Abstract
Tropical acute febrile illness (TAFI) is one of the most frequent causes of acute kidney injury (AKI). The prevalence of AKI varies worldwide because there are limited reports available and different definitions are used. This retrospective study aimed to determine the prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of AKI associated with TAFI among patients. Patients with TAFI were classified into non-AKI and AKI cases based on the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria. Of 1019 patients with TAFI, 69 cases were classified as having AKI, a prevalence of 6.8%. Signs, symptoms, and laboratory results were significantly abnormal in the AKI group, including high-grade fever, dyspnea, leukocytosis, severe transaminitis, hypoalbuminemia, metabolic acidosis, and proteinuria. 20.3% of AKI cases required dialysis and 18.8% received inotropic drugs. Seven patients died, all of which were in the AKI group. Risk factors for TAFI-associated AKI were being male (adjusted odds ratio (AOR) 3.1; 95% CI 1.3–7.4), respiratory failure (AOR 4.6 95% CI 1.5–14.1), hyperbilirubinemia (AOR 2.4; 95% CI 1.1–4.9), and obesity (AOR 2.9; 95% CI 1.4–6). We recommend clinicians investigate kidney function in patients with TAFI who have these risk factors to detect AKI in its early stages and offer appropriate management.
1. Introduction
Fever, or acute febrile illness (AFI), is defined as an increase in body temperature caused by alterations in the hypothalamic thermoregulatory center [1]. There is a wide range of AFIs with different etiologies and induced by local outbreaks of disease, which can vary from region to region and country to country [2]. Tropical acute febrile illness (TAFI), which occurs in individuals living in tropical and subtropical regions, is defined as an AFI with a fever of duration less than 14 days. TAFI has no specific clinical signs and symptoms; most patients complain of fever, myalgia, arthralgia, vomiting, breathlessness, cough, chest pain, headache, rash, conjunctival congestion, or other symptoms. There are many infections that manifest as AFI in tropical countries, including dengue fever, typhoid fever, leptospirosis, rickettsia, influenza, and malaria [3,4]. In some AFI cases, patients also develop acute kidney injury (AKI). AKI is characterized by a rapid loss of the kidney’s excretory function, with or without oliguria, which commonly occurs over the course of hours to days. AKI is common in hospitalized patients, especially critically ill patients [5].
The pathophysiology of AKI in TAFI remains unclear. It is likely multifactorial and may differ based on infectious etiologies and their clinical presentation. Different hypotheses have been proposed, including direct injury to kidney tissue, immune mechanisms, hemolysis, cytoadherence of parasite-infected erythrocytes, intravascular coagulation, severe hyperpyrexia, vasculitis, and a secondary outcome of rhabdomyolysis [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. In 2016, the incidence of AKI in Asia was as follows: 31% in Southeastern Asia, 19.4% in Eastern Asia, 16.7% in Western Asia, 9% in Central Asia, and 7.5% in Southern Asia [21]. The reported incidence of AKI varied based on the definition of AKI used and by ethnicity [22]. Mortality in AKI remains high globally, even in high-resource settings [23]. Poor health awareness and a lack of good diagnostic tests, limited resources, and poor sanitation are the major reasons for the differences in AKI outcomes between developing and developed countries [23]. AKI in the tropics is little known due to limited reporting and differences in the definitions of AKI used. Early diagnosis is essential to prevent AKI in patients with TAFI, which can be a common outcome of many infections, such as dengue, malaria, influenza, rickettsia, and leptospirosis. The present study aimed to determine the prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of AKI associated with tropical acute febrile illness.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This retrospective study received ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Thailand (Certificate No. MUTM 2019–018-01). The Ethics Committee waived the requirement for informed consent and the data were fully anonymized before analysis. We assessed the medical records of patients with TAFI who were admitted to the Hospital for Tropical Diseases, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Thailand, between January 2015 and December 2018. The international statistical classification of diseases and related health problems, 10th revision (ICD10) criteria were used to search for medical records of patients diagnosed with TAFI. The inclusion criteria were TAFI patients aged ≥ 18 years who had a history of fever < 2 weeks and a fever ≥ 37.5 °C during their first 24-h period of hospitalization. Patients with no serum creatinine result during hospitalization, missing clinical data in their medical records, non-specific or non-infectious causes of AFI, specific organ involvement with non-tropical diseases, or a fever of unknown origin were excluded from the study. The medical records of included cases were classified into AKI and non-AKI groups, based on the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria [24]. A diagnosis of AKI was based solely on serum creatinine (SCr) results. Patient data, including both hard copies and electronic records, were reviewed on a case-by-case basis. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data of eligible patients were obtained. Demographic details and clinical presentations were recorded upon hospital admission, while laboratory data were collected during a patient’s hospitalization.
2.2. Clinical Definitions
AKI is a complex clinical disorder characterized by a rapid loss in the kidney’s excretory function, with or without oliguria, occuring over the course of a few hours to days. It is closely associated with severe morbidity and mortality [5]. According to the KDIGO criteria, AKI is defined as an increase in SCr of ≥0.3 mg/dL within 48 h or an increase of ≥1.5 times the baseline within 7 days. It is divided into: stage 1, SCr increase >0.3 mg/dL or SCr increase 1.5–1.9-times the baseline; stage 2, SCr increase 2–2.9-times the baseline; stage 3, SCr increase 3-times the baseline, or the initiation of renal replacement therapy (RRT) [25,26]. Patients’ SCr results on admission were used as the baseline for comparison of their kidney function during hospitalization. For patients who had a single SCr result, the baseline SCr was estimated using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation [27]. Other AKI criteria, including conventional, RIFLE and AKIN, were defined (see Supplementary File S1) and explored in this study.
In this study, patients were observed for the presence of clinical conditions and their severity grading. These included hyperbilirubinemia, transaminitis, metabolic acidosis, proteinuria, hematuria, pyuria, severe thrombocytopenia, respiratory failure, multi-organ dysfunction (MOD), and obesity. Further details on the definition of these conditions can be found in Supplementary File S1.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The sample size required was 1013 patients, based on the estimated proportion of patients with TAFI of 0.54 (Nair et al., 2016), with a margin of error of 0.025 and alpha 0.05 [28,29]. The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software (version 18) Chicago: SPSS Inc. (Chicago, IL, USA) Quantitative variables are given as medians with interquartile ranges (IQRs). For hypothesis testing, appropriate tests, including the Student’s t-test or the Mann-Whitney U test, were selected, depending on the data distribution. All categorical variables are presented as numbers and percentages. The chi-square test and Fisher’s exact test were used for group comparisons based on cell values in the tables. A p-value of 0.05 or less was considered to indicate statistical significance. The Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve was applied to evaluate the diagnostic ability of tests. The optimal cut-off value of a test was obtained by maximizing the area under the ROC curve, at which the sensitivity and specificity were then reported.
3. Results
Overall, a total of 2056 medical records of patients diagnosed with TAFI were screened for the study, of which 1037 cases were excluded, leaving 1019 patients who were eligible for the study, as shown in Figure 1. Of the eligible cases, 603 (59%) had just one SCr result. Therefore, their baseline SCr was estimated using the CKD-EPI equation.
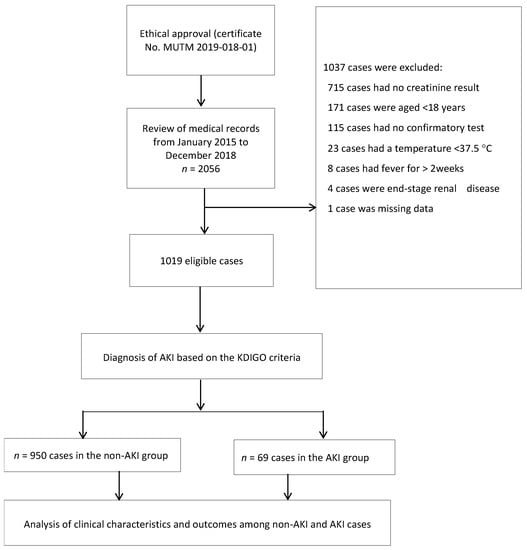
Figure 1.
Study flow-diagram.
3.1. Characteristics of Eligible Cases and Prevalence of AKI in Patients with TAFI
In total, 950 cases were classified into the non-AKI group, with the remaining 69 cases classified into the AKI group. Of the latter cases, 41/69 (59.4%) had dengue, 14/69 (20.3%) had malaria, 11/69 (15.9%) had influenza, 2/69 (2.9%) had rickettsial illness (murine typhus), and 1/69 (1.4%) had leptospirosis; there were no patients with mixed infections (Table 1). The prevalence of AKI by KDIGO criteria, AKIN criteria, RIFLE criteria, and conventional criteria was 6.8%, 5.9%, 4.1%, and 4.0%, respectively. The proportion of AKI by KDIGO criteria in stages 1, 2, and 3 was 45/69 (65.2%), 8/69 (11.6%), and 16/69 (23.2%), respectively (Table 2). In comparison with the non-AKI group, the AKI group comprised mostly males (50/69, 72.5%, p = 0.004), with a female to male ratio of 1:2.6. The distribution of AKI by TAFI is shown in Table 1. Among dengue infections, 41/767 (5.3%) had AKI; among malaria infections, 14/131 (10.7%) had AKI; among influenza infections, 11/106 (10.4%) had AKI; among rickettsial infections, 2/11 (18.2%) had AKI; and 1/2 (50%) of leptospirosis infections had AKI. According to the WHO 2009 case definition for dengue, 15/48 (31.3%) of severe dengue cases were in the AKI group. There were 131 malaria cases, of which 14 (10.7%) were in the AKI group: 10 with Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) malaria and 4 with Plasmodium vivax (Pv) malaria. Of the 11 (10.4%) influenza cases in the AKI group, 9 had influenza A and 2 had influenza B. Lastly, 2/2 (100%) of rickettsial cases in the AKI group had murine typhus.

Table 1.
Prevalence of acute kidney injury (AKI) among cases of tropical acute febrile illness (TAFI).

Table 2.
Acute kidney injury (AKI) criteria and staging.
The clinical characteristics of the patients with TAFI in the AKI and non-AKI groups are summarized in Table 3. All, except two, patients complained of fever on admission. Chills and headache were reported among half of all patients in both groups. Nausea/vomiting and other symptoms, including abdominal pain and cough, were around 30% in both groups. Arthralgia was rarely detected, at less than 5% in each group. Pallor and dyspnea were significantly more common among AKI cases than non-AKI cases, at 10.1% and 14.5%, respectively. Myalgia was significantly lower in the AKI compared with the non-AKI group, i.e., 45% vs. 66%, respectively. The major underlying diseases in patients with AKI were diabetes mellitus (11/69, 15.9%), chronic kidney disease (6/69, 8.7%), hepatitis B virus (4/69, 5.8%), human immunodeficiency virus (5/69, 7.2%), and asthma (6/69, 8.7%), with statistically significant differences between the AKI and non-AKI groups. Hypertension (8/69, 11.6%) and dyslipidemia (21/69, 30.4%) showed no statistically significant differences between the AKI and non-AKI groups.

Table 3.
Demographic and clinical characteristics for patients with TAFI with and without AKI.
Laboratory test results from patient samples collected on admission are shown in Table 4. Statistically significant differences were observed between the AKI and non-AKI groups in serum sodium, serum potassium, serum bicarbonate, serum total bilirubin, urine specific gravity, WBCs, neutrophils, lymphocytes, atypical lymphocytes, RBCs, and AST. In the AKI group, 8/69 (11.6%) cases had serum creatinine > 3.0 mg/dL and presented with AKI stage 3 on admission. In AKI cases, 31/58 (53.4%) developed hyperbilirubinemia (TB > 1.2 mg/dL) on admission. There were 22/56 (39.3%) AKI cases with moderate to severe transaminitis. The median specific gravity of urine from patients in the AKI group was 1.020 (1.01–1.025; p < 0.001), which was significantly higher than in the non-AKI group. Proteinuria was significantly higher in the AKI group (27/53, 50.9%, p < 0.001). Urine sedimentation was higher in the AKI group, including hematuria (11/53, 20.8%) and pyuria (8/53, 15.1%), but this was not statistically significant (p > 0.05).

Table 4.
Laboratory test results among patients with TAFI with and without AKI.
3.2. Complications and Outcomes of AKI in Patients with TAFI
Complications present in cases of AKI included severe transaminitis (13/56, 23.2%) and hypoalbuminemia (21/58, 36.2%), which were significantly higher than in the non-AKI group (p < 0.05). Metabolic acidosis was present in 10/69 (14.5%) cases; 23/69 (33.3%) cases developed respiratory failure and required mechanical ventilation; 20/69 (28.9%) patients were admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU); 13/69 (18.8%) patients developed multi-organ dysfunction, and 6/69 (8.7%) had underlying CKD. All were significantly higher than in the non-AKI groups. Only severe thrombocytopenia (29/69, 42%) showed no significant difference. There were 60/69 (86.9%) patients with AKI who improved and recovered, while one patient did not improve. Another case was transferred to lung cancer treatment. There were 13/69 (18.8%) and 14/69 (20.3%) patients who received inotropic drugs (norepinephrine) and hemodialysis, respectively. Among patients with hemodialysis, 4/14 (28.6%) patients were on intermittent hemodialysis, 3/14 (21.4%) patients on sustained low-efficiency dialysis (SLED), and 7/14 (50%) patients on continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). There were 7/69 (10.1%) patients who died; all were in the AKI group. Most patients who died (5/7, 71.4%) were female. As shown in Table 5, 6/7 (85.7%) patients developed multi-organ dysfunction and all patients developed respiratory failure. All patients who died were classified as having severe dengue with AKI stage 3. The parameters with 5% occurrence of cases and non-complete separation (perfect predictor) were further processed to the risk association analysis.

Table 5.
Complications and outcomes among patients with TAFI with and without AKI.
3.3. Factors Associated with AKI
Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify independent risk factors for AKI, quantified by the adjusted odds ratio (AOR), with 95% CI. Categorical variables were assigned to the model, with entry at 0.05 and removal at 0.10, and were scored using “no” as the reference category. We found that male sex (AOR 3.1; 95% CI 1.3–7.4), respiratory failure (AOR 4.6; 95% CI 1.5–14.1), hyperbilirubinemia (AOR 2.4; 95% CI 1.1–4.9), and obesity (AOR 2.9; 95% CI 1.4–6) were risk factors associated with AKI (Table 6).

Table 6.
Factors associated with AKI by univariate and multivariate analysis.
Based on the common model discrimination method using the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC), the optimal sensitivity and specificity obtained at the maximum area under the curve of 0.767 (95% CI 0.69–0.85) were 70% and 72%, respectively.
4. Discussion
This retrospective study assessed the prevalence and clinical characteristics of AKI in patients with TAFI. We observed a prevalence of AKI by KDIGO, AKIN, RIFLE, and conventional definitions of 6.8%, 5.9%, 4.1%, and 4.0%, respectively. Three studies of TAFI-associated AKI conducted in India between 2010 and 2018 reported a prevalence between 28–54% using either RIFLE or KDIGO criteria [4,30,31]. One study from Malaysia in 2017 reported TAFI-associated AKI with a prevalence of 41.1%, using KDIGO [32]. The wide range of reported AKI prevalence was due to the different AKI criteria being used, as well as the different etiology of AKI in these places. For the present study, we found six patients with underlying chronic kidney disease (CKD). There were seven underlying CKD cases in our study. However, there remained the possibility of other cases of undiagnosed CKD. CKD has previously been reported as a risk factor for developing AKI [33]. Similarly, many previous studies reported some underlying CKD cases which subsequently developed AKI [30,34]. In our study, we excluded approximately 34.8% (715/2056) of the total screened medical records due to the absence of a creatinine investigation. The clinicians did not request SCr investigation in these patients because they did not have symptoms and signs of AKI, and the clinicians did not suspect AKI. A previous study experienced a similar rate of exclusion (810/2476, 32.7%) during screening due to an absence of SCr results [34]. The infections present in patients with TAFI-associated AKI in our study were dengue (59.4%), malaria (20.3%), influenza (15.9%), rickettsia (2.9%), and leptospirosis (1.5%). The mechanisms of TAFI-associated AKI are complex. The alteration of kidney tubular function resulting from hemodynamic instability and hypotension, cytokine production, and immune complex deposition has been noted for the three major TAFI listed (dengue, malaria, and influenza) in this study [35,36,37]. Dengue shock syndrome (DSS) also increases the risk of AKI [35]. Hemodynamic derangement from parasitized red blood cells and platelets resulting in microvascular blockage (sequestration) is also a major mechanism in malarial AKI [38]. Note that in our study dengue was the largest TAFI group at 75.3% (767/1019). Different studies have reported a high proportion of leptospirosis [4], scrub typhus, malaria, and HIV [30,39,40] among TAFI-associated AKI patients. The causes of TAFI associated with AKI were different from region to region or country to country due to infection cause and population demographics [22,30,41]. In our study, the proportion of patients with AKI in stages 1, 2, and 3 were 65.2%, 11.6%, and 23.2%, respectively. All cases of stage 3 AKI in our study were associated with severe dengue infection or falciparum malaria.
Most of the patients with stage 1 AKI were diagnosed by laboratory investigations [4]; all deaths were in stage 3 AKI. A high-grade fever (>39 °C) was observed in 29% of cases in the AKI group, which was significantly higher than the proportion of patients with high-grade fever in the non-AKI group. Pyrexia causes dehydration and is characteristic of AFI [4]. On admission, a significantly higher proportion of patients with dyspnea (14.5%) and pallor (10.1%) were detected in the AKI group in our study. Previous studies have reported that 20% of AKI cases presenting with dyspnea, metabolic acidosis, and shock are significantly likely to occur with dengue-associated AKI [4,10,34]. There were 50.9% of AKI cases with proteinuria, which was significantly higher than in the non-AKI group, while 20.8% and 15.1% of AKI cases had hematuria and pyuria, respectively, which was not significantly different compared with the non-AKI group. Proteinuria, hematuria, and pyuria have been reported to be associated with AKI elsewhere [42].
The median WBC increased significantly in the AKI group compared to the non-AKI group. Both leukocytosis and leukopenia can increase the risk of developing AKI in critical patients in the ICU [43]. Inflammation plays an important role in tubular cell damage during AKI, with neutrophils being an obvious factor in the inflammatory cascade [44,45]. Lymphocytes play a critical role in the immune inflammatory response, and the production of cytokines participates in the AKI process [46]. We also observed severe transaminitis (23.2%), hypoalbuminemia (36.2%), and hyperbilirubinemia (53.4%) to be higher in the AKI group than in the non-AKI group. Patients who exhibited an increase in transaminitis, hyperbilirubinemia, and hypoalbuminemia were shown in a previous study to be more likely to develop AKI [47]. Hypoalbuminemia is a risk factor for AKI [48]. In this study, the AKI group had a higher proportion of hyponatremia (53.8%) and metabolic acidosis (14.5%) than the non-AKI group. A decline in GFR will cause the retention of waste products, aggravating electrolyte imbalance, including hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and metabolic acidosis. Metabolic acidosis has been reported to be associated with AKI [49,50,51]. In our study, most of the patients in both the non-AKI and AKI groups recovered and had improved by the time they were discharged. However, all of the deaths we recorded occurred in cases of AKI (10.1%). The etiology of their deaths was unknown, as no autopsies were performed. Among the deaths, 5/7 cases (71.4%) were female, while all patients who died developed respiratory failure, and 6/7 cases (85.7%) had multi-organ dysfunction. All these cases had severe dengue infection and stage 3 AKI. Among the death cases in our study, 5 out of 7 death cases were referred from another hospital with severe dengue, multi-organ dysfunction, and shock on presentation, and 4 out of 5 referred cases were female. In our study, the mortality rate in patients with TAFI was 7/1019 (0.69%). Other studies have reported mortality rates in all cases of AFI, irrespective of AKI, of 3% and 12.3% [4,30]. The variation in mortality rates observed in those studies could be explained by differences in the study populations, rates of ICU admission, underlying diseases, and the different criteria used for the classification of AKI in different studies. However, patients with AKI had significantly higher in-hospital mortality than non-AKI cases, regardless of the AKI definition used [33]. Mortality in the AKI group (10.1%) in our study was significantly lower than the study of acute kidney injury in a tropical country by Daher et al., which reported a mortality of 62.8% [39]. The low mortality rate of our study can be explained by the fact that it was conducted in a tertiary care hospital for tropical diseases in Thailand, where the medical care and services include high-quality ICU settings, the availability of extensive laboratory investigations, mechanical ventilator support, and renal replacement therapy.
In the present study, 18.5% and 20.3% of AKI cases required inotropic drugs and dialysis, respectively. Among the dialysis cases, 21.4% and 50% of them were on SLED and CRRT mode, respectively, according to the hemodynamically unstable conditions. There were no cases in the non-AKI group that required inotropic drugs or dialysis. Previous studies have reported between 7.9% and 44.8% of patients with TAFI-associated AKI requiring dialysis [4,30,39,40,52,53]. In our study, patients in the AKI group had significantly longer hospital stays than patients in the non-AKI group. A similar result was observed in a previous study [34].
Similar to some previous studies, males showed a higher risk of developing AKI than females (AOR 3.1; 95% CI 1.3–7.4) [54,55]. Many studies have shown that endoplasmic reticulum stress participates in the development of AKI in both animals and humans, and that the kidney of the male is more vulnerable to endoplasmic reticulum stress [56,57]. Additionally, testosterone has apoptotic and fibrotic effects that are aggravated by the release of TNF-α, and the generation of inflammation leading to AKI. Respiratory failure was shown to be another risk factor for AKI in the present study (AOR 4.6; 95% CI 1.5–14.1). This same result has been noted previously [58]. The pathophysiology of AKI in respiratory failure is not completely understood, but studies have reported many mechanisms that participate in the aggravation of AKI during respiratory failure. For example, increasing intrathoracic pressures with poorly compliant lungs can reduce cardiac output, resulting in inadequate renal perfusion that aggravates AKI [59,60,61]. Hyperbilirubinemia was shown to be one of the risk factors for AKI in the present study (AOR 2.4; 95% CI 1.1–4.9), which agrees with a previous report [62]. There has also been a report of severe hyperbilirubinemia and association of severe AKI in patients with cardiac surgery [63]. Bilirubin and bile salt cause direct damage to the tubular epithelium of the kidney [64]. Furthermore, high bilirubin levels would stimulate renal ischemic-reperfusion injury [65]. Obesity is another risk factor for AKI identified in the present study (AOR 2.9; 95% CI 1.4–6); again, this is in agreement with the findings of previous studies [66,67]. There was evidence of a linear correlation between a higher BMI and a higher incidence of AKI [68]. The pathophysiology linking obesity and AKI is unclear. One explanation would be that obesity causes a change in renal hemodynamics that may lead to vulnerability to kidney injury [69]. Furthermore, inflammatory cytokine production from adipose tissue during acute illness has been shown to participate in the development of AKI [70]. Subsequently, the increase of intra-abdominal pressure and central venous pressure from obesity was proposed as another mechanism which increases AKI risk [71]. Lastly, the meta-analysis study of COVID-19 suggested that obesity increases severe clinical course, ICU admission, and death among COVID-19 patients [72].
The limitations of this study were as follows. First, we excluded around 50% of screened medical records because of the exclusion criteria, such as no SCr investigation or an unconfirmed diagnosis of TAFI. Second, the diagnosis of AKI was based only on SCr criteria.
5. Conclusions
The overall prevalence of TAFI-associated AKI was 6.8%. TAFI-associated AKI can lead to an increased mortality rate. The risk factors for TAFI-associated AKI were being male, having respiratory failure or hyperbilirubinemia, and being obese. The combination of these identified risk factors produced a predictive algorithm, which achieves a value of sensitivity (70%) and specificity (72%) similar to previous studies [73]. We suggest that clinicians investigate kidney function in patients with TAFI who also have these associated risk factors to assist in the detection of AKI in its early stages and to offer appropriate management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/tropicalmed8030147/s1, File S1: Supplementary Materials of Clinical characteristics of acute kidney injury associated with tropical acute febrile illness. References [74,75,76,77] are cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.D.O. and W.P.; methodology, F.D.O.; formal analysis, F.D.O., W.P. and W.P.-n.; data curation, F.D.O.; writing—original draft preparation, F.D.O.; writing—review and editing, W.P. and W.P.-n.; supervision, U.S., B.H., N.S. and J.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded in part by the Wellcome Trust [Grant number 220211] and the Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Thailand. For the purpose of open access, the author has applied a CC BY public copyright licence to any author accepted manuscript version arising from this submission. The funder played no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, (Certificate No. MUTM 2019–018-01).
Data Availability Statement
Due to the patients’ confidentiality, data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the staff of the Bangkok Hospital for Tropical Diseases and the Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University for their honest support throughout our research work, both directly and indirectly.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Eskerud, J.R.; Laerum, E.; Fagerthun, H.; Lunde, P.K.; Naess, A. Fever in general practiceI. Frequency and diagnoses. Fam. Pract. 1992, 9, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.A.; Ittyachen, A.M. Aetiology of acute febrile illness: A multicentre study from the province of Kerala in southern India. Trop. Dr. 2018, 48, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luvira, V.; Silachamroon, U.; Piyaphanee, W.; Lawpoolsri, S.; Chierakul, W.; Leaungwutiwong, P.; Thawornkuno, C.; Wattanagoon, Y. Etiologies of Acute Undifferentiated Febrile Illness in Bangkok, Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, J.J.; Bhat, A.; Prabhu, M.V. A Clinical Study of Acute Kidney Injury in Tropical Acute Febrile Illness. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, OC01–OC05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koza, Y. Acute kidney injury: Current concepts and new insights. J. Inj. Violence Res. 2014, 8, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Attur, R.P.; Kuppasamy, S.; Bairy, M.; Nagaraju, S.P.; Pammidi, N.R.; Kamath, V.; Kamath, A.; Rao, L.; Bairy, I. Acute kidney injury in scrub typhus. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2013, 17, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonpucknavig, V.; Bhamarapravati, N.; Boonpucknavig, S.; Futrakul, P.; Tanpaichitr, P. Glomerular changes in dengue hemorrhagic fever. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1976, 100, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boonpucknavig, V.; Soontornniyomkij, V. Pathology of renal diseases in the tropics. Semin. Nephrol. 2003, 23, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, C.; Patel, M.; Nugent, A.; Dimas, V.V.; Guleserian, K.J.; Quigley, R.; Modem, V. Serum Cystatin C as an Early Marker of Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin-positive Acute Kidney Injury Resulting from Cardiopulmonary Bypass in Infants with Congenital Heart Disease. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2015, 10, E180–E188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommel, D.; Talarmin, A.; Reynes, J.M.; Hulin, A. Acute renal failure associated with dengue fever in French Guiana. Nephron 1999, 83, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susilawati, T.N.; McBride, W.J. Acute undifferentiated fever in Asia: A review of the literature. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2014, 45, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-M.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, J.O.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, H.L.; Park, C.Y.; Lim, S.-C. Acute renal failure due to acute tubular necrosis caused by direct invasion of Orientia tsutsugamushi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, B.Y.; Yang, H.H.; Liou, J.H.; Chen, L.K.; Hsu, Y.H. Immunohistochemical study of scrub typhus: A report of two cases. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2008, 24, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, R.; Yu, L.; Younes-Ibrahim, M.; Schor, N.; Burdmann, E.A. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in Latin America. Semin. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Das, B.S. Malaria and acute kidney injury. Semin. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.F.; Burdmann, E.A. Dengue-associated acute kidney injury. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plewes, K.; Royakkers, A.A.; Hanson, J.; Hasan, M.M.; Alam, S.; Ghose, A.; Maude, R.J.; Stassen, P.M.; Charunwatthana, P.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Correlation of biomarkers for parasite burden and immune activation with acute kidney injury in severe falciparum malaria. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenouda, A.; Hatch, F.E. Influenza A viral infection associated with acute renal failure. Am. J. Med. 1976, 61, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, U.; Scheld, W.M. Infectious etiologies of rhabdomyolysis: Three case reports and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. Renal complications of seasonal and pandemic influenza A virus infections. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2013, 172, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. Acute Kidney Injury in Asia. Kidney Dis. 2016, 2, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda, J.; Lameire, N.; Eggers, P.; Pannu, N.; Uchino, S.; Wang, H.; Bagga, A.; Levin, A. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyachandran Dhanapriya, T.D. Ramanathan Sakthirajan, Natarajan Gopalakrishnan. Acute Kidney Injury in Tropical Countries. EMJ 2017, 5, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Eckardt, K.U.; Kasiske, B.L. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, M.; Mori, J.; Ohashi, K.; Akiyama, H.; Morito, T.; Tsuchiya, K.; Nitta, K.; Sakamaki, H. A comparative assessment of the RIFLE, AKIN and conventional criteria for acute kidney injury after hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2010, 45, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, P.; Rodriguez, E.; Piano, S.; Ariza, X.; Morando, F.; Sola, E.; Romano, A.; Garcia, E.; Pavesi, M.; Risso, A.; et al. Acute kidney injury and acute-on-chronic liver failure classifications in prognosis assessment of patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gut 2015, 64, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jeong, T.D. Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rates Show Minor but Significant Differences Between the Single and Subgroup Creatinine-Based Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration Equations. Ann. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enderlein, J. Maximum-likelihood criterion and single-molecule detection. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngamjarus, C.; Chongsuvivatwong, V.; McNeil, E.; Holling, H. Enhancement of Learning on Sample Size Calculation with a Smartphone Application: A Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2017, 48, 240–252. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, G.; Chrispal, A.; Boorugu, H.; Gopinath, K.G.; Chandy, S.; Prakash, J.A.J.; Thomas, K.; Abraham, A.M.; John, G.T. Acute kidney injury in tropical acute febrile illness in a tertiary care centre—RIFLE criteria validation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 26, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.D.; Jain, A.D. Acute Kidney Injury in Tropical Acute Febrile Illness of Malwa Region. Sch. J. Appl. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 1274–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Kamil, W.M.; Abdullah, R.; Thabit, A.; Din, M.; Azman, S.; Arumugam, M.; Singh, S.; Rosli, N. 117 A Prospective Study of Acute Kidney Injury in Tropical Acute Febrile Illness in West Pahang, Malaysia. In Kidney International Reports; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ferenbach, D.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: From the laboratory to the clinic. Nephrol. Ther. 2016, 12 (Suppl. S1), S41–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diptyanusa, A.; Phumratanaprapin, W.; Phonrat, B.; Poovorawan, K.; Hanboonkunupakarn, B.; Sriboonvorakul, N.; Thisyakorn, U. Characteristics and associated factors of acute kidney injury among adult dengue patients: A retrospective single-center study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diptyanusa, A.; Phumratanaprapin, W. Predictors and Outcomes of Dengue-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 105, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.D.; Solomon, S.; Lerner, D.; Del Rio, M. Malaria and acute kidney injury. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbhi, S.A.; Alshahrani, H.A.; Almadi, A.; Busaleh, H.; Alotaibi, M.; Almutairi, W.; Almukhrq, Z. Prevalence and mortality due to acute kidney injuries in patients with influenza A (H1N1) viral infection: A systemic narrative review. Int. J. Health Sci. (Qassim) 2019, 13, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Berendt, A.R. Sequestration and its discontents: Infected erythrocyte-endothelial cell interactions in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Res. Immunol. 1993, 144, 740–745; discussion 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, E.F.; Vieira, A.P.; Jacinto, C.N.; Lima, R.S.; Girao, M.M.; Fernandes, A.T.; Neto, R.J.; Silva, G.B.J. Differences among children, adolescents and adults with severe leptospirosis: A comparative analysis. Indian J. Nephrol. 2014, 24, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.; Pajai, A.; Bhurke, S.; Shirkande, A.; Bhadade, R.; D’Souza, R. Acute Kidney Injury of Infectious Etiology in Monsoon Season: A Prospective Study Using Acute Kidney Injury Network Criteria. Indian J. Nephrol. 2018, 28, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, E.A.J.; Kellum, J.A.; Selby, N.M.; Zarbock, A.; Palevsky, P.M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Goldstein, S.L.; Cerda, J.; Chawla, L.S. Global epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Ahn, S.Y.; Ryu, J.; Baek, S.H.; Chin, H.J.; Na, K.Y.; Chae, D.W.; Kim, S. Proteinuria and hematuria are associated with acute kidney injury and mortality in critically ill patients: A retrospective observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Ahn, S.Y.; Ryu, J.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, K.I.; Chin, H.J.; Na, K.Y.; Chae, D.W.; Kim, S. U-shape relationship of white blood cells with acute kidney injury and mortality in critically ill patients. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2014, 232, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnikov, V.Y.; Faubel, S.; Siegmund, B.; Lucia, M.S.; Ljubanovic, D.; Edelstein, C.L. Neutrophil-independent mechanisms of caspase-1- and IL-18-mediated ischemic acute tubular necrosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadagavadi, R.; Reeves, W.B. Neutrophils in cisplatin AKI-mediator or marker? Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabb, H. The T cell as a bridge between innate and adaptive immune systems: Implications for the kidney. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Roy, D.K.; Debnath, C.R.; Roy, A.S.; Muqueet, M.A.; Kabir, M.S.; Ahammed, S.U.; Rabbani, M.G.; Asadujjaman, M.; Hossain, M.B.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Acute Viral Hepatitis: A Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Mymensingh Med. J. 2017, 26, 790–796. [Google Scholar]
- Wiedermann, C.J.; Wiedermann, W.; Joannidis, M. Causal relationship between hypoalbuminemia and acute kidney injury. World J. Nephrol. 2017, 6, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, X.; Chen, R.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Teng, J.; Ding, X. Metabolic acidosis as a risk factor for the development of acute kidney injury and hospital mortality. Exp. Med. 2017, 13, 2362–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachvanichsanong, P.; Thisyakorn, U.; Thisyakorn, C. Dengue hemorrhagic fever and the kidney. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viera, A.J.; Wouk, N. Potassium Disorders: Hypokalemia and Hyperkalemia. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 92, 487–495. [Google Scholar]
- Vikrant, S.; Gupta, D.; Singh, M. Epidemiology and outcome of acute kidney injury from a tertiary care hospital in India. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2018, 29, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, B.E.; Rajahram, G.S.; Grigg, M.J.; William, T.; Anstey, N.M. World Malaria Report: Time to acknowledge Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallhi, T.H.; Khan, A.H.; Adnan, A.S.; Sarriff, A.; Khan, Y.H.; Jummaat, F. Incidence, Characteristics and Risk Factors of Acute Kidney Injury among Dengue Patients: A Retrospective Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.L.; Chertow, G.M. Acute renal failure definitions and classification: Time for change? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodeify, R.; Megyesi, J.; Tarcsafalvi, A.; Mustafa, H.I.; Hti Lar Seng, N.S.; Price, P.M. Gender differences control the susceptibility to ER stress-induced acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 304, F875–F882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, T.; Inagi, R.; Takano, H.; Sato, S.; Ingelfinger, J.R.; Fujita, T.; Nangaku, M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces autophagy in renal proximal tubular cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 2665–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panitchote, A.; Mehkri, O.; Hastings, A.; Hanane, T.; Demirjian, S.; Torbic, H.; Mireles-Cabodevila, E.; Krishnan, S.; Duggal, A. Factors associated with acute kidney injury in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, J.W.; Vaschetto, R.; Della Corte, F.; Plotz, F.B.; Groeneveld, A.B. Bench-to-bedside review: Ventilation-induced renal injury through systemic mediator release—Just theory or a causal relationship? Crit Care 2011, 15, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain-Syed, F.; Slutsky, A.S.; Ronco, C. Lung-Kidney Cross-Talk in the Critically Ill Patient. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, R.A.; Mulloy, E.M.; O’Neill, S.J. The acute effects of oxygen and carbon dioxide on renal vascular resistance in patients with an acute exacerbation of COPD. Chest 1999, 115, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, K.K.; Thanachartwet, V.; Wattanagoon, Y.; Jerraksuwan, S.; Ruangweerayut, R.; Desakorn, V. Factors associated with acute renal failure in adults with severe falciparum malaria. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2012, 43, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kraev, A.I.; Torosoff, M.T.; Fabian, T.; Clement, C.M.; Perez-Tamayo, R.A. Postoperative hyperbilirubinemia is an independent predictor of longterm outcomes after cardiopulmonary bypass. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2008, 206, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, M.K.; Behera, A.K.; Karua, P.C.; Bariha, P.K.; Rath, A.; Aggrawal, K.C.; Nahak, S.R.; Gudaganatti, S.S. Urinary bile casts in bile cast nephropathy secondary to severe falciparum malaria. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Liao, P.P.; Song, H.C.; Zhou, J.H.; Chu, H.C.; Lyu, L. Hyperbilirubinemia Induces Pro-Apoptotic Effects and Aggravates Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Nephron 2019, 142, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gameiro, J.; Goncalves, M.; Pereira, M.; Rodrigues, N.; Godinho, I.; Neves, M.; Gouveia, J.; Silva, Z.C.E.; Jorge, S.; Lopes, J.A. Obesity, acute kidney injury and mortality in patients with sepsis: A cohort analysis. Ren. Fail. 2018, 40, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffl, H.; Lang, S.M. Obesity, acute kidney injury and outcome of critical illness. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druml, W.; Metnitz, B.; Schaden, E.; Bauer, P.; Metnitz, P.G. Impact of body mass on incidence and prognosis of acute kidney injury requiring renal replacement therapy. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagnac, A.; Weinstein, T.; Korzets, A.; Ramadan, E.; Hirsch, J.; Gafter, U. Glomerular hemodynamics in severe obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2000, 278, F817–F822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Fuster, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines: A link between obesity and cardiovascular disease. J. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danziger, J.; Chen, K.P.; Lee, J.; Feng, M.; Mark, R.G.; Celi, L.A.; Mukamal, K.J. Obesity, Acute Kidney Injury, and Mortality in Critical Illness. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, M.; Ling, W.; Sui, Y.; Zhao, H.L. Obesity in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2020, 113, 154378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Grandas, F.G.; Flechet, M.; Meyfroidt, G. Clinical prediction models for acute kidney injury. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 2020, 32, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, P.; Ginès, P.; Wong, F.; Bernardi, M.; Boyer, T.D.; Gerbes, A.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Sarin, S.K.; Piano, S.; et al. Diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: Revised consensus recommendations of the International Club of Ascites. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, R.; Ronco, C.; Kellum, J.A.; Mehta, R.L.; Palevsky, P.; ADQI Workgroup. Acute renal failure-definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: The Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.L.; Kellum, J.A.; Shah, S.V.; Molitoris, B.A.; Ronco, C.; Warnock, D.G.; Levin, A.; Acute Kindey Injury Network. Acute Kidney Injury Network: Report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 2007, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).