Diversity and Plasticity of Virulent Characteristics of Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
1. Introduction
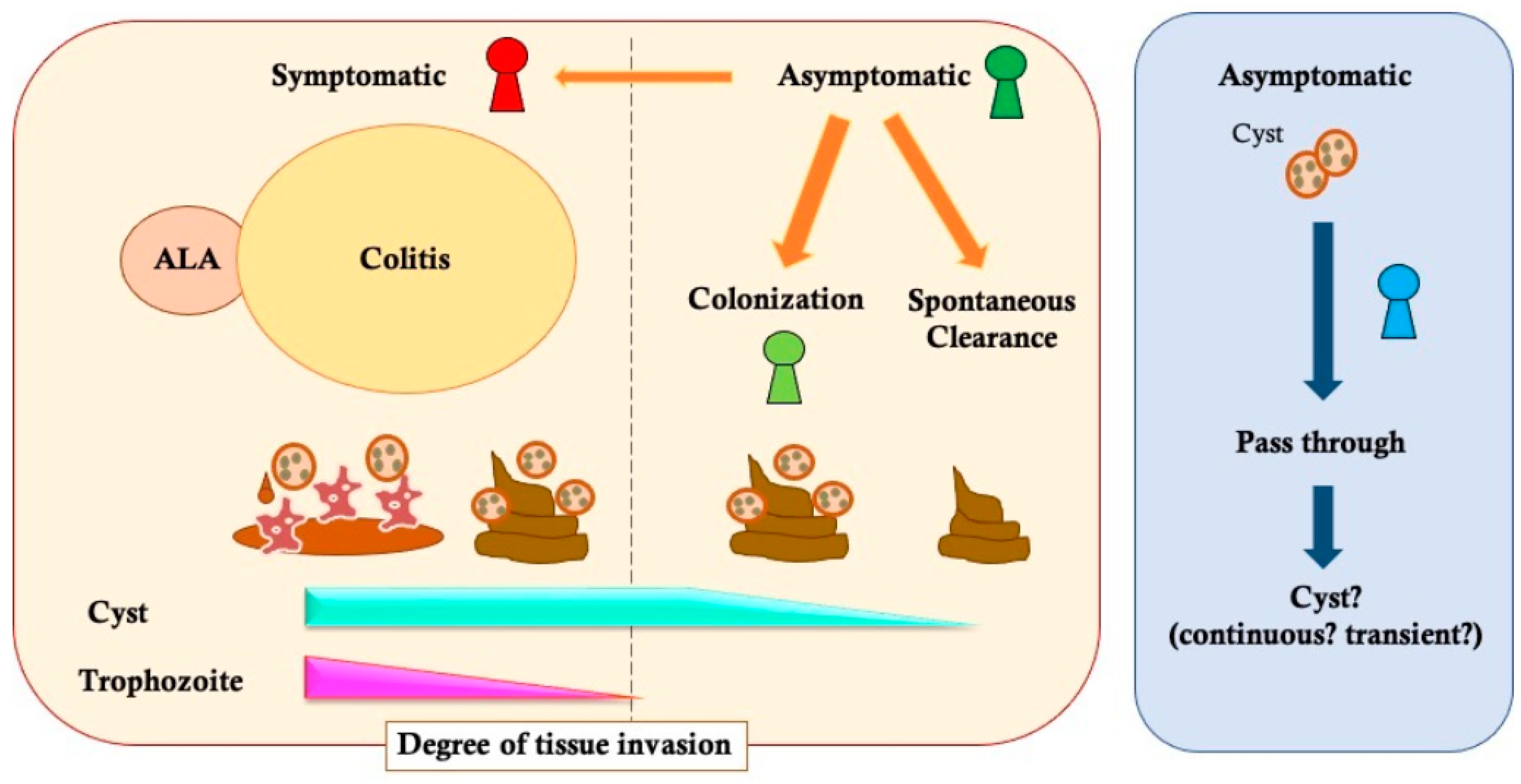
2. Variety of E. histolytica Infectious Disease Status
2.1. Symptomatic Infection
2.2. Asymptomatic Infection
2.3. The Diagnostic Gap about “Cyst Carrier”
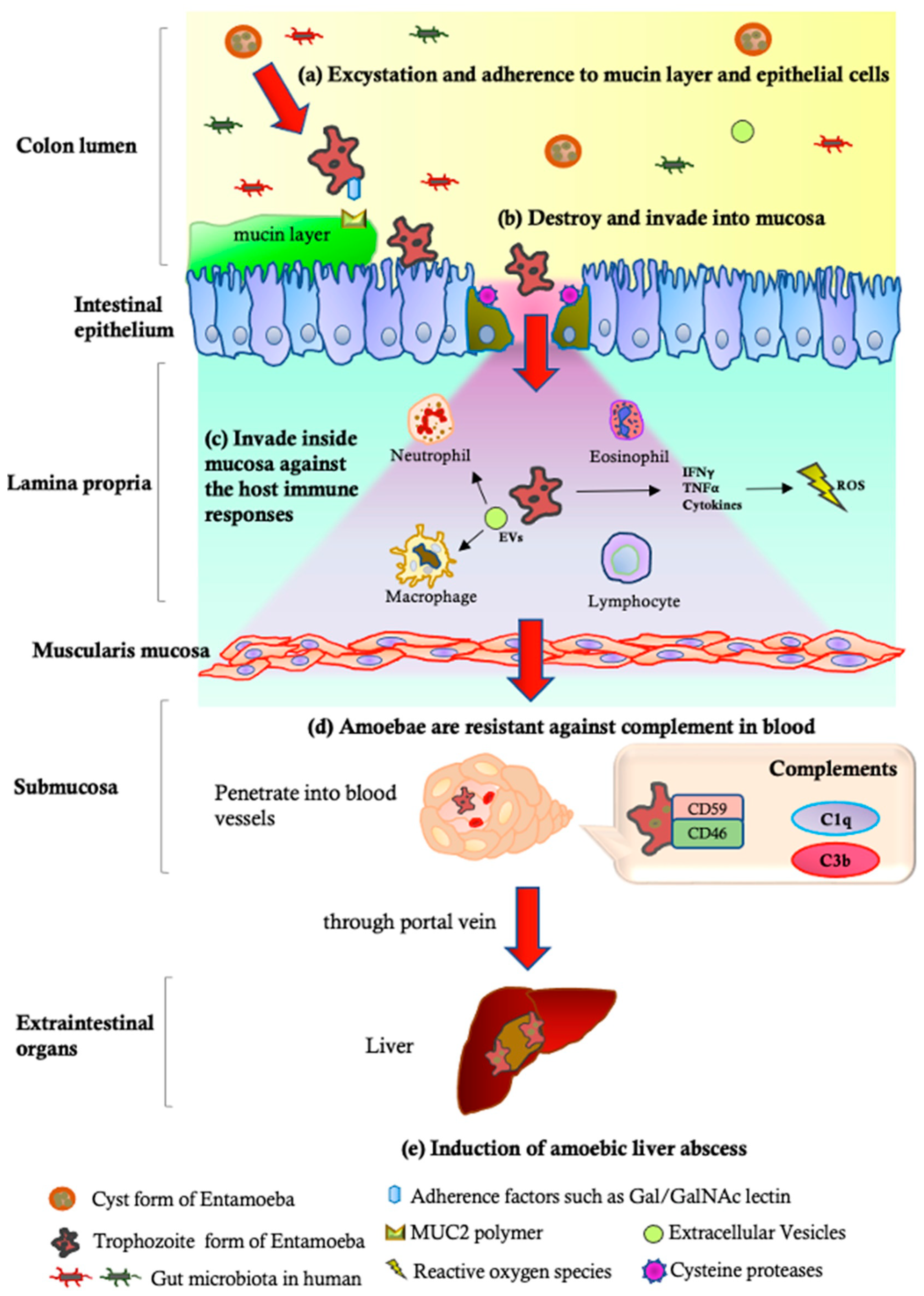
3. Plasticity of E. histolytica Virulence
3.1. Attenuation and Reactivation of the Parasite Virulence through Animal Models
3.2. Impacts of the Parasite’s Factors on the Diversity of Amoebic Infection
| Pathogenetic Steps | Parasite | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. histolytica | E. dispar | |||
| Pathological Strain, HM1:IMSS | Non-Pathological Strain, Rahman | |||
| (a) Excystation and adherence to mucin layer | Gal/GalNAc-specific lectins [77], LPPG [77], KERP1 and KERP2 [78], STIRP [79], ADH112 [80], Jacob lectin [82], SREHP [83] | Deficiency in the expression of the 35 kDa subunits of the Gal-lectin complex [117] | Decreased surface lectin; deficiencies in immunodominant 1G7 epitopes [118] | [77,78,79,80,82,83,117,118] |
| (b) Destruction and invasion into mucosa | CPs [64,85,109], AP [88], CPADH [119], Phospholipase [120], and ROMs [121] | Decreased ESP (eg. Carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes) [122]; decreased CP activity in response to degradation [87] | Rarely expression levels of CP-1 and CP-5 [109]; decreased CP activity in response to degradation [87] | [64,85,88,109,119,120,121] |
| (c) Invasion inside the mucosa and escape from the host immune responses | Gal/GalNAc lectin [123], ROM1 [124], CPs [125], LPG [126], Phosphatidylcholine [120], HSPs [127], Superoxide dismutase [128], NADPH:flavin oxidoreductase [129], and MIF [130] | Decreased mRNA levels of MUC2, poly-lg receptor, and SOCS1 [131] | No induction of NET formation and ROS production [132] | [120,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132] |
| (d) Amoebic resistance to complements | CRT 1 [102], Gal/GalNAc lectins [97], LPG [133], and Secretory IgA proteases [134] | Sensitive to complement [135] | Decreased expression of CRT levels [102]; near-total absence of LPG-like glycoconjugates to protect against complements [116]; highly sensitive to C9 complements [115] | [97,102,115,116,133,134,135] |
| (e) Induction of amoebic liver abscess | AP [89,90], Gal/GalNAc lectins [117,136], CPs [64,134], Phospholipases [137,138], Peroxynitrite [106] | ND | Ability to induce liver abscess in inoculated animals [110,111,112,113,114] | [64,89,90,106,110,111,112,113,114,117,134,136,137,138] |
4. Variation in E. histolytica Strains
4.1. The List of Major E. histolytica Laboratory Strains Studied until Now
4.2. Genetic Variation among the Main Laboratory Strains
4.3. Genetic Differences and Variable Patterns of Gene Expression between Laboratory and Clinical Strains
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanley, S.L. Amoebiasis. Lancet 2003, 361, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabati, H.; Kassiri, H.; Shamloo, E.; Akbari, M.; Atamaleki, A.; Sahlabadi, F.; Linh, N.T.T.; Rostami, A.; Fakhri, Y.; Khaneghah, A.M. The association between the lack of safe drinking water and sanitation facilities with intestinal Entamoeba spp. infection risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagawa, Y.; Nagashima, M.; Gatanaga, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Oka, S.; Yokoyama, K.; Shinkai, T.; Sadamasu, K.; Watanabe, K. Seroprevalence of Entamoeba histolytica at a voluntary counselling and testing centre in Tokyo: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e031605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagawa, Y.; Shimogawara, R.; Takano, M.; Aoki, T.; Mizushima, D.; Gatanaga, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Oka, S.; Yagita, K.; Watanabe, K. Identification of asymptomatic Entamoeba histolytica infection by a serological screening test: A cross-sectional study of an HIV-negative men who have sex with men cohort in Japan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0009793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Nagata, N.; Sekine, K.; Igari, T.; Tanuma, J.; Kikuchi, Y.; Oka, S.; Gatanaga, H. Asymptomatic intestinal amebiasis in Japanese HIV-1-infected individuals. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, R.; Huston, C.D.; Hughes, M.; Houpt, E.; Petri, W.A. Amebiasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, A.; Chand, A.B.; Pokhrel, N.; Gurung, P.; Rai, J.R.; Bajracharya, S.; Acharya, S.; Shrestha, L.B. Status of Intestinal Parasitic Infections in a Tertiary Care Center. J. Nepal. Health Res. Counc. 2022, 20, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, J.; Akhoundi, M.; Haouchine, D.; Marteau, A.; Mantelet, S.; Wind, P.; Benamouzig, R.; Bouchaud, O.; Dhote, R.; Izri, A. Updates on the worldwide burden of amoebiasis: A case series and literature review. J. Infect. Public. Health 2022, 15, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Phillips, G.E.; McBride, W.J.H.; Hanson, J. Case Report: Endemic Amebiasis in Australia: Implications for Residents, Travelers, and Clinicians. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.H.; Chen, B.C.; Chou, Y.C.; Chien, W.C.; Chung, C.H.; Hsieh, C.J.; Yu, C.P. The Epidemiology of Entamoeba histolytica infection and its associated risk factors among domestic and imported patients in Taiwan during the 2011-2020 period. Medicina 2022, 58, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Petri, W.A. Molecular biology research to benefit patients with Entamoeba histolytica infection. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 98, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weedall, G.D.; Clark, C.G.; Koldkjaer, P.; Kay, S.; Bruchhaus, I.; Tannich, E.; Paterson, S.; Hall, N. Genomic diversity of the human intestinal parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiyer, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Bhattacharya, S. Advances in Entamoeba histolytica biology through transcriptomic analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Ganguly, S. Evolutionary genomics and population structure of Entamoeba histolytica. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Koutero, M.; Dillies, M.A.; Varet, H.; Lopez-Camarillo, C.; Coppée, J.Y.; Hon, C.C.; Guillén, N. Extensive transcriptome analysis correlates the plasticity of Entamoeba histolytica pathogenesis to rapid phenotype changes depending on the environment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, E.; Perdomo, D. Entamoeba histolytica under Oxidative Stress: What Countermeasure Mechanisms Are in Place? Cells 2017, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, Y.; Nagata, N.; Yagita, K.; Watanabe, K.; Okubo, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Gatanaga, H.; Oka, S. Clinical Features and Gut Microbiome of Asymptomatic Entamoeba histolytica Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3163–e3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, N.; Shimbo, T.; Sekine, K.; Tanaka, S.; Niikura, R.; Mezaki, K.; Morino, E.; Yazaki, H.; Igari, T.; Ohmagari, N.; et al. Combined endoscopy, aspiration, and biopsy analysis for identifying infectious colitis in patients with ileocecal ulcers. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 673–680.e672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Broucke, S.; Verschueren, J.; Van Esbroeck, M.; Bottieau, E.; Van den Ende, J. Clinical and microscopic predictors of Entamoeba histolytica intestinal infection in travelers and migrants diagnosed with Entamoeba histolytica/dispar infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, B.S.; Tuteja, A.K.; Kaur, M.; Alam, S.M.; Aggarwal, D.S.; Mehta, S.P.; Baveja, U.K. Entamoeba histolytica cyst passers. Clinical profile and spontaneous eradication of infection. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1993, 38, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, R.; Baveja, U.; Anand, B.S. Entamoeba histolytica cyst passers: Clinical features and outcome in untreated subjects. Lancet 1984, 2, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuar, T.S.; Al-Mekhlafi, H.M.; Abdul Ghani, M.K.; Azreen, S.N.; Salleh, F.M.; Ghazali, N.; Bernadus, M.; Moktar, N. Different clinical outcomes of Entamoeba histolytica in Malaysia: Does genetic diversity exist? Korean J. Parasitol. 2013, 51, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, R.; Cooper, C.J.; Ramirez-Vega, R.; Huerta-Alardin, A.; Boman, D.; Zuckerman, M.J. Clinical manifestations and endoscopic findings of amebic colitis in a United States-Mexico border city: A case series. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirley, D.T.; Farr, L.; Watanabe, K.; Moonah, S. A Review of the Global Burden, New Diagnostics, and Current Therapeutics for Amebiasis. Open. Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roure, S.; Valerio, L.; Soldevila, L.; Salvador, F.; Fernández-Rivas, G.; Sulleiro, E.; Mañosa, M.; Sopena, N.; Mate, J.L.; Clotet, B. Approach to amoebic colitis: Epidemiological, clinical and diagnostic considerations in a non-endemic context (Barcelona, 2007–2017). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, B.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Zong, Y. Characteristics of endoscopic and pathological findings of amebic colitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasszade, J.H.; Little, R.; Yeaman, F.; Robertson, M.; Bell, S. Amoebic colitis: A case series of a recurring missed diagnosis. JGH Open 2021, 5, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, T.Z.; Kin, W.W.; Mustafa, S.; Ahmed, A.; Noordin, R.; Cheong, T.G.; Alfonso, O.G.; Huat, L.B. Detection of Entamoeba histolytica in experimentally induced amoebic liver abscess: Comparison of three staining methods. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, D.A.; Moonah, S. Fulminant Amebic Colitis after Corticosteroid Therapy: A Systematic Review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria-Hernández, J.A.; Ventura-Saucedo, A.; López-Morones, A.; Martínez-Hernández, S.L.; Medina-Rosales, M.N.; Muñoz-Ortega, M.; Ávila-Blanco, M.E.; Cervantes-García, D.; Barba-Gallardo, L.F.; Ventura-Juárez, J. Case report: Multiple and atypical amoebic cerebral abscesses resistant to treatment. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, K.M.; Dundoo, M.; Dunne, E.F.; Dwinnell, B.G.; Stephens, J.K. Inguinal lymphadenitis caused by Entamoeba histolytica: Case report and literature review. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2000, 75, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.; Soni, S.; Gupta, A.; Agstam, S. A case report of ruptured amoebic liver abscess causing cardiac tamponade and requiring pericardial window. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2020, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Leiva, J.; Jeri-Yabar, A.; Hernandez Fernandez, W.; Damian Bello, E. Biliary Peritonitis due to a Ruptured Amebic Liver Abscess Mimicking a Periampullary Tumor and Liver Metastases with the Elevation of CA 19-9 and CA 125: A Case Report. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 26, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.H.; Ismail, A.N. Endometrial amoebiasis. Eur. J. Obs. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 1993, 52, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecuit, M.; Martinez, F.; Deray, G.; Beaufils, H.; Gubler, M.C.; Nozais, J.P.; Bricaire, F.; Jacobs, C. Clinical and pathophysiological aspects of immune complex glomerulonephritis associated with Entamoeba histolytica abscess of the liver. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 25, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Ali, I.M.; Sack, R.B.; Farr, B.M.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Petri, W.A. Amebiasis and mucosal IgA antibody against the Entamoeba histolytica adherence lectin in Bangladeshi children. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez, E.; del Carmen Martínez, M.; Gómez, A.; Cedillo, R.; Arellano, J.; Pérez, M.E.; Ramos, F.; Morán, P.; González, E.; Valenzuela, O.; et al. HLA characterization in adult asymptomatic cyst passers of Entamoeba histolytica/E. dispar. Parasitol. Res. 1999, 85, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khaliq, I.M.A.; Mahdi, B.M. Association between Entamoeba histolytica infection and human leukocyte antigen HLA- DRB1. Ann. Med. Surg. 2018, 36, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggal, P.; Haque, R.; Roy, S.; Mondal, D.; Sack, R.B.; Farr, B.M.; Beaty, T.H.; Petri, W.A. Influence of human leukocyte antigen class II alleles on susceptibility to Entamoeba histolytica infection in Bangladeshi children. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano, J.; Peŕez-Rodríguez, M.; López-Osuna, M.; Velázquez, J.R.; Granados, J.; Justiniani, N.; Santos, J.I.; Madrazo, A.; Muñoz, L.; Kretschmer, R. Increased frequency of HLA-DR3 and complotype SCO1 in Mexican mestizo children with amoebic abscess of the liver. Parasite Immunol. 1996, 18, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Alla, M.D.; Jackson, T.F.; Rogers, T.; Reddy, S.; Ravdin, J.I. Mucosal immunity to asymptomatic Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar infection is associated with a peak intestinal anti-lectin immunoglobulin A antibody response. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3897–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, Y.; Arisaka, T.; Kawai, S.; Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Fukushima, A.; Hiraishi, H.; Chigusa, Y.; Gatanaga, H.; Oka, S.; Nozaki, T.; et al. Case Report: Acute Amebic Colitis Triggered by Colonoscopy: Exacerbation of Asymptomatic Chronic Infection with. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 101, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, M.; Kawabe, T.; Ohata, K.; Togo, G.; Hada, T.; Katamoto, T.; Tanno, M.; Matsumura, M.; Yamaji, Y.; Watabe, H.; et al. Amebic colitis in asymptomatic subjects with positive fecal occult blood test results: Clinical features different from symptomatic cases. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 934–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidin, S.; Othman, N.; Noordin, R. Update on laboratory diagnosis of amoebiasis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.K.; Haque, R.; Siddique, A.; Kabir, M.; Sherman, N.E.; Gray, S.A.; Cangelosi, G.A.; Petri, W.A. Proteomic analysis of the cyst stage of Entamoeba histolytica. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantor, M.; Abrantes, A.; Estevez, A.; Schiller, A.; Torrent, J.; Gascon, J.; Hernandez, R.; Ochner, C. Entamoeba Histolytica: Updates in Clinical Manifestation, Pathogenesis, and Vaccine Development. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 4601420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornick, S.; Chadee, K. Entamoeba histolytica: Host parasite interactions at the colonic epithelium. Tissue Barriers 2017, 5, e1283386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotter, H.; Zhang, T.; Seydel, K.B.; Stanley, S.L.; Tannich, E. Identification of an epitope on the Entamoeba histolytica 170-kD lectin conferring antibody-mediated protection against invasive amebiasis. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Yanagawa, Y.; Oka, S.; Watanabe, K. Two cases of endoscopically diagnosed amebic colitis treated with paromomycin monotherapy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, G.V.; Variyam, E.P. Noninvasive intestinal amebiasis: Entamoeba histolytica colonization without invasion. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 27, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, J.B.; Herwaldt, B.L.; Stokes, S.L.; Becher, J.A.; Roberts, J.M.; Michelson, M.K.; Juranek, D.D. Diloxanide furoate for treating asymptomatic Entamoeba histolytica cyst passers: 14 years’ experience in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 15, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, W.A.; Singh, U. Diagnosis and management of amebiasis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kip, A.E.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Dorlo, T.P.C. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Systemically Administered Antileishmanial Drugs. Clin. Pharm. 2018, 57, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinjari, K.M.J.S.; Somani, R.; Gilhotra, R.M. Investigation of in vitro absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion and in vivo pharmacokinetics of paromomycin: Influence on oral bioavailability. Indian. J. Pharm. 2017, 49, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracha, R.; Mirelman, D. Virulence of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Effects of bacteria, microaerobic conditions, and metronidazole. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 160, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, L.S.; Phillips, B.P.; Bartgis, I.L. Virulence of axenically cultivated E. histolytica. Arch. Investig. Med. 1973, 4, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Orozco, E.; Guarneros, G.; Martinez-Palomo, A.; Sánchez, T. Entamoeba histolytica. Phagocytosis as a virulence factor. J. Exp. Med. 1983, 158, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.A.; Melo, M.N.; Pena, G.P.; Silva, E.F. Virulence parameters in the characterization of strains of Entamoeba histolytica. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1997, 39, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinertson, J.W.; Thompson, P.E. Experimental amebic hepatitis in hamsters. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1951, 76, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, R.A.; Vincent, P. Strain variation in Entamoeba histolytica. II. The effect of serial liver passage on the virulence. Parasitology 1956, 46, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gögler, H.; Knight, R. The effect of hepatic injury upon the development of amoebic liver abscess in hamsters. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1974, 68, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivos-García, A.; Tello, E.; Nequiz-Avendaño, M.; González-Canto, A.; López-Vancell, R.; García de León, M.C.; Montfort, I.; Pérez-Tamayo, R. Cysteine proteinase activity is required for survival of the parasite in experimental acute amoebic liver abscesses in hamsters. Parasitology 2004, 129, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito-Nakano, Y.; Makiuchi, T.; Tochikura, M.; Gilchrist, C.A.; Petri, W.A.; Nozaki, T. ArfX2 GTPase Regulates Trafficking from the Trans-Golgi to Lysosomes and Is Necessary for Liver Abscess Formation in the Protozoan Parasite. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 794152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankri, S.; Stolarsky, T.; Bracha, R.; Padilla-Vaca, F.; Mirelman, D. Antisense inhibition of expression of cysteine proteinases affects Entamoeba histolytica-induced formation of liver abscess in hamsters. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 421–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza-Rosales, P.; Santiago-Mauricio, M.G.; Guzmán-Delgado, N.E.; Vargas-Villarreal, J.; Lozano-Garza, G.; Viveros-Valdez, E.; Ortiz-López, R.; Morán-Martínez, J.; Gandolfi, A.J. Induction of virulence factors, apoptosis, and cytokines in precision-cut hamster liver slices infected with Entamoeba histolytica. Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 132, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, H.J.; Hage, A.J. Virulence of bacteria-associated, Crithidia-associated, and axenic Entamoeba histolytica: Experimental hamster liver infections with strains from patients and carriers. Z. Parasitenkd. 1975, 47, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigothier, M.C.; Khun, H.; Tavares, P.; Cardona, A.; Huerre, M.; Guillén, N. Fate of Entamoeba histolytica during establishment of amoebic liver abscess analyzed by quantitative radioimaging and histology. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3208–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Fehling, H.; Matthiesen, J.; Lorenzen, S.; Schuldt, K.; Bernin, H.; Zaruba, M.; Lender, C.; Ernst, T.; Ittrich, H.; et al. Overexpression of Differentially Expressed Genes Identified in Non-pathogenic and Pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica Clones Allow Identification of New Pathogenicity Factors Involved in Amoebic Liver Abscess Formation. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.G.; Diamond, L.S. Methods for cultivation of luminal parasitic protists of clinical importance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.R.; Ghoshal, S. Restoration of virulence to rat of axenically grown Entamoeba histolytica by cholesterol and hamster liver passage. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1976, 70, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, G.D.; Mirelman, D. Entamoeba histolytica: Virulence potential and sensitivity to metronidazole and emetine of four isolates possessing nonpathogenic zymodemes. Exp. Parasitol. 1988, 66, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivos, A.; Ramos, E.; Nequiz, M.; Barba, C.; Tello, E.; Castañón, G.; González, A.; Martínez, R.D.; Montfort, I.; Pérez-Tamayo, R. Entamoeba histolytica: Mechanism of decrease of virulence of axenic cultures maintained for prolonged periods. Exp. Parasitol. 2005, 110, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.A.; Costa, A.O.; Tafuri, W.L.; Silva, E.F. An attempt at reversibility and increase of the virulence of axenic strains of Entamoeba histolytica. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1993, 35, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-López, L.A.; Gil-Becerril, K.; Galindo-Gómez, S.; Estrada-García, T.; Ximénez, C.; Leon-Coria, A.; Moreau, F.; Chadee, K.; Tsutsumi, V. Entamoeba histolytica Interaction with Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Increases Parasite Virulence and Inflammation in Amebiasis. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00279-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willhoeft, U.; Hamann, L.; Tannich, E. A DNA sequence corresponding to the gene encoding cysteine proteinase 5 in Entamoeba histolytica is present and positionally conserved but highly degenerated in Entamoeba dispar. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 5925–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, J.C.; Reyes-López, M.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Shibayama, M.; Unzueta, J.; León-Sicairos, N.; de la Garza, M. Intestinal amoebiasis: 160 years of its first detection and still remains as a health problem in developing countries. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 310, 151358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, W.A.; Smith, R.D.; Schlesinger, P.H.; Murphy, C.F.; Ravdin, J.I. Isolation of the galactose-binding lectin that mediates the in vitro adherence of Entamoeba histolytica. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 80, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seigneur, M.; Mounier, J.; Prevost, M.C.; Guillén, N. A lysine- and glutamic acid-rich protein, KERP1, from Entamoeba histolytica binds to human enterocytes. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, R.C.; Singh, U. Identification of an Entamoeba histolytica serine-, threonine-, and isoleucine-rich protein with roles in adhesion and cytotoxicity. Eukaryot. Cell. 2007, 6, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rivera, G.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Ocádiz, R.; Martínez-López, M.C.; Arroyo, R.; González-Robles, A.; Orozco, E. Entamoeba histolytica: A novel cysteine protease and an adhesin form the 112 kDa surface protein. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 33, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, D.M.; Guillen, N. Virulence and virulence factors in Entamoeba histolytica, the agent of human amoebiasis. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Van Dellen, K.L.; Chatterjee, A.; Dey, T.; Haque, R.; Robbins, P.W.; Samuelson, J. The Jacob2 lectin of the Entamoeba histolytica cyst wall binds chitin and is polymorphic. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.E.; Huston, C.D. Participation of the serine-rich Entamoeba histolytica protein in amebic phagocytosis of apoptotic host cells. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibeaux, R.; Avé, P.; Bernier, M.; Morcelet, M.; Frileux, P.; Guillén, N.; Labruyère, E. The parasite Entamoeba histolytica exploits the activities of human matrix metalloproteinases to invade colonic tissue. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidell, M.E.; Moncada, D.M.; Chadee, K.; Hansson, G.C. Entamoeba histolytica cysteine proteases cleave the MUC2 mucin in its C-terminal domain and dissolve the protective colonic mucus gel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9298–9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, T.; Bruchhaus, I.; Dandekar, T.; Tannich, E.; Leippe, M. Isolation and molecular characterization of a surface-bound proteinase of Entamoeba histolytica. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 27, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibeaux, R.; Dufour, A.; Roux, P.; Bernier, M.; Baglin, A.C.; Frileux, P.; Olivo-Marin, J.C.; Guillén, N.; Labruyère, E. Newly visualized fibrillar collagen scaffolds dictate Entamoeba histolytica invasion route in the human colon. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrä, J.; Herbst, R.; Leippe, M. Amoebapores, archaic effector peptides of protozoan origin, are discharged into phagosomes and kill bacteria by permeabilizing their membranes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracha, R.; Nuchamowitz, Y.; Leippe, M.; Mirelman, D. Antisense inhibition of amoebapore expression in Entamoeba histolytica causes a decrease in amoebic virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 34, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Alexander, D.; Bracha, R.; Mirelman, D.; Stanley, S.L. Expression of amoebapores is required for full expression of Entamoeba histolytica virulence in amebic liver abscess but is not necessary for the induction of inflammation or tissue damage in amebic colitis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.T.; Green, E.R.; Mecsas, J. Neutrophils to the ROScue: Mechanisms of NADPH Oxidase Activation and Bacterial Resistance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchhaus, I.; Richter, S.; Tannich, E. Recombinant expression and biochemical characterization of an NADPH:flavin oxidoreductase from Entamoeba histolytica. Biochem. J. 1998, 330, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.H.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Townsend, R.R.; Stanley, S.L. Comparative proteomic analysis of two Entamoeba histolytica strains with different virulence phenotypes identifies peroxiredoxin as an important component of amoebic virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 61, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, G.; Bruno, F.; Saieva, L.; Alessandro, R.; Galluzzi, L.; Diotallevi, A.; Vitale, F. Exosome secretion by Leishmania infantum modulate the chemotactic behavior and cytokinic expression creating an environment permissive for early infection. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 198, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Godínez, C.; Ríos-Valencia, D.G.; García-Aguirre, S.; Martínez-Calvillo, S.; Carrero, J.C. Immunomodulatory effect of extracellular vesicles from Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites: Regulation of NETs and respiratory burst during confrontation with human neutrophils. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1018314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Fu, Y.; Yosri, M.; Chen, Y.; Sun, P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, D.; Strickland, A.B.; Mackey, Z.B.; et al. CRIg plays an essential role in intravascular clearance of bloodborne parasites by interacting with complement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24214–24220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, L.L.; Ninomiya, H.; McCoy, J.J.; Eacker, S.; Wiedmer, T.; Pham, C.; Wood, S.; Sims, P.J.; Petri, W.A. Inhibition of the complement membrane attack complex by the galactose-specific adhesion of Entamoeba histolytica. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.L.; Ember, J.A.; Herdman, D.S.; DiScipio, R.G.; Hugli, T.E.; Gigli, I. The extracellular neutral cysteine proteinase of Entamoeba histolytica degrades anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano-Villa, S.; Rosales-Borjas, D.; Carrero, J.C.; Ortiz-Ortiz, L. How protozoan parasites evade the immune response. Trends Parasitol. 2002, 18, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, V.Q.; Herdman, D.S.; Torian, B.E.; Reed, S.L. The neutral cysteine proteinase of Entamoeba histolytica degrades IgG and prevents its binding. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 177, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Nieto, R.M.; Rico-Mata, R.; Arias-Negrete, S.; Avila, E.E. Degradation of human secretory IgA1 and IgA2 by Entamoeba histolytica surface-associated proteolytic activity. Parasitol. Int. 2008, 57, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ximénez, C.; González, E.; Nieves, M.E.; Silva-Olivares, A.; Shibayama, M.; Galindo-Gómez, S.; Escobar-Herrera, J.; García de León, M.e.C.; Morán, P.; Valadez, A.; et al. Entamoeba histolytica and E. dispar Calreticulin: Inhibition of classical complement pathway and differences in the level of expression in amoebic liver abscess. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 127453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellau, J.; Groneberg, M.; Hoenow, S.; Lotter, H. The underlying cellular immune pathology of Entamoeba histolytica-induced hepatic amoebiasis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 481–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, S.L.; Zhang, T.; Rubin, D.; Li, E. Role of the Entamoeba histolytica cysteine proteinase in amebic liver abscess formation in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santi-Rocca, J.; Rigothier, M.C.; Guillén, N. Host-microbe interactions and defense mechanisms in the development of amoebic liver abscesses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Yepez, J.; Jarillo-Luna, R.A.; Gutierrez-Meza, M.; Abarca-Rojano, E.; Larsen, B.A.; Campos-Rodriguez, R. Peroxynitrite and peroxiredoxin in the pathogenesis of experimental amebic liver abscess. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 324230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.G. Axenic cultivation of Entamoeba dispar Brumpt 1925, Entamoeba insolita Geiman and Wichterman 1937 and Entamoeba ranarum Grassi 1879. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1995, 42, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattern, C.F.; Diamond, L.S.; Keister, D.B. Amebal viruses and the virulence of Entamoeba histolytica. Arch. Investig. Med. 1978, 9 (Suppl. S1), 165–166. [Google Scholar]
- Bruchhaus, I.; Jacobs, T.; Leippe, M.; Tannich, E. Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar: Differences in numbers and expression of cysteine proteinase genes. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 22, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.A.; Brito, K.N.; Gomes, M.A.; Caliari, M.V. Morphometric study of the hepatic lesions experimentally induced in hamsters by Entamoeba dispar and E. histolytica. Parasite 2007, 14, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Silva, M.A.; Santos, H.L.; Peralta, R.S.; Peralta, J.M.; de Macedo, H.W. Experimental amoebic liver abscess in hamsters caused by trophozoites of a Brazilian strain of Entamoeba dispar. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 134, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolabella, S.S.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Navarro-García, F.; Cerritos, R.; Ximénez, C.; Galván-Moroyoqui, J.M.; Silva, E.F.; Tsutsumi, V.; Shibayama, M. Amoebic liver abscess production by Entamoeba dispar. Ann. Hepatol. 2012, 11, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, M.; Dolabella, S.S.; Silva, E.F.; Tsutsumi, V. A Brazilian species of Entamoeba dispar (ADO) produces amoebic liver abscess in hamsters. Ann. Hepatol. 2007, 6, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, C.A.V.; de Oliveira, I.M.C.; Cruz, R.E.; Silva Prado, G.K.; Santos, F.V.; Neves, N.C.V.; Gomes, M.A.; Silva Oliveira, F.M.; Caliari, M.V. South American Entamoeba dispar strains produce amoebic liver abscesses with different pathogenicities and evolutionary kinetics. Acta Trop. 2021, 224, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.A.; Nunes, A.C.; Ferreira, A.J.; Gomes, M.A.; Caliari, M.V. Entamoeba histolytica and E. dispar trophozoites in the liver of hamsters: In vivo binding of antibodies and complement. Parasit. Vectors 2010, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Arya, R.; Clark, C.G.; Ackers, J.P. Absence of lipophosphoglycan-like glycoconjugates in Entamoeba dispar. Parasitology 2000, 120, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankri, S.; Padilla-Vaca, F.; Stolarsky, T.; Koole, L.; Katz, U.; Mirelman, D. Antisense inhibition of expression of the light subunit (35 kDa) of the Gal/GalNac lectin complex inhibits Entamoeba histolytica virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 33, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, D.R.; Kobayashi, S.; Kain, K.C. Entamoeba dispar: Molecular characterization of the galactose/N-acetyl-d-galactosamine lectin. Exp. Parasitol. 2001, 99, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar, P.; Hernández-Nava, E.; García-Rivera, G.; Chávez-Munguía, B.; Schnoor, M.; Betanzos, A.; Orozco, E. EhCP112 Dislocates and Degrades Claudin-1 and Claudin-2 at Tight Junctions of the Intestinal Epithelium. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Castro, S.; Bolaños, J.; Orozco, E. Lipids in Entamoeba histolytica: Host-Dependence and Virulence Factors. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastew, E.; Morf, L.; Singh, U. Entamoeba histolytica rhomboid protease 1 has a role in migration and motility as validated by two independent genetic approaches. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 154, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.S.; Kim, J.G.; Shin, M.H.; Lee, Y.A.; Kong, Y. Comparison of Secretome Profile of Pathogenic and Non-Pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proteomics 2018, 18, e1700341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, J.J.; Mann, B.J.; Petri, W.A. Adherence and cytotoxicity of Entamoeba histolytica or how lectins let parasites stick around. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 3045–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxt, L.A.; Baker, R.P.; Singh, U.; Urban, S. An Entamoeba histolytica rhomboid protease with atypical specificity cleaves a surface lectin involved in phagocytosis and immune evasion. Genes. Dev. 2008, 22, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, S.L.; Reed, S.L. Microbes and microbial toxins: Paradigms for microbial-mucosal interactions. VI. Entamoeba histolytica: Parasite-host interactions. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 280, G1049–G1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávila, E.E.; Salaiza, N.; Pulido, J.; Rodríguez, M.C.; Díaz-Godínez, C.; Laclette, J.P.; Becker, I.; Carrero, J.C. Entamoeba histolytica Trophozoites and Lipopeptidophosphoglycan Trigger Human Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammanadiminti, S.J.; Chadee, K. Suppression of NF-kappaB activation by Entamoeba histolytica in intestinal epithelial cells is mediated by heat shock protein 27. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26112–26120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.B.; Ehrenkaufer, G.M.; Saraiva, L.M.; Teixeira, M.; Singh, U. Entamoeba histolytica modulates a complex repertoire of novel genes in response to oxidative and nitrosative stresses: Implications for amebic pathogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, I.W.; Weedall, G.D.; Hall, N. Host-Parasite interactions in Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar: What have we learned from their genomes? Parasite Immunol. 2012, 34, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonah, S.N.; Abhyankar, M.M.; Haque, R.; Petri, W.A. The macrophage migration inhibitory factor homolog of Entamoeba histolytica binds to and immunomodulates host macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3523–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard-Misguich, F.; Delgado-Ortega, M.; Berthon, P.; Rossignol, C.; Larcher, T.; Bruel, T.; Guibon, R.; Guillén, N.; Meurens, F. Porcine colon explants in the study of innate immune response to Entamoeba histolytica. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 145, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, Z.; Uribe-Querol, E.; Díaz-Godínez, C.; Carrero, J.C.; Rosales, C. Pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica, but not Entamoeba dispar, induce neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimer, L.; Chadee, K. The immunopathogenesis of Entamoeba histolytica. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 126, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, X.; Reed, S.L. Cysteine proteinases and the pathogenesis of amebiasis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, B.; Ebert, F.; Horstmann, R.D. Complement sensitivity of Entamoeba histolytica and various nonpathogenic amoeba species. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1994, 45, 355–356. [Google Scholar]
- Blazquez, S.; Rigothier, M.C.; Huerre, M.; Guillén, N. Initiation of inflammation and cell death during liver abscess formation by Entamoeba histolytica depends on activity of the galactose/N-acetyl-D-galactosamine lectin. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Ramírez, B.; Escalante, B.; Rosales-Encina, J.L.; Talamás-Rohana, P. Role of prostaglandin E2 on amoebic liver abscess formation in hamsters. Prostaglandins 1997, 53, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinets, A.; Zhang, T.; Guillén, N.; Gounon, P.; Bohle, B.; Vollmann, U.; Scheiner, O.; Wiedermann, G.; Stanley, S.L.; Duchêne, M. Protection against invasive amebiasis by a single monoclonal antibody directed against a lipophosphoglycan antigen localized on the surface of Entamoeba histolytica. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchat, L.A.; Hernández-de la Cruz, O.N.; Ramírez-Moreno, E.; Silva-Cázares, M.B.; López-Camarillo, C. Proteomics approaches to understand cell biology and virulence of Entamoeba histolytica protozoan parasite. J. Proteom. 2020, 226, 103897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, R.C.; Temesvari, L.A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms that underlie Entamoeba histolytica pathogenesis: Prospects for intervention. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2005, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manich, M.; Hernandez-Cuevas, N.; Ospina-Villa, J.D.; Syan, S.; Marchat, L.A.; Olivo-Marin, J.C.; Guillén, N. Morphodynamics of the Actin-Rich Cytoskeleton in. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, M.; Huston, C.D.; Oue, M.; Mann, B.J.; Petri, W.A.; Kita, K.; Nozaki, T. Kinetics and strain variation of phagosome proteins of Entamoeba histolytica by proteomic analysis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 145, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibeaux, R.; Weber, C.; Hon, C.C.; Dillies, M.A.; Avé, P.; Coppée, J.Y.; Labruyère, E.; Guillén, N. Identification of the virulence landscape essential for Entamoeba histolytica invasion of the human colon. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieslak, P.R.; Virgin, H.W.; Stanley, S.L. A severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mouse model for infection with Entamoeba histolytica. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, J.; Kobayashi, S.; Imada, M.; Tolba, M.E.; Takeuchi, T. Characterization of a novel Entamoeba histolytica strain from Burkina Faso, Africa, possessing a unique hexokinase-2 gene. Parasite 2011, 18, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, C.; Petri, W.A. Regulation of virulence of Entamoeba histolytica. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 493–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadirian, E.; Kongshavn, P.A. Genetic control of susceptibility of mice to infection with E. histolytica. Parasite Immunol. 1984, 6, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiman, Q.M.; Becker, C.E. In vitro growth and metabolism of Endamoeba histolytica. Ann. N.Y Acad. Sci. 1953, 56, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, D.; Kagan, I.G. Susceptibility of various strains of mice to Entamoeba histolytica. J. Parasitol. 1978, 64, 937–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.P.; Diamond, L.S.; Bartgis, I.L.; Stuppler, S.A. Results of intracecal inoculation of germfree and conventional guinea pigs and germfree rats with axenically cultivated Entamoeba histolytica. J. Protozool. 1972, 19, 498–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobie, J.E. Experimental infection of the rabbit with Endamoeba histolytica. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1949, 29, 859–870, illust. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadirian, E.; Meerovitch, E. Pathogenicity of axenically cultivated Entamoeba histolytica, strain 200:NIH, in the hamster. J. Parasitol. 1979, 65, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarumilinta, R.; Maegraith, B.G. Intestinal amoebiasis associated with amoebic liver abscess produced by intracaecal inoculation of Entamoeba histolytica in hamsters. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1961, 55, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarumilinta, R.; Maegraith, B.G. The induction of amoebic liver abscesses in hamsters by the intraperitoneal inoculation of trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1962, 56, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kradolfer, F.; Jarumilinta, R. CIBA 32,644-Ba, A New Systemically Active Amoebicide. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1965, 59, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.G. Attempts at oral infection of rats and mice with trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1984, 78, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.M.; Horta, B.C.; Prata, L.O.; Santiago, A.F.; Alves, A.C.; Faria, A.M.; Gomes, M.A.; Caliari, M.V. Susceptibility to Entamoeba histolytica intestinal infection is related to reduction in natural killer T-lymphocytes in C57BL/6 mice. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2012, 4, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escueta-de Cadiz, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Tachibana, H.; Nozaki, T. Identification of an avirulent Entamoeba histolytica strain with unique tRNA-linked short tandem repeat markers. Parasitol. Int. 2010, 59, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Haghighi, A. Diversity of clinical isolates of Entamoeba histolytica in Japan. Arch. Med. Res. 2006, 37, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadirian, E.; Meerovitch, E. Behavior of axenic IP-106 strain of Entamoeba histolytica in the golden hamster. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1978, 27, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, B.; Anderson, I.; Davies, R.; Alsmark, U.C.; Samuelson, J.; Amedeo, P.; Roncaglia, P.; Berriman, M.; Hirt, R.P.; Mann, B.J.; et al. The genome of the protist parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Nature 2005, 433, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzi, H.A.; Puiu, D.; Miller, J.R.; Brinkac, L.M.; Amedeo, P.; Hall, N.; Caler, E.V. New assembly, reannotation and analysis of the Entamoeba histolytica genome reveal new genomic features and protein content information. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano-Sugaya, T.; Izumiyama, S.; Yanagawa, Y.; Saito-Nakano, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Nozaki, T. Near-chromosome level genome assembly reveals ploidy diversity and plasticity in the intestinal protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weedall, G.D.; Hall, N. Evolutionary genomics of Entamoeba. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willhoeft, U.; Tannich, E. The electrophoretic karyotype of Entamoeba histolytica. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1999, 99, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.H.; MacFarlane, R.C.; Bhattacharya, D.; Matese, J.C.; Demeter, J.; Stroup, S.E.; Singh, U. Comparative genomic hybridizations of Entamoeba strains reveal unique genetic fingerprints that correlate with virulence. Eukaryot. Cell. 2005, 4, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, R.C.; Singh, U. Identification of differentially expressed genes in virulent and nonvirulent Entamoeba species: Potential implications for amebic pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naiyer, S.; Kaur, D.; Ahamad, J.; Singh, S.S.; Singh, Y.P.; Thakur, V.; Bhattacharya, A.; Bhattacharya, S. Transcriptomic analysis reveals novel downstream regulatory motifs and highly transcribed virulence factor genes of Entamoeba histolytica. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penuliar, G.M.; Furukawa, A.; Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Husain, A.; Sato, D.; Nozaki, T. Transcriptional and functional analysis of trifluoromethionine resistance in Entamoeba histolytica. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilchrist, C.A.; Houpt, E.; Trapaidze, N.; Fei, Z.; Crasta, O.; Asgharpour, A.; Evans, C.; Martino-Catt, S.; Baba, D.J.; Stroup, S.; et al. Impact of intestinal colonization and invasion on the Entamoeba histolytica transcriptome. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 147, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenkaufer, G.M.; Weedall, G.D.; Williams, D.; Lorenzi, H.A.; Caler, E.; Hall, N.; Singh, U. The genome and transcriptome of the enteric parasite Entamoeba invadens, a model for encystation. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biller, L.; Schmidt, H.; Krause, E.; Gelhaus, C.; Matthiesen, J.; Handal, G.; Lotter, H.; Janssen, O.; Tannich, E.; Bruchhaus, I. Comparison of two genetically related Entamoeba histolytica cell lines derived from the same isolate with different pathogenic properties. Proteomics 2009, 9, 4107–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Sekizuka, T.; Sato-Ebine, E.; Escueta-de Cadiz, A.; Ji, D.D.; Tomii, K.; Kuroda, M.; Nozaki, T. AIG1 affects in vitro and in vivo virulence in clinical isolates of Entamoeba histolytica. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagawa, Y.; Izumiyama, S.; Saito-Nakano, Y.; Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Yoshida, N.; Kikuchi, Y.; Gatanaga, H.; Oka, S.; Nozaki, T.; et al. Gene expression of axenically-isolated clinical Entamoeba histolytica strains and its impact on disease severity of amebiasis. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Strain | Clinical Status in Human | Virulence | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver Abscess Model | Animal Model | Colitis Model | Animal Model | |||
| HM-1:IMSS | Amebic colitis with dysentery [147] | Attenuated virulence | 0~100% in wild type of hamsters [71,73]; 100% in SCID mice [144] | Attenuated virulence | 67% in wild type of rats [71] | [71,73,144,147] |
| Rahman | Asymptomatic [71,108] | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of hamsters [71] | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of mouse [93,143] | [71,93,143] |
| HK9 | Amebic colitis with dysentery [148] | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of hamsters [149] | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of guinea pigs and germfree rats [149,150] | [148,149,150] |
| NIH-200 | Amebic colitis with dysentery [151] | Attenuated virulence | 0~100% in wild type of hamsters [71] | Attenuated virulence | 0% in wild type of hamsters, guinea pigs, and rats [70,150,152] | [70,71,150,151,152] |
| ABRM | Amebic colitis with rectal abscess [150] | N.D | N.D | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of guinea pigs [150] | [150] |
| ICB-CSP | Amebic colitis with dysentery [73] | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of hamsters [58,73] | ND | ND | [58,73] |
| ICB-462 | Asymptomatic [73] | Attenuated virulence | 25% in wild type of hamsters [58,73] | ND | ND | [58,73] |
| ICB-32 | Asymptomatic [73] | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of hamsters [58,73] | ND | ND | [58,73] |
| ICB-RPS | Asymptomatic [73] | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of hamsters [58,73] | ND | ND | [58,73] |
| DC | Amebic colitis with dysentery [153] | Virulence | 87% in wild type of hamsters; 0% in wild type of guinea pigs [153] | Attenuated virulence * | 29% in wild type of hamsters [154] | [153,154] |
| SF | Amebic colitis with dysentery [153] | Virulence | 100% in wild type of hamsters; 0% in wild type of guinea pigs [153] | Attenuated virulence * | 58% in wild type of rats; 100% in wild type of guinea-pigs [155] | [153,155] |
| SAW:1734 | Asymptomatic [71] | Attenuated virulence | 60% in wild type of hamsters [71] | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of rats [71] | [71] |
| CDC:0784:4 | Asymptomatic [71] | Attenuated virulence | 50% in wild type of hamsters [71] | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of rats [71] | [71] |
| SAW:408 | Amoebiasis (details unavailable) | ND | ND | Virulent * | 100% in athymic rats; 80% in Wister rats [156] | [156] |
| EGG | Amebic colitis with dysentery and amebic liver abscess (details unavailable) | Virulent | 100% in wild type of hamster [110] | Virulent | 100% in C57BL/6CD-/- mouse [157] | [110,157] |
| KU27 | Asymptomatic [158] | Avirulent | 0% in wild type of hamster [159] (details unavailable) | ND | ND | [158,159] |
| BF-841 | Asymptomatic [145] | Virulent | Ability in wild type of hamster [145] (details unavailable) | ND | ND | [145] |
| IP-106 | Fulminating amebic colitis with dysentery [160] | Virulent | 100% in wild type of hamster [160] | Attenuated Virulent | 50% in wild type of hamster [160] | [160] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanagawa, Y.; Singh, U. Diversity and Plasticity of Virulent Characteristics of Entamoeba histolytica. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8050255
Yanagawa Y, Singh U. Diversity and Plasticity of Virulent Characteristics of Entamoeba histolytica. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(5):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8050255
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanagawa, Yasuaki, and Upinder Singh. 2023. "Diversity and Plasticity of Virulent Characteristics of Entamoeba histolytica" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 5: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8050255
APA StyleYanagawa, Y., & Singh, U. (2023). Diversity and Plasticity of Virulent Characteristics of Entamoeba histolytica. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(5), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8050255






