Factors Related to Severity, Hospitalization, and Mortality of COVID-19 Infection among Patients with Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
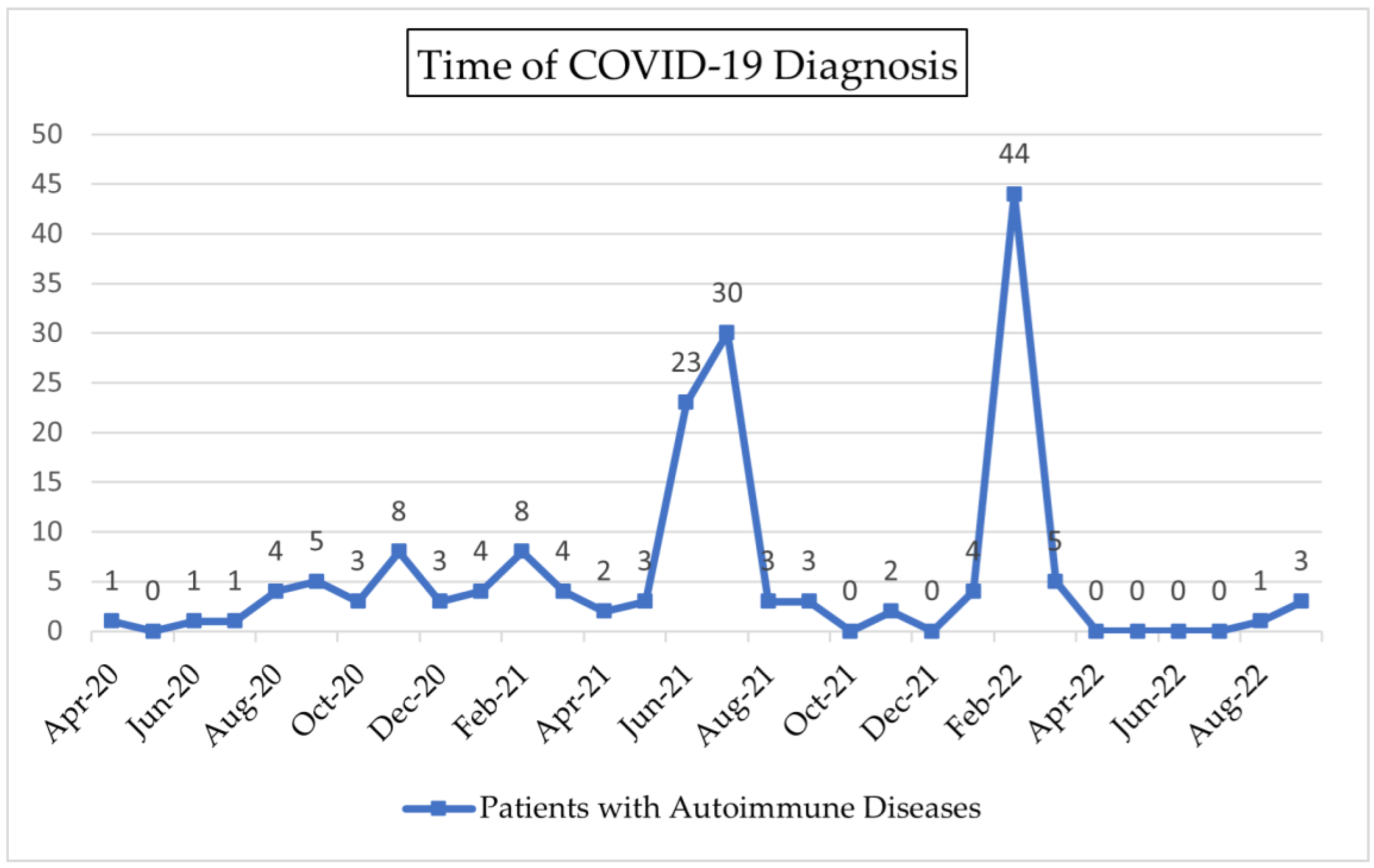
3.1. Characteristics of Subjects
3.2. Factors Associated with Severity, Hospitalization, and Mortality of COVID-19 in Patients with Autoimmune Diseases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, Y.; Yang, H. The transmission and diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus infection disease (COVID-19): A Chinese perspective. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report–96. Available online: https://covid19.go.id/peta-sebaran (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Hu, L.; Ming, Q.; Wei, X.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, L.D.; Wang, M.H.; Yao, W.Z.; Huang, Q.F.; Ye, Z.Q.; et al. Risk factors for mortality of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) patients in two centers of Hubei province, China: A retrospective analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fang, X.; Cai, Z.; Wu, X.; Gao, X.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Comorbid Chronic Diseases and Acute Organ Injuries Are Strongly Correlated with Disease Severity and Mortality among COVID-19 Patients: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Research 2020, 2020, 2402961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caso, F.; Costa, L.; Ruscitti, P.; Navarini, L.; del Puente, A.; Giacomelli, R.; Scarpa, R. Could Sars-coronavirus-2 trigger autoimmune and/or autoinflammatory mechanisms in genetically predisposed subjects? Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Han, T.; Chen, J.; Hou, C.; Hua, L.; He, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; et al. Clinical and Autoimmune Characteristics of Severe and Critical Cases of COVID-19. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zen, M.; Fuzzi, E.; Astorri, D.; Saccon, F.; Padoan, R.; Ienna, L.; Cozzi, G.; Depascale, R.; Zanatta, E.; Gasparotto, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases in northeast Italy: A cross-sectional study on 916 patients. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 112, 102502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Shen, G.; Yang, H.; Huang, A.; Chen, X.; Dong, L.; Wu, B.; Zhang, A.; Su, L.; Hou, X.; et al. COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic disease in Hubei province, China: A multicentre retrospective observational study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e557–e564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strangfeld, A.; Schäfer, M.; Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Lawson-Tovey, S.; Liew, J.W.; Ljung, L.; Mateus, E.F.; Richez, C.; Santos, M.J.; Schmajuk, G.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death in people with rheumatic diseases: Results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician-reported registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabbazi, A.; Kavandi, H.; Paribanaem, R.; Khabbazi, R.; Malek Mahdavi, A. Adherence to medication in patients with rheumatic diseases during COVID-19 pandemic. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humas LIPI. Lonjakan Kasus COVID-19 di Indonesia Didominasi oleh Varian Delta. Available online: http://lipi.go.id/berita/%E2%80%8Blonjakan-kasus-covid-19-di-indonesia-didominasi-oleh-varian-delta/22446 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Ministry of Communication and Information of Indonesia. Available online: https://covid19.go.id/id/edukasi/masyarakat-umum/ini-asal-muasal-kasus-varian-omicron-pertama-di-indonesia (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Sehat Negeriku. Available online: https://sehatnegeriku.kemkes.go.id/baca/rilis-media/20211219/5339013/kasus-pertama-omicron-di-indonesia-diduga-dari-wni-yang-datang-dari-nigeria/#:~:text=Kasus%20Pertama%20Omicron%20di%20Indonesia%20Diduga%20dari%20WNI%20yang%20Datang%20dari%20Nigeria,-by%20Rokom&text=Kementerian%20Kesehatan%20telah%20melakukan%20pelacakan,pada%20tanggal%2027%20November%202021 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Izda, V.; Jeffries, M.A.; Sawalha, A.H. COVID-19: A review of therapeutic strategies and vaccine candidates. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 222, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekomendasi PAPDI Tentang Pemberian Vaksinasi COVID-19 Pada Pasien Dengan Penyakit Penyerta/Komorbid (Revisi 18 Maret 2021). Available online: https://www.papdi.or.id/berita/info-papdi/1024-rekomendasi-papdi-tentang-pemberian-vaksinasi-covid-19-pada-pasien-dengan-penyakit-penyerta-komorbid-revisi-18-maret-2021 (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Zheng, C.; Shao, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W. Real-world Effectiveness of COVIF-19 vaccines: A literature review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 114, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratama, N.R.; Wafa, I.A.; Budi, D.S.; Sutanto, H.; Asmarawati, T.P.; Barlian Effendi, G.; Wungu, C.D.K. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant (B.1.1.529): A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.; Stowe, J.; Kirsebom, F.; Toffa, S.; Rickeard, T.; Gallagher, E.; Gower, C.; Kall, M.; Groves, N.; O’Connell, A.M.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.S.; Antolin, S.C.; Morales, C.M.; Herrero, J.G.; Alvarez, E.D.; Ortega, F.R.; de Morales, J.G.R. Immune responses to mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with immune mediated inflammatory rheumatic diseases. RMD Open 2022, 8, e001898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, S.; Paul, A.; Ahmed, S.; Alias, B.; Manoj, M.; Santhosh, A.K.; Varghese, D.R.; Krishnan, N.; Shenoy, P. Safety of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and the BBV152 vaccines in 724 patients with rheumatic diseases: A post-vaccination cross-sectional survey. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisen, U.M.; Berner, D.K.; Tran, F.; Sümbül, M.; Vullriede, L.; Ciripoi, M.; Reid, H.M.; Schaffarzyk, A.; Longardt, A.C.; Franzenburg, J.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of anti-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with chronic inflammatory conditions and immunosuppressive therapi in a monocentric cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinjo, S.K.; de Souza, F.H.C.; Borges, I.B.P.; dos Santos, A.M.; Miossi, R.; Misse, R.G.; Medeiros-Ribeiro, A.C.; Saad, C.G.; Yuki, E.F.; Pasoto, S.G.; et al. Systemic autoimmune myopathies: A prospective phase 4 controlled trial of an inactivated virus vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Rheumatology 2021, 61, 3351–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soy, M.; Keser, G.; Atagunduz, P.; Mutlu, M.Y.; Gunduz, A.; Koybaşi, G.; Bes, C. A practical approach for vaccinations including COVID-19 in autoimmune/autoinflammatory rheumatic diseases: A non-systematic review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3533–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianfrancesco, M.; Hyrich, K.L.; Al-Adely, S.; Carmona, L.; Danila, M.I.; Gossec, L.; Izadi, Z.; Jacobsohn, L.; Katz, P.; Lawson-Tovey, S.; et al. Characteristics associated with hospitalisation for COVID-19 in people with rheumatic disease: Data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician-reported registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.H.; Shin, J.I.; Moon, S.Y.; Jin, H.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Yang, J.M.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, M.; Park, Y.; et al. Autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and COVID-19 outcomes in South Korea: A nationwide cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e698–e706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuñez, D.D.F.; Leon, L.; Mucientes, A.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, L.; Urgelles, J.F.; García, A.M.; Colomer, J.I.; Jover, J.A.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, B.; Abasolo, L. Risk factors for hospital admissions related to COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, A.; Leverenz, D.; Balevic, S.J.; Sadun, R.E.; Tarrant, T.K.; Rogers, J.L. Hydroxychloroquine and COVID-19: A Rheumatologist’s Take on the Lessons Learned. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautret, P.; Lagier, J.C.; Parola, P.; Hoang, V.T.; Meddeb, L.; Mailhe, M.; Doudier, B.; Courjon, J.; Giordanengo, V.; Vieira, V.E.; et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: Results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnabas, R.V.; Brown, E.R.; Bershteyn, A.; Karita, H.C.S.; Johnston, C.; Thorpe, L.E.; Kottkamp, A.; Neuzil, K.M.; Laufer, M.K.; Deming, M.; et al. Hydroxychloroquine as postexposure prophylaxis to prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection a randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodini, I.; Gatti, D.; Soranna, D.; Merlotti, D.; Mingiano, C.; Fassio, A.; Adami, G.; Falchetti, A.; Eller-Vainicher, C.; Rossini, M.; et al. Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 736665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, A.; Mohammadi, V.; Aghababaee, S.K.; Golzarand, M.; Clark, C.C.T.; Babajafari, S. Association of Vitamin D Status with SARS-CoV-2 Infection or COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1636–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.H.; Choe, H.J.; Holick, M.F.; Lim, S. Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 and its severity: Vitamin D and COVID-19: A narrative review. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sîrbe, C.; Rednic, S.; Grama, A.; Pop, T.L. An Update on the Effects of Vitamin D on the Immune System and Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, K.; Ding, N.; Kou, M.; Hu, X.; Chen, M.; Gao, Y.; Honda, Y.; Zhao, D.; Dowdy, D.; Mok, Y.; et al. The Relationship of COVID-19 severity with cardiovascular disease and its traditional risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Global Heart 2020, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xiao, W.; Liang, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. A meta-analysis on the risk factors adjusted association between cardiovascular disease and COVID-19 severity. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidi, A.M.; Belanger, M.J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Commentary: COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: What we know, how our patients should be treated now, and what should happen next. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2020, 107, 154245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, F.A.; Saeed, M.A.; Shaltout, S.W.; Nofal, H.A.E.; Nafae, R.M.; Arslan, K.; Tanoglu, A.; Nechifor, M.; Luca, C.; Al-Kadhim, Z.H.A.; et al. Assessment and outcome of hospitalized patients during delta variant COVID-19 pandemic: A multicenter international study. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 16, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nersesjan, V.; Amiri, M.; Christensen, H.K.; Benros, M.E.; Kondziella, D. Thirty-Day Mortality and Morbidity in COVID-19 Positive vs. COVID-19 Negative Individuals and vs. Individuals Tested for Influenza A/B: A Population-Based Study. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 598272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Arora, A.; Sharma, P.; Anikhindi, S.A.; Bansal, N.; Singla, V.; Khare, S.; Srivastava, A. Is diabetes mellitus associated with mortality and severity of COVID-19? A meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J. Coagulopathy in COVID-19 and anticoagulation clinical trials. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2022, 35, 101377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakota, K.; Perdan-Pirkmajer, K.; Hočevar, A.; Sodin-Semrl, S.; Rotar, Z.; Čučnik, S.; Žigon, P. COVID-19 in Association with Development, Course, and Treatment of Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 611318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmarajan, T.; Paudel, K.R.; Candasamy, M.; Chellian, J.; Madheswaran, T.; Sakthivel, L.P.; Goh, B.H.; Gupta, P.K.; Jha, N.K.; Devkota, H.P.; et al. Autoantibodies and autoimmune disorders in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Pathogenicity and immune regulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 54072–54087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, V.; Gianesello, L.; Horton, A. Antiphospholipid antibodies in critically ill COVID-19 patients with thromboembolism: Cause of disease or epiphenomenon? J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Female | 154 (93.3) |
| Male | 11 (6.7) |
| Age Group (Years) | |
| <60 | 157 (95.2) |
| ≥60 | 8 (4.8) |
| Body Mass Index | |
| Severely Underweight (≤16.49) | 10 (6.1) |
| Underweight (16.5–18.49) | 9 (5.5) |
| Normal (18.5–22.9) | 58 (35.2) |
| Overweight (23–24.9) | 18 (10.9) |
| Obese (≥25) | 54 (32.7) |
| No data | 16 (9.7) |
| Autoimmune Diagnosis | |
| SLE | 90 (54.5) |
| Sjogren’s syndrome | 55 (33.5) |
| Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) | 38 (23) |
| Autoimmune vasculitis | 9 (5.5) |
| Autoimmune thyroid diseases | 6 (3.6) |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 5 (3.03) |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease | 5 (3.03) |
| Scleroderma/Systemic sclerosis | 4 (2.4) |
| Autoimmune Haemolytic Anemia (AIHA) | 3 (1.82) |
| Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) | 3 (1.82) |
| Myasthenia gravis | 3 (1.82) |
| Other autoimmune diseases * | 43 (26.06) |
| Routine Immunosuppressant therapy | |
| Steroid | 118 (71.5) |
| ≥10 mg of Prednisone-equivalent per day | 43 (36.4) |
| <10 mg of Prednisone-equivalent per day | 72 (61.0) |
| No data | 3 (2.5) |
| Hydroxychloroquine | 68 (41.2) |
| Mycophenolate mofetil/mycophenolic acid (MMF/MPA) | 68 (41.2) |
| Azathioprine | 11 (6.7) |
| Cyclophosphamide | 2 (1.2) |
| Cyclosporine | 2 (1.2) |
| Tacrolimus | 3 (1.8) |
| Methotrexate | 3 (1.8) |
| Rituximab | 1 (0.6) |
| Routine medications | |
| ACE-Inhibitor | 9 (5.5) |
| Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) | 12 (7.3) |
| Antiplatelet | 22 (13.3) |
| Anticoagulant | 14 (8.5) |
| Vitamin D3 supplement | 45 (27.3) |
| COVID-19 Vaccination Status | |
| Vaccinated | 70 (42.4) |
| CoronaVac | 28 (40) |
| BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) | 17 (24.3) |
| mRNA-1273 (Moderna) | 8 (11.4) |
| ChAdOx1 nCov-19 (Oxford-AstraZeneca) | 2 (2.9) |
| Not vaccinated | 95 (57.6) |
| Time of vaccination | |
| Before COVID-19 infection | 23 (32.8) |
| After COVID-19 infection | 34 (48.5) |
| No data | 13 (18.6) |
| Comorbidities | |
| Hypertension | 30 (18.3) |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 9 (5.5) |
| Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) | 18 (11) |
| Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) | 13 (7.9) |
| COVID-19 Severity | |
| Moderate-Severe | 34 (20.6) |
| Mild | 131 (79.4) |
| COVID-19 Hospitalization | |
| Hospitalization in isolation ward or ICU | 61 (36.9) |
| Self-isolation | 104 (63) |
| COVID-19 Outcome | |
| Alive | 161 (97.6) |
| Deceased | 4 (2.4) |
| Patient Variables | Severity | Hospitalization | Outcome | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate-Severe N = 34 | Mild N = 131 | Bivariate | Multivariate | Isolation Ward/ICU N = 61 | Self-Isolation N = 104 | Bivariate | Multivariate | Deceased N = 4 | Alive N = 161 | Bivariate | ||||||
| n (%) | n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | n (%) | n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | n (%) | n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| Sex | ||||||||||||||||
| Female | 33 (21.4) | 121 (78.6) | 2.73 | 0.295 | 57 (37.0) | 97 (63.0) | 1.028 | 0.618 | 3 (1.9) | 151 (98.1) | 0.19 | 0.243 | ||||
| Male | 1 (9.1) | 10 (90.9 | (0.34–22.08) | 4 (36.4) | 7 (63.6) | (0.29–3.67) | 1 (9.1) | 10 (90.9) | (0.02–2.09) | |||||||
| Age group | ||||||||||||||||
| <60 | 32 (20.4) | 125 (79.6) | 0.77 | 0.518 | 58 (36.9) | 99 (63.1) | 0.97 | 0.622 | 3 (1.9) | 154 (98.1) | 0.14 | 0.182 | ||||
| ≥60 | 2 (25.0) | 6 (75.0) | (0.15–3.99) | 3 (37.5) | 5 (62.5) | (0.23–4.24) | 1 (12.5) | 7 (87.5) | (0.01–1.48) | |||||||
| Autoimmune Diagnosis | ||||||||||||||||
| SLE | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 19 (21.1) | 71 (78.9) | 1.07 | 1.000 | 37 (41.1) | 53 (58.9) | 1.48 | 0.227 | 1.13 | 0.836 | 4 (4.4) | 86 (95.6) | - | 0.086 | ||
| (−) | 15 (20.0) | 60 (80.0) | (0.50–2.29) | 24 (32.0) | 51 (68.0) | (0.78–2.82) | (0.36–3.51) | 0 (0) | 75 (100) | |||||||
| Sjogren’s syndrome | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 10 (18.2) | 45 (81.8) | 0.79 | 0.734 | 17 (30.9) | 38 (69.1) | 0.67 | 0.254 | 0 (0) | 55(100) | - | 0.194 | ||||
| (−) | 24 (21.8) | 86 (78.2) | (0.35–1.81) | 44 (40.0) | 66 (60.0) | (0.34–1.34) | 4 (3.6) | 106 (96.4) | ||||||||
| APS | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 10 (26.3) | 28 (73.7) | 1.53 | 0.445 | 18 (47.4) | 20 (52.6) | 1.76 | 0.130 | 2.36 | 0.100 | 1 (2.6) | 37 (97.4) | 1.11 | 0.653 | ||
| (−) | 24 (18.9) | 103 (81.1) | (0.66–3.58) | 43 (33.9) | 84 (66.1) | (0.84–3.67) | (0.85–6.54) | 3 (2.4) | 124 (97.6) | (0.11–11.06) | ||||||
| Autoimmune thyroid | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 1 (16.7) | 5 (83.3) | 0.76 | 0.640 | 1 (16.7) | 5 (83.3) | 0.33 | 0.279 | 0 (0) | 6 (100) | - | 0.861 | ||||
| (−) | 33 (20.8) | 126 (79.2) | (0.86–6.76) | 60 (37.7) | 99 (62.3) | (0.04–2.89) | 4 (2.5) | 155 (97.5) | ||||||||
| Autoimmune vasculitis | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 0 (0) | 9 (100) | - | 0.118 | 4 (44.4) | 5 (55.9) | 1.39 | 0.440 | 0 (0) | 9 (100) | - | 0.797 | ||||
| (−) | 34 (21.8) | 122 (78.2) | 57 (36.5) | 99 (63.5) | (0.36–5.38) | 4 (2.6) | 152 (97.4) | |||||||||
| COVID-19 Vaccination Status | ||||||||||||||||
| Not vaccinated | 26 (27.4) | 69 (72.6) | 2.92 | 0.021 * | 5.65 | 0.019 * | 42 (44.2) | 53 (55.8) | 2.13 | 0.025 * | 2.63 | 0.050 | 4 (4.2) | 91 (95.8) | - | 0.107 |
| Vaccinated | 8 (11.4) | 62 (88.6) | (1.23–6.92) | (1.32–24.16) | 19 (27.1) | 51 (72.9) | (1.09–4.13) | (0.99–6.95) | 0 (0) | 70 (100) | ||||||
| Comorbidities | ||||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 8 (24.2) | 25 (75.8) | 1.305 | 0.736 | 14 (42.4) | 19 (57.6) | 1.33 | 0.468 | 1 (3) | 32 (97) | 1.34 | 0.594 | ||||
| (−) | 26 (19.7) | 106 (80.3) | (0.53–3.22) | 47 (35.6) | 85 (64.4) | (0.61–2.89) | 3 (2.3) | 129 (97.7) | (0.13–13.35) | |||||||
| Diabetes mellitus | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 5 (55.6) | 4 (44.4) | 5.47 | 0.019 * | 4.23 | 0.102 | 6 (66.7) | 3 (33.3) | 3.67 | 0.064 | 3.39 | 0.197 | 1 (11.1) | 8 (88.9) | 6.37 | 0.203 |
| (−) | 29 (18.6) | 127 (81.4) | (1.38–21.65) | (0.75–23.85) | 55 (35.3) | 101 (64.7) | (0.88–15.26) | (0.53–21.78) | 3 (1.9) | 153 (98.1) | (0.59–68.34) | |||||
| CKD | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 3 (16.7) | 15 (83.3) | 0.75 | 0.468 | 10 (55.6) | 8 (44.4) | 2.35 | 0.084 | 3.06 | 0.061 | 2 (11.1) | 16 (88.9) | 8.17 | 0.059 | ||
| (−) | 31 (21.1) | 116 (78.9) | (0.20–2.75) | 51 (34.7) | 96 (65.3) | (0.87–6.31) | (0.95–9.88) | 2 (1.4) | 145 (98.6) | (1.22–54.48) | ||||||
| CVD | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 6 (40.0) | 9 (60.0) | 2.90 | 0.060 | 7.22 | 0.022 * | 7 (46.7) | 8 (53.3) | 1.56 | 0.415 | 2 (13.3) | 13 (86.7) | 11.38 | 0.042 * | ||
| (−) | 28 (18.7) | 122 (81.3) | (0.95–8.83) | (1.34–39.00) | 54 (36.0) | 96 (64.0) | (0.53–4.52) | 2 (1.3) | 148 (98.7) | (1.48–87.58) | ||||||
| Obesity | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 11 (20.4) | 43 (79.6) | 1.05 | 1.000 | 16 (29.6) | 38 (70.4) | 0.65 | 0.241 | 0.54 | 0.226 | 0 (0) | 54 (100) | - | 0.262 | ||
| (−) | 19 (19.6) | 78 (80.4) | (0.46–2.41) | 38 (39.2) | 59 (60.8) | (0.32–1.33) | (0.19–1.46) | 3 (3.1) | 94 (96.9) | |||||||
| Routine Immunosuppressant/Immunomodulator Therapy | ||||||||||||||||
| Corticosteroid | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 23 (19.5) | 95 (80.5) | 0.79 | 0.728 | 44 (37.3) | 74 (63.2) | 1.05 | 1.000 | 4 (3.4) | 114 (96.6) | - | 0.668 | ||||
| (−) | 11 (23.4) | 36 (76.6) | (0.35–1.79) | 17 (36.2) | 30 (62.5) | (0.52–2.12) | 0 (0.0) | 47 (100) | ||||||||
| Corticosteroid dosage, prednisone equivalent | ||||||||||||||||
| ≥10 mg/day | 13 (30.2) | 30 (69.8) | 3.47 | 0.010 * | 3.01 | 0.037 * | 26 (60.5) | 17 (39.5) | 5.35 | <0.001 * | 5.36 | <0.001 * | 2 (4.7) | 41 (95.3) | - | 0.140 |
| <10 mg/day | 8 (11.1) | 64 (88.9) | (1.29–9.25) | (1.06–8.48) | 16 (22.2) | 56 (77.8) | (2.34–12.23) | (2.10–13.65) | 0 (0) | 71 (100) | ||||||
| Azathioprine | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 0 (0) | 11 (100) | - | 0.072 | 4 (36.4) | 7 (63.6) | 0.97 | 0.618 | 0 (0) | 11 (100) | - | 0.757 | ||||
| (−) | 34 (22.1) | 120 (77.9) | 57 (37.0) | 97 (63.0) | (0.27–3.47) | 4 (2.6) | 150 (97.4) | |||||||||
| Hydroxychloroquine | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 11 (16.2) | 57 (83.8) | 0.62 | 0.239 | 2.53 | 0.117 | 18 (26.5) | 50 (73.5) | 0.45 | 0.011 * | 1.69 | 0.315 | 1 (1.5) | 67 (98.5) | 0.47 | 0.453 |
| (−) | 23 (23.7) | 74 (76.3) | (0.28–1.38) | (0.79–8.09) | 43 (44.3) | 54 (55.7) | (0.23–0.88) | (0.60–4.77) | 3 (3.1) | 94 (96.9) | (0.05–4.59) | |||||
| MMF/MPA | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 13 (19.1) | 55 (80.9) | 0.85 | 0.692 | 21 (30.9) | 47 (69.1) | 0.64 | 0.175 | 2 (2.9) | 66 (97.1) | 1.44 | 0.547 | ||||
| (−) | 21 (21.6) | 76 (78.4) | (0.39–1.85) | 41 (41.2) | 57 (58.8) | (0.33–1.22) | 3 (2.1) | 95 (97.9) | (0.19–10.47) | |||||||
| Cyclophosphamide | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 3.94 | 0.371 | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | 1.71 | 0.604 | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | - | 0.952 | ||||
| (−) | 33 (20.2) | 130 (79.8) | (0.24–64.65) | 60 (36.8) | 103 (63.2) | (0.10–27.95) | 4 (2.5) | 159 (97.5) | ||||||||
| Cyclosporine | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | - | 0.629 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (100) | - | 0.396 | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | - | 0.952 | ||||
| (−) | 34 (20.9) | 129 (79.1) | 61 (37.4) | 102 (62.6) | 4 (2.5) | 159 (97.5) | ||||||||||
| Tacrolimus | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | 1.95 | 0.502 | 3 (100) | 0 (0) | - | 0.049 * | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | 26.5 | 0.071 | ||||
| (−) | 33 (20.4) | 129 (79.6) | (0.17–22.22) | 58 (35.8) | 104 (64.2) | 3 (1.9) | 159 (98.1) | (1.86–378.23) | ||||||||
| Methotrexate | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 0 (0) | 3 (100) | - | 0.489 | 0 (0.0) | 3 (100) | - | 0.248 | 0 (0) | 3 (100) | - | 0.929 | ||||
| (−) | 34 (21.0) | 128 (79) | 61 (37.7) | 101 (62.3) | 4 (2.5) | 158 (97.5) | ||||||||||
| Routine Medications | ||||||||||||||||
| ACE-Inhibitor | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 1 (11.1) | 8 (88.9) | 0.47 | 0.412 | 4 (44.4) | 5 (55.6) | 1.39 | 0.440 | 0 (0) | 9 (100) | - | 0.797 | ||||
| (−) | 33 (21.2) | 123 (78.8) | (0.05–3.86) | 57 (36.5) | 99 (63.5) | (0.36–5.38) | 4 (2.6) | 152 (97.4) | ||||||||
| ARB | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 3 (25.0) | 9 (75) | 1.31 | 0.466 | 4 (33.3) | 8 (66.7) | 0.84 | 0.525 | 1 (8.3) | 11 (91.7) | 4.54 | 0.263 | ||||
| (−) | 31 (20.3) | 122 (79.7) | (0.33–5.14) | 57 (37.3) | 96 (62.7) | (0.24–2.92) | 3 (2.0) | 150 (98.0) | (0.44–47.40) | |||||||
| Antiplatelet | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 4 (17.4) | 19 (82.6) | 0.78 | 0.463 | 9 (39.1) | 14 (60.9) | 1.11 | 0.817 | 0 (0) | 23 (100) | - | 0.545 | ||||
| (−) | 30 (21.1) | 112 (78.9) | (0.25–2.48) | 52 (36.6) | 90 (63.4) | (0.45–2.75) | 4 (2.8) | 138 (97.2) | ||||||||
| Anticoagulant | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 3 (21.4) | 11 (78.6) | 1.05 | 0.582 | 5 (35.7) | 9 (64.3) | 0.94 | 0.919 | 1 (7.1) | 13 (92.9) | 3.79 | 0.301 | ||||
| (−) | 31 (20.5) | 120 (79.5) | (0.27–4.02) | 56 (37.1) | 95 (62.9) | (0.30–2.95) | 3 (2.0) | 148 (98.0) | (0.37–39.12) | |||||||
| Vitamin D3 supplement | ||||||||||||||||
| (+) | 7 (15.6) | 38 (84.4) | 0.63 | 0.444 | 11 (24.4) | 34 (75.6) | 0.45 | 0.041 * | 2.63 | 0.129 | 0 (0) | 45 (100) | - | 0.276 | ||
| (−) | 27 (22.5) | 93 (77.5) | (0.25–1.58) | 50 (41.7) | 70 (58.3) | (0.21–0.98) | (0.75–9.18) | 4 (3.3) | 116 (96.7) | |||||||
| Variables | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (in years) | 62 | 27 | 22 | 33 |
| Sex | Female | Female | Female | Male |
| Body mass index (category) | 20.44 (underweight) | No data | 13.67 (severely underweight) | 23.88 (normal) |
| Autoimmune Diagnosis | SLE | SLE, APS | SLE | SLE |
| Comorbidities | Cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease | Dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease, hypercoagulable state, deep vein thrombosis | Cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease | Hypertension, Diabetes Mellitus, Tuberculosis |
| COVID-19 Vaccination | Not vaccinated | Not vaccinated | Not vaccinated | Not vaccinated |
| First COVID-19 Diagnosis | June 2020 | September 2020 | June 2021 | February 2022 |
| Second COVID-19 Diagnosis | - | - | February 2022 | - |
| COVID-19 Severity | Severe | Severe | Severe | Moderate |
| Immunosuppressant Therapy before COVID-19 diagnosis | Corticosteroid 5 mg prednisone-equivalent per day; MPA | Not visiting the doctor nor taking autoimmune treatment since the start of pandemic | Corticosteroid 40 mg prednisone-equivalent per day; MPA; Tacrolimus | Corticosteroid 60 mg prednisone-equivalent per day; Rituximab; MPA |
| Immunosuppressant therapy during COVID-19 infection | MPA discontinued | - | MPA and tacrolimus discontinued | MPA discontinued |
| Hospitalization | Isolation room | ICU | Isolation Room | Isolation Room |
| Time to Death (days) | 7 | 12 | 1 | 13 |
| Cause of Death | Cardiogenic shock | Respiratory failure | Septic shock | Hypovolemic shock due to active haemoptysis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Widhani, A.; Koesnoe, S.; Maria, S.; Widjanarko, A.L.; Karjadi, T.H.; Hasibuan, A.S.; Yunihastuti, E.; Rengganis, I.; Djauzi, S. Factors Related to Severity, Hospitalization, and Mortality of COVID-19 Infection among Patients with Autoimmune Diseases. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040227
Widhani A, Koesnoe S, Maria S, Widjanarko AL, Karjadi TH, Hasibuan AS, Yunihastuti E, Rengganis I, Djauzi S. Factors Related to Severity, Hospitalization, and Mortality of COVID-19 Infection among Patients with Autoimmune Diseases. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(4):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040227
Chicago/Turabian StyleWidhani, Alvina, Sukamto Koesnoe, Suzy Maria, Annisa Layalia Widjanarko, Teguh Harjono Karjadi, Anshari Saifuddin Hasibuan, Evy Yunihastuti, Iris Rengganis, and Samsuridjal Djauzi. 2023. "Factors Related to Severity, Hospitalization, and Mortality of COVID-19 Infection among Patients with Autoimmune Diseases" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 4: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040227
APA StyleWidhani, A., Koesnoe, S., Maria, S., Widjanarko, A. L., Karjadi, T. H., Hasibuan, A. S., Yunihastuti, E., Rengganis, I., & Djauzi, S. (2023). Factors Related to Severity, Hospitalization, and Mortality of COVID-19 Infection among Patients with Autoimmune Diseases. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(4), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040227








