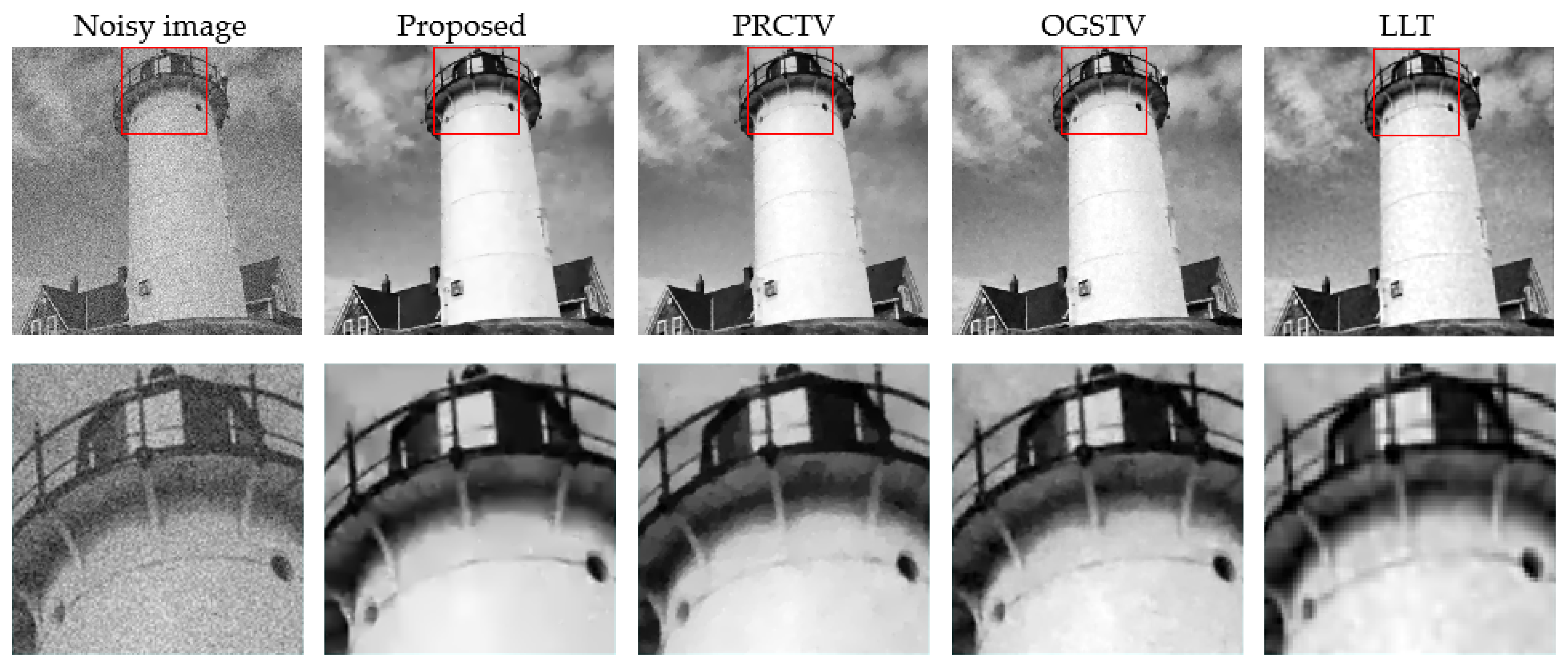
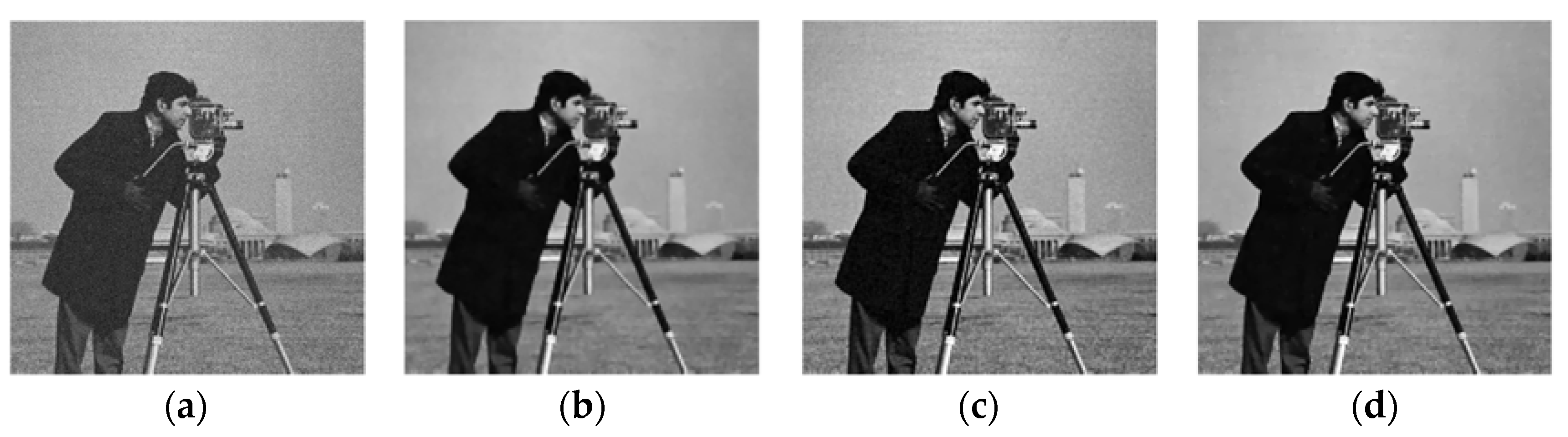
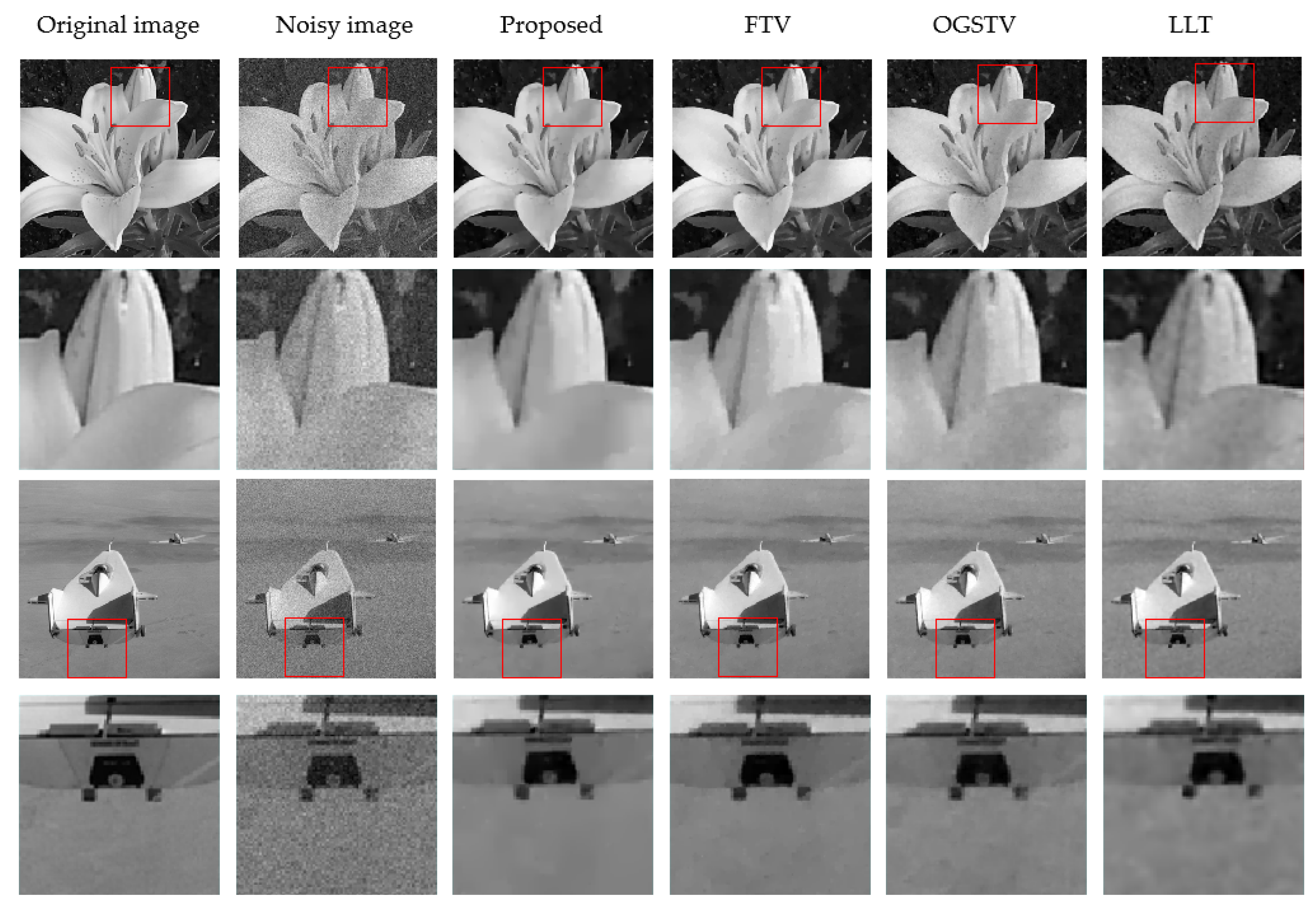
4.2. Experiments on Image Denoising
4.3. Additional Comments on the Regularizers
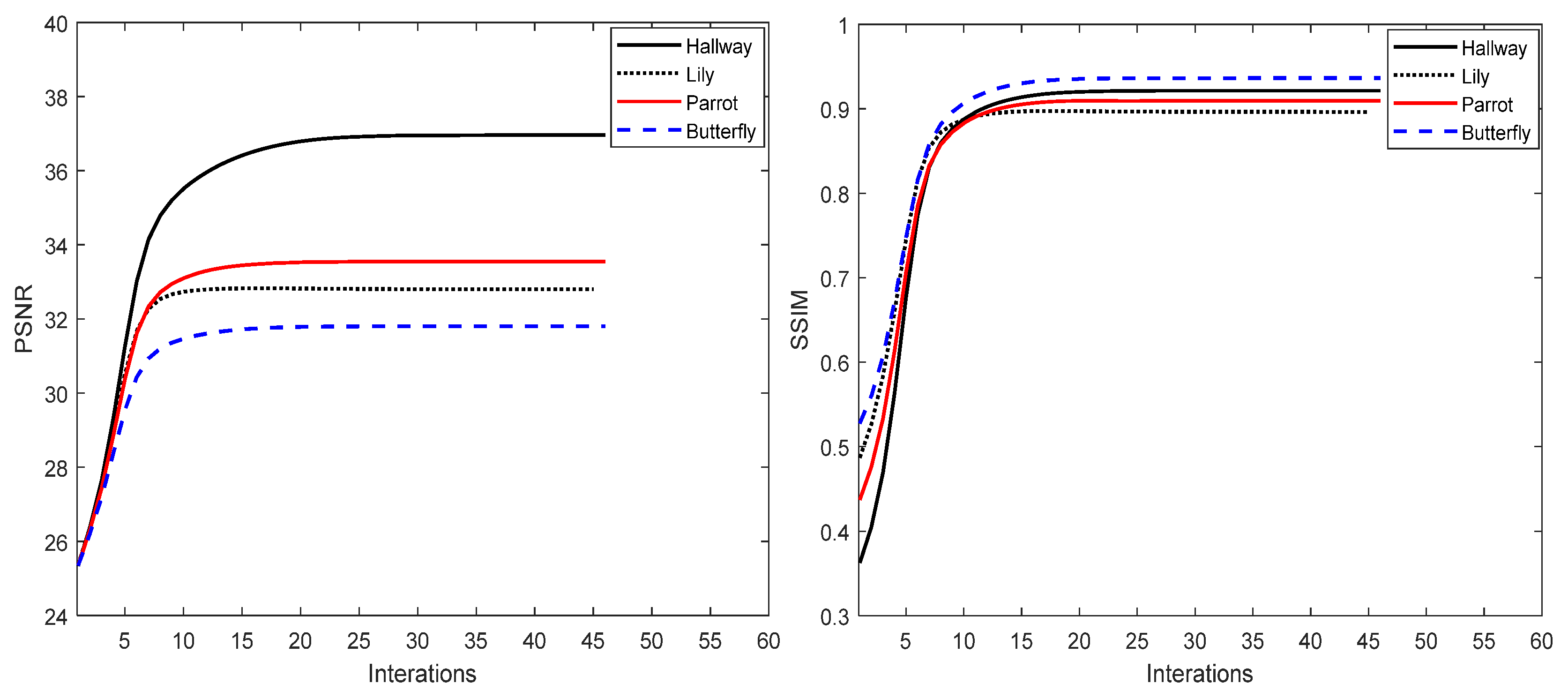
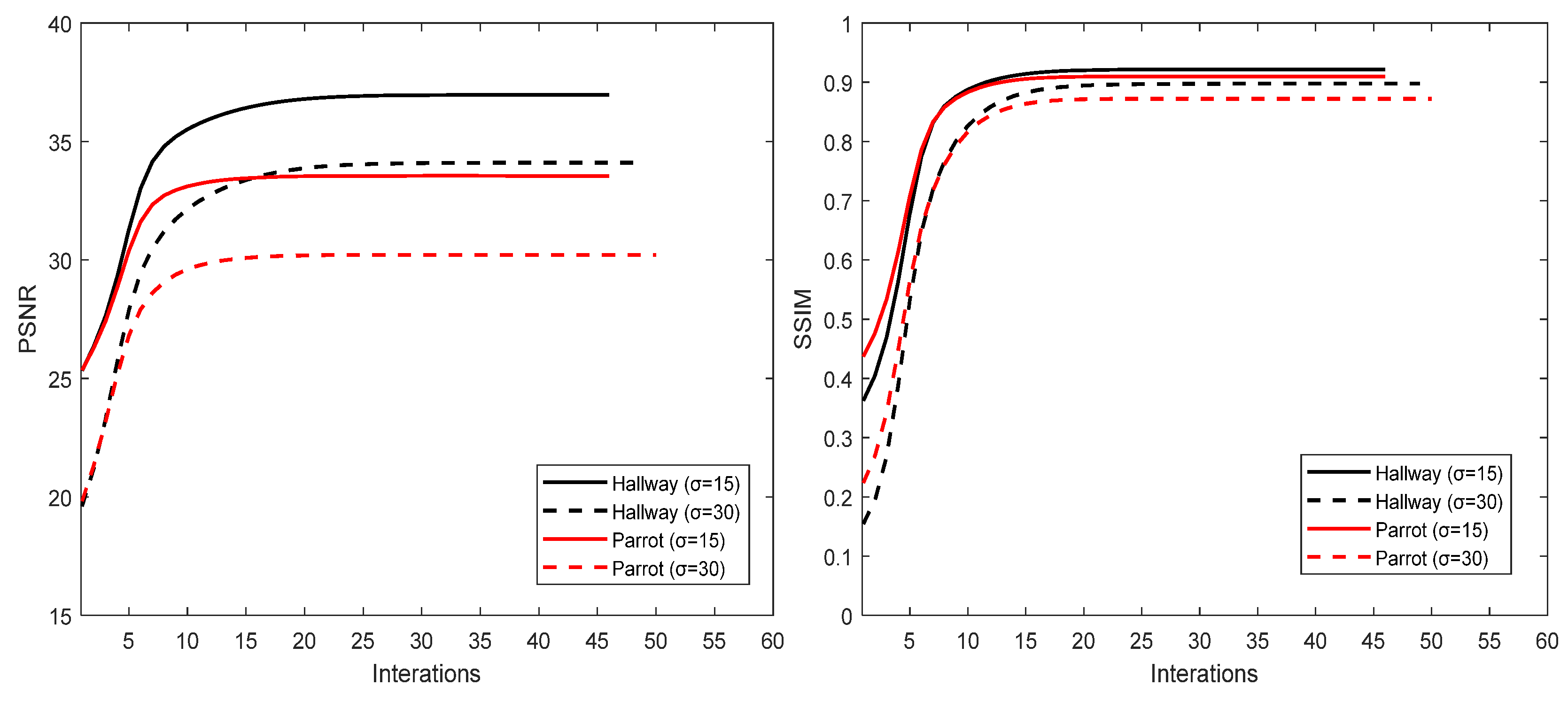
4.4. Convergence
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribes, A.; Schmitt, F. Linear inverse problems in imaging. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilton, D.; Ongie, G.; Willett, R. Neumann networks for linear inverse problems in imaging. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2019, 6, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, L.; Osher, S.; Fatemi, E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1992, 60, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, C. A primal-dual multiplier method for total variation image restoration. Appl. Numer. Math. 2019, 145, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Z.; Shi, B.; Sun, Y. Primal-dual method to smoothing TV-based model for image denoising. J. Algorithms Comput. Technol. 2016, 10, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Hu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. A parallel primal-dual splitting method for image restoration. Inf. Sci. 2016, 358, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Osher, S.; Shen, Z. Split Bregman methods and frame based image restoration. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2010, 8, 337–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Akram, F.; Choi, K.N. Image denoising feedback framework using split Bregman approach. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2017, 87, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Pang, Z.F.; Yang, Y.F. A projection method based on the splitting Bregman iteration for the image denoising. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 39, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ng, M.K.; Zhao, X. Alternating direction method of multipliers for nonlinear image restoration problems. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 24, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Nagy, J.G. An effective alternating direction method of multipliers for color image restoration. Appl. Numer. Math. 2021, 164, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sniba, F.; Karami, F.; Meskine, D. ADMM algorithm for some regularized Perona-Malik equation and applications to image denoising. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.; Marquina, A.; Mulet, P. High-order total variation-based image restoration. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2000, 22, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Le, J. Image restoration with a high-order total variation minimization method. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 8210–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, D.N.; Prasath, V.S.; Hieu, L.M.; Dvoenko, S. An adaptive method for image restoration based on high-order total variation and inverse gradient. Signal Image Video Process. 2020, 14, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysaker, M.; Lundervold, A.; Tai, X. Noise removal using fourth-order partial differential equation with applications to medical magnetic resonance images in space and time. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2003, 12, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredies, K.; Kunisch, K.; Pock, T. Total generalized variation. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2010, 3, 492–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Yang, X. Total generalized variation restoration with non-quadratic fidelity. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 29, 1459–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y. Total generalized variation denoising of speckled images using a primal-dual algorithm. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 62, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, L. A new nonlocal total variation regularization algorithm for image denoising. Math. Comput. Simul. 2014, 97, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Malgouyres, F.; Zeng, T. Regularized non-local total variation and application in image restoration. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2017, 59, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jidesh, P.; Holla, S. Non-local total variation regularization models for image restoration. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 67, 114–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Chen, Y. A fractional-order derivative based variational framework for image denoising. Inverse Probl. Imaging. 2016, 10, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meng, X.; Xiong, B. A fractional variational image denoising model with two-component regularization terms. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 427, 127178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Xue, D. Fractional-order total variation image denoising based on proximity algorithm. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 257, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Xue, D.; Wang, D. A fractional-order adaptive regularization primal-dual algorithm for image denoising. Inf. Sci. 2015, 296, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.J.; Dong, Y.; Huang, T.Z. Simultaneous image fusion and denoising by using fractional-order gradient information. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2019, 351, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, R.; Zeng, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, H. An efficient non-convex total variation approach for image deblurring and denoising. Appl. Math. Comput. 2021, 397, 125977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Tang, L.; Yuan, X. Non-convex weighted ℓp nuclear norm based ADMM framework for image restoration. Neurocomputing 2018, 311, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, Q. Image denoising based on nonconvex anisotropic total-variation regularization. Signal Process. 2021, 186, 108124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Mei, J.; Wang, S.; Ma, T.; Huang, T. Total variation and high-order total variation adaptive model for restoring blurred images with Cauchy noise. Comput. Math. Appl. 2019, 77, 1255–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi Golbaghi, F.; Rezghi, M.; Eslahchi, M.R. A hybrid image denoising method based on integer and fractional-order total variation. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A-Sci. 2020, 44, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, T.; Paramesran, R. Image denoising using combined higher order non-convex total variation with overlapping group sparsity. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 30, 503–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ren, Y.; Fang, Z.; He, C. A generalized hybrid nonconvex variational regularization model for staircase reduction in image restoration. Neurocomputing 2019, 359, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyré, G.; Fadili, J. Group sparsity with overlapping partition functions. In Proceedings of the 2011 19th European Signal Processing Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 29 August–2 September 2011; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Selesnick, I.W.; Chen, P. Total variation denoising with overlapping group sparsity. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 5696–5700. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Huang, T.; Selesnick, I.W.; Lv, X.; Chen, P. Image restoration using total variation with overlapping group sparsity. Inf. Sci. 2015, 295, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wei, Y.; Wei, J.; Hao, B. A Non-Convex Hybrid Overlapping Group Sparsity Model with Hyper-Laplacian Prior for Multiplicative Noise. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ahmad, M.O.; Swamy, M.N.S. An efficient denoising framework using weighted overlapping group sparsity. Inf. Sci. 2018, 454, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jon, K.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W. Image restoration using overlapping group sparsity on hyper-Laplacian prior of image gradient. Neurocomputing 2021, 420, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Huang, T.; Wang, S.; Mei, J.; Zhao, X. Total variation with overlapping group sparsity for deblurring images under Cauchy noise. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 341, 128–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Adam, T.; Paramesran, R.; Hassan, M.F. An ℓ0-overlapping group sparse total variation for impulse noise image restoration. Signal Process.-Image Commun. 2022, 102, 116620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micchelli, C.A.; Shen, L.; Xu, Y. Proximity algorithms for image models: Denoising. Inverse Probl. 2011, 27, 045009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| α | Camera | Hallway | Parrot | Planes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 33.9562 | 36.7828 | 33.3577 | 35.5842 |
| 1.1 | 34.1734 | 36.9008 | 33.4138 | 35.6634 |
| 1.2 | 34.2049 | 36.9644 | 33.5486 | 35.7519 |
| 1.3 | 34.1718 | 36.9445 | 33.4561 | 35.6872 |
| 1.4 | 34.1873 | 36.9039 | 33.4772 | 35.6516 |
| 1.5 | 34.1551 | 36.9161 | 33.4026 | 35.6633 |
| 1.6 | 34.1290 | 36.8760 | 33.3926 | 35.6024 |
| 1.7 | 34.1272 | 36.8339 | 33.3683 | 35.5833 |
| 1.8 | 34.0845 | 36.8497 | 33.3449 | 35.5661 |
| 1.9 | 34.0715 | 36.8308 | 33.3274 | 35.5621 |
| σ | Images | Proposed | FTV | OGSTV | LLT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR/SSIM/Time(s) | PSNR/SSIM/Time(s) | PSNR/SSIM/Time(s) | PSNR/SSIM/Time(s) | ||
| 15 | Lily | 32.80/0.90/1.53 | 32.51/0.90/2.05 | 32.38/0.89/0.43 | 32.29/0.88/1.29 |
| Butterfly | 31.80/0.94/3.29 | 31.51/0.92/2.42 | 31.27/0.90/0.63 | 31.05/0.90/1.27 | |
| Foosball | 33.01/0.93/3.07 | 32.77/0.92/2.27 | 32.52/0.92/0.67 | 31.87/0.90/1.10 | |
| Peppers | 32.34/0.92/0.79 | 32.12/0.91/1.10 | 31.99/0.91/0.18 | 31.54/0.91/0.41 | |
| planes | 35.72/0.92/1.14 | 35.40/0.92/1.41 | 35.11/0.91/0.21 | 34.33/0.90/0.52 | |
| Gantry | 32.15/0.95/0.94 | 31.98/0.94/1.50 | 31.51/0.93/0.30 | 30.70/0.90/0.63 | |
| Lighthouse | 33.18/0.93/3.93 | 32.92/0.91/2.86 | 32.85/0.91/0.85 | 32.15/0.90/1.52 | |
| Parrot | 33.55/0.91/1.14 | 33.18/0.90/1.69 | 32.81/0.90/0.57 | 32.66/0.89/0.55 | |
| Camera | 34.21/0.92/5.12 | 34.08/0.91/3.46 | 33.79/0.91/1.13 | 33.40/0.91/2.68 | |
| Hallway | 36.96/0.92/11.02 | 36.67/0.91/9.16 | 36.18/0.90/2.08 | 35.30/0.90/7.32 | |
| (Average) | 33.57/0.92/3.20 | 33.31/0.91/2.79 | 33.04/0.91/0.71 | 32.53/0.90/1.73 | |
| 30 | Lily | 29.49/0.83/1.87 | 29.02/0.83/1.89 | 28.75/0.82/0.51 | 28.18/0.81/1.65 |
| Butterfly | 28.07/0.89/3.65 | 27.51/0.88/3.20 | 27.29/0.87/0.95 | 26.72/0.86/2.07 | |
| Foosball | 29.31/0.89/3.47 | 28.89/0.88/2.70 | 28.35/0.87/1.37 | 27.49/0.83/0.94 | |
| Peppers | 28.78/0.87/0.93 | 28.52/0.86/1.22 | 28.22/0.85/0.21 | 27.75/0.85/0.57 | |
| planes | 32.49/0.90/1.20 | 32.05/0.89/1.61 | 31.68/0.88/0.60 | 30.82/0.86/1.12 | |
| Gantry | 28.14/0.89/1.43 | 28.15/0.89/1.48 | 27.48/0.86/0.43 | 26.58/0.81/0.87 | |
| Lighthouse | 29.77/0.89/4.61 | 29.46/0.88/3.55 | 29.04/0.85/1.31 | 28.35/0.84/2.55 | |
| Parrot | 30.27/0.87/1.75 | 29.81/0.87/1.66 | 29.42/0.86/0.64 | 29.08/0.84/0.79 | |
| Camera | 30.88/0.87/5.76 | 30.89/0.87/4.09 | 30.35/0.86/1.75 | 29.86/0.85/3.20 | |
| Hallway | 34.11/0.90/11.88 | 33.79/0.89/11.55 | 33.47/0.88/4.49 | 32.02/0.86/8.50 | |
| (Average) | 30.13/0.88/3.66 | 29.81/0.87/3.30 | 29.41/0.86/1.23 | 28.69/0.84/2.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Cai, G.; Li, M.; Bi, S. An Image-Denoising Framework Using ℓq Norm-Based Higher Order Variation and Fractional Variation with Overlapping Group Sparsity. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7080573
Zhang X, Cai G, Li M, Bi S. An Image-Denoising Framework Using ℓq Norm-Based Higher Order Variation and Fractional Variation with Overlapping Group Sparsity. Fractal and Fractional. 2023; 7(8):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7080573
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xi, Guangcheng Cai, Minmin Li, and Shaojiu Bi. 2023. "An Image-Denoising Framework Using ℓq Norm-Based Higher Order Variation and Fractional Variation with Overlapping Group Sparsity" Fractal and Fractional 7, no. 8: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7080573
APA StyleZhang, X., Cai, G., Li, M., & Bi, S. (2023). An Image-Denoising Framework Using ℓq Norm-Based Higher Order Variation and Fractional Variation with Overlapping Group Sparsity. Fractal and Fractional, 7(8), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7080573





