Plasmodium knowlesi (Pk) Malaria: A Review & Proposal of Therapeutically Rational Exchange (T-REX) of Pk-Resistant Red Blood Cells
Abstract
1. Background
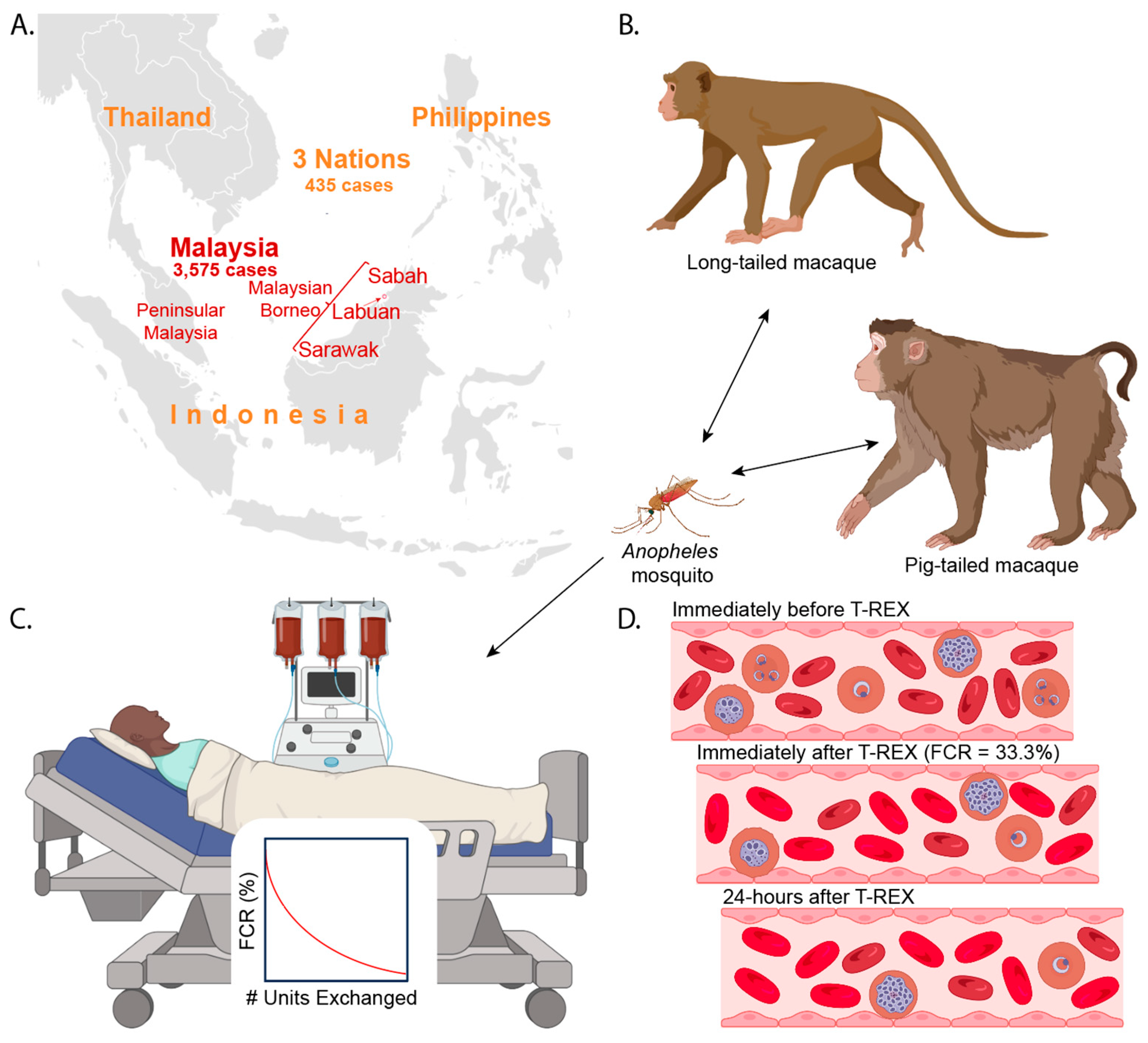
2. Pathophysiology
2.1. Pk Life Cycle
2.2. RBC Invasion
2.3. Pk Intraerythrocytic Cycle
2.4. RBC Deformability
2.5. Cytoadhesion & SICA Antigens
2.6. Pediatric Patients Rarely Develop Severe Pk Malaria
2.7. Tissue Expression of Duffy Antigen
3. Clinical Course
3.1. Signs and Symptoms
3.2. Deaths
4. Differential Diagnosis
5. Pk Diagnosis
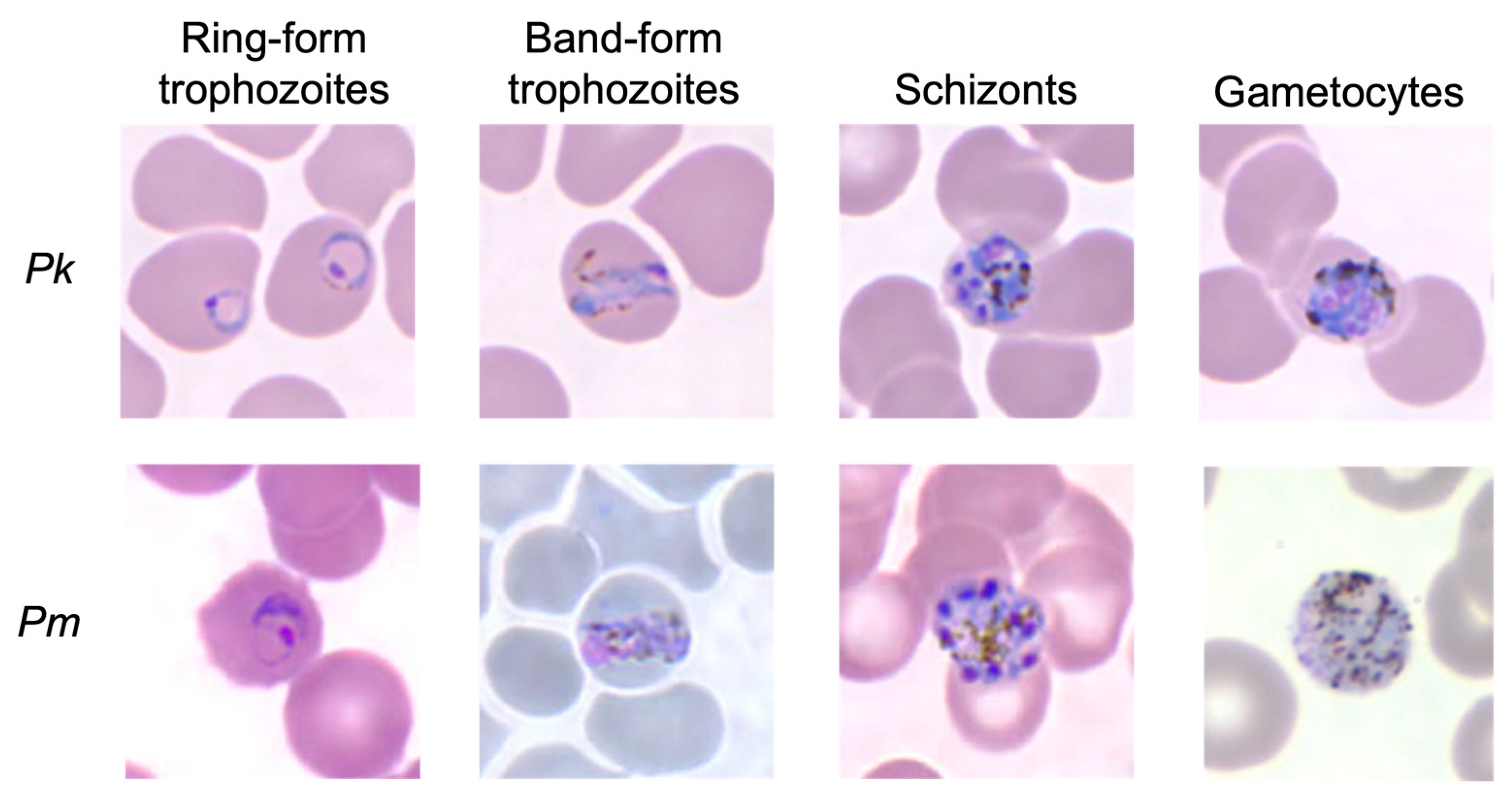
5.1. Microscopy
5.2. Molecular Testing
5.3. RDTs
5.4. Uncomplicated Vs. Severe Malaria
6. Rapidly Increasing Numbers of Pk Malaria Cases
7. Currently Still No Pk Vaccine
8. Antimalarial Medications
9. Manual Exchange Transfusion (ET)/Automated RBC Exchange (RBCX)
9.1. Manual ET/RBCX
9.2. Manual ET/RBCX for Malaria
10. Therapeutically Rational Exchange Transfusion (T-REX)
10.1. T-REX of Fy(a-b-) RBCs
10.2. T-REX of G6PDd RBCs
10.3. T-REX of Southeast Asian Ovalocytes
10.4. Performing Anti-Pk T-REX
10.5. Timeline of Therapeutic Benefits of Anti-Pk T-REX
10.6. After Anti-Pk T-REX
11. ABO Blood Group and Pk Malaria
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
References
- Antinori, S.; Galimberti, L.; Milazzo, L.; Corbellino, M. Plasmodium knowlesi: The emerging zoonotic malaria parasite. Acta Tropica. 2013, 125, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, R.; Gupta, B.M.D. A Study of Monkey-Malaria, and Its Experimental Transmission to Man. Ind. Med. Gaz. 1932, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kantele, A.; Jokiranta, T.S. Review of Cases With the Emerging Fifth Human Malaria Parasite, Plasmodium knowlesi. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, N.J. Plasmodium knowlesi: The Fifth Human Malaria Parasite. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 172–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.L.; Amir, A.; Lau, Y.L.; Fong, M.Y. The Duffy binding protein (PkDBPαII) of Plasmodium knowlesi from Peninsular Malaysia and Malaysian Borneo show different binding activity level to human erythrocytes. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etymologia: Plasmodium knowlesi. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 10. [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mahittikorn, A.; Masangkay, F.R.; Kotepui, K.U.; Milanez, G.D.J.; Kotepui, M. Comparison of Plasmodium ovale curtisi and Plasmodium ovale wallikeri infections by a meta-analysis approach. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-C.; Cheong, F.W.; Amir, A.; Lai, M.Y.; Tan, J.H.; Phang, W.K.; Shahari, S.; Lau, Y.-L. Plasmodium knowlesi: The game changer for malaria eradication. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempang, M.E.P.; Dewayanti, F.K.; Syahrani, L.; Permana, D.H.; Malaka, R.; Asih, P.B.S.; Syafruddin, D. Primate malaria: An emerging challenge of zoonotic malaria in Indonesia. One Heal. 2022, 14, 100389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. Health Indicators. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/index.php/pages/view/58?mid=19 (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Aftab, H.; Kemp, M.; Stensvold, C.R.; Nielsen, H.V.; Jakobsen, M.M.; Porskrog, A.; Dessau, R.B. First molecular documented case of a rarely reported parasite: Plasmodium knowlesi infection in Denmark in a traveller returning from Malaysian Borneo. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 53, 102580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Schlagenhauf, P. Plasmodium knowlesi in travellers, update 2014. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 22, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mace, K.E.; Lucchi, N.W.; Tan, K.R. Malaria Surveillance—United States, 2018. MMWR. Surveill. Summ. 2022, 71, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.K.-F.; Plewes, K.; Sharma, S.; Low, A.; Su, L.D.; Belga, S.; Salazar, F.V.; Hajek, J.; Morshed, M.; Hogan, C.A. Plasmodium knowlesi Infection in Traveler Returning to Canada from the Philippines, 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, N.J.; Hossain, H.; Nada-Raja, T.; Ngui, R.; Muslim, A.; Hoh, B.-P.; Khaw, L.T.; Kadir, K.A.; Divis, P.C.S.; Vythilingam, I.; et al. Natural Human Infections with Plasmodium cynomolgi, P. inui, and 4 other Simian Malaria Parasites, Malaysia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, R. Zoonotic Malaria—Global Overview and Research and Policy Needs. Front. Public Heal. 2014, 2, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, G.; Chua, T.H.; Cook, A.; Speldewinde, P.; Weinstein, P. Defining the ecological and evolutionary drivers of Plasmodium knowlesi transmission within a multi-scale framework. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornace, K.M.; Laporta, G.Z.; Vythilingham, I.; Chua, T.H.; Ahmed, K.; Jeyaprakasam, N.K.; Duarte, A.M.R.d.C.; Amir, A.; Phang, W.K.; Drakeley, C.; et al. Simian malaria: A narrative review on emergence, epidemiology and threat to global malaria elimination. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Straat, B.; Sebayang, B.; Grigg, M.J.; Staunton, K.; Garjito, T.A.; Vythilingam, I.; Russell, T.L.; Burkot, T.R. Zoonotic malaria transmission and land use change in Southeast Asia: What is known about the vectors. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, I.; Aure, W.; Manin, B.O.; Vythilingam, I.; Ferguson, H.M.; Drakeley, C.J.; Chua, T.H.; Fornace, K.M. Environmental and spatial risk factors for the larval habitats of Plasmodium knowlesi vectors in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malijan, R.P.B.; Mechan, F.; Braganza, J.C.; Valle, K.M.R.; Salazar, F.V.; Torno, M.M.; Aure, W.E.; Bacay, B.A.; Espino, F.E.; Torr, S.J.; et al. The seasonal dynamics and biting behavior of potential Anopheles vectors of Plasmodium knowlesi in Palawan, Philippines. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyes, C.L.; Shearer, F.M.; Huang, Z.; Wiebe, A.; Gibson, H.S.; Nijman, V.; Mohd-Azlan, J.; Brodie, J.F.; Malaivijitnond, S.; Linkie, M.; et al. Predicting the geographical distributions of the macaque hosts and mosquito vectors of Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in forested and non-forested areas. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naserrudin, N.A.; Hod, R.; Jeffree, M.S.; Ahmed, K.; Hassan, M.R. The Emerging Threat of Plasmodium knowlesi Malaria Infection: A Concept Paper on the Vulnerable Factors in Human. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, C.H.; Phang, W.K.; Liew, J.W.K.; Atroosh, W.M.; Lau, Y.L. Epidemiology of indigenous Plasmodium knowlesi infection in Sarawak, 2011–2019. Trop. Med. Int. Heal. 2022, 27, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boissière, A.; Tchioffo, M.T.; Bachar, D.; Abate, L.; Marie, A.; Nsango, S.E.; Shahbazkia, H.R.; Awono-Ambene, P.H.; Levashina, E.A.; Christen, R.; et al. Midgut Microbiota of the Malaria Mosquito Vector Anopheles gambiae and Interactions with Plasmodium falciparum Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.H.; Vythilingam, I.; Matusop, A.; Chan, S.T.; Singh, B. Bionomics of Anopheles latens in Kapit, Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo in relation to the transmission of zoonotic simian malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi. Malar. J. 2008, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, W.; Alpert, E.; Collins, W.E.; Jeter, M.H.; Contacos, P.G. Experimental Mosquito-Transmission of Plasmodium Knowlesi to Man and Monkey. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1968, 17, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornace, K.M.; Topazian, H.M.; Routledge, I.; Asyraf, S.; Jelip, J.; Lindblade, K.A.; Jeffree, M.S.; Cuenca, P.R.; Bhatt, S.; Ahmed, K.; et al. No evidence of sustained nonzoonotic Plasmodium knowlesi transmission in Malaysia from modelling malaria case data. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Daneshvar, C. Human Infections and Detection of Plasmodium knowlesi. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapabandara, A.M.G.M.; Mota, M.D.R.d.F.; Sarmento, R.; Bosco, J.D.; Wickremasinghe, R. From malaria control to elimination within a decade: Lessons learned from Timor Leste, a newly independent country. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIA. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 2022. Available online: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/about/archives/2022/ (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2022; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/reports/world-malaria-report-2022 (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Canuckguy. File: Southeast Asia Blank Political Map.svg: Wikimedia. 2016. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Southeast_Asia_blank_political_map.svg (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Austin, S.C.; Stolley, P.D.; Lasky, T. The history of malariotherapy for neurosyphilis. Modern parallels. JAMA 1992, 268, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamm, L.V.; Gherardini, F.C.; Parrish, E.A.; Moomaw, C.R. Heat shock response of spirochetes. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 1572–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, S.; Posey, J.E.; Chenoweth, M.R.; Gherardini, F.C. Treponema pallidum 3-Phosphoglycerate Mutase Is a Heat-Labile Enzyme That May Limit the Maximum Growth Temperature for the Spirochete. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 4702–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, R.N.; Das Gupta, B.M. A Preliminary Note on the Treatment of Neuro-Syphilis with Monkey Malaria. Ind. Med. Gaz. 1936, 71, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Rooyen, C.E.; Pile, G.R. Observations on infection by plasmodium knowlesi (ape malaria) in the treatment of general paralysis of the insane. Br. Med. J. 1935, 2, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treatment of Malaria: Guidelines for Clinicians (United States): The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2023. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/diagnosis_treatment/clinicians1.html (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Tintó-Font, E.; Michel-Todó, L.; Russell, T.J.; Casas-Vila, N.; Conway, D.J.; Bozdech, Z.; Llinás, M.; Cortés, A. A heat-shock response regulated by the PfAP2-HS transcription factor protects human malaria parasites from febrile temperatures. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajahram, G.S.; Cooper, D.J.; William, T.; Grigg, M.J.; Anstey, N.M.; Barber, B.E. Deaths From Plasmodium knowlesi Malaria: Case Series and Systematic Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaria Biology: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/about/biology/index.html (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Quansah, E.; Pappoe, F.; Shen, J.; Liu, M.; Yang, S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C. ApiAP2 Gene-Network Regulates Gametocytogenesis in Plasmodium Parasites. Cell. Microbiol. 2022, 2022, 5796578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.N.; Mohring, F.; DonVito, S.M.; Thomas, J.A.; Muller-Sienerth, N.; Wright, G.J.; Knuepfer, E.; Saibil, H.R.; Moon, R.W. Sequential roles for red blood cell binding proteins enable phased commitment to invasion for malaria parasites. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.L.; Lee, W.-C.; Lau, Y.-L.; Fong, M.Y. The Impact of Geographical Variation in Plasmodium knowlesi Apical Membrane Protein 1 (PkAMA-1) on Invasion Dynamics of P. knowlesi. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.H.; Thomas, A.W.; Margos, G.; Dluzewski, A.R.; Bannister, L.H. Apical Membrane Antigen 1, a Major Malaria Vaccine Candidate, Mediates the Close Attachment of Invasive Merozoites to Host Red Blood Cells. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muh, F.; Lee, S.-K.; Hoque, M.R.; Han, J.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Firdaus, E.R.; Moon, R.W.; Lau, Y.L.; Han, E.-T. In vitro invasion inhibition assay using antibodies against Plasmodium knowlesi Duffy binding protein alpha and apical membrane antigen protein 1 in human erythrocyte-adapted P. knowlesi A1-H.1 strain. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, Y.L.; Fong, M.Y.; Lau, Y.L. Genetic diversity of the full length apical membrane antigen-1 of Plasmodium knowlesi clinical isolates from Peninsular Malaysia. Trop. Biomed. 2021, 38, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulliez-Le Normand, B.; Faber, B.W.; Saul, F.A.; van der Eijk, M.; Thomas, A.W.; Singh, B.; Kocken, C.H.; Bentley, G.A. Crystal structure of Plasmodium knowlesi apical membrane antigen 1 and its complex with an invasion-inhibitory monoclonal antibody. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdi Abdel Hamid, M.; Remarque, E.J.; van Duivenvoorde, L.M.; van der Werff, N.; Walraven, V.; Faber, B.W.; Kocken, C.H.M.; Thomas, A.W. Vaccination with Plasmodium knowlesi AMA1 Formulated in the Novel Adjuvant Co-Vaccine HT™ Protects against Blood-Stage Challenge in Rhesus Macaques. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmolia, T.; Ahmed, M.A.; Sathishkumar, V.; Sarma, N.P.; Bhattacharyya, D.R.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Bansal, D.; Bharti, P.K.; Sehgal, R.; Mahanta, J.; et al. Genetic diversity of Plasmodium falciparum AMA-1 antigen from the Northeast Indian state of Tripura and comparison with global sequences: Implications for vaccine development. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 008 FY Alleles: International Society of Blood Transfusion. 2021. Available online: https://www.isbtweb.org/resource/008fy.html (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Crosnier, C.; Bustamante, L.Y.; Bartholdson, S.J.; Bei, A.K.; Theron, M.; Uchikawa, M.; Mboup, S.; Ndir, O.; Kwiatkowski, D.P.; Duraisingh, M.T.; et al. Basigin is a receptor essential for erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 2011, 480, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.H.; Mason, S.J.; Dvorak, J.A.; McGinniss, M.H.; Rothman, I.K. Erythrocyte receptors for (Plasmodium knowlesi) malaria: Duffy blood group determinants. Science 1975, 189, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, E.S.; Jiang, R.H.; Moechtar, M.A.; Barteneva, N.S.; Weekes, M.P.; Nobre, L.V.; Gygi, S.P.; Paulo, J.A.; Frantzreb, C.; Tani, Y.; et al. Malaria. A forward genetic screen identifies erythrocyte CD55 as essential for Plasmodium falciparum invasion. Science 2015, 348, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Bukhari, F.D.; Lau, Y.L.; Fong, M.Y. Erythrocyte Binding Activity of PkDBPαII of Plasmodium knowlesi Isolated from High and Low Parasitemia Cases. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 104, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.W.; Sharaf, H.; Hastings, C.H.; Ho, Y.S.; Nair, M.B.; Rchiad, Z.; Knuepfer, E.; Ramaprasad, A.; Mohring, F.; Amir, A.; et al. Normocyte-binding protein required for human erythrocyte invasion by the zoonotic malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7231–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohring, F.; Hart, M.N.; Rawlinson, T.A.; Henrici, R.; Charleston, J.A.; Diez Benavente, E.; Patel, A.; Hall, J.; Almond, N.; Campino, S.; et al. Rapid and iterative genome editing in the malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi provides new tools for P. vivax research. eLife 2019, 8, e45829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Wu, S.C.; Zheng, L.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G.; Josephson, C.D.; Hollenhorst, M.A.; Sackstein, R.; Cummings, R.D.; Arthur, C.M.; et al. ABO blood group antigens and differential glycan expression: Perspective on the evolution of common human enzyme deficiencies. iScience 2023, 26, 105798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, A.; Russell, B.; Liew, J.W.K.; Moon, R.W.; Fong, M.Y.; Vythilingam, I.; Subramaniam, V.; Snounou, G.; Lau, Y.L. Invasion characteristics of a Plasmodium knowlesi line newly isolated from a human. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.; Hansen, E.; DeSimone, T.M.; Moreno, Y.; Junker, K.; Bei, A.; Brugnara, C.; Buckee, C.O.; Duraisingh, M.T. Expansion of host cellular niche can drive adaptation of a zoonotic malaria parasite to humans. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, Y.W.; Russell, B.; Malleret, B.; Rénia, L. Erythrocyte tropism of malarial parasites: The reticulocyte appeal. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1022828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.W.; Hall, J.; Rangkuti, F.; Ho, Y.S.; Almond, N.; Mitchell, G.H.; Pain, A.; Holder, A.A.; Blackman, M.J. Adaptation of the genetically tractable malaria pathogen Plasmodium knowlesi to continuous culture in human erythrocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reticulocyte Count: Cleveland Clinic. 2022. Available online: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/22787-reticulocyte-count (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Grigg, M.J.; William, T.; Barber, B.E.; Rajahram, G.S.; Menon, J.; Schimann, E.; Piera, K.; Wilkes, C.S.; Patel, K.; Chandna, A.; et al. Age-Related Clinical Spectrum of Plasmodium knowlesi Malaria and Predictors of Severity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, C.; Davis, T.M.; Cox-Singh, J.; Rafa’ee, M.Z.; Zakaria, S.K.; Divis, P.C.; Singh, B. Clinical and laboratory features of human Plasmodium knowlesi infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, B.E.; William, T.; Grigg, M.J.; Menon, J.; Auburn, S.; Marfurt, J.; Anstey, N.M.; Yeo, T.W. A prospective comparative study of knowlesi, falciparum, and vivax malaria in Sabah, Malaysia: High proportion with severe disease from Plasmodium knowlesi and Plasmodium vivax but no mortality with early referral and artesunate therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, B.E.; Russell, B.; Grigg, M.J.; Zhang, R.; William, T.; Amir, A.; Lau, Y.L.; Chatfield, M.D.; Dondorp, A.M.; Anstey, N.M.; et al. Reduced red blood cell deformability in Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Blanch, A.J.; Namvar, A.; Carmo, O.; Tiash, S.; Andrew, D.; Hanssen, E.; Rajagopal, V.; Dixon, M.W.A.; Tilley, L. Multimodal analysis of Plasmodium knowlesi-infected erythrocytes reveals large invaginations, swelling of the host cell, and rheological defects. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. DPDx—Laboratory Identification of Parasites of Public Health Concern—Malaria. 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/malaria/index.html#tabs-2-3 (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Lee, K.-S.; Cox-Singh, J.; Singh, B. Morphological features and differential counts of Plasmodium knowles i parasites in naturally acquired human infections. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.; Ramdani, G.; Tatu, U.; Langsley, G.; Natarajan, V. Studying the rigidity of red blood cells induced by Plasmodium falciparum infection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstey, N.M.; Grigg, M.J.; Rajahram, G.S.; Cooper, D.J.; William, T.; Kho, S.; Barber, B.E. Knowlesi malaria: Human risk factors, clinical spectrum, and pathophysiology. Adv. Parasitol. 2021, 113, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.S.; Joyner, C.J.; Lapp, S.A.; Brady, J.A.; Wood, J.S.; Cabrera-Mora, M.; Saney, C.L.; Fonseca, L.L.; Cheng, W.T.; Jiang, J.; et al. Plasmodium knowlesi Cytoadhesion Involves SICA Variant Proteins. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 888496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.C.; Shahari, S.; Nguee, S.Y.T.; Lau, Y.L.; Rénia, L. Cytoadherence Properties of Plasmodium knowlesi-Infected Erythrocytes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 804417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.G.; Khairul, M.F.; Patil, P.R. Cytoadherence and severe malaria. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 19, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, H.; Sakaguchi, M.; Lucky, A.B.; Yamagishi, J.; Katakai, Y.; Kawai, S.; Kaneko, O. SICA-mediated cytoadhesion of Plasmodium knowlesi-infected red blood cells to human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox-Singh, J.; Hiu, J.; Lucas, S.B.; Divis, P.C.; Zulkarnaen, M.; Chandran, P.; Wong, K.T.; Adem, P.; Zaki, S.R.; Singh, B.; et al. Severe malaria—A case of fatal Plasmodium knowlesi infection with post-mortem findings: A case report. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.J. Malaria parasite clearance. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Severe Malaria. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2014, 19, 7–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adukpo, S.; Kusi, K.A.; Ofori, M.F.; Tetteh, J.K.; Amoako-Sakyi, D.; Goka, B.Q.; Adjei, G.O.; Edoh, D.A.; Akanmori, B.D.; Gyan, B.A.; et al. High plasma levels of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 are associated with cerebral malaria. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, M.J.; Cox, J.; William, T.; Jelip, J.; Fornace, K.M.; Brock, P.M.; von Seidlein, L.; Barber, B.E.; Anstey, N.M.; Yeo, T.W.; et al. Individual-level factors associated with the risk of acquiring human Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in Malaysia: A case-control study. Lancet Planet Health 2017, 1, e97–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotepui, M.; Kotepui, K.U.; Milanez, G.D.; Masangkay, F.R. Prevalence of severe Plasmodium knowlesi infection and risk factors related to severe complications compared with non-severe P. knowlesi and severe P. falciparum malaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, B.E.; Grigg, M.J.; William, T.; Piera, K.A.; Boyle, M.J.; Yeo, T.W.; Anstey, N.M. Effects of Aging on Parasite Biomass, Inflammation, Endothelial Activation, Microvascular Dysfunction and Disease Severity in Plasmodium knowlesi and Plasmodium falciparum Malaria. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1908–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Nielsen, S.; Elkjaer, M.-L.; Zbrzezna, V.; Fang, F.; Pogo, A.O. Detection of Duffy Antigen in the Plasma Membranes and Caveolae of Vascular Endothelial and Epithelial Cells of Nonerythroid Organs. Blood 1997, 89, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.; Chaudhuri, A.; Pogo, A.O. Which Are the Nonerythroid Cells That Constitutively Express the Duffy Antigen? Blood 1997, 90, 3231–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phyo, A.P.; Dahal, P.; Mayxay, M.; Ashley, E.A. Clinical impact of vivax malaria: A collection review. PLoS Med. 2022, 19, e1003890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.H.; Rosli, N.; Mohamad, D.S.A.; Kadir, K.A.; Ching, Z.H.; Chai, Y.H.; Ideris, N.N.; Ting, L.S.C.; Dihom, A.A.; Kong, S.L.; et al. A comparison of the clinical, laboratory and epidemiological features of two divergent subpopulations of Plasmodium knowlesi. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMorran, B.J. Immune role of platelets in malaria. ISBT Sci. Ser. 2019, 14, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wolfswinkel, M.E.; Hesselink, D.A.; Zietse, R.; Hoorn, E.J.; van Genderen, P.J. Hyponatraemia in imported malaria is common and associated with disease severity. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngernna, S.; Rachaphaew, N.; Thammapalo, S.; Prikchoo, P.; Kaewnah, O.; Manopwisedjaroen, K.; Phumchuea, K.; Suansomjit, C.; Roobsoong, W.; Sattabongkot, J.; et al. Case Report: Case Series of Human Plasmodium knowlesi Infection on the Southern Border of Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 101, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, S.P.; Zmora, P.; Pielok, Ł.; Kuszel, Ł.; Kierzek, R.; Stefaniak, J.; Paul, M. Case of Plasmodium knowlesi Malaria in Poland Linked to Travel in Southeast Asia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1772–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Lee, S.Y.; Koay, E.; Harkensee, C. Plasmodium knowlesi infection: A diagnostic challenge. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2013009558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajahram, G.S.; Barber, B.E.; Yeo, T.W.; Tan, W.W.; William, T. Case report: Fatal Plasmodium knowlesi malaria following an atypical clinical presentation and delayed diagnosis. Med. J. Malays. 2013, 68, 71–72. [Google Scholar]
- Takaya, S.; Kutsuna, S.; Suzuki, T.; Komaki-Yasuda, K.; Kano, S.; Ohmagari, N. Case Report: Plasmodium knowlesi Infection with Rhabdomyolysis in a Japanese Traveler to Palawan, the Philippines. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 967–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Rahim, M.J.; Mohammad, N.; Besari, A.M.; Wan Ghazali, W.S. Severe Plasmodium knowlesi with dengue coinfection. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr2016218480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.E.; Mohamad Zaini, R.H.; Suraiya, S.; Lee, K.T.; Lim, J.A. The dangers of accepting a single diagnosis: Case report of concurrent Plasmodium knowlesi malaria and dengue infection. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.W.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Koh, W.H.; Ooi, E.-E.; Tambyah, P.A. Monkey Malaria in Humans: A Diagnostic Dilemma with Conflicting Laboratory Data. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 927–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackroth, M.S.; Tappe, D.; Tannich, E.; Addo, M.; Rothe, C. Rapid-Antigen Test Negative Malaria in a Traveler Returning From Thailand, Molecularly Diagnosed as Plasmodium knowlesi. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, ofw039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Dengue Testing Guidance. 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dengue/healthcare-providers/testing/testing-guidance.html (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- WHO. Dengue and Severe Dengue. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dengue-and-severe-dengue (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- CDC. Dengue and Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dengue/resources/healthcarepract.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- CDC. Dengue Clinical Presentation; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.K.; Md Fuzi, N.H.; Baherin, M.F.; Lee, H.G. A case of co-infection: First reported case of severe plasmodium knowlesi malaria and dengue co-infection in Sabah, Malaysia. Med. J. Malays. 2020, 75, 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. Typhoid Fever and Paratyphoid Fever. 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/typhoid-fever/index.html (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- CDC. Yellow Book: Typhoid & Paratyphoid Fever. 2024. Available online: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/infections-diseases/typhoid-and-paratyphoid-fever (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Marchello, C.S.; Birkhold, M.; Crump, J.A. Complications and mortality of typhoid fever: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Yellow Book: Leptospirosis. 2024. Available online: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/infections-diseases/leptospirosis (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Karpagam, K.B.; Ganesh, B. Leptospirosis: A neglected tropical zoonotic infection of public health importance—An updated review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Management Guidelines of Malaria in Malaysia: Ministry of Health Malaysia. 2013. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/index.php/file_manager/dl_item/554756755a584a69615852686269394859584a70637942515957356b645746754c31426c626d6431636e567a595734675330567a615768686447467549435967613246335957786862694277655774706443394e515535425230564e52553555583064565355524654456c4f52564e6654305a665455464d51564a4a5156394a546c394e5155784257564e4a515335775a475978587935775a47593d (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Barber, B.E.; Grigg, M.J.; Cooper, D.J.; van Schalkwyk, D.A.; William, T.; Rajahram, G.S.; Anstey, N.M. Clinical management of Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Adv. Parasitol. 2021, 113, 45–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algorithm for Diagnosis and Treatment of Malaria in the United States: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2023. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/resources/pdf/Malaria_Managment_Algorithm_202208.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Tan, A.F.; Sakam, S.S.B.; Rajahram, G.S.; William, T.; Abd Rachman Isnadi, M.F.; Daim, S.; Barber, B.E.; Kho, S.; Sutherland, C.J.; Anstey, N.M.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy and limit of detection of ten malaria parasite lactate dehydrogenase-based rapid tests for Plasmodium knowlesi and P. falciparum. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1023219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahittikorn, A.; Masangkay, F.R.; Kotepui, K.U.; Milanez, G.D.J.; Kotepui, M. Quantification of the misidentification of Plasmodium knowlesi as Plasmodium malariae by microscopy: An analysis of 1569 P. knowlesi cases. Malar. J. 2021, 20, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yek, C.; Lay, S.; Bohl, J.A.; Man, S.; Chea, S.; Lon, C.; Ahyong, V.; Tato, C.M.; DeRisi, J.L.; Sovannaroth, S.; et al. Case Report: Cambodian National Malaria Surveillance Program Detection of Plasmodium knowlesi. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 107, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piera, K.A.; Aziz, A.; William, T.; Bell, D.; González, I.J.; Barber, B.E.; Anstey, N.M.; Grigg, M.J. Detection of Plasmodium knowlesi, Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) in a co-endemic area in Malaysia. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.Z.; Maluda, M.C.M.; Jelip, J.; Jeffree, M.S.B.; Culleton, R.; Ahmed, K. Malaria elimination in Malaysia and the rising threat of Plasmodium knowlesi. J. Physiol. Anthr. 2020, 39, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, C.H.; Phang, W.K.; Liew, J.W.K.; Atroosh, W.M.; Lau, Y.L. Profiling the imported human malaria in Sarawak, Malaysia in 2011-2019. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2023, 28, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genrich, G.L.; Guarner, J.; Paddock, C.D.; Shieh, W.J.; Greer, P.W.; Barnwell, J.W.; Zaki, S.R. Fatal malaria infection in travelers: Novel immunohistochemical assays for the detection of Plasmodium falciparum in tissues and implications for pathogenesis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mohammad, A.H.; Naserrudin, N.A.; Syed Abdul Rahim, S.S.; Jelip, J.; Atil, A.; Sazali, M.F.; Muyou, A.J.; Kunasagran, P.D.; Ahmad Kamarudin, N.; Azhar, Z.I.; et al. Narrative Review of the Control and Prevention of Knowlesi Malaria. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Malaria Programme: Diagnostic Testing: World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/case-management/diagnosis (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Amir, A.; Cheong, F.W.; de Silva, J.R.; Liew, J.W.K.; Lau, Y.L. Plasmodium knowlesi malaria: Current research perspectives. Infect. Drug Resist 2018, 11, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- How Malaria RDTs Work: World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/case-management/diagnosis/rapid-diagnostic-tests/how-malaria-rdts-work (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Tan, J.H.; Ding, H.X.; Fong, M.Y.; Lau, Y.L. Genetic diversity and in silico analysis of Plasmodium knowlesi Serine Repeat Antigen (SERA) 3 antigen 2 in Malaysia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2023, 114, 105490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornace, K.M.; Herman, L.S.; Abidin, T.R.; Chua, T.H.; Daim, S.; Lorenzo, P.J.; Grignard, L.; Nuin, N.A.; Ying, L.T.; Grigg, M.J.; et al. Exposure and infection to Plasmodium knowlesi in case study communities in Northern Sabah, Malaysia and Palawan, The Philippines. PLoS Neglected. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kim Sung, L.; Matusop, A.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Shamsul, S.S.; Cox-Singh, J.; Thomas, A.; Conway, D.J. A large focus of naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi infections in human beings. Lancet 2004, 363, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, Y.L.; Cadigan, F.C.; Coatney, G.R. A presumptive case of naturally occurring Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in man in Malaysia. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1971, 65, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Cuenca, P.; Key, S.; Lindblade, K.A.; Vythilingam, I.; Drakeley, C.; Fornace, K. Is there evidence of sustained human-mosquito-human transmission of the zoonotic malaria Plasmodium knowlesi? A systematic literature review. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccines: Mosquirix: World Health Organization. Available online: https://extranet.who.int/pqweb/content/mosquirix (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Laurens, M.B. RTS,S/AS01 vaccine (Mosquirix™): An overview. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2020, 16, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeson, J.G.; Kurtovic, L.; Valim, C.; Asante, K.P.; Boyle, M.J.; Mathanga, D.; Dobano, C.; Moncunill, G. The RTS,S malaria vaccine: Current impact and foundation for the future. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RTS, S.C.T.P. Efficacy and safety of RTS,S/AS01 malaria vaccine with or without a booster dose in infants and children in Africa: Final results of a phase 3, individually randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkman, A.; Benn, C.S.; Aaby, P.; Schapira, A. RTS,S/AS01 malaria vaccine-proven safe and effective? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, E318–E322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO recommends groundbreaking malaria vaccine for children at risk: World Health Organization. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/06-10-2021-who-recommends-groundbreaking-malaria-vaccine-for-children-at-risk (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Agency, E.M. Mosquirix: Opinion on Medicine for Use Outside EU. 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/opinion-medicine-use-outside-EU/human/mosquirix (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Malaria Vaccine: WHO Position Paper—March 2022: World Health Organization. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/who-wer9709-61%E2%80%9380 (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Q&A on RTS,S Malaria Vaccine: World Health Organization. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/q-a-on-rts-s-malaria-vaccine (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Venkatesan, P. The future of malaria control in light of RTS,S. Lancet Microbe. 2022, 3, e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.H.; Cheong, F.W.; Lau, Y.L.; Fong, M.Y. Plasmodium knowlesi circumsporozoite protein: Genetic characterisation and predicted antigenicity of the central repeat region. Trop. Biomed. 2023, 40, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaria in the United States: Treatment Tables: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/resources/pdf/Malaria_Treatment_Table_202306.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Arnold, M.S.; Engel, J.A.; Chua, M.J.; Fisher, G.M.; Skinner-Adams, T.S.; Andrews, K.T. Adaptation of the [3H]Hypoxanthine Uptake Assay for In Vitro-Cultured Plasmodium knowlesi Malaria Parasites. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2016, 60, 4361–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisciotta, J.M.; Scholl, P.F.; Shuman, J.L.; Shualev, V.; Sullivan, D.J. Quantitative characterization of hemozoin in Plasmodium berghei and vivax. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2017, 7, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coban, C. The host targeting effect of chloroquine in malaria. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 66, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-W.; Spaccapelo, R.; Schwarzer, E.; Sajid, M.; Annoura, T.; Deroost, K.; Ravelli, R.B.; Aime, E.; Capuccini, B.; Mommaas-Kienhuis, A.M.; et al. Replication of Plasmodium in reticulocytes can occur without hemozoin formation, resulting in chloroquine resistance. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai Rathnam, J.T.; Grigg, M.J.; Dini, S.; William, T.; Sakam, S.S.; Cooper, D.J.; Rajahram, G.S.; Barber, B.E.; Anstey, N.M.; Haghiri, A.; et al. Quantification of parasite clearance in Plasmodium knowlesi infections. Malar. J. 2023, 22, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schalkwyk, D.A.; Blasco, B.; Davina Nuñez, R.; Liew, J.W.K.; Amir, A.; Lau, Y.L.; Leroy, D.; Moon, R.W.; Sutherland, C.J. Plasmodium knowlesi exhibits distinct in vitro drug susceptibility profiles from those of Plasmodium falciparum. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2019, 9, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, P. Antimalarial and anticancer properties of artesunate and other artemisinins: Current development. Monatsh. Chem. 2021, 152, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intravenous Artesunate for Treatment of Severe Malaria in the United States: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/diagnosis_treatment/artesunate.html (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Djimdé, A.; Lefèvre, G. Understanding the pharmacokinetics of Coartem. Malar. J. 2009, 8 (Suppl. S1), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajosky, R.P. Clarifying the terms parasitemia, parasite density, and parasite count. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2023, 103788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hequet, O.; Boisson, C.; Joly, P.; Revesz, D.; Kebaili, K.; Gauthier, A.; Renoux, C.; Creppy, S.; Nader, E.; Nicolas, J.F.; et al. Priming With Red Blood Cells Allows Red Blood Cell Exchange for Sickle Cell Disease in Low-Weight Children. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 743483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.E.; Balogun, R.A. Principles of separation: Indications and therapeutic targets for plasma exchange. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Kulkarni, R. Overview of blood components and their preparation. Indian. J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northwestern. Headline for Red Blood Cell Exchange. Available online: https://www.nm.org/conditions-and-care-areas/treatments/red-blood-cell-exchange#:~:text=The%20length%20of%20the%20procedure,about%201%20to%202%20hours. (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- van Genderen, P.J.; Hesselink, D.A.; Bezemer, J.M.; Wismans, P.J.; Overbosch, D. Efficacy and safety of exchange transfusion as an adjunct therapy for severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria in nonimmune travelers: A 10-year single-center experience with a standardized treatment protocol. Transfusion 2010, 50, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, X.; Qin, G.; Zhang, S.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Ren, K.; Xu, J.; Han, X. Manual exchange transfusion for severe imported falciparum malaria: A retrospective study. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genstler, J.T.; Abdipour, A. Red blood cell exchange in treatment of severe cerebral P. falciparum malaria: A case report. J. Clin. Apher. 2019, 34, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongare, H.C.; Khatib, K.I. Exchange Transfusion in Severe Falciparum Malaria. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, OD05–OD06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boctor, F.N. Red Blood Cell Exchange Transfusion as an Adjunct Treatment for Severe Pediatric Falciparum Malaria, Using Automated or Manual Procedures. Pediatrics 2005, 116, e592–e595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, E.G.; King, K.E.; Ness, P.M.; Eshleman, S.H. Automated RBC exchange transfusion:treatment for cerebral malaria. Transfusion 2000, 40, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auer-Hackenberg, L.; Staudinger, T.; Bojic, A.; Locker, G.; Leitner, G.C.; Graninger, W.; Winkler, S.; Ramharter, M.; Worel, N. Automated red blood cell exchange as an adjunctive treatment for severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria at the Vienna General Hospital in Austria: A retrospective cohort study. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Telleria, L.; Vinetz, J.M.; Yawn, D.; Rossmann, S.; Indrikovs, A.J. Erythrocytapheresis for Plasmodium falciparum infection complicated by cerebral malaria and hyperparasitemia. J. Clin. Apher. 2001, 16, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.; Price, S.; Senthuran, S.; Cochupanachimootil, J.; Norton, R. Automated erythrocytapheresis for severe falciparum malaria. Intern. Med. J. 2011, 41, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macallan, D.C.; Pocock, M.; Bishop, E.; Bevan, D.H.; Parker-Williams, J.; Harrison, T.; Robinson, G.T. Automated erythrocytapheresis in the treatment of severe falciparum malaria. J. Infect. 1999, 39, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelat, S.G.; Lott, J.P.; Braga, M.S. Considerations on the use of adjunct red blood cell exchange transfusion in the treatment of severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Transfusion 2010, 50, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, H. Exchange transfusion in complicated pediatric malaria: A critical appraisal. Indian. J. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 19, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkl Renar, K.; Iskra, J.; Križaj, I. Understanding malarial toxins. Toxicon 2016, 119, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly-Smith, L.; Alquist, C.R.; Aqui, N.A.; Hofmann, J.C.; Klingel, R.; Onwuemene, O.A.; Patriquin, C.J.; Pham, H.P.; Sanchez, A.P.; Schneiderman, J.; et al. Guidelines on the Use of Therapeutic Apheresis in Clinical Practice—Evidence-Based Approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Ninth Special Issue. J. Clin. Apher. 2023, 38, 77–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, S.L.; Alles, H.K.; Bandara, S.; Phone-Kyaw, M.; Perera, M.K.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; Mendis, K.N.; Handunnetti, S.M. ABO-blood-group types and protection against severe, Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2005, 99, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, J.A.; Handel, I.G.; Thera, M.A.; Deans, A.M.; Lyke, K.E.; Koné, A.; Diallo, D.A.; Raza, A.; Kai, O.; Marsh, K.; et al. Blood group O protects against severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria through the mechanism of reduced rosetting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17471–17476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, N.M.; Petersen, N.; Clark, M.A.; Buckee, C.O.; Childs, L.M.; Duraisingh, M.T. Resistance to Plasmodium falciparum in sickle cell trait erythrocytes is driven by oxygen-dependent growth inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7350–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.; Nash, G.B.; Gabutti, V.; al-Yaman, F.; Wahlgren, M. Natural protection against severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria due to impaired rosette formation. Blood 1994, 84, 3909–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cserti, C.M.; Dzik, W.H. The ABO blood group system and Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Blood 2007, 110, 2250–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebel, E.R.; Uricchio, L.H.; Petrov, D.A.; Egan, E.S. Revisiting the malaria hypothesis: Accounting for polygenicity and pleiotropy. Trends. Parasitol. 2022, 38, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piel, F.B.; Patil, A.P.; Howes, R.E.; Nyangiri, O.A.; Gething, P.W.; Williams, T.N.; Weatherall, D.J.; Hay, S.I. Global distribution of the sickle cell gene and geographical confirmation of the malaria hypothesis. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akide-Ndunge, O.B.; Ayi, K.; Arese, P. The Haldane malaria hypothesis: Facts, artifacts, and a prophecy. Redox. Rep. 2003, 8, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandas, N.; An, X. Malaria and human red blood cells. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 201, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, L.; Vege, S.; Kessler, D.; Shaz, B.; Westhoff, C.M. Screening of blood donors for sickle cell trait using a DNA-based approach: Frequency in a multiethnic donor population. Transfusion 2021, 61, 2008–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, V.I.; Grima, K. Exchange transfusion for malaria and babesia infection. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2002, 16, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.C. Red cell exchange: Special focus on sickle cell disease. Hematology 2014, 2014, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, J.L.; Triulzi, D.J.; Ness, P.M. Indications for and Adverse Effects of Red-Cell Transfusion. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, C.L.; Gross, P.J.; Dean, C.L.; Chonat, S.; Ip, A.; McLemore, M.; El Rassi, F.; Stowell, S.R.; Josephson, C.D.; Fasano, R.M. Transfusion-transmitted malaria masquerading as sickle cell crisis with multisystem organ failure. Transfusion 2018, 58, 1550–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejura, B.; Sass, D.A.; Fischer, R.A.; Daskal, I.; Eiger, G. Transfusion-associated falciparum malaria successfully treated with red blood cell exchange transfusion. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2000, 320, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanaboonyongcharoen, P.; Park, Y.A.; Poisson, J.L.; Brecher, M.E. Rapid increases in parasitemia following red cell exchange for malaria. J. Clin. Apher. 2011, 26, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Patel, K.R.; Allen, J.W.; Zerra, P.E.; Chonat, S.; Ayona, D.; Maier, C.L.; Morais, D.; Wu, S.C.; Luckey, C.J.; et al. Antibody-mediated antigen loss switches augmented immunity to antiobdy-mediated immunosuppresion. Blood 2023, 142, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Patel, S.R.; Wu, S.C.; Patel, K.R.; Covington, M.L.; Vallecillo-Zuniga, M.L.; Ayona, D.; Bennett, A.; Luckey, C.J.; Hudson, K.E.; et al. Prior Immunization to an Intracellular Antigen Enhances Subsequent Red Blood Cell Alloimmunization in Mice. Blood 2023, 141, 2642–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.M.; Stowell, S.R. The Development and Consequences of Red Blood Cell Alloimmunization. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2023, 18, 537–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.M.; Allen, J.W.L.; Verkerke, H.; Yoo, J.; Jajosky, R.P.; Girard-Pierce, K.; Chonat, S.; Zerra, P.; Maier, C.; Rha, J.; et al. Antigen density dictates RBC clearance, but not antigen modulation, following incompatible RBC transfusion in mice. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mener, A.; Patel, S.R.; Arthur, C.M.; Chonat, S.; Wieland, A.; Santhanakrishnan, M.; Liu, J.; Maier, C.L.; Jajosky, R.P.; Girard-Pierce, K.; et al. Complement serves as a switch between CD4+ T cell-independent and -dependent RBC antibody responses. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e121631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Smith, N.H.; Bennett, A.; Kamili, N.A.; Mener, A.; Gerner-Smidt, C.; Sullivan, H.C.; Hale, J.S.; Wieland, A.; et al. Antigen Density Dictates Immune Responsiveness following Red Blood Cell Transfusion. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 2671–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, C.L.; Jajosky, R.; Verkerke, H.; Patel, S.R.; Allen, J.W.; Fuller, M.; Stowell, S.R. Storage Differentially Impacts Immunization to Red Cell Antigens. Transfusion, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Zerra, P.E.; Patel, S.R.; Jajosky, R.P.; Arthur, C.M.; McCoy, J.W.; Allen, J.W.L.; Chonat, S.; Fasano, R.M.; Roback, J.D.; Josephson, C.D.; et al. Marginal zone B cells mediate a CD4 T-cell-dependent extrafollicular antibody response following RBC transfusion in mice. Blood 2021, 138, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Sharma, A.; Zerra, P.E.; Chonat, S.; Jajosky, R.P.; Fasano, R.M.; Patel, R.; Bennett, A.; Zhou, X.; et al. Clodronate inhibits alloimmunization against distinct red blood cell alloantigens in mice. Transfusion 2022, 62, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.R.; Bennett, A.; Girard-Pierce, K.; Maier, C.L.; Chonat, S.; Arthur, C.M.; Zerra, P.E.; Mener, A.; Stowell, S.R. Recipient priming to one RBC alloantigen directly enhances subsequent alloimmunization in mice. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.R.; Gibb, D.R.; Girard-Pierce, K.; Zhou, X.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Arthur, C.M.; Bennett, A.L.; Jajosky, R.P.; Fuller, M.; Maier, C.L.; et al. Marginal Zone B Cells Induce Alloantibody Formation Following RBC Transfusion. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thein, S.L.; Pirenne, F.; Fasano, R.M.; Habibi, A.; Bartolucci, P.; Chonat, S.; Hendrickson, J.E.; Stowell, S.R. Hemolytic transfusion reactions in sickle cell disease: Underappreciated and potentially fatal. Haematologica 2020, 105, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonat, S.; Graciaa, S.; Shin, H.S.; Newton, J.G.; Quarmyne, M.O.; Boudreaux, J.; Tang, A.; Zerra, P.E.; Rollins, M.R.; Josephson, C.D.; et al. Eculizumab for complement mediated thrombotic microangiopathy in sickle cell disease. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirenne, F.; Yazdanbakhsh, K. How I safely transfuse patients with sickle-cell disease and manage delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions. Blood 2018, 131, 2773–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floch, A.; Morel, A.; Zanchetta-Balint, F.; Cordonnier-Jourdin, C.; Allali, S.; Grall, M.; Ithier, G.; Carpentier, B.; Pakdaman, S.; Merle, J.C.; et al. Anti-C5 antibody treatment for delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions in sickle cell disease. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, C.L.; Maier, C.L.; Roback, J.D.; Stowell, S.R. Multiple hemolytic transfusion reactions misinterpreted as severe vaso-occlusive crisis in a patient with sickle cell disease. Transfusion 2019, 59, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, R.S.; Hendrickson, J.E.; Fasano, R.M.; Meyer, E.K.; Winkler, A.M.; Yee, M.M.; Lane, P.A.; Jones, Y.A.; Pashankar, F.D.; New, T.; et al. Impact of red blood cell alloimmunization on sickle cell disease mortality: A case series. Transfusion 2016, 56, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.T.; Alsawas, M.; Fasano, R.M.; Field, J.J.; Hendrickson, J.E.; Howard, J.; Kameka, M.; Kwiatkowski, J.L.; Pirenne, F.; Shi, P.A.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for sickle cell disease: Transfusion support. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 327–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooling, L. Blood Groups in Infection and Host Susceptibility. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 801–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Arthur, C.M.; Jan, H.M.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Patel, K.R.; Rathgeber, M.; Verkerke, H.; Cheedarla, N.; Jajosky, R.P.; Paul, A.; et al. Blood Group A Enhances SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Blood 2023, 142, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severe Covid, G.G.; Ellinghaus, D.; Degenhardt, F.; Bujanda, L.; Buti, M.; Albillos, A.; Invernizzi, P.; Fernandez, J.; Prati, D.; Baselli, G.; et al. Genomewide Association Study of Severe COVID-19 with Respiratory Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G. Can Therapeutically-Rational Exchange (T-REX) of Thalassemic Red Blood Cells Improve the Clinical Course of Plasmodium falciparum Malaria? Eurasian J. Med. 2018, 50, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G. To prevent or ameliorate severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria, why not evaluate the impact of exchange transfusions of sickle cell trait red blood cells? Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2018, 57, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G. Can the Therapeutically-rational Exchange (T-REX) of Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficient Red Blood Cells Reduce Plasmodium falciparum Malaria Morbidity and Mortality? J. Nepal. Health Res. Counc. 2018, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, P.G.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G. Can therapeutically-rational exchange (T-REX) of type-O red blood cells (RBCs) benefit Plasmodium falciparum malaria patients? Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2019, 58, 344–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G. Can exchange transfusions using red blood cells from donors with Southeast Asian ovalocytosis prevent or ameliorate cerebral malaria in patients with multi-drug resistant Plasmodium falciparum? Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2017, 56, 865–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G. Can Exchange Transfusions Using Red Blood Cells from Donors with Hemoglobin E Trait Prevent or Ameliorate Severe Malaria in Patients with Multi-drug Resistant Plasmodium falciparum? Indian. J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2018, 34, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G. “Dual-gene” malaria-resistance: Therapeutically-rational exchange (T-REX) of group-O sickle trait and group-O C-traittrait red blood cells can be evaluated in Benin and Nigeria. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2020, 59, 102733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G. Therapeutically-rational exchange (T-REX) of Gerbich-negative red blood cells can be evaluated in Papua New Guinea as “a rescue adjunct” for patients with Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2021, 25, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G. Optimizing exchange transfusion for patients with severe Babesia divergens babesiosis: Therapeutically-Rational Exchange (T-REX) of M antigen-negative and/or S antigen-negative red blood cells should be evaluated now. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2019, 26, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, A.M.; Phyo, A.P.; Landier, J.; Parker, D.M.; Nosten, F.H. Combating multidrug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 2569–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meny, G.M. The Duffy blood group system: A review. Immunohematology 2010, 26, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höher, G.; Fiegenbaum, M.; Almeida, S. Molecular basis of the Duffy blood group system. Blood Transfus. 2018, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, J.R.; Lau, Y.L.; Fong, M.Y. Genotyping of the Duffy Blood Group among Plasmodium knowlesi-Infected Patients in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntumngia, F.B.; Thomson-Luque, R.; Pires, C.V.; Adams, J.H. The role of the human Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines in malaria susceptibility: Current opinions and future treatment prospects. J. Recept. Ligand. Channel. Res. 2016, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüring, C.; Moon, R.W.; Lim, C.; Holder, A.A.; Blackman, M.J.; Duraisingh, M.T. Human red blood cell-adapted Plasmodium knowlesi parasites: A new model system for malaria research. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.-J.; Dietrich, M.H.; Nguitragool, W.; Tham, W.-H. Plasmodium vivax Reticulocyte Binding Proteins for invasion into reticulocytes. Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.E., Jr.; Miller, L.H.; Ibrahim, L.; Wong, P.W.; McGinniss, M.; Ooi, W.L. Duffy phenotypes in Malaysian populations: Correction of previous unusual findings. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1988, 82, 509–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Silva, J.R.; Amir, A.; Lau, Y.L.; Ooi, C.-H.; Fong, M.Y. Distribution of the Duffy genotypes in Malaysian Borneo and its relation to Plasmodium knowlesi malaria susceptibility. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Ao, H.; Soemantri, A.; Tiwawech, D.; Settheetham-Ishida, W.; Kayame, O.W.; Kimura, M.; Nishioka, T.; Ishida, T. Sero- and molecular typing of Duffy blood group in Southeast Asians and Oceanians. Hum. Biol. 2000, 72, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Howes, R.E.; Patil, A.P.; Piel, F.B.; Nyangiri, O.A.; Kabaria, C.W.; Gething, P.W.; Zimmerman, P.A.; Barnadas, C.; Beall, C.M.; Gebremedhin, A.; et al. The global distribution of the Duffy blood group. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Simian malaria in a U.S. traveler—New York, 2008. MMWR 2009, 58, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Alemayehu, A. Zoonotic malaria in sub-Saharan Africa: A Mini-Review. J. Clin. Med. Rev. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyedibe, K.I.; Iroezindu, M.O.; Obishakin, E.T.; Ojogba, M.O.; Shobowale, E.O.; Ita, I.O.; Udoh, U.A.; Isa, S.E.; Egah, D.Z. Plasmodium knowlesi Infection: Should Africa be Prepared for a New Human Malaria Threat? Int. J. Trop. Dis. Health 2016, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawani, A.J.; Saboor, M.; Abu-Tawil, H.I.; Mahzari, A.A.; Mansor, A.S.; Bantun, F. Prevalence of Duffy Blood Group Antigens and Phenotypes among Saudi Blood Donors in Southwestern Saudi Arabia. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owaidah, A.Y.; Naffaa, N.M.; Alumran, A.; Alzahrani, F. Phenotype Frequencies of Major Blood Group Systems (Rh, Kell, Kidd, Duffy, MNS, P, Lewis, and Lutheran) Among Blood Donors in the Eastern Region of Saudi Arabia. J. Blood Med. 2020, 11, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahar, M.A.; Patel, R.D. Phenotype frequencies of blood group systems (Rh, Kell, Kidd, Duffy, MNS, P, Lewis, and Lutheran) in blood donors of south Gujarat, India. Asian J. Transfus. Sci. 2014, 8, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero-Santacruz, M.; Flórez Elvira, L.; Mejía Hurtado, A.F.; Macia Mejía, C. Estimated prevalence of the Duffy null phenotype Fy (a-b-) among black blood-donors in Southwestern Colombia. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2020, 59, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, R.; Deora, N.; Bhandari, D.; Parvez, S.; Sinha, A.; Sharma, A. Trends of neglected Plasmodium species infection in humans over the past century in India. One Health 2020, 11, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, C.; Pramanik, A.; Kumari, K.; Mandage, R.; Dinda, A.K.; Sankar, J.; Bagga, A.; Agarwal, S.K.; Sinha, A.; Singh, G.; et al. Renal detection of Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium knowlesi in malaria associated acute kidney injury: A retrospective case–control study. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, R.K.; Das, M.K.; Singh, S.S.; Sharma, Y.D. Discordance in drug resistance-associated mutation patterns in marker genes of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium knowlesi during coinfections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.K.; Singh, S.S.; Adak, T.; Vasantha, K.; Mohanty, D. The Duffy blood groups of Jarawas—The primitive and vanishing tribe of Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Transfus. Med. 2005, 15, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhya, P.T.; Sunish, I.P.; Maile, A.; Zahid, A.K. Anopheles sundaicus Mosquitoes as Vector for Plasmodium knowlesi, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awab, G.R.; Aaram, F.; Jamornthanyawat, N.; Suwannasin, K.; Pagornrat, W.; Watson, J.A.; Woodrow, C.J.; Dondorp, A.M.; Day, N.P.J.; Imwong, M.; et al. Protective effect of Mediterranean-type glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency against Plasmodium vivax malaria. eLife 2021, 10, e62448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindo, A.; Fairhurst, R.M.; Doumbo, O.K.; Wellems, T.E.; Diallo, D.A. X-linked G6PD deficiency protects hemizygous males but not heterozygous females against severe malaria. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappadoro, M.; Giribaldi, G.; O’Brien, E.; Turrini, F.; Mannu, F.; Ulliers, D.; Simula, G.; Luzzatto, L.; Arese, P. Early phagocytosis of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)-deficient erythrocytes parasitized by Plasmodium falciparum may explain malaria protection in G6PD deficiency. Blood 1998, 92, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruwende, C.; Khoo, S.C.; Snow, R.W.; Yates, S.N.; Kwiatkowski, D.; Gupta, S.; Warn, P.; Allsopp, C.E.; Gilbert, S.C.; Peschu, N.; et al. Natural selection of hemi- and heterozygotes for G6PD deficiency in Africa by resistance to severe malaria. Nature 1995, 376, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, B.E.; Grigg, M.J.; William, T.; Yeo, T.W.; Anstey, N.M. The Treatment of Plasmodium knowlesi Malaria. Trends. Parasitol. 2017, 33, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Testing for G6PD Deficiency for Safe Use of Primaquine in Radical Cure of P. vivax and P. ovale: Policy Brief Geneva: World Health Organization. 2016. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/250297 (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- World Health Organization. Technical Consultation to Review the Classification of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD). 2022. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/malaria/mpac-documentation/mpag-mar2022-session2-technical-consultation-g6pd-classification.pdf?sfvrsn=1f36be5e_12&download=true (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Omisakin, C.T.; Esan, A.J.; Ogunleye, A.A.; Ojo-Bola, O.; Owoseni, M.F.; Omoniyi, D.P. Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6pd) Deficiency and Sickle Cell Trait among Blood Donors in Nigeria. Am. J. Public Health Res. 2014, 2, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamghorashi, F.; Hoshmand, F.; Mohtashamifar, A. Screening for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in blood donors. Hematology 2010, 15, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittisares, K.; Palasuwan, D.; Noulsri, E.; Palasuwan, A. Thalassemia trait and G6PD deficiency in Thai blood donors. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2019, 58, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojphoung, P.; Rungroung, T.; Siriboonrit, U.; Vejbaesya, S.; Permpikul, P.; Kittivorapart, J. Prevalence of G6PD deficiency in Thai blood donors, the characteristics of G6PD deficient blood, and the efficacy of fluorescent spot test to screen for G6PD deficiency in a hospital blood bank setting. Hematology 2022, 27, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, F.; Ismail, E.; Zilfalil, B.A. Prevalence and molecular study of G6PD deficiency in Malaysian Orang Asli. Intern. Med. J. 2011, 41, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, F.; Liu, R.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Z.; Yang, Z.; et al. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency at the China-Myanmar Border. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutagalung, J.; Kusnanto, H.; Supargiyono; Sadewa, A.H.; Satyagraha, A.W. The first evaluation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD) gene mutation in malaria-endemic region at South Central Timor (SCT) district, Eastern Indonesia 2015-2016. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 125, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalloh, A.; Tantular, I.S.; Pusarawati, S.; Kawilarang, A.P.; Kerong, H.; Lin, K.; Ferreira, M.U.; Matsuoka, H.; Arai, M.; Kita, K.; et al. Rapid epidemiologic assessment of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in malaria-endemic areas in Southeast Asia using a novel diagnostic kit. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2004, 9, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderle, A.; Bancone, G.; Domingo, G.J.; Gerth-Guyette, E.; Pal, S.; Satyagraha, A.W. Point-of-Care Testing for G6PD Deficiency: Opportunities for Screening. Int. J. Neonatal Screen 2018, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacajornsuk, P.; Sriwangpon, P. Prevalence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G-6-PD) using methemoglobin reduction test in blood donors of Chiang Mai Province. J. Assoc. Med. Sci. 2015, 48, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Mansor, H.; Mohd Tohit, E.R.; Idris, F.; Awang Abd Rahman, A. Prevalence, sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of G6PD deficient blood donors in Terengganu and the effects of storage on their donated blood. Malays. J. Med. Health Sci. 2020, 16, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, R.O.; Jhang, J.; Hendrickson, J.E.; Zimring, J.C.; Hod, E.A.; Spitalnik, S.L. Frequency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient red blood cell units in a metropolitan transfusion service. Transfusion 2013, 53, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Guide to Fluorescent Spot Testing for G6PD Deficiency. 2014. Available online: https://media.path.org/documents/FST_Guidebook.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- World Health Organization. Blood Donor Selection: Guidelines on Assessing Donor Suitability for Blood Donation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, R.O.; Belpulsi, D.; Soffing, M.; Yeh, R.; Coronel, E.E.; Sheikh, A.; Spitalnik, S.; Hod, E.A. Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency in Blood Donors Is Associated with Decreased Post-Transfusion Red Cell Recovery. Blood 2017, 130 (Suppl. S1), 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, J.R. Scientific problems in the regulation of red blood cell products. Transfusion 2012, 52, 1827–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajibthong, S.; Sahntipurna, V.; Parnsamut, C.; Pitakpolrat, P.; Pattanapongsak, W.; Watanaboonyongcharoen, P.; Rojnuckarin, P. Randomised controlled trial of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient versus non-deficient red blood cell transfusion in patients with hypoproliferative anaemia. Transfus. Med. 2022, 32, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karafin, M.S.; Francis, R.O. Impact of G6PD status on red cell storage and transfusion outcomes. Blood Transfus. 2019, 17, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowe, S.A.; Ransome-Kuti, O. Exchange transfusion using G-6-PG deficient or Hgb-AS blood in icteric neonates. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 1981, 73, 811–819. [Google Scholar]
- Flatt, J.F.; Stevens-Hernandez, C.J.; Cogan, N.M.; Eggleston, D.J.; Haines, N.M.; Heesom, K.J.; Picard, V.; Thomas, C.; Bruce, L.J. Expression of South East Asian Ovalocytic Band 3 Disrupts Erythroblast Cytokinesis and Reticulocyte Maturation. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, V.; Proust, A.; Eveillard, M.; Flatt, J.F.; Couec, M.-L.; Caillaux, G.; Fénéant-Thibault, M.; Finkelstein, A.; Raphaël, M.; Delaunay, J.; et al. Homozygous Southeast Asian ovalocytosis is a severe dyserythropoietic anemia associated with distal renal tubular acidosis. Blood 2014, 123, 1963–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, K. Exploring the Potential Roles of Band 3 and Aquaporin-1 in Blood CO2 Transport–Inspired by Comparative Studies of Glycophorin B-A-B Hybrid Protein GP.Mur. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavinya, A.A.; Razali, R.A.; Razak, M.A.; Mohamed, R.; Moses, E.J.; Soundararajan, M.; Bruce, L.J.; Eswaran, J.; Yusoff, N.M. Homozygous Southeast Asian ovalocytosis in five live-born neonates. Haematologica 2020, 106, 1758–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Castaño, A.B.; Diaz-Ricart, M.; Escolar, G.; García, E.; Mañú-Pereira, M.D.M.; Idrizovic, A.; Matute, M.; Molina, A.; Faneca, J.; Merino, A. Southeast Asian ovalocytosis detected in a critical patient with COVID-19 pneumonia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2022, 44, e215–e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrong, O.; Bruce, L.J.; Unwin, R.J.; Toye, A.M.; Tanner, M.J.A. Band 3 mutations, distal renal tubular acidosis, and Southeast Asian ovalocytosis. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton-Maggs PH, B.; Stevens, R.F.; Dodd, N.J.; Lamont, G.; Tittensor, P.; King, M.J.; General Haematology Task Force of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hereditary spherocytosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 126, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, T.; Saul, A.; Lamont, G.; Hudson, D.E.; Miller, L.H.; Kidson, C. Resistance of Melanesian elliptocytes (ovalocytes) to invasion by Plasmodium knowlesi and Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites in vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1983, 71, 780–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondorp, A.M.; Fanello, C.I.; Hendriksen, I.C.; Gomes, E.; Seni, A.; Chhaganlal, K.D.; Bojang, K.; Olaosebikan, R.; Anunobi, N.; Maitland, K.; et al. Artesunate versus quinine in the treatment of severe falciparum malaria in African children (AQUAMAT): An open-label, randomised trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondorp, A.; Nosten, F.; Stepniewska, K.; Day, N.; White, N. Artesunate versus quinine for treatment of severe falciparum malaria: A randomised trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Zaloumis, S.G.; Grigg, M.J.; Haque, A.; Davenport, M.P. Malaria Parasite Clearance: What Are We Really Measuring? Trends. Parasitol. 2020, 36, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, K.R.; Biagini, G.A.; Craig, A.G. Continued cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum infected red blood cells after antimalarial treatment. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2010, 169, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phyo, A.P.; Nkhoma, S.; Stepniewska, K.; Ashley, E.A.; Nair, S.; McGready, R.; ler Moo, C.; Al-Saai, S.; Dondorp, A.M.; Lwin, K.M.; et al. Emergence of artemisinin-resistant malaria on the western border of Thailand: A longitudinal study. Lancet 2012, 379, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byakika-Kibwika, P.; Nyakato, P.; Lamorde, M.; Kiragga, A.N. Assessment of parasite clearance following treatment of severe malaria with intravenous artesunate in Ugandan children enrolled in a randomized controlled clinical trial. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immacolata, A.; Roberta, R.; Antonella, G.; Achille, I. New insights on hereditary erythrocyte membrane defects. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, P.G. Red Cell Membrane Disorders. Hematology 2005, 2005, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instructions to Authors and Reviewers Concerning Description of Apheresis Procedures. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/pb-assets/assets/10981101/Apheresis_Procedures_Reporting_Guide-1509463686000.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Jajosky, R.P.; Jajosky, A.N.; Jajosky, P.G. ABO blood group should be considered and reported when red blood cell exchange transfusion is used to treat Plasmodiumfalciparum Malaria patients. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2020, 27, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| RBCs | Evidence for Resistance against Pk |
|---|---|
| Fy(a-b-) |
|
| G6PDd |
|
| SAO |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jajosky, R.P.; Wu, S.-C.; Jajosky, P.G.; Stowell, S.R. Plasmodium knowlesi (Pk) Malaria: A Review & Proposal of Therapeutically Rational Exchange (T-REX) of Pk-Resistant Red Blood Cells. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8100478
Jajosky RP, Wu S-C, Jajosky PG, Stowell SR. Plasmodium knowlesi (Pk) Malaria: A Review & Proposal of Therapeutically Rational Exchange (T-REX) of Pk-Resistant Red Blood Cells. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(10):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8100478
Chicago/Turabian StyleJajosky, Ryan Philip, Shang-Chuen Wu, Philip G. Jajosky, and Sean R. Stowell. 2023. "Plasmodium knowlesi (Pk) Malaria: A Review & Proposal of Therapeutically Rational Exchange (T-REX) of Pk-Resistant Red Blood Cells" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 10: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8100478
APA StyleJajosky, R. P., Wu, S.-C., Jajosky, P. G., & Stowell, S. R. (2023). Plasmodium knowlesi (Pk) Malaria: A Review & Proposal of Therapeutically Rational Exchange (T-REX) of Pk-Resistant Red Blood Cells. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(10), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8100478






