A Fractional Measles Model Having Monotonic Real Statistical Data for Constant Transmission Rate of the Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analysis of the Model
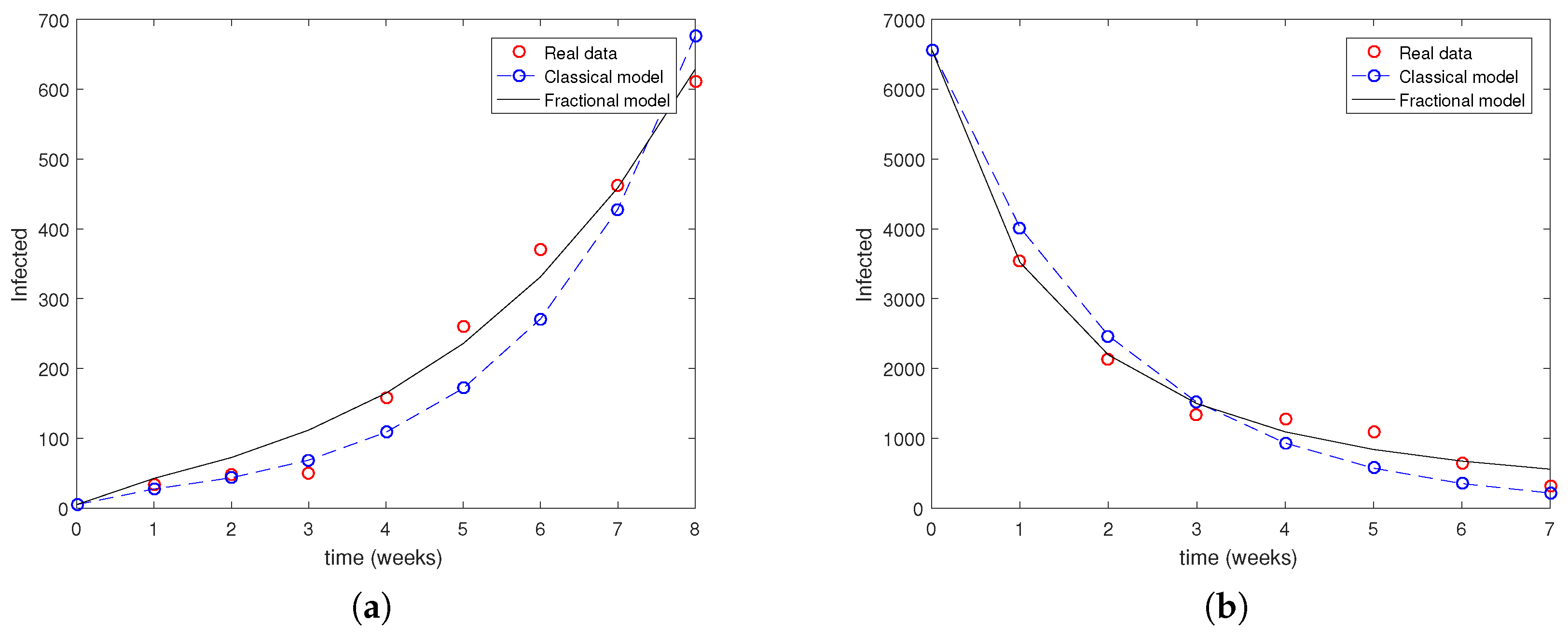
3. Numerical Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics, II—The problem of endemicity. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1932, 138, 55–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics, III—Further studies of the problem of endemicity. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1933, 141, 94–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angstmann, C.N.; Henry, B.I.; McGann, A.V. A fractional-order infectivity SIR model. Physica A 2016, 452, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Area, I.; Batarfi, H.; Losada, J.; Nieto, J.J.; Shammakh, W.; Torres, Á. On a fractional order Ebola epidemic model. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2015, 2015, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goufo, E.F.D.; Noutchie, S.C.O.; Mugisha, S. A fractional SEIR epidemic model for spatial and temporal spread of measles in metapopulations. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 2014, 781028. [Google Scholar]
- Hanert, E.; Schumacher, E.; Deleersnijder, E. Front dynamical in fractional-order epidemic models. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 279, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özalp, N.; Demirci, E. A fractional order SEIR model with vertical transmission. Math. Comput. Model. 2011, 54, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedian, M.; Khalighi, M.; Azimi-Tafreshi, N.; Jafari, G.R.; Ausloos, M. Memory effects on epidemic evolution: The susceptible-infected-recovered epidemic model. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 022409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, Y. Dynamic analysis of a fractional-order delayed SIR model with saturated incidence and treatment functions. Int. J. Bifur. Chaos 2018, 28, 1850180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ruan, S.; Wu, X.; Zhou, X. Seasonal transmission dynamics of measles in China. Theory Biosci. 2018, 137, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samko, S.G.; Kilbas, A.A.; Marichev, O.I. Fractional Integrals and Derivatives, Translated from the 1987 Russian Original; Gordon and Breach: Yverdon, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Diethelm, K.A. A fractional calculus based model for the simulation of an outbreak of dengue fever. Nonlinear Dyn. 2013, 71, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W. Global existence theory and chaos control of fractional differential equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2007, 332, 709–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.; da Cruz, A.M.C.B.; Martins, N.; Monteiro, M.T.T. An epidemiologial MSEIR model described by the Caputo frational derivative. Int. J. Dynam. Control 2019, 7, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diethelm, K.A. The Analysis of Fractional Differential Equations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, E.; El-Sayed, A.M.A.; El-Saka, H.A.A. Equilibrium points, stability and numerical solutions of fractional-order predator-prey and rabies models. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2007, 325, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, S.; Torres, D.F.M. Parameter estimation, sensitivity analysis and optimal control of a periodic epidemic model with application to HRSV in Florida. Stat. Optim. Inf. Comput. 2018, 6, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrappa, R. Numerical Solution of Fractional Differential Equations: A Survey and a Software Tutorial. Mathematics 2018, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesolowski, A.; Winter, A.; Tatem, A.J.; Qureshi, T.; Engø-Monsen, K.; Buckee, C.O.; Cummings, D.A.T.; Metcalf, C.J.E. Measles outbreak risk in Pakistan: Exploring the potential of combining vaccination coverage and incidence data with novel data-streams to strengthen control. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IndexMundi. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/pakistan/demographics_profile.html (accessed on 20 June 2019).
| disease transmission rate | Estimated | |
| A | birth rate | Fixed |
| natural mortality rate | Fixed | |
| percentage of vaccinated individuals | Fixed | |
| rate at which an exposed person becomes infective | Fixed | |
| rate an infected recovers | Fixed | |
| fractional order parameter | Estimated |
| Parameter | Sensitivity Indices |
|---|---|
| A | |
| Parameter | Sensitivity Indices |
|---|---|
| A | |
| Monotonicity | Classical | Fractional |
|---|---|---|
| Increasing | ||
| Decreasing | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida, R.; Qureshi, S. A Fractional Measles Model Having Monotonic Real Statistical Data for Constant Transmission Rate of the Disease. Fractal Fract. 2019, 3, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract3040053
Almeida R, Qureshi S. A Fractional Measles Model Having Monotonic Real Statistical Data for Constant Transmission Rate of the Disease. Fractal and Fractional. 2019; 3(4):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract3040053
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida, Ricardo, and Sania Qureshi. 2019. "A Fractional Measles Model Having Monotonic Real Statistical Data for Constant Transmission Rate of the Disease" Fractal and Fractional 3, no. 4: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract3040053
APA StyleAlmeida, R., & Qureshi, S. (2019). A Fractional Measles Model Having Monotonic Real Statistical Data for Constant Transmission Rate of the Disease. Fractal and Fractional, 3(4), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract3040053






