Extensible Steganalysis via Continual Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Proposed Scheme
2.1. Preliminary
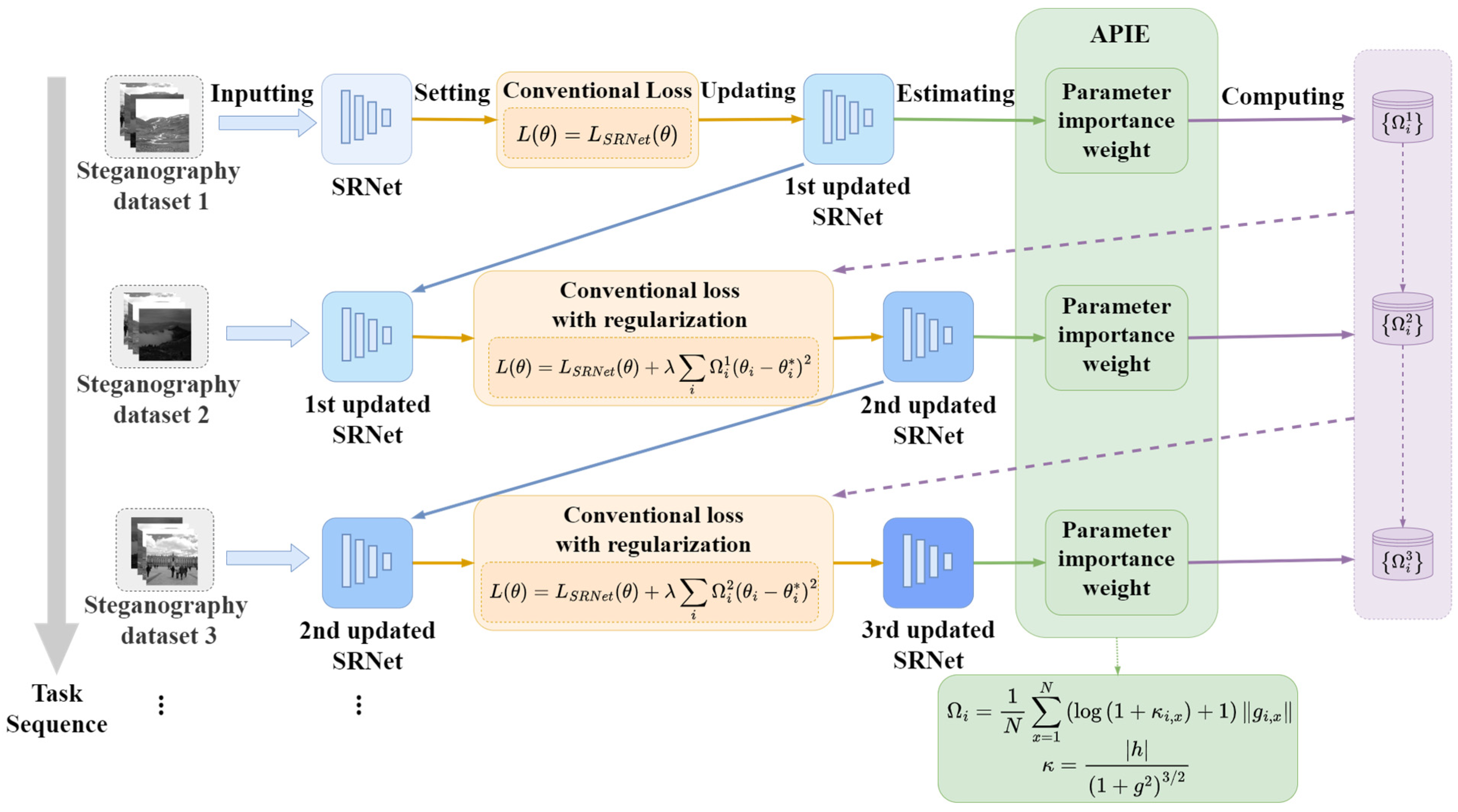
2.2. The Proposed APIE-Based Continual Learning for Steganalysis
2.2.1. Motivation
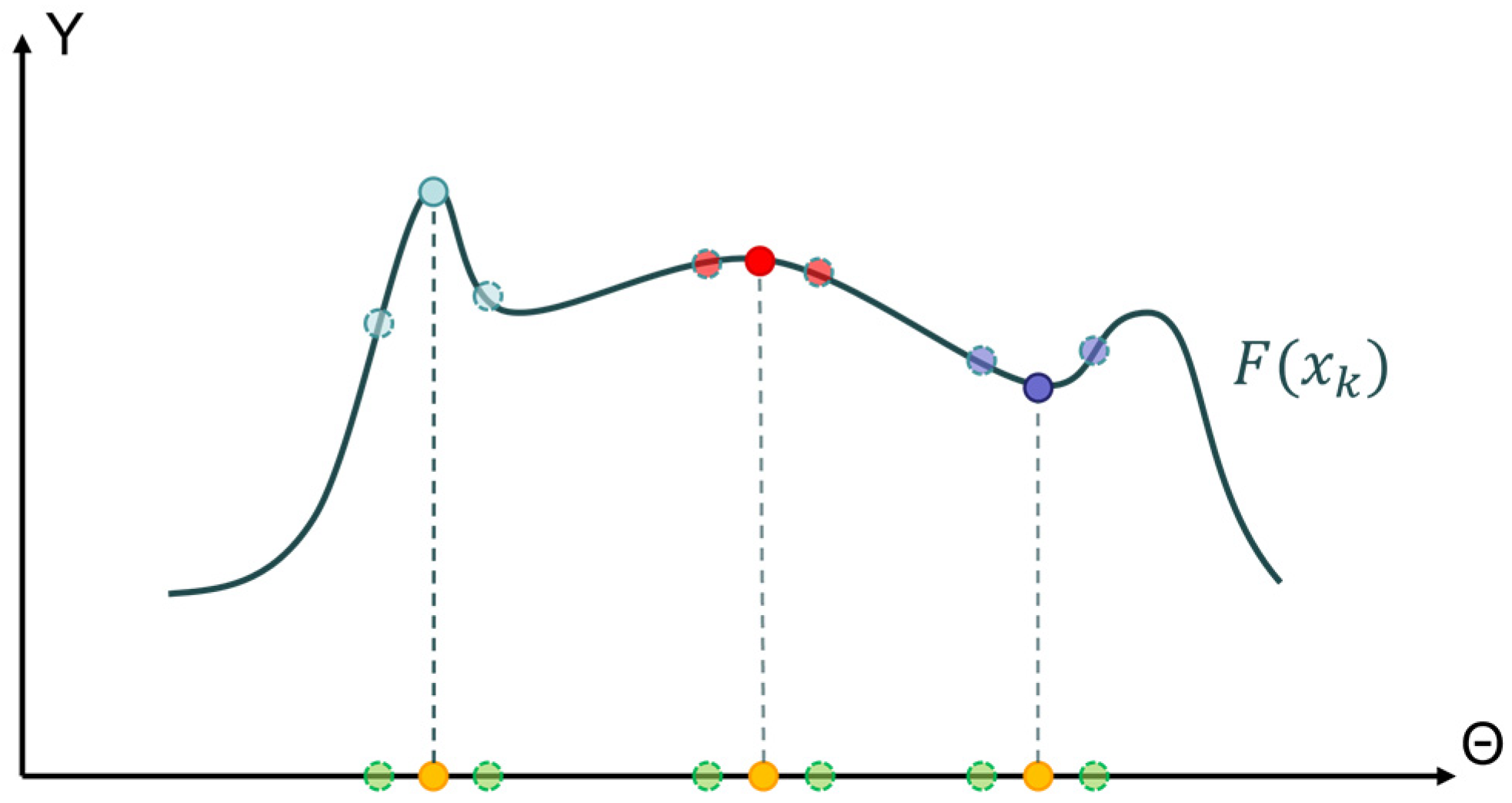
2.2.2. Gradient-Curvature Weight Importance Estimation
2.2.3. Peak-Mean Weight Importance Accumulation
3. Experiments
3.1. Dataset and Experimental Platform
3.2. Implement Details
3.3. Results on Benchmark Datasets
3.3.1. Baseline Setup
3.3.2. Comparison with Baselines
3.4. Results on Fractal Images Datasets
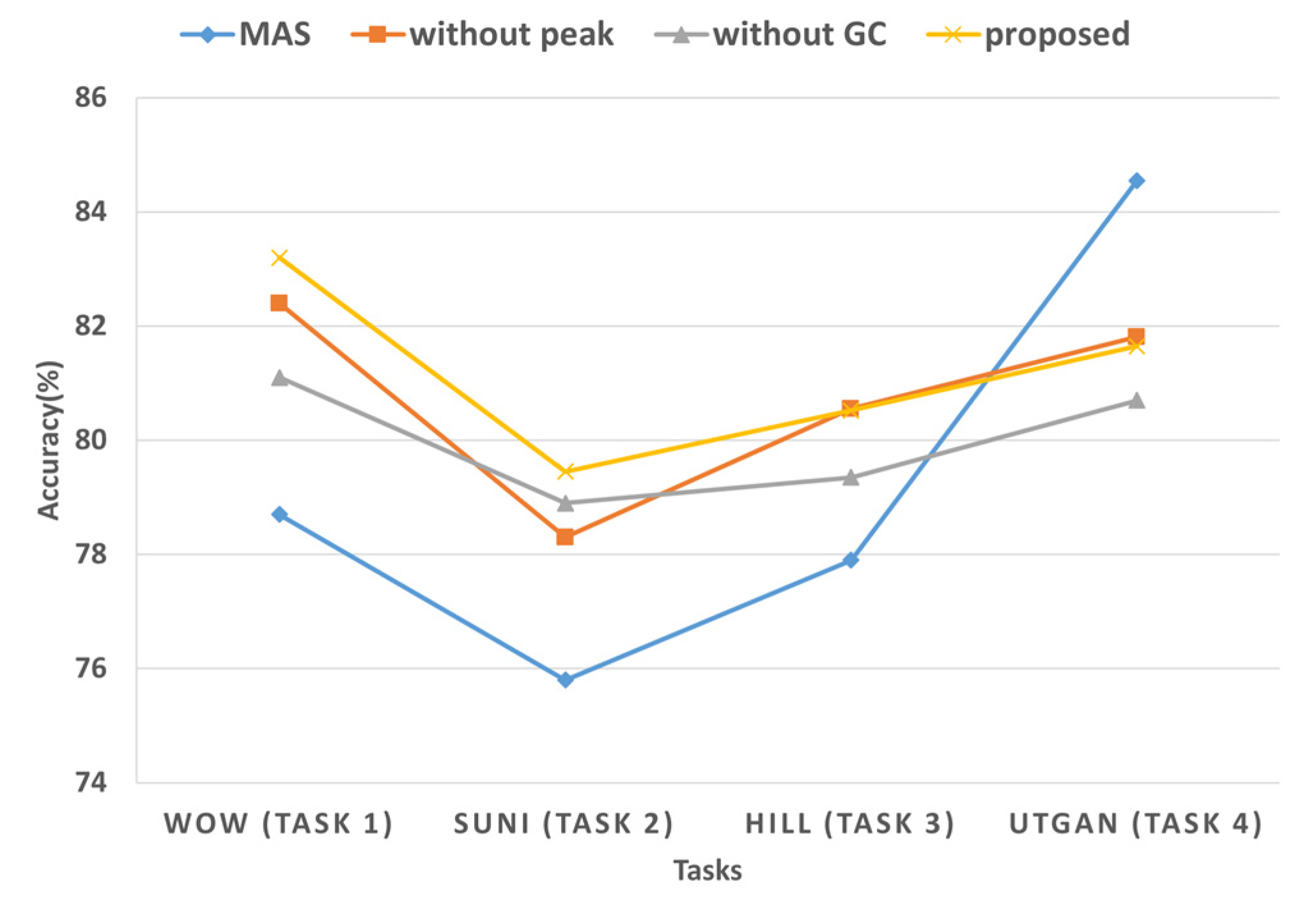
3.5. Ablation Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pevný, T.; Filler, T.; Bas, P. Using high-dimensional image models to perform highly undetectable steganography. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6387 LNCS, pp. 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Cheng, L.M. Hiding data in images by simple LSB substitution. Pattern Recognit. 2004, 37, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Li, X. A new cost function for spatial image steganography. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 4206–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, P.; Filler, T.; Pevný, T. Break our steganographic system’: The ins and outs of organizing BOSS. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 6958 LNCS, pp. 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ruan, D.; Huang, J.; Kang, X.; Shi, Y.Q. An Embedding Cost Learning Framework Using GAN. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tan, S.; Wang, M.; Huang, J. Investigation on cost assignment in spatial image steganography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2014, 9, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holub, V.; Fridrich, J.; Denemark, T. Universal distortion function for steganography in an arbitrary domain. Eurasip J. Inf. Secur. 2014, 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holub, V.; Fridrich, J. Designing steganographic distortion using directional filters. In Proceedings of the WIFS 2012—Proceedings 2012 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Tenerife, Spain, 2–5 December 2012; pp. 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Su, Y.; Wu, Q.M.J.; Fu, Z.; Shi, Y. Secret-to-Image Reversible Transformation for Generative Steganography. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chakraborty, C.; Wang, M. Generative Steganography Based on Long Readable Text Generation. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfeld, A.; Pfitzmann, A. Attacks on Steganographic Systems. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrich, J.; Goljan, M.; Du, R. Steganalysis based on JPEG compatibility. In Proceedings of the SPIE Multimedia Systems and Applications IV, Denver, CO, USA, 20–24 August 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevný, T.; Bas, P.; Fridrich, J. Steganalysis by subtractive pixel adjacency matrix. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2010, 5, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrich, J.; Kodovsky, J. Rich models for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodovský, J.; Fridrich, J.; Holub, V. Ensemble classifiers for steganalysis of digital media. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcibas, I.; Memon, N.D.; Sankur, B. Steganalysis of watermarking techniques using image quality metrics. Proc. SPIE -Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2011, 4314, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denemark, T.; Boroumand, M.; Fridrich, J. Steganalysis Features for Content-Adaptive JPEG Steganography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 11, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denemark, T.; Sedighi, V.; Holub, V.; Cogranne, R.; Fridrich, J. Selection-channel-aware rich model for Steganalysis of digital images. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security WIFS 2014, Atlanta, GA, USA, 3–5 December 2014; pp. 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Tan, T. Deep learning for steganalysis via convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Media Watermarking, Security, and Forensics, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 February 2015; p. 94090J. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wu, H.Z.; Shi, Y.Q. Structural design of convolutional neural networks for steganalysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ni, J.; Yi, Y. Deep Learning Hierarchical Representations for Image Steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2017, 12, 2545–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroumand, M.; Chen, M.; Fridrich, J. Deep residual network for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 14, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, G. Depth-Wise Separable Convolutions and Multi-Level Pooling for an Efficient Spatial CNN-Based Steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.C. Structural Design of Convolutional Neural Network-Based Steganalysis. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2021, 1276, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sur, A.; Mitra, P. Steganalysis of Digital Images Using Deep Fractal Network. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2021, 8, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Luo, M.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Consensus-Clustering-Based Automatic Distribution Matching for Cross-Domain Image Steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Tan, T. Learning and transferring representations for image steganalysis using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing ICIP, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 2752–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, E.M.; Elshafey, M.A.; Fouad, M.M. Accuracy enhancement of a blind image steganalysis approach using dynamic learning rate-based CNN on GPUs. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications IDAACS, Metz, France, 18–21 September 2019; Volume 1, pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, R.M. Catastrophic forgetting in connectionist networks. Trends Cogn. Sci. 1999, 3, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenke, F.; Poole, B.; Ganguli, S. Continual Learning Through Synaptic Intelligence. Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. 2017, 70, 3987–3995. Available online: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v70/zenke17a.html (accessed on 25 August 2017).
- Lee, S.-W.; Kim, J.-H.; Jun, J.; Ha, J.-W.; Zhang, B.-T. Overcoming Catastrophic Forgetting by Incremental Moment Matching. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 4655–4665. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2017/file/f708f064faaf32a43e4d3c784e6af9ea-Paper.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2017).
- James, K.; Pascanu, R.; Rabinowitz, N.; Veness, J.; Desjardins, G.; Rusu, A.A.; Milan, K.; Quan, J.; Ramalho, T.; Grabska-Barwinska, A.; et al. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3521–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hoiem, D. Learning without Forgetting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 2935–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljundi, R.; Babiloni, F.; Elhoseiny, M.; Rohrbach, M.; Tuytelaars, T. Memory Aware Synapses: Learning What (not) to Forget. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 11207 LNCS, pp. 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomponi, J.; Scardapane, S.; Lomonaco, V.; Uncini, A. Efficient continual learning in neural networks with embedding regularization. Neurocomputing 2020, 397, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Steganographic Methods | Baseline | Proposed | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| WOW | 77.16 | 83.20 | 91.73 |
| S-UNIWARD | 74.95 | 79.45 | 89.15 |
| HILL | 80.52 | 85.80 | 88.83 |
| UTGAN | 85.48 | 81.65 | 86.43 |
| Steganographic Methods | Baseline | Proposed | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| WOW | 71.23 | 75.81 | 83.81 |
| S-UNIWARD | 74.95 | 76.24 | 81.28 |
| UTGAN | 78.44 | 75.63 | 79.64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Yin, Z.; Meng, R.; Peng, F. Extensible Steganalysis via Continual Learning. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6120708
Zhou Z, Yin Z, Meng R, Peng F. Extensible Steganalysis via Continual Learning. Fractal and Fractional. 2022; 6(12):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6120708
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zhili, Zihao Yin, Ruohan Meng, and Fei Peng. 2022. "Extensible Steganalysis via Continual Learning" Fractal and Fractional 6, no. 12: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6120708
APA StyleZhou, Z., Yin, Z., Meng, R., & Peng, F. (2022). Extensible Steganalysis via Continual Learning. Fractal and Fractional, 6(12), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6120708








