Murine Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis: Appropriate Model for Evaluating Anthelminthic and Anti-Inflammatory Treatment Schedules
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
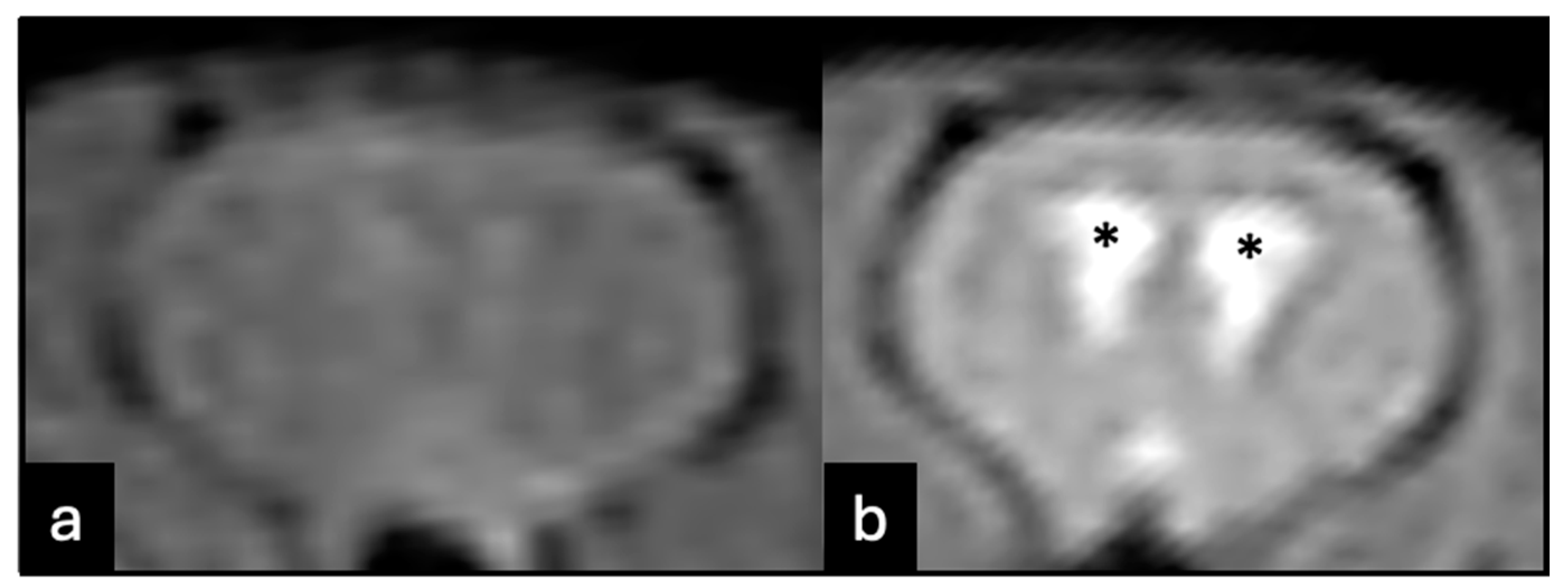
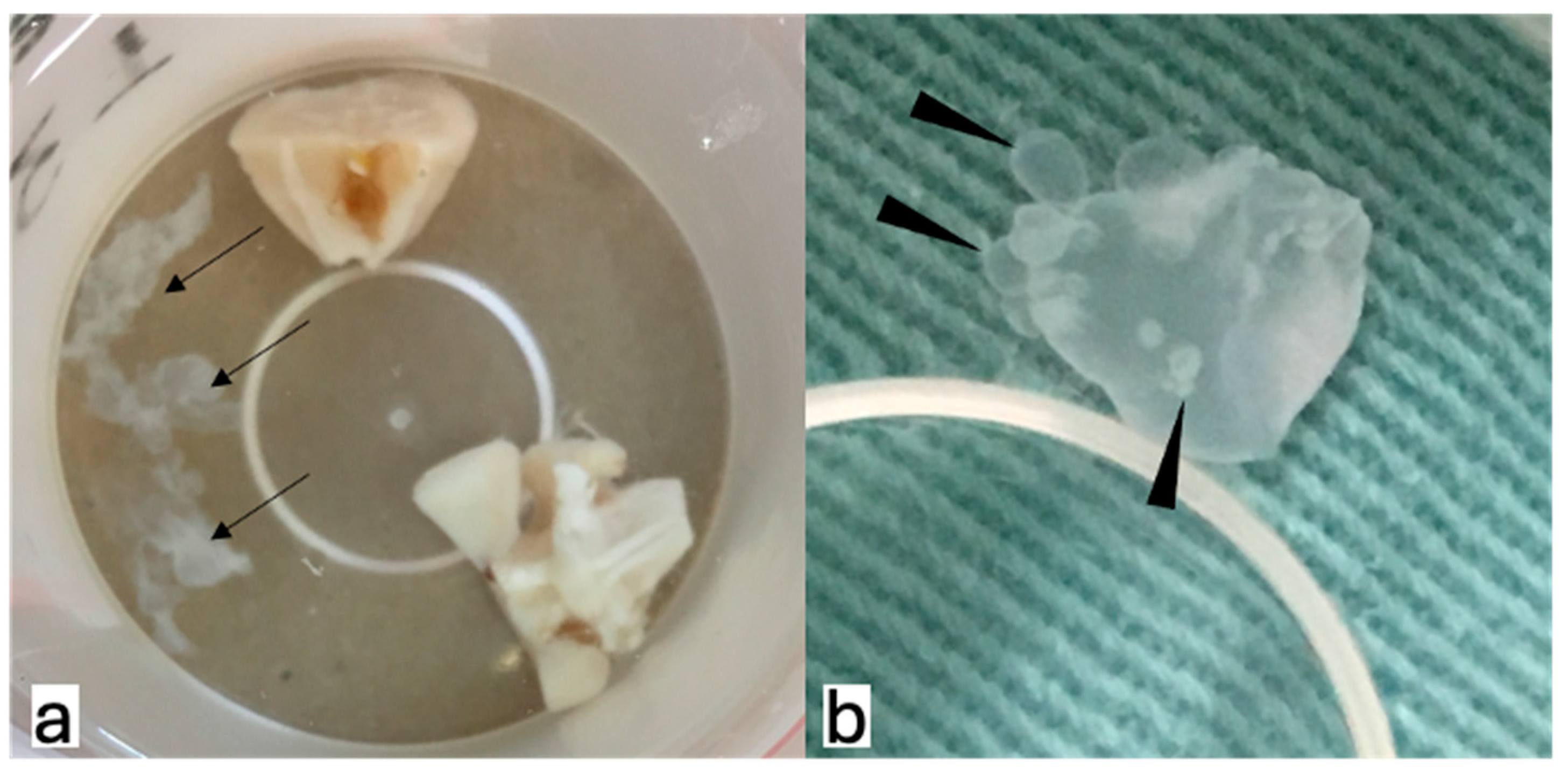
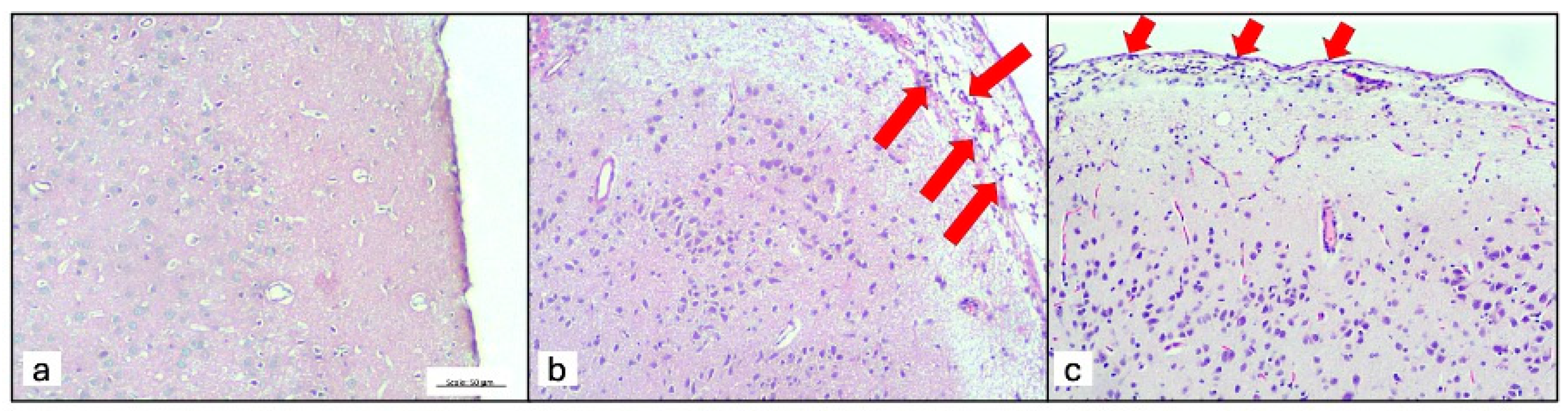
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pineda-Reyes, R.; White, A.C., Jr. Neurocysticercosis: An update on diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 35, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Rivas, R.; Flisser, A.; Norcia, L.F.; Hamamoto Filho, P.T.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Carpio, A.; Romo, M.L.; Fleury, A. Neurocysticercosis in Latin America: Current epidemiological situation based on official statistics from four countries. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010652. [Google Scholar]
- Fleury, A.; Carrillo-Mezo, R.; Flisser, A.; Sciutto, E.; Corona, T. Subarachnoid basal neurocysticercosis: A focus on the most severe form of the disease. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nash, T.E.; O’Connell, E.M. Subarachnoid neurocysticercosis: Emerging concepts and treatment. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 33, 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Arce-Sillas, A.; Cárdenas, G.; Álvarez-Luquín, D.; Hernandez, M.; Del Rey, A.; Besedovsky, H.; Gómez-Fuentes, S.; Fragoso, G.; Fleury, A.; Sciutto, E.; et al. Treatment-resistant human extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis: An immune-inflammatory approach to cysticidal treatment outcome. Neuroimmunomodulation 2018, 25, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- de Lange, A.; Mahanty, S.; Raimondo, J.V. Model systems for investigating disease processes in neurocysticercosis. Parasitology 2019, 146, 553–562. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, J.I.; Mishra, B.B.; Gundra, U.M.; Mishra, P.K.; Teale, J.M. Mesocestoides corti intracranial infection as a murine model for neurocysticercosis. Parasitology 2010, 137, 359–372. [Google Scholar]
- Matos-Silva, H.; Reciputti, B.P.; Paula, E.C.; Oliveira, A.L.; Moura, V.B.; Vinaud, M.C.; Oliveira, M.A.; Lino-Júnior, R.S. Experimental encephalitis caused by Taenia crassiceps cysticerci in mice. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2010, 70, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Fleury, A.; Trejo, A.; Cisneros, H.; García-Navarrete, R.; Villalobos, N.; Hernández, M.; Villeda Hernández, J.; Hernández, B.; Rosas, G.; Bobes, R.J.; et al. Taenia solium: Development of an Experimental Model of Porcine Neurocysticercosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003980. [Google Scholar]
- Verastegui, M.R.; Mejia, A.; Clark, T.; Gavidia, C.M.; Mamani, J.; Ccopa, F.; Ângulo, N.; Chile, N.; Carmen, R.; Medina, R.; et al. Novel rat model for neurocysticercosis using Taenia solium. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto Filho, P.T.; Fogaroli, M.O.; Oliveira, M.A.C.; Oliveira, C.C.; Batah, S.S.; Fabro, A.T.; Vulcano, L.C.; Bazan, R.; Zanini, M.A. A Rat model of neurocysticercosis-induced hydrocephalus: Chronic progressive hydrocephalus with mild clinical impairment. World Neurosurg. 2019, 132, e535–e544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto Filho, P.T.; Fabro, A.T.; Rodrigues, M.V.; Bazan, R.; Vulcano, L.C.; Biondi, G.F.; Zanini, M.A. Taenia crassiceps injection into the subarachnoid space of rats simulates radiological and morphological features of racemose neurocysticercosis. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Cerón, A.; Méndez, A.; Hernández-Aceves, J.; Juárez-González, J.C.; Villalobos, N.; Hernández, M.; Díaz, G.; Soto, P.; Concha, L.; Pérez-Osorio, I.N.; et al. Standardizing an experimental murine model of extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis that immunologically resembles human infection. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, A.; Osorio, R.; Matus, C.; Martinez Lopez, Y.; Ramirez Cruz, N.; Sciutto, E.; Fragoso, G.; Arauz, A.; Carrillo-Mezo, R.; Fleury, A. Human extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis: The control of inflammation favors the host… but also the parasite. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2652. [Google Scholar]
- Hamamoto Filho, P.T.; Fragoso, G.; Sciutto, E.; Fleury, A. Inflammation in neurocysticercosis: Clinical relevance and impact on treatment decisions. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 1503–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nateros, F.; Saenz, E.; Saavedra, H.; Gonzales, I.; Pretell, E.J.; Perez, E.; Castillo, Y.; Bustos, J.A.; Garcia, H.H. Older Age in Subarachnoid Neurocysticercosis Reflects a Long Prepatent Period. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2023, 108, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez-Arellano, C.A.; Kuschick-Fehér, J.; Romero-Gonzalez, F.G.; Fleury, A. Neurocysticercosis: The duration of its preclinical phase relies on the parasite location. Trop. Med. Int. Health. 2024, 29, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo, M.L.; Osorio, R.; Toledo, A.; Carrillo-Mezo, R.; Valdez, R.; Romano, M.C.; Sciutto, E.; Fragoso, G.; Fleury, A. Low responsiveness of peripheral lymphocytes in extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011386. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.C., Jr.; Coyle, C.M.; Rajshekhar, V.; Singh, G.; Hauser, W.A.; Mohanty, A.; Garcia, H.H.; Nash, T.E. Diagnosis and treatment of neurocysticercosis: 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 945–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, T.E.; O’Connell, E.M.; Hammoud, D.A.; Wetzler, L.; Ware, J.M.; Mahanty, S. Natural History of Treated Subarachnoid Neurocysticercosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 102, 78–89. [Google Scholar]
- Hamamoto Filho, P.T.; Rodríguez-Rivas, R.; Fleury, A. Neurocysticercosis: A Review into Treatment Options, Indications, and Their Efficacy. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2022, 13, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nash, T.E.; Mahanty, S.; Garcia, H.H.; Cysticercosis Group in Peru. Corticosteroid use in neurocysticercosis. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas, G.; Carrillo-Mezo, R.; Jung, H.; Sciutto, E.; Hernandez, J.L.; Fleury, A. Subarachnoidal Neurocysticercosis non-responsive to cysticidal drugs: A case series. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, R.C.S.; Prudente, T.P.; Guerra, C.H.S.; Lima, N.F.; Lino Junior, R.S.; Vinaud, M.C. Albendazole – Ivermectin combination decreases inflammation in experimental neurocysticercosis. Exp. Parasitol. 2023, 251, 108568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, J.A.A.; Gomes, T.C.; Lima, V.C.N.; Silva, Y.B.S.; Lino Junior, R.S.; Vinaud, M.C. Oxfendazole Nitazoxanide combination in experimental neurocysticercosis – Anti-inflammatory and cysticidal effects. Exp. Parasitol. 2024, 262, 108764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.C., Jr. Controlling the host response in neurocysticercosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 483–484. [Google Scholar]
- Mahale, R.R.; Mehta, A.; Rangasetty, S. Extraparenchymal (Racemose) Neurocysticercosis and Its Multitude Manifestations: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 11, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Palomares-Alonso, F.; Toledo, A.; Hernández, G.P.; Jung-Cook, H.; Fleury, A. Effect of dexamethasone on albendazole cysticidal activity in experimental cysticercosis by Taenia crassiceps in BALB/c mice: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 208, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.C.; Jiménez, P.; Miranda-Brito, C.; Valdez, R.A. Parasites and steroid hormones: Corticosteroid and sex steroid synthesis, their role in the parasite physiology and development. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 224. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, V.T.; Martins, T.d.C.; Conceição, R.T.; Generoso, D.; Machado, V.M.d.V.; Batah, S.S.; Fabro, A.T.; Zanini, M.A.; Sciutto, E.; Fleury, A.; et al. Murine Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis: Appropriate Model for Evaluating Anthelminthic and Anti-Inflammatory Treatment Schedules. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9090215
Oliveira VT, Martins TdC, Conceição RT, Generoso D, Machado VMdV, Batah SS, Fabro AT, Zanini MA, Sciutto E, Fleury A, et al. Murine Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis: Appropriate Model for Evaluating Anthelminthic and Anti-Inflammatory Treatment Schedules. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2024; 9(9):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9090215
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Vinícius Tadeu, Tatiane de Camargo Martins, Renato Tavares Conceição, Diego Generoso, Vânia Maria de Vasconcelos Machado, Sabrina Setembre Batah, Alexandre Todorovic Fabro, Marco Antônio Zanini, Edda Sciutto, Agnès Fleury, and et al. 2024. "Murine Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis: Appropriate Model for Evaluating Anthelminthic and Anti-Inflammatory Treatment Schedules" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 9, no. 9: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9090215
APA StyleOliveira, V. T., Martins, T. d. C., Conceição, R. T., Generoso, D., Machado, V. M. d. V., Batah, S. S., Fabro, A. T., Zanini, M. A., Sciutto, E., Fleury, A., & Hamamoto Filho, P. T. (2024). Murine Extraparenchymal Neurocysticercosis: Appropriate Model for Evaluating Anthelminthic and Anti-Inflammatory Treatment Schedules. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 9(9), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9090215








