Exploiting Inter- and Intra-Base Crossing with Multi-Mappings: Application to Environmental Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Environmental Data
1.2. Points of View
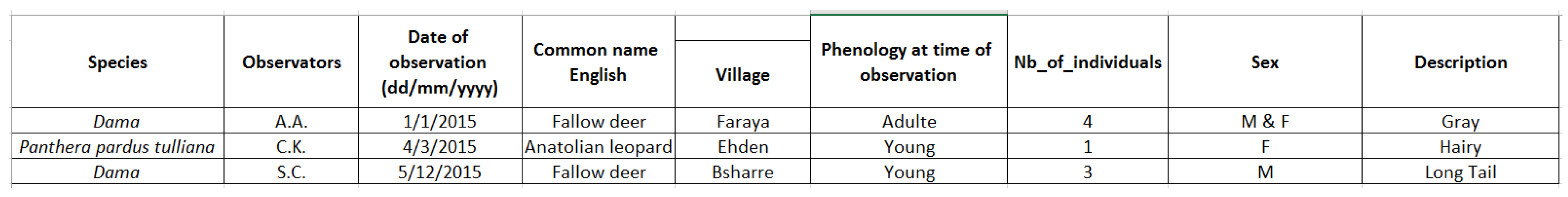
1.3. Case Study
1.4. Contributions of the Work
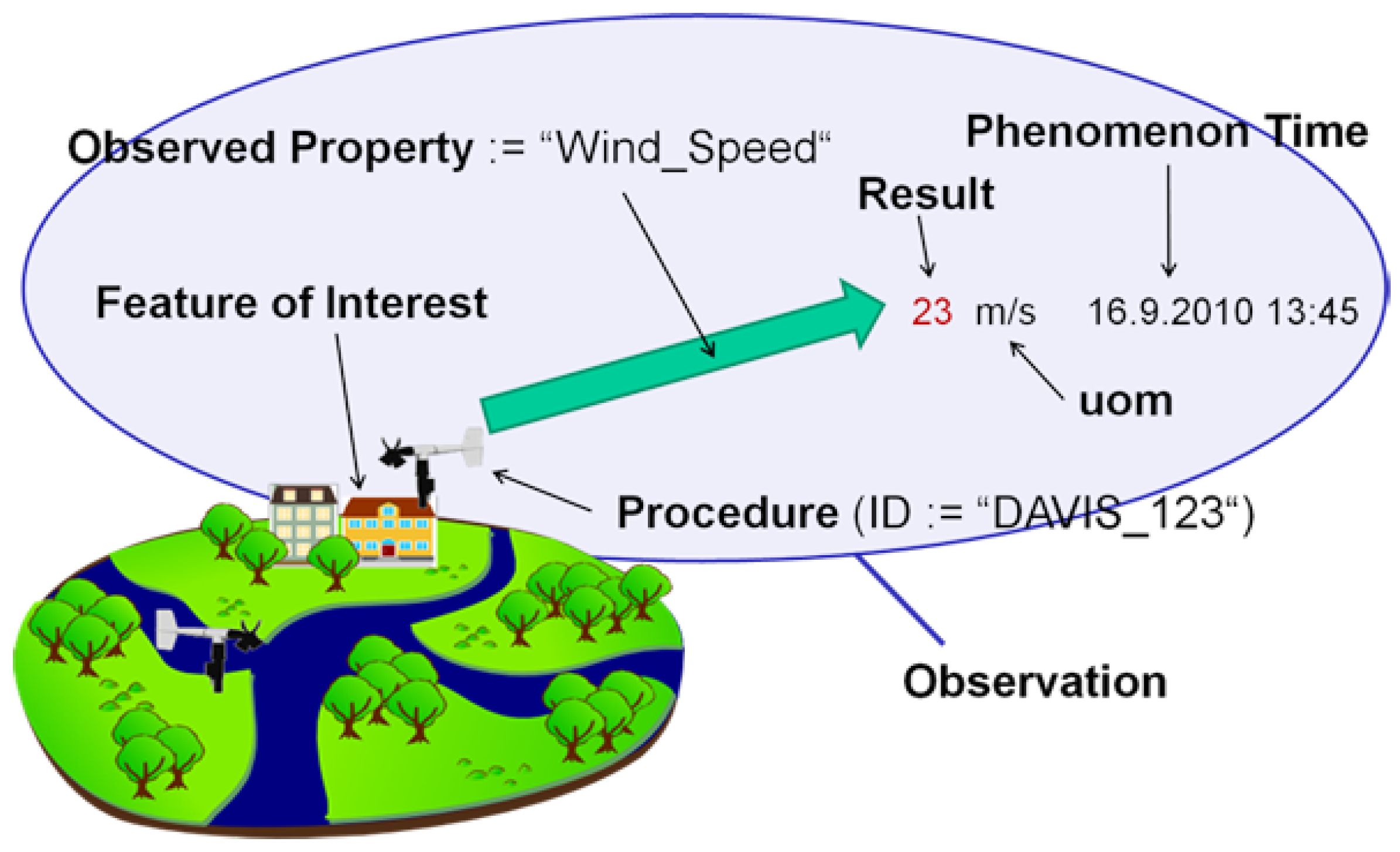
2. Methodology
- reconciling data schemes with standards;
- exploding and duplicating points of view over the data;
- cataloging the points of view;
- enabling/disabling navigation through the points of view;
- crossing data.
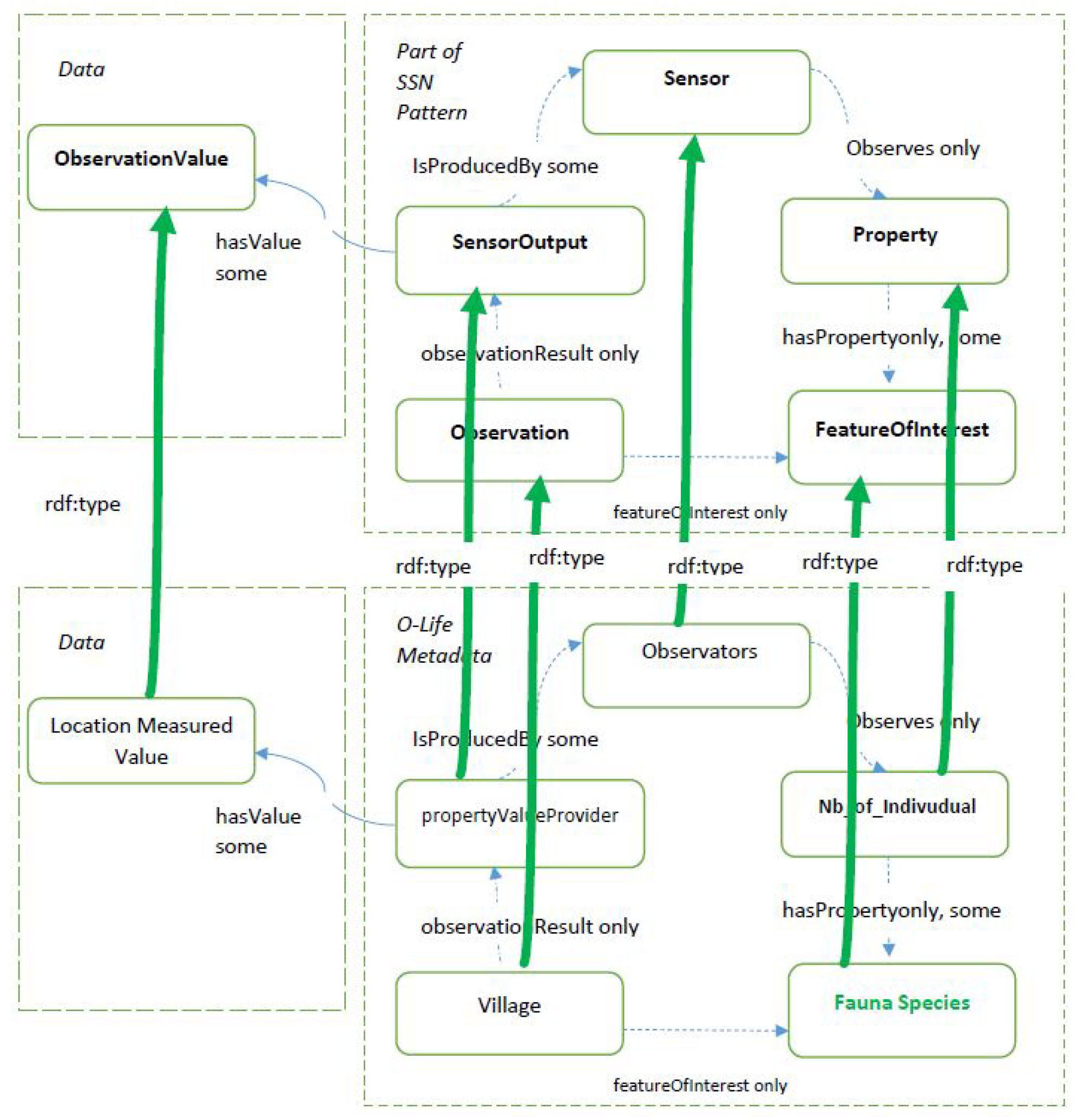
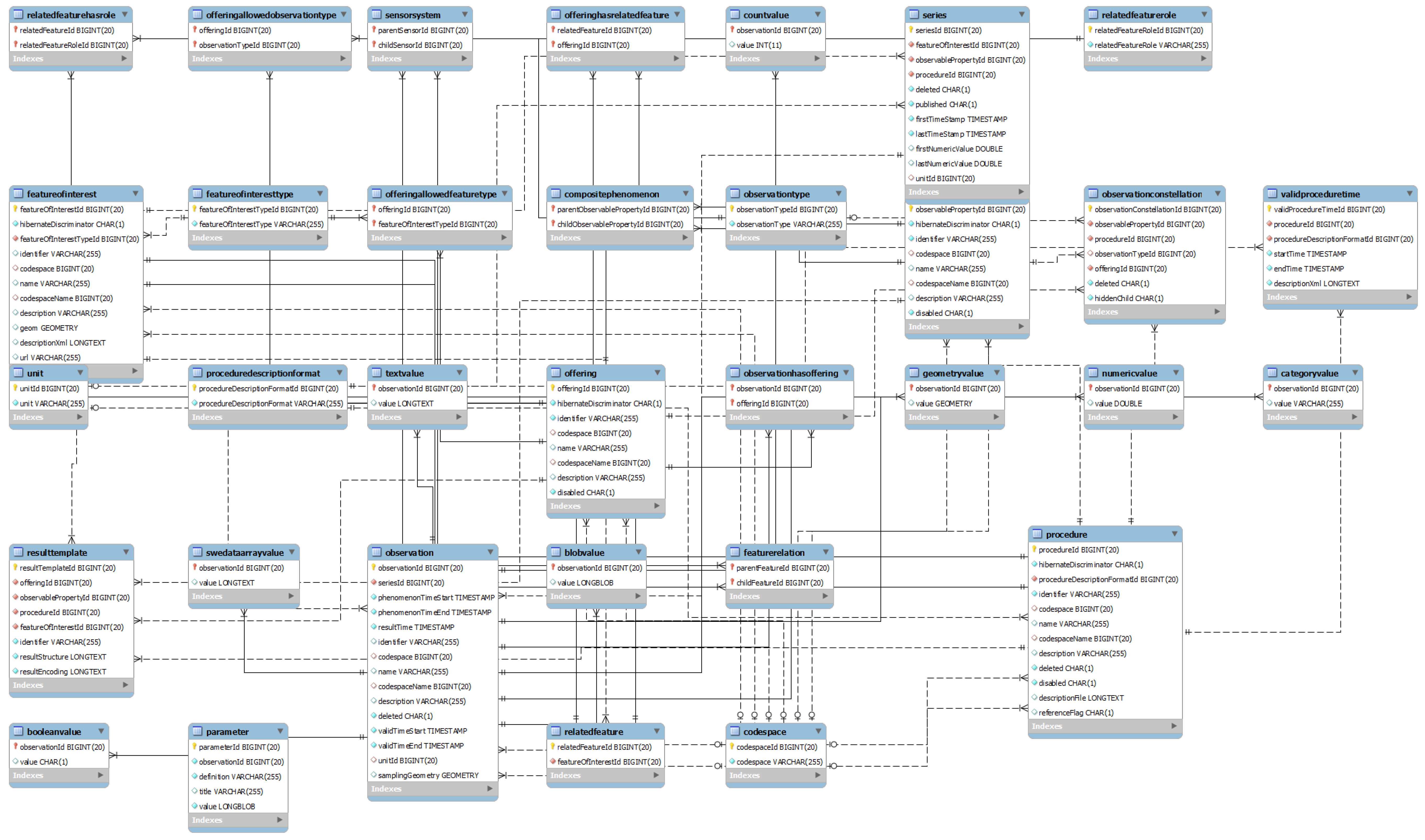
2.1. Reconciling Data Schemes with Standards
2.2. Exploding and Duplicating Points of View with Multi-Mapping
2.2.1. Multiple Mappings
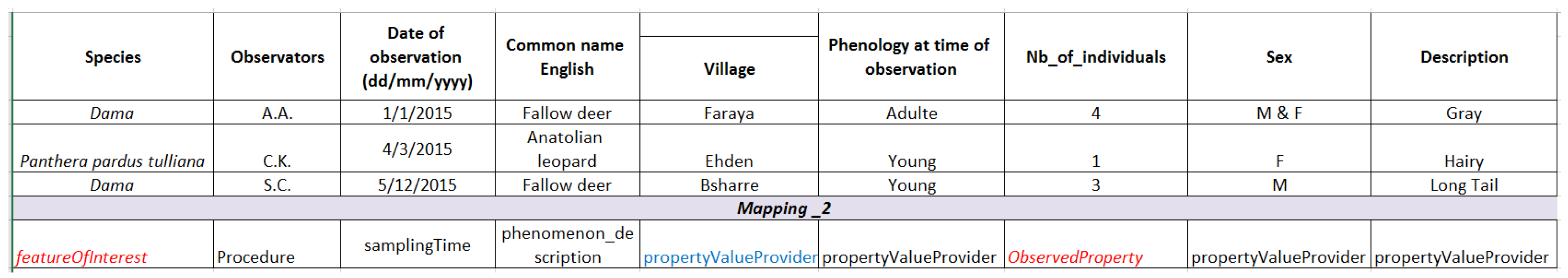
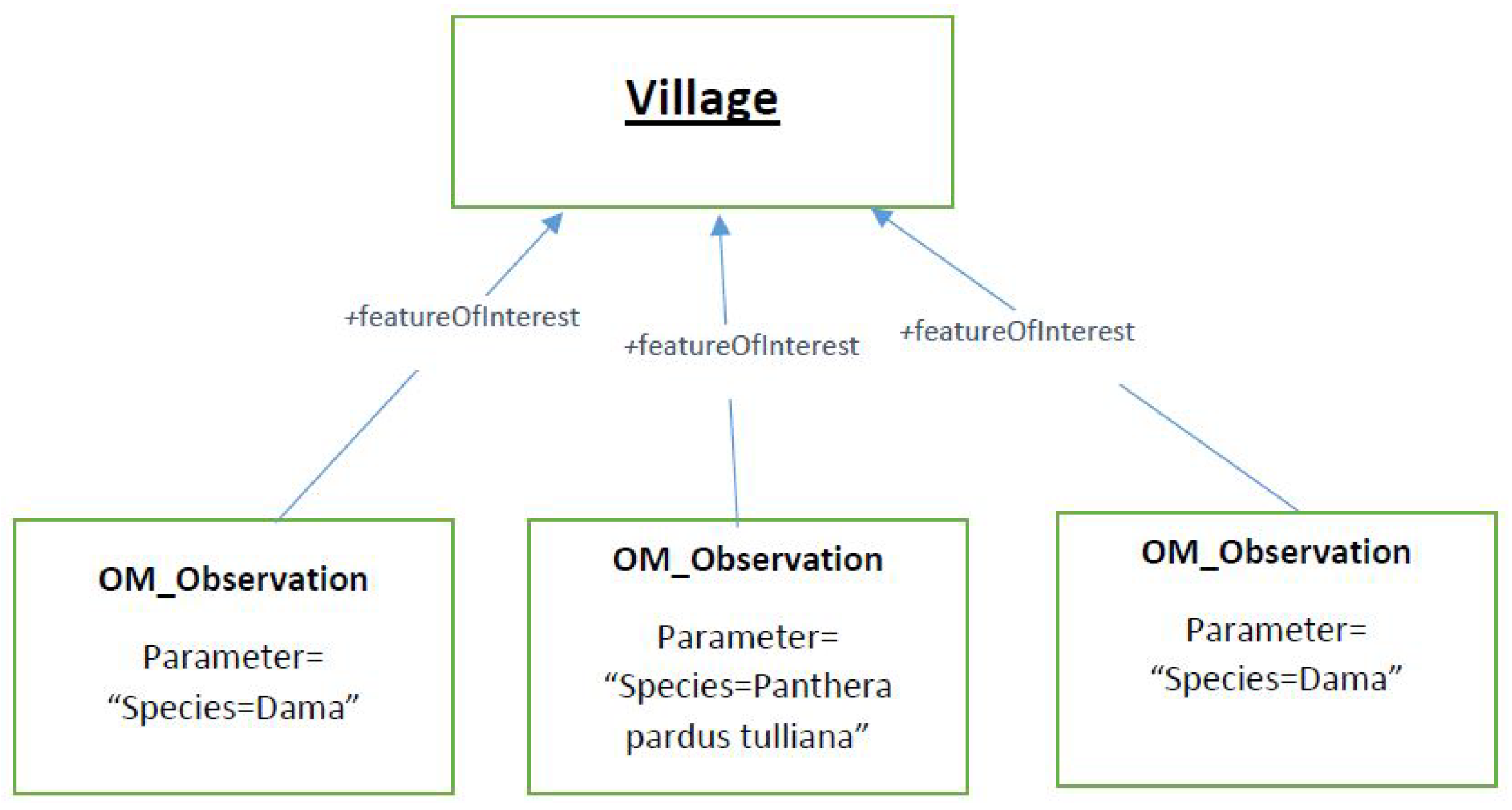
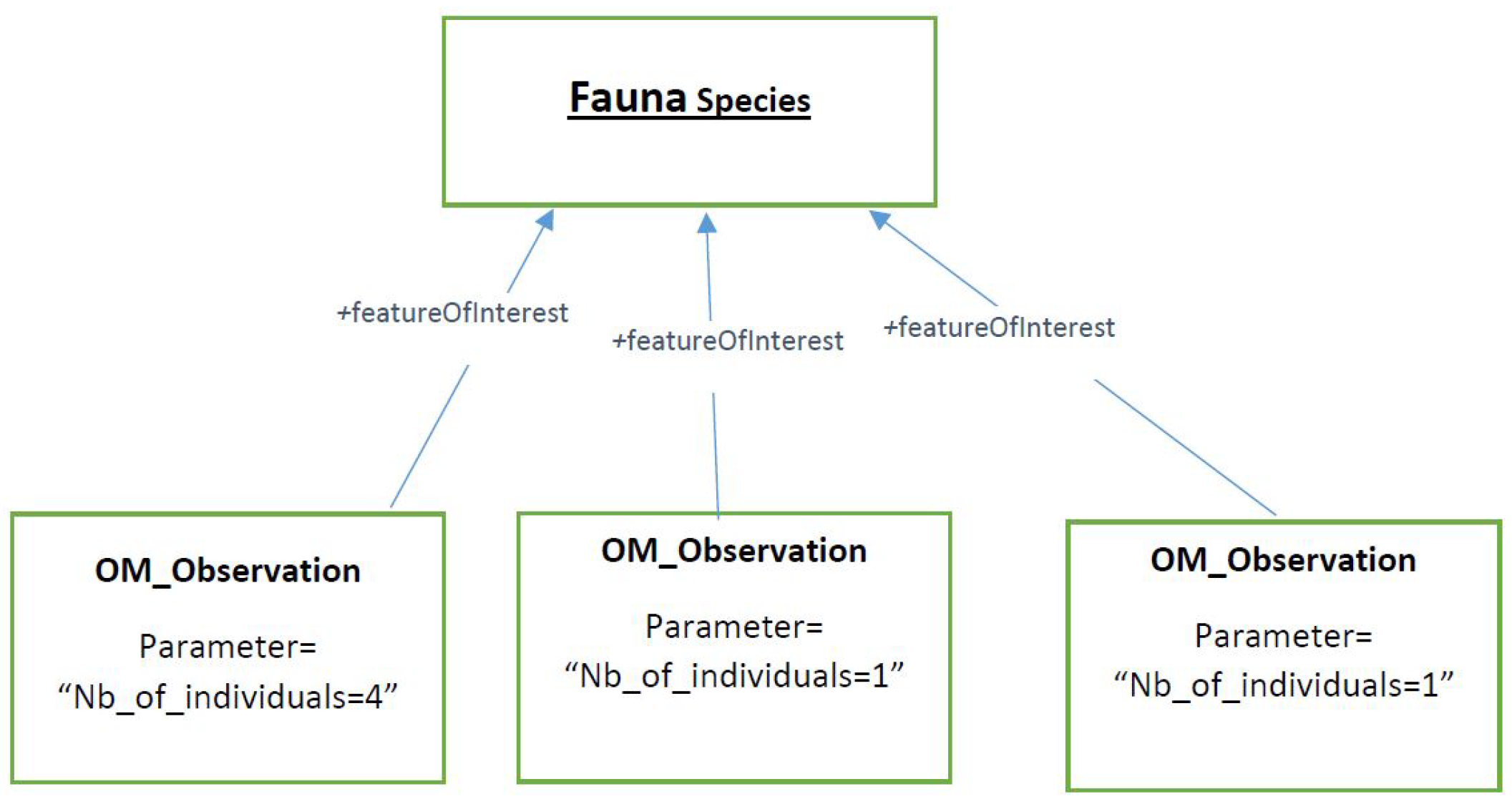
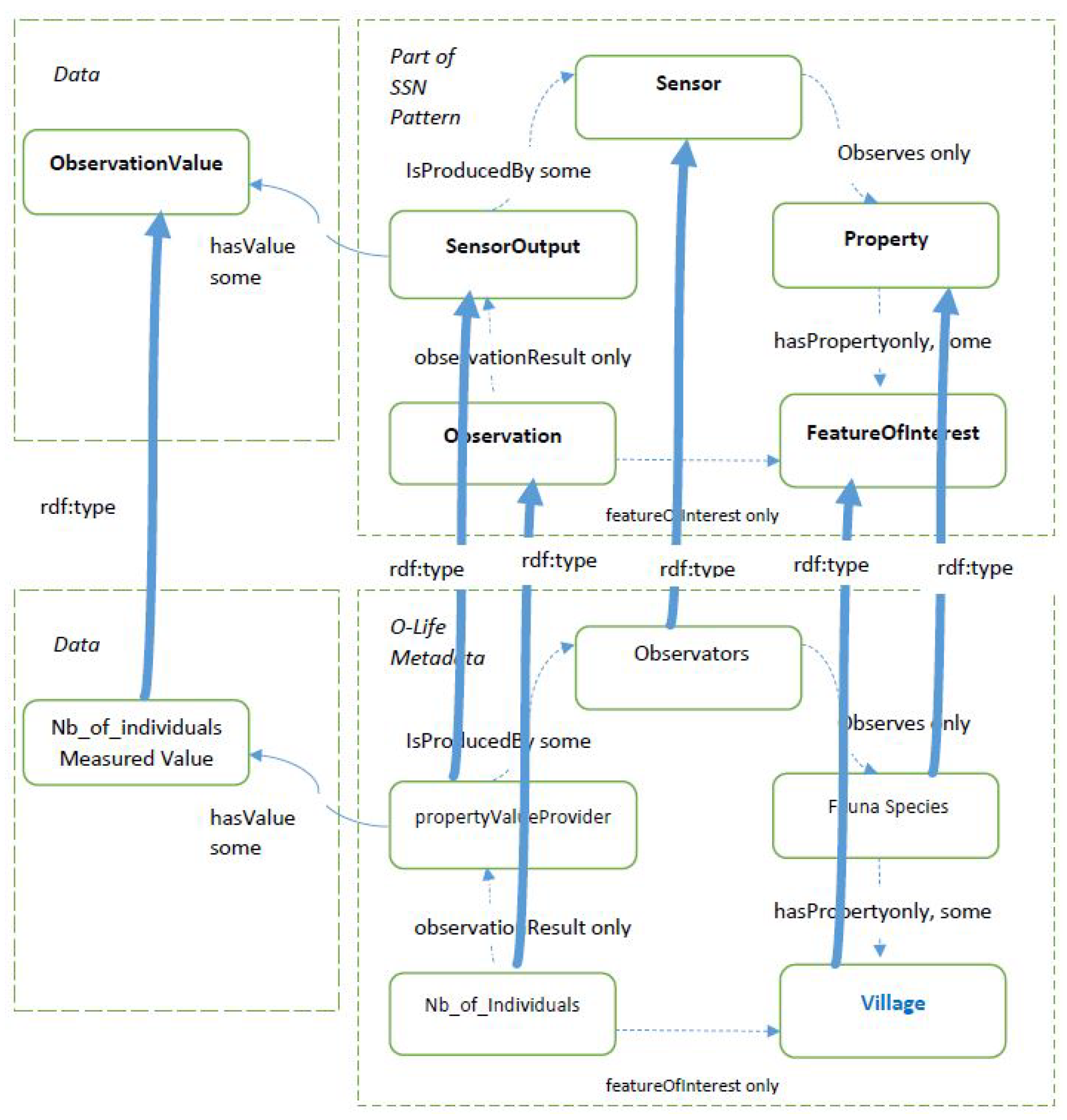
2.2.2. Running Example
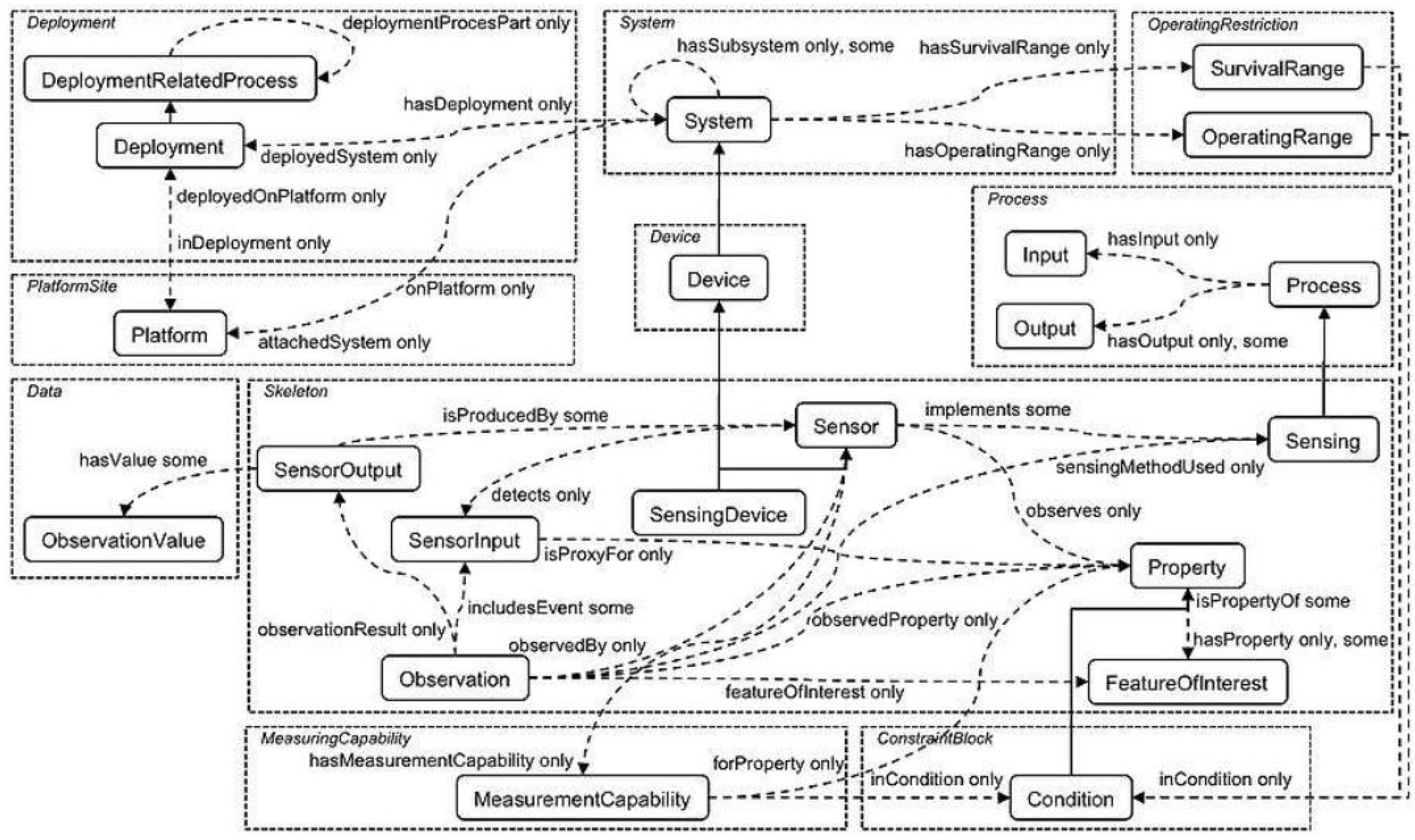
2.2.3. Extending and Refining the Ontology
- the alternative observation class allows a given observation from the real dataset to be designed in different manners, meaning multiple mappings are available;
- the alternative feature of interest property makes it possible to highlight the fact that the observation being considered can be designed in various manners in order to define the feature of interest;
- the alternative observed property makes it possible to highlight the fact that the observation being considered can be designed in various manners in order to define the observed property;
- the alternative observed by property makes it possible to highlight the fact that the observation being considered can be designed in various manners in order to define the sensor.
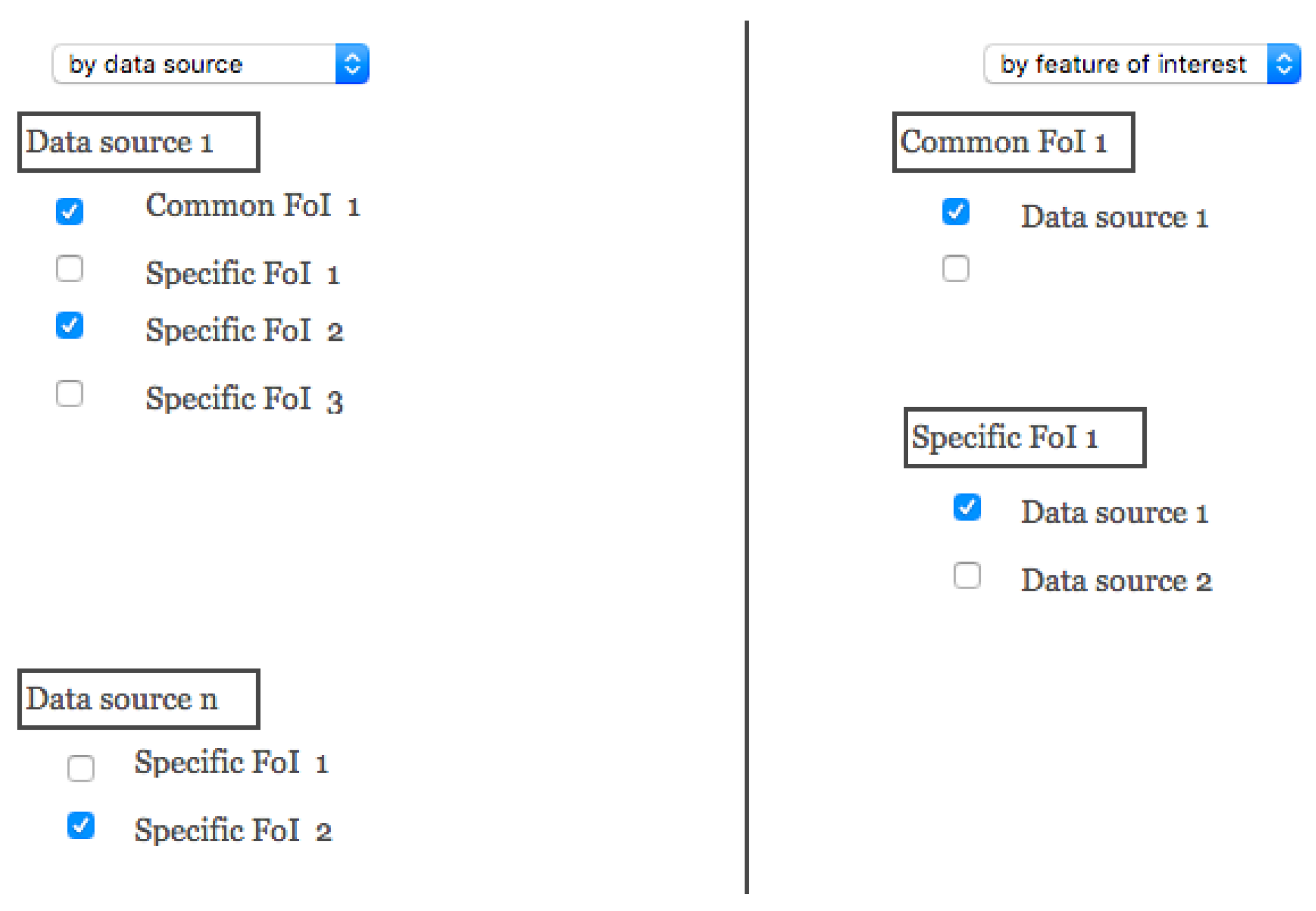
2.3. Cataloging the Points of View
2.4. Enabling/Disabling Navigation through the Points of View and Crossing Data
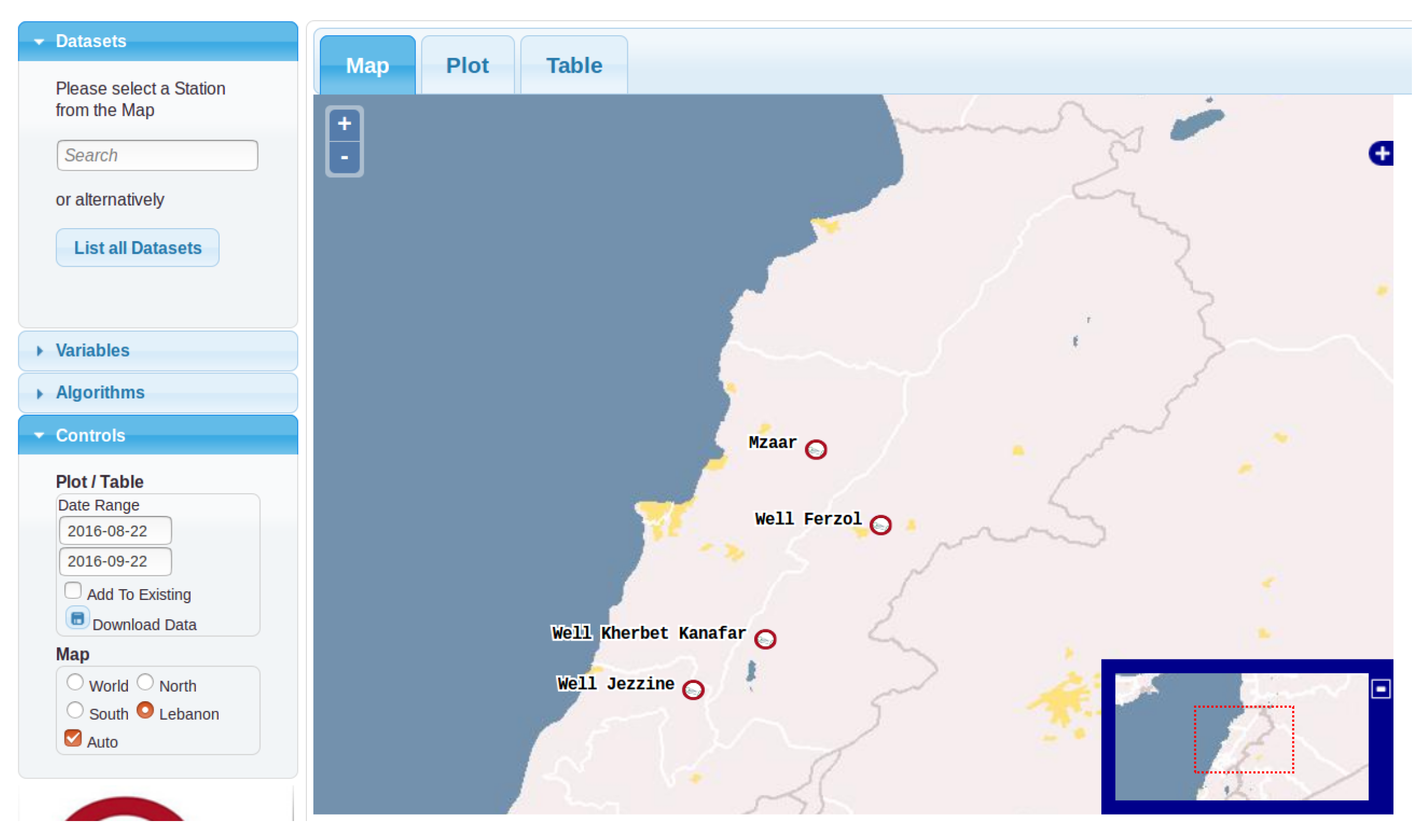
3. Experimental Data
3.1. O-LiFE Information System
- Simultaneously conduct: observation, research, training and valorization;
- Federate skills through common tools and objects;
- Organize, share, sustain and enhance environmental data.
3.2. Data Description
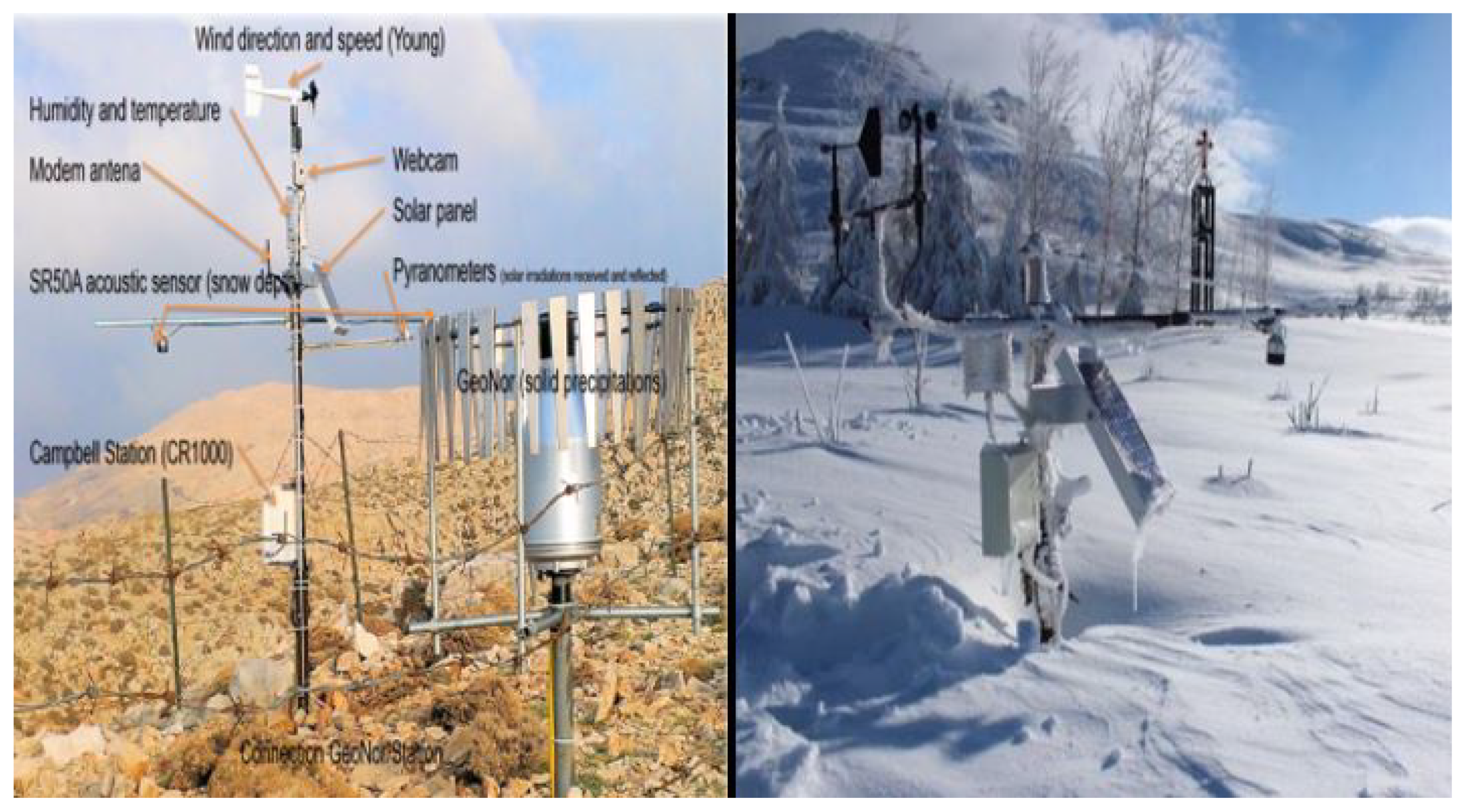
3.2.1. Snow Data
- temperature and relative humidity;
- wind horizontal speed and direction;
- snow depth, by sonar (acoustic sensor);
- solar radiation, by two pyranometers;
- the atmospheric pressure by barometry;
- the monitoring of the ambient weather in real time via a digital camera.
3.2.2. Wells Data
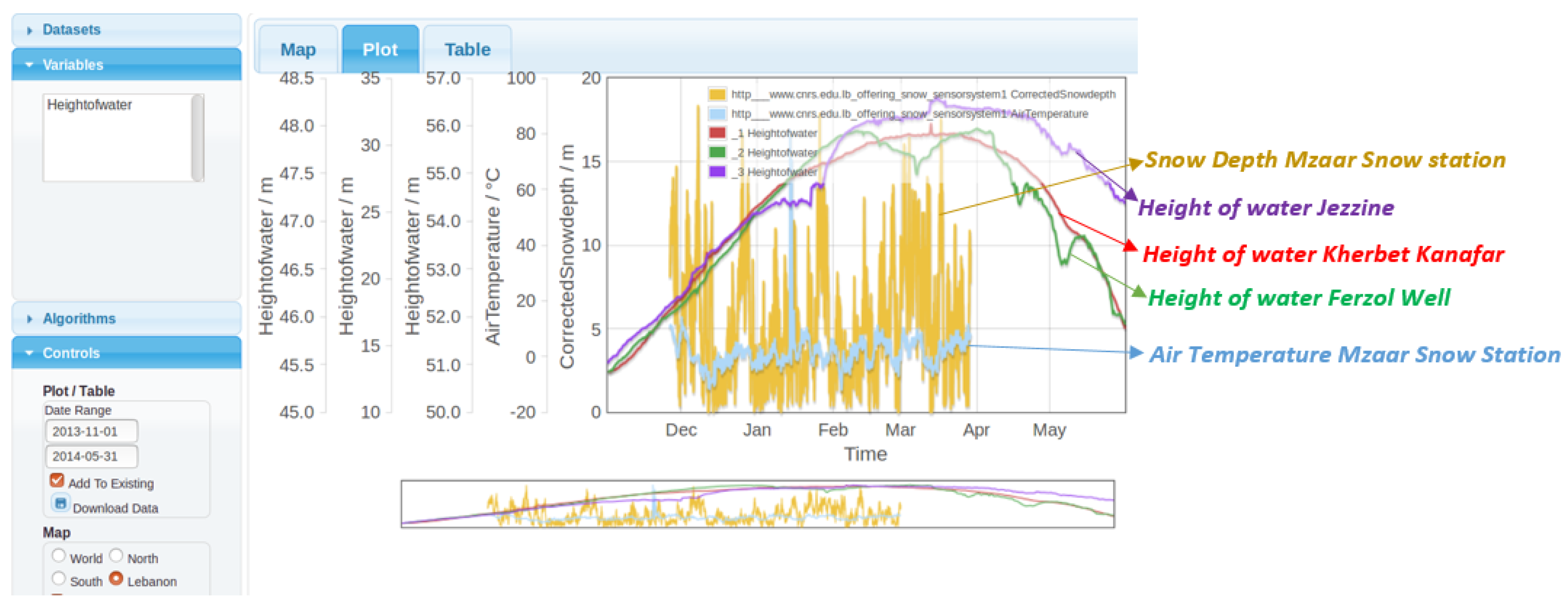
3.3. Interpretation
- a very high frequency variation related to day/night alternations;
- a frequency variation of approximately eight days, which may correspond to one or two synoptic situations;
- a low monthly frequency variation.
3.4. An Example of a Data Crossing between Two Data Sources
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| O-LiFE | L’Observatoire Libano-Francais pour l’Environnement |
| OGC | Open Geospatial Consortium |
| SWE | Sensor Web Enablement |
| SOS | Sensor Observation Service |
| O&M | Observations and Measurements |
| FoI | Feature of Interest |
| IS | Information System |
| GAV | Global As View |
| LAV | Local As View |
References
- Catarci, T.; Lenzerini, M. Representing and Using Interschema Knowledge in Cooperative Information Systems. Int. J. Coop. Inf. Syst. 1993, 2, 375–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, U.; Castellanos, M.; Simitsis, A.; Wilkinson, K. Data integration flows for business intelligence. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Extending Database Technology: Advances in Database Technology, Saint Petersburg, Russia, 24–26 March 2009; ACM International Conference Proceeding Series; Kersten, M.L., Novikov, B., Teubner, J., Polutin, V., Manegold, S., Eds.; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 360, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, P.; Romero, O.; Simitsis, A.; Abelló, A. Integrating ETL Processes from Information Requirements. In International Conference on Data Warehousing and Knowledge Discovery; Cuzzocrea, A., Dayal, U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; Volume 7448, pp. 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Simitsis, A.; Vassiliadis, P. A method for the mapping of conceptual designs to logical blueprints for ETL processes. Decis. Support Syst. 2008, 45, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsis, Y.; Papakonstantinou, Y. View-based Data Integration. In Encyclopedia of Database Systems; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 3332–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miu, M.; Zhang, X.; Dewan, M.A.A.; Wang, J. Development of Framework for Aggregation and Visualization of Three-Dimensional (3D) Spatial Data. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2018, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madera, C.; Laurent, A. The next information architecture evolution: The data lake wave. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Management of Digital EcoSystems 2016, Biarritz, France, 1–4 November 2016; Chbeir, R., Agrawal, R., Biskri, I., Eds.; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajj-Hassan, H.; Arnaud, N.; Castelltort, A.; Drapeau, L.; Laurent, A.; Lobry, O.; Khater, C. Multimapping Design of Complex Sensor Data in Environmental Observatories. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Web Intelligence, Mining and Semantics, Nîmes, France, 13–15 June 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 2:1–2:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desconnets, J.; Moyroud, N.; Libourel, T. Méthodologie de mise en place d’observatoires virtuels via les métadonnées. In Proceedings of the Actes du XXIème Congrès INFORSID, Nancy, France, 24–27 May 2003; pp. 253–267. (In French). [Google Scholar]
- Broring, A.; Echterhoff, J.; Jirka, S.; Simonis, I.; Everding, T.; Stasch, C.; Liang, S.; Lemmens, R. New Generation Sensor Web Enablement. Sensors 2011, 11, 2652–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirka, S.; Bröring, A.; Stasch, C. Applying OGC Sensor Web Enablement to risk monitoring and disaster management. In Proceedings of the GSDI 11 World Conference, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 15–19 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Broring, A.; Stasch, C.; Echterhoff, J. OGC Sensor Observation Service Interface Standard (Version 2.0). In OGC Document; Available online: http://www.opengis.net/doc/IS/SOS/2.0 (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Michener, W.K.; Brunt, J.W.; Helly, J.J.; Kirchner, T.B.; Stafford, S.G. Nongeospatial metadata for the ecological sciences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 330–342. [Google Scholar]
- Compton, M.; Barnaghi, P.; Bermudez, L.; Garcıa-Castro, R.; Corcho, O.; Cox, S.; Graybeal, J.; Hauswirth, M.; Henson, C.; Herzog, A.; et al. The SSN Ontology of the W3C Semantic Sensor Network Incubator Group. J. Web Semant. 2012, 17, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, M.; Henson, C.; Lefort, L.; Neuhaus, H.; Sheth, A. A survey of the semantic specification of sensors. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Semantic Sensor Networks Workshop, Aachen, Germany, 26 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Janowicz, K.; Schade, S.; Bröring, A.; Keßler, C.; Maué, P.; Stasch, C. Semantic Enablement for Spatial Data Infrastructures. Trans. GIS 2010, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, C.A.; Pschorr, J.; Sheth, A.P.; Thirunarayan, K. SemSOS: Semantic sensor Observation Service. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Symposium on Collaborative Technologies and Systems, Baltimore, MD, USA, 18–22 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vitolo, C.; Elkhatib, Y.; Reusser, D.; Macleod, C.; Buytaert, W. Web technologies for environmental Big Data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 63, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Liang, S.H. A Sensor Data Mediator Bridging the OGC Sensor Observation Service (SOS) and the OASIS Open Data Protocol (OData). In The 12th International Symposium on Web and Wireless Geographical Information System; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Banff, AB, Canada, 2013; Volume 7820. [Google Scholar]
- Nešić, S.; Rizzoli, A.E.; Athanasiadis, I.N. Towards a Semantically Unified Environmental Information Space. In Proceedings of the 9th IFIP WG 5.11, International Symposium on Environmental Software Systems—ISESS 2011, Brno, Czech Republic, 27–29 June 2011; Springer: Brno, Czech Republic, 2011; Volume 359/2011. [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh, J.S.; Tarboton, D.G.; Maidment, D.R.; Zaslavsky, I. Components of an environmental observatory information system. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moßgraber, J.; Hilbring, D. Automating the web publishing process of environmental data by using semantic annotations. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Environnmental Multimedia Retrieval Co-Located with ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, EMR@ICMR 2014, Glasgow, UK, 1 April 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Liu, Y. Using Linked Data in a Heterogeneous Sensor Web: Challenges, Experiments and Lessons Learned. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2015, 8, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Lee, J. SSTDE: An Open Source Semantic Spatiotemporal Data Engine for Sensor Web. In Proceedings of the First ACM SIGSPATIAL Workshop on Sensor Web Enablement, Redondo Beach, CA, USA, 6 November 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, S.; Dayal, U. An Overview of Data Warehousing and OLAP Technology. SIGMOD Rec. 1997, 26, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, J.; Song, I.Y.; Chen, P.P. An Analysis of Additivity in OLAP Systems. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Workshop on Data Warehousing and OLAP, Washington, DC, USA, 12–13 November 2004; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C.; Han, J. (Eds.) Frequent Pattern Mining; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Trafalis, T.B.; Alwazzi, S.A. Support vector regression with noisy data: A second order cone programming approach. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2007, 36, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, A.; Lesot, M.; Rifqi, M. GRAANK: Exploiting Rank Correlations for Extracting Gradual Itemsets. In International Conference on Flexible Query Answering Systems; Andreasen, T., Yager, R.R., Bulskov, H., Christiansen, H., Larsen, H.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; Volume 5822, pp. 382–393. [Google Scholar]
- Hajj-Hassan, H.; Arnaud, N.; Drapeau, L.; Laurent, A.; Lobry, O.; Khater, C. Integrating Sensor Data Using Sensor Observation Service: Towards a Methodology for the O-Life Observatory. Sens. Transducers J. 2015, 194, 99–105. [Google Scholar]




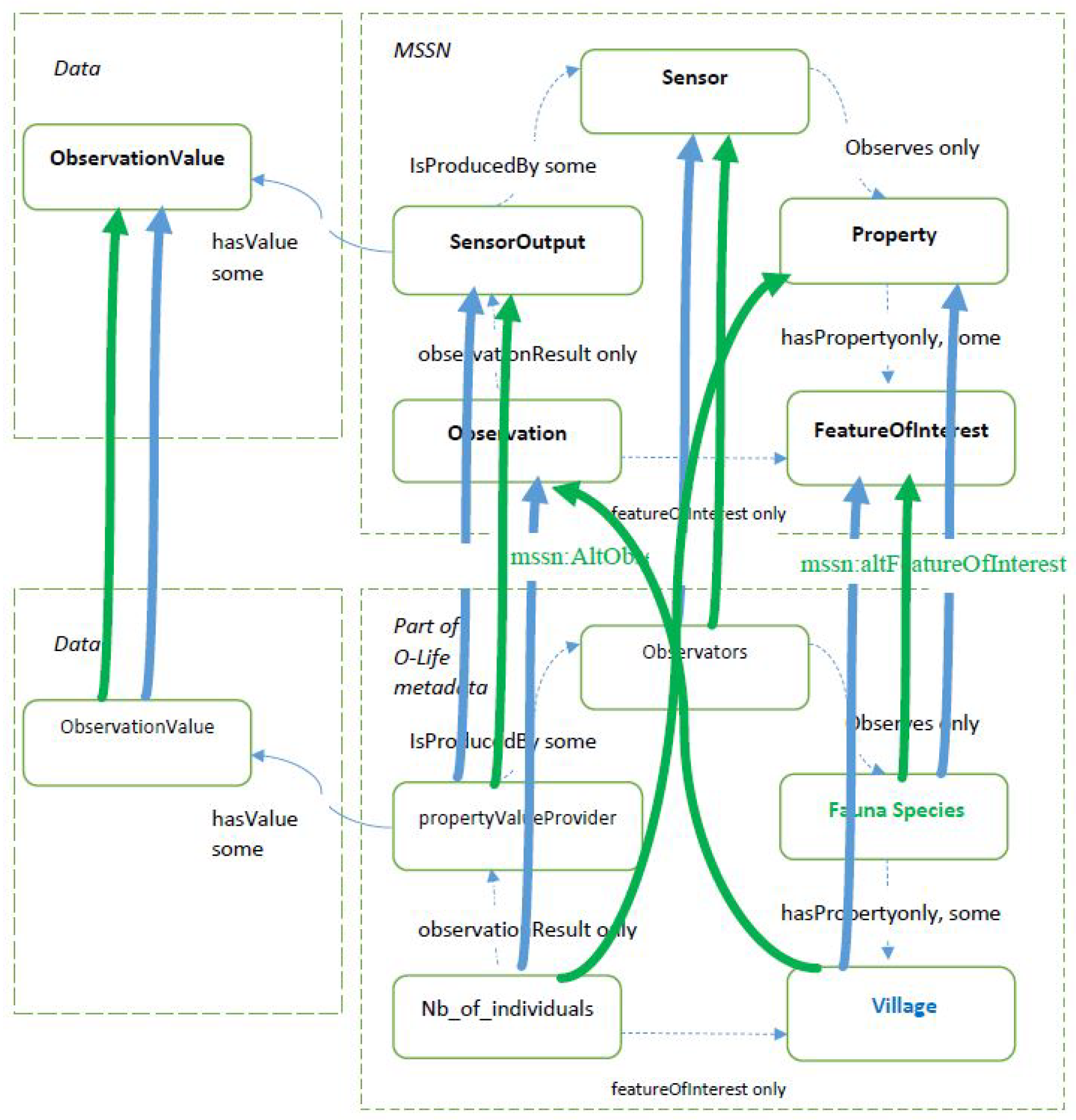



| Description | Proposed Property |
|---|---|
| Alternative Observation | mssn:AltObservationDesign |
| Alternative Feature of Interest | mssn:altFeatureOfInterest |
| Alternative Observed Property | mssn:altObservedProperty |
| Alternative Observed By | mssn:altObservedBy |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hajj-Hassan, H.; Laurent, A.; Martin, A. Exploiting Inter- and Intra-Base Crossing with Multi-Mappings: Application to Environmental Data. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2018, 2, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc2030025
Hajj-Hassan H, Laurent A, Martin A. Exploiting Inter- and Intra-Base Crossing with Multi-Mappings: Application to Environmental Data. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2018; 2(3):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc2030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleHajj-Hassan, Hicham, Anne Laurent, and Arnaud Martin. 2018. "Exploiting Inter- and Intra-Base Crossing with Multi-Mappings: Application to Environmental Data" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 2, no. 3: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc2030025
APA StyleHajj-Hassan, H., Laurent, A., & Martin, A. (2018). Exploiting Inter- and Intra-Base Crossing with Multi-Mappings: Application to Environmental Data. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 2(3), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc2030025






