Evaluating the Effectiveness of a Novel Systematic Screening Approach for Tuberculosis among Individuals Suspected or Recovered from COVID-19: Experiences from Niger and Guinea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Period and Population
2.2. Setting
2.3. Intervention/Strategy
2.4. Study Variables
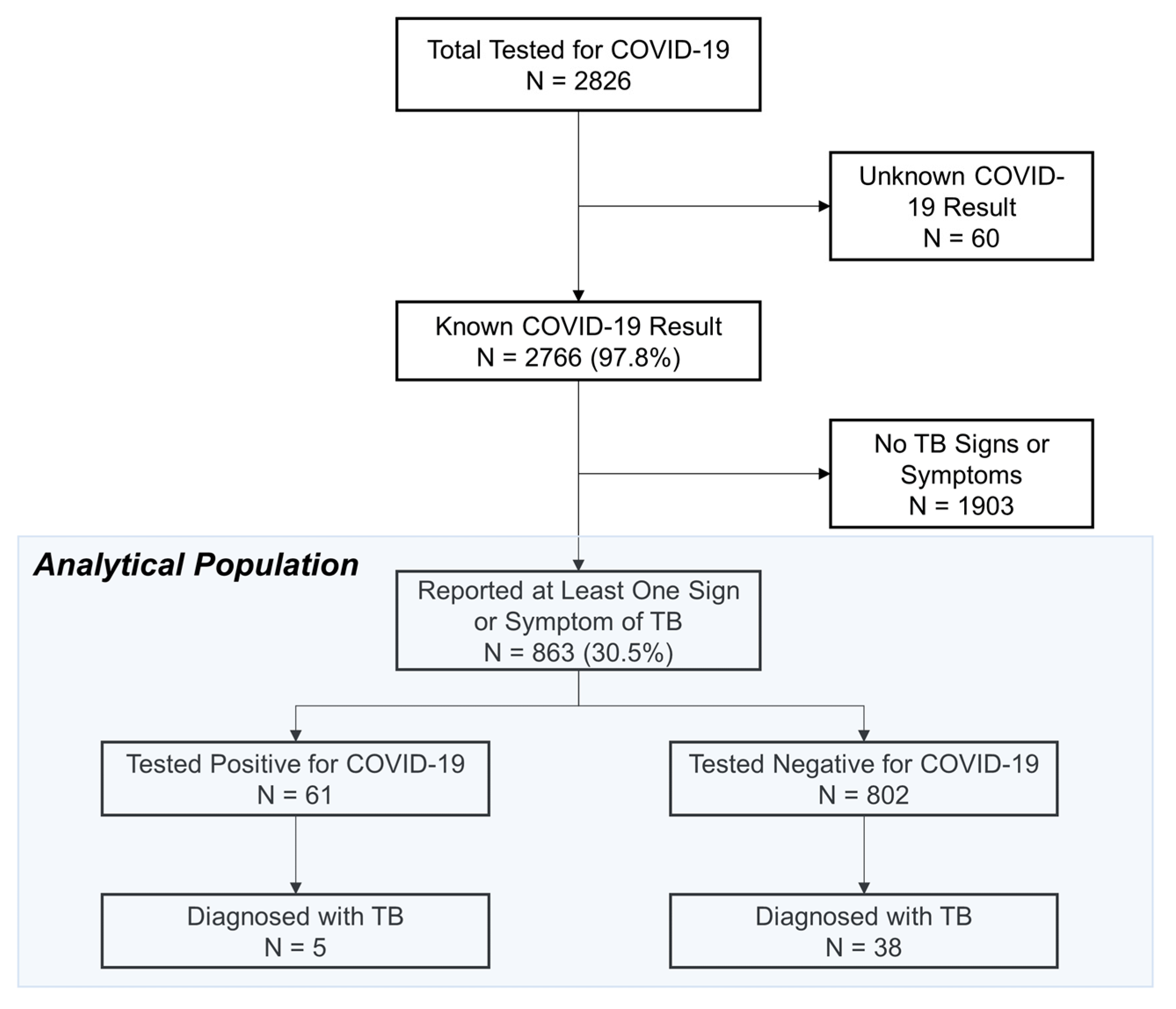
2.5. Sampling Procedure and Data Collection
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
Cost Assessment
4. Discussion
Difficulties and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Tiwari, S.; Deb, M.K.; Marty, J.L. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): A global pandemic and treatment strategies. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegarty, P.K.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Giannarini, G.; DiNardo, A.R.; Kamat, A.M. COVID-19 and Bacillus Calmette-Guérin: What is the Link? Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewole, O.O. Impact of COVID-19 on TB care: Experiences of a treatment centre in Nigeria. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2020, 24, 981–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, C.D.F.; Coutinho, H.S.; Costa, M.M.; Magalhães, M.A.F.M.; Carmo, R.F. Impact of COVID-19 on TB diagnosis in Northeastern Brazil. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2020, 24, 1220–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliori, G.B.; Thong, P.M.; Akkerman, O.; Alffenaar, J.W.; Álvarez-Navascués, F.; Assao-Neino, M.M.; Bernard, P.V.; Biala, J.S.; Blanc, F.X.; Bogorodskaya, E.M.; et al. Worldwide Effects of Coronavirus Disease Pandemic on Tuberculosis Services, January–April 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2709–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilloni, L.; Fu, H.; Vesga, J.F.; Dowdy, D.; Pretorius, C.; Ahmedov, S.; Nair, S.A.; Mosneaga, A.; Masini, E.; Sahu, S.; et al. The potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the tuberculosis epidemic a modelling analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 28, 100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaziou, P. Predicted impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on global tuberculosis deaths in 2020. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Tuberculosis and COVID-19; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Information Note, Tuberculosis and COVID-19; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/hq-tuberculosis/covid-19-tb-clinical-management-info-note-dec-update-2020.pdf?sfvrsn=554b68a7_0 (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Kodish, S.R.; Rohner, F.; Beauliere, J.M.; Daffe, M.; Ayoya, M.A.; Wirth, J.P.; Ngnie-Teta, I. Implications of the Ebola virus disease outbreak in Guinea: Qualitative findings to inform future health and nutrition-related responses. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202468. [Google Scholar]
- PNLAT. Plan d’Attenuation de L’Impact du COVID-19 Sur la Lutte Antituberculeuse; Ministère de la Santé de Guinée: Conakry, Guinea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- NTP. Plan Strategique National de Lutte Antituberculeuse en Guinée, 2021–2025; Ministère de la Santé de Guinée: Conakry, Guinea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, E.; Bodson, O.; Le Marcis, F.; Faye, A.; Sambieni, N.E.; Fournet, F.; Boyer, F.; Coulibaly, A.; Kadio, K.; Diongue, F.B.; et al. The COVID-19 pandemic in francophone West Africa: From the first cases to responses in seven countries. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjobimey, M.; Ade, S.; Wachinou, P.; Esse, M.; Yaha, L.; Bekou, W.; Campbell, J.R.; Toundoh, N.; Adjibode, O.; Attikpa, G.; et al. Prevalence, acceptability, and cost of routine screening for pulmonary tuberculosis among pregnant women in Cotonou, Benin. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis Module 2: Screening–Systematic Screening for Tuberculosis Disease; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240022676 (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Stop TB Partnership. Simultaneous, Integrated Diagnostic Testing Approach to Detect COVID-19 and TB in High TB Burden Countries. 2021. Available online: https://www.stoptb.org/file/9145/download (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria. Testing for both Tuberculosis and SARS-CoV-2. 2021. Available online: https://www.theglobalfund.org/media/11438/covid19_tb-testing_briefingnote_en.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Tovar, M.A.; Puma, D.; Palomino, S.; Peinado, J.; Llanos, F.; Martinelli, C.; Jimenez, J.; Calderon, R.; Yuen, C.M.; Lecca, L. Integrated screening and testing for TB and COVID-19 in Peru. Public Health Action 2022, 12, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A.; Hussain, H.; Maniar, R.; Safdar, N.; Mohiuddin, A.; Riaz, N.; Pasha, A.; Khan, S.; Hasan Kazmi, S.S.; Kazmi, E.; et al. Integrated Tuberculosis and COVID-19 Activities in Karachi and Tuberculosis Case Notifications. Trop Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Acceptability of TB Screening among At-Risk and Vulnerable Groups; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Heemskerk, D.; Caws, M.; Marais, B.; Farrar, J. Clinical Manifestations. In Tuberculosis in Adults and Children; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, R.; Bayindir, Y.; Sevinc, A.; Bahceci, F.; Ozen, S. The triad of weight loss, fever and night sweating: Isolated bone marrow tuberculosis, a case report. J. Chemother. 2002, 14, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Shi, S.; Geng, J.; Tian, J. Association between tuberculosis and COVID-19 severity and mortality: A rapid systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zykov, M.P.; de Souza, F.; Roulet, H. Routine diagnosis of tuberculosis with phase-contrast microscopy. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1974, 109, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muyoyeta, M.; Kasese, N.C.; Milimo, D.; Mushanga, I.; Ndhlovu, M.; Kapata, N.; Moyo-Chilufya, M.; Ayles, H. Digital CXR with computer aided diagnosis versus symptom screen to define presumptive tuberculosis among household contacts and impact on tuberculosis diagnosis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
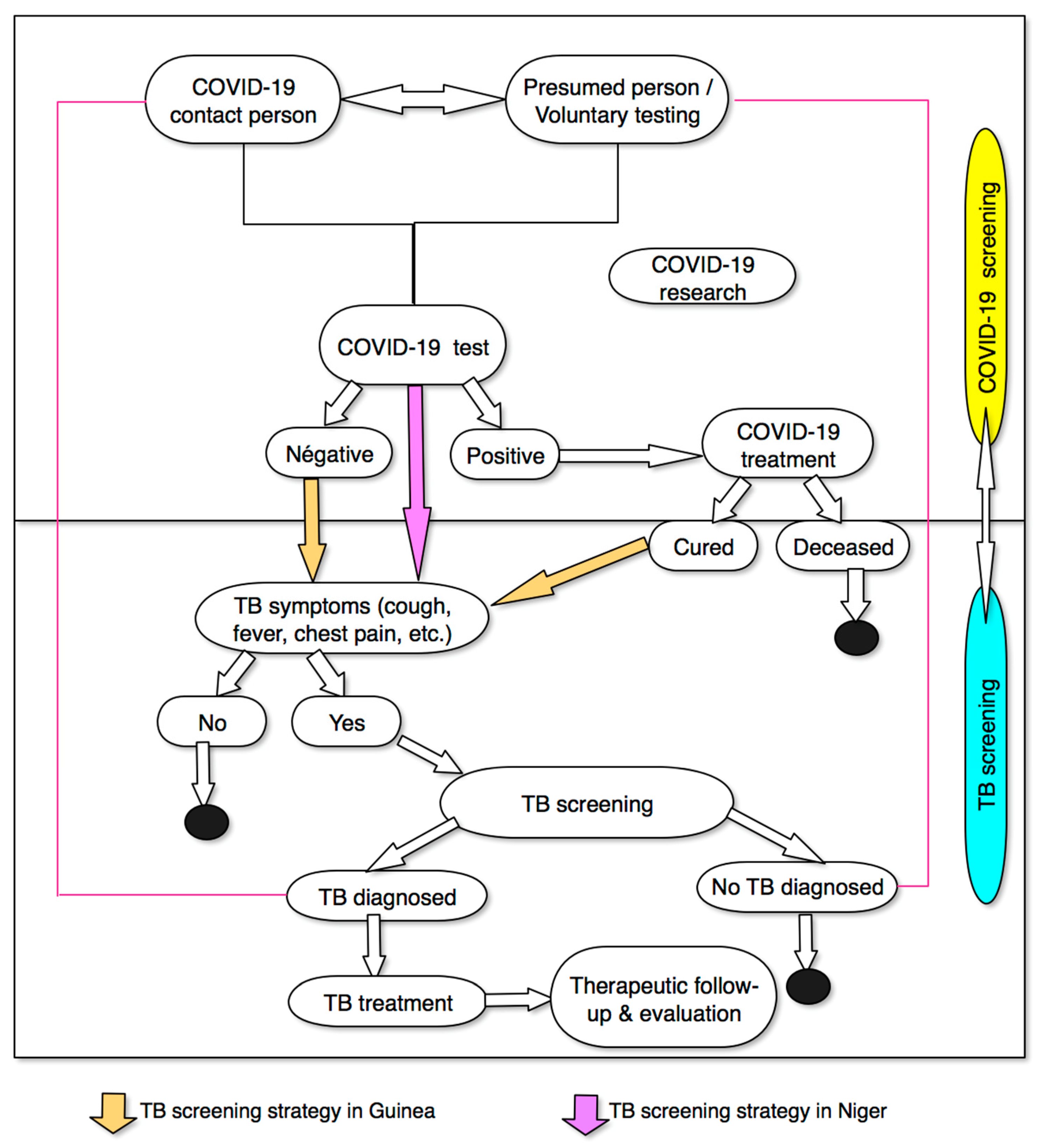
| Guinea | Niger | |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Cross-sectional study | |
| Period | May to December 2020 | December 2020 to March 2021 |
| Setting | 5 COVID-19 screening and treatment centers in Conakry | 4 COVID-19 screening and treatment centers in Niamey |
| Study population | Persons with a negative COVID-19 test or recovered from COVID-19 disease and with symptoms of TB | Persons with presumptive COVID-19 and with symptoms of TB regardless of the COVID-19 test result |
| COVID-19 diagnostic method | Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test | |
| TB diagnostic method | Sputum smear microscopy (SSM) and/or Xpert MTB/RIF | |
| Sample transportation and data collection | Health workers/community workers | |
| Total | Guinea | Niger | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | p-Value # | |
| Total | 863 | 758 | 105 | |
| Gender | 0.004 | |||
| Female | 342 (39.6) | 314 (41.4) | 28 (26.7) | |
| Male | 521 (60.4) | 444 (58.6) | 77 (73.3) | |
| Age group | <0.001 | |||
| <=15 | 27 (3.1) | 26 (3.4) | 1 (1.0) | |
| >15–30 | 332 (38.5) | 311 (41.0) | 21 (20.0) | |
| >30–45 | 289 (33.5) | 261 (34.4) | 28 (26.7) | |
| >45–50 | 48 (5.6) | 40 (5.3) | 8 (7.6) | |
| >50–65 | 104 (12.1) | 89 (11.7) | 15 (14.3) | |
| >65 | 63 (7.3) | 31 (4.1) | 32 (30.5) | |
| History of TB | 0.4 | |||
| No | 816 (94.6) | 714 (94.2) | 102 (97.1) | |
| Yes | 40 (4.6) | 38 (5.0) | 2 (1.9) | |
| Unknown | 7 (0.8) | 6 (0.8) | 1 (1.0) | |
| Cough (≥2 weeks) | 0.1 | |||
| No | 435 (50.4) | 389 (51.3) | 46 (43.8) | |
| Yes | 428 (49.6) | 369 (48.7) | 59 (56.2) | |
| Fever | 0.7 | |||
| No | 473 (54.8) | 419 (55.3) | 54 (51.4) | |
| Yes | 385 (44.6) | 335 (44.2) | 50 (47.6) | |
| Unknown | 5 (0.6) | 4 (0.5) | 1 (1.0) | |
| Weight loss | <0.001 | |||
| No | 599 (69.4) | 545 (71.9) | 54 (51.4) | |
| Yes | 261 (30.2) | 211 (27.8) | 50 (47.6) | |
| Unknown | 3 (0.3) | 2 (0.3) | 1 (1.0) | |
| Recent TB contact | 0.02 | |||
| No | 718 (83.2) | 621 (81.9) | 97 (92.4) | |
| Yes | 140 (16.2) | 133 (17.5) | 7 (6.7) | |
| Unknown | 5 (0.6) | 4 (0.5) | 1 (1.0) | |
| COVID-19 Test Result | ||||
| Negative | 802 (92.9) | 745 (98.3) | 57 (54.3) | |
| Positive | 61 (7.1) | 13 (1.7) | 48 (45.7) | |
| Final TB Diagnosis | 0.2 | |||
| No TB | 820 (95.0) | 723 (95.4) | 97 (92.4) | |
| TB | 43 (5.0) | 35 (4.6) | 8 (7.6) | |
| Diagnosed with Xpert MTB/RIF Alone | 14 (1.6) | 11 (1.5) | 3 (2.9) | |
| Diagnosed with SSM Alone | 20 (2.3) | 17 (2.2) | 3 (2.9) | |
| Both Xpert & SSM Positive | 3 (0.3) | 2 (0.3) | 1 (1.0) | |
| Clinically Diagnosed * | 6 (0.7) | 5 (0.7) | 1 (1.0) | |
| Xpert MTB/RIF | <0.001 | |||
| Negative | 59 (6.8) | 21 (2.8) | 38 (36.2) | |
| MTB detected | 17 (2.0) | 12 (1.6) | 5 (4.8) | |
| Xpert not done | 787 (91.2) | 725 (95.6) | 62 (59.0) | |
| Sputum smear microscopy (SSM) | ||||
| SSM negative * | 772 (89.5) | 701 (92.5) | 71 (67.6) | |
| SSM positive | 27 (3.1) | 22 (2.9) | 5 (4.8) | |
| SSM not done | 64 (7.4) | 35 (4.6) | 29 (27.6) |
| Cost Parameter | Guinea | Niger | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients | Cost per Patient (2020 USD) | Total Cost (2020 USD) | Number of Patients | Cost per Patient (2020 USD) | Total Cost (2020 USD) | |
| Training of Health Workers | -- | -- | $641 | -- | -- | $143 |
| Symptom Screening | 2640 | $2.70 | $7128 | 126 | $14.70 | $1852 |
| Smear Microscopy | 723 | $1.88 | $1359 | 76 | $2.56 | $195 |
| Xpert MTB/RIF | 33 | $16.28 | $537 | 43 | $23.33 | $1003 |
| TB disease treatment | 35 | $90.97 | $3184 | 7 | $109.62 | $767 |
| Overall cost | $12,849 | $3960 | ||||
| Cost per patient screened for TB disease | $4.87 | $31.43 | ||||
| Cost per patient initiating TB disease treatment | $367 | $566 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magassouba, A.S.; Bassirou, S.M.; Touré, A.A.; Diallo, B.D.; Alphazazi, S.; Cissé, D.; Keita, M.S.; Seyabatou, E.S.; Bangoura, A.M.; Traoré, H.A.; et al. Evaluating the Effectiveness of a Novel Systematic Screening Approach for Tuberculosis among Individuals Suspected or Recovered from COVID-19: Experiences from Niger and Guinea. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090228
Magassouba AS, Bassirou SM, Touré AA, Diallo BD, Alphazazi S, Cissé D, Keita MS, Seyabatou ES, Bangoura AM, Traoré HA, et al. Evaluating the Effectiveness of a Novel Systematic Screening Approach for Tuberculosis among Individuals Suspected or Recovered from COVID-19: Experiences from Niger and Guinea. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(9):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090228
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagassouba, Aboubacar Sidiki, Souleymane Mahamadou Bassirou, Almamy Amara Touré, Boubacar Djelo Diallo, Soumana Alphazazi, Diao Cissé, Mohamed Sitan Keita, Elhadj Saidou Seyabatou, Adama Marie Bangoura, Hugues Asken Traoré, and et al. 2022. "Evaluating the Effectiveness of a Novel Systematic Screening Approach for Tuberculosis among Individuals Suspected or Recovered from COVID-19: Experiences from Niger and Guinea" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 9: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090228
APA StyleMagassouba, A. S., Bassirou, S. M., Touré, A. A., Diallo, B. D., Alphazazi, S., Cissé, D., Keita, M. S., Seyabatou, E. S., Bangoura, A. M., Traoré, H. A., Decroo, T., Campbell, J. R., Veronese, V., & Merle, C. S. C. (2022). Evaluating the Effectiveness of a Novel Systematic Screening Approach for Tuberculosis among Individuals Suspected or Recovered from COVID-19: Experiences from Niger and Guinea. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(9), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090228





