Abstract
Leishmaniasis is a neglected tropical disease and an infectious disease transmitted by sandflies that occurs worldwide. In the absence of physicians seeking to identify the causes of disease in non-endemic areas, appropriate diagnoses cannot be made, thereby hampering effective treatment. In this report, we examined a nodular lesion on a patient’s chin by performing a biopsy and molecular analysis. The biopsy finding led to the identification of a Leishmania amastigote. On the basis of PCR analysis of the internal transcribed spacer 1 gene and 5.8 S ribosomal RNA with a subsequent BLAST search, we identified the causal organism as Leishmania infantum. The patient, who had visited Spain from 1 July to 31 August 2018, was accordingly diagnosed with cutaneous leishmaniasis and was administered liposomal amphotericin B, which successfully treated the skin lesion. Travel history plays an important role in the diagnosis of leishmaniasis, and physicians should bear in mind that travelers can also introduce diseases and pathogens to non-endemic areas. Identification of Leishmania at the species level will increase the efficacy of treatment.
1. Introduction
Leishmaniasis is a zoonotic protozoan parasitic disease transmitted by sandflies infected with species of Leishmania. According to the World Health Organization, the incidence of leishmaniasis has increased globally over recent decades. Leishmaniasis is endemic in 200 countries in Asia, Africa, America, and the Mediterranean region [1].
Leishmaniasis is classified into three types according to its clinical manifestations, namely, cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), mucocutaneous leishmaniasis (MCL), and visceral leishmaniasis (VL). Among these, CL is the most common type and is known as Aleppo boil or Baghdad boil or Jericho button [2], with over 600,000 cases reported annually worldwide. It is caused by a range of Leishmania subgenera, including Leishmania major, Leishmania tropica, Leishmania aethiopica, Leishmania mexicana, Leishmania amazonensis, and Leishmania braziliensis. VL, also referred to as post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL) or black fever or dum-dum fever [2], is the most serious form of the disease, caused by L. donovani and L. infantum. Although generally considered a causative agent of VL, L. infantum can also cause skin and mucosal leishmaniasis [3]. Of the 200 countries in which leishmaniasis is endemic, CL and VL are considered endemic in 89 and 79 countries, respectively, with 71 countries being endemic for both CL and VL [1]. Recently, CL caused by L. infantum has been reported in several countries in the Mediterranean region, including France, Italy, Portugal, and Malta. The clinical form of CL, as caused by L. infantum, is a single painless papule that progresses to an ulcero-necrotic nodular lesion in a few weeks or months [4,5,6].
To the best of our knowledge, no Leishmania-transmitting vector (belonging to the genera Phlebotomus and Lutzomyia from the Old and New World, respectively) has been reported in the Republic of Korea, in which leishmaniasis is currently non-endemic. However, to date, since the first case of imported visceral leishmaniasis in the Republic of Korea in 1952, a total of 25 imported cases have been reported (20 and 5 cases of CL and VL, respectively). These cases were reported to be associated with travel for professional reasons in areas endemic for Leishmania, with patients returning from China, Argentina, and Saudi Arabia [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. The most recent case of imported leishmaniasis was a case of New World CL, in which the infected individual had been bitten by an insect whist travelling in Brazil in 2013 [15]. There are, however, increasing concerns regarding the importation of leishmaniasis from endemic countries to the Republic of Korea. Here, we present a rare case of imported CL via a patient who had traveled to Spain in the Republic of Korea. The infection was confirmed by microscopic examination and molecular analysis. This is the first reported case of imported CL caused by L. infantum in the Republic of Korea.
2. Case Presentation
A 78-year-old female patient presented with a 6-month history of a nodular lesion on the left side of her chin. She had a history of hypertension and had traveled to Spain in 2018. She had been living in Gyeonggi in the Republic of Korea, although for 2 months (1 July to 31 August 2018) she had visited her daughter’s house in Tarragona, Spain, an endemic area for leishmaniasis. During her time in Spain, she did not engage in outdoor activities, such as climbing, farming, or camping, and did not recall being bitten by any insects. Moreover, she had no contact with wild animals and did not keep any pets. In January 2021, on examination, a painful and erythematous nodule (10 mm) was detected on the left side of her chin (Figure 1a). She had no fever, and a clinical laboratory examination revealed no abnormalities.
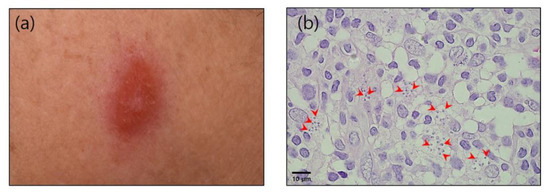
Figure 1.
(a) Cutaneous nodular lesion caused by Leishmania infection on the left side of the patient’s chin (24 May 2021). (b) Microscopic appearance of skin lesions with an amastigote form of Leishmania (red arrowheads) (hematoxylin and eosin staining; 1000× magnification).
A skin biopsy revealed numerous intracellular cocci-like microorganisms, which led to the diagnosis of chronic granulomatous inflammation. Results obtained from acid-fast bacilli staining, fungal staining, and a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for tuberculosis were all negative. Although she was treated with different antibiotics and itraconazole 200 mg, there were no improvements in the skin lesion. A further skin biopsy was therefore performed 4 months after the first, which yielded the same findings. Eventually, the possibility of leishmaniasis was considered, based on the fact that the type of microorganism detected was thought to likely be a Leishmania amastigote (Figure 1b). The patient was accordingly referred to the Department of Infectious Diseases at the Ajou University School of Medicine.
To identify the Leishmania species, skin biopsy samples were collected from the patient at Ajou University Medical Center, and microscopic examinations and genetic analyses were performed at the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA). DNA was extracted from the patient’s skin lesion using a DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (Qiagen GmbH, Hilden, Germany) and the Leishmania internal transcribed spacer 1 and 5.8 S ribosomal RNA genes were detected based on PCR analysis [16,17]. For species identification, a phylogenetic analysis was performed using the maximum likelihood method to identify the best tree. Analysis was conducted using MEGA software (Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA, USA) version 6, and bootstrap scores were calculated for 1000 replicates. The obtained sequence (314 bp; GenBank accession No. MZ596307) was identified based on a BLAST search. The sequence clustered with L. infantum (GenBank accession number: AJ634340-AJ634344) with 100% alignment. These clusters contained L. infantum that have been isolated from patients in different regions (the sequences of which are available in GenBank), including Spain (MHOM/ES/93/PM1; AJ634341, MHOM/ES/86/BCN16; AJ634343), France (MHOM/FR/95/LPN114; AJ634340, MHOM/FR/97/LSL29; AJ634342), and Portugal (MHOM/PT/00/IMT260; AJ634344) (Figure 2). Having been diagnosed with L. infantum-caused CL, the patient underwent surgical excision and was treated with liposomal amphotericin B at a dose of 3 mg/kg for 15 days. The patient experienced no other side-effects during treatment. The lesion was treated, and no recurrence has been reported.
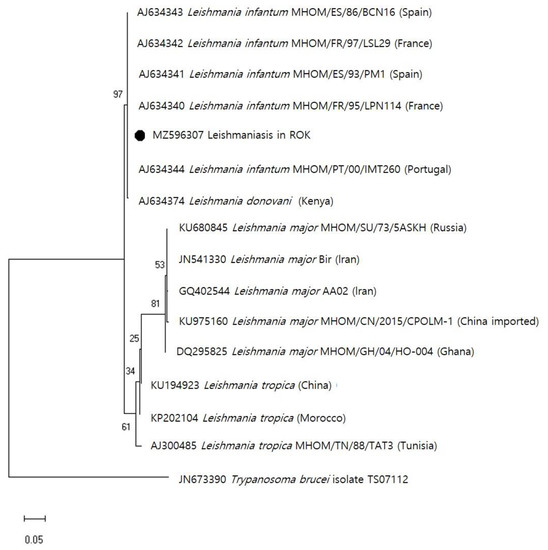
Figure 2.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of internal transcribed spacer 1 and 5.8 S ribosomal RNA sequences of Leishmania. The Leishmania infantum sequence identified in this study is indicated by a solid circle (●, GenBank accession no. MZ596307). The scale bar indicates 0.05 nucleotide substitutions per site.
3. Discussion
Human leishmaniasis, which is caused by more than 20 species of Leishmania, is classified as a neglected tropical disease, although it continues to be a major health problem in endemic regions.
Leishmaniasis is distinguished based on geographical distribution as Old World (southern Europe, Mediterranean basin, Middle East, Asia, and Africa) or New World (Latin America). It is generally transmitted by the bite of female Phlebotomus (Old World) and Lutzomyia (New World) sandflies. Although the distribution of sandflies tends to be confined to subtropical and tropical regions between 50° N and 40° S [18,19], leishmaniasis has spread steadily to non-endemic regions in response to climatic and environmental changes, which are promoting the spread of Leishmania-transmitting vectors and reservoirs [20,21,22]. In Portugal, for example, the seroprevalence of canine leishmaniasis is 20% higher than that previously reported in endemic foci [23]. In Italy, a comparison with historical data revealed that both the canine reservoir and sandflies have increased and expanded northward [24]. Moreover, sandflies have been detected in Spain at higher altitudes than previously reported [25].
To date, however, there is no evidence to indicate the occurrence of leishmaniasis vectors in the Republic of Korea, thereby limiting the risk of introduction and autochthonous transmission. Nevertheless, although the probability of Leishmania spreading to the Republic of Korea is low, notification of imported cases remains necessary, given the rapid growth in international travel. There is currently no vaccine available for leishmaniasis, and, thus, travelers to leishmaniasis endemic areas should be aware that protection from sandfly bites and avoiding outdoor activities when sandflies are most active (from dusk to dawn) are the only practical preventive measures.
Owing to the increasing frequency and intensity of travel and transport over the past century, travelers are generally at a higher risk of infection with Leishmania than other individuals [26]. Imported leishmaniasis is typically associated with travelers and migrants who have returned from regions endemic for this disease [27]. According to the recent literature, more than 10,000 cases of leishmaniasis were reported in non-endemic areas between 2000 and 2021, reflecting the increase in global tourism and human migration [28]. According to a recent WHO report, 979 cases (880 of CL and 99 of VL) of imported leishmaniasis were recorded worldwide in 2020 [1]. One study has shown that leishmaniasis is one of the most frequently diagnosed dermatological diseases among travelers, with 3.3% of 4,594 returning travelers contracting travel-related leishmaniasis [29]. Recently, several cases of travel-related leishmaniasis have been reported in other countries. Leishmaniasis surveillance data have revealed that 77% (799/1044) of the leishmaniasis cases recorded in Europe between 2014 and 2019 were travel related [30]. Similarly, 55% of imported VL cases in the UK were found to be related to tourism [31]. Eighty-nine cases of travel-related VL and CL reported in France were established to have originated in America and Africa [32], whereas in Japan, a Leishmania non-endemic area, an imported case of CL caused by L. tropica was reported to have originated from Pakistan [33].
Microscopic examination is the most widely used method for parasitological diagnosis. Upon Giemsa staining, Leishmania amastigotes are observed within macrophages. They appear round in shape, with a diameter of 2 to 4 µm, and have a blue cytoplasm, red nucleus, and purple-pink-stained kinetoplasts [34]. The amastigote stage is the only Leishmania stage detected in human hosts. The observation of Leishmania amastigotes in stained smears of tissue, such as skin, spleen and lymph node, is taken to be a conclusive diagnosis for leishmaniasis [35]. However, depending on the skill of technicians, it has been reported that the sensitivity of microscopic examination is between only 42% and 70% [36,37]. Furthermore, such examinations have limitations, in that Leishmania species are microscopically indistinguishable. Such observations may also yield false positive results, as artifacts can sometimes erroneously be identified as amastigotes [38]. Consequently, it is not always possible to make a reliable diagnosis. As alternatives, a range of molecular methods have been developed for the diagnosis of leishmaniasis [39,40]. Numerous PCR-based analyses have been described, which are more sensitive than parasite culture, immunohistochemistry, and microscopic examination. PCR provides a sensitive tool for the diagnosis of leishmaniasis and the identification of Leishmania species [41], for which the commonly used targets are the mini-exon of nucleus DNA, heatshock protein 70 (hsp70), mini-circle kinetoplast DNA (kDNA), and internal transcribed space (ITS1 and ITS2) ribosomal RNA. In clinical samples, PCR-RFLP for ITS1 and 5.8 S RNA has been demonstrated to be an effective approach for the identification of Leishmania species [42]. Several commercial kits based on PCR testing and identification of Leishmania species have been developed [39], and, more recently, whole-genome sequencing (WGS) has been used for the diagnosis of travel-related leishmaniasis in an immunosuppressed patient [43]. The advantages of WGS are that it does not require parasite cultivation and can be used to detect variants of parasite genomes in clinical samples [44].
In the Republic of Korea, there have to date been 25 imported cases of leishmaniasis reported, with the most recent case being identified in 2013 [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Of these cases, owing to the technical limitations of PCR, diagnosis was made by confirming the amastigote of Leishmania by microscopic examination. Furthermore, unidentified Leishmania species have resulted in a prolonged treatment period. In this study, the travel-related acquisition of CL was confirmed based on evidence of the amastigotes in tissues and identification of the species L. infantum via PCR amplification and a subsequent BLAST search. Although it was not possible to ascertain the geographical origin of Leishmania based on these results alone, given the patient’s travel history to an endemic region and the associated clinical symptoms of Leishmania, we were able to determine the suspected country of origin with reasonable confidence. Consequently, when diagnosing leishmaniasis in non-endemic areas, physicians should carefully assess the incubation period of the patient’s disease based on their symptoms and travel history.
As previously mentioned, CL is the most prevalent clinical manifestation of leishmania; however, it is typically a neglected disease, given that it is generally self-healing and rarely fatal [45]. CL is predominantly caused by L. major, L. tropica, L. donovani, and L. aethiopica in the Old World. However, L. mexicana, L. amazonensis, and L. braziliensis have been implicated as causal agents of CL in the New World. In contrast, the causative agent of the CL reported in this study was identified as L. infantum, which has been established to cause VL. Historically, atypical CL due to L. infantum has been reported from France in 1980 [46], and more recently, L. infantum has been identified as the causal agent of CL in cases from several regions [4,5,6,47,48]. Given these cases of atypical leishmaniasis, accurate species identification is vital to enable the most appropriate course of treatment. With respect to the case reported herein, on the basis of our understanding of the species-specific information for Leishmania, appropriate treatment was administered to the infected patient, as confirmed by the improvement in her condition.
The incubation period for CL is generally known to last from 2 weeks to over several months [2,34], with symptoms typically presenting as a small erythematous papule at the site of a sandfly bite, which gradually increases in size up to 10 mm or more, thereby forming a nodule, at which point it can become ulcerous with a raised border. Such lesions can persist for at least a few months [34]. Occasionally, longer periods of incubation have been reported. For example, twins who had traveled to Tuscany were subsequently diagnosed with leishmaniasis, 7 and 15 months later [49]. Moreover, a case of CL caused by L. infantum was found to be associated with an incubation period of 19 years [50]. In addition, there have been report of cutaneous leishmaniasis with a long incubation period of 11 to 16 months in Sicily, Italy [51]. Similarly, in the case reported herein, the patient symptoms developed approximately 2 years after returning to Korea from Spain. Thus, given the potentially long incubation period of leishmaniasis, it is essential for physicians to take into consideration past travel to endemic areas.
Cases of leishmaniasis are currently expanding to countries in which it has previously been unknown, due to a number of factors, including climate change and an increase in the volume of international travel. Surveillance of the emerging leishmaniasis situation is accordingly necessary to determine the extent of the disease in both endemic and non-endemic areas, and to monitor the appearance of vectors. Epidemiological efforts should be complemented by training public health professionals to identify the disease and to become acquainted with the appropriate clinical diagnosis, management, and preventive measures.
4. Conclusions
The case reported in this study highlights the potential risks posed to individuals with travel-acquired leishmaniasis. Diagnosing leishmaniasis remains a challenge in non-endemic regions, given the unfamiliarity of physicians with the clinical spectrum and treatment options, as well as the limitation of appropriate diagnostic tools. Consequently, physicians should be mindful with respect to travel history, taking into consideration the destination and disease endemicity when diagnosing leishmaniasis. Furthermore, knowledge of specific Leishmania species provides important information regarding the risk of the disease and can guide treatment decisions. Although a diagnosis of leishmaniasis may not always be feasible in non-endemic regions, the risk can be mitigated by raising awareness of this emerging problem among physicians and public health officials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-I.S. and H.J.K.; methodology, H.J.K.; writing—original draft preparation, H.J.K., E.J.K., J.W.C. and Y.C.K.; writing—review and editing, H.-I.L. and H.-I.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, grant number 6331-311-210.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical approval was not required because this study was conducted to evaluate public health through the Infectious Disease Diagnosis and Surveillance Survey (Infectious Disease Control and Prevention Act) and the patient’s specimen was obtained after oral consent during a general medical procedure.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in the Nucleotide database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), GenBank accession number MZ596307.1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Global Leishmaniasis Surveillance. A Baseline for the 2030 Road Map. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/who-wer9635-401-419 (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Nazzaro, G.; Rovaris, M.; Veraldi, S. Leishmaniasis: A disease with many names. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Guerrero, E.; Quintanilla-Cedillo, M.R.; Ruiz-Esmenjaud, J.; Arenas, R. Leishmaniasis: A review. F1000Research 2017, 6, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Giudice, P.; Marty, P.; Lacour, J.P.; Perrin, C.; Pratlong, F.; Haas, H.; Dellamonica, P.; Le Fichoux, Y. Cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania infantum. Case reports and literature review. Arch. Dermatol. 1998, 134, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campino, L.; Pratlong, F.; Abranches, P.; Rioux, J.A.; Santos-Gomes, G.; Alves-Pires, C.; Cortes, S.; Ramada, J.; Cristovão, J.M.; Afonso, M.O.; et al. Leishmaniasis in Portugal: Enzyme polymorphism of Leishmania infantum based on the identification of 213 strains. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2006, 11, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, D.; Williams, T.N.; Grochowska, A.; Betts, A.; Attard-Montalto, S.; Boffa, M.J.; Vella, C. Manifestations of paediatric Leishmania infantum infections in Malta. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2011, 9, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heu, I.M. Three Cases of Kala-Azar, Especially on the Various Serologic Reaction. Korean J. Intern. Med. 1952, 1, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, T.Y.; Chang, B.K.; Lee, S.H. Two Cases of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Korean J. Dermatol. 1978, 16, 447–486. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, Y.W. Five Cases of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Korean J. Dermatol. 1984, 22, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, T.Y.; Eun, H.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Chi, J.G.; Ham, E.K.; Hong, S.T.; Lee, S.H. Two Cases of Imported Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Korea. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 1985, 23, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Lee, D.K.; Hong, S.J.; Son, S.J.; Cho, M.K. A Case of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Korean J. Dermatol. 2001, 39, 725–727. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.Y.; Cho, S.B.; Chung, K.Y. A Case of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Treated with Intralesional Injection of Meglumine Antimoniate. Korean J. Dermatol. 2006, 44, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, J.G.; Shong, Y.K.; Hong, S.T.; Lee, S.H.; Seo, B.S.; Choe, K.W. An Imported Case of Kala-Azar in Korea. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 1983, 21, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Jung, S.E.; Park, K.W.; Kim, W.K. Visceral Leishmaniasis in a Child. J. Korean Assoc. Pediatr. Surg. 2004, 10, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.Y.; Lee, Y.B.; Cho, B.K.; Park, H.J. New World Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Treated with Intralesional Injection of Pentavalent Antimony. Ann. Dermatol. 2013, 25, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönian, G.; Nasereddin, A.; Dinse, N.; Schweynoch, C.; Schallig, H.D.; Presber, W.; Jaffe, C.L. PCR Diagnosis and Characterization of Leishmania in Local and Imported Clinical Samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 47, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaidi, I.; El Kacem, S.; Ait Kbaich, M.; El Hamouchi, A.; Sarih, M.; Akarid, K.; Lemrani, M. Molecular Identification of Leishmania Infection in the Most Relevant Sand Fly Species and in Patient Skin Samples from a Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Focus, in Morocco. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecílio, P.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A.; Oliveira, F. Sand flies: Basic information on the vectors of leishmaniasis and their interactions with Leishmania parasites. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Singh, S. Insect Vectors of Leishmania: Distribution, Physiology and Their Control. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2008, 45, 255–272. [Google Scholar]
- González, C.; Wang, O.; Strutz, S.E.; González-Salazar, C.; Sánchez-Cordero, V.; Sarkar, S. Climate Change and Risk of Leishmaniasis in North America: Predictions from Ecological Niche Models of Vector and Reservoir Species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunze, S.; Kochmann, J.; Koch, L.K.; Hasselmann, K.J.Q.; Klimpel, S. Leishmaniasis in Eurasia and Africa: Geographical Distribution of Vector Species and Pathogens. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Sáez, V.; Corpas-López, V.; Merino-Espinosa, G.; Morillas-Mancilla, M.J.; Abattouy, N.; Martín-Sánchez, J. Seasonal Dynamics of Phlebotomine Sand Flies and Autochthonous Transmission of Leishmania infantum in High-Altitude Ecosystems in Southern Spain. Acta Trop. 2021, 213, 105749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroli, M.; Rossi, L.; Baldelli, R.; Capelli, G.; Ferroglio, E.; Genchi, C.; Gramiccia, M.; Mortarino, M.; Pietrobelli, M.; Gradoni, L. The Northward Spread of Leishmaniasis in Italy: Evidence from Retrospective and Ongoing Studies on the Canine Reservoir and Phlebotomine Vectors. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2008, 13, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barón, S.D.; Morillas-Márquez, F.; Morales-Yuste, M.; Díaz-Sáez, V.; Irigaray, C.; Martín-Sánchez, J. Risk Maps for the Presence and Absence of Phlebotomus Perniciosus in an Endemic Area of Leishmaniasis in Southern Spain: Implications for the Control of the Disease. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavli, A.; Maltezou, H.C. Leishmaniasis, an Emerging Infection in Travelers. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e1032–e1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berriatua, E.; Maia, C.; Conceição, C.; Özbel, Y.; Töz, S.; Baneth, G.; Pérez-Cutillas, P.; Ortuño, M.; Muñoz, C.; Jumakanova, Z.; et al. Leishmaniases in the European Union and Neighboring Countries. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.; Pereira, A.; Maia, C. Non-Endemic Leishmaniases Reported Globally in Humans between 2000 and 2021-A Comprehensive Review. Pathogens. 2022, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederman, E.R.; Weld, L.H.; Elyazar, I.R.; von Sonnenburg, F.; Loutan, L.; Schwartz, E.; Keystone, J.S. Dermatologic conditions of the ill returned traveler: An analysis from the GeoSentinel Surveillance Network. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Auwera, G.; Davidsson, L.; Buffet, P.; Ruf, M.T.; Gramiccia, M.; Varani, S.; Chicharro, C.; Bart, A.; Harms, G.; Chiodini, P.L.; et al. LeishMan Surveillance Network members who contributed to this article (in addition to authors above). Surveillance of Leishmaniasis Cases from 15 European Centres, 2014 to 2019: A Retrospective Analysis. Eurosurveillance 2022, 27, 2002028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.N.; John, L.; Bruceson, A.D.; Lockwood, D.N. Changing pattern of visceral leishmaniasis, United Kingdom, 1985–2004. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1257–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aissaoui, N.; Hamane, S.; Gits-Muselli, M.; Petit, A.; Benderdouche, M.; Denis, B.; Alanio, A.; Dellière, S.; Bagot, M.; Bretagne, S. Imported Leishmaniasis in Travelers: A 7-Year Retrospective from a Parisian Hospital in France. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, H.; Sanjoba, C.; Goto, Y.; Iwamoto, K.; Kitagawa, H.; Nomura, T.; Omori, K.; Shigemoto, N.; Hide, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; et al. Complicated Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by an Imported Case of Leishmania tropica in Japan: A Case Report. Trop. Med. Health 2021, 49, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockmeyer, W.T.; Kager, P.A.; Rees, P.H.; Hendricks, L.D. The culture of Leishmania donovani in Schneider’s insect medium: Its value in the diagnosis and management of patients with visceral leishmaniasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 75, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markle, W.H.; Makhoul, K. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: Recognition and treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2004, 69, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Aviles, H.; Belli, A.; Armijos, R.; Monroy, F.P.; Harris, E. PCR detection and identification of Leishmania parasites in clinical specimens in Ecuador: A comparison with classical diagnostic methods. J. Parasitol. 1999, 85, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, H.; Lindoso, J.A. Current diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2010, 8, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, C.; Campino, L. Methods for Diagnosis of Canine Leishmaniasis and Immune Response to Infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 158, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimão, J.Q.; Coser, E.M.; Lee, M.R.; Coelho, A.C. Laboratory Diagnosis of Cutaneous and Visceral Leishmaniasis: Current and Future Methods. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gow, I.; Smith, N.C.; Stark, D. Laboratory diagnostics for human Leishmania infections: A polymerase chain reaction-focussed review of detection and identification methods. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ruiter, C.M.; Van Der Veer, C.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Deborggraeve, S.; Lucas, C.; Adams, E.R. Molecular tools for diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3147–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, G.; Bruno, F.; Reale, S.; Catanzaro, S.; Valenza, V.; Vitale, F. Molecular Diagnosis of Leishmaniasis: Quantification of Parasite Load by a Real-Time PCR Assay with High Sensitivity. Pathogens 2021, 10, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.; Isles, N.S.; Seemann, T. Case Report: Confirmation by Metagenomic Sequencing of Visceral Leishmaniasis in an Immunosuppressed Returned Traveler. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1930–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagalska, M.A.; Imamura, H.; Sanders, M.; Van den Broeck, F.; Bhattarai, N.R.; Vanaerschot, M.; Maes, I.; D’Haenens, E.; Rai, K.; Rijal, S. Genomes of Leishmania parasites directly sequenced from patients with visceral leishmaniasis in the Indian subcontinent. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S.; Frasca, K.; Scherrer, S.; Henao-Martínez, A.F.; Newman, S.; Ramanan, P.; Suarez, J.A. A Review of Leishmaniasis: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2021, 8, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.; Azam, M.; Ramesh, V.; Singh, R. Unusual Observations in Leishmaniasis—An Overview. Pathogens 2023, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux, J.A.; Lanotte, G.; Maazoun, R.; Perello, R.; Pratlong, F. Leishmania infantum Nicolle, 1908, agent du bouton d’Orient autochtone. A propos de l’identification biochimique de deus souches isolées dans les Pyrénées-Orientales [Leishmania infantum Nicolle, 1908, the agent of the autochthonous oriental sore. Apropos of the biochemical identification of 2 strains isolated in the eastern Pyrenees]. C. R. Seances Acad. Sci. D. 1980, 291, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elmazini, S.; Ejghal, R.; Bekhti, K.; Lemrani, M. The Sporadic cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania infantum in Morocco: A presumably trend towards endemicity. Acta Trop. 2021, 227, 106288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, L.; Singh, K.K.; Shanker, V.; Negi, A.; Jain, A.; Matlashewski, G.; Jain, M. Atypical leishmaniasis: A global perspective with emphasis on the Indian subcontinent. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczick, C.; Dierig, A.; Welzel, T.; Schifferli, A.; Blum, I.; Ritz, N. Double trouble: Visceral leishmaniasis in twins after traveling to Tuscany—A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, A.; Slavin, J.; Sark, D.; Aboltins, C. A case of imported Leishmania infantum cutaneous leishmaniasis; an unusual presentation occurring 19 years after travel. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraldi, S.; Gianotti, R.; Sala, F.; Coggi, A.; Venegoni, L.; Persico, M.C.; Berti, E. Latency time in cutaneous leishmaniasis. G Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 146, 159–161. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).