Synonym Substitution Steganalysis Based on Heterogeneous Feature Extraction and Hard Sample Mining Re-Perception
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- This paper proposes a two-stage synonym substitution linguistic steganalysis framework. Between the two stages, both the sentence-level decision features and the high-dimensional representations at the sentence level are transmitted, thereby achieving effective segment-level linguistic steganalysis at low embedding rates.
- (2)
- This paper proposes a heterogeneous feature extraction module to mine steganographic replacement words and extract inter-word association features between these words and other words in the sentence, ultimately obtaining sentence-level decision features and sentence-level high-dimensional representations.
- (3)
- This paper proposes a difficult sentence mining re-perception module. For sentence-level decision features, we achieve the simultaneous capture of local mutations and overall trends to comprehensively understand whether the segment contains hidden information. For sentence-level high-dimensional representations, a long-distance attention network is utilized to achieve full-segment attention to perceive whether the segment contains hidden information. Finally, the above dual decision features are fully integrated to achieve information hiding detection.
2. Background and Related Works
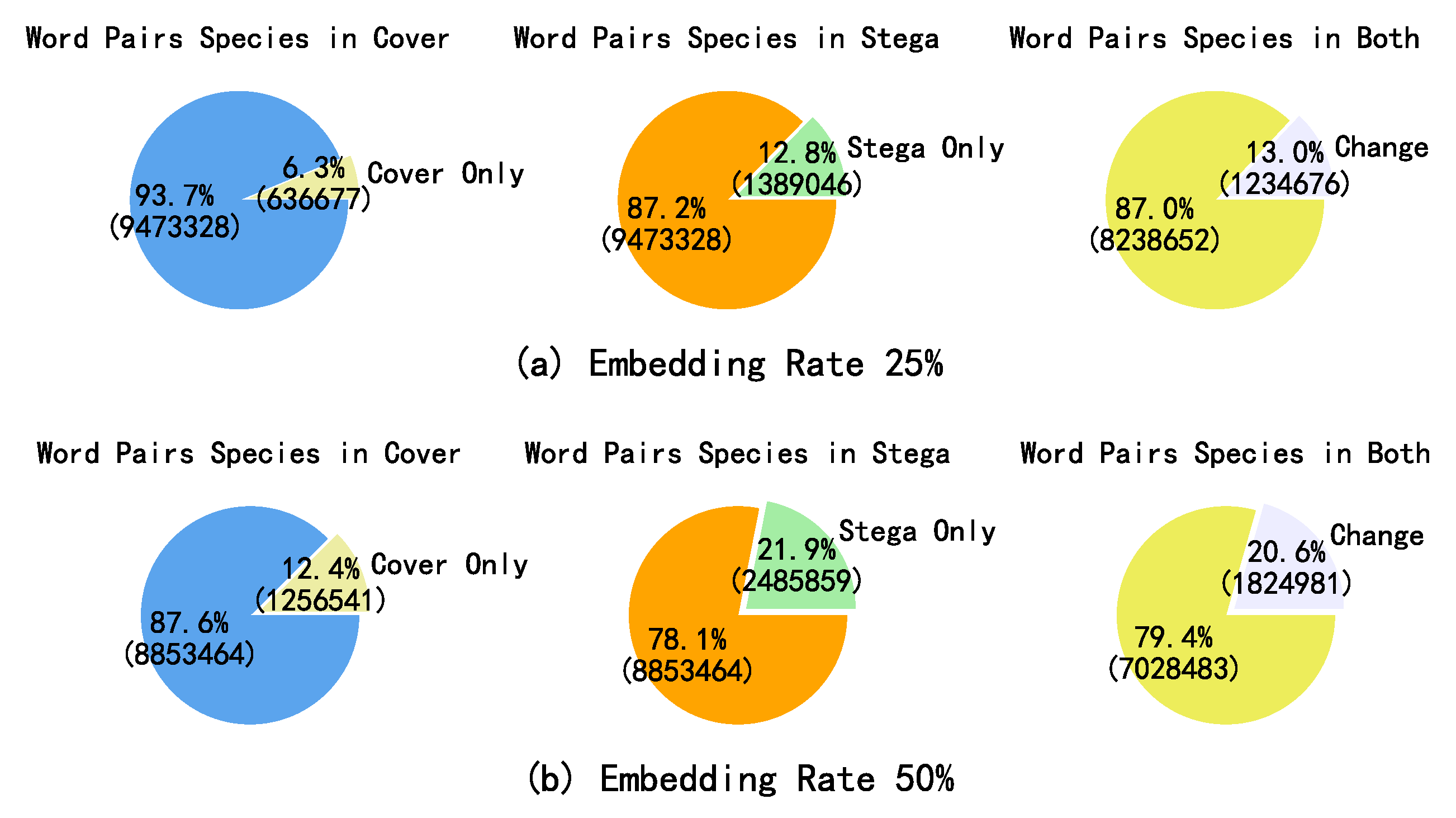
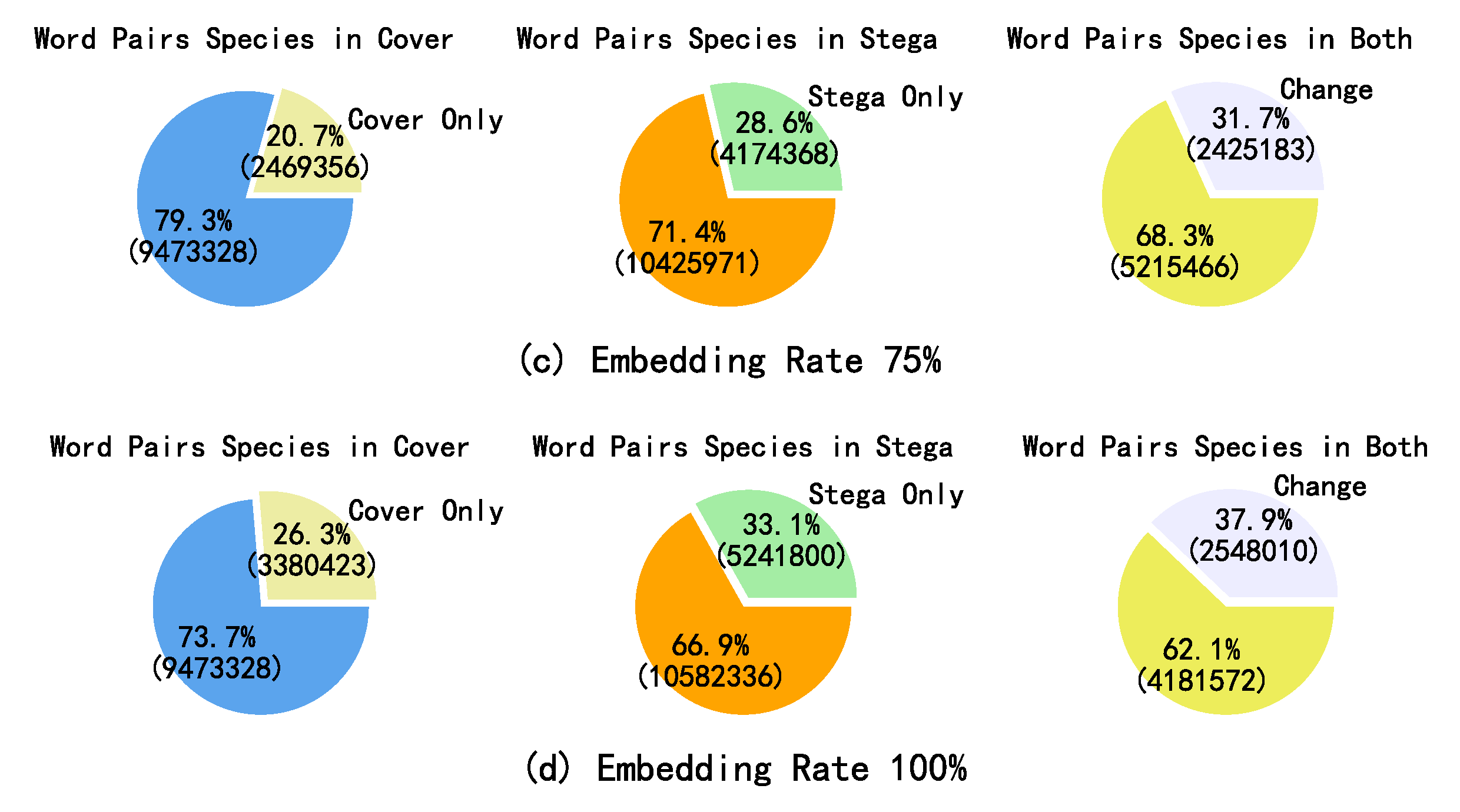
3. Statistical Analysis of Word Pairs Before and After Synonym Substitution-Based Linguistic Steganography
4. Method
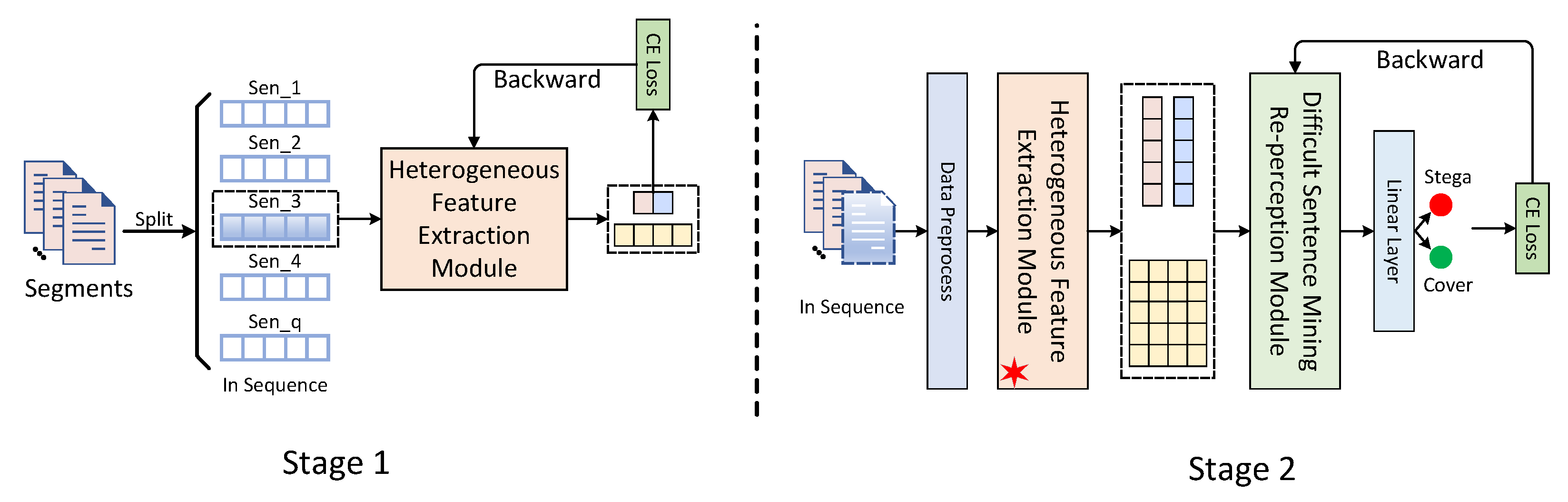
4.1. Overall Structure
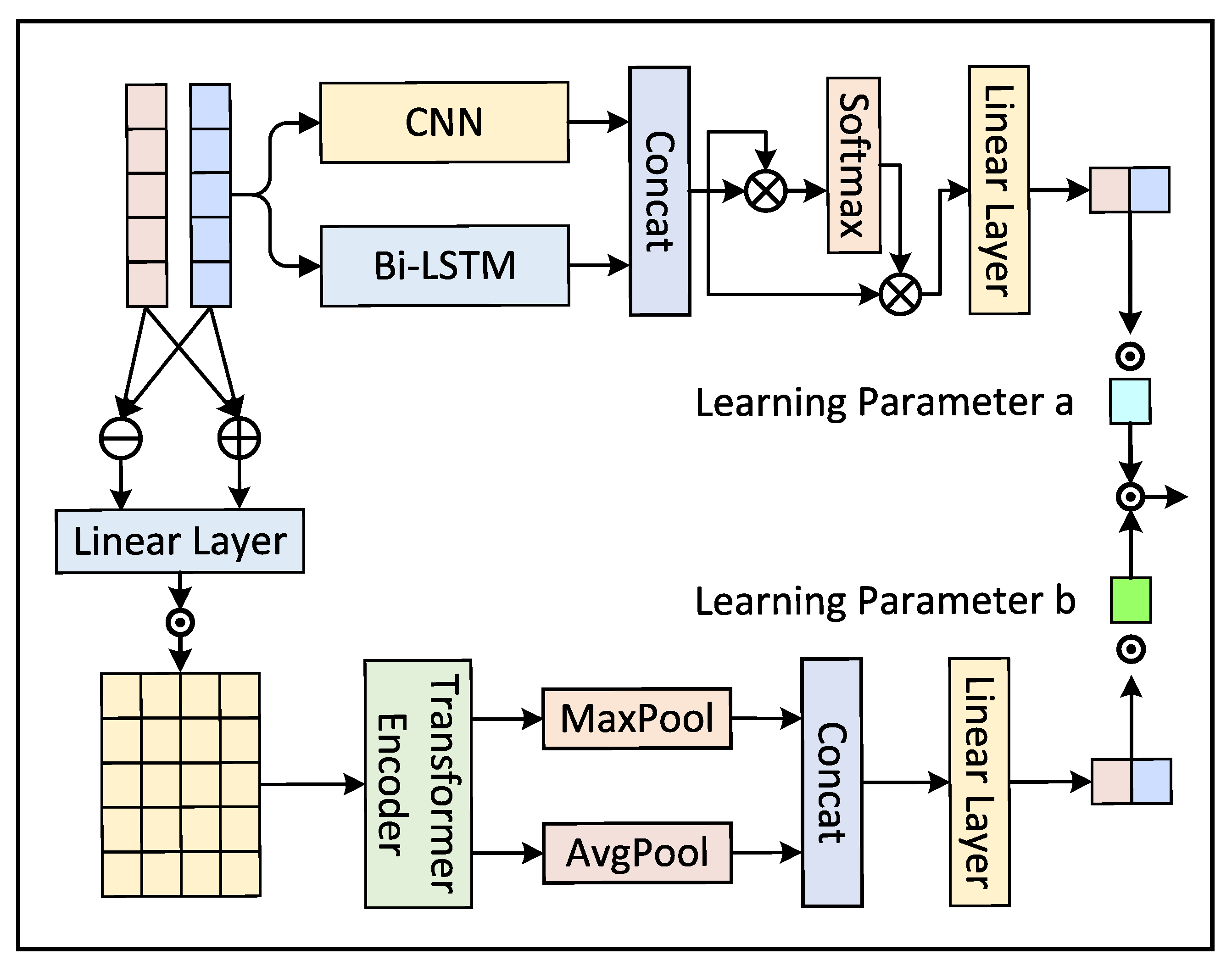
4.2. Heterogeneous Feature Extraction Module
4.3. Difficult Sentence Mining Re-Perception Module
5. Experiments and Analysis
5.1. Experimental Settings
5.1.1. Steganography Algorithms and Training Corpora
5.1.2. Embedding Rate Settings
5.1.3. Datasets
5.1.4. Comparison Methods
5.1.5. Training Settings
5.2. Constructing Dataset for Performance Analysis of Detection
5.2.1. Hybrid Steganographic Algorithm Steganalysis Tasks
5.2.2. Hybrid Corpora Steganalysis Tasks
5.2.3. Hybrid Steganography Algorithms and Corpora Steganalysis Tasks
5.2.4. Cross-Steganography Algorithm Steganalysis Tasks
5.2.5. Cross-Corpus Steganalysis Tasks
5.2.6. Cross-Steganography Algorithm and Corpus Steganalysis Tasks
5.3. Analysis of Detection Performance on Native Dataset
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Ni, T.; Xu, W.; Gu, T. SwipePass: Acoustic-based Second-factor User Authentication for Smartphones. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2022, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winstein, K. Lexical Steganography Through Adaptive Modulation of the Word Choice Hash. 1998. Available online: http://web.mit.edu/keithw/tlex/ (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Chang, C.-Y.; Clark, S. Practical linguistic steganography using contextual synonym substitution and a novel vertex coding method. Comput. Linguist. 2014, 40, 403–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmawi, A. Linguistic based steganography using lexical substitution and syntactical transformation. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th International Conference on IT Convergence and Security (ICITCS), Prague, Czech Republic, 26 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, P. A novel linguistic steganography based on synonym run-length encoding. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2017, 100, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, F.; Xiang, L. Synonym substitution-based steganographic algorithm with matrix coding. Chin. Comput. Syst. 2015, 36, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Huanhuan, H.; Xin, Z.; Weiming, Z.; Nenghai, Y. Adaptive text steganography by exploring statistical and linguistical distortion. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Second International Conference on Data Science in Cyberspace (DSC), Shenzhen, China, 26–29 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, L.; Wu, W.; Li, X.; Yang, C. A linguistic steganography based on word indexing compression and candidate selection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 28969–28989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W. A word-frequency-preserving steganographic method based on synonym substitution. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2019, 19, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Xiao, Y.-c. Synonym substitution-based steganographic algorithm with vector distance of two-gram dependency collocations. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 14–17 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 2776–2780. [Google Scholar]
- Taskiran, C.M.; Topkara, U.; Topkara, M.; Delp, E.J. Attacks on lexical natural language steganography systems. In Security, Steganography, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents VIII; SPIE: San Jose, CA, USA, 2006; Volume 6072, pp. 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Huang, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Y. Detection of synonym-substitution modified articles using context information. In Proceedings of the 2008 Second International Conference on Future Generation Communication and Networking, Hainan, China, 13–15 December 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, L.; Miao, H.; Yang, W.; Meng, P. Steganalysis against substitution-based linguistic steganography based on context clusters. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2011, 37, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Sun, X.; Luo, G.; Xia, B. Linguistic steganalysis using the features derived from synonym frequency. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2014, 71, 1893–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, L.; Yang, W. Detection of substitution-based linguistic steganography by relative frequency analysis. Digit. Investig. 2011, 8, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Yu, J.; Yang, C.; Zeng, D.; Shen, X. A word-embedding-based steganalysis method for linguistic steganography via synonym substitution. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 64131–64141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, P.; Xue, Y. Convolutional neural network based text steganalysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Guo, G.; Yu, J.; Sheng, V.S.; Yang, P. A convolutional neural network-based linguistic steganalysis for synonym substitution steganography. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2020, 17, 1041–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.-J. Rits: Real-time interactive text steganography based on automatic dialogue model. In International Conference on Cloud Computing and Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 253–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y. Linguistic steganography: From symbolic space to semantic space. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 28, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wei, N.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Gan-tstega: Text steganography based on generative adversarial networks. In Digital Forensics and Watermarking, Proceedings of the 18th International Workshop, IWDW 2019, Chengdu, China, November 2–4, 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Revised Selected Papers 18; pp. 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhu, C. Novel linguistic steganography based on character-level text generation. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-L.; Guo, X.-Q.; Chen, Z.-M.; Huang, Y.-F.; Zhang, Y.-J. Rnn-stega: Linguistic steganography based on recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 14, 1280–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-L.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Hu, Y.-T.; Hu, Z.-W.; Huang, Y.-F. Vae-stega: Linguistic steganography based on variational auto-encoder. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 16, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Peng, W.; Yang, B.; Wen, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhong, P. Linguistic Steganography Based on Adaptive Probability Distribution. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2022, 19, 2982–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Yan, H. Interword distance changes represented by sine waves for watermarking text images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2001, 11, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Information hiding in text using typesetting tools with stego-encoding. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Innovative Computing, Information and Control-Volume I (ICICIC’06), Beijing, China, 30 August–1 September 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 459–462. [Google Scholar]
- Azzawi, A.F.A. A multi-layer arabic text steganographic method based on letter shaping. Int. J. Netw. Secur. Its Appl. (IJNSA) 2019, 11, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, O.W.; Iranmanesh, V. Information hiding using whitespace technique in microsoft word. In Proceedings of the 2016 22nd International Conference on Virtual System & Multimedia (VSMM), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–21 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.A.; Khan, A.; Hussain, A. Text steganography using character spacing after normalization. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res 2020, 11, 949–957. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, A.; Hammad, A.S.; Selim, M.M. A high capacity algorithm for information hiding in arabic text. J. King Saud-Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 32, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, N.A.A. Text hiding in text using invisible character. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 10, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.G.; Bertini, F.; Montesi, D.; Stomeo, C. Text watermarking in social media. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining 2017, Sydney, Australia, 31 July–3 August 2017; pp. 208–211. [Google Scholar]
- Alanazi, N.; Khan, E.; Gutub, A. Inclusion of unicode standard seamless characters to expand arabic text steganography for secure individual uses. J. King Saud-Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nofaie, S.; Gutub, A.; Al-Ghamdi, M. Enhancing arabic text steganography for personal usage utilizing pseudo-spaces. J. King Saud-Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2021, 33, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditta, A.; Yongquan, C.; Azeem, M.; Rana, K.G.; Yu, H.; Memon, M.Q. Information hiding: Arabic text steganography by using unicode characters to hide secret data. Int. J. Electron. Secur. Digit. Forensics 2018, 10, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.; Bhayani, R.; Huang, L. Twitter sentiment classification using distant supervision. CS224N Proj. Rep. Stanf. 2009, 1, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, A.; Daly, R.E.; Pham, P.T.; Huang, D.; Ng, A.Y.; Potts, C. Learning word vectors for sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Portland, OR, USA, 21 June 2011; pp. 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/snapcrack/all-the-news (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J. Linguistic Steganalysis by Enhancing and Integrating Local and Global Features. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Deng, Y.; Peng, W.; Xue, Y. Linguistic Steganalysis via Fusing Multi-Granularity Attentional Text Features. Chin. J. Electron. 2023, 32, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Movie | News | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sentence number | 1,283,813 | 2,639,290 | 1,962,040 |
| Words number | 25,601,794 | 25,551,044 | 43,626,829 |
| Average length | 19.94 | 9.68 | 22.24 |
| Unique number | 48,342 | 46,341 | 42,745 |
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Embedding dimension | 300 |
| Convolution kernel number in HFE | 200 |
| Convolution kernel size in HFE | (3, 5, 7) |
| Convolution kernel number in DSMP | 4 |
| Convolution kernel size in DSMP | 5 |
| Hidden dimension (Bi-LSTM) in DSMP | 2 |
| EILG | SDC | LS-CNN | TCNNS | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Movie | 85.88% | 88.74% | 91.21% | 92.49% | 95.09% |
| News | 86.47% | 88.92% | 93.59% | 95.17% | 97.27% |
| 91.75% | 94.24% | 94.12% | 96.04% | 97.44% | |
| Avg | 88.03% | 90.63% | 92.97% | 94.57% | 96.60% |
| EILG | SDC | LS-CNN | TCNNS | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Params | 603.14 K | 3.39 M | 43.77 M | 42.04 M | 45.69 M |
| Inference times | 1.73 ms | 4.21 ms | 1.06 ms | 60.42 ms | 188.80 ms |
| Tlex-25% | Tlex-50% | Tlex-75% | Tlex-100% | MC (3 bit) | MC (4 bit) | WFP | Avg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EILG | 87.24 | 88.48 | 91.14 | 93.03 | 90.39 | 94.61 | 89.05 | 90.56 |
| SDC | 88.61 | 90.46 | 90.49 | 93.86 | 91.49 | 95.15 | 90.29 | 91.48 |
| LS-CNN | 93.46 | 96.94 | 97.48 | 99.83 | 97.54 | 90.18 | 99.22 | 96.87 |
| TCNNS | 94.85 | 97.67 | 98.93 | 99.78 | 98.12 | 91.85 | 99.24 | 97.60 |
| Ours | 96.51 | 98.64 | 99.34 | 99.94 | 99.23 | 94.25 | 99.60 | 98.50 |
| EILG | SDC | LS-CNN | TCNNS | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | 88.65 | 89.28 | 93.49 | 95.71 | 97.00 |
| F1-Score | 67.59 | 69.25 | 93.37 | 95.73 | 97.10 |
| T→M | T→W | M→T | M→W | W→T | W→M | Avg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS-CNN | 78.29 | 97.74 | 90.85 | 97.73 | 85.75 | 91.26 | 90.27 |
| TCNNS | 79.61 | 98.17 | 93.24 | 96.66 | 89.46 | 91.90 | 91.51 |
| Ours | 81.72 | 99.74 | 94.63 | 98.77 | 90.37 | 95.40 | 93.44 |
| M→N | M→T | N→T | N→M | T→M | T→N | Avg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS-CNN | 85.96 | 79.71 | 75.87 | 78.65 | 74.19 | 66.35 | 76.79 |
| TCNNS | 84.56 | 83.61 | 77.27 | 80.77 | 74.49 | 74.47 | 79.20 |
| Ours | 89.53 | 91.08 | 87.42 | 87.22 | 79.85 | 79.20 | 85.72 |
| LS-CNN | TCNNS | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TM→MN | 73.31 | 75.37 | 77.52 |
| TN→WT | 73.63 | 74.61 | 83.47 |
| MM→TT | 76.13 | 80.19 | 87.39 |
| MN→WM | 77.82 | 78.93 | 86.45 |
| WM→TN | 81.88 | 80.74 | 84.66 |
| WT→MM | 72.61 | 72.66 | 76.56 |
| Avg | 75.90 | 77.08 | 82.68 |
| LS-CNN | TCNNS | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Movie | 94.32 | 96.26 | 97.71 |
| News | 93.12 | 93.98 | 95.16 |
| 81.61 | 82.48 | 84.47 | |
| Avg | 89.68 | 90.91 | 92.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Du, H.; Liu, P. Synonym Substitution Steganalysis Based on Heterogeneous Feature Extraction and Hard Sample Mining Re-Perception. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9080192
Wang J, Du H, Liu P. Synonym Substitution Steganalysis Based on Heterogeneous Feature Extraction and Hard Sample Mining Re-Perception. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2025; 9(8):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9080192
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jingang, Hui Du, and Peng Liu. 2025. "Synonym Substitution Steganalysis Based on Heterogeneous Feature Extraction and Hard Sample Mining Re-Perception" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 9, no. 8: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9080192
APA StyleWang, J., Du, H., & Liu, P. (2025). Synonym Substitution Steganalysis Based on Heterogeneous Feature Extraction and Hard Sample Mining Re-Perception. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 9(8), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9080192






