Challenges and Prospective of Enhancing Hydatid Cyst Chemotherapy by Nanotechnology and the Future of Nanobiosensors for Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
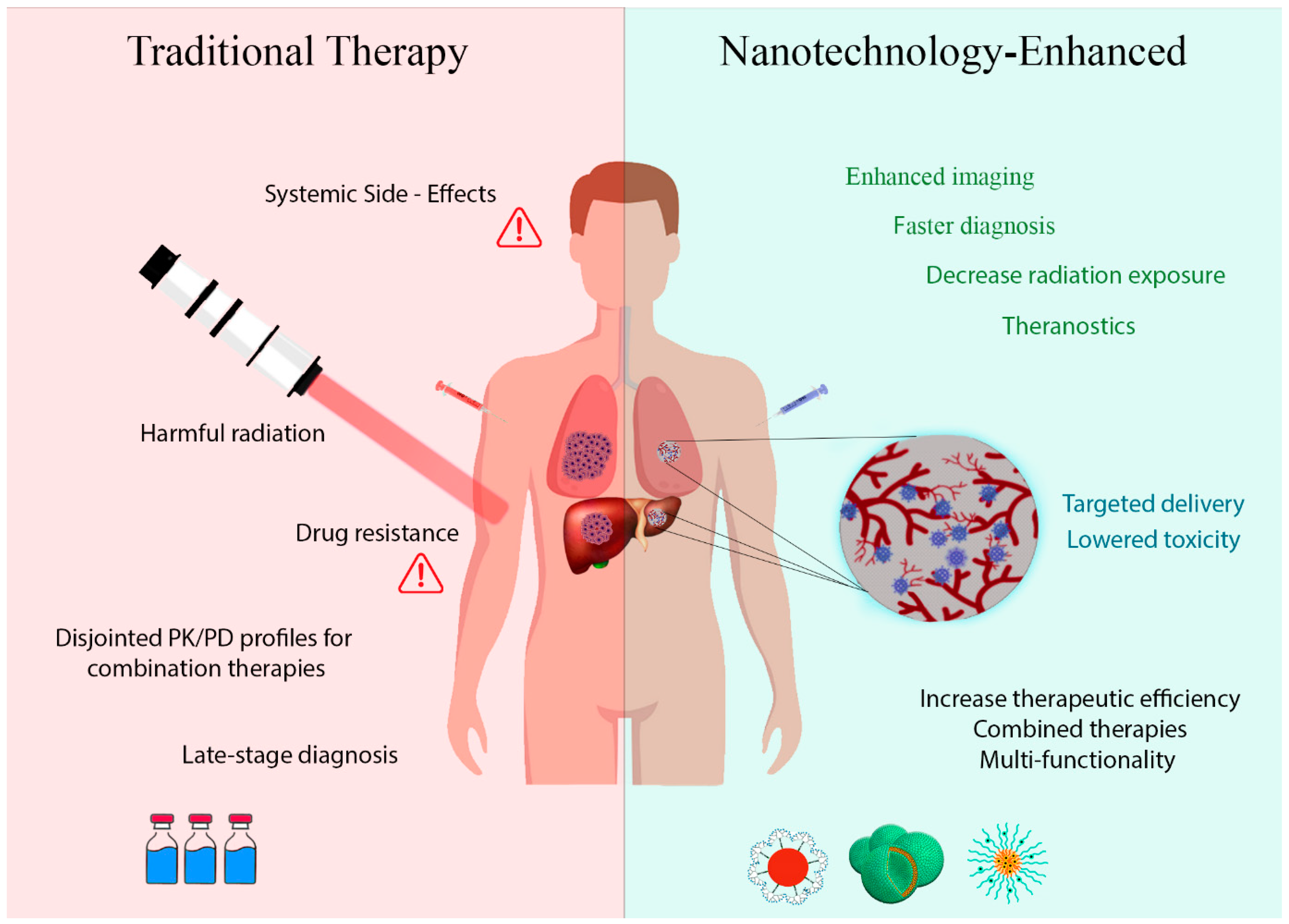
2. Challenges in Conventional Chemotherapy
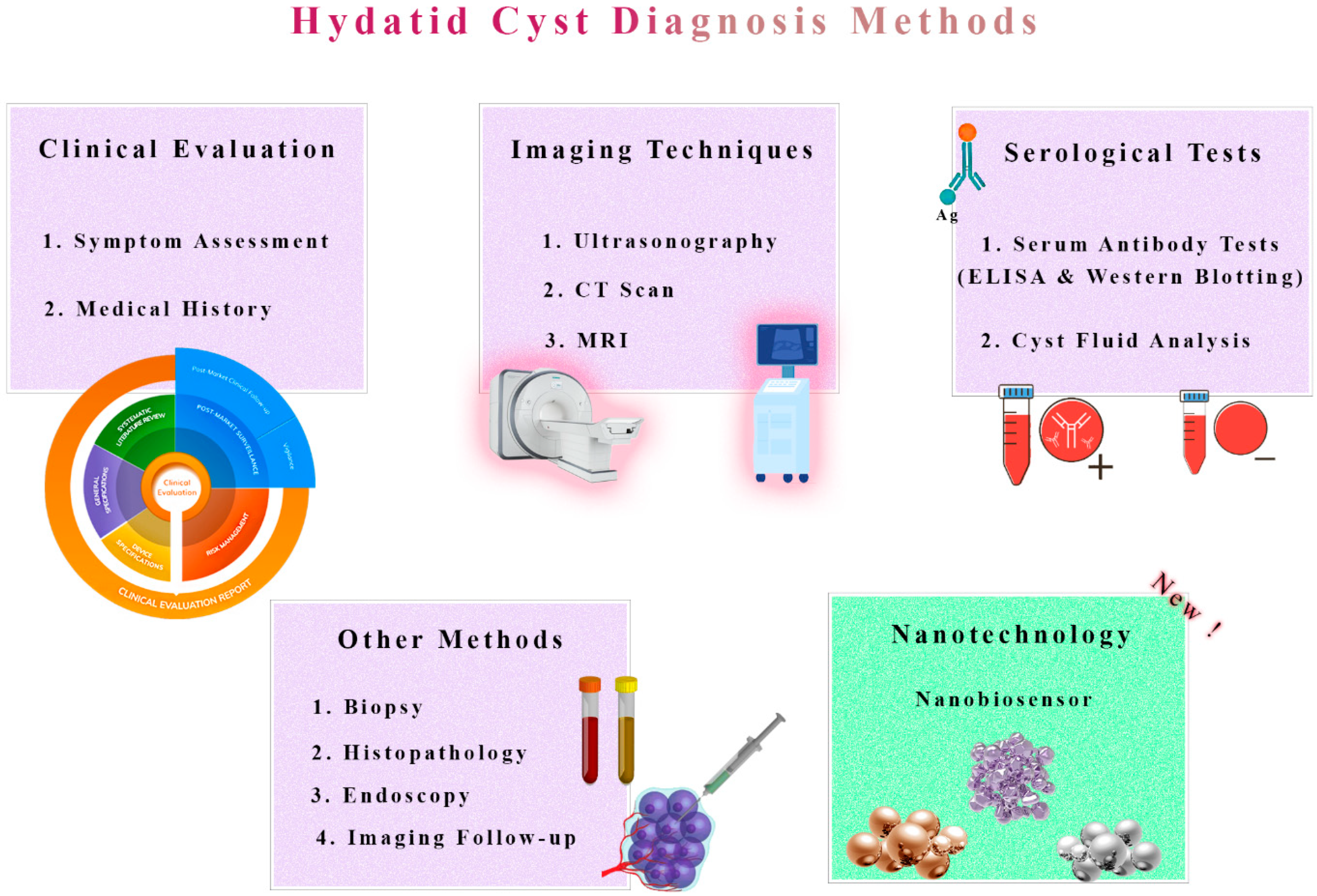
3. Detection of Hydatid Cysts: Current Approaches and Limitations
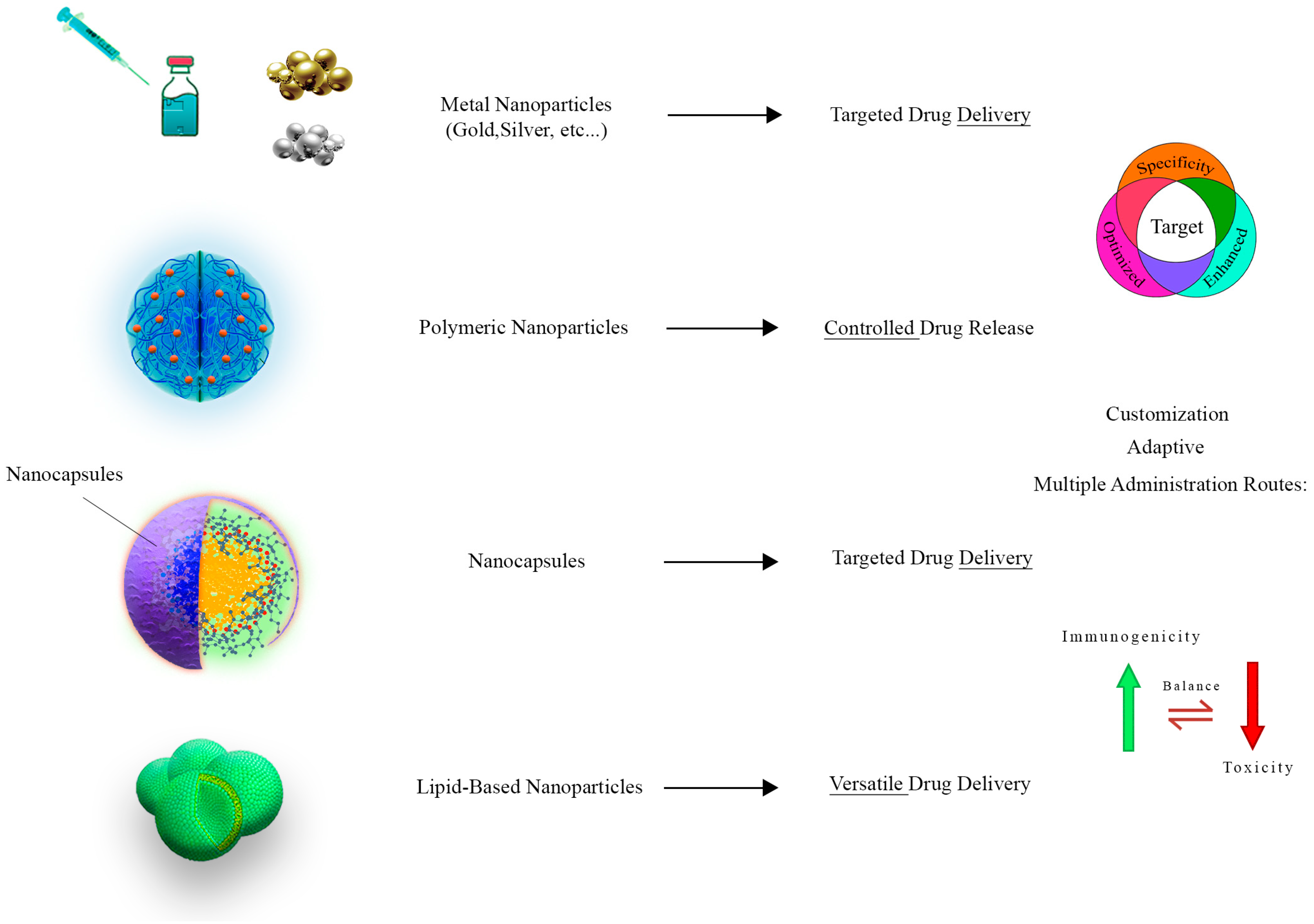
4. Nanotechnology and Nanoparticle Applications
5. Revolutionizing Chemotherapy through Nanotechnology
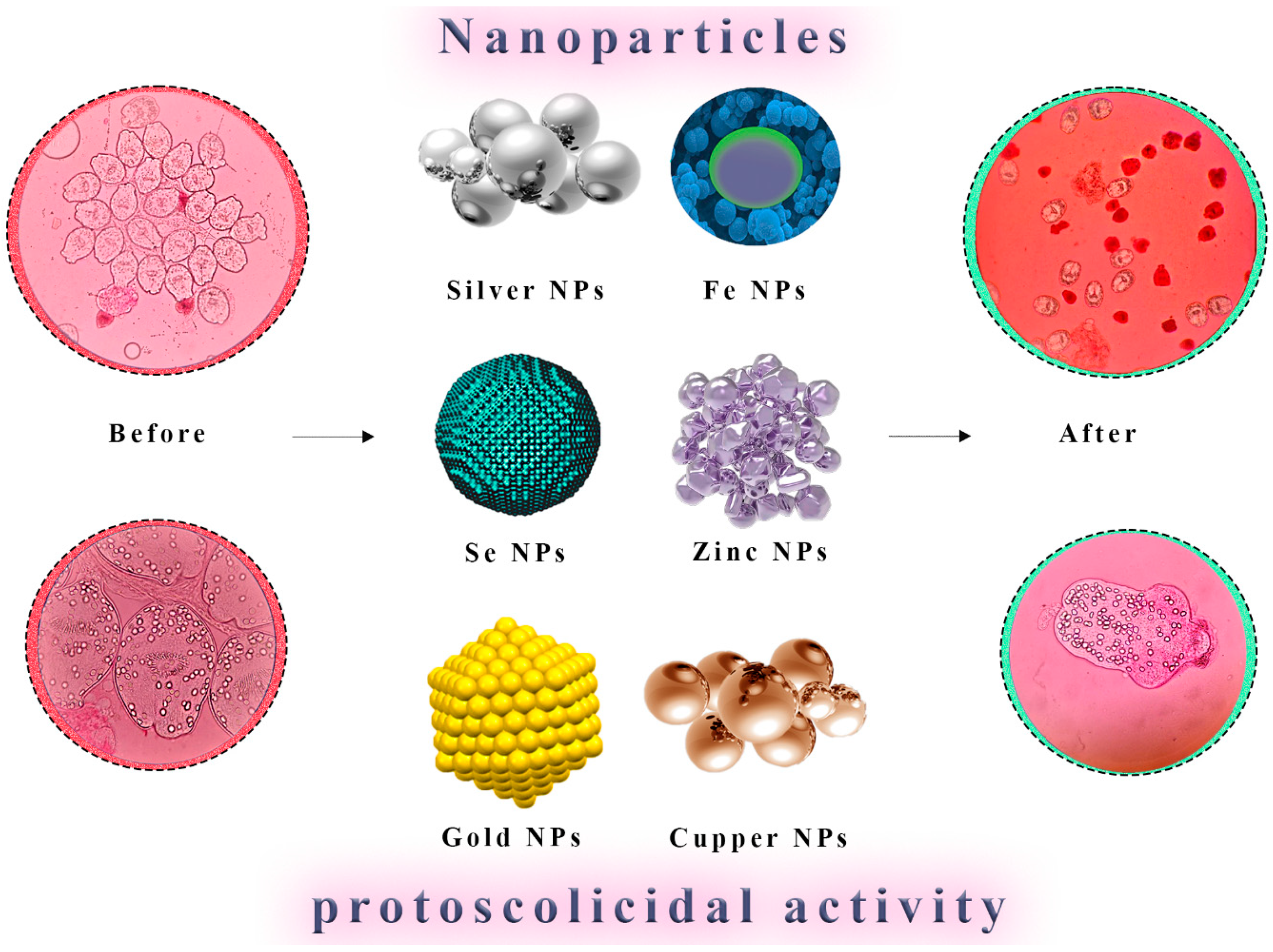
5.1. Metallic Nanoparticles
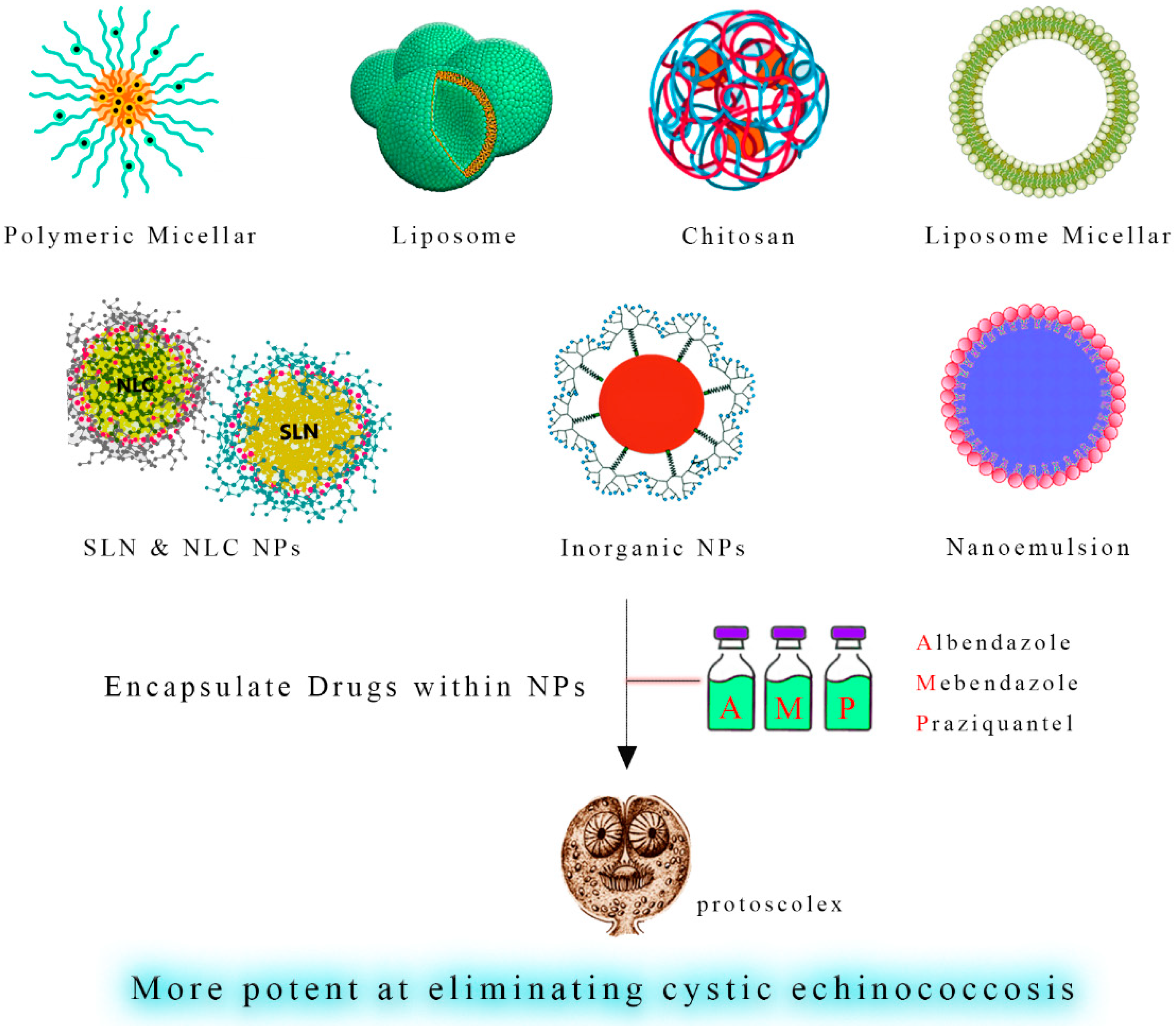
5.2. Antiparasitic-Loaded Nanodrugs
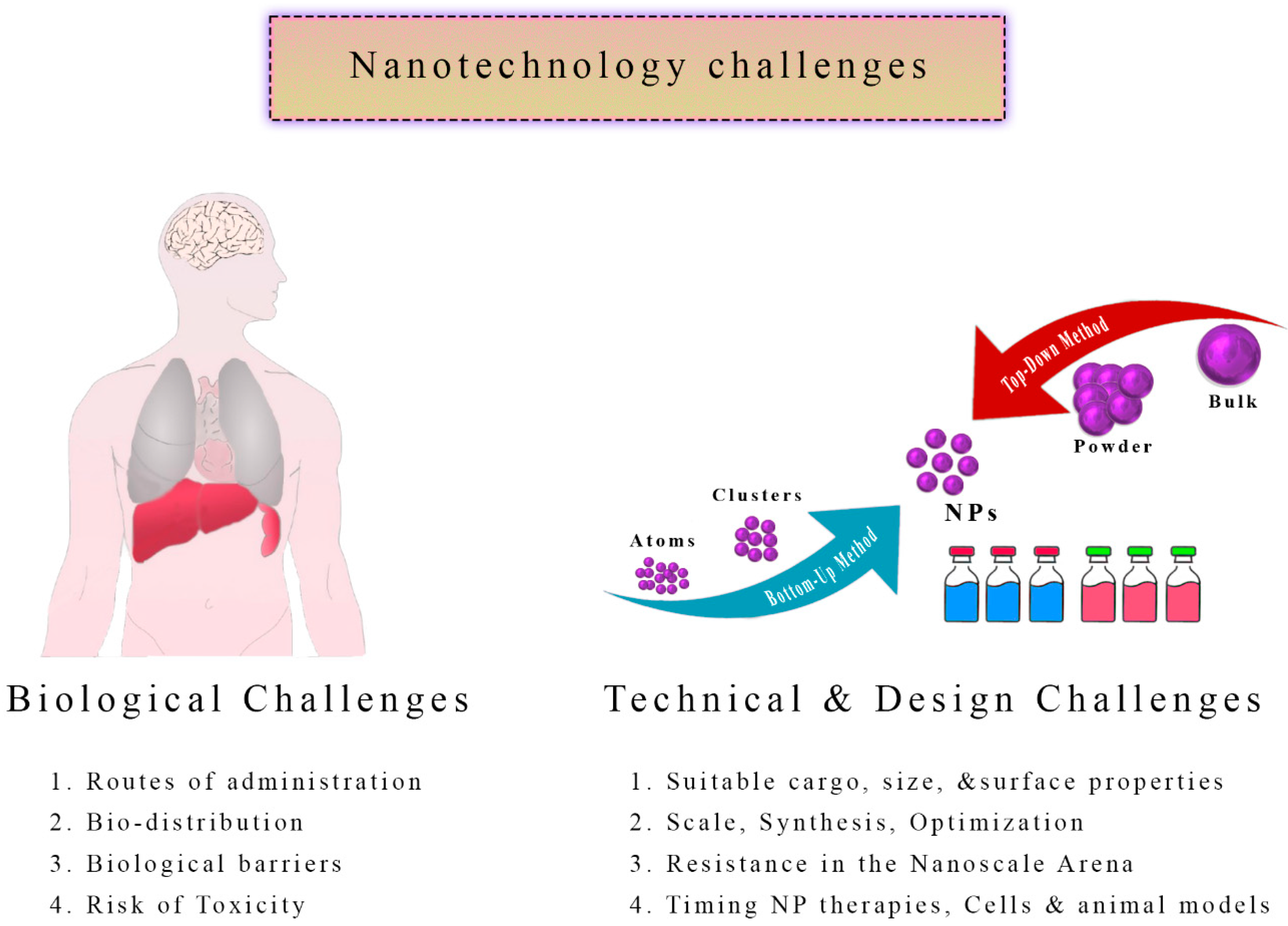
6. Nanotechnology Chemotherapy Challenges
6.1. Bio-Distribution: Navigating the Intricacies
6.2. Nanoparticle Toxicity
6.3. Nanoparticles Resistance
6.4. Intricacies of Design: Tailoring for Efficacy
7. Nanobiosensors for Early Diagnosis and Treatment Effectiveness
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
10. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lupia, T.; Corcione, S.; Guerrera, F.; Costardi, L.; Ruffini, E.; Pinna, S.M.; Rosa, F.G.D. Pulmonary echinococcosis or lung hydatidosis: A narrative review. Surg. Infect. 2021, 22, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessese, A.T. Review on epidemiology and public health significance of hydatidosis. Vet. Med. Int. 2020, 2020, 8859116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karshima, S.N.; Ahmed, M.I.; Adamu, N.B.; Magaji, A.A.; Zakariah, M.; Mohammed, K. Africa-wide meta-analysis on the prevalence and distribution of human cystic echinococcosis and canine Echinococcus granulosus infections. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, M.A.; Alsayeqh, A.F. Food-borne zoonotic echinococcosis: A review with special focus on epidemiology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1072730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casulli, A.; Massolo, A.; Saarma, U.; Umhang, G.; Santolamazza, F.; Santoro, A. Species and genotypes belonging to Echinococcus granulosussensu lato complex causing human cystic echinococcosis in Europe (2000–2021): A systematic review. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadr, S.; Charbgoo, A.; Borji, H.; Hajjafari, A. Interactions between innate immunity system and Echinococcus granulosus: Permission for vaccine development. Ser. Med. Sci. 2022, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, Á. Immunology of cystic echinococcosis (hydatid disease). Br. Med. Bull. 2017, 124, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, C.; Stoore, C.; Strull, K.; Franco, C.; Corrêa, F.; Jiménez, M.; Hernández, M.; Lorenzatto, K.; Ferreira, H.B.; Galanti, N. New insights of the local immune response against both fertile and infertile hydatid cysts. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.; Casaravilla, C.; Irigoín, F.; Lin, G.; Previato, J.O.; Ferreira, F. Understanding the laminated layer of larval Echinococcus I: Structure. Trends. Parasitol. 2011, 27, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goussard, P.; Eber, E.; Mfingwana, L.; Nel, P.; Schubert, P.; Janson, J.; Pitcher, R.; le Roux, C. Paediatric pulmonary echinococcosis: A neglected disease. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2022, 43, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, K.; Koziol, U. Echinococcus—Hst interactions at cellular and molecular levels. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 147–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R. Biology and systematics of Echinococcus. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 65–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadr, S.; Poorjafari Jafroodi, P.; Haratizadeh, M.J.; Ghasemi, Z.; Borji, H.; Hajjafari, A. Current status of nano-vaccinology in veterinary medicine science. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 2294–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, P.K.D.; Solanki, A.; Debnath, A.; Nayyar, A.; El-Sappagh, S.; Kwak, K.-S. Advancing modern healthcare with nanotechnology, nanobiosensors, and internet of nano things: Taxonomies, applications, architecture, and challenges. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 65230–65266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, T.; Ratre, Y.K.; Chauhan, S.; Bhaskar, L.; Nair, M.P.; Verma, H.K. Nanotechnology based drug delivery system: Current strategies and emerging therapeutic potential for medical science. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhwani, S.; Chan, W.C. Nanotechnology for modern medicine: Next step towards clinical translation. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.D.; Charmode, N.; Shrivastav, O.P.; Prasad, S.R.; Moghe, A.; Sarvalkar, P.D.; Prasad, N.R. A review on concept of nanotechnology in veterinary medicine. ES Food Agrofor. 2021, 4, 28–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnawa, B.H.; Al-Ali, S.J.; Swar, S.O. Nanoparticles as a new approach for treating hydatid cyst disease. In Veterinary Pathobiology and Public Health; Unique Scientific Publishers: Punjab, Pakistan, 2021; pp. 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Rafiei, A.; Ramezani, Z.; Abbaspour, M.R.; Jelowdar, A.; Kahvaz, M.S. Evaluation of the hydatid cyst membrane permeability of albendazole and albendazole sulfoxide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2017, 12, e34723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassef, N.E.; Saad, A.-G.E.; Harba, N.M.; Beshay, E.V.; Gouda, M.A.; Shendi, S.S.; Mohamed, A.S.E.-D. Evaluation of the therapeutic efficacy of albendazole-loaded silver nanoparticles against Echinococcus granulosus infection in experimental mice. J. Parasit. Dis. 2019, 43, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fateh, R.; Norouzi, R.; Mirzaei, E.; Nissapatron, V.; Nawaz, M.; Khalifeh-Gholi, M.; Hamta, A.; Sadati, S.J.A.; Siyadatpanah, A.; Bafghi, A.F. In vitro evaluation of albendazole nanocrystals against Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices. Ann. Parasitol. 2021, 67, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maurice, M.N.; Huseein, E.A.M.; Monib, M.E.S.M.; Alsharif, F.M.; Namazi, N.I.; Ahmad, A.A. Evaluation of the scolicidal activities of eugenol essential oil and its nanoemulsion against protoscoleces of hydatid cysts. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsharedeh, R.H.; Rezigue, M.; Bashatwah, R.M.; Amawi, H.; Aljabali, A.A.; Obeid, M.A.; Tambuwala, M.M. Nanomaterials as a Potential Target for Infectious Parasitic Agents. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2023, 250, 108548. [Google Scholar]
- Shnawa, B.H.; Jalil, P.J.; Aspoukeh, P.; Mohammed, D.A.; Biro, D.M. Protoscolicidal and Biocompatibility Properties of Biologically Fabricated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Ziziphus spina-christi Leaves. Pak. Vet. J. 2022, 42, 2074–7764. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiei, A.; Soltani, S.; Ramezani, Z.; Abbaspour, M.R.; Jelowdar, A.; Kahvaz, M.S. Ultrastructural changes on fertile and infertile hydatid cysts induced by conventional and solid lipid nanoparticles of albendazole and albendazole sulfoxide. Comp. Clin. Path. 2019, 28, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, B.; Aksoy, F.; Yavuz, S.; Demircili, M.E. Investigating the effect of gold nanoparticles on hydatid cyst protoscolices under low-power green laser irradiation. Turk. J. Surg. 2019, 35, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminpour, S.; Rafiei, A.; Jelowdar, A.; Kouchak, M. Evaluation of the protoscolicidal effects of albendazole and albendazole loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2019, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, R.; Ataei, A.; Hejazy, M.; Noreddin, A.; El Zowalaty, M.E. Scolicidal effects of nanoparticles against hydatid cyst protoscolices in vitro. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 2020, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, E.; Godrati-Azar, Z.; Spotin, A.; Norouzi, R.; Hamishehkar, H.; Nami, S.; Heydarian, P.; Rajabi, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Perez-Cordon, G. Nanostructured lipid carriers of ivermectin as a novel drug delivery system in hydatidosis. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, R.H. Green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their potential applications as therapeutics in cancer therapy. A review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 143, 109610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohansal, K.; Rafiei, A.; Kalantari, H.; Jelowdar, A.; Salimi, A.; Rezaie, A.; Jalali, M.R. Nephrotoxicity of Albendazole and Albendazole Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles in Mice with Experimental Hydatidosis. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shnawa, B.H.; Hamad, S.M.; Barzinjy, A.A.; Kareem, P.A.; Ahmed, M.H. Scolicidal activity of biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles by Mentha longifolia L. leaves against Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices. Emergent. Mater. 2021, 5, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishik, S.; Nagati, I.; El Hayawan, I.; Ali, I.; Fawzy, M.; Ali, H. Efficacy of Nigella sativa oil and its chitosan loaded nanoparticles on experimental cystic echinoncoccosis with immunological assessment. Parasitol. United J. 2020, 13, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawi, A.E.; Alanazi, A.D.; Baharvand, P.; Sepahvand, M.; Mahmoudvand, H. High potency of organic and inorganic nanoparticles to treat cystic echinococcosis: An evidence-based review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, M.M.; Moazeni, M.; Alizadeh, M.; Abedi, M.; Tamaddon, A.M. Evaluation of the efficacy of albendazole sulfoxide (ABZ-SO)–loaded chitosan-PLGA nanoparticles in the treatment of cystic echinococcosis in laboratory mice. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 4233–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, S.M.; Shnawa, B.H.; Jalil, P.J.; Ahmed, M.H. Assessment of the therapeutic efficacy of silver nanoparticles against secondary cystic echinococcosis in BALB/c mice. Surfaces 2022, 5, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, T.A.; Hassan, K.T.; Majeed, S.R.; Ibraheem, I.J.; Hassan, O.M.; Obaid, A. In vitro scolicidal activity of synthesised silver nanoparticles from aqueous plant extract against Echinococcus granulosus. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 28, e00545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, A.; Jafarpour Azami, S.; Hashemi Hafshejani, S.; Ghanimatdan, M.; Bahreini, M.S.; Alimi, R.; Sadjjadi, S.M. Protoscolicidal effects of curcumin nanoemulsion against protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navvabi, A.; Homaei, A.; Khademvatan, S.; Ansari, M.H.K.; Keshavarz, M. Combination of TiO2 nanoparticles and Echinometra mathaeis gonad extracts: In vitro and in vivo scolicidal activity against hydatid cysts. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzeh, N.; Eslaminejad, T.; Shafiei, R.; Faridi, A.; Fasihi Harandi, M. Lethal in vitro effects of optimized chitosan nanoparticles against protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2021, 36, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, P.J.; Shnawa, B.H.; Hamad, S.M. Silver Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis, Characterization, Blood Compatibility and Protoscolicidal Efficacy against Echinococcus granulosus. Pak. Vet. J. 2021, 41, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, R.; Hejazy, M.; Ataei, A. Scolicidal activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles against hydatid cyst protoscolices in vitro. Nanomed. Res. J. 2019, 4, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhtiar, N.M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Ahmadpour, E.; Mahami-Oskouei, M.; Casulli, A.; Norouzi, R.; Asadi, M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Asadi, N.; Oliveira, S.M.R. In vitro efficacy of albendazole-loaded β-cyclodextrin against protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto. Exp. Parasitol. 2022, 243, 108428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, M.; Haniloo, A.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Ahmadi, N. In vitro evaluation of albendazole-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers on Echinococcus granulosus microcysts and their prophylactic efficacy on experimental secondary hydatidosis. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 4049–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishik, S.; Nagati, I.; Ali, I.; Aly, N.; Fawzy, M.; Ali, H. Pathological assessment of Nigella sativa oil and its chitosan loaded nanoparticles on experimental hepatic cystic echinoncoccosis. Parasitol. United J. 2021, 14, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, L.; Alsayari, A.; Tak, H.; Mir, S.A.; Almoyad, M.A.A.; Wahab, S.; Bader, G.N. An Insight into the Global Problem of Gastrointestinal Helminth Infections amongst Livestock: Does Nanotechnology Provide an Alternative? Agriculture 2023, 13, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, X.-C.; Wu, X.-W.; Zhang, S.-J.; Sun, H.; Ma, X.; Peng, X.-Y. Efficacy of albendazole chitosan microspheres against Echinococcus granulosus infection in mice. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi 2014, 32, 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedan, M.B.; Aljohani, I.M.; Alghofaily, K.A.; Loutfi, S.; Ghosh, S. Thoracic hydatid disease: A radiologic review of unusual cases. World. J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, T.S.; Deplazes, P.; Gottstein, B.; Jenkins, D.; Mathis, A.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Torgerson, P.R.; Ziadinov, I.; Heath, D.D. Challenges for diagnosis and control of cystic hydatid disease. Acta Trop. 2012, 123, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, K.; Zargar, S.A.; Telwani, A.A. Hydatid cyst of spleen: A diagnostic challenge. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, M.K.; Sharma, M.; Gulati, A.; Gorsi, U.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Agarwal, R.; Khandelwal, N. Imaging in pulmonary hydatid cysts. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inayat, F.; Azam, S.; Baig, A.S.; Nawaz, G.; Ullah, W. Presentation patterns, diagnostic modalities, management strategies, and clinical outcomes in patients with hydatid disease of the pelvic bone: A comparative review of 31 cases. Cureus 2019, 11, e4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, F.; Maghsood, A.H.; Fallah, M.; Jalilvand, A.; Matini, M.; Amini, B. Design of highly sensitive nano-biosensor for diagnosis of hydatid cyst based on gold nanoparticles. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 38, 102786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, U.; Shakya, S.; Saxena, K. Nano-Biosensing Devices Detecting Biomarkers of Communicable and Non-communicable Diseases of Animals. In Biosensors in Agriculture: Recent Trends and Future Perspectives; Concepts and Strategies in Plant Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerbu, C.; White, J.C.; Sabliov, C.M. Nanotechnology in livestock: Improving animal production and health. In Nano-Enabled Sustainable and Precision Agriculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 181–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Sayed-ElAhl, R.M.; El Hamaky, A.M.; Mansour, M.K.; Oraby, N.H.; Barakat, M.H. Nanodiagnostics: New Tools for Detection of Animal Pathogens. In Nanorobotics and Nanodiagnostics in Integrative Biology and Biomedicine; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 299–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.-Y.; Jung, B.-K.; Hong, S.-J. Albendazole and mebendazole as anti-parasitic and anti-cancer agents: An update. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021, 59, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ün, M.; Yaman, S.S.; Erbaş, O. Hydatid cyst and treatment. Demiroglu Sci. Univ. Florence Nightingale J. Transplant. 2020, 5, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, C.O.; Egbuna, C.; Oladosun, T.O.; Akram, M.; Micheal, O.S.; Olisaka, F.N.; Ozolua, P.; Adetunji, J.B.; Enoyoze, G.E.; Olaniyan, O.T. Efficacy of Phytochemicals of Medicinal Plants for the Treatment of Human Echinococcosis: Echinococcal Disease, Hydatidosis, or Hydatid Disease Drug Discovery. In Neglected Tropical Diseases and Phytochemicals in Drug Discovery; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, A.; Shahriarirad, R.; Eskandarisani, M.; Rastegarian, M.; Sarkari, B. Management of Liver Hydatid Cysts: A Retrospective Analysis of 293 Surgical Cases from Southern Iran. J. Trop. Med. 2023, 2023, 9998739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, M.A.; Khan, S.; Ali, R.M.A.; Qamar, W.; Saqib, M.; Faridi, N.Y.; Li, L.; Fu, B.-Q.; Yan, H.-B.; Jia, W.-Z. Herbal medicines against hydatid disease: A systematic review (2000–2021). Life 2022, 12, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muqaddas, H.; Mehmood, N.; Ahmed, F.; Fatima, M.; Rasool, M.; Zafar, S.; Riaz, A.; Nauman, M. Problems and perspectives related to cystic echinococcosis in Pakistan: Solutions in one health context. One Health Triad Unique Sci. Publ. Faisalabad Pak. 2023, 3, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Vuitton, L.; Tuxun, T.; Li, J.; Vuitton, D.A.; Zhang, W.; McManus, D.P. Echinococcosis: Advances in the 21st century. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00075-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, P.; Da Silva, A.M.; Akhan, O.; Müllhaupt, B.; Vizcaychipi, K.; Budke, C.; Vuitton, D. The echinococcoses: Diagnosis, clinical management and burden of disease. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 96, 259–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipour, A.; Ghaffarifar, F.; Horton, J.; Dalimi, A.; Sharifi, Z. Silybum marianum ethanolic extract: In vitro effects on protoscolices of Echinococcus granulosus G1 strain with emphasis on other Iranian medicinal plants. Trop. Med. Health 2021, 49, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.S.; Cherian, S.; Sumithra, T.; Raina, O.; Sankar, M. Edible vaccines against veterinary parasitic diseases—Current status and future prospects. Vaccine 2013, 31, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Y. Finding high-quality groundwater resources to reduce the hydatidosis incidence in the Shiqu County of Sichuan Province, China: Analysis, assessment, and management. Expos. Health 2020, 12, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnari, G.; Pinzone, M.R.; Gruttadauria, S.; Celesia, B.M.; Madeddu, G.; Malaguarnera, G.; Pavone, P.; Cappellani, A.; Cacopardo, B. Hepatic echinococcosis: Clinical and therapeutic aspects. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzucu, A.; Ulutas, H.; Reha Celik, M.; Yekeler, E. Hydatid cysts of the lung: Lesion size in relation to clinical presentation and therapeutic approach. Surg. Today 2014, 44, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thys, S.; Sahibi, H.; Gabriël, S.; Rahali, T.; Lefèvre, P.; Rhalem, A.; Marcotty, T.; Boelaert, M.; Dorny, P. Community perception and knowledge of cystic echinococcosis in the High Atlas Mountains, Morocco. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightowlers, M.W.; Gasser, R.B.; Hemphill, A.; Romig, T.; Tamarozzi, F.; Deplazes, P.; Torgerson, P.R.; Garcia, H.H.; Kern, P. Advances in the treatment, diagnosis, control and scientific understanding of taeniid cestode parasite infections over the past 50 years. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 1167–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, B.; Gholami, S.; Bagheri, A.; Fakhar, M.; Moradi, A.; Khazeei Tabari, M.A. Cystic echinococcosis microRnas as potential non-invasive biomarkers: Current insights and upcoming perspective. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 23, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Douira-Khomsi, W.; Gharbi, H.; Sharma, M.; Cui, X.W.; Sparchez, Z.; Richter, J.; Kabaalioğlu, A.; Atkinson, N.S.; Schreiber-Dietrich, D. Cystic and alveolar echinococcosis of the hepatobiliary tract—The role of new imaging techniques for improved diagnosis. Med. Ultrason. 2020, 22, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, I.F.; Jabbar, A.S. Hepatic Hydatid Cyst Diseases during Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Management and Best Practice. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 689–694. [Google Scholar]
- Caraiani, C.; Yi, D.; Petresc, B.; Dietrich, C. Indications for abdominal imaging: When and what to choose? J. Ultrason. 2020, 20, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, B.; Akhavan, R.; Khameneh, A.G.; Amirkhiz, G.D.H.; Rezaei-Dalouei, H.; Tayebi, S.; Hashemi, J.; Aminizadeh, B.; Amirkhiz, S.D.H. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of hydatid disease: A pictorial review of uncommon imaging presentations. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calame, P.; Weck, M.; Busse-Cote, A.; Brumpt, E.; Richou, C.; Turco, C.; Doussot, A.; Bresson-Hadni, S.; Delabrousse, E. Role of the radiologist in the diagnosis and management of the two forms of hepatic echinococcosis. Insights Imaging 2022, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamarozzi, F.; Silva, R.; Fittipaldo, V.A.; Buonfrate, D.; Gottstein, B.; Siles-Lucas, M. Serology for the diagnosis of human hepatic cystic echinococcosis and its relation with cyst staging: A systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, M.A.; Ali, R.M.A.; Khan, S.; Saqib, M.; Qamar, W.; Li, L.; Fu, B.-Q.; Yan, H.-B.; Jia, W.-Z. Past and Present of Diagnosis of Echinococcosis: A Review (1999–2021). Acta Trop. 2023, 243, 106925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meftahi, G.H.; Bahari, Z.; Zarei Mahmoudabadi, A.; Iman, M.; Jangravi, Z. Applications of western blot technique: From bench to bedside. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2021, 49, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshoabi, S.A.; Alkalady, A.H.; Almas, K.M.; Magram, A.O.; Algaberi, A.K.; Alareqi, A.A.; Hamid, A.M.; Alhazmi, F.H.; Qurashi, A.A.; Abdulaal, O.M. Hydatid disease: A radiological pictorial review of a great neoplasms mimicker. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouhan, M.; Wiley, E.; Chiodini, P.; Amin, Z. Hepatic alveolar hydatid disease (Echinococcus multilocularis), a mimic of liver malignancy: A review for the radiologist in non-endemic areas. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, N.; Iranpour, P.; Khalili, N.; Haseli, S. Hydatid Disease: A Pictorial Review of Uncommon Locations. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 48, 118–129. [Google Scholar]
- Pakala, T.; Molina, M.; Wu, G.Y. Hepatic echinococcal cysts: A review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramita, A.A.K.Y.; Wibawa, I.D.N. Multimodal Treatment of Cystic Echinococcosis. Indones. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Dig. Endosc. 2023, 24, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhani, M.; Fathi, S.; Darabi, E.; Jalousian, F.; Simsek, S.; Ahmed, H.; Kesik, H.K.; Hosseini, S.H.; Romig, T.; Harandi, M.F. Echinococcoses in Iran, Turkey, and Pakistan: Old diseases in the new millennium. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0029020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, C.N.; Curvino, E.J.; Chen, J.-L.; Permar, S.R.; Fouda, G.G.; Collier, J.H. Advances in nanomaterial vaccine strategies to address infectious diseases impacting global health. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.T.; Adil, S.F.; Shaik, M.R.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Khan, M.; Khan, M. Engineered nanomaterials in soil: Their impact on soil microbiome and plant health. Plants 2021, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, R.; Gulshad, L.; Haq, I.U.; Farooq, M.A.; Al-Farga, A.; Siddique, R.; Manzoor, M.F.; Karrar, E. Advances and challenges in nanocarriers and nanomedicines for veterinary application. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 580, 119214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria, R. Nanotechnological improvement of veterinary anthelmintics. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2021, 9, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehbasharzad, P.; Fatehbasharzad, P.; Sillanpää, M.; Shamsi, Z. Investigation of bioimpacts of metallic and metallic oxide nanostructured materials: Size, shape, chemical composition, and surface functionality: A review. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2021, 38, 2100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Karishma, S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Jeevanantham, S.; Yaashikaa, P.; George, C.S. A review on biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles and its environmental applications. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikal, W.M.; Bratovcic, A.; Baeshen, R.S.; Tkachenko, K.G.; Said-Al Ahl, H.A. Nanobiotechnology for the detection and control of waterborne parasites. Open J. Ecol. 2021, 11, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badirzadeh, A.; Alipour, M.; Najm, M.; Vosoogh, A.; Vosoogh, M.; Samadian, H.; Hashemi, A.S.; Farsangi, Z.J.; Amini, S.M. Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin coated silver nanoparticle in the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania major in-vitro and in a murine model. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 74, 103576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gong, J.; Jiang, Y.; Long, Y.; Lei, W.; Gao, X.; Guo, D. Application of Silver Nanoparticles in Parasite Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Afzal, M.; Verma, M.; Bhattacharya, S.M.; Ahmad, F.; Samim, M.; Abidin, M.Z.; Dinda, A.K. Therapeutic efficacy of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles encapsulated ivermectin (nano-ivermectin) against brugian filariasis in experimental rodent model. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, J.; Hasan, M.W.; Yan, R.; Xu, L.; Song, X.; Li, X. Nanoparticles of Chitosan/Poly (D, L-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) enhanced the immune responses of haemonchus contortus HCA59 antigen in model mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 3125–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Tian, M.; Qi, W.; An, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; et al. Oral Delivery of Anti-Parasitic Agent-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles: Enhanced Liver Targeting and Improved Therapeutic Effect on Hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 2021, 3069–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirescu, V.A.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Andronescu, E. Polymeric nanoparticles for antimicrobial therapies: An up-to-date overview. Polymers 2021, 13, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghipour, K.; Rouzbahani, A.K.; Fallahi, S.; Taherpour, F.; Moradifard, F.; Shakib, P.; Lashgarian, H.E.; Marzban, A. Recent Advances in Therapeutic Strategies against Hydatid Cysts using Nanomaterials: A Systematic Review. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2023, 20, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.K.; Shandilya, R.; Mishra, P.K. Lipid based nanocarriers: A translational perspective. Nanomed. NBM. 2018, 14, 2023–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, S.; Saudagar, P. Encapsulation and delivery of antiparasitic drugs: A review. Encapsul. Act. Mol. Deliv. Syst. 2020, 2020, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisgin, A.A.; Cetinel, S.; Zuvin, M.; Kosar, A.; Kutlu, O. Therapeutic nanoparticles and their targeted delivery applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, E.; Abouelfetouh, M.M.; Pan, Y.; Chen, D.; Xie, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles for enhanced oral absorption: A review. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 196, 111305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.A.; Molento, M.B. Nanotechnology: Meeting the future of Veterinary Parasitology Research. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2015, 35, 842–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadeer, A.; Ullah, H.; Sohail, M.; Safi, S.Z.; Rahim, A.; Saleh, T.A.; Arbab, S.; Slama, P.; Horky, P. Potential application of nanotechnology in the treatment, diagnosis, and prevention of schistosomiasis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1013354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haby, M.M.; Sosa Leon, L.A.; Luciañez, A.; Nicholls, R.S.; Reveiz, L.; Donadeu, M. Systematic review of the effectiveness of selected drugs for preventive chemotherapy for Taenia solium taeniasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, N.M.; Ghazy, A.A. Advances in diagnosis and control of anthelmintic resistant gastrointestinal helminths infecting ruminants. J. Parasit. Dis. 2022, 46, 901–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, R.; Gulshad, L.; Haq, I.U.; Farooq, M.A.; Al-Farga, A.; Siddique, R.; Manzoor, M.F.; Karrar, E. Nanotechnology: A novel tool to enhance the bioavailability of micronutrients. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3354–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Nanotechnology: A revolution in modern industry. Molecules 2023, 28, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, W.; Dai, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Li, F. Status and prospect of novel treatment options toward alveolar and cystic echinococcosis. Acta Trop. 2022, 226, 106252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, M.; Soltani, M.; Kashkooli, F.M.; Shahvandi, M.K. Engineered strategies to enhance tumor penetration of drug-loaded nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, H.; Du, X.; Wang, J. Mucosal vaccine delivery: A focus on the breakthrough of specific barriers. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2022, 12, 3456–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, H.U.R.; Khan, M.K.; Abbas, Z.; Riaz, R.; Rehman, T.; Abbas, R.Z.; Almutairi, M.M.; Alshammari, F.A.; Alraey, Y. Nanoparticles: Synthesis and their role as potential drug candidates for the treatment of parasitic diseases. Life 2022, 12, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, G.; Fortunka, K.; Majchrzak, M.; Piktel, E.; Paprocka, P.; Mańkowska, A.; Lesiak, A.; Karasiński, M.; Strzelecka, A.; Durnaś, B. Metallic Nanoparticles and Core-Shell Nanosystems in the Treatment, Diagnosis, and Prevention of Parasitic Diseases. Pathogens 2023, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudier, A.; Le Faou, A. Nanoparticles and Other Nanostructures and the Control of Pathogens: From Bench to Vaccines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napooni, S.; Arbabi, M.; Delavari, M.; Hooshyar, H.; Rasti, S. Lethal effects of gold nanoparticles on protoscolices of hydatid cyst: In vitro study. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 28, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelowdar, A.; Rafiei, A.; Abbaspour, M.R.; Rashidi, I.; Rahdar, M. Efficacy of combined albendazol and praziquntel and their loaded solid lipid nanoparticles components in chemoprophylaxis of experimental hydatidosis. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.T.; Ahmadpour, E.; Esboei, B.R.; Spotin, A.; Koshki, M.H.K.; Alizadeh, A.; Honary, S.; Barabadi, H.; Mohammadi, M.A. Scolicidal activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles against Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 19, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashkarizadeh, M.R.; Asgaripour, K.; Dezaki, E.S.; Harandi, M.F. Comparison of scolicidal effects of amphotricin B, silver nanoparticles, and Foeniculum vulgare Mill on hydatid cysts protoscoleces. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2015, 10, 206. [Google Scholar]
- Laffleur, F.; Keckeis, V. Advances in drug delivery systems: Work in progress still needed? Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 119912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.d.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S. Nano-based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, H.; Ghaedi, M.; Rafiei, A.; Jelowdar, A.; Salimi, A.; Asfaram, A.; Ostovan, A. Magnetic solid lipid nanoparticles co-loaded with albendazole as an anti-parasitic drug: Sonochemical preparation, characterization, and in vitro drug release. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Kumar, S.; Kapoor, A.; Lohan, S. A Review on the Drug Delivery Strategies for Parasitic Infections: Scope and Assertion. Drug Deliv. 2022, 12, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Sehgal, R. Nano-targeted drug delivery for parasitic infections. In Emerging Nanomaterials and Nano-Based Drug Delivery Approaches to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 395–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.-J. Scolicidal activity of zirconium oxide (ZrO2) nanoparticles against protoscolices of hydatid cysts. Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2020, 14, 469–472. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, G.; Quadir, S.S.; Yadav, K.S. Road map to the treatment of neglected tropical diseases: Nanocarriers interventions. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.; El-Sawy, H.S. Polymeric nanoparticles: Promising platform for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 528, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, P.; Jain, K.; Jain, N.K. Dendrimer as nanocarrier for drug delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 268–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Bansal, K.K.; Verma, A.; Yadav, N.; Thakur, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Rosenholm, J.M. Solid lipid nanoparticles: Emerging colloidal nano drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandian, S.R.K.; Panneerselvam, T.; Pavadai, P.; Govindaraj, S.; Ravishankar, V.; Palanisamy, P.; Sampath, M.; Sankaranarayanan, M.; Kunjiappan, S. Nano based approach for the treatment of neglected tropical diseases. Front. Nanotechnol. 2021, 3, 665274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Mourya, A.; Handa, M.; Ujjwal, R.R. Role of nanomedicines in neglected tropical diseases. In Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems; Scrivener Publishing: Beverly, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 407–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezerlou, A.; Alizadeh-Sani, M.; Azizi-Lalabadi, M.; Ehsani, A. Nanoparticles and their antimicrobial properties against pathogens including bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 123, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashan, K.S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Hussain, S.A.; Marzoog, T.R.; Jabir, M.S. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of anti-bacterial, anti-parasitic and anti-cancer activities of aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3677–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzatkhah, F.; Khalaf, A.K.; Mahmoudvand, H. Copper nanoparticles: Biosynthesis, characterization, and protoscolicidal effects alone and combined with albendazole against hydatid cyst protoscoleces. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 136, 111257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Spotin, A.; Akbari, N.A.R.; Mahami-Oskouei, M.; Ahmadpour, E. Scolicidal and apoptotic activities of albendazole sulfoxide and albendazole sulfoxide-loaded PLGA-PEG as a novel nanopolymeric particle against Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4595–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa, G.V.; Pensel, P.E.; Elissondo, M.C.; Bruni, S.F.; Benoit, J.P.; Palma, S.D.; Allemandi, D.A. Albendazole-lipid nanocapsules: Optimization, characterization and chemoprophylactic efficacy in mice infected with Echinococcus granulosus. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 198, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napooni, S.; Delavari, M.; Arbabi, M.; Barkheh, H.; Rasti, S.; Hooshyar, H.; Mostafa Hosseinpour Mashkani, S. Scolicidal effects of chitosan-curcumin nanoparticles on the hydatid cyst protoscolices. Acta Parasitol. 2019, 64, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.H.; Zhong, L.Y.; Kamolnetr, O.; Limpanont, Y.; Lv, Z.Y. Detection of helminths by loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay: A review of updated technology and future outlook. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosetti, R.; Vereeck, L. Future of nanomedicine: Obstacles and remedies. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devadasu, V.R.; Bhardwaj, V.; Kumar, M.R. Can controversial nanotechnology promise drug delivery? Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1686–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirumala, M.G.; Anchi, P.; Raja, S.; Rachamalla, M.; Godugu, C. Novel methods and approaches for safety evaluation of nanoparticle formulations: A focus towards in vitro models and adverse outcome pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 612659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roco, M.C.; Mirkin, C.A.; Hersam, M.C. Nanotechnology research directions for societal needs in 2020: Summary of international study. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 897–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Famta, P.; Bagasariya, D.; Charankumar, K.; Amulya, E.; Khatri, D.K.; Raghuvanshi, R.S.; Singh, S.B.; Srivastava, S. Nanotechnology based drug delivery systems: Does shape really matter? Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 2022, 122101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann-Amtenbrink, M.; Grainger, D.W.; Hofmann, H. Nanoparticles in medicine: Current challenges facing inorganic nanoparticle toxicity assessments and standardizations. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.U.; Nazir, S.; Irshad, R.; Tahir, K.; ur Rehman, K.; Islam, R.U.; Wahab, Z. Toxicity of heavy metals in plants and animals and their uptake by magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Liew, K. Deciphering structural biological materials: Viewing from the mechanics perspective and their prospects. Compos. B Eng. 2022, 2022, 110213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Vásquez, P.; Mosier, N.S.; Irudayaraj, J. Nanoscale drug delivery systems: From medicine to agriculture. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundschuh, M.; Filser, J.; Lüderwald, S.; McKee, M.S.; Metreveli, G.; Schaumann, G.E.; Schulz, R.; Wagner, S. Nanoparticles in the environment: Where do we come from, where do we go to? Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajitha, N.; Athira, S.; Mohanan, P. Bio-interactions and risks of engineered nanoparticles. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 2017, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyshevski, S.E. MEMS and NEMS: Systems, Devices, and Structures; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenthamara, D.; Subramaniam, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.G.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Essa, M.M.; Lin, F.H.; Qoronfleh, M.W. Therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles and routes of administration. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Madhunapantula, S.V.; Robertson, G.P. Toxicological considerations when creating nanoparticle-based drugs and drug delivery systems. Exp. Opin. Drug. Metab. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panariti, A.; Miserocchi, G.; Rivolta, I. The effect of nanoparticle uptake on cellular behavior: Disrupting or enabling functions? Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2012, 2012, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaguera, C.; García-Celma, M.J. Personalized nanomedicine: A revolution at the nanoscale. J. Pers. Med. 2017, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.J.; Ekweremadu, C.; Patel, N. Advanced drug delivery system with nanomaterials for personalised medicine to treat breast cancer. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, J.; Siltanen, C.; Zhou, Q.; Revzin, A.; Simonian, A. Biosensor technology: Recent advances in threat agent detection and medicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8733–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luis, A.I.S.; Campos, E.V.R.; de Oliveira, J.L.; Fraceto, L.F. Trends in aquaculture sciences: From now to use of nanotechnology for disease control. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Rab, S.; Suman, R. Exploring the potential of nanosensors: A brief overview. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Santana, W.; Dolabella, S.S.; Santos, A.L.; Souto, E.B.; Severino, P. Are Nanobiosensors an improved solution for diagnosis of leishmania? Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Suh, Y.J.; Park, D.; Yim, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.J.; Yoon, D.S.; Hwang, K.S. Technological advances in electrochemical biosensors for the detection of disease biomarkers. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2021, 11, 309–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, T.; Gopinath, S.C. Nanosensors: Recent perspectives on attainments and future promise of downstream applications. Process. Biochem. 2022, 117, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankireddy, S.R.; Kim, J. Status and recent developments in analytical methods for the detection of foodborne microorganisms. Rec. Dev. Appl. Microbiol. Biochem. 2019, 2019, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phafat, B.; Bhattacharya, S. Quantum Dots as Theranostic Agents: Recent Advancements, Surface Modifications & Future Applications. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.K.; Na, J.; Younus, M.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Bando, Y.; Shiddiky, M.J.; Yamauchi, Y. Superparamagnetic nanoarchitectures for disease-specific biomarker detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5717–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerry, R.G.; Ukhurebor, K.E.; Kumari, S.; Maurya, G.K.; Patra, S.; Panigrahi, B.; Majhi, S.; Rout, J.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Das, G. A comprehensive review on the applications of nano-biosensor-based approaches for non-communicable and communicable disease detection. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 3576–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattani, A.; Mandal, S.; Khan, M.H.; Jain, A.; Ceaser, D.; Mishra, A.; Tiwari, S.P. Novel Electrochemical biosensing for detection of neglected tropical parasites of animal origin: Recent Advances. Electroanalysis 2023, 35, e202200255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Upadhyay, S.S.; Rawool, C.R.; Punde, N.S.; Rajpurohit, A.S. Voltammetric techniques for the analysis of drugs using nanomaterials based chemically modified electrodes. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2019, 15, 249–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, U.; Kaur, G.; Chaudhary, G.R. Development of environmental nanosensors for detection monitoring and assessment. New Front. Nanomater. Environ. Sci. 2021, 2021, 91–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergquist, R.; Lustigman, S. Control of Important Helminthic Infections: VaccineDevelopment as Part of the Solution. Adv. Parasitol. 2010, 73, 297–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmoghazy, W.; Alqahtani, J.; Kim, S.W.; Sulieman, I.; Elaffandi, A.; Khalaf, H. Comparative analysis of surgical management approaches for hydatid liver cysts: Conventional vs. minimally invasive techniques. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2023, 408, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manterola, C.; Rivadeneira, J.; Pogue, S.D.; Rojas, C. Morphology of Echinococcus granulosus Protoscolex. Int. J. Morphol. 2023, 41, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminu, N.; Bello, I.; Umar, N.M.; Tanko, N.; Aminu, A.; Audu, M.M. The influence of nanoparticulate drug delivery systems in drug therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, J.; Taratula, O.; Minko, T. Nanocarrier-based systems for targeted and site specific therapeutic delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geramizadeh, B. Isolated peritoneal, mesenteric, and omental hydatid cyst: A clinicopathologic narrative review. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 42, 517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Momčilović, S.; Cantacessi, C.; Arsić-Arsenijević, V.; Otranto, D.; Tasić-Otašević, S. Rapid diagnosis of parasitic diseases: Current scenario and future needs. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 290–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlGabbani, Q. Nanotechnology: A promising strategy for the control of parasitic infections. Exp. Parasitol. 2023, 2023, 108548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljanabi, A.A.; Al-Mussawi, K.A.; Bashi, A.M. Scolicidal effects of silver-copper (core-shell) nanoparticles against Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices in vitro. Ann. Roman. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 19, 4335–4342. [Google Scholar]
- Cheraghipour, K.; Azarhazine, M.; Zivdari, M.; Beiranvand, M.; Shakib, P.; Rashidipour, M.; Mardanshah, O.; Mohaghegh, M.A.; Marzban, A. Evaluation of scolicidal potential of salicylate coated zinc nanoparticles against Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces. Exp. Parasitol. 2023, 246, 108456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Look, M.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Blum, J.S.; Fahmy, T.M. Application of nanotechnologies for improved immune response against infectious diseases in the developing world. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibaie, M.; Khalaf, A.K.; Rashidipour, M.; Mahmoudvand, H. Effects of green synthesized zinc nanoparticles alone and along with albendazole against hydatid cyst protoscoleces. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 78, 103746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraleedharan, K.; Chhabra, M. Nanotechnology Applications and Potential in Parasitology: An Overview. Vet. Immunol. Biotechnol. 2018, 1, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Qian, X.; Gao, C.; Pang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.; Pang, M.; Wu, D.; Yu, W. Advances in the pharmacological treatment of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: From laboratory to clinic. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 953846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikam, P.B.; Salunkhe, J.D.; Minkina, T.; Rajput, V.D.; Kim, B.S.; Patil, S.V. A review on green synthesis and recent applications of red nano Selenium. Results Chem. 2022, 2022, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenel, S.; Yüksel, S. Chitosan-based particulate systems for drug and vaccine delivery in the treatment and prevention of neglected tropical diseases. Drug. Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1644–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olawoyin, R. Nanotechnology: The future of fire safety. Saf. Sci. 2018, 110, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdussalam-Mohammed, W. Review of therapeutic applications of nanotechnology in medicine field and its side effects. J. Chem. Rev. 2019, 1, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| References | Efficacy Assessment | Treatment Period | Disease | Dosage | Experimental Design | Compounds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [35] | The weight and volume of cysts in the treated group were statistically significant compared with the control group | 45 days | CE: Hydatid cyst of Echinococcus granulosus | 10 mg/kg/day | In vivo | Albendazole sulfoxide-loaded chitosan-PLGA NPs (ABZ-SO-loaded CS-PGLA NPs) |
| [137] | The treated (ABZ-LNCs) group did not show any cysts | 30 days by an intragastric tube | CE | 5 mg/kg/day | In vivo | Albendazole-lipid Nanocapsule (ABZ-LNCs) |
| [20] | High efficacy in experimentally infected mice | 8 weeks by an gastric tube | CE | 100 mg/kg/day | In vivo | Albendazole on Ag NPs, ABZ, and Ag NPs |
| [43] | Only at a concentration of 800 μg/mL (100% PSCs mortality rate after 4 days of exposure) | - | CE | 200, 400, and 800 μg/mL | In vitro | ABZ-loaded β-cyclodextrin (ABZ-β-CD) |
| [44] | Both in vitro and in vivo treatments with ABZ-NLCs are significantly more efficient than treatment with free ABZ | Treatment was performed on Balb/C mice 1 day before intraperitoneal injection of viable protoscoleces | CE | 1, 5, and 10 μg/mL | In vitro and in vivo | Albendazole-loaded nanostructured lipid (ABZ-NLCs) |
| [21] | 1 µg/mL ABZ-NCs as a scolicidal agent against hydatid cyst protoscolices in 17 and 23 days | 5–30 days | CE | Protoscolices were cultured in 1 mL of RPMI 1640+ 1 µg/mL ABZ- nanocrystal and ABZ were added to culture, incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2 | In vitro | ABZ nanocrystals (ABZ-NCs) |
| [28] | Ag NPs showed the highest effect, followed by SiNPs, CuNPs, FeNPs, and ZnNPs | 10–60 min | CE | 0.25, 0.5, and 1 mg/mL | In vitro | Ag NPs, Fe NPs, Cu NPs, Si NPs, and Zn NPs |
| [37] | 47.8% after 45 min mortality rate of the protoscolices, in-creased from 10.4% after 15 min to 47.8% after 45 min. | 15, 30, and 45 min | CE | 10 μg/mL | In vitro | AgNPs |
| [36] | The cysts in the treated animals were slightly smaller, the weight of infected treated mice was more reduced than those in the non-treated control group | Treatment every 2 days for 30 days, orally administered, BALB/c Mice | CE | 50, 100, 200, and 300 mg/kg AgNPs diluted in distilled water | In vivo | Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Z. spina-christi (sidr) leaf extract |
| [138] | The mortality rate was 68% in 4 mg/mL concentration | 5, 10, 20, 30, and 60 min | CE | 0.25, 0.05, 1, 2, and 4 mg/mL, | In vitro | Chitosan–Curcumin Nanoparticles |
| [135] | Mortality rate was 100% after 10 min of incubation with 750 mg/mL of CuNPs and with Albendazole | 5–60 min | CE | CuNPs 250, 500, and 750 mg/mL and Albendazole 200 mg/mL | In vitro and ex vivo | Copper NPs (CuNPs) |
| [139] | The effect of concentrations of 250 and 500 mg/mL was the greatest and most clear since the first ten minutes of exposure | 10, 30, and 60 min | CE | 50, 125, 250, and 500 micrograms/mL | In vitro | Copper(core-shell) Nanoparticles |
| [38] | Mortality of the protoscoleces was 100% after 120 min of exposure to 1250 and 625 µg/mL concentrations of CUR-NE | 10, 20, 30, 60, and 120 min | CE | 156, 312, 625, and 1250 µg/mL | In vitro | Curcumin nanoemulsion (CUR-NE) |
| [117] | 4000 μg/mL of gold NPs killed 76% of protoscoleces in 60 min | 5, 10, 20, 30, and 60 min | CE | 250, 500, 1000, 2000, and 4000 μg/mL | In vitro | Gold NPs |
| [41] | Mortality rate was 100% after 2 h of incubation with Ag NPs 0.4 mg/L | 10–120 min | CE | 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 mg/mL | In vitro | Silver Nanoparticles Ag NPs |
| [140] | At 20 min, SA-ZnO-NPs at 2000 μg/mL exhibited the greatest activity on protoscolices with 100% mortality | 10, 20, and 30 min | CE | 1500 and 2000 μg/mL | In vitro | Salicylate-coated Zinc oxide nanoparticles (SA-ZnO-NPs) |
| [39] | Killed 84% of the treated protoscolices | 60 min | CE | 15 μg/mL gonad extract + TiO2 Nanoparticles | In vivo and In vitro | TiO2 Nanoparticles and Echinometra mathaeis gonad extracts |
| [42] | The mortality rate of 50 mg/mL ZnO NPs is 19.6% of protoscolices at 10 min | 10, 30, and 60 min | CE | 50, 100, and 150 mg/mL | In vitro | Zinc oxide Nanoparticles ZnO-NPs |
| [126] | 1000, 2000, and 4000 μg/mL were significantly effective in the killing of protoscoleces | 60 min | CE | 250, 500, 1000, 2000, and 4000 μg/mL | In vitro | Zirconium Oxide (ZrO2) |
| [141] | The concentration of 200 μg/mL, completely killed the protoscolices after 10 min | 50, 100, and 200 μg/mL) alone and combined with albendazole (ALZ, 100 μg/mL) | CE | 50, 100, and 200 μg/mL) | In vitro and ex vivo | ZnNPs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadr, S.; Lotfalizadeh, N.; Abbasi, A.M.; Soleymani, N.; Hajjafari, A.; Roohbaksh Amooli Moghadam, E.; Borji, H. Challenges and Prospective of Enhancing Hydatid Cyst Chemotherapy by Nanotechnology and the Future of Nanobiosensors for Diagnosis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8110494
Sadr S, Lotfalizadeh N, Abbasi AM, Soleymani N, Hajjafari A, Roohbaksh Amooli Moghadam E, Borji H. Challenges and Prospective of Enhancing Hydatid Cyst Chemotherapy by Nanotechnology and the Future of Nanobiosensors for Diagnosis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(11):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8110494
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadr, Soheil, Narges Lotfalizadeh, Amir Mohammad Abbasi, Nooshinmehr Soleymani, Ashkan Hajjafari, Elahe Roohbaksh Amooli Moghadam, and Hassan Borji. 2023. "Challenges and Prospective of Enhancing Hydatid Cyst Chemotherapy by Nanotechnology and the Future of Nanobiosensors for Diagnosis" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 11: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8110494
APA StyleSadr, S., Lotfalizadeh, N., Abbasi, A. M., Soleymani, N., Hajjafari, A., Roohbaksh Amooli Moghadam, E., & Borji, H. (2023). Challenges and Prospective of Enhancing Hydatid Cyst Chemotherapy by Nanotechnology and the Future of Nanobiosensors for Diagnosis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(11), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8110494







