The Optimization of a Volute Downstream of a Vaned Radial Compressor †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Optimization
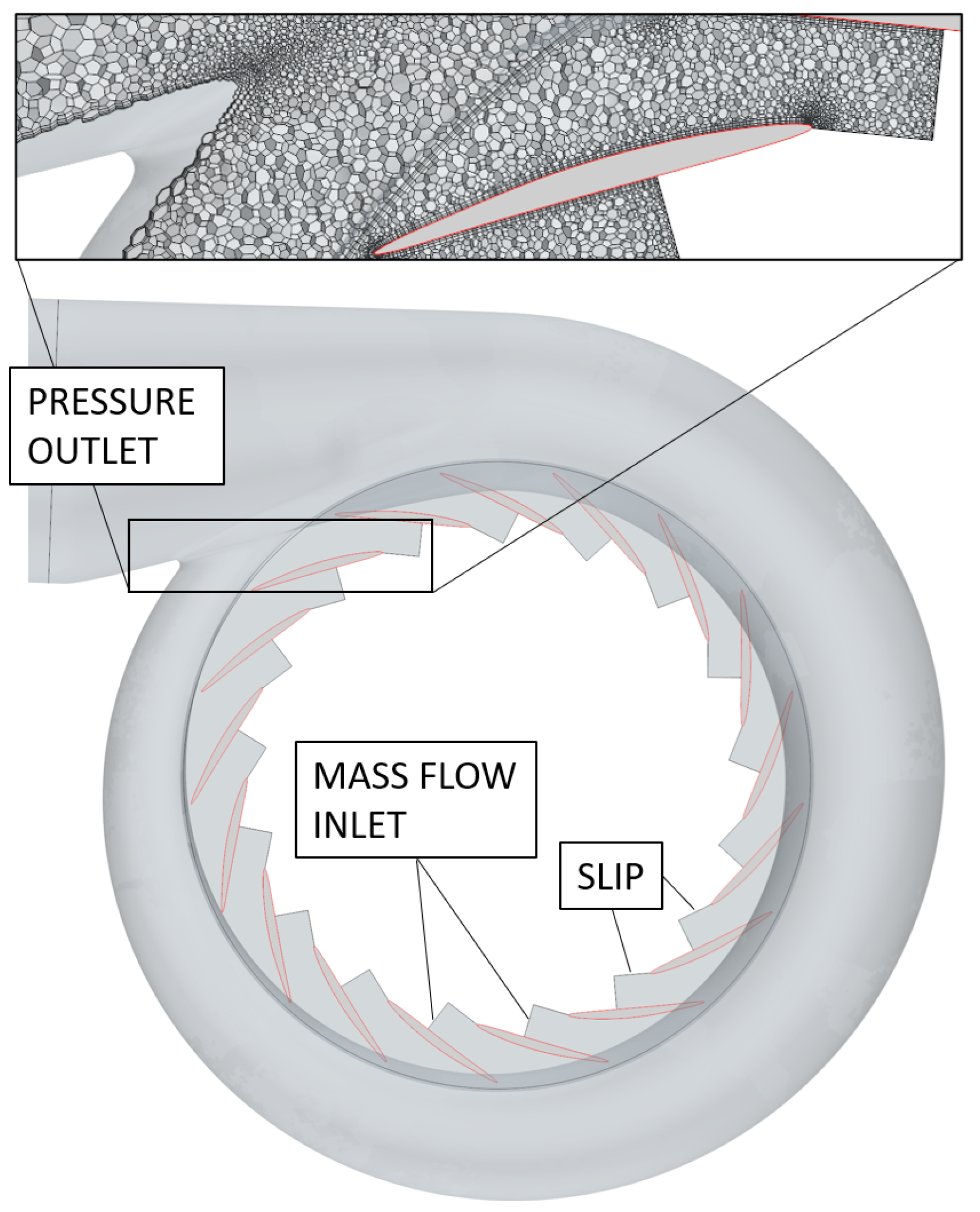
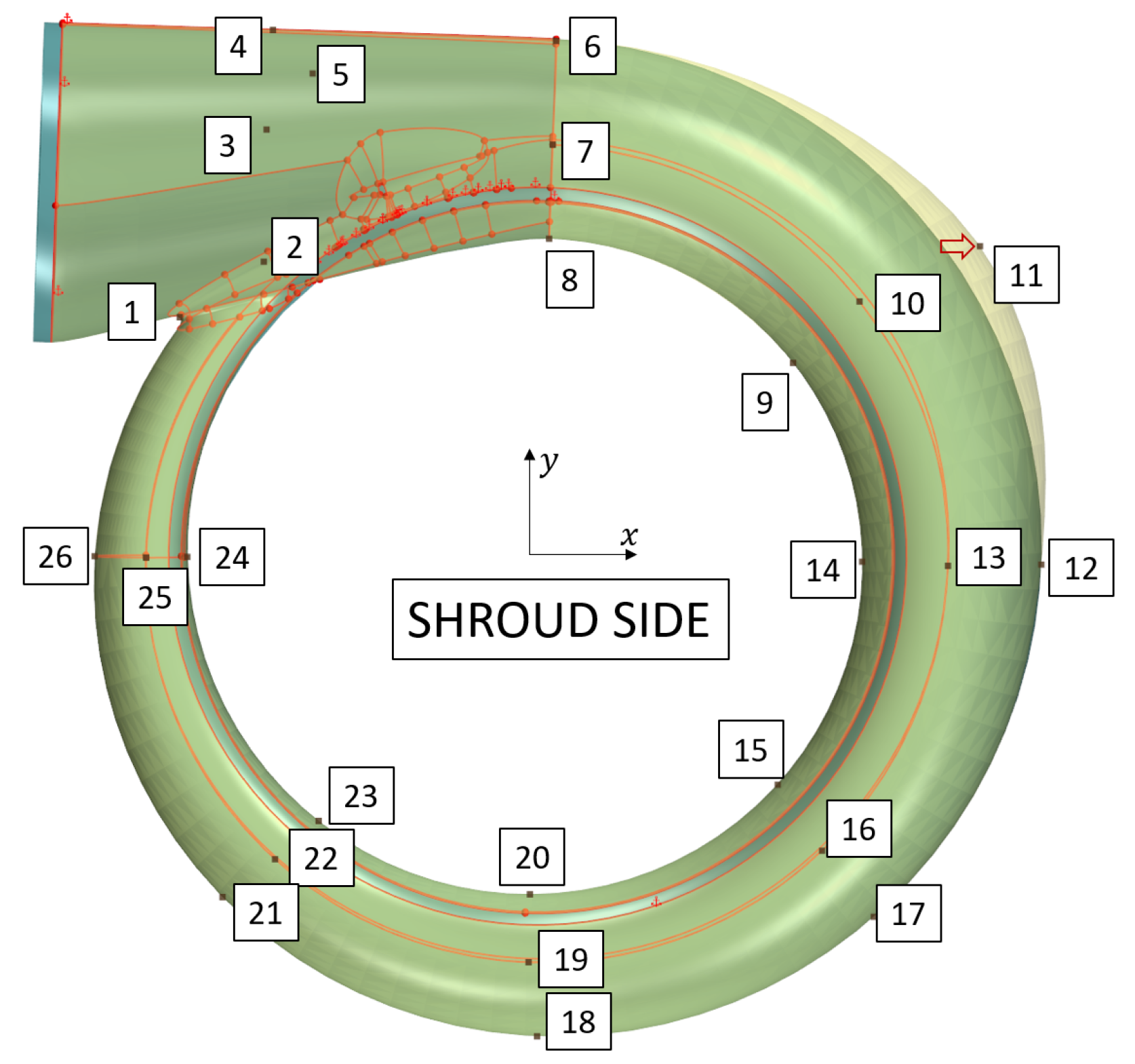
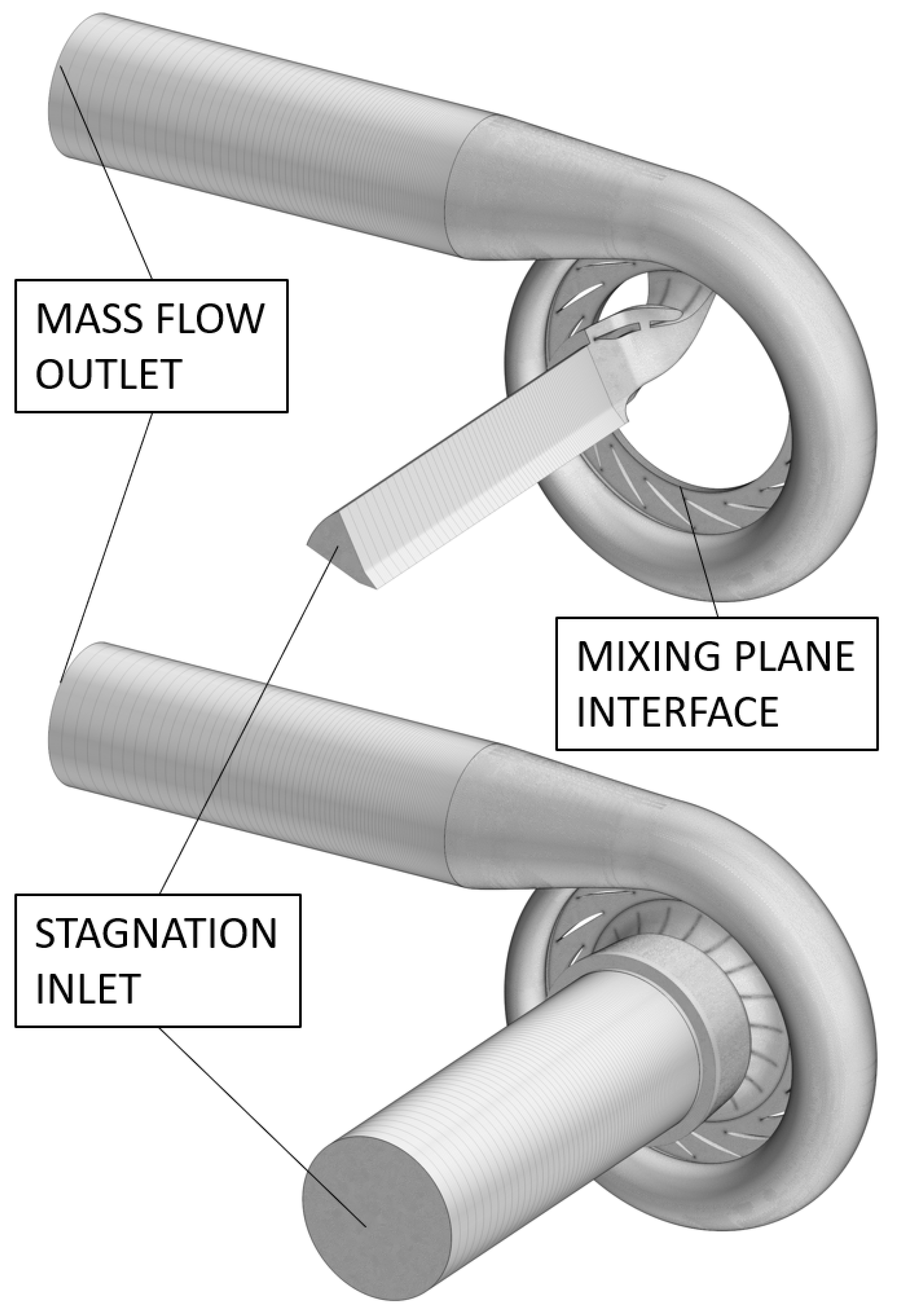
2.1. Geometry and CFD Setup
2.2. Optimization Algorithms
2.2.1. Opt1 gf-pb: Parameter-Based, Gradient-Free Optimization
2.2.2. Opt2 gb-pf: Parameter-Free, Gradient-Based Optimization
Step 1: Primal CFD Simulation
Step 2: Shape Sensitivities
- 1.
- The residuals of the primal problem have to be driven as close to machine precision as possible, i.e.,with representing the flow variables. Application of the chain rule to the state equation (Equation (1)) delivers
- 2.
- Second, the adjoint variables have to be evaluated, which are a counterpart to the state variables and defined as the solution of the linear systemwith being the sensitivity of the residual with regard to the flow field and representing the sensitivity of the cost function with regard to the flow. The total derivative of with regard to the mesh X is
- 3.
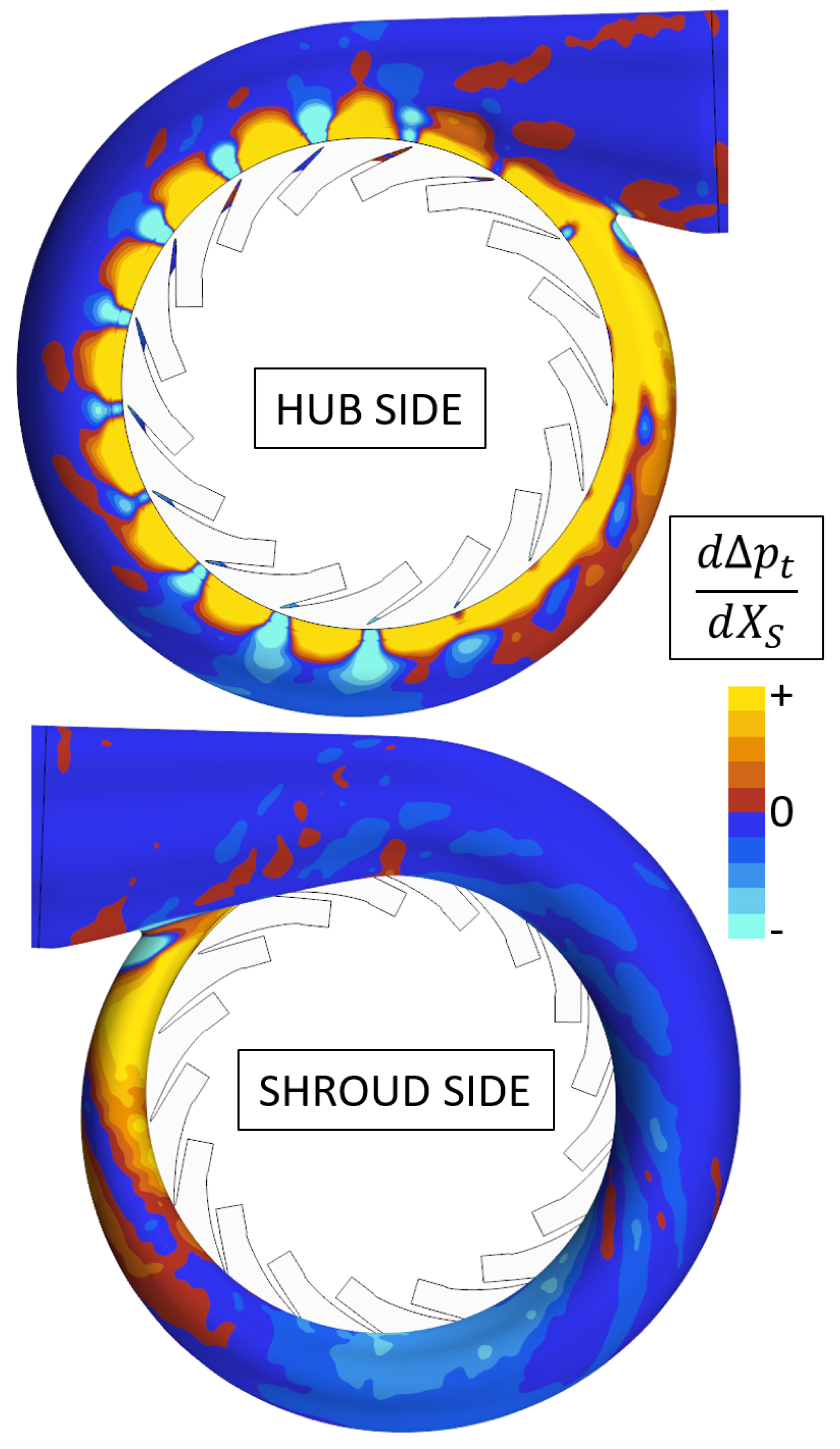
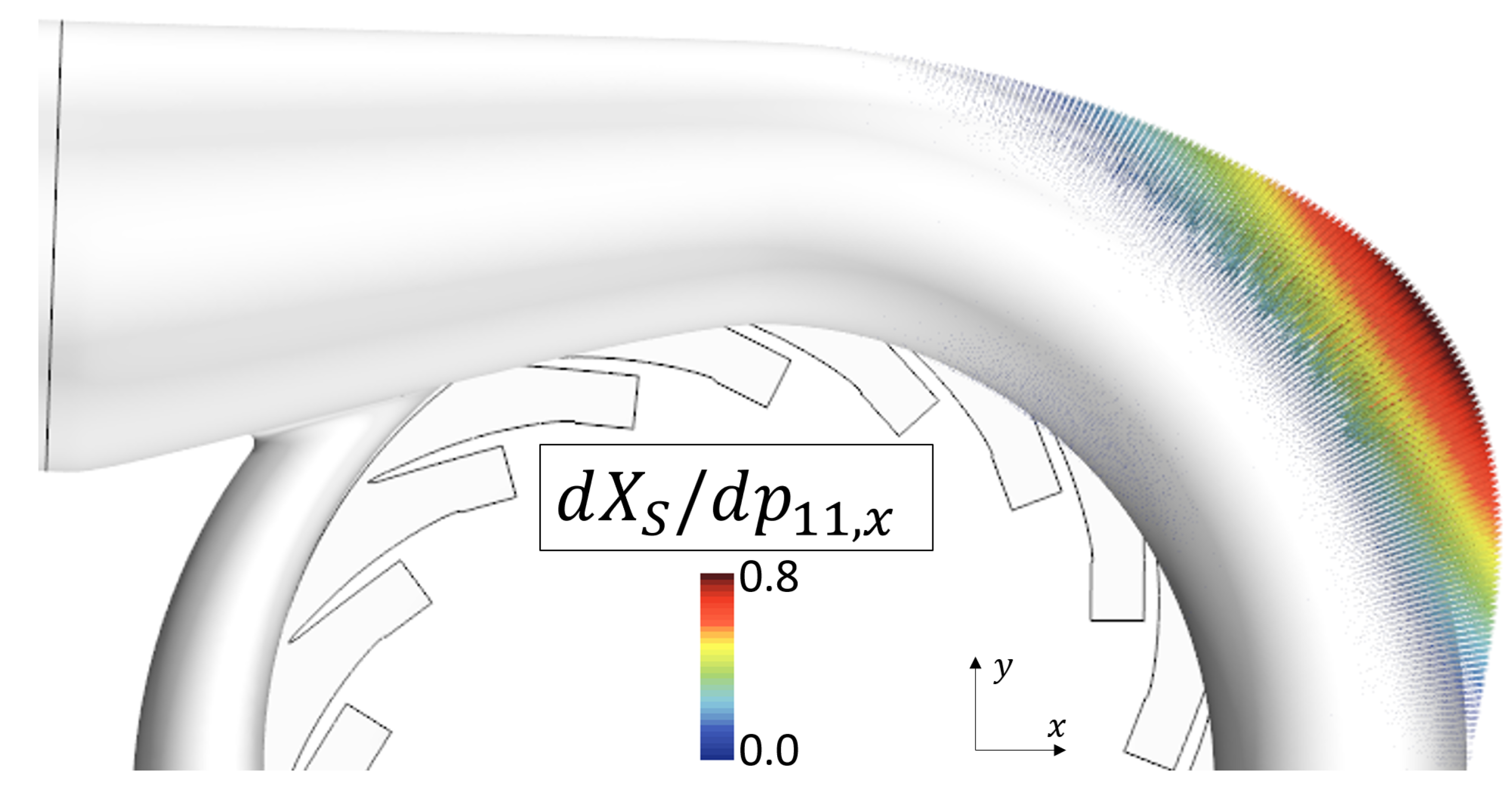
- Third, we wish to use the mesh sensitivity to determine how a change in the surface mesh affects the cost function ; that is, we want to find . Star-CCM+ provides a method for this purpose, which utilizes a spring analogy. The respective computation is cheap. For the studied volute, these surface sensitivities are visualized in Figure 3 for the baseline design. They tell us where we need to push and pull the volute geometry in order to minimize . These sensitivities serve as input for the Vertex Morphing algorithm, as described below.
Step 3: Vertex Morphing
Step 4: Mesh Deformation
2.2.3. Opt3 gb-pb: Parameter-Based, Gradient-Based Optimization
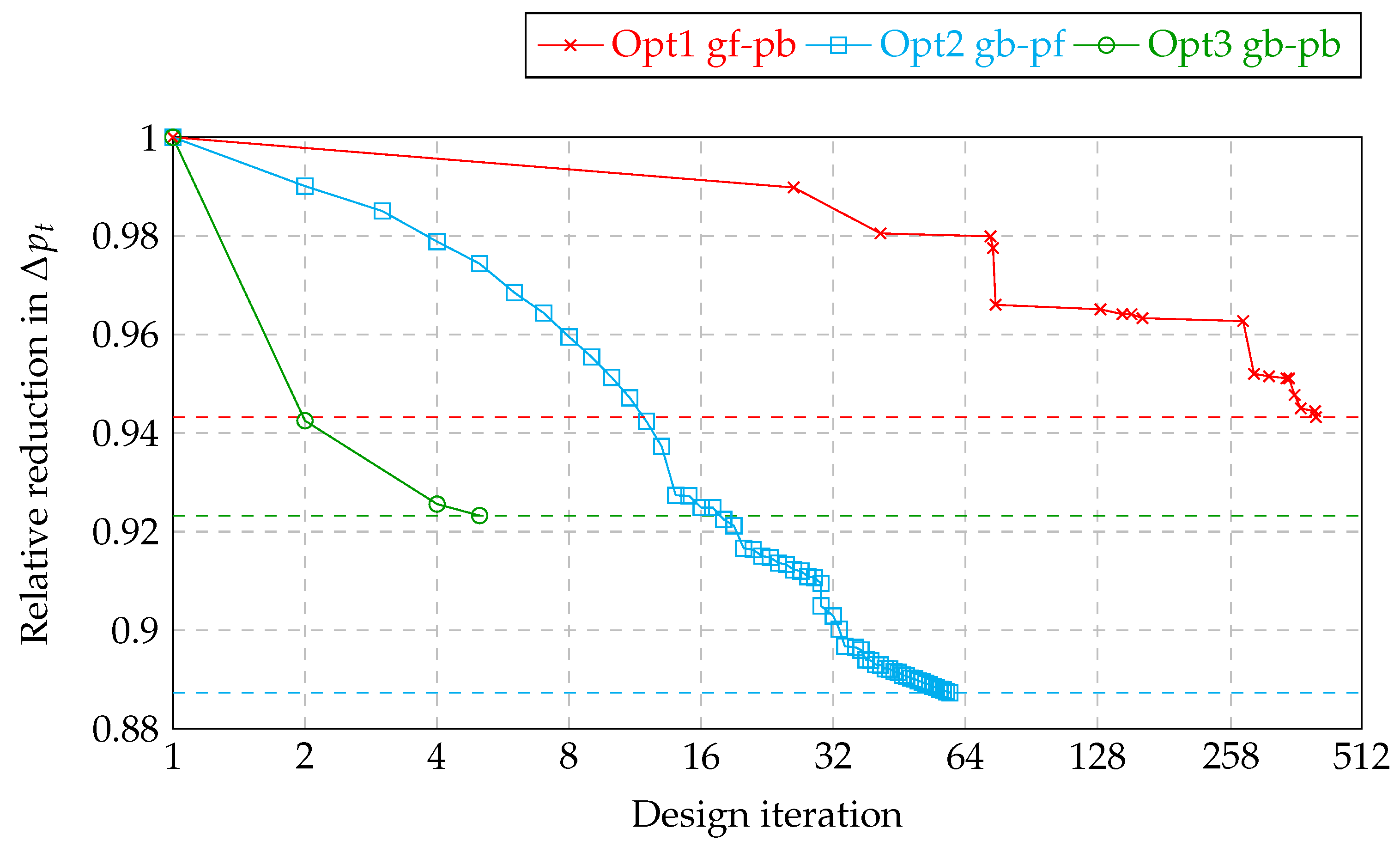
2.3. Optimization Results
3. Effect on Compressor Performance
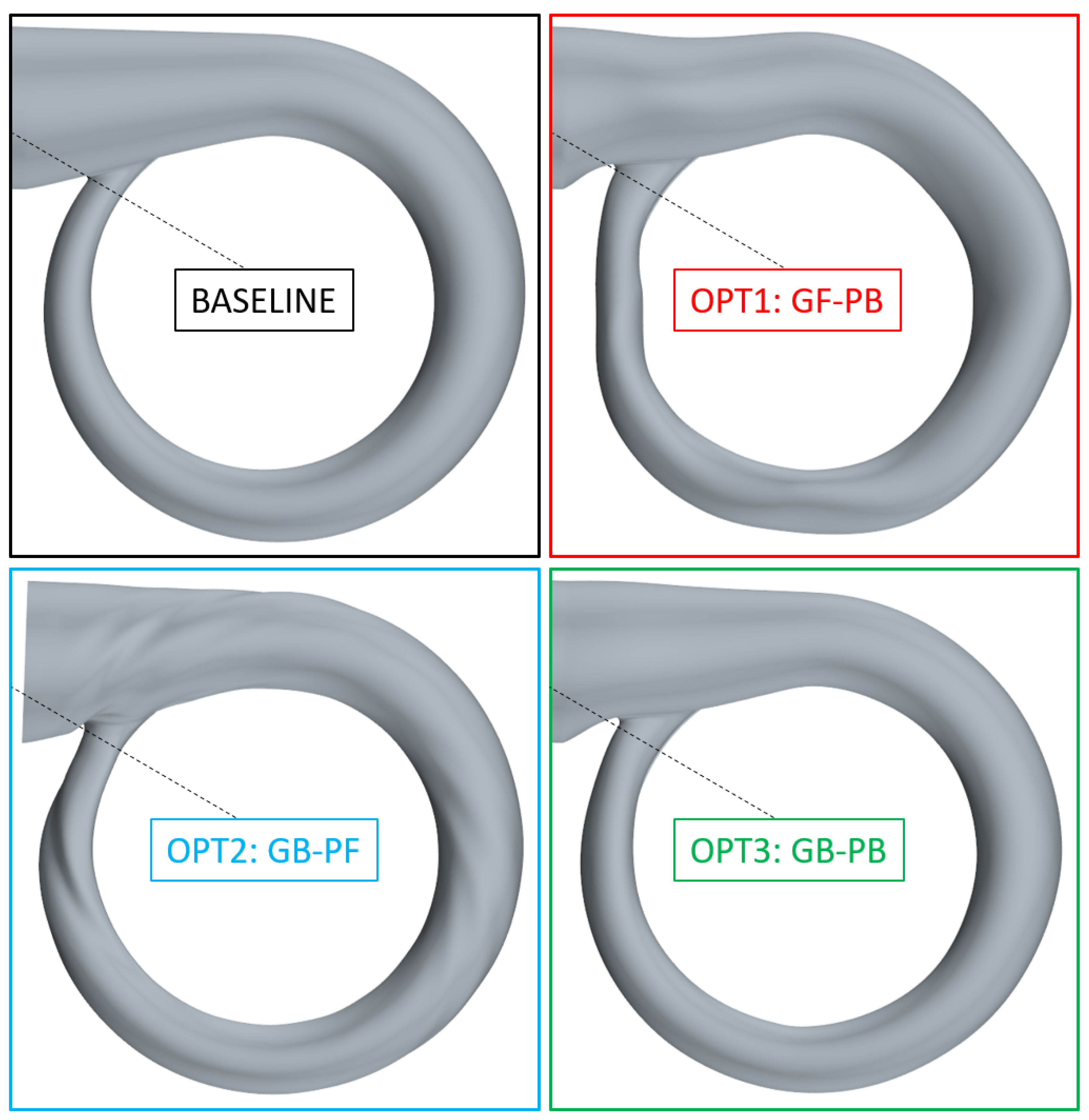
- Opt2 gb-pf introduces helical structures into the volute that follow the wake of the guide vanes.
- Both Opt2 gb-pf and Opt3 gb-pb substantially alter the tongue area, which greatly impacts the circumferential pressure distribution.
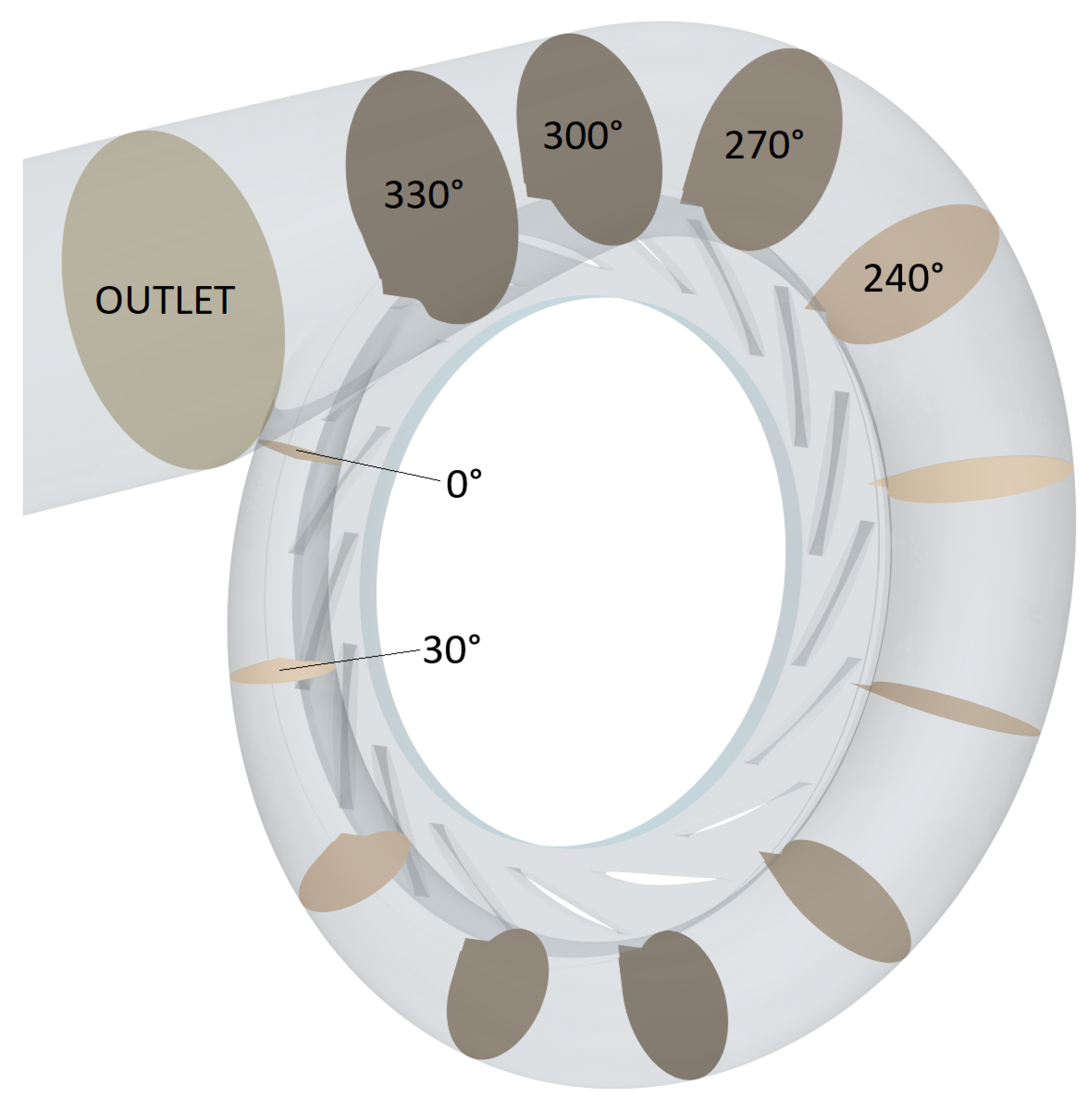
3.1. Geometry and CFD Setup
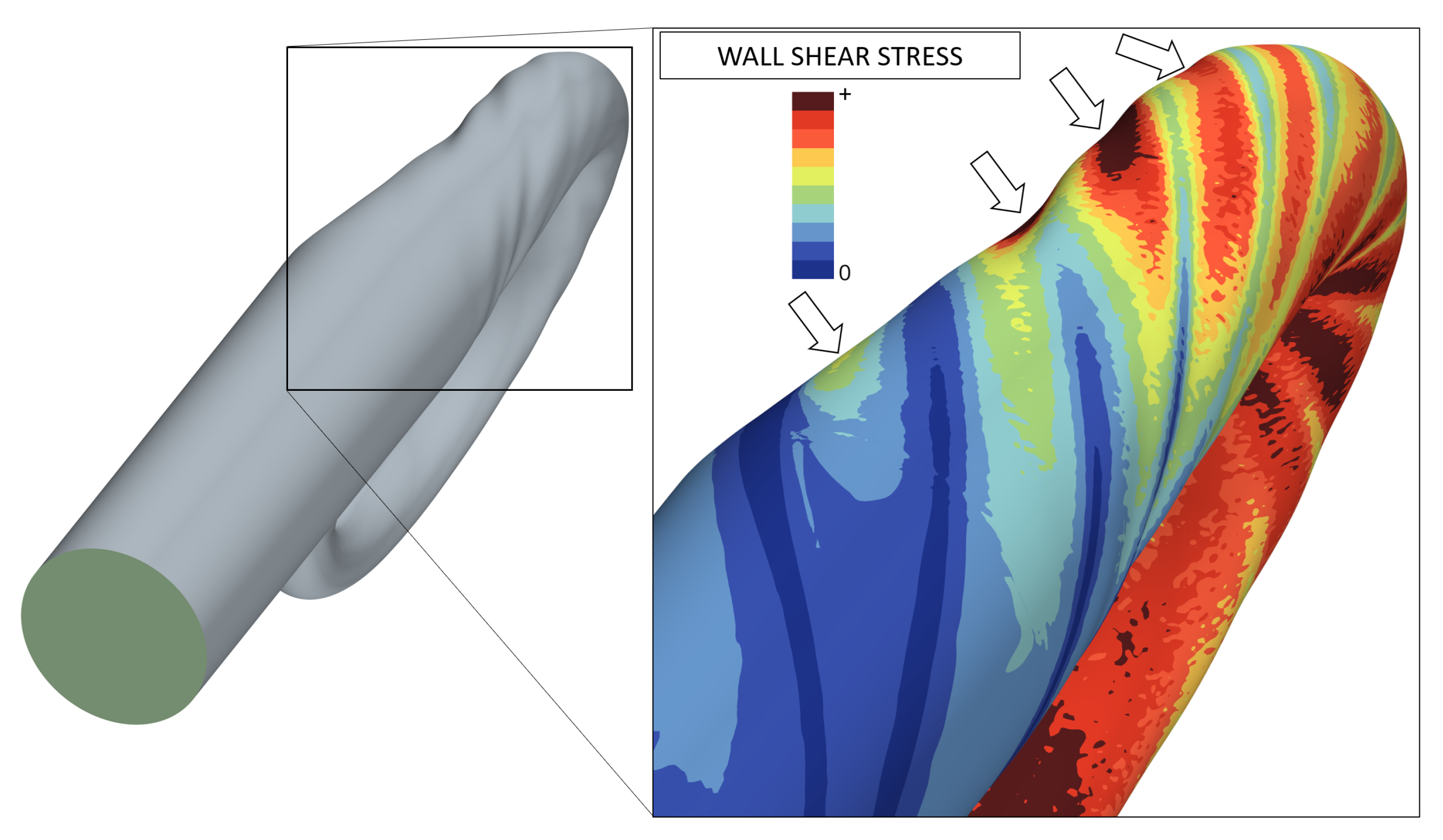
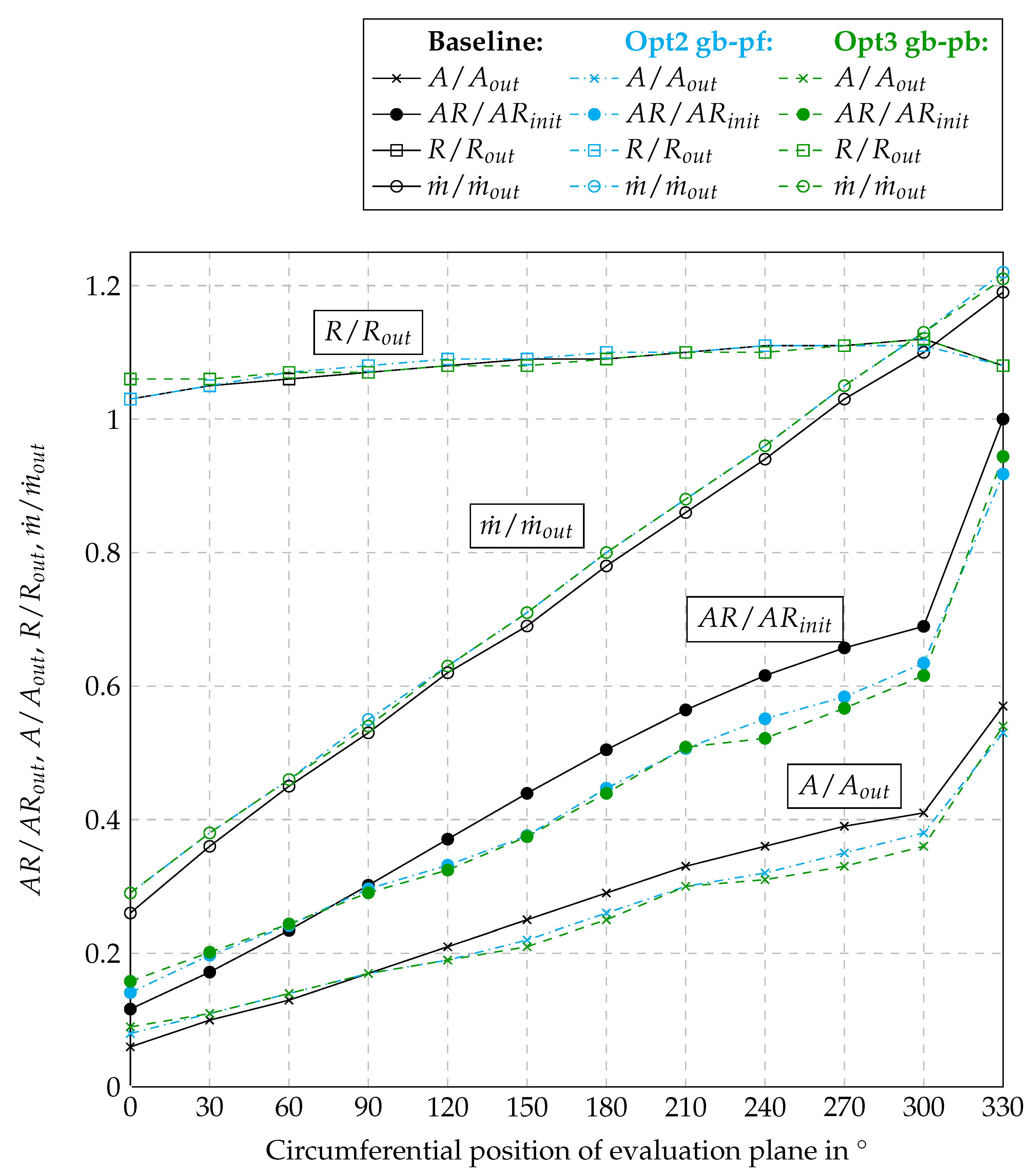
3.2. Helical Dents
3.3. Tongue
- The ratio for Opt2 gb-pf;
- The ratio for Opt3 gb-pb.
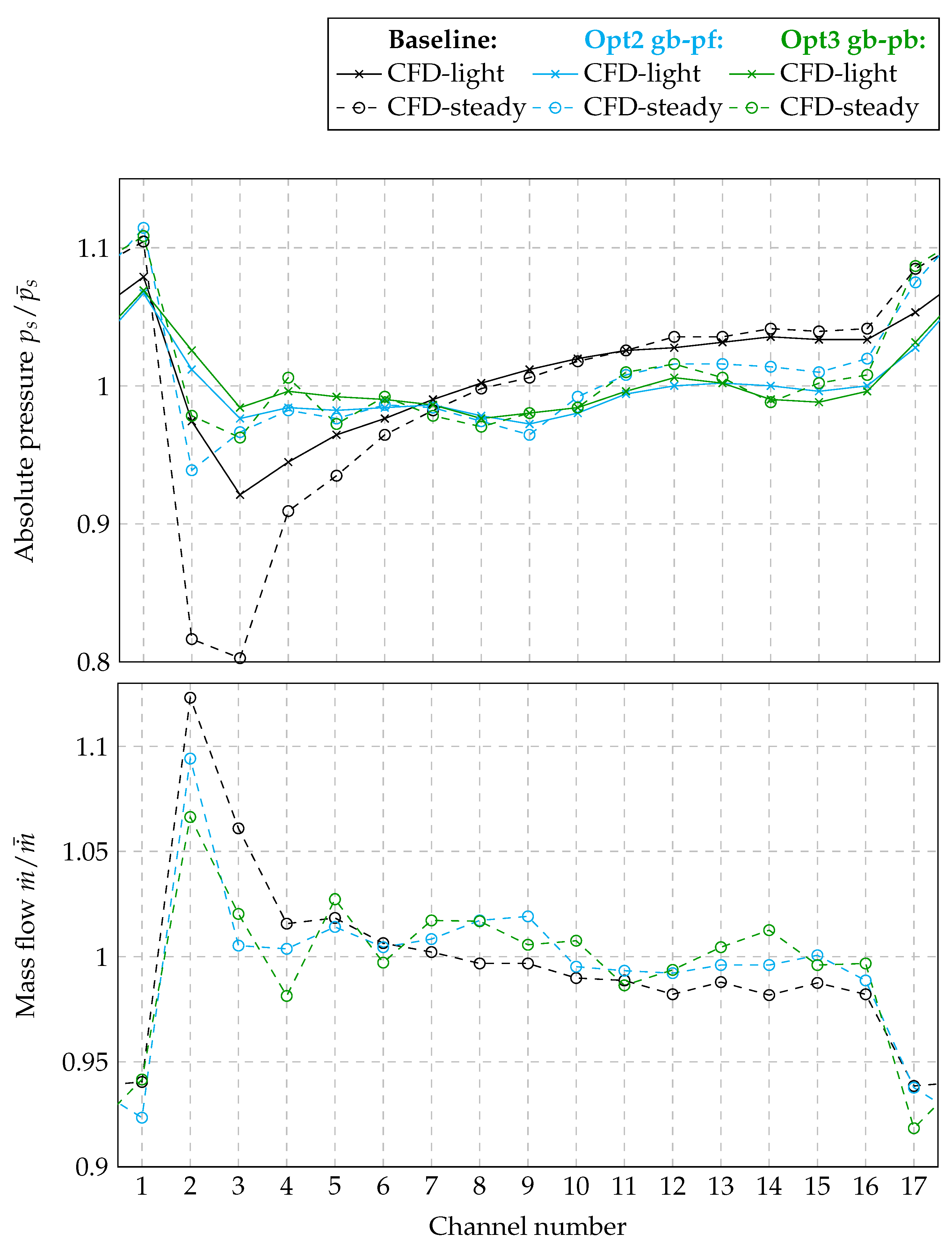
3.4. Volute Performance in Different CFD Setups
- In CFD-steady, the volute Opt3: gb-pb performs best. Based on the optimization results, we expected Opt2: gb-pf to be the best. Our hypothesis is that this is a consequence of the two simulation setups (CFD-steady and CFD-light) being too different in terms of mesh resolution and mass flow distribution, which apparently prohibits the transferability of the results.
- In CFD-unsteady, the volute Opt3: gb-pb performs best in terms of total pressure at the outlet, and the volute Opt2: gb-pf performs best in terms of efficiency; that is, Opt2: gb-pf shows lower temperatures at the outlet . Hence, the impeller works more efficiently in the latter setup.
4. Summary
- The gradient-based work flows are fast and, thus, well-suited to find the best clocking position of guide vanes compared to the tongue.
- The equalization of pressures might have an effect on low-engine-order blade excitation that one may study by means of harmonic balance simulations.
- The design space may be increased even further to incorporate the guide vanes’ shape, position and angle into the setup.
- Finally, a back-to-back measurement is necessary to fully confirm the success of our optimization efforts. Furthermore, it will reveal whether the design changes affect compressor stability and, with that, surge margin.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Acronyms: | |
| A/R | Area-to-radius ratio |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| SHERPA | Simultaneous exploration that is robust, progressive, and adaptive |
| SQP | Sequential quadratic programming |
| VM | Vertex morphing |
| Subscripts: | |
| Inlet | |
| Outlet | |
| Reduced | |
| s | Static |
| t | Total |
| Latin: | |
| A | Area |
| Mass flow | |
| R | Radius, filter width |
| Residual | |
| 298 | |
| T | Temperature |
| u | Circumferential speed |
| X | Mesh |
| Surface mesh | |
| Dimensionless wall distance |
References
- Casey, M.; Robinson, C. Radial Flow Turbocompressors; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ratz, J. Simultane Optimierung von Impeller, Beschaufeltem Diffusor und Volute hinsichtlich des Wirkungsgrads und des Pumpgrenzabstands; Forschungsberichte aus dem Institut für Gasturbinen, Luft-und Raumfahrtantriebe; Shaker Verlag: Düren, Germany, 2024; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, M.; Schwarze, R. Genetic Algorithm Optimization of the Volute Shape of a Centrifugal Compressor. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2016, 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J. Numerische Untersuchung und Optimierung des Laufrades einer Pkw-Abgasturboladerturbine. Ph.D. Dissertation, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arifin, M.; Fudholi, A.; Wahyudie, A.; Vogt, D.M. Surrogate-based optimization of multiple-splitters radial compressor for solar hybrid microturbine. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2022, 16, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hottois, R.; Châtel, A.; Verstraete, T. Adjoint-Based Design Optimization of a Volute for a Radial Compressor. Int. J. Turbomach. Propuls. Power 2023, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmaier, N.; Baumgärtner, D.; Schiffer, H.P.; Kech, J. Gradient-based optimization of a radial turbine volute and a downstream bend using vertex morphing. In Proceedings of the Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, Virtual, 21–25 September 2020. Number GT2020-14145. [Google Scholar]
- Del Rio, A.; Casartelli, E.; Fleischli, B.; Mangani, L. New Concept for Design in Turbomachinery Applications Using Full RANS Gradient Methodology. J. Turbomach. 2022, 145, 041009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L. Numerical Analysis and Optimization of the Volute in a Centrifugal Compressor. In Proceedings of the Challenges of Power Engineering and Environment; Cen, K., Chi, Y., Wang, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1352–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Hazby, H.; O’Donoghue, R.; Robinson, C. Design and Modelling of Circular Volutes for Centrifugal Compressors. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Turbochargers and Turbocharging, London, UK, 11–12 May 2021; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ceyrowsky, T.; Hildebrandt, A.; Heinrich, M.; Schwarze, R. Reassessment of the Conventional: Numerical Validation of a 1D Model for the Prediction of Volute Losses. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2024: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, London, UK, 24–28 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lachenmaier, N.; Fröehlig, F.; Männle, T. Optimization of a Volute downstream of a Vaned Radial Compressor. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid dynamics & Thermodynamics, Hannover, Germany, 24–28 March 2025; paper n. ETC2025-331. Available online: https://www.euroturbo.eu/publications/conference-proceedings-repository/ (accessed on 30 August 2025).
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcenter Star-CCM+. Available online: https://www.plm.automation.siemens.com/global/de/products/simcenter/STAR-CCM.html (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Simcenter HEEDS. Available online: https://plm.sw.siemens.com/de-DE/simcenter/integration-solutions/heeds/ (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Peter, J.E.; Dwight, R.P. Numerical sensitivity analysis for aerodynamic optimization: A survey of approaches. Comput. Fluids 2010, 39, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bletzinger, K.U. A consistent frame for sensitivity filtering and the vertex assigned morphing of optimal shape. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2014, 49, 873–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.; Oliphant, T.; Peterson, P. SciPy: Open Source Scientific Tools for Python, 2001–2025. Available online: http://www.scipy.org/ (accessed on 30 August 2025).
- Lachenmaier, N. Multidisciplinary Gradient-Based Optimization of Radial Turbines; Forschungsberichte aus dem Institut für Gasturbinen, Luft- und Raumfahrtantriebe; Shaker Verlag: Düren, Germany, 2023; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbach, M.; Verstraete, T.; Müller, L.; Gauger, N. CAD-based adjoint multidisciplinary optimization of a radial turbine under structural constraints. In Proceedings of the GPPS, Montreal, QB, Canada, 7–9 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, N.; Kanzake, T.; Verstraete, T. Parametric Optimization of Centrifugal Compressor using adjoint Method. In Proceedings of the Aufladetechnische Konferenz, Dresden, Germany, 26–27 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lucian, H.; Fleischli, B.; Casartelli, E.; Mangani, L.; Lehr, A.; Weickgenannt, A. Adjoint Optimization of Real Gas Centrifugal Compressor. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid dynamics & Thermodynamics, Budapest, Hungary, 24–28 April 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatel, A.; Verstraete, T. Multidisciplinary optimization of the SRV2-O radial compressor using an adjoint-based approach. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2023, 66, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittkowski, K. NLPQLP: A Fortran Implementation of a Sequential Quadratic Programming Algorithm with Distributed and Non-Monotone Line Search—User’s Guide, Version 3.0. 2006. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/238690491_NLPQLP_A_Fortran_Implementation_of_a_Sequential_Quadratic_Programming_Algorithm_with_Distributed_and_Non-Monotone_Line_Search_-_User%27s_Guide_Version_30 (accessed on 30 August 2025).

| Opt1 | Opt2 | Opt3 | |
| Abbreviation | gf-pb | gb-pf | gb-pb |
| Algorithm | SHERPA | Steepest Descent | SQP |
| DOFs | 78 | ca. 284k | 78 |
| Adjoint gradients | No | Yes | Yes |
| reduction | 5.7% | 11.3% | 7.7% |
| Best design | 403 | 59 | 5 |
| CFD-Light | CFD-Steady | CFD-Unsteady | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Opt1: gf-pb | - | - | |
| Opt2: gb-pf | |||
| Opt3: gb-pb | |||
| Opt2: gb-pf | - | ||
| Opt3: gb-pb | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the EUROTURBO. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY-NC-ND) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lachenmaier, N.; Fröhlig, F.; Männle, T. The Optimization of a Volute Downstream of a Vaned Radial Compressor. Int. J. Turbomach. Propuls. Power 2025, 10, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp10040047
Lachenmaier N, Fröhlig F, Männle T. The Optimization of a Volute Downstream of a Vaned Radial Compressor. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power. 2025; 10(4):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp10040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleLachenmaier, Nicolas, Friedrich Fröhlig, and Tobias Männle. 2025. "The Optimization of a Volute Downstream of a Vaned Radial Compressor" International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power 10, no. 4: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp10040047
APA StyleLachenmaier, N., Fröhlig, F., & Männle, T. (2025). The Optimization of a Volute Downstream of a Vaned Radial Compressor. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power, 10(4), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp10040047




