Abstract
Echinococcosis, one of the most serious and life-threatening parasitic forms of zoonosis worldwide, is caused by the larvae of Echinococcus granulosus (E. granulosus) and Echinococcus multilocularis (E. multilocularis). Various drugs are being applied clinically to treat zoonosis; however, their therapeutic efficacy remains a great challenge, especially with albendazole as the preferred drug of choice. Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling controls normal cellular proliferation, differentiation, and metabolism in humans and mammals, which are intermediate hosts of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis. Disruption of RTK signaling can cause various forms of carcinogenesis and exacerbate the progression of certain forms of parasitic disease. As a result, a significant number of studies on tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been conducted for the treatment of cancer and parasitic infection, with some TKIs already approved for clinical use for cancer. Notably, RTK signaling has been identified in the parasites E. granulosus and E. multilocularis; however, the mechanisms of RTK signaling response in Echinococcus–host intercommunication are not fully understood. Thus, understanding the RTK signaling response in Echinococcus–host intercommunication and the potential effect of RTK signaling is crucial for identifying new drug targets for echinococcosis. The present review illustrates that RTK signaling in the host is over-activated following infection by E. granulosus or E. multilocularis and can further facilitate the development of metacestodes in vitro. In addition, some TKIs exert strong parasitostatic effects on E. granulosus or E. multilocularis, both in vitro and/or in vivo, through downregulation of RTK signaling molecules. The summarized findings suggest that RTK signaling may be a promising drug target and that TKIs could be potential anti-Echinococcus drugs warranting further research.
1. Introduction
Echinococcosis, a parasitic form of zoonosis, is caused by the larval stage of the tapeworm of the genus Echinococcus [1,2]. The two main types of the disease prevalent in humans are cystic echinococcosis (CE), caused by Echinococcus granulosus (E. granulosus), and alveolar echinococcosis (AE), caused by Echinococcus multilocularis (E. multilocularis), which pose a substantial threat to public health globally [3,4]. Of these two prevalent forms, CE has a global distribution, while AE is predominantly distributed in the cooler and temperate latitudes of the northern hemisphere [4,5,6,7], particularly in the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau area of China [8,9]. AE causes a more significant economic and public health burden for humans than CE due to the cancer-like invasive growth manner of E. multilocularis metacestodes [10,11]. Upon infection, the parasite larvae reside most commonly in the liver of humans and mammals, with the latter serving as intermediate hosts in transmission [12,13]. Growing metacestodes lead to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in the host, particularly E. multilocularis metacestodes, which are fatal if left untreated or inadequately treated because of their cancer-like invasive growth manner, earning them the title “parasitic cancer” [14,15]. At present, the main options for the treatment of liver echinococcosis include drug treatment, surgical resection, and liver transplantation (mainly for AE patients) [16,17]. Among the available chemotherapies, albendazole (ABZ), a benzimidazole derivative, is the preferred drug of choice [18,19]. However, the effectiveness of ABZ, the severe adverse effects caused by long-term application, and clinical recurrence remain significant challenges [18,19]. Thus, finding new drug targets and therapeutic agents is urgently required.
Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-mediated signaling regulates essential cellular physiological processes, such as cell proliferation and migration, glucose uptake, and energy metabolism in humans and mammals [20,21], with the latter often acting as the intermediate host of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis. Published data show that the disruption of RTK signaling can cause various forms of carcinogenesis and promote cancer progression [22,23], indicating RTK signaling as a potential and promising therapeutic target in cancer. More importantly, an increasing number of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are in development for the treatment of cancer [23,24,25], such as linifanib, targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which induces excessive angiogenesis in solid cancers; gefitinib and cetuximab, targeting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in non-small cell lung cancer and metastatic colon cancer; and some that act on chronic diseases, such as imatinib, targeting platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling in pulmonary hypertension and respiratory dysfunction. More importantly, some of these TKIs have been approved for the clinical treatment of certain types of cancer [23,24,25]. Thus, RTK signaling is a potential and promising therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer and other forms of chronic disease. Interestingly, RTK signaling has also been found to play an important regulatory role in the progression of many forms of parasitic diseases, such as schistosomiasis [26,27] and echinococcosis [28,29]. For example, a study by Brehm and Koziol demonstrates that the activation of RTK signaling can facilitate the development of E. granulosus germinative cells and protoscoleces [30]. In comparison, in other studies, some TKIs have been shown to inhibit E. multilocularis metacestode development in vitro and/or in vivo [31,32,33]. Herein, we summarize and discuss the recent studies (from January 2001 to April 2024) focusing on the RTK signaling response in the host after Echinococcus infection, the role of RTK signaling in E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestode development, and its anti-echinococcal effect in vitro and in vivo to provide information referring to potential drug targets for echinococcosis.
2. RTK Signaling in Humans and Mammals
RTKs, a family of evolutionarily conserved transmembrane proteins, govern cellular pathological processes in humans and mammals [20], such as sheep, goats, cattle, camels, mice, and pikas, which are intermediate hosts of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis larvae [13]. In these hosts, the RTK family contains a variety of essential receptors, such as EGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), VEGF receptor (VEGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), insulin receptor (IR) or insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGFR), hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR or C-Met), and ephrin receptor (Ephr) [34,35]. As is widely acknowledged, distinct RTK classes can recognize different growth factors and hormone ligands, which include EGF, fibroblast growth factors (FGFs), VEGF, PDGF, insulin and insulin-like growth factor (IGF), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), and nerve growth factor (NGF) [24,35]. Interestingly, different receptors in RTK signaling show some common structural characteristics, including an extracellular ligand-binding region (ELR), a membrane-spanning helix, and a tyrosine kinase-containing intracellular region [36]. In general, each of these receptors carries catalytic kinases that remain inactive as monomers but are promptly activated when the ELR binds to a specific ligand that is a soluble polypeptide, small-molecule protein, or hormone [35,36]. Once the ligand–receptor conjugation forms, leading to dimerization or oligomerization, it facilitates trans-autophosphorylation and relieves autoinhibition of the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain, promoting cell growth and proliferation by initiating downstream signaling cascades [37,38,39], such as Src homology-2 (SH2), mitogen-activated protein kinases/protein kinase B (MAPK/Akt), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK).
3. RTK Signaling Identification in E. granulosus and E. multilocularis
It is recognized that genome-wide analyses have shown that RTK signaling is widely present in many parasite species, such as Trypanosoma cruzi [40], Toxoplasma gondii [41], Plasmodium falciparum [42], Schistosoma [43,44], and even E. granulosus and E. multilocularis [28,45] and the model invertebrate organism Caenorhabditis elegans [46]. In E. granulosus and E. multilocularis, some encoding genes for not only growth factor ligands but also their receptors in RTK signaling, such as EGFR and EGF, FGFR, IGF receptor (IGFR, e.g., EmIR1 and EmIR2), and insulin-like ligands (e.g., EmILP1 and EmILP2), excluding FGF, PDGF, PDGFR, VEGF, and VEGFR, have been identified [28,45,47] (Table 1). Interestingly, E. granulosus and E. multilocularis show a high degree of sequence homology with the receptors involved in RTK signaling that are derived from humans and mammals [28,45]. Furthermore, the sequence analyses indicate that these receptors and ligands in the RTK family have a high degree of similarity within the conserved motifs between the parasite and its intermediate hosts, respectively [28,45,48].

Table 1.
Receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in E. granulosus and E. multilocularis and the parasite hosts.
The results of the above studies indicate that RTK signaling may play important roles in Echinococcus–host intercommunication, although the detailed molecular mechanisms underlying the activation of RTK signaling in Echinococcus metacestode growth remain unclear. Further discussion should be conducted to provide clues as to the development of new anti-echinococcal drugs targeting RTK signaling.
4. RTK Signaling Response in Echinococcus Infected Hosts
Following Echinococcus metacestode infection, the host liver, as the primary organ of infection [49], undergoes a chronic, continuous, and gradual damaging progression, mainly exhibiting liver fibrosis and cirrhosis [50,51]. Simultaneously, the host shows a significant response in RTK signaling after infection of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis larvae [50,52,53]. For example, in Echinococcus-infected mice, a significant increase in VEGF mRNA/protein expression was observed in the liver around the parasite metacestodes, accompanied by a rise in VEGF content in the serum [52,54,55]. In studies conducted by our research group, excessive VEGF-induced pathological angiogenesis was found to occur in the liver around the parasite metacestodes in mice following intraperitoneal infection with E. multilocularis metacestodes [52,56]. However, whether this phenomenon was caused by excessive expression of VEGF and VEGFR in the infected hosts remains unclear and thus necessitates further investigation.
Insulin, a regulatory molecule involved in RTK signaling, has been studied extensively in humans and mammals, with high concentrations mainly found in the liver [30]. Beyond this, insulin signaling has been studied in Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster [57,58] because in the two model organisms, cell metabolic processes, growth, proliferation, and reproduction are controlled by conserved insulin signaling. Interestingly, insulin signaling has been shown to play an important role in many helminths, such as Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma mansoni [59,60], in addition to Echinococcus spp. [30,61]. Organ tropism toward the host liver has been demonstrated in E. granulosus and E. multilocularis larvae [30,62]. In an in vitro study, human insulin showed a growth-promoting effect on E. multilocularis metacestodes in vitro, indicating that insulin or IGF-mediated signaling is closely related to Echinococcus metacestode growth [31]. However, how RTK signaling is involved in the host response to E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestode infection remains unclear.
Moreover, the expression of FGF was significantly increased in the host liver after infection with E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestodes [50]. Similarly, Förster’s study demonstrated that human FGF, which is widely expressed in the fibrotic liver but not in the normal liver, can stimulate the development of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis protoscoleces in vitro [32]. This finding indirectly indicates the over-activation of FGF signaling in the host after infection with the parasite; however, the response of FGF signaling following E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestode infection is not fully clarified.
Overall, E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestode infection can cause an excessive activation state of RTK signaling with a significant increase in growth factors in the parasite’s host. However, whether these growth factors in the infected host could promote E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestodes development remains unclear and thus necessitates further investigation.
5. Activation of RTK Signaling Involves Echinococcus Metacestode Development
Since human- or mammalian-derived growth factors or hormone ligands in RTK signaling have been found to promote the entry, survival, and replication of intracellular pathogens [63,64], an increasing number of investigators have begun to explore whether extracellular parasites can utilize these growth factors or hormones to maintain their survival and growth [32,33,65]. For example, Jin’s study showed that a putative EGFR-like kinase in Toxoplasma Gondii was activated under the stimuli of human EGF or rNcMIC3, which contains four EGF domains [64]. Similarly, in vitro, human EGF was shown to promote the growth and development of Planaria, which is a free-living cestode [66], and Schistosoma mansoni [43]. Therefore, understanding whether the ligand molecules in host RTK signaling could promote E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestode development is important for developing effective anti-echinococcal drugs.
The results of Feng’s study showed that EGFR signaling in E. multilocularis may be activated by human EGF in vitro, and human EGF could promote the development of E. multilocularis protoscoleces into microcysts [65]. Furthermore, evidence from in vitro studies indicates that the concentration of 10 ng/mL or higher of human recombinant EGF could significantly facilitate the growth and development of germinative cells of E. multilocularis metacestodes; in comparison, a physiological concentration of 1 ng/mL only exhibited a modest effect on E. multilocularis metacestode growth and development [33] (Table 2). This finding indicates that in humans and the intermediate host, under the stimuli of the physiological concentration of host EGF, the development of E. multilocularis metacestodes occurs over long periods spanning several years or decades, rather than as a swift or transitory process.

Table 2.
Activation of RTK signaling for E. multilocularis metacestode development by host growth factors in vitro.
As is widely acknowledged, FGFR signaling, one of the conserved RTK signaling systems in humans and mammals, may be activated by FGF binding to FGFR, promoting cell homeostasis and persistent differentiation [63,67,68]. In E. granulosus and E. multilocularis, the FGFR encoding gene was identified through the use of high-throughput sequencing analysis; however, the FGF ligand was absent [28,45]. In Forster’s study, under the stimuli of different concentrations of mammalian FGF in vitro, ranging from 10 nM to 100 nM, the growth and development of E. multilocularis metacestode vesicles and primary cells were significantly boosted [32]. Notably, physiological concentrations of mammalian FGF lower than 10 nM showed only a moderate effect on the growth promotion of E. multilocularis metacestodes in vitro [32]. It is suggested that, with the support of physiological concentrations of host FGF, inapparent E. multilocularis metacestode infection in the infected host progresses for a longer duration.
IR/IGFR signaling is widely distributed in humans and mammals (e.g., rodents, artiodactyls, and Canidae) [69,70] and even in some parasites, such as Schistosoma as a helminth [59], and E. granulosus [63]. In IGF-R/IR signaling, there are three ligands (including IGF-I, IGF-II, and insulin) and three receptors (including IGF-IR, IGF-IIR, and insulin receptor) [70]. Evidently, IGFs, which are structurally and functionally similar to insulin, regulate longer-term glucose homeostasis by controlling insulin sensitivity [30,70]. Interestingly, the genes encoding IR (e.g., Em1 and Em2) and insulin-like ligands (e.g., EmILP1 and EmILP2) in E. granulosus and E. multilocularis show high structural and functional homology to those in humans and mammals (e.g., Canidae, artiodactyls, and rodents) [30]. Thus, we speculate that, in the infected host, IGFR/IR signaling in E. granulosus and E. multilocularis could be activated by host IGF and insulin. Furthermore, in vitro cultivation suggests that a continuous supply of glucose is crucial for nutrient uptake and energy metabolism in the parasite, depending on the activation of IGFR signaling supported by host-derived IGFs [61]. In summary, IGFR/IR signaling plays an important role in Echinococcus–host interaction and is a potential drug target for the treatment of liver echinococcosis in the future.
In both in vivo mouse models and humans, VEGF and VEGFR mRNA and/or protein levels in a number of studies were found to significantly increase following Echinococcus metacestode infection [52,56,71], indicating that abundant pathological angiogenesis or neovascularization in the liver around E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestodes may be caused by the excessive expression of VEGF and VEGFR. Angiogenesis is a crucial contributory factor in exacerbating liver fibrosis [72], which is the most typical process of Echinococcus–host intercommunication [31,73]. Thus, VEGF/VEGFR-induced angiogenesis is an important regulator in Echinococcus–host intercommunication; however, how the VEGF/VEGFR-induced angiogenesis promotes parasite growth and metastasis to other organs is not well understood.
HGF, a growth factor in RTK signaling secreted by stromal cells, can bind the specific receptor (c-Met) to regulate cellular proliferation and apoptosis, extracellular matrix invasion, and angiogenesis in the liver [74,75]. The dysregulation of the HGF/c-Met axis leads to the invasion and progression of solid cancers by initiating the downstream PI3K/Akt and p38/MAPK signaling cascades [76,77]. In addition, it has been demonstrated that the activation of HGF/c-Met signaling can not only boost the growth and development of Plasmodium berghei and Plasmodium falciparum [78,79] but also induce angiogenesis [80,81], which contributes to E. granulosus and E. mutilocularis metacestode development and metastasis [30,73]. However, the detailed role of HGF/c-Met signaling in Echinococcus–host interaction remains unclear and thus necessitates further investigation.
Overall, infection with E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestodes can cause liver fibrosis in humans and intermediate hosts, and the fibrotic liver often shows hyperactivation of RTK signaling, with excessive expression of growth factor ligands in RTK signaling. Simultaneously, the increased number of growth factors can promote E. granulosus and E. mutilocularis growth and development in vitro. Thus, in Echinococcus–host intercommunication, RTK signaling plays important roles in E. granulosus and E. mutilocularis development, implying that RTK signaling is an important and promising drug target for echinococcosis.
6. Targeting RTK Signaling Implies Potential Drug Target for Echinococcosis
The expression of growth factors or hormone ligands in RTK signaling is significantly increased in the host liver following infection caused by E. granulosus and E. mutilocularis larvae [82,83]. Host growth factors in RTK signaling can promote E. granulosus and E. mutilocularis metacestode growth and development in vitro [31,32,33], indicating that treatment of echinococcosis through the inhibition of RTK signaling is possible.
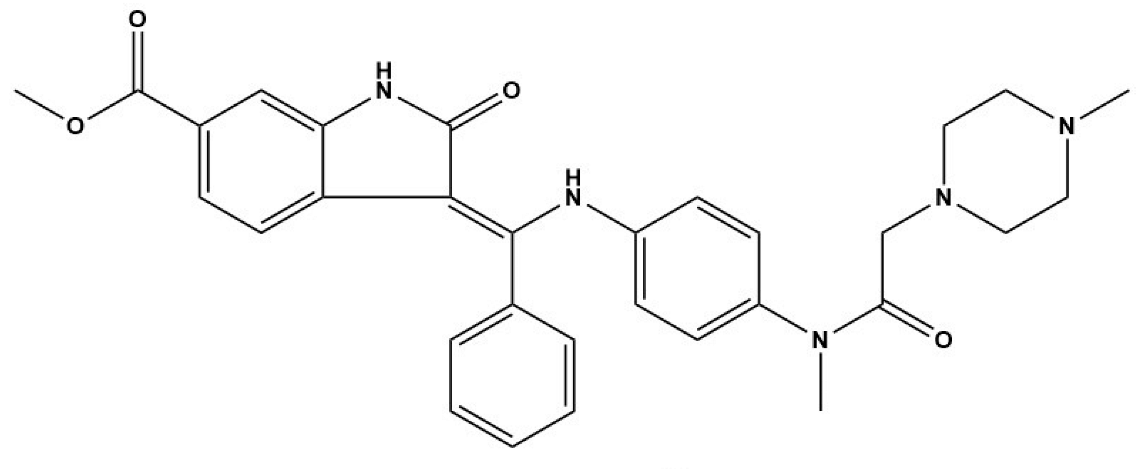
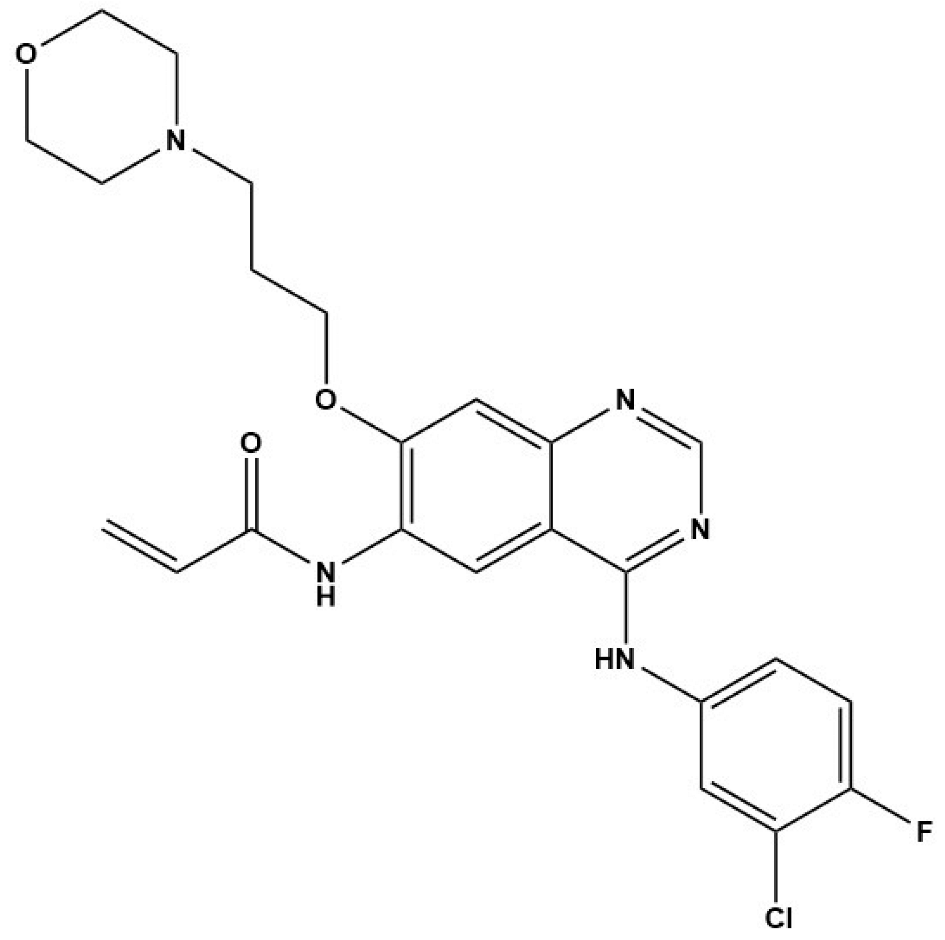
In Cheng’s study, EGFR inhibitors (BIBW2992 and CI-1033) and the MEK/ERK inhibitor (U0126) displayed strong inhibitory effects on the viability of E. multilocularis metacestode germinal cells in vitro [33]. Concurrently, BIBW2992 showed strong protoscolicidal activities for E. multilocularis metacestodes in the infected mice used in the study [33]. Furthermore, the results of Forster’s study demonstrate that BIBF 1120, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has a clear concentration-dependent parasiticidal effect on E. multilocularis metacestode vesicles in vitro by inhibiting the activity of three Echinococcus-derived FGF receptors [32]. Thus, we speculate that the excessive expression of EGF and FGF in the fibrotic liver caused by E. granulosus and E. multilocularis infection is indispensable for E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestode growth and development. This finding further suggests that EGFR and FGFR signaling are potential drug targets for the treatment of echinococcosis. However, further exploration of new methods for screening anti-Echinococcus drugs using EGFR and FGFR signaling as target molecules is required.
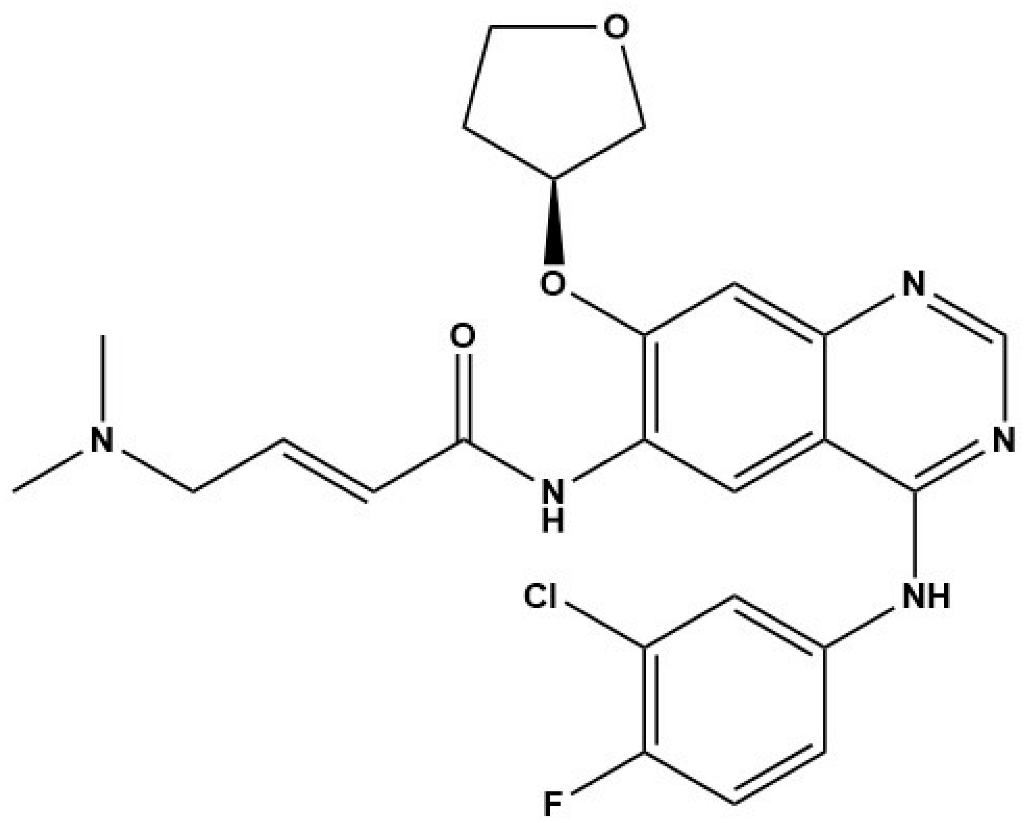
Additionally, in in vitro cultivation systems of E. multilocularis larvae, the addition of human insulin can promote the phosphorylation of two insulin receptor-like kinases (EmIR1 and EmIR2), which are mainly distributed in Echinococcus’s glycogen storage cells, thereby boosting the increase in glucose uptake in E. multilocularis metacestode germinal cells [31,63]. However, the insulin receptor inhibitor HNMPA(AM)3 was shown to prevent E. multilocularis germinal cells from developing into metacestodes by inhibiting insulin signaling in the parasite [31]. Moreover, data from Yuan’s study show that anacardic acid, a natural product isolated from Brazilian cashew nutshell liquid, inhibited E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestode development in vitro and in infected mice, accompanied by the suppression of angiogenesis in the liver around E. multilocularis metacestodes and the downregulation of the expression of VEGF in the mice [52]. This finding indicates that inhibiting excessive vascularization caused by E. multilocularis metacestode infection in the host liver for the treatment of echinococcosis seems feasible. Therefore, the results of Jiang’s study show that the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib not only damaged E. multilocularis metacestode vesicles in vitro but also inhibited the development of E. multilocularis metacestodes in mice [84], accompanied by the inhibition of pathological angiogenesis. More importantly, anti-Echinococcus trials involving more inhibitors of RTK signaling should be initiated in vitro and in vivo to prove the efficacy of screening anti-Echinococcus drugs for RTK signaling in the future.
Overall, many putative RTK signaling inhibitors have been shown to suppress the larval growth and development of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis in vitro and/or in vivo, accompanied by a significant decrease in the expression of RTK signaling molecules (Table 3). Thus, the results of such investigations support RTK signaling as a potential and important drug target for the treatment of echinococcosis, and RTK signaling inhibitors represent promising anti-echinococcal drugs. However, the clinical use of RTK signaling inhibitors in in vivo trials still requires further exploration, although the results of the majority of the published studies conducted in vitro support this finding.

Table 3.
TKR signaling inhibitors for the potential treatment of echinococcosis.
7. Conclusions and Outlook
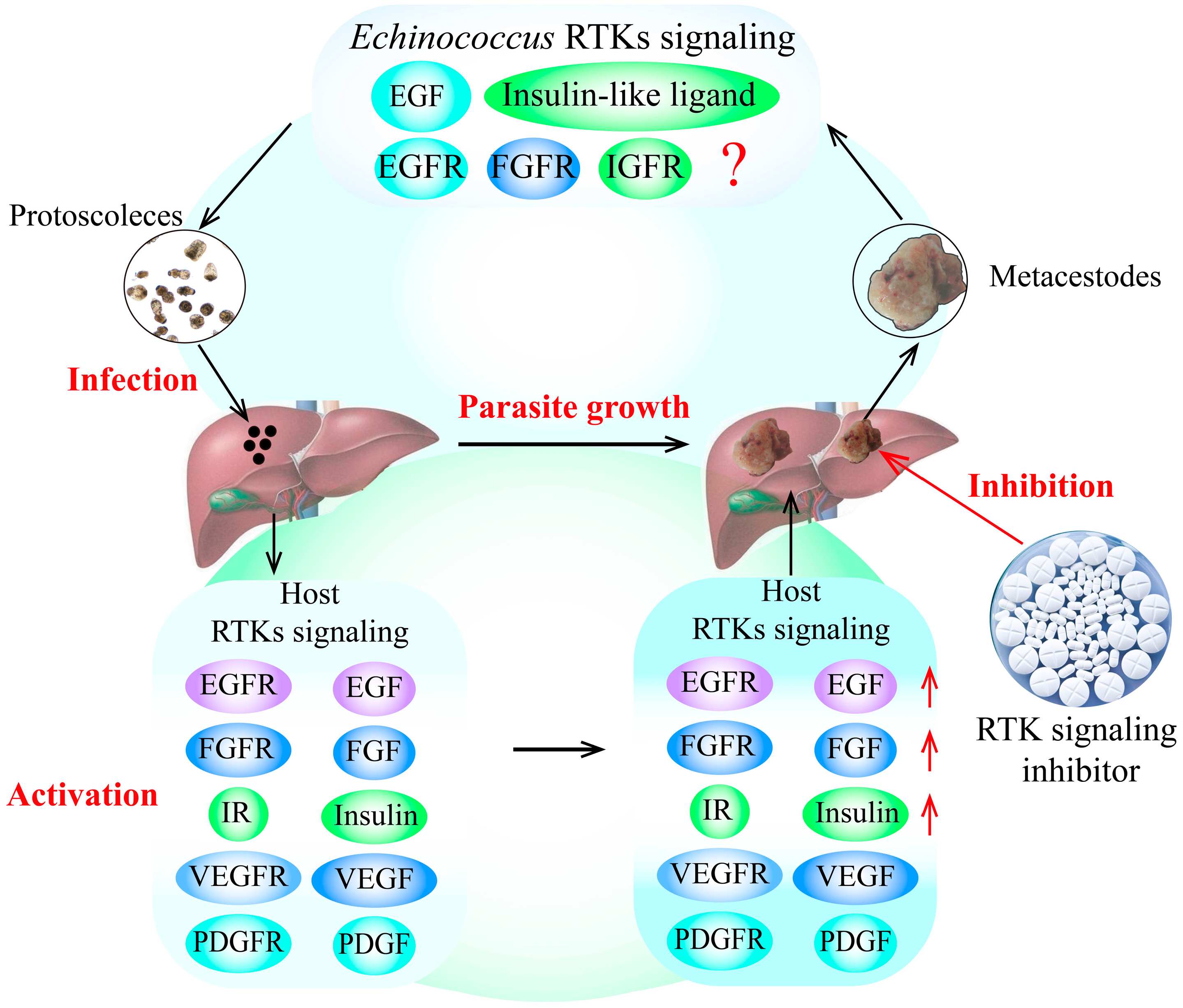
E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestode infection can cause excessive activation of RTK signaling pathways in the host, significantly increasing the expression of growth factors and hormone ligands. Furthermore, the over-expression of these growth factors and hormones in RTK signaling pathways in the host can stimulate the growth and development of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestodes in vitro, possibly by activating the specific receptors of RTK signaling in the parasite, as the receptors from the parasite and its intermediate hosts have highly homologous protein sequences. Additionally, some putative RTK signaling pathway inhibitors block the growth and development of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestodes, which is performed by downregulating RTK signaling pathways (Figure 1).
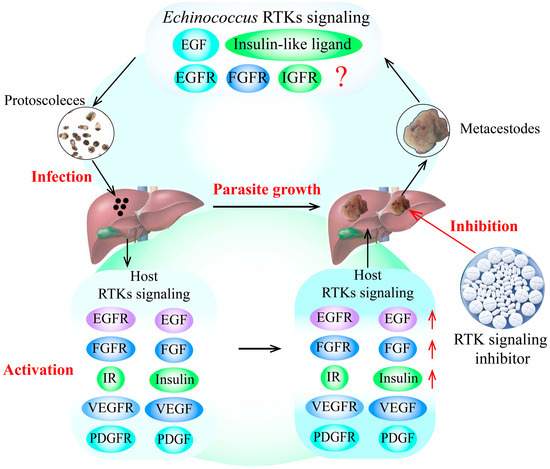
Figure 1.
RTK signaling as a potential drug target for the treatment of echinococcosis. The findings indicate that the growth factors and hormone ligands involved in RTK signaling in the host are over-activated by E. granulosus and E. multilocularis infection. These over-expressed ligands can stimulate the growth and development of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestodes by activating the specific receptors of RTK signaling in the parasite, indicating that RTK signaling may be an important drug target for the treatment of echinococcosis. In addition, the putative inhibitors of RTK signaling can block the development of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis metacestodes by decreasing the expression of RTK signaling molecules, indicating that TKIs are potential drugs for the treatment of echinococcosis. The red arrows indicates the upregulation of RTK siganling molecules expression, and the red question mark indictates that whether other host growth factors can combinate some Echinococcus receptors in RTK signaling to regulate Echinococcus spp. development remains unknown. Abbreviations: EGF, epidermal growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IR, insulin receptor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; RTKs, receptor tyrosine kinases; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
Therefore, RTK signaling plays an important contributory role in Echinococcus–host interactions, and it is an important drug target for echinococcosis. RTK signaling pathway inhibitors stand as promising future anti-echinococcal drugs. However, future efforts toward drug exploration for echinococcosis should focus on RTK signaling in vitro and in vivo. In addition, some lead compounds targeting RTK signaling need in-depth investigation before clinical trials are conducted.
Author Contributions
Writing, design, and analysis of the manuscript (H.G., Z.B., X.M., W.H. and F.Z.); critical revisions, coordination, and drafting of the manuscript (T.Z., Z.F. and H.G.). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFC2300800; 2021YFC2300802), the Open Project program of the NHC Key Laboratory of Parasite and Vector Biology (National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, the Chinese Center for Diseases Control and Prevention) (NHCKFKT2022-02), the Open Project program of the NHC Key Laboratory of Echinococcosis Prevention and Control (2021WZK1003). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, and the writing of this report.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank Bolor Bold from the School of Global Health, Chinese Center for Tropical Diseases Research, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, for language polishing of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
ABZ, albendazole; AE, alveolar echinococcosis; AS, alternativesplicin; CE, cystic echinococcosis; E. multilocularis, Echinococcus multilocularis; E. granulosus, Echinococcus granulosus; EGF, epidermal growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IR, insulin receptor; MCs, microcysts; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PSC, protoscolece; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
References
- Eckert, J.; Thompson, R.C. Historical aspects of echinococcosis. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knapp, J.; Gottstein, B.; Saarma, U.; Millon, L. Taxonomy, phylogeny and molecular epidemiology of Echinococcus multilocularis: From fundamental knowledge to health ecology. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 213, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, P.; Menezes da Silva, A.; Akhan, O.; Mullhaupt, B.; Vizcaychipi, K.; Budke, C.; Vuitton, D.A. The Echinococcoses: Diagnosis, clinical management and burden of disease. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 96, 259–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deplazes, P.; Rinaldi, L.; Alvarez Rojas, C.A.; Torgerson, P.R.; Harandi, M.F.; Romig, T.; Antolova, D.; Schurer, J.M.; Lahmar, S.; Cringoli, G.; et al. Global distribution of alveolar and cystic echinococcosis. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 315–493. [Google Scholar]
- Conraths, F.J.; Deplazes, P. Echinococcus multilocularis: Epidemiology, surveillance and state-of-the-art diagnostics from a veterinary public health perspective. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 213, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deplazes, P.; Gottstein, B.; Junghanss, T. Alveolar and cystic echinococcosis in Europe: Old burdens and new challenges. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 213, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda, J.R.; Buttke, D.E.; Ballweber, L.R. Echinococcus spp. Tapeworms in North America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Ning, X.; Shi-Jie, Y.; Dong, W.; Jia, P. Epidemiological characteristics of canine Echinococcus infection in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi 2017, 29, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, A.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Loukas, A.; McManus, D.P.; Mulvenna, J. Proteomic characterisation of Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cyst fluid from sheep, cattle and humans. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiderski, Z.; Miquel, J.; Azzouz-Maache, S.; Petavy, A.F. Echinococcus multilocularis (Cestoda, Cyclophyllidea, Taeniidae): Origin, differentiation and functional ultrastructure of the oncospheral tegument and hook region membrane. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C. Biology and systematics of Echinococcus. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 65–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Urach Monteiro, D.; de Azevedo, M.I.; Weiblen, C.; Correia Ribeiro, T.; Emmanouilidis, J.; Tonin, A.A.; Botton, S.; Rue, M.L. Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto, Echinococcus canadensis (G7), and Echinococcus ortleppi in fertile hydatid cysts isolated from cattle in Southern Brazil. Acta. Trop. 2016, 164, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romig, T.; Deplazes, P.; Jenkins, D.; Giraudoux, P.; Massolo, A.; Craig, P.S.; Wassermann, M.; Takahashi, K.; Rue, M. Ecology and life cycle patterns of Echinococcus Species. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 213–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Craig, P.S.; Hegglin, D.; Lightowlers, M.W.; Torgerson, P.R.; Wang, Q. Echinococcosis: Control and prevention. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 96, 55–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moro, P.; Schantz, P.M. Echinococcosis: A review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 13, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakos, M.; Sargedi, C.; Stefanaki, C.; Safioleas, C.; Matthaiopoulou, I.; Safioleas, M. Anthelminthic treatment: An adjuvant therapeutic strategy against Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitol. Int. 2009, 58, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemphill, A.; Muller, J. Alveolar and cystic echinococcosis: Towards novel chemotherapeutical treatment options. J. Helminthol. 2009, 83, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiger, U.; Cotting, J.; Reichen, J. Albendazole treatment of echinococcosis in humans: Effects on microsomal metabolism and drug tolerance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1990, 47, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, A.C.; Celina, E.M. Efficacy of albendazole in combination with thymol against Echinococcus multilocularis protoscoleces and metacestodes. Acta. Trop. 2014, 140, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, S.R.; Miller, W.T. Receptor tyrosine kinases: Mechanisms of activation and signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2007, 19, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibilia, M.; Kroismayr, R.; Lichtenberger, B.M.; Natarajan, A.; Hecking, M.; Holcmann, M. The epidermal growth factor receptor: From development to tumorigenesis. Differentiation 2007, 75, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roviello, G.; Ravelli, A.; Polom, K.; Petrioli, R.; Marano, L.; Marrelli, D.; Roviello, F.; Generali, D. Apatinib: A novel receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016, 372, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, N.; Fardi, E.; Ghaderi, H.; Palizdar, S.; Khorram, R.; Vafadar, R.; Ghanaatian, M.; Rezaei-Tazangi, F.; Baziyar, P.; Ahmadi, A.; et al. Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Jian, J.; Jiang, Z.; Van Schepdael, A. Screening assays for tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 223, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; McManus, D.P.; Fogarty, C.E.; Jones, M.K.; You, H. Schistosoma mansoni fibroblast growth factor receptor A orchestrates multiple functions in Schistosome biology and in the host-parasite interplay. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 868077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Moreira, B.; Weber, M.H.W.; Haeberlein, S.; Mokosch, A.S.; Spengler, B.; Grevelding, C.G.; Falcone, F.H. Drug repurposing and De Novo drug discovery of protein kinase inhibitors as new drugs against Schistosomiasis. Molecules 2022, 27, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Lu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. The genome of the hydatid tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, K. The role of evolutionarily conserved signalling systems in Echinococcus multilocularis development and host-parasite interaction. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 199, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, K.; Koziol, U. Echinococcus-Host interactions at cellular and molecular levels. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 147–212. [Google Scholar]
- Hemer, S.; Konrad, C.; Spiliotis, M.; Koziol, U.; Schaack, D.; Förster, S.; Gelmedin, V.; Stadelmann, B.; Dandekar, T.; Hemphill, A.; et al. Host insulin stimulates Echinococcus multilocularis insulin signalling pathways and larval development. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, S.; Koziol, U.; Schäfer, T.; Duvoisin, R.; Cailliau, K.; Vanderstraete, M.; Dissous, C.; Brehm, K. The role of fibroblast growth factor signalling in Echinococcus multilocularis development and host-parasite interaction. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0006959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, X.; Dai, M.; Wu, J.; Guo, X.; Tian, H.; Heng, Z.; Lu, Y.; Chai, X.; et al. EGF-mediated EGFR/ERK signaling pathway promotes germinative cell proliferation in Echinococcus multilocularis that contributes to larval growth and development. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, S.A. Acquired resistance to drugs targeting receptor tyrosine kinases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trenker, R.; Jura, N. Receptor tyrosine kinase activation: From the ligand perspective. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2020, 63, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, S.; Lu, L.; Fan, Z.; Ye, S. Activation of neurotrophin signalling with light inducible receptor tyrosine kinases. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelmedin, V.; Spiliotis, M.; Brehm, K. Molecular characterisation of MEK1/2- and MKK3/6-like mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases (MAPKK) from the fox tapeworm Echinococcus multilocularis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, K.; Bergmann, M.; Spiliotis, M.; Brehm, K. A MEKK1-JNK mitogen activated kinase (MAPK) cascade module is active in Echinococcus multilocularis stem cells. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0010027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, J.A.; Dávila, V.A.; Brehm, K.; Cumino, A.C. Metformin Suppresses Development of the Echinococcus multilocularis Larval Stage by Targeting the TOR Pathway. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Sartori, M.J.; Mezzano, L.; de Fabro, S.P. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) in the human placental infection with Trypanosoma cruzi. Placenta 2004, 25, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz-Feliciano, L.; Van Grol, J.; Portillo, J.A.; Liew, L.; Liu, B.; Carlin, C.R.; Carruthers, V.B.; Matthews, S.; Subauste, C.S. Toxoplasma gondii-induced activation of EGFR prevents autophagy protein-mediated killing of the parasite. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, A.I.; Carvalho, T.G.; Wilkes, J.M.; Doerig, C. A secreted Plasmodium falciparum kinase reveals a signature motif for classification of tyrosine kinase-like kinases. Microbiology 2013, 159, 2533–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, H.; Skelly, P.J.; Shoemaker, C.B. The Schistosoma mansoni epidermal growth factor receptor homologue, SER, has tyrosine kinase activity and is localized in adult muscle. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1996, 83, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Zhai, X.; Huang, S.; Jiang, L.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J. Protein kinases: Potential drug targets against Schistosoma japonicum. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 691757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, I.J.; Zarowiecki, M.; Holroyd, N.; Garciarrubio, A.; Sanchez-Flores, A.; Brooks, K.L.; Tracey, A.; Bobes, R.J.; Fragoso, G.; Sciutto, E.; et al. The genomes of four tapeworm species reveal adaptations to parasitism. Nature 2013, 496, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, S.-J.V. Recent Progress in Regulation of Aging by Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Cells 2022, 45, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konrad, C. Identification and molecular characterisation of a gene encoding a member of the insulin receptor family in Echinococcus multilocularis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.S.; Kim, J.G.; Han, X.; Kang, I.; Kong, Y. Comparison of Echinococcus multilocularis and Echinococcus granulosus hydatid fluid proteome provides molecular strategies for specialized host-parasite interactions. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97009–97024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.J.; Sun, X.D.; Luo, Y.P.; Pang, H.S.; Ma, X.M.; Zhang, T.; Jing, T.; Hu, W.; Shen, Y.J.; Cao, J.P. Anti-echinococcal effect of verapamil involving the regulation of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II response in vitro and in a murine infection model. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Chong, S.; Qin, M.; Li, S.; Wei, R.; Zhao, Y. Mechanism of fibrosis induced by Echinococcus spp. Diseases 2019, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Jiang, T.; Qi, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Aibibula, M.; Min, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X. Role of cytokines on the progression of liver fibrosis in mice infected with Echinococcus multilocularis. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2021, 14, 5651–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Song, X.; Lv, W.; Xin, Q.; Wang, L.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Liao, W.; Lian, S.; Jing, T. Effect of anacardic acid against echinococcosis through inhibition of VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosratabadi, S.J.; Roodbari, N.H.; Modarresi, M.H.; Farsinejad, A.; Harandi, M.F. The Effect of alpha-tocopherol on the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and transforming growth factor beta genes in three developmental stages of Echinococcus granulosus. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2020, 15, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yimingjiang, M.; Aini, A.; Tuergan, T.; Zhang, W. Differential gene expression profiling in alveolar echinococcosis identifies potential biomarkers associated with angiogenesis. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, Microvessel Density-CD34 in Hepaticalveolar Hydatid Tissue in Gerbil Model; Shihezi University: Shihezi, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.J. The Study of Relation between Calcium/Angiogenesis Signal Pathway and Growth Status of Hydatid; Lanzhou University: Lanzhou, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Teng, H.; Deng, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ai, C.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J.; Chen, L. Effects of Rhodiola rosea and its major compounds on insulin resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Future Foods 2022, 2, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglou, S.G.; Bendena, W.G.; Chin-Sang, I. An overview of the insulin signaling pathway in model organisms Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans. Peptides 2021, 145, 170640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Zhang, W.; Jones, M.K.; Gobert, G.N.; Mulvenna, J.; Rees, G.; Spanevello, M.; Blair, D.; Duke, M.; Brehm, K.; et al. Cloning and characterisation of Schistosoma japonicum insulin receptors. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayath, N.; Vicogne, J.; Ahier, A.; BenYounes, A.; Konrad, C.; Trolet, J.; Viscogliosi, E.; Brehm, K.; Dissous, C. Diversification of the insulin receptor family in the helminth parasite Schistosoma mansoni. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshani, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Rezaei, M.; Afgar, A.; Keyhani, A.R.; Mohammadi, M.A.; Dabiri, S.; Fasihi Harandi, M. Natural history of Echinococcus granulosus microcyst development in long term in vitro culture and molecular and morphological changes induced by insulin and BMP-4. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1068602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Huo, L.; Mo, X.; Jiang, B.; Luo, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, J.; Ma, X.; Jing, T.; Feng, Z.; et al. Suppressive effect of pseudolaric acid B on Echinococcus multilocularis involving regulation of TGF-beta1 signaling in vitro and in vivo. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1008274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Su, N.; Yang, J.; Tan, Q.; Huang, S.; Jin, M.; Ni, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Luo, F.; et al. FGF/FGFR signaling in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Gong, P.; Yu, Y.; Li, J. Activation of a neospora caninum EGFR-like kinase facilitates intracellular parasite proliferation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Tian, H.; Liu, F.; Luo, D.; Wang, Y. EmCyclinD-EmCDK4/6 complex is involved in the host EGF-mediated proliferation of Echinococcus multilocularis germinative cells via the EGFR-ERK pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 968872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.; Thi-Kim Vu, H.; Mohan, R.D.; McKinney, S.A.; Seidel, C.W.; Alexander, R.; Gotting, K.; Workman, J.L.; Sanchez Alvarado, A. EGF signaling directs neoblast repopulation by regulating asymmetric cell Division in Planarians. Dev. Cell. 2016, 38, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Kim, K.H.; Lim, H.J.; Adashek, J.J.; Persha, H.E.; Okamura, R.; Lee, S.; Sicklick, J.K.; Kato, S.; et al. Targeting the FGF/FGFR axis and its co-alteration allies. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Therapeutic uses of FGFs. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 53, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titchenell, P.M.; Chu, Q.; Monks, B.R.; Birnbaum, M.J. Hepatic insulin signalling is dispensable for suppression of glucose output by insulin in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Bovi, R.J.; Miller, W.T. Expression and purification of functional insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 holoreceptors from mammalian cells. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 536, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Cao, J.; Zhang, H.; Field, M.C.; Yin, J. Extracellular vesicles secreted by Echinococcus multilocularis: Important players in angiogenesis promotion. Microbes Infect. 2023, 25, 105147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zuo, B.; He, Y. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells as potential drivers of liver fibrosis (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 29, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stadelmann, B.; Spiliotis, M.; Muller, J.; Scholl, S.; Muller, N.; Gottstein, B.; Hemphill, A. Echinococcus multilocularis phosphoglucose isomerase (EmPGI): A glycolytic enzyme involved in metacestode growth and parasite-host cell interactions. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, N.B.; Tang, B.; Wang, G.Z.; Xie, R.; Hu, C.J.; Wang, S.M.; Wu, Y.Y.; Liu, E.; Xie, X.; Yang, S.M. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) upregulates heparanase expression via the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling pathway for gastric cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2015, 361, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, P. Effect of FGF-21 on implant bone defects through hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, F.; Giovannetti, E.; Peters, G.J.; Firuzi, O. Combination of HGF/MET-targeting agents and other therapeutic strategies in cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 160, 103234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, D.M.; Roy, A.; Kato, T.; Cecchi, F.; Lee, Y.H.; Matsumoto, K.; Bottaro, D.P. Targeting the hepatocyte growth factor/Met pathway in cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, N.; Huang, F.; Tan, G. Effect of hepatocyte growth factor signaling pathway activation on Plasmodium berghei infection. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2010, 4, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; King, J.G.; Tweedell, R.E.; Jost, P.J.; Boddey, J.A.; Dinglasan, R.R. The acute transcriptomic and proteomic response of HC-04 hepatoma cells to hepatocyte growth factor and its implications for Plasmodium falciparum sporozoite invasion. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2014, 13, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaga, T.; Kawano, H.; Sakaguchi, M.; Nakazawa, T.; Taniyama, Y.; Morishita, R. Hepatocyte growth factor stimulated angiogenesis without inflammation: Differential actions between hepatocyte growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2012, 57, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Yang, S.; Ingle, G.; Zlot, C.; Rangell, L.; Kowalski, J.; Schwall, R.; Ferrara, N.; Gerritsen, M.E. Hepatocyte growth factor enhances vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.; Casaravilla, C.; Barrios, A.A.; Ferreira, A.M. Parasite molecules and host responses in cystic echinococcosis. Parasite Immunol. 2016, 38, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, K.; Koziol, U. On the importance of targeting parasite stem cells in anti-echinococcosis drug development. Parasite 2014, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Tan, X.; Gui, X.; Liao, Z.; Li, Z.; Xhen, X.; Wu, X. Effect of sunitinib against Echinococcus multilocularis through inhibition of VEGFA-induced angiogenesis. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).