Abstract
In this paper, we prove some new Newton’s type inequalities for differentiable convex functions through the well-known Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals. Moreover, we prove some inequalities of Riemann–Liouville fractional Newton’s type for functions of bounded variation. It is also shown that the newly established inequalities are the extension of comparable inequalities inside the literature. Finally, we give some examples with graphs and show the validity of newly established inequalities.
1. Introduction
Fractional calculus (that is, calculus of integrals and derivatives of any arbitrary real or complex order) has grown in popularity and relevance over the last three decades, owing to its demonstrated applications in a wide range of seemingly disparate domains of science and engineering. It does give some potentially valuable tools for solving differential and integral equations, a variety of other problems involving mathematical physics special functions, and their extensions and generalizations in one or more variables.
The concept of fractional calculus is widely thought to have originated with a question posed to Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (1646–1716) by Marquis de L’Hôpital (1661–1704) in 1695, in which he tried to understand the meaning of Leibniz’s notation for the derivative of order , when (What if ?). Leibniz replied to L’Hôpital on 30 September 1695, with the following message: “… This is an apparent paradox from which, one day, useful consequences will be drawn. …”.
The theories of differential, integral, and integro-differential equations, and special functions of mathematical physics, as well as their extensions and generalizations in one and more variables, some of the areas of present applications of fractional calculus include fluid flow, rheology, dynamical processes in self-similar and porous structures, diffusive transport akin to diffusion, electrical networks, probability and statistics, control theory of dynamical systems, viscoelasticity, electrochemistry of corrosion, chemical physics, optics, signal processing, etc.
Because of the importance of fractional calculus, researchers have utilized it to establish various fractional integral inequalities that are quite useful in approximation theory. Inequalities, such as Hermite–Hadamard, Simpson’s, midpoint, Ostrowski’s, and trapezoidal inequalities are examples, and by using these inequalities, we can obtain the bounds of formulas used in numerical integration. In [1], Sarikaya et al. proved some Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities and trapezoidal-type inequalities for the first time using the Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals.
Set [2] proved a Riemann–Liouville fractional version of Ostrowski’s inequalities for differentiable functions. İşcan and Wu used harmonic convexity and proved Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities in [3]. Sarikaya and Yildrim [4] used Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals to prove some new Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities and midpoint-type inequalities for differentiable convex functions. Sarikaya et al. [5] proved the general version of Simpson’s type inequalities for differentiable s-convex functions.
In [6], the authors used Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals, and proved some of Simpson’s type inequalities for general convex functions. Chen and Huang provided another version of Simpson’s type inequalities for differentiable s-convex functions in [7]. Mubeen and Habibulla [8] introduced the notions of general Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals, called k-fractional integrals, and the authors used these integrals to prove some new Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities in [9]. Using the k-fractional integrals, the authors proved Ostrowski’s type inequalities for differentiable functions in [10]. In [11], Zhang et al. used k-fractional integrals and proved different integral inequalities for general convex functions.
Recently, Sarikaya and Ertugral [12] defined a new class of fractional integrals, called generalized fractional, and they used these integrals to prove the general version of Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities for convex functions. In [13], the authors used generalized fractional integrals and proved some trapezoidal-type inequalities for convex harmonic functions. Budak et al. [14] proved several variants of Ostrowski’s and Simpson’s type for differentiable convex functions via generalized fractional integrals. In [15], Awan et al. established some new Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities involving Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals, and in [16], some new Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities for k-fractional integrals were established. Khan et al. [17,18] proved some new estimates of Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities for Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals and conformable fractional integrals. Set et al. [19] and Tunc [20] proved some new variants of Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities for convex and h-convex functions, respectively using the fractional integrals. Zaho et al. [21] established generalized Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities for interval-valued functions.
On the other hand, several papers focused on the functions of bounded vatiation to prove some important inequalities, such as Ostrowski-type [22], Simpson-type [23,24], trapezoid-type [25,26], and midpoint-type [27].
Motivated by the ongoing studies, we establish Newton’s formula-type inequalities for differentiable convex functions and bounded variations via Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals, and give some examples of their graphs to show the validity.
The following is a summary of the paper: The basics of fractional calculus and other relevant research in this discipline are briefly discussed in Section 2. We establish an integral identity in Section 3 that is critical in establishing the primary outcomes of the paper. Section 4 gives some new Newton’s type inequalities for differentiable convex functions using Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals. Section 5 contains some fractional Newton-type inequalities for functions of bounded variation. Section 6 finishes with some research ideas for the future.
2. Fractional Integrals and Related Inequalities
In this section, we review several fundamental, fractional, integral notations and concepts. Different fractional integrals are also used to recall various inequalities.
Definition 1.
([28,29]) Let The Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals (RLFIs) and of order with are defined as follows:
and
respectively, where Γ is the well-known Gamma function.
For the first time in 2013, Sarikaya et al. proved the following fractional Hermite–Hadmard-type inequality:
Theorem 1.
([1]) For a positive convex function with and the following inequality holds:
Sarikaya and Yildrm then demonstrated the following new form of the fractional Hermite–Hadamard inequality:
Theorem 2.
([4]) For a positive convex function with and the following inequality holds:
Remark 1.
Chen and Huang proposed the following fractional form of Simpson’s type inequality for differentiable s-convex functions:
Theorem 3.
([7]) Suppose that a differentiable function with , and (interior of I). If is a s-convex function, then following inequality holds:
where
Remark 2.
From inequality (4), we have
- (i)
- If we set , then we obtain the classical Simpson’s inequality for s-convex functions (see, [5] [Theorem 7]):
- (ii)
- If we set , then we obtain the classical Simpson’s inequality for convex functions (see, [5] [Corollary 1]):
3. An Identity
We prove integral equality in this section to prove the main results of this paper.
Lemma 1.
For a mapping , which is differentiable over with , we have the following RLFIs identity:
where
4. Fractional Newton’s Inequalities for Differentiable Convex Functions
In this section, we use RLFIs to show some new Newton’s inequalities for differentiable convex functions. We use the following notations for the sake of brevity:
Theorem 4.
Assume that the conditions of Lemma 1 hold. If is convex function, then we have the following Newton’s type inequality:
Proof.
Taking modulus in (7) and using convexity of , we have
This completes the proof. □
Example 1.
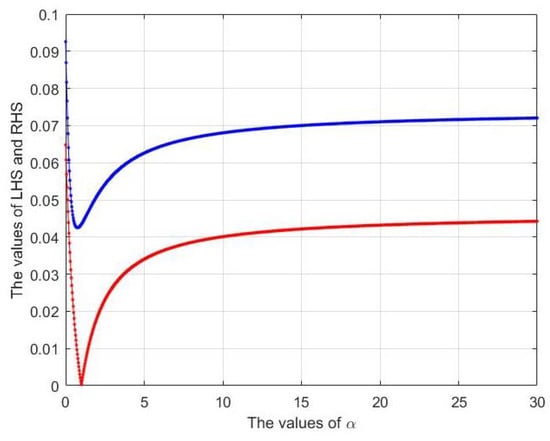
Let and define the function such that and is convex on Under these assumptions, we have
By definition of Riemann-Liouville fractional integrals, we obtain
and
By these equalities, we have
The left hand side of the inequality (11) reduce to
On the other hand, since and , we have the right hand side of the inequality (11) as follows:
It is clear from Figure 1 that for all

Figure 1.
An example to Theorem 4.
Remark 3.
In Theorem 4, if we set , then we have the following inequality:
Theorem 5.
Assume that the conditions of Lemma 1 hold. If is convex function, then we have the following Newton’s type inequality:
Proof.
By taking modulus in (7) and applying power mean inequality, we have
Using convexity of , we have
Thus, the proof is completed. □
Remark 4.
In Theorem 5, if we set , then we have the following inequality:
Theorem 6.
Assume that the conditions of Lemma 1 hold. If is convex function, then we have the following Newton’s type inequality:
where and
Proof.
Taking modulus in (7) and applyin Hölder inequality, we have
By using convexity of with , we obtain
Thus, the proof is completed. □
Remark 5.
In Theorem 6, if we set , then we have the following inequality:
5. Fractional Newton Type Inequality for Functions of Bounded Variation
In this section, we prove a fractional Newton type inequality for the function of bounded variation.
Theorem 7.
Let be a function of bounded variation on Then we have the following Newton type inequality for Riemann-Liouville fractional integrals
where denotes the total variation of Υ on
Proof.
Define the mapping by
It follows from that
Integrating by parts, we get
Similarly, we have
and
It is well known that if are such that g is continuous on and is of bounded variation on then exist and
On the other hand, using (19), we get
This completes the proof. □
Remark 6.
If we take in Theorem 7, then we get the inequality
which is given by Alomari in [31].
6. Conclusions
We demonstrated some new Newton’s type inequalities for differentiable convex functions using Riemann-Liouville fractional integrals. Furthermore, we established fractional Newton’s type inequalities for bounded variation functions via the Riemann-Liouville fractional integrals. We demonstrated the validity of newly obtained results with a mathematical example and graphs. We also proved that the newly established results are the extension of already existing results inside the literature. It is new problem that the upcoming researchers can obtain the similar inequalities for fractal sets and coordinated convex functions in their future work.
Author Contributions
We confirm that T.S., K.N., M.A.A. and H.B. contribute equally. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has received funding support from the NSRF via the Program Management Unit for Human Resources & lnstitutional Development, Research and lnnovation [grant number B05F640163].
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research has received funding support from the National Science, Research and Innovation Fund (NSRF), Thailand. We thanks to worthy referees and editor for their valuable comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sarikaya, M.Z.; Set, E.; Yaldiz, H.; Başak, N. Hermite–Hadamard’s inequalities for fractional integrals and related fractional inequalities. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 2013, 57, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Set, E. New inequalities of Ostrowski type for mappings whose derivatives are s-convex in the second sense via fractional integrals. Comput. Math. 2012, 63, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar]
- İşcan, İ.; Wu, S. Hermite–Hadamard type inequalities for harmonically convex functions via fractional integrals. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 238, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikaya, M.Z.; Yildrim, H. On Hermite-Hadamard type inequalities for Riemann-Liouville fractional integrals. Miskolc Math. Notes 2016, 17, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikaya, M.Z.; Set, E.; Özdemir, M.E. On new inequalities of Simpson’s type for s-convex functions. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 60, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhou, C.; Du, T.S. Riemann-Liouville fractional Simpson’s inequalities through generalized (m, h1, h2)-preinvexity. Ital. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2017, 38, 345–367. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Huang, X. Some New Inequalities of Simpson’s Type for s-convex Functions via Fractional Integrals. Filomat 2017, 31, 4989–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubeen, S.; Habibullah, G.M. k-fractional integrals and application. Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sci. 2012, 7, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, P.; Jleli, M.; Tamor, M. Certain Hermite-Hadamard type inequalities via generalized k-fractional integrals. J. Inequal. Appl. 2017, 2017, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, G.; Usman, M. Ostrowski type k-fractional integral inequalities for MT-convex and h-convex functions. Nonlinear Funct. Anal. Appl. 2017, 22, 627–639. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, T.S.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.J.; Kashuri, A. Extensions of different type parameterized inequalities for generalized (m, h)-preinvex mappings via k-fractional integrals. J. Inequal. Appl. 2018, 2018, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarikaya, M.Z.; Ertugral, F. On the generalized Hermite-Hadamard inequalities. Ann. Univ. Craiova Math. 2020, 47, 193–213. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Ali, M.A.; Kashuri, A.; Budak, H. Generalized fractional integral inequalities of Hermite–Hadamard type for harmonically convex functions. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, H.; Hezenci, F.; Kara, H. On parametrized inequalities of Ostrowski and Simpson type for convex functions via generalized fractional integral. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2021, 44, 12522–12536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.U.; Talib, S.; Chu, Y.M.; Noor, M.A.; Noor, K.I. Some new refinements of Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities involving-Riemann–Liouville fractional integrals and applications. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 3051920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, G.; Rehman, A.U.; Zahra, M. On Hadamard inequalities for k-fractional integrals. Nonlinear Funct. Anal. Appl. 2016, 21, 463–478. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, A.; Suleman, M.; Chu, Y.M. Hermite–Hadamard type inequalities for fractional integrals via Green’s function. J. Inequal. Appl. 2018, 2018, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ali, T.; Dragomir, S.S.; Sarikaya, M.Z. Hermite–Hadamard type inequalities for conformable fractional integrals. Matemáticas 2018, 112, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Set, E.; Choi, J.; Gözpinar, A. Hermite-Hadamard type inequalities for the generalized k-fractional integral operators. J. Inequal. Appl. 2017, 2017, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tunc, M. On new inequalities for h-convex functions via Riemann-Liouville fractional integration. Filomat 2013, 27, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Ali, M.A.; Kashuri, A.; Budak, H.; Sarikaya, M.Z. Hermite–Hadamard-type inequalities for the interval-valued approximately h-convex functions via generalized fractional integrals. J. Inequal. Appl. 2020, 2020, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, S.S. On the Ostrowskiís integral inequality for mappings with bounded variation and applications. Math. Inequal. Appl. 2001, 4, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomir, S.S.; Agarwal, R.P.; Cerone, P. On Simpson’s inequality and applications. J. Inequal. Appl. 2000, 5, 533–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, S.S. On Simpson’s quadrature formula for mappings of bounded variation and applications. Tamkang J. Math. 1999, 30, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, M.W. A companion of the generalized trapezoid inequality and applications. J. Math. Appl. 2013, 36, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomir, S.S. On trapezoid quadrature formula and applications. Kragujevac J. Math. 2001, 23, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomir, S.S. On the midpoint quadrature formula for mappings with bounded variation and applications. Kragujevac J. Math. 2000, 22, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gorenflo, R.; Mainardi, F. Fractional Calculus: Integral and Differential Equations of Fractional Order; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kilbas, A.A.; Srivastava, H.M.; Trujillo, J.J. Theory and Applications of Fractional Differential Equations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pečarić, J.E.; Proschan, F.; Tong, Y.L. Convex Functions, Partial Orderings and Statistical Applications; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Alomari, M.W. A companion of Dragomir’s generalization of Ostrowski’s inequality and applications in numerical integration. Ukranianian Math. J. 2012, 64, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).