UHBR Open-Test-Case Fan ECL5/CATANA †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Low-speed fans predominantly operate on the flat part of the compression characteristic, making them more susceptible to stall-driven instability [9].
- The flutter frequencies (in the stationary frame) are lower compared to high-speed designs. Acoustic liners in the intake, which are designed to attenuate higher-frequency community noise, do not affect the modes relevant for aeroelastic instability.
- The intake length is shorter for low-speed fans, leading to stronger inflow asymmetry and altered acoustic interactions [10]. This gives rise to stronger broadband excitation and shifted resonance frequencies.
- The relative Mach number and shock strength are lower, and the tip clearance relative to the blade chord and solidity (solidity = blade chord length/pitch) are smaller than for conventional direct-drive fans and more sensitive to geometric variability [11].
- A strongly non-linear fluid–structure interaction has been observed at low frequencies for fans with low solidity related to the pressure untwist of the blades. Under transonic conditions, slight deviations of the local stagger angle at the blade tip can cause a fundamentally different shock structure between adjacent blades that affects the stability of distinct rotor sections [12]. This circumstance affects the applicability of promising methods such as intentional blade mistuning [13] for suppressing the development of circumferentially propagating modes.
- 1.
- General aerodynamic design parameters (Mach number, blade loading, solidity, aspect ratio, hub-to-tip ratio, mass flow density, etc.)
- 2.
- Aerodynamic flow structure, due to its influence on instability mechanisms (shock patterns, radial flow migration, secondary flow, separations, etc.)
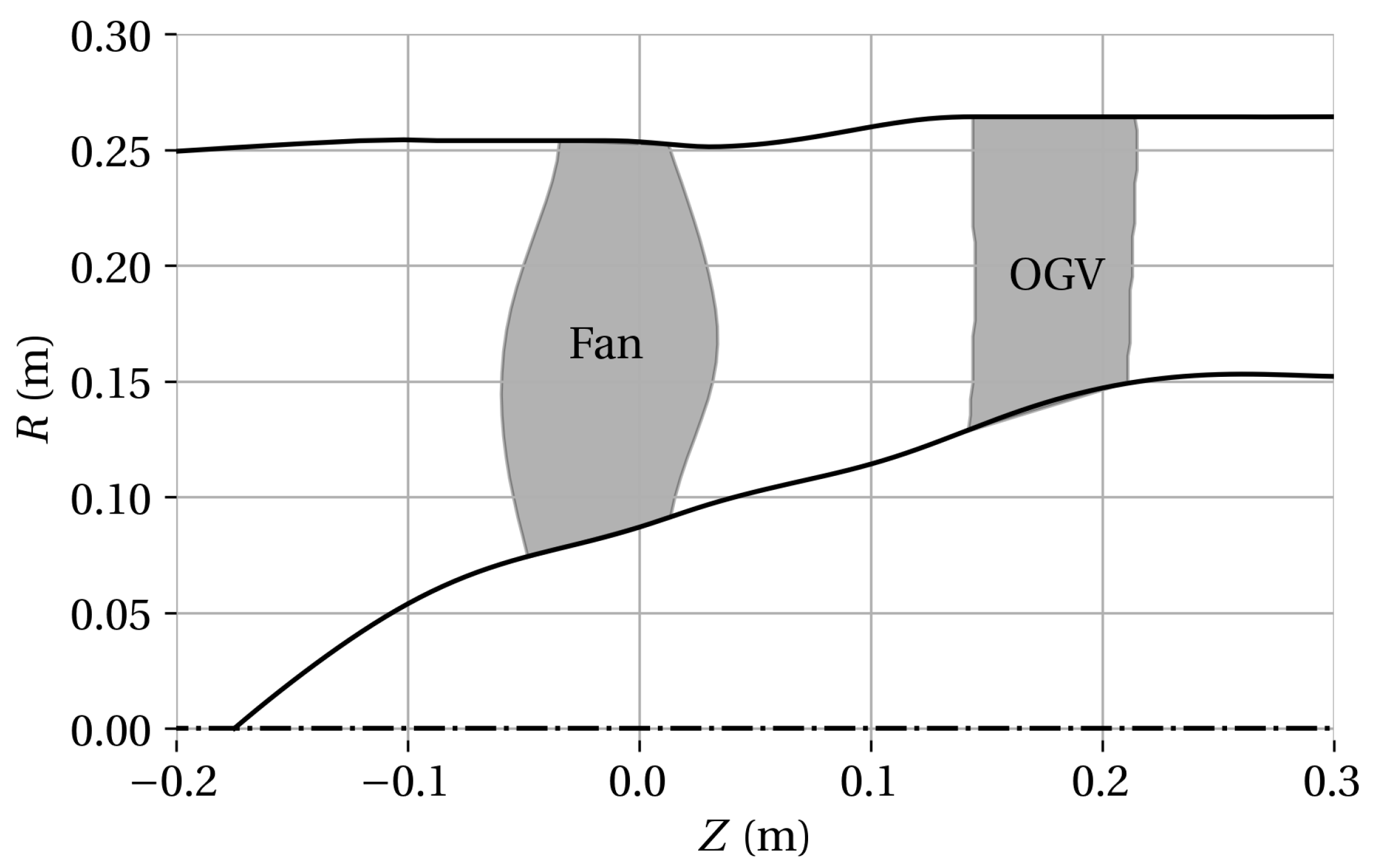
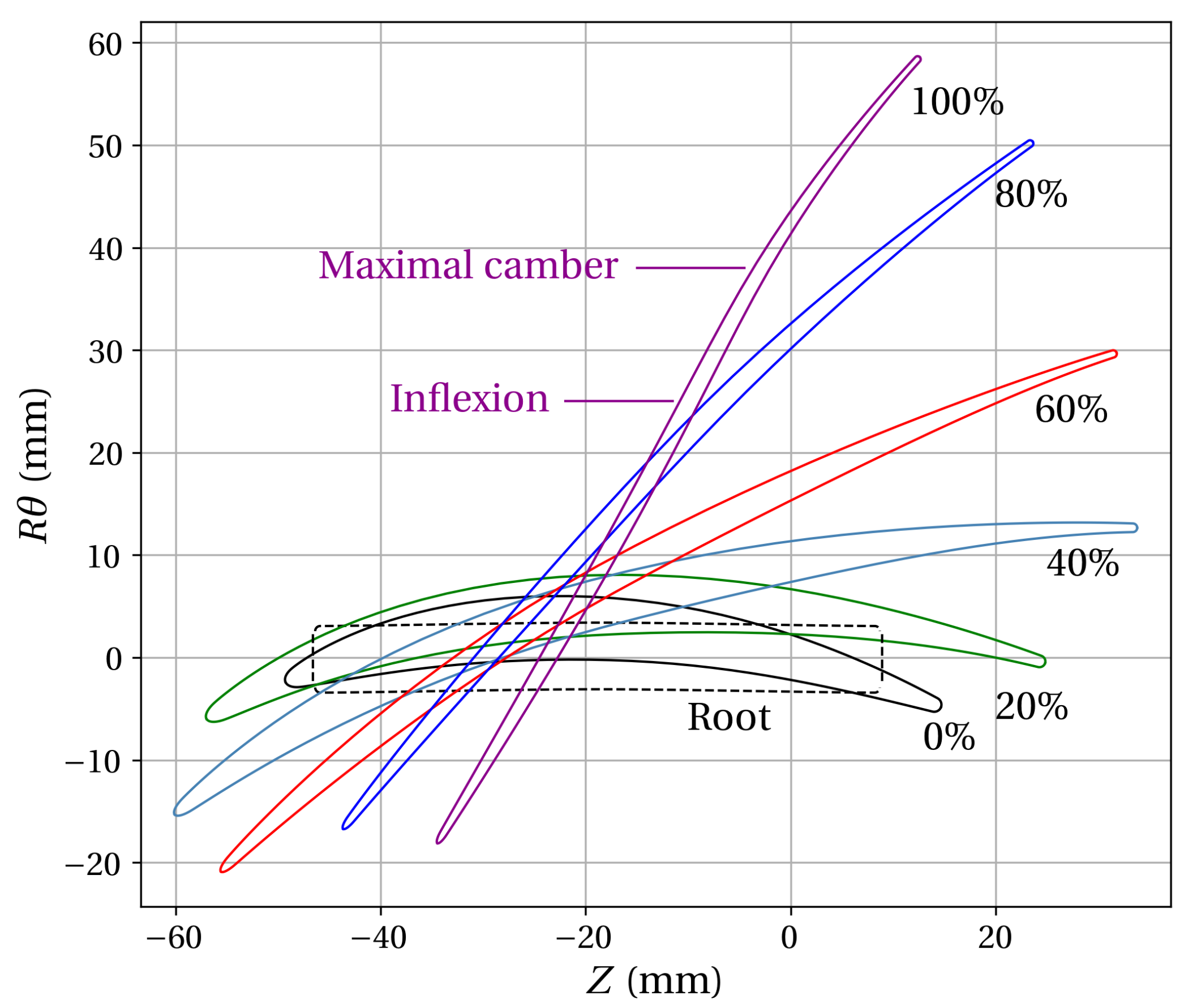
2. ECL5 Description
2.1. Design Approach
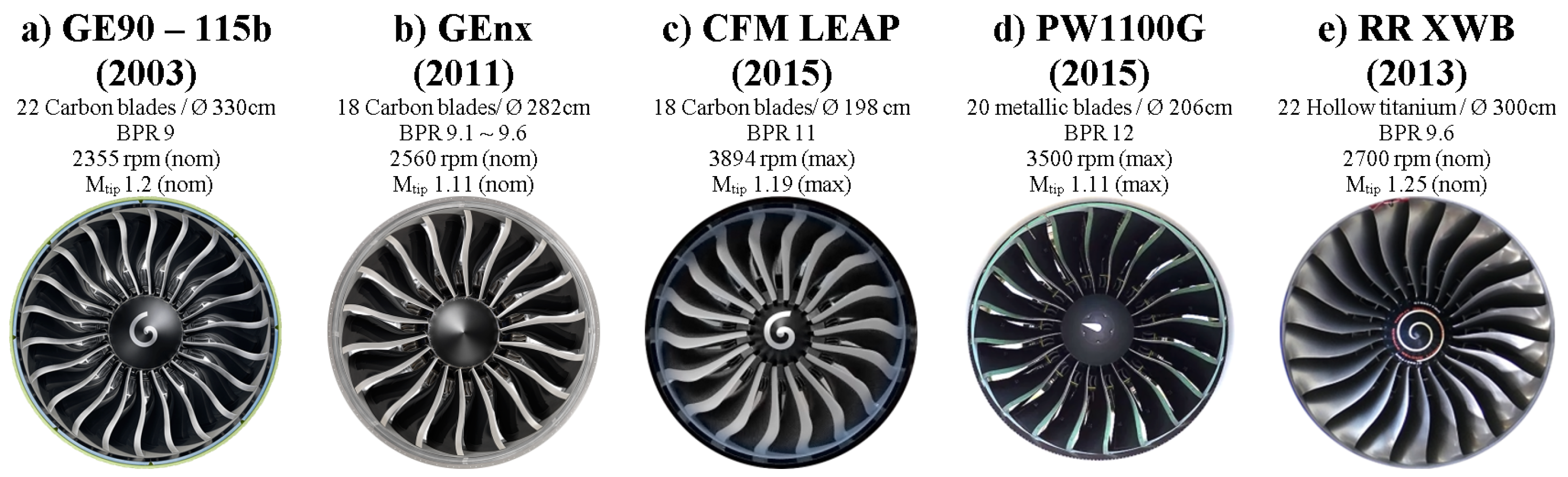
- A blade number of 16 (lowest blade count in technology demonstrators as shown above).
- A fan diameter of 508 mm to enable integration into the test facility PHARE-2, with blade root compatible with the existing disk from Project ENOVAL [18].
- Aerodynamic design point (fan only) at peak efficiency with a pressure ratio of 1.36, a mass flow density maximum of 200 kg/s/m and a rotation speed of 11,000 rpm.
- Near-sonic relative tip Mach number at the design point.
- Isentropic efficiency (fan only) exceeding at the design point.
- At peak pressure at the design speed, no flow separation at the trailing edge.
- Peak efficiency at and speed not lower than (transonic speedline).
- Nominal tip clearance of ∼1 mm ( tip chord) to ensure stall inception and surge experiments without casing contact. Future experiments are planned with further reduced tip clearance.
- Fan to be fabricated without integration of a metallic leading edge.
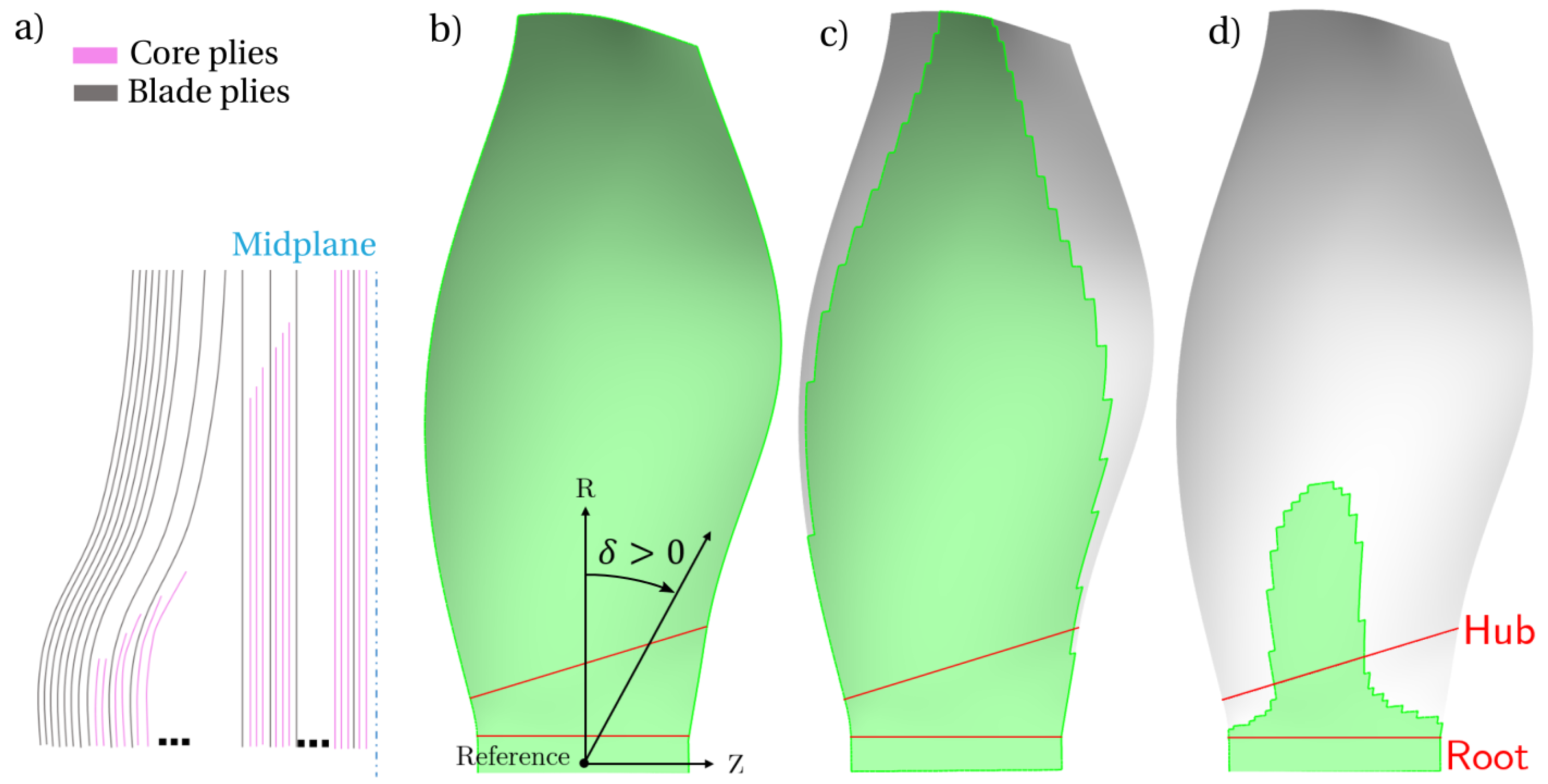
2.2. Fan Composite Structure
3. Modelling Strategies
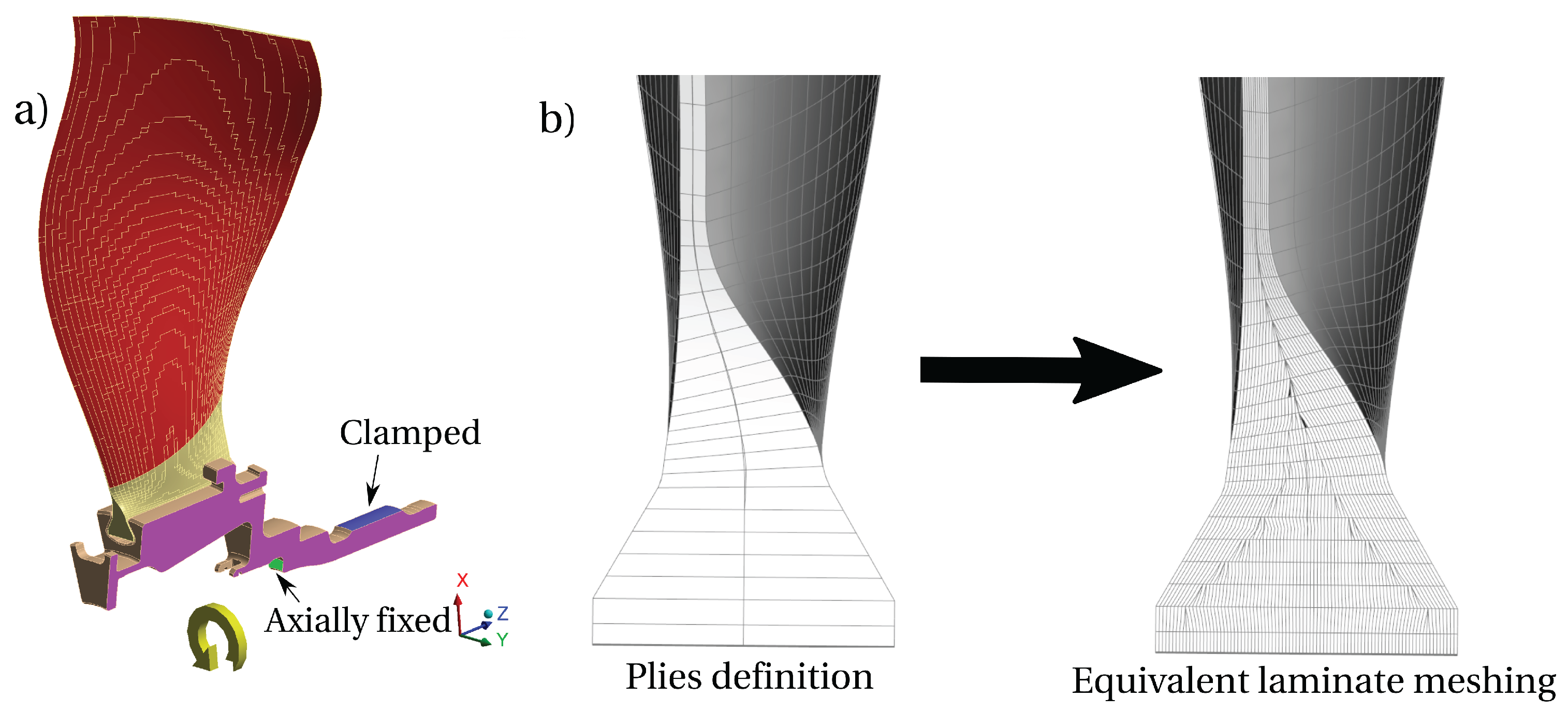
3.1. Aerodynamics
3.2. Mechanics
3.3. Aeroelasticity
3.3.1. Energy Method
3.3.2. Time-Linearized Simulations
4. Results
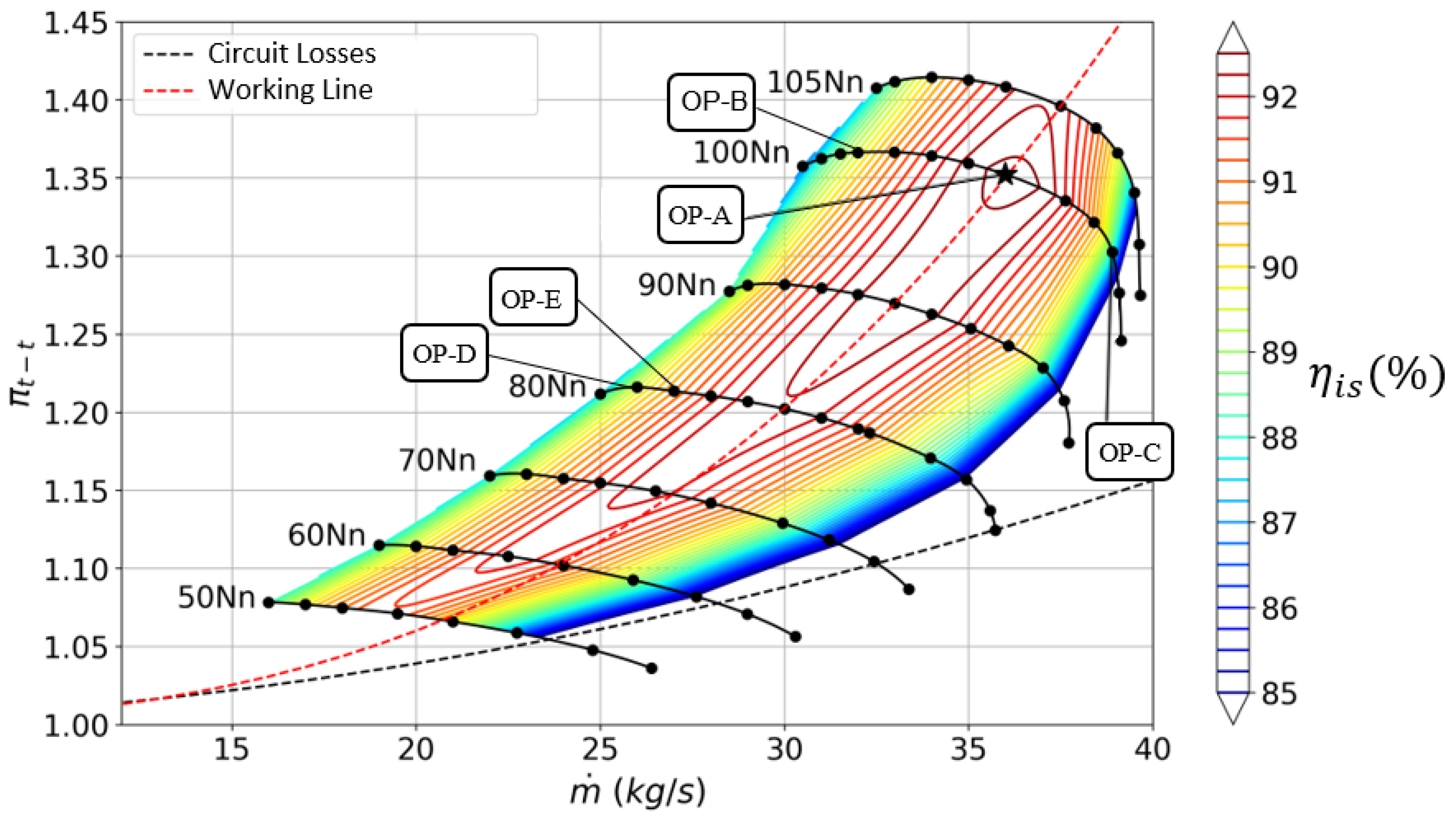
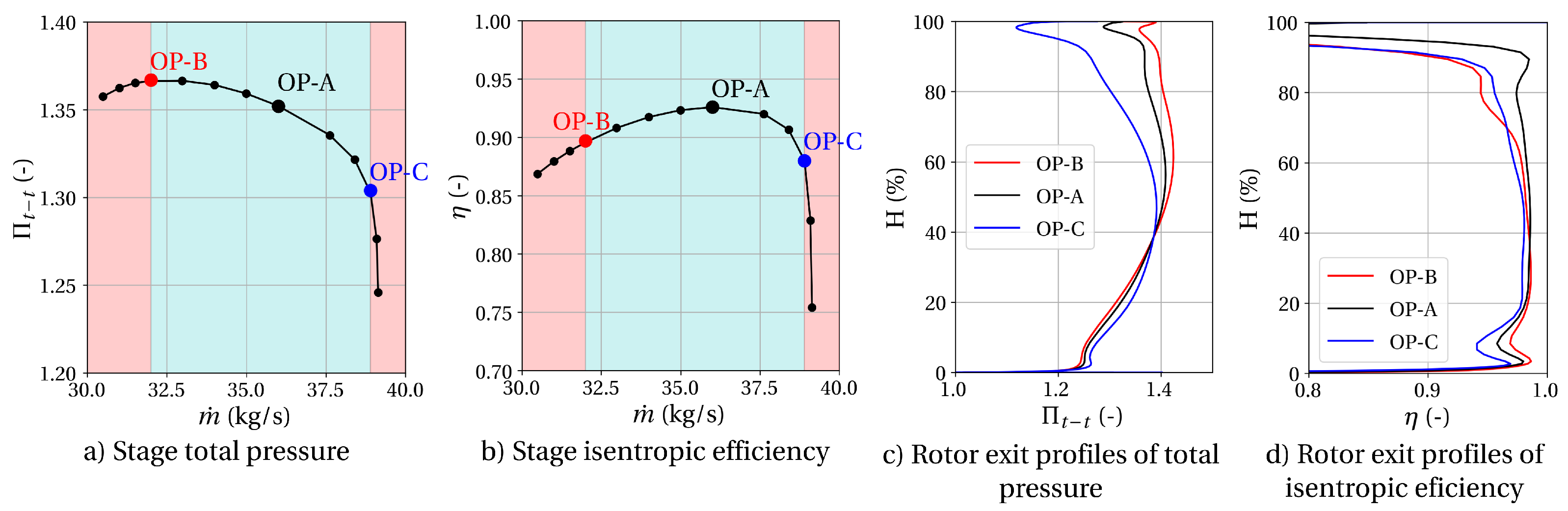
4.1. Aerodynamic Characteristics
4.2. Mechanics
4.2.1. Static Mechanics
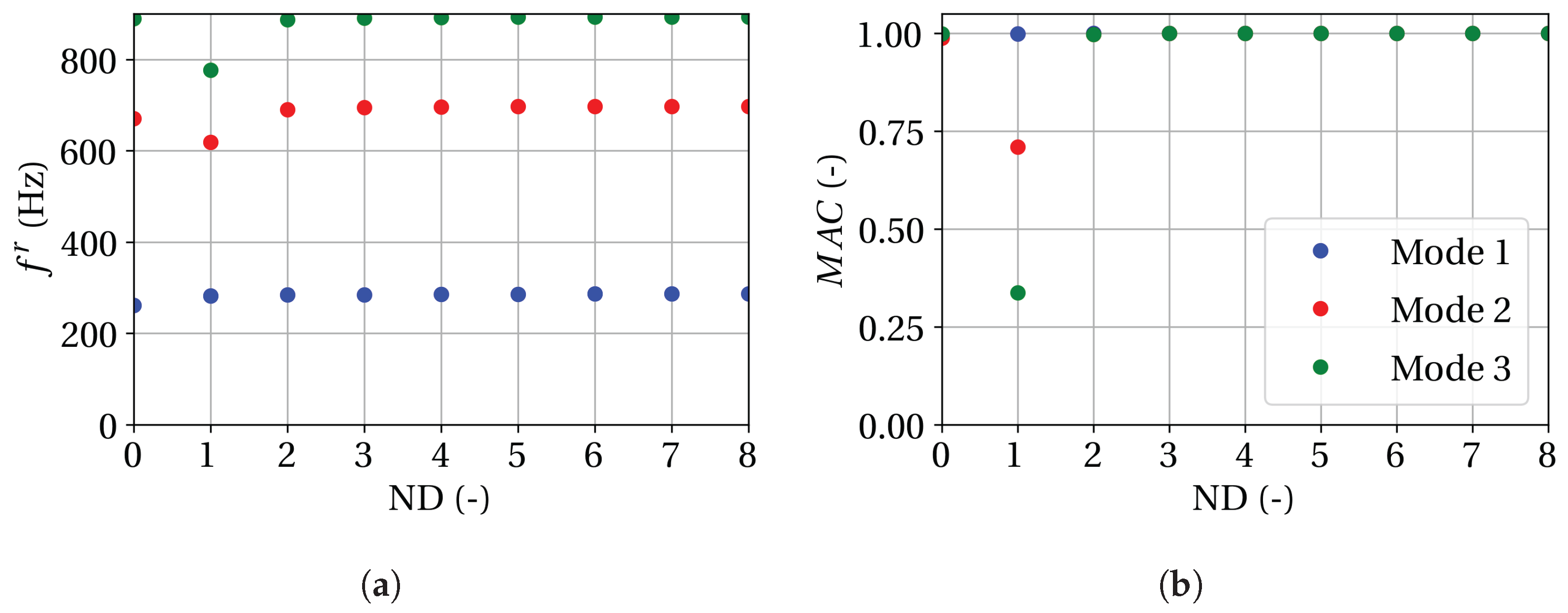
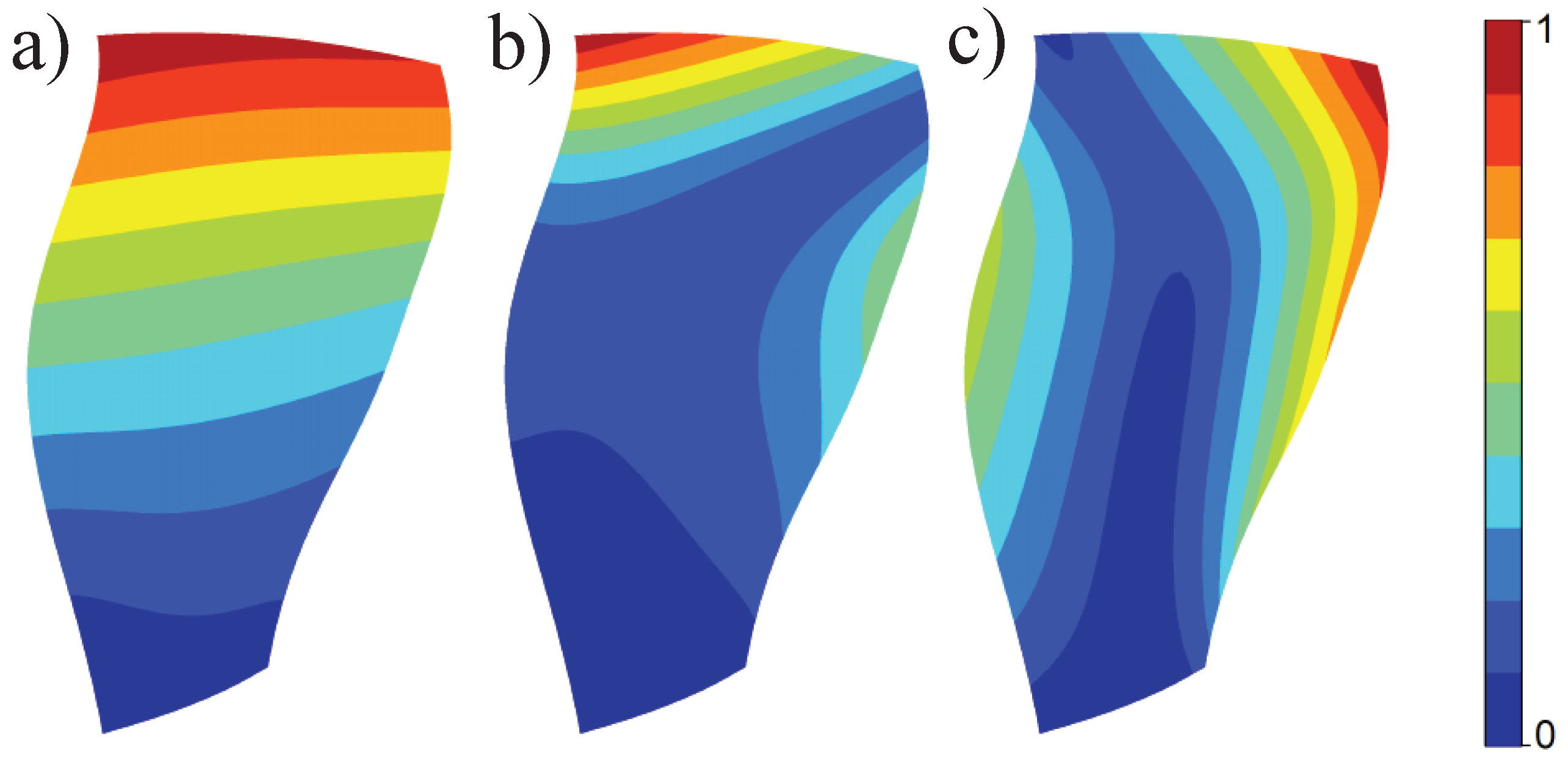
4.2.2. Mode Shapes
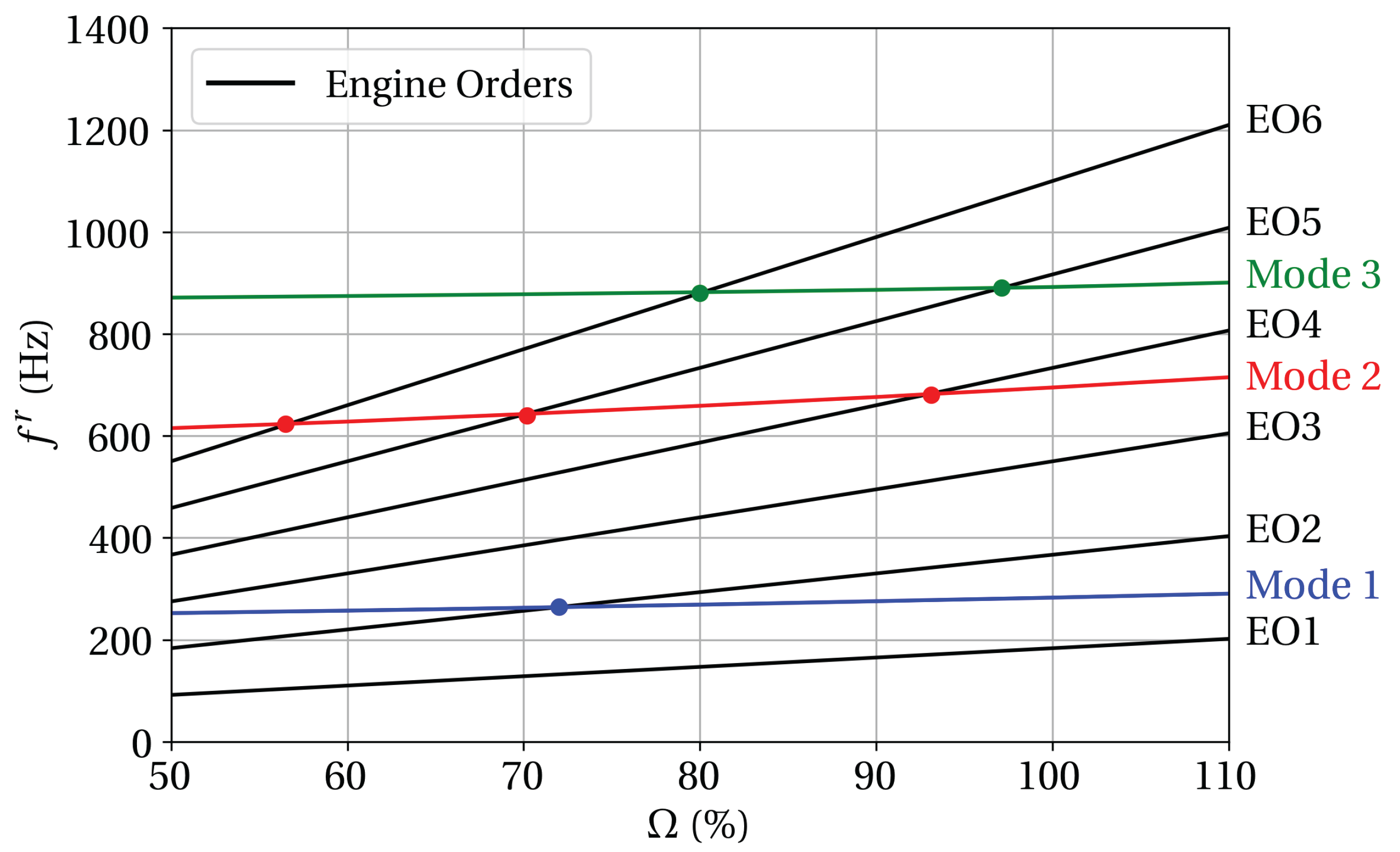
4.2.3. Campbell Diagram
4.3. Overall Stability Analysis
4.3.1. Strategy
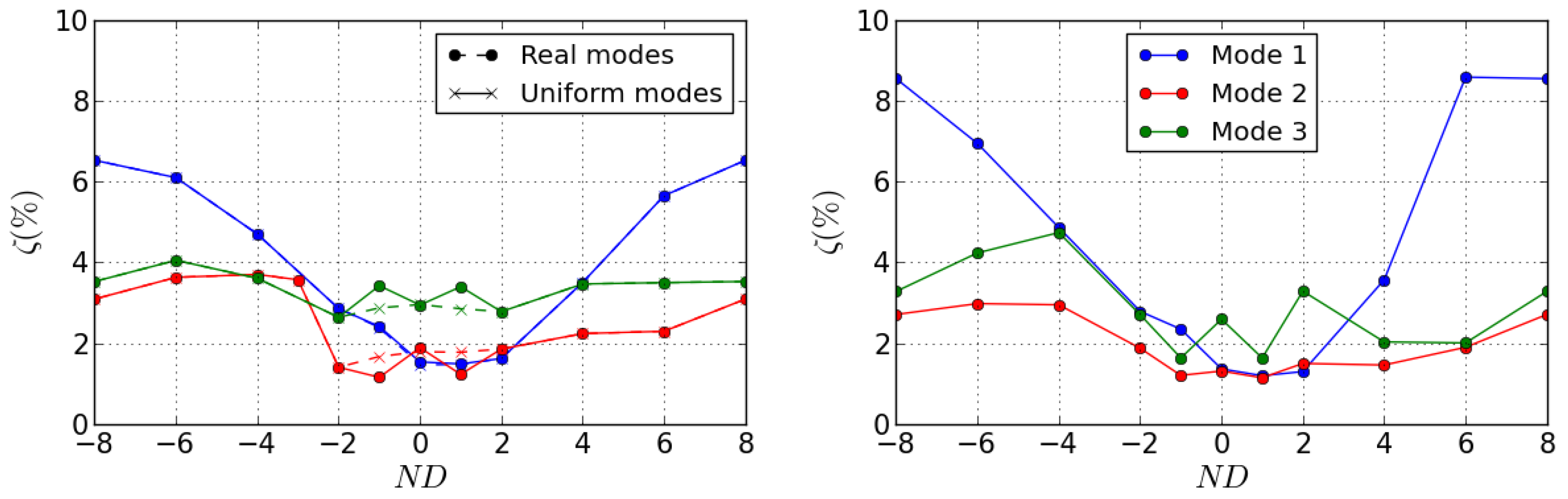
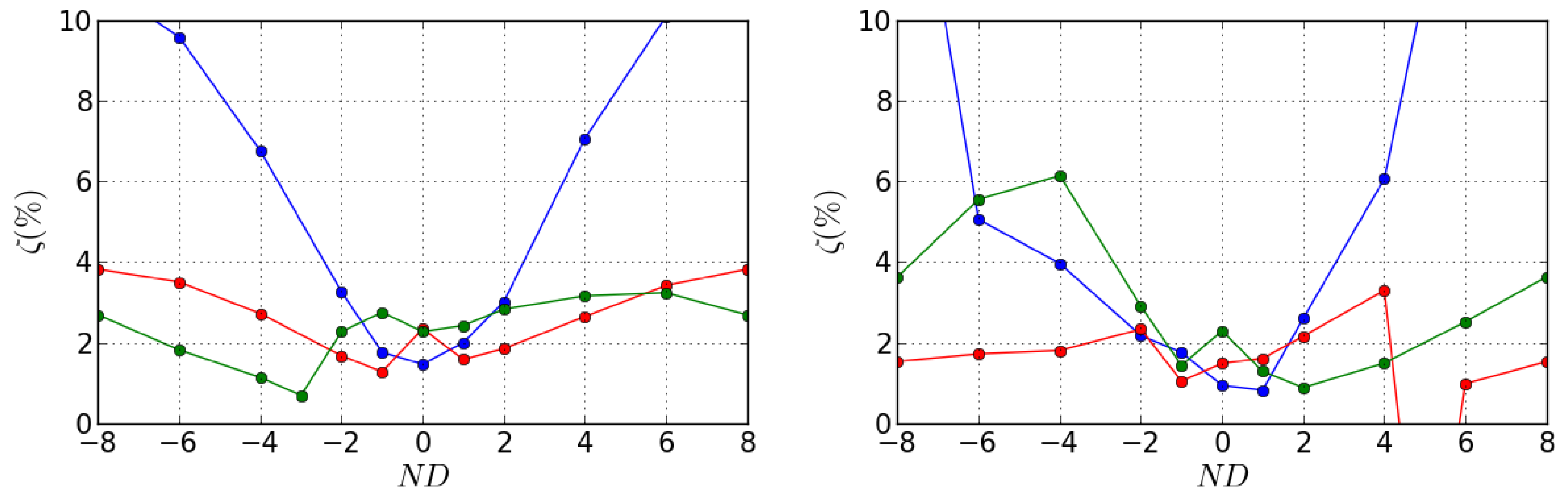
4.3.2. Aerodynamic Damping
4.3.3. Influence of Mode Frequency and Mode Shapes on Damping
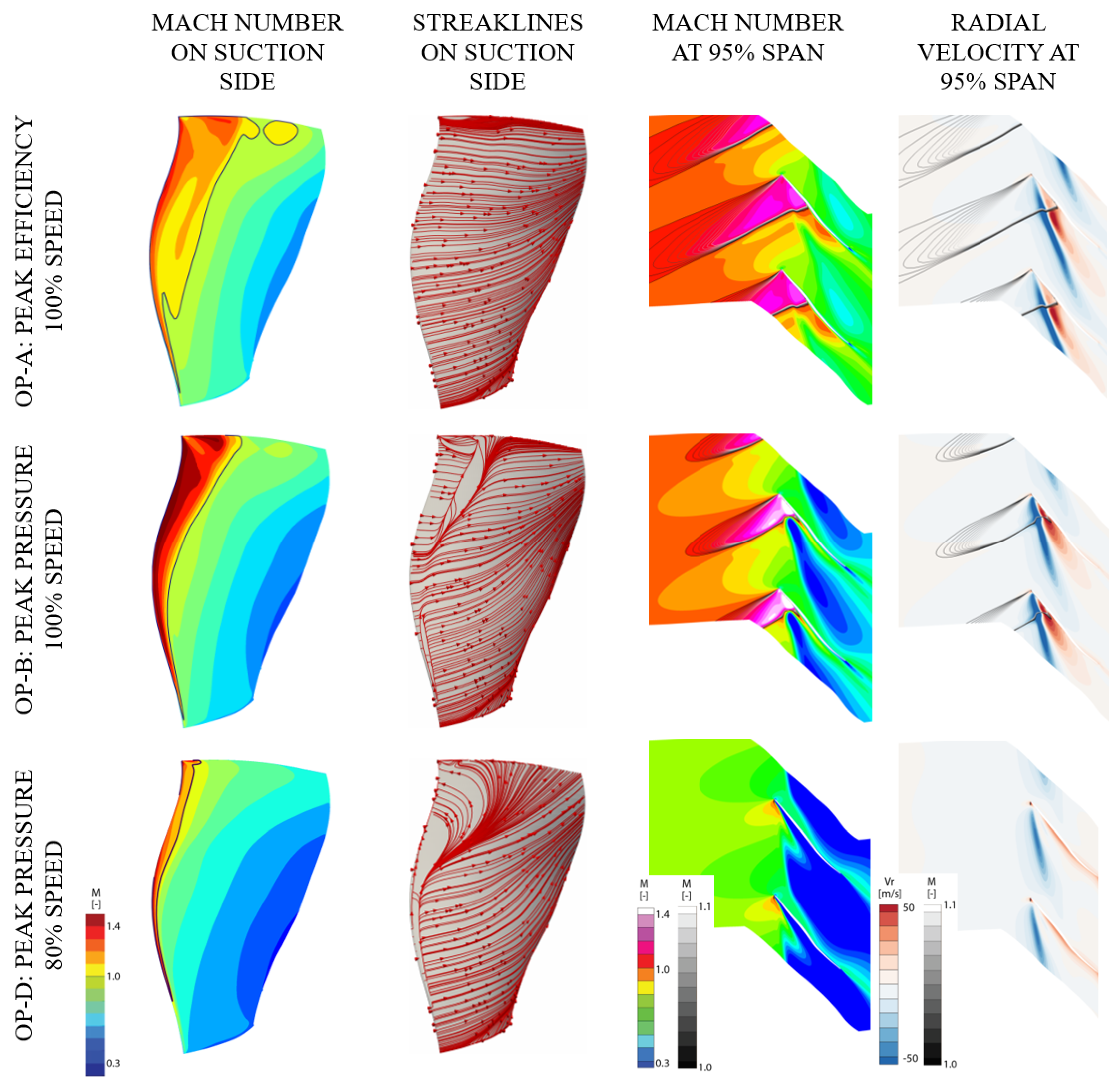
4.4. Instability Analysis
- For Mode 2ND-3 at OP-A, the stability curve is flat at each side of the discontinuity and the fan remains stable (see Figure 15a).
- For Mode 3ND-3 at OP-C, the stability reaches a minimum but the fan remains stable (see Figure 16a).
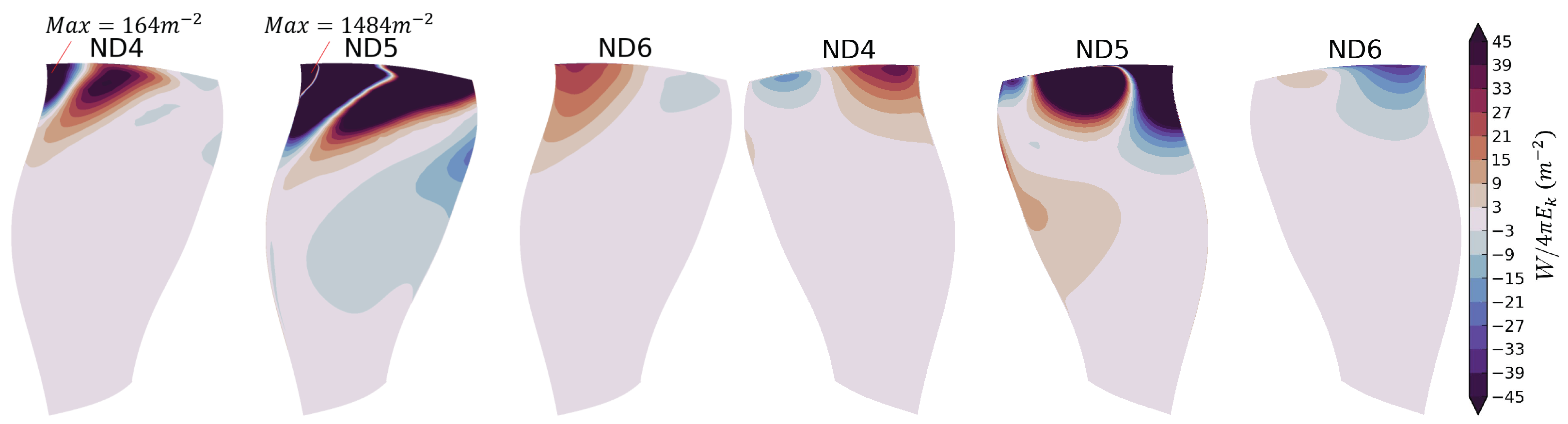
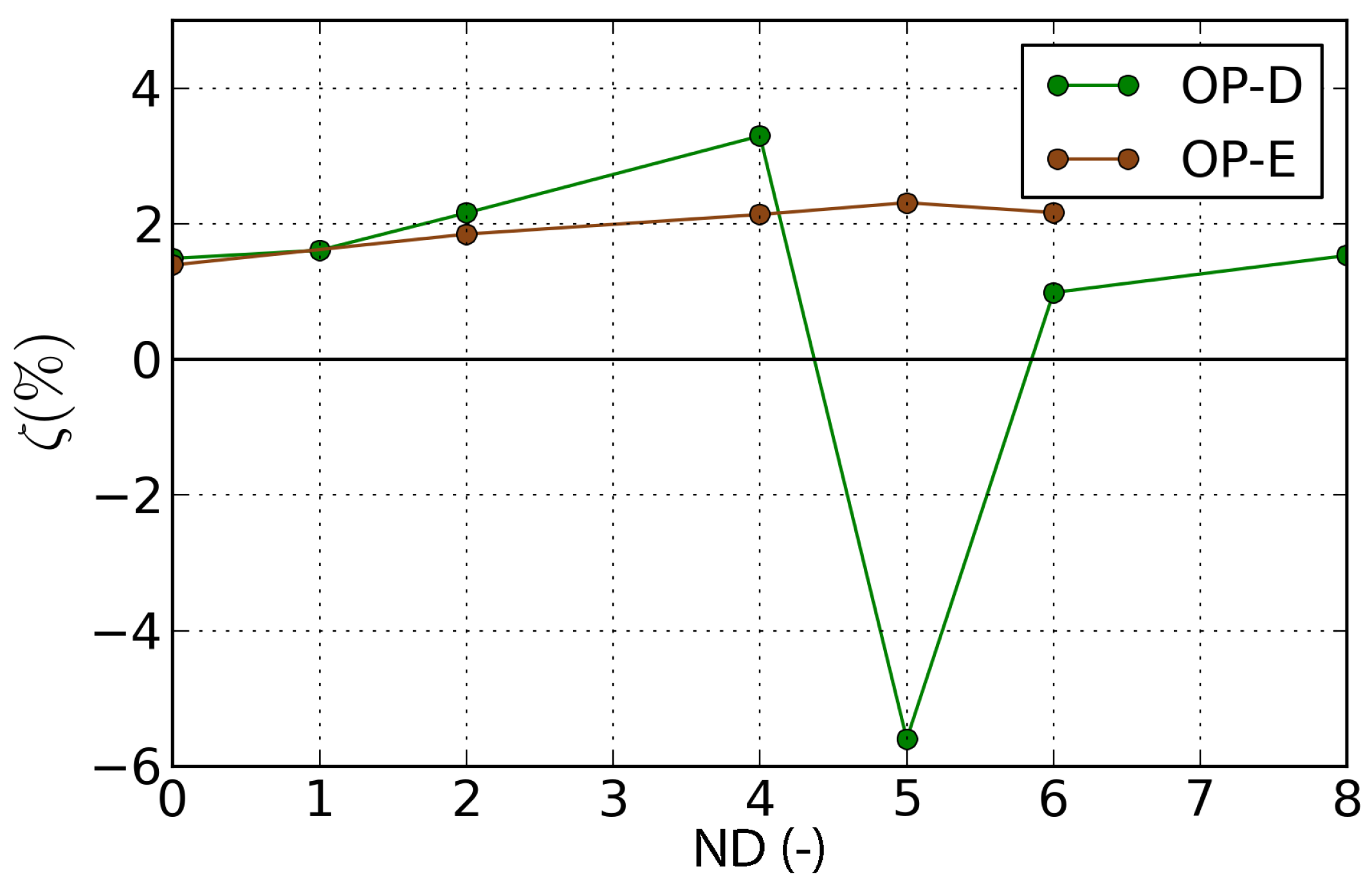
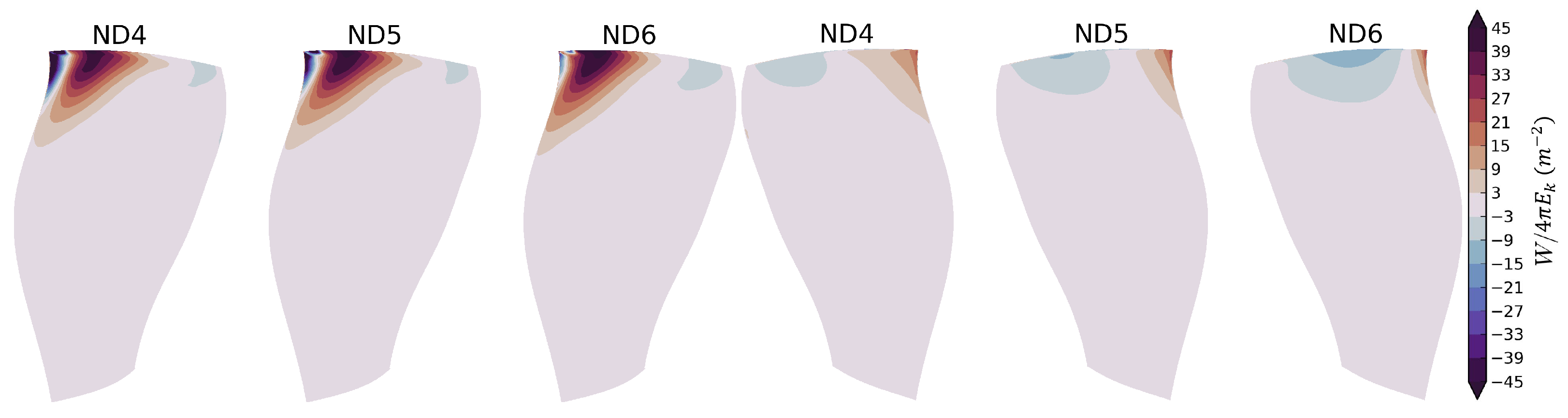
- For Mode 2ND5 at OP-D, the fan is predicted to be unstable (see Figure 16b). The stability behaviour for ND4 to ND6 is investigated in the following.
4.4.1. Aeroelastic Instability of Mode 2 at OP-D
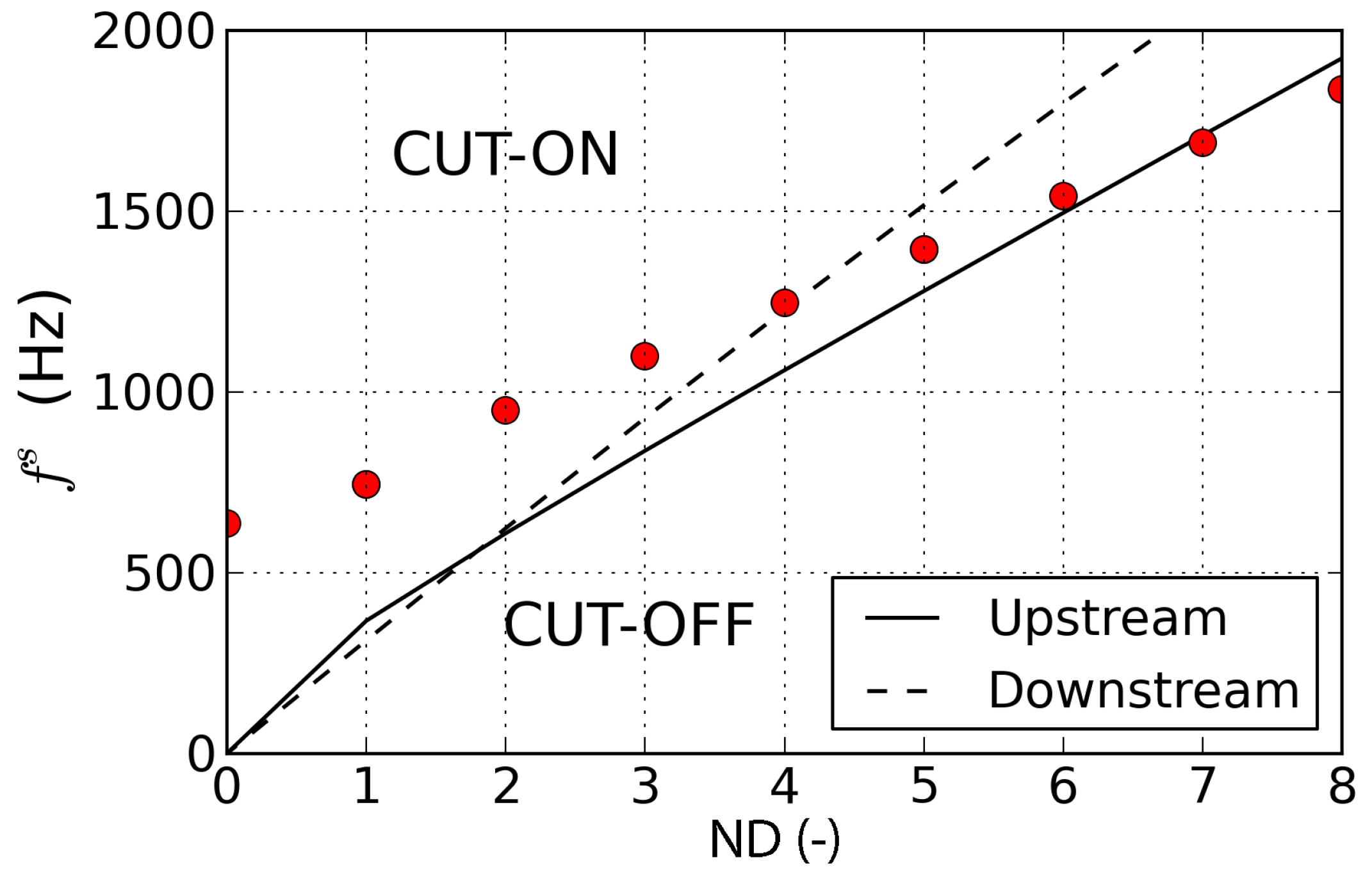
4.4.2. Acoustic Propagation Conditions
4.4.3. Influence of Operating Point
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EO | Engine Order |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| LRANS | Linearized Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes |
| ND | Nodal Diameter |
| NSV | Non-Synchronous Vibration |
| OGV | Outlet Guide Vanes (Stator) |
| OP | Operating Point |
| RANS | Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes |
| UHBR | Ultra-High Bypass Ratio |
References
- Brandstetter, C.; Pagès, V.; Duquesne, P.; Ottavy, X.; Ferrand, P.; Aubert, S. UHBR Open-Test-Case Fan ECL5/CATANA, Part 1: Geometry And Aerodynamic Performance. In Proceedings of the European Turbomachinery Conference ETC14 2021, Paper No. 625, Gdansk, Poland, 12–16 April 2021; Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03257374 (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Pagès, V.; Duquesne, P.; Ottavy, X.; Ferrand, P.; Aubert, S.; Blanc, L.; Brandstetter, C. UHBR Open-Test-Case Fan ECL5/CATANA, Part 2: Mechanical And Aeroelastic Stability. In Proceedings of the European Turbomachinery Conference ETC14 2021, Paper No. 626, Gdansk, Poland, 12–16 April 2021; Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03257377 (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Vahdati, M.; Cumpsty, N. Aeroelastic Instability in Transonic Fans. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2015, 138, 022604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.K. Self-sustained shock oscillations on airfoils at transonic speeds. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2001, 37, 147–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, J.; Vahdati, M. Rotating Stall Observations in a High Speed Compressor—Part I: Experimental Study. J. Turbomach. 2015, 137, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiquet, A.L.; Vercoutter, A.; Buffaz, N.; Aubert, S.; Brandstetter, C. Acoustic resonance in an axial multistage compressor leading to non-synchronous blade vibration. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2020 & Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, Online, 21–25 September 2020; ASME: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kielb, R.E.; Barter, J.W.; Thomas, J.P.; Hall, K.C. Blade Excitation by Aerodynamic Instabilities: A Compressor Blade Study. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2003, Collocated with the 2003 International Joint Power Generation Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–19 June 2003; American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 4, pp. 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stapelfeldt, S.; Brandstetter, C. Non-synchronous vibration in axial compressors: Lock-in mechanism and semi-analytical model. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 488, 115649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.B.; Wilson, M.; Vahdati, M. Validation of a Numerical Model for Predicting Stalled Flows in a Low-Speed Fan—Part I: Modification of Spalart–Allmaras Turbulence Model. J. Turbomach. 2018, 140, 051008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Spakovszky, Z.S.; Lord, W.K.; Rose, B. Ultrashort Nacelles for Low Fan Pressure Ratio Propulsors. J. Turbomach. 2015, 137, 021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Imregun, M.; Sayma, A.I. The Effect of Stagger Variability in Gas Turbine Fan Assemblies. J. Turbomach. 2006, 129, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Green, J.; Stapelfeldt, S.C.; Vahdati, M. Effect of Geometric Variability on Running Shape and Performance of a Transonic Fan. J. Turbomach. 2019, 141, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Bladh, R.; Dyverfeldt, G. Aeroelastic Stability Assessment of an Industrial Compressor Blade Including Mistuning Effects. J. Turbomach. 2012, 134, 060903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerke, D.; Le Denmat, A.L.; Schmidt, T.; Kocian, F.; Nicke, E. Aerodynamic and Mechanical Optimization of CF/PEEK Blades of a Counter Rotating Fan. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2012: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, Copenhagen, Denmark, 11–15 June 2012; ASME: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012; Volume 7: Structures and Dynamics, Parts A and B, pp. 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, T.; Lengyel-Kampmann, T.; Schimdt, T.; Nicke, E. Optimization of a carbon fiber composite blade of a counter-rotating fan for aircraft engines. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid Dynamics & Thermodynamics, Lausanne, Switzerland, 8–12 April 2019; European Turbomachinery Society: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Reiber, C.; Blocher, M. Potential of aeroelastic tailoring to improve flutter stability of turbomachinery compressor blades. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid Dynamics & Thermodynamics, Stockholm, Sweden, 3–7 April 2017; European Turbomachinery Society: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendu, Q. Modélisation des Écoulements Transsoniques Décollés pour L’étude des Interactions Fluide-Structure. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lyon, Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, M.; Soulat, L.; Paoletti, B.; Ottavy, X.; Brandstetter, C. Aerodynamic Investigation of a Composite Low-Speed Fan for UHBR Application. J. Turbomach. 2021, 143, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, V. Conception du Fan UHBR ECL5 pour une Analyse des Mécanismes D’interactions Multi-physiques à L’origine du Flottement. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Centrale de Lyon, Lyon, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Paton, R.; Page, J.R. The draping of woven fabric preforms and prepregs for production of polymer composite components. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1999, 30, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, E.J. Finite Element Analysis of Composite Materials Using ANSYS®, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Carta, F.O. Coupled Blade-Disk-Shroud Flutter Instabilities in Turbojet Engine Rotors. J. Eng. Power 1967, 89, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, A.J.; Hassan, K.K.; Rabe, D.C. Experimental and Numerical Study of Stall Flutter in a Transonic Low-Aspect Ratio Fan Blisk. J. Turbomach. 2004, 126, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aotsuka, M.; Murooka, T. Numerical Analysis of Fan Transonic Stall Flutter. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2014: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, Düsseldorf, Germany, 16–20 June 2014; ASME: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2014;B: Structures and Dynamics; Volume V07BT35A020; Volume 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendu, Q.; Philit, M.; Rozenberg, Y.; Labit, S.; Chassaing, J.C. Time-linearized and harmonic balance navier-stokes computations of a transonic flow over an oscillating bump. In Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Unsteady Aerodynamics, Aeroacoustics & Aeroelasticity of Turbomachines, Stockholm, Sweden, 8–11 September 2015; ISUAAAT: Stockholm, Sweden, 2015; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Philit, M.; Ferrand, P.; Labit, S.; Chassaing, J.C.; Aubert, S.; Fransson, T. Derivated Turbulence Model to Predict Harmonic Loads in Transonic Separated Flows over a Bump. In Proceedings of the 28th International Congress of the Aeroanautical Sciences, Brisbane, Australia, 23–28 September 2012; ICAS: Brisbane, Australia, 2012; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Duquesne, P.; Aubert, S.; Rendu, Q.; Ferrand, P. Effect of nodal diameter on the local blades vibration on the choke flutter instability in transonic UHBR fan. In Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Unsteady Aerodynamics, Aeroacoustics and Aeroelasticity of Turbomachines, Gothenburg, Sweden, 16–17 October 2018; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Brandstetter, C.; Paoletti, B.; Ottavy, X. Compressible Modal Instability Onset in an Aerodynamically Mistuned Transonic Fan. J. Turbomach. 2019, 141, 031004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemang, R.J. The Modal Assurance Criterion—Twenty Years of Use and Abuse. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 37, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Duquesne, P.; Mahieux, B.; Aubert, S.; Ferrand, P. Sensitivity of the aerodynamics damping coefficient prediction to the turbulence modelling conjugated with the vibration mode shape. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid Dynamics & Thermodynamics ETC13, Lausanne, Switzerland, 8–12 April 2019; European Turbomachinery Society: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2019; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Ferria, H.; Ferrand, P.; Pacull, F.; Aubert, S. Numerical investigation of flutter stability in subsonic space turbine blisk with emphasis on cut-on/cut-off modes and interblade phase angles. J. Therm. Sci. 2012, 21, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmich, B.; Seume, J.R. Causes of Acoustic Resonance in a High-Speed Axial Compressor. J. Turbomach. 2008, 130, 031003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atassi, H.M.; Fang, J.; Ferrand, P. Acoustic blockage effects in unsteady transonic nozzle and cascade flows. In Proceedings of the 33rd Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 9–12 January 1995; AIAA: Reno, NV, USA, 1995; Volume 95-0303, p. 9. [Google Scholar]




| Rotation Speed | Tip Clearance (mm) | Tip Clearance (% Tip Chord) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ( 11,000 rpm) | Leading Edge | Trailing Edge | Leading Edge | Trailing Edge |
| kg/m3 | GPa | GPa | GPa | GPa |
| Ply Nr. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orientation | |||||||||
| Ply Nr. | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| Orientation |
| Speedline | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mode 1 | ||
| Mode 2 | ||
| Mode 3 |
| Operating Point | Mode 1 | Mode 2 | Mode 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| OP-A (, ) | |||
| OP-B (, ) | |||
| OP-C (, ) | |||
| OP-D (, ) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY-NC-ND) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pagès, V.; Duquesne, P.; Aubert, S.; Blanc, L.; Ferrand, P.; Ottavy, X.; Brandstetter, C. UHBR Open-Test-Case Fan ECL5/CATANA. Int. J. Turbomach. Propuls. Power 2022, 7, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp7020017
Pagès V, Duquesne P, Aubert S, Blanc L, Ferrand P, Ottavy X, Brandstetter C. UHBR Open-Test-Case Fan ECL5/CATANA. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power. 2022; 7(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp7020017
Chicago/Turabian StylePagès, Valdo, Pierre Duquesne, Stéphane Aubert, Laurent Blanc, Pascal Ferrand, Xavier Ottavy, and Christoph Brandstetter. 2022. "UHBR Open-Test-Case Fan ECL5/CATANA" International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power 7, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp7020017
APA StylePagès, V., Duquesne, P., Aubert, S., Blanc, L., Ferrand, P., Ottavy, X., & Brandstetter, C. (2022). UHBR Open-Test-Case Fan ECL5/CATANA. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power, 7(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp7020017







