Abstract
In recent years, people have expressed their opinions and sentiments about products, services, and other issues on social media platforms and review websites. These sentiments are typically classified as either positive or negative based on their text content. Research interest in sentiment analysis for text reviews written in Greek is limited compared to that in English. Existing studies conducted for the Greek language have focused more on posts collected from social media platforms rather than on consumer reviews from e-commerce websites and have primarily used traditional machine learning (ML) methods, with little to no work utilizing advanced methods like neural networks, transfer learning, and large language models. This study addresses this gap by testing the hypothesis that modern methods for sentiment classification, including artificial neural networks (ANNs), transfer learning (TL), and large language models (LLMs), perform better than traditional ML models in analyzing a Greek consumer review dataset. Several classification methods, namely, ML, ANNs, TL, and LLMs, were evaluated and compared using performance metrics on a large collection of Greek product reviews. The empirical findings showed that the GreekBERT and GPT-4 models perform significantly better than traditional ML classifiers, with BERT achieving an accuracy of 96% and GPT-4 reaching 95%, while ANNs showed similar performance to ML models. This study confirms the hypothesis, with the BERT model achieving the highest classification accuracy.
1. Introduction
Sentiment analysis is a modern discipline and an important task in natural language processing (NLP), considering the expressed sentiments or opinions of people on various topics. There is a vast volume of content generated by users on social media platforms, forums, and websites that includes texts, posts, photos, audios, and videos. In many cases, this content includes users’ reviews and comments about products, services, and events. The sentiments expressed in reviews and comments can be classified by polarity (such as positive and negative) or by emotion (such as happiness, fear, or sadness) based on the content within them. The extracted sentiments of the text can avail very important information that will enable companies or organizations in better decision-making. For instance, consumer reviews could help a business structure their products and services better and the customers make better purchasing decisions as a result.
The sentiment classification task can be conducted at three distinct levels in text reviews: review, sentence, and aspect. The sentiment is classified into polarity or emotion at the review level based on the entire text review. A review is split into sentences, and each sentence is classified into polarity at the sentence level. At the aspect level, sentiment classification first identifies an aspect or feature in a sentence, such as price or rating, and then classifies it as positive or negative []. Sentiment classification can present challenges due to several reasons, such as the high volume of online text reviews, language complexity, and the diverse aspects of reviews. Consequently, there is a need for developing computational solutions to address these challenges in sentiment analysis.
Numerous research studies have been conducted on sentiment and emotion classification at three levels for reviews written in the English language [,]. There is also a growing interest in aspect sentiment analysis, as shown by various studies [,]. Most studies focus on various application domains, such as tourism [], COVID-19 and infectious diseases [], consumer products [], marketing [], e-commerce [], and social media platforms []. According to the literature, researchers address the sentiment classification problem using five main computational techniques: lexicon-based, machine learning (ML) and artificial neural networks (ANNs), deep learning (DL), transfer learning (TL), and large language models (LLMs), such as GPT [,,].
The lexicon-based approach is an old technique that assigns a sentiment score to words or expressions in a sentence based on a dictionary []. The machine learning approach is another popular method for sentiment classification. This method includes a set of supervised learning techniques that train classifiers to learn sentiments or patterns from labeled text reviews. These trained classifiers can then make sentiment predictions on new text reviews. Studies have shown that applying various ML approaches to several English review datasets, such as Amazon or hotel reviews, provides reliable sentiment predictions and satisfactory classification performance []. Deep learning methods, on the other hand, consist of advanced learning techniques for training artificial neural networks with multiple hidden layers such that the features are learned automatically from text data without manual intervention in feature engineering, as in ML. DL promises superior performance results compared to ML methods for the task of sentiment classification on product and hotel review datasets [,].
In recent years, significant advancements in NLP have occurred with the introduction of new variants of deep learning models such as transfer learning and large language models. Transfer learning involves a model pre-trained on large datasets and then fine-tuning the model on a specific dataset for solving specific tasks, such as sentiment analysis or text summarization. Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) [] is one such model that saves training time and provides satisfactory performance. Transfer learning models generally outperform lexicon-based and machine learning models in sentiment classification, as shown in the study by Hartmann et al. []. Finally, large language models such as generative pre-trained transformers (GPTs) are a further development of transfer learning model similar to BERT, but they give the ability to understand and generate human language using prompt techniques. Such prompts indicate to the GPT model which features it should extract from the text review in the sentiment case. GPT models have been utilized in sentiment classification with several English review datasets, showing comparable performance results to BERT [,], and in some cases, GPT outperforms transfer leaning models [].
This work is motivated by the fact that most sentiment classification research focuses on English, with limited attention paid to the Greek language [,]. Most sentiment classification studies for Greek have focused on hotel reviews [], product reviews [], social media posts [,], and newspaper articles [] using traditional ML methods. Some studies [,,] have utilized advanced methods such as deep learning and transfer learning on Greek posts from social media platforms. However, few studies have concentrated on consumer reviews, and these have been conducted on a small dataset using only ML and BERT models []. No study has systematically compared the performance of advanced methods like neural networks and large language models on a large collection of Greek reviews collected from e-commerce websites.
This paper aims to address this gap by comparing the performance of widely used classification methods, including machine learning, artificial neural networks, transfer learning, and large language models, for sentiment analysis of a large collection of Greek consumer reviews. The main research hypothesis addressed in this work is that the performance of current methods, including neural networks, transfer learning, and large language models, is expected to be better than that of traditional machine learning models in analyzing a Greek product review dataset. Therefore, the aim is to confirm or not the above hypothesis through the evaluation of sentiment classification models. Finally, this study also provides valuable insights into the capabilities of advanced models for Greek sentiment classification.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the theoretical background on text representation models and computational methods for sentiment analysis, as well as related research on sentiment classification for texts in the Greek language. Section 3 presents the methodology for studying the performance of classification methods. Section 4 presents the performance results, while Section 5 discusses these results and their limitations. Finally, Section 6 contains conclusions and future directions.
2. Theoretical Background and Review
This section first presents the background on text representation and computational methods used in sentiment classification to provide a better understanding of the rest of the paper. Then, it reviews related works conducted on sentiment classification for the Greek language using these computational methods.
2.1. Text Representation
For efficient processing of sentiment analysis, texts should be converted into a computer-readable form, such as a numerical document-term matrix. There are two main ways to represent text: discrete and distributed. In discrete representations, also known as bag of words, every review or document is mapped as a vector of term frequency (TF) or term frequency–inverse document frequency (TF-IDF). TF measures the occurrence frequency of a word in a document, whereas TF-IDF assigns higher scores to words that are frequent in a particular document, but less common across other documents. However, words that occur often in many documents receive low TF-IDF scores. In distributed representations, commonly referred to as word embeddings, each document is represented by averaging the vectors of the words it contains. These word vectors capture the meanings and relationships of words based on their usage in a document. Popular word embedding models include Word2Vec [], GloVe [], and FastText [,]. This process of text representation is known as feature extraction because it extracts features or words from the text. Often, before the feature extraction process, several preprocessing choices are performed on texts, such as tokenization, removing special characters (i.e., white spaces or punctuation), removing stop words, stemming, and lemmatization.
2.2. Computational Methods for Sentiment Classification
The widely used computational methods for sentiment classification can be categorized into five different groups: machine learning, artificial neural networks, deep learning, transfer learning, and large language models [,,,,].
Machine learning methods train statistical models or classifiers to predict sentiment labels for new text reviews based on labeled text data. This process is known as supervised learning because the training is supervised by the specific and annotated sentiment labels of reviews. Implementing sentiment classification using ML requires manually extracting representations or word vectors (features) from text reviews, as discussed in Section 2.1. Additionally, the document-term matrix is split into a training set and a testing set for processing by ML methods. The training set consists of pairs of word vectors or features of the document-term matrix and sentiment labels of reviews, which are used by ML methods to train the model. The testing set is then used by the trained model to predict sentiment labels for word vectors or features of a new text review []. The traditional ML methods frequently used in training include logistic regression (LR), support vector machine (SVM), decision tree (DT), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), Naïve Bayes (NB), and random forest (RF). More details about these methods can be found in [].
Artificial neural networks are a subset of ML. ANNs are mathematical representation of connected processing units, similar to the human brain’s structure. These units are called artificial neurons and are grouped into layers: an input layer, hidden layers, and an output layer. The input layer receives features or vector representations from text reviews, while the output layer predicts the sentiment labels. The hidden layers learn a non-linear mapping between input and output []. One type of such simple neural network is the multilayer perceptron (MLP).
Deep learning, or deep neural networks, is another popular method and an advanced form of ANNs for extracting sentiments from text reviews without manually feeding word vectors as input. Deep neural networks consist of many hidden layers organized in complex and nested architectures. The neurons in these networks are advanced and perform more complex operations compared to those in ANNs. This allows the networks to be fed raw text reviews and automatically learn the word vectors (features) or hierarchical representations of texts, including words, expressions, or context, necessary for the sentiment classification task [,,]. There are two kinds of deep neural networks: convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs). Details of these types for sentiment analysis can be found in [].
Transfer learning and large language models are deep neural networks based on the transformer framework. This framework was introduced by Vaswani et al. [], replacing the structure of RNNs with an attention unit, specifically “self-attention.” The transformer framework employs an encoder–decoder configuration. The encoder processes the raw text into representations with multiple layers of self-attention and neural networks. The decoder then takes these representations and creates an output sequence. Each layer in the decoder includes self-attention, attention to the encoder’s output, and another neural network layer. Building upon the transformer model, BERT and GPT models were developed. The BERT model, introduced by [], exemplifies transfer learning and relies solely on the encoder to examine the words of the input text bidirectionally using a bidirectional attention mechanism to gather rich contextual information instead of manually creating them. The training of BERT includes pre-training on extensive corpora followed by fine-tuning on a specific dataset to address particular NLP tasks such as question answering or sentiment analysis. It should be noted that fine-tuning BERT for specific tasks requires appropriate preprocessing, which is offered by the model and is automatic rather than manual. Variants and optimizations of BERT include DistilBERT [] and RoBERTa []. Furthermore, there is a version of BERT model for the Greek language, named GreekBERT, that was pre-trained on a large Greek corpus [].
The GPT model, on the other hand, is an example of a large language model proposed by OpenAI. It uses only the decoder to generate sequential human-like text from left to right by next-word prediction based only on the words that come before it. GPT is accommodated by prompt techniques, where the user gives instructions in natural language for performing specific NLP tasks. Recent versions of the GPT model, such as GPT 3.5 and GPT 4, operate in two modes: zero-shot and few-shot. In the zero-shot setting, the model performs tasks based on user prompts without any specific training examples, whereas in the few-shot setting, the model receives prompts along with minimal training examples to perform the required task [].
2.3. Related Research for Greek Sentiment Classification
Greek is a low-resource language because of limited linguistic resources and tools, highlighting the need for automated computational solutions for sentiment analysis. In recent years, sentiment classification research for texts written in Greek has increased. Early studies conducted sentiment analysis for Greek texts using lexicon-based approaches [,,,]. These include the analysis of Greek tweets for different hashtags to identify six emotion categories using a lexicon [], as well as the sentiment analysis of Greek tweets regarding the COVID-19 pandemic [,].
Subsequent studies have employed ML models. Specifically, Markopoulos et al. [] applied the SVM model to 1800 hotel reviews collected from the TripAdvisor platform using two feature extraction schemes: TF-IDF and term occurrence. They showed that the TF-IDF scheme achieved a satisfactory accuracy of 95.78%. Bilianos [] implemented two ML models, Naïve Bayes and SVM, as well as a transfer learning model, a Greek version of BERT, on a set of 480 Greek reviews from the e-commerce website Skroutz. His study reported that BERT achieved an outstanding performance accuracy of 97%, while the SVM with TF-IDF model had the second-best performance, reaching accuracy of 92%. Dontaki et al. [] applied ML models, including LR, DT, RF, SVM, and XGBoost Classifier (XGB), for three-class sentiment classification of 61,109 Greek tweets regarding COVID-19 vaccinations. Their study found that the highest accuracy was achieved when tweets were processed using TextBlob and DT, reaching an accuracy of 99.97%. Charalampakis et al. [] implemented a text classification for irony detection in Greek political tweets using classical ML algorithms. Specifically, they trained models such as NB, functional trees, and RF on a small labeled dataset of 126 Greek tweets. The best-performing model was functional trees, with an accuracy rate of 82.4%. They then used this model to predict irony in a large dataset of 44,500 unlabeled Greek tweets, aiming to identify relationships between the irony directed at political parties and their results in the May 2012 Greek election. Giatsoglou et al. [] presented a hybrid method that combines the SVM algorithm with Word2Vec word embeddings and dictionaries for sentiment prediction. They demonstrated the efficiency of their approach on a Greek dataset, MOBILE-PAR, achieving an accuracy of 83.60%. Athanasiou et al. [] performed experiments on binary sentiment classification on different versions of the original dataset of articles collected from an online Greek newspaper. They showed that the gradient boosting machine (GBM) model significantly outperforms classical ML methods in handling high-dimensional and imbalanced data.
Finally, a number of studies have been conducted on sentiment classification using modern deep neural networks and transfer learning models. For instance, Patsiouras et al. [] introduced a dataset named GreekPolitics, which consists of 2578 Greek tweets annotated across four sentiment dimensions: polarity, figurativeness, aggressiveness, and bias. They demonstrated the efficiency of deep neural networks and data augmentation methods in handling class imbalances and improving classification accuracy. The results indicated the superiority of the BERT-based transformer model over CNNs, achieving an accuracy of over 88%. Katika et al. [] applied sentiment analysis to Greek tweets about long COVID-19 using a pre-trained Greek BERT language model, achieving an accuracy of 94%. Alexandridis et al. [] performed experiments on two sentiment classification problems, binary and three-class, using a large Greek dataset containing over 44,000 posts collected from various social media platforms. They demonstrated that the GPT-2 language model achieved nearly 99% accuracy for binary classification. Similarly, they showed the effectiveness of three transformer models for three-class sentiment classification: the GreekBERT model, the PaloBERT model based on RoBERTa, and an extended version of GreekBERT known as GreekSocialBERT. Their findings showed that these models achieved over 80% classification accuracy.
Most of the above studies focused on sentiment classification at the document level. However, very few works have been conducted on aspect-level sentiment analysis, such as the recent work by Aivatoglou et al. [] using a transformer model.
Based on the aforementioned studies, it is clear that most works have focused on traditional ML methods, with only a few studies using neural networks, deep learning, transfer learning, and large language models, as mentioned in the introduction. Furthermore, a large number of studies have focused on datasets such as social media posts, with fewer studies on product reviews. This work focuses on comparing traditional ML methods with advanced models like ANNs, transfer learning, and large language models for sentiment analysis of Greek consumer reviews.
3. Methodology
This study employed an experimental methodology to evaluate the performance of popular classification methods for sentiment analysis of Greek reviews. The research workflow for sentiment classification involved four steps, as shown in Figure 1: dataset selection, text preprocessing, experiments with various classification models, and model evaluation.
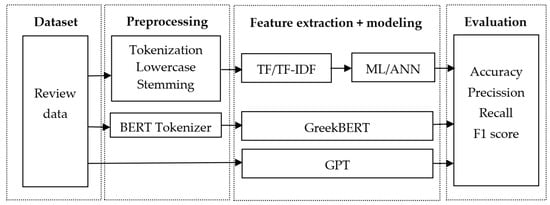
Figure 1.
Research workflow for sentiment classification.
3.1. Dataset Selection
Although there is a lack of similar and large Greek datasets for sentiment classification in public repositories, one such dataset was found on the Kaggle platform. Specifically, the dataset selected for this experimental sentiment analysis consists of the Greek shop reviews from the e-commerce website Skroutz, which is publicly available on Kaggle []. This dataset contains 6552 reviews (3276 positive and 3276 negative) about a diverse variety of products provided by the e-shop Skroutz. Each review record consists of three fields: review-id, text review, and sentiment label. The review texts have an average length of 78 words. The shortest review in the dataset consists of 2 words, whereas the longest review has approximately 1200 words. Greek reviews would probably be somewhat longer on average compared to English reviews in that they include more descriptive language and thereby become more detailed.
3.2. Text Preprocessing
The text preprocessing of text reviews depends on the classification model used each time. For traditional machine learning (ML) and artificial neural network (ANN) models, the preprocessing steps included tokenizing all reviews into individual words, converting all words to lowercase, and removing spaces, numbers, and punctuation to reduce noise and improve computational processing. Additionally, all words were stemmed using the Spacy library in Python to reduce them to their root forms. The sentiment labels (“positive” or “negative”) were converted into numbers using the corresponding function in the Scikit-learn [] library for easier processing.
For the BERT-based transfer learning model, the input text data were preprocessed directly using a specific tokenizer, eliminating the need for manual intervention. This step ensures that the raw text data are prepared in a format suitable for processing by the BERT model. In this study, the “bert-base-greek-uncased” version of the BERT tokenizer was used, which converts all words to lowercase, as indicated by the “uncased” label.
Finally, no text preprocessing was required for the GPT models, as they are designed to handle raw text data directly, which simplifies the overall workflow and reduces the need for manual data preparation steps.
After completing the preprocessing steps for each model, the dataset was divided into an 80% training set and a 20% testing set.
3.3. Modeling Experiments
A series of experiments with several classification models for sentiment analysis were conducted using Google Colab with CPU/GPU support. The selection of techniques was based on their widespread use and proven effectiveness in sentiment classification studies.
3.3.1. Machine Learning Approaches
Firstly, two-phase experiments were performed using ML models. In the first phase, several popular ML models were used based on their successful application in the sentiment analysis literature []. These models were logistic regression (LR), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), decision tree (DT), multinomial naïve Bayes (MNB), support vector machine (SVM), random forest (RF), AdaBoost, and stochastic gradient boosting (SGB). These models were tested with default parameters and two feature extraction schemes: TF and TF-IDF. For both feature schemes, words appearing in less than 0.1% or more than 75% of the documents were filtered out and omitted from the sentiment analysis. This was to reduce the impact of extremely frequent or rare words. In the second phase, the three best-performing models were fine-tuned with various parameters of the models. Furthermore, the models were implemented in Python using the Scikit-learn library []. The performance results of the ML models can be used as baseline.
3.3.2. Artficial Neural Network Models
Second, artificial neural networks (ANN) were used for Greek sentiment classification. More specifically, a multilayer perceptron (MLP) model featuring a single hidden layer was utilized due to its effectiveness in similar tasks []. This model was tested with various values of hidden neurons using the TF and TF-IDF feature extraction schemes, combined with word filtering similar to the machine learning case. The model was implemented using the corresponding function provided by the Scikit-learn library [], and the early stopping parameter was activated in order to avoid overfitting.
3.3.3. Transfer Learning Models
After implementing the ANN models, a transfer learning model was employed in the experiments. Specifically, the pre-trained GreekBERT language model from Hugging Face was utilized for the sentiment classification task [,]. Transfer learning was chosen due to its ability to leverage pre-trained knowledge and provide superior performance []. This model was implemented using the Hugging Face Transformers library in Python with the PyTorch framework. It included a classification or output layer of the pre-trained BERT model that was modified to provide binary classification outputs for sentiment analysis. This was done through the BertForSequenceClassification function. Several values for the learning rate, sequence lengths, and batch size were tested, and the values that provided the best performance were selected. Therefore, the parameters used in the BERT experiment were as follows: 4 epochs, a sequence of length 200, batch size of 32, learning rate of 5 × 10−6 and the AdamW optimizer for the loss function. It should be noted that the number of epochs was kept small to avoid overfitting.
3.3.4. Large Language Models
Two state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) were used in the final experiment. Specifically, the GPT-3.5 (i.e., gpt-3.5-turbo-0125) and GPT-4 models were tested for the binary sentiment classification task. These models were chosen due to their advanced capabilities and proven success in various NLP tasks [,]. They were employed in a zero-shot setting without explicitly specific training examples, and the model temperature was set to zero, making the output nearly deterministic. These models were accessed through OpenAI API calls in Python, which provided the prompt to initiate sentiment analysis. In this work, the zero-shot setting was used to understand the capabilities of the model and its usefulness in scenarios where labeled review data were not available. On the other hand, a few-shot approach was not used in the experiments because it requires a significant amount of processing time and cost, given that GPT models provided by OpenAI are available by subscription. Therefore, based on limited resources, a zero-shot approach was a more feasible choice.
3.4. Model Evaluation
The effectiveness of several classification methods was assessed using metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. These metrics are used to assess the performance of ML, ANN, and LLM models. These measures are derived from the confusion matrix values, which include the true positive (TP), false positive (FP), true negative (TN), and false negative (FN). The four performance metrics can be defined as follows []:
These metrics were extracted using the classification report function provided by the Scikit-learn library in Python.
For the GreekBERT model, besides accuracy, both training loss and testing loss metrics were utilized. These metrics are important as they assess the reliability of the model’s predictions, and help determine if the model is prone to overfitting or underfitting.
Finally, 10-fold cross-validation was utilized in the experiments to assess the effectiveness of the classification models. This method ensures that each model is trained and validated using the training dataset, providing an accurate and reliable performance estimate. The model’s performance metrics were computed as the mean of the values obtained over 10 iterations. At the end of cross-validation, each model is trained on the entire training dataset and then evaluated on the testing dataset. This process ensures an accurate assessment of the model’s effectiveness on new and unseen data, providing an objective measure of the performance metrics.
4. Results
In this section, the experimental results of the classification models are presented.
4.1. Machine Learning
The performance results of the ML models with default parameters for TF and TF-IDF feature extraction schemes are shown in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. These results concern both the training and testing datasets.

Table 1.
The performance results (in percentages) of the ML models using TF representation with filtered words. Training results are derived from 10-fold cross validation (highest values in bold).

Table 2.
The performance results (in percentages) of the ML models using TF-IDF representation with filtered words. Training results are derived from 10-fold cross validation (highest values in bold).
The results show that the MNB classifier performs well with the TF feature extraction scheme, achieving accuracies of 93% and 94% on the training and testing datasets, respectively. Following MNB, the LR and SVM classifiers also perform well on new test data. On the other hand, the TF-IDF feature selection works well in favor of the SVM model. More specifically, SVM has an outstanding performance, achieving accuracies of 93% and 94% on the training and testing datasets, respectively. Following SVM, the MNB and LR classifiers perform well. Finally, Table 1 and Table 2 also show that the performance metrics (accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score) have small differences between the training and testing sets.
The performance results of the top three ML models (LR, MNB and SVM) with fine-tuning parameters for TF and TF-IDF are shown in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively. GridSearch with 10-fold cross-validation was used to find the fine-tuning parameters that achieved the best performance metrics for this dataset. The parameter values tested during the GridSearch process were as follows: for the LR model, C = [0.001, 0.01, 0.8, 0.9, 1, 1.1, 1.4, 5, 10, 15, 100] and penalty = “l2”; for the MNB model, alpha = [1, 2, 4, 0.1, 0.5, 0.6, 0.9, 0.01, 0.0001, 0.00001]; and for the SVM model, C = [0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 1, 1.7, 2, 8, 9, 10] and kernel = [“linear,” “poly,” “rbf,” “sigmoid”]. For the TF selection scheme, the optimal fine-tuning parameters were as follows: for the LR model, C = 0.9 and penalty = l2; for the MNB model, alpha = 0.5; and for the SVM model, C = 9 and kernel = rbf. On the other hand, the fine-tuning parameters for the TF-IDF case were as follows: for the LR model, C = 10 and penalty = l2; for the MNB model, alpha = 0.5; and for the SVM model, C = 1 and kernel = linear.

Table 3.
The performance results (in percentages) of the tuning ML models using TF representation with filtered words. Training results are derived from 10-fold cross validation (highest values in bold).

Table 4.
The performance results (in percentages) of the tuning ML models using TF-IDF representation with filtered words. Training results are derived from 10-fold cross validation (highest values in bold).
Table 3 and Table 4 show a slight increase in performance metrics (accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score) for the top three ML models compared to the results shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The MNB model continues to have the best performance in sentiment classification for the TF scheme, while the SVM model performs best with the TF-IDF scheme. However, in the case of TF-IDF, the LR classifier performs slightly better on the testing dataset. This is because the data can be separated by a straight line, making the linear LR classifier particularly effective.
4.2. Artificial Neural Networks
The performance results of the ANN models, utilized with several values of neurons (60, 70, 80, 90 and 100), for TF and TF-IDF feature extraction schemes are shown in Table 5 and Table 6, respectively. These results concern both the training and testing datasets.

Table 5.
The performance results (in percentages) of the ANN models using TF representation with filtered words. Training results are derived from 10-fold cross validation (highest values in bold).

Table 6.
The performance results (in percentages) of the ANN models using TF-IDF representation with filtered words. Training results are based on 10-fold cross validation (highest values in bold).
For the word frequency feature selection scheme, the results in Table 5 show that the ANN model with 90 neurons achieved satisfactory accuracy and other metrics of 94% during the training phase. However, the ANN model with 100 neurons achieved high performance accuracy and other metrics, reaching 95% only in the testing phase. This means that the ANN model with 90 neurons learns from the data well but lacks sufficient generalization to new and unseen data. On the other hand, the ANN classifier with 100 neurons performs well in classification predictions on new testing dataset.
For the TF-IDF selection scheme, the results in Table 6 demonstrate that the ANN with 70 neurons produced the highest performance metrics, with 94% in the training phase and 95% in the testing phase. Beyond 70 neurons, there is a downward trend in all performance metrics.
4.3. Transfer Learning Model
The training and validation scores, including both loss and accuracy, for the Greek BERT-based transformer model are displayed in Table 7.

Table 7.
The performance scores of the BERT model.
The results demonstrated that the training loss and testing losses decreased as the number of epochs increased. This means that the BERT model learns effectively from the training data, but it also performs well on new test data. Furthermore, the results showed that the accuracy during the testing phase increased as the number of epochs increased, indicating that the BERT model became more accurate over time. Therefore, the BERT classifier provides the best classification performance in terms of accuracy on this dataset, reaching 96%.
4.4. Large Language Models
The performance results for two LLM models are shown in Table 8. These models were tested using only the 20% testing dataset.

Table 8.
The performance scores (in percentages) for LLM models (zero-shot) (highest values in bold).
Table 8 shows that the GPT-4 model slightly surpasses GPT-3.5 across all performance metrics. Specifically, GPT-4 achieves the highest classification performance, with an accuracy rate of 95%. This performance is particularly notable, given that the GPT models were tested in a zero-shot setting. Finally, it was observed that the execution time of GPT models was slow compared to other models, likely due to the additional time needed to interpret and construct prompts for each query.
5. Discussion
Based on the results section, I concluded that the three top fine-tuned machine learning models (LR, MNB and SVM) generally achieved high classification performance with the TD-IDF feature extraction scheme, with the exception of the MNB model. The MNB model with TF (or word frequency) representation performed better on testing data than the SVM model. On the other hand, the SVM model with the TD-IDF scheme excelled in making predictions with new testing data. These performance trends confirm findings from other studies involving similar and small datasets [,]. However, the LR classifier with the TF-IDF representation appears to provide the best baseline performance, with an accuracy rate of approximately 95%. This accuracy is slightly higher than the 92% achieved by the SVM classifier on a similar small dataset, as in []. Another advantage of the LR model is that it trains and classifies quickly, and provides high-accuracy predictions compared to other machine learning algorithms.
The study revealed that the ANN classifiers performed similarly with both TF and TF-IDF representations, showing no significant differences in performance. Furthermore, the ANN model with 70 neurons and the TF-IDF representation achieved a classification accuracy of 95%. In this case, only a constant performance was observed with the ANN compared to the LR machine learning model.
The GreekBERT and GPT-4 language models demonstrated outstanding performance in sentiment analysis, achieving accuracy rates of 96% and 95%, respectively. These results confirm findings from other studies that report similar performance in sentiment analysis, such as studies [,] for the GreekBERT case and another study [] for the GPT-4 case in the English language. However, the GreekBERT model delivered the best classification performance relative to the GPT-4 model. This is because BERT utilizes a bidirectional architecture, allowing it to fully grasp the meaning of words within a sentence, whereas OpenAI GPT employs a unidirectional left-to-right approach. As a result, BERT often provides better results on many NLP tasks, including sentiment analysis [].
Regarding the main research hypothesis in the introduction, it was validated. The effectiveness of cutting-edge classification models, including ANNs, transfer learning, and LLMs, is high, but shows only marginal improvements compared to traditional ML models. In other words, the performance gains of transfer learning and LLMs over the LR model are marginal, typically in the range of 1%. Specifically, GreekBERT delivers the best performance, followed by GPT-4, ANNs, and traditional ML models, with only minor differences. The classification performance of the ANNs and LR classifiers in this study appears comparable to that of GreekBERT and GPT-4. This suggests that for sentiment classification of Greek reviews, using traditional ML models such as LR alongside more advanced models like BERT and LLMs yields similar effectiveness for the dataset used in this work.
Although the classification performance of ML, ANN, and DL models is comparable, they have different capabilities. Notably, advanced models like BERT and GPT-4 offer significant advantages over ML and ANN models, such as the ability to automatically learn word vectors from text without manual feature extraction, a better understanding of word context and language, and the ability to leverage pre-trained knowledge, which enhances their adaptability to specific NLP tasks.
The findings on the performance of GreekBERT and GPT-4 in this study can be compared with existing studies using similar datasets and metrics, but with caution, as the dataset sizes and application domains differ. For instance, Katika et al. [] and Giatsoglou et al. [] achieved accuracies of 94% and 84% for sentiment classification, respectively. While these results are lower than the 96% accuracy achieved by BERT and 95% by GPT-4, they should be considered with caution due to differences in dataset characteristics and contexts. On the other hand, Dontaki et al. [] and Alexandridis et al. [], which focused on social media datasets rather than consumer reviews as in this study, achieved accuracies of 99% using ML and GPT-2 models, respectively. These results are higher than the performance results of GreekBERT and GPT-4 achieved in this study due to differences in dataset characteristics. Although the performance of BERT and GPT-4 in this study is slightly lower, it demonstrates the strong capabilities of BERT and GPT-4 compared to the ML and GPT-2 approaches. Specifically, the BERT and GPT-4 models are commendable, given that they require automatic preprocessing of text without manual feature extraction, unlike the ML approaches used in [] which involved manual text preprocessing and feature extraction. Furthermore, the GPT-4 model in a zero-shot setting showed strong performance without additional training data, which is particularly useful in real-world scenarios where labeled review data are limited. This contrasts with the GPT-2 model used in [], which required more fine-tuning and training examples for specific NLP tasks. Therefore, the highest accuracy of 99% reported in the literature is impressive. The results with GreekBERT and GPT-4 in this study are competitive, especially considering the simplicity of the BERT model and the zero-shot capabilities of GPT-4. It should be noted that the focus of this study was on comparing and demonstrating the applicability of advanced models for Greek sentiment analysis rather than solely maximizing accuracy.
This study encountered some limitations. A limitation faced by the present comparative study is the lack of large and more Greek review datasets, which restricts a more thorough examination of the performance improvements offered by state-of-the-art methods. Another limitation is that this work focused on binary sentiment classification (positive/negative), which does not account for the complexity of human emotions that might be present in the product reviews. Often, reviews contain a range of emotions, from extreme positivity to deep negativity, and sometimes mixed or neutral sentiments. This, therefore, means that binary categorization would lack some degree of explicit detail in the subtlety of information and richness of emotional content within these reviews. A more nuanced understanding of sentiments could focus on specific aspects of a product or service mentioned in the reviews. Finally, although the findings of this study are promising and the size of the product review dataset was larger than the dataset in [], the findings should be viewed cautiously given the relatively limited size of the current dataset.
6. Conclusions
In this work, an exploratory performance study was conducted using popular and state-of-the-art classification models to address the problem of sentiment analysis based on a publicly available Greek review dataset. This study has clarified the performance of these models, offering valuable insights into their effectiveness in Greek sentiment analysis and evaluating the research hypothesis introduced in the introduction section.
The findings indicated that advanced models, such as BERT and GPT-4, achieved high classification performance accuracies of 95–96%. These results illustrate the important benefits of using advanced NLP models for sentiment analysis tasks. However, it is important to mention that these models are more computationally expensive compared to simpler ML models such as LR, SVM, and MNB classifiers. This trade-off between performance metrics and computational cost is an important factor for practical applications.
The comparable performance results of BERT and GPT-4 confirm the expectation that high classification accuracy in sentiment analysis with pre-trained language models and transfer learning is possible, even for languages that have significantly fewer NLP resources like the Greek language. This is one of the relevant findings for creating more robust and reliable sentiment analysis systems for several domains such as customer feedback, social media monitoring, and market research.
In future work, this study could be expanded to include larger and more Greek review datasets to confirm the superior performance of advanced classification models compared to traditional ML models. Furthermore, future research could focus on exploring the performance of advanced models in emotion classification to identify a variety of human emotions, extending beyond binary sentiment classification to include more distinct categories. This effort may require additional human labor to accurately categorize the original Greek reviews into diverse emotional categories. Additionally, leveraging NLP capabilities for fine-grained sentiment analysis, such as aspect-based sentiment analysis in the reviews, could be a focus of future work to gain more insights into the sentiment expressed in reviews. Finally, it could be interesting to apply Greek sentiment analysis to other novel study contexts, such as emotional experience detection in electronic sports (eSports) [] or sentiment, emotion, and partiality analysis of the attitudes of Greeks on the Russia–Ukraine conflict [].
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the reviewers for their helpful comments in improving the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nandwani, P.; Verma, R. A Review on Sentiment Analysis and Emotion Detection from Text. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2021, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Maruf, A.; Khanam, F.; Haque, M.M.; Jiyad, Z.M.; Mridha, M.F.; Aung, Z. Challenges and Opportunities of Text-Based Emotion Detection: A Survey. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 18416–18450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Bing, L.; Lam, W. A Survey on Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis: Tasks, Methods, and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 11019–11038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, H.; Feng, F.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Hovy, E. DualGCN: Exploring Syntactic and Semantic Information for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 7642–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaei, A.R.; Becken, S.; Stantic, B. Sentiment Analysis in Tourism: Capitalizing on Big Data. J. Travel. Res. 2019, 58, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamoodi, A.H.; Zaidan, B.B.; Zaidan, A.A.; Albahri, O.S.; Mohammed, K.I.; Malik, R.Q.; Almahdi, E.M.; Chyad, M.A.; Tareq, Z.; Albahri, A.S.; et al. Sentiment Analysis and Its Applications in Fighting COVID-19 and Infectious Diseases: A Systematic Review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 167, 114155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Pamula, R.; Srivastava, G. A Systematic Literature Review on Machine Learning Applications for Consumer Sentiment Analysis Using Online Reviews. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 41, 100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambocas, M.; Pacheco, B.G. Online Sentiment Analysis in Marketing Research: A Review. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2018, 12, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, F.; Chen, T.; Pan, L.; Beliakov, G.; Wu, J. A Brief Survey of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for E-Commerce Research. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2023, 18, 2188–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachanou, A.; Crestani, F. Like It or Not: A Survey of Twitter Sentiment Analysis Methods. ACM Comput. Surv. 2016, 49, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugmann, J.O.; Hartmann, J. Sentiment Analysis in the Age of Generative AI. Cust. Needs Solut. 2024, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, J.; Heitmann, M.; Siebert, C.; Schamp, C. More than a Feeling: Accuracy and Application of Sentiment Analysis. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2023, 40, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Feng, Y.; Ding, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xia, R. Is ChatGPT a Good Sentiment Analyzer? A Preliminary Study. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.04339. [Google Scholar]
- Tsakalidis, A.; Papadopoulos, S.; Voskaki, R.; Ioannidou, K.; Boididou, C.; Cristea, A.I.; Liakata, M.; Kompatsiaris, Y. Building and Evaluating Resources for Sentiment Analysis in the Greek Language. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2018, 52, 1021–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilianos, D. Experiments in Text Classification: Analyzing the Sentiment of Electronic Product Reviews in Greek. J. Quant. Linguist. 2022, 29, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markopoulos, G.; Mikros, G.; Iliadi, A.; Liontos, M. Sentiment Analysis of Hotel Reviews in Greek: A Comparison of Unigram Features. In Cultural Tourism in a Digital Era, Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics; Katsoni, V., Ed.; Springer Science and Business Media B.V.: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 373–383. [Google Scholar]
- Dontaki, C.; Koukaras, P.; Tjortjis, C. Sentiment Analysis on English and Greek Twitter Data Regarding Vaccinations. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems and Applications, IISA, Volos, Greece, 10–12 July 2023; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Charalampakis, B.; Spathis, D.; Kouslis, E.; Kermanidis, K. Detecting Irony on Greek Political Tweets: A Text Mining Approach. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks (INNS), Island, Rhodes, Greece, 25–28 September 2015; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Athanasiou, V.; Maragoudakis, M. A Novel, Gradient Boosting Framework for Sentiment Analysis in Languages Where NLP Resources Are Not Plentiful: A Case Study for Modern Greek. Algorithms 2017, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katika, A.; Zoulias, E.; Koufi, V.; Malamateniou, F. Mining Greek Tweets on Long COVID Using Sentiment Analysis and Topic Modeling. In Healthcare Transformation with Informatics and Artificial Intelligence; IOS Press BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 305, pp. 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Patsiouras, E.; Koroni, I.; Mademlis, I.; Pitas, I. GreekPolitics: Sentiment Analysis on Greek Politically Charged Tweets. In Proceedings of the 2023 31st European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Helsinki, Finland, 4–8 September 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1320–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandridis, G.; Varlamis, I.; Korovesis, K.; Caridakis, G.; Tsantilas, P. A Survey on Sentiment Analysis and Opinion Mining in Greek Social Media. Information 2021, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and Their Compositionality. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–8 December 2013; pp. 3111–3119. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Joulin, A.; Grave, E.; Bojanowski, P.; Mikolov, T. Bag of Tricks for Efficient Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Valencia, Spain, 3–7 April 2017; pp. 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Janiesch, C.; Zschech, P.; Heinrich, K. Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Electron. Mark. 2021, 31, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Vishwakarma, D.K. Sentiment Analysis Using Deep Learning Architectures: A Review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 4335–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Brain, G.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the NIPS’17: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. DistilBERT, a Distilled Version of BERT: Smaller, Faster, Cheaper and Lighter. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsikakis, J.; Chalkidis, I.; Malakasiotis, P.; Androutsopoulos, I. GREEK-BERT: The Greeks Visiting Sesame Street. In Proceedings of the 11th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Athens, Greece, 2–4 September 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kalamatianos, G.; Mallis, D.; Symeonidis, S.; Arampatzis, A. Sentiment Analysis of Greek Tweets and Hashtags Using a Sentiment Lexicon. In Proceedings of the 19th Panhellenic Conference on Informatics, Athens, Greece, 1–3 October 2015; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kydros, D.; Argyropoulou, M.; Vrana, V. A Content and Sentiment Analysis of Greek Tweets during the Pandemic. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaras, L.; García-Barriocanal, E.; Sicilia, M.A. Sentiment Analysis of COVID-19 Cases in Greece Using Twitter Data. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2023, 230, 120577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatsoglou, M.; Vozalis, M.G.; Diamantaras, K.; Vakali, A.; Sarigiannidis, G.; Chatzisavvas, K.C. Sentiment Analysis Leveraging Emotions and Word Embeddings. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2017, 69, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aivatoglou, G.; Fytili, A.; Arampatzis, G.; Zaikis, D.; Stylianou, N.; Vlahavas, I. End-to-End Aspect Extraction and Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis Framework for Low-Resource Languages. In Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, Proceedings of the Intelligent Systems and Applications, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 7–8 September 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 824, pp. 841–858. [Google Scholar]
- Fragkis, N. Skroutz Shops Greek Reviews. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/nikosfragkis/skroutz-shop-reviews-sentiment-analysis (accessed on 13 April 2024).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Cauteruccio, F.; Kou, Y. Investigating the Emotional Experiences in ESports Spectatorship: The Case of League of Legends. Inf. Process Manag. 2023, 60, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, M.; Khamis, M.A.; Yahia, A.; Khaled, S.A.; Ashraf, A.; Gomaa, W. Arab Reactions towards Russo-Ukrainian War. EPJ Data Sci. 2023, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).