Prevalence of Fascioliasis in Livestock and Humans in Pakistan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Extraction
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Databases
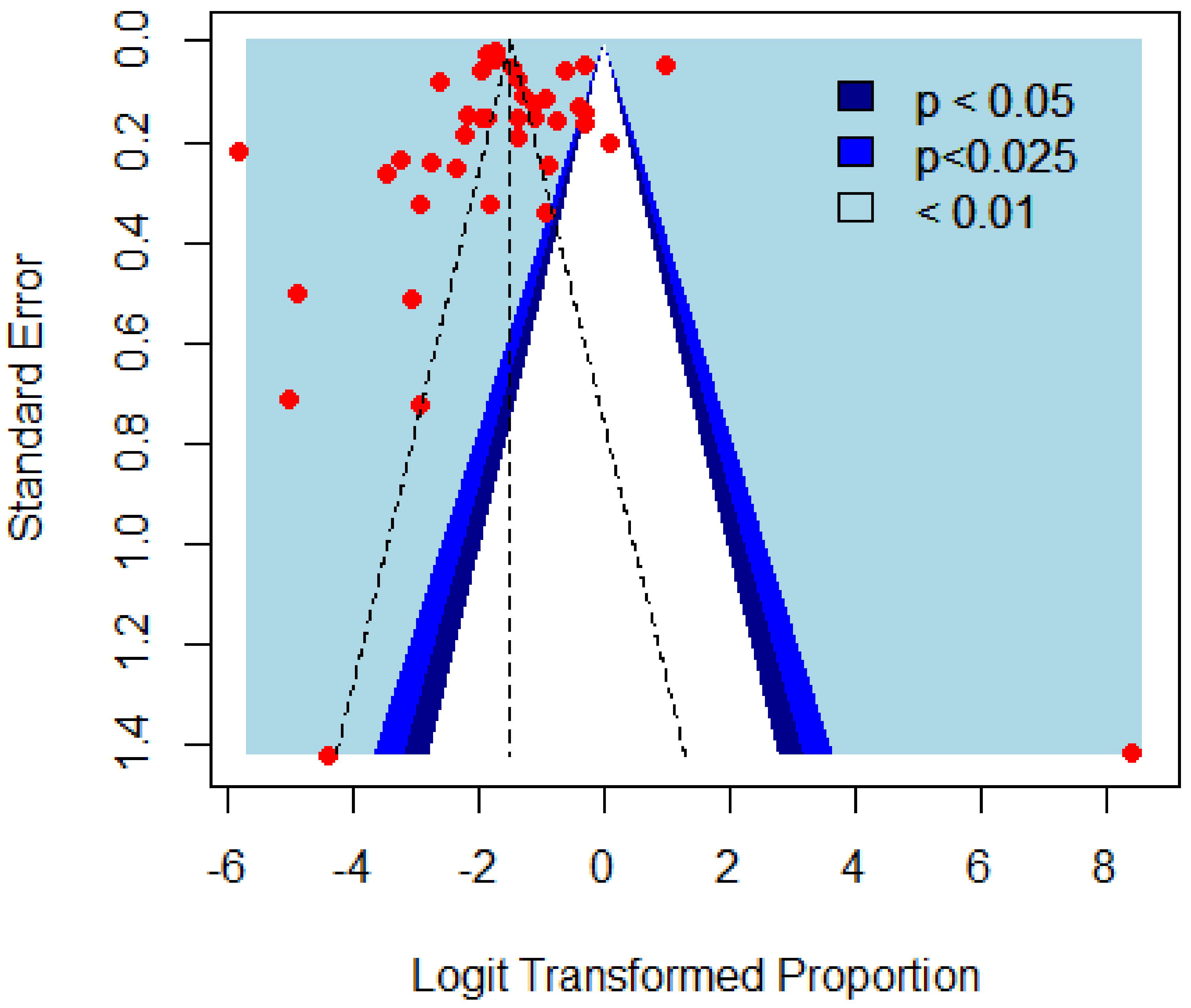
2.5. Publication Bias and Heterogeneity Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Fascioliasis in Humans
3.2. Fascioliasis in Sheep
3.3. Fascioliasis in Goat
3.4. Fascioliasis in Buffalo
3.5. Fascioliasis in Cattle
3.6. Fascioliasis in Cow
3.7. Publication Bias and Heterogeneity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashrafi, K.; Bargues, M.D.; O’Neill, S.; Mas-Coma, S. Fascioliasis: A worldwide parasitic disease of importance in travel medicine. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2014, 12, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Foodborne Trematode Infections. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/foodborne_trematode_infections/fascioliasis/en/#:~:text=WHO%20estimates%20that%20at%20least,reported%2C%20human%20cases%20also%20exist (accessed on 25 December 2021).
- Szyfres, B. Zoonosis y Enfermedades Transmisibles Comunes al Hombre y a los Animals; Pan American Health Organization: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Fasciola, lymnaeids and human fascioliasis, with a global overview on disease transmission, epidemiology, evolutionary genetics, molecular epidemiology and control. Adv. Parasitol. 2009, 69, 41–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Bargues, M.D.; Valero, M.A. Plant-Borne Trematode Zoonoses: Fascioliasis and Fasciolopsiasis. In Food-Borne Parasitic Zoonoses; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 293–334. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Bargues, M.D.; Valero, M.A. Human fascioliasis infection sources, their diversity, incidence factors, analytical methods and prevention measures. Parasitology 2018, 145, 1665–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaouadi, M.; Harhoura, K.; Aissi, M.; Zait, H.; Zenia, S.; Tazerouti, F. A post-mortem study of bovine fasciolosis in the Mitidja (north center of Algeria): Prevalence, risk factors, and comparison of diagnostic methods. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Bargues, M.; Valero, M. Diagnosis of human fascioliasis by stool and blood techniques: Update for the present global scenario. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1918–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.-Y. Intestinal Flukes. In Food-Borne Parasitic Zoonoses; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 53–115. [Google Scholar]
- Sithithaworn, P.; Yongvanit, P.; Tesana, S.; Pairojkul, C. Liver Flukes. In Food-Borne Parasitic Zoonoses; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 3–52. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Bargues, M.D.; Valero, M. Fascioliasis and other plant-borne trematode zoonoses. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1255–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; He, B.; Wang, C.; Zhu, X. Characterisation of Fasciola species from Mainland China by ITS-2 ribosomal DNA sequence. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 120, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.R.; Maco, V.; Marcos, L.; Saez, S.; Neyra, V.; Terashima, A.; Samalvides, F.; Gotuzzo, E.; Chavarry, E.; Huaman, M.C. Evaluation of Fas2-ELISA for the serological detection of Fasciola hepatica infection in humans. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahed-Toral, J.; López-Tirado, Q.; Mendoza-Martınez, G.; Aluja-Schunemann, A.; Trigo-Tavera, F. Epidemiology of parasitosis in the Tzotzil sheep production system. Small Rumin. Res. 2003, 49, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguía-Xóchihua, J.; Ibarra-Velarde, F.; Ducoing-Watty, A.; Montenegro-Cristino, N.; Quiroz-Romero, H. Prevalence of Fasciola hepatica (ELISA and fecal analysis) in ruminants from a semi-desert area in the northwest of Mexico. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, D.; Prepelitchi, L.; Kleiman, F.; Carnevale, S.; Wisnivesky-Colli, C. Estudio del foco en un caso de fasciolosis humana en Neuquén. Medicina 2005, 65, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cuervo, P.; Sidoti, L.; Fantozzi, C.; Neira, G.; Gerbeno, L.; Mera y Sierra, R. Fasciola hepatica infection and association with gastrointestinal parasites in Creole goats from western Argentina. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2013, 22, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cunha, F.O.V.D.; Marques, S.M.T.; Mattos, M.J.T.D. Prevalence of slaughter and liver condemnation due to Fasciola hepatica among sheep in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil 2000 and 2005. Parasitol. Latinoam. 2007, 62, 188–191. [Google Scholar]
- Raunelli, F.; Gonzalez, S. Strategic control and prevalence of Fasciola hepatica in Cajamarca, Peru. A pilot study. J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2009, 7, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Valencia-López, N.; Malone, J.B.; Carmona, C.G.; Velásquez, L.E. Climate-based risk models for Fasciola hepatica in Colombia. Geospat. Health 2012, 6, S75–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehmood, K.; Zhang, H.; Sabir, A.J.; Abbas, R.Z.; Ijaz, M.; Durrani, A.Z.; Saleem, M.H.; Rehman, M.U.; Iqbal, M.K.; Wang, Y. A review on epidemiology, global prevalence and economical losses of fasciolosis in ruminants. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 109, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soosaraei, M.; Fakhar, M.; Teshnizi, S.H.; Emameh, R.Z.; Hezarjaribi, H.Z.; Asfaram, S.; Faridnia, R.; Kalani, H. Status of fasciolosis among domestic ruminants in Iran based on abattoir data: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Parasitol. 2020, 66, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Afshan, K.; Fortes-Lima, C.A.; Artigas, P.; Valero, M.A.; Qayyum, M.; Mas-Coma, S. Impact of climate change and man-made irrigation systems on the transmission risk, long-term trend and seasonality of human and animal fascioliasis in Pakistan. Geospat. Health 2014, 4, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Tanveer, A.; Maqbool, A.; Niaz, S. Seasonal and monthly prevalence pattern of fasciolosis in buffaloes and its relation to some climatic factors in northeastern areas of Punjab, Pakistan. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 13, 134–137. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.W.; Tanveer, A.; Mas-Coma, S. Epidemiological analysis of human fascioliasis in northeastern Punjab, Pakistan. Acta Trop. 2016, 156, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Ullah, S.; Malik, M.I.; Umar, M.; Shah, S.M.K.; Shakirullah, M.S.K.; Muhammad, K.; Noman, M.; Naeem, M. 12. Prevalence of Fasciola hepatica infestation and pathological examination in sheep (Ovis aries) in Dera Ismail Khan. Pure Appl. Biol. 2020, 9, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Khan, M.K.; Sindhu, D.; Abbas, R.Z.; Masood, S.; Abbas, Z.; Mahmood, M.S.; Saleemi, M.K.; Khan, J.A.; Hussain, R. Seroprevalence of Fasciola hepatica in small ruminants of District Chakwal, Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. Vet. J. 2019, 39, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.W.; Zeb, A.; Mansoor, A.; Hayat, A.; Mas-Coma, S. Fasciola hepatica infection in children actively detected in a survey in rural areas of Mardan district, Khyber Pakhtunkhawa province, northern Pakistan. Parasitol. Int. 2019, 69, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Khan, M.N.; Sajid, M.S.; Muhammad, G.; Qudoos, A.; Rizwan, H.M. Prevalence, economic analysis and chemotherapeutic control of small ruminant fasciolosis in the Sargodha district of Punjab, Pakistan. Vet. Ital. 2017, 53, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haleem, S.; Shadab, F.; Niaz, S.; Rehman, H.U.; Sajad, S.; Qureshi, N.A.; Kabir, M. Prevalence of fascioliasis in cows and sheep in district Mardan (KPK), Pakistan. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2016, 4, 330–334. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, A.A.; Lashari, M.H.; Akhtar, M.S.; Awais, M.M.; Inayat, S.; Akhtar, M. Prevalence of bovine fascioliasis in different commercial and non-commercial dairy farms of District Rajanpur, Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. J. Life Soc. Sci. 2015, 13, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ayaz, S.; Ullah, R.; AbdEl-Salam, N.M.; Shams, S.; Niaz, S. Fasciola hepatica in some buffaloes and cattle by PCR and microscopy. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 462084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashraf, S.; Iqbal, Z.; Ali, M.; Chaudhry, H.R.; Sial, N.; Ahsan, U.; Ali, A.; Asif, M.Z. Seasonal prevalence of Fasciola hepatica infection in buffaloes of Bahawalpur district of Punjab, Pakistan. J. Infect. Mol. Biol. 2014, 2, 30–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, M.; Younas, M.; Schlecht, E. Prevalence of gastrointestinal helminths in pastoral sheep and goat flocks in the Cholistan desert of Pakistan. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2014, 24, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, R.; Khan, M.N.; Sajid, M.S.; Javed, M.T. Frequency distribution of fasciolosis in small ruminants population at district Sargodha. Glob. Vet. 2014, 12, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, A.; Khan, K.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, A.; Alam, A. Prevalence of Fasciola hepatica in domesticated cattle of Distt: Lower Dir, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Int. J. Biosci. 2013, 3, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, A.; Arshad, M.; Ameer, M. Prevalence of Fasciola Hepatica in sheep and goats in district Dera Ismail Khan. Pak. J. Sci. 2012, 64, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Shahzad, W.; Mehmood, K.; Munir, R.; Aslam, W.; Ijaz, M.; Ahmad, R.; Khan, M.S.; Sabir, A.J. Prevalence and molecular diagnosis of Fasciola hepatica in sheep and goats in different districts of Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. Vet. J. 2012, 32, 535–538. [Google Scholar]
- Bhutto, B.; Arijo, A.; Phullan, M.S.; Rind, R. Prevalence of fascioliasis in buffaloes under different agro-climatic areas of Sindh Province of Pakistan. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2012, 14, 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, U.J.; Maqbool, A. Prevalence of fasciolosis in cattle under different managemental conditions in Punjab. Pak. J. Zool. 2012, 44, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Lashari, M.H.; Tasawar, Z. Prevalence of some gastrointestinal parasites in sheep in southern Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. Vet. J. 2011, 31, 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Sajid, M.; Khan, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Arshad, M.; Hussain, A. Point prevalence of bovine fascioliasis and the influence of chemotherapy on the milk yield in a lactating bovine population from the district of Toba Tek Singh, Pakistan. J. Helminthol. 2011, 85, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadahi, J.; Arshed, M.; Ali, Q.; Javaid, S.; Shah, S. Prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites of sheep and goat in and around Rawalpindi and Islamabad, Pakistan. Vet. World 2009, 2, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.K.; Sajid, M.S.; Khan, M.N.; Iqbal, Z.; Iqbal, M.U. Bovine fasciolosis: Prevalence, effects of treatment on productivity and cost benefit analysis in five districts of Punjab, Pakistan. Res. Vet. Sci. 2009, 87, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, M.; Kakarsulemankhel, J. Prevalence of endo (trematodes) and ecto-parasites in cows and buffaloes of Quetta, Pakistan. Pak. Vet. J. 2008, 28, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Tasawar, Z.; Minir, U.; Hayat, C.; Lashari, M. The prevalence of Fasciola hepatica in goats around Multan. Infection 2007, 32, 23–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Nawaz, M.; Gul, R.; Zakir, M.; Razzaq, A. Diversity and prevalence of trematodes in livers of sheep and goat in Quetta, Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 2005, 37, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.W.; Tanveer, A.; Qureshi, S.; Maqbool, A.; Gill, T.J.; Ali, S.A. Epidemiology of human fasciolosis in rural areas of Lahore, Pakistan. Punjab Univ. J. Zool. 2005, 20, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Maqbool, A.; Sikandar Hayat, C.; Akhtar, T.; Hashmi, H.A. Epidemiology of fasciolosis in buffaloes under different managemental conditions. Vet. Arh. 2002, 72, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, G. Update on fasciolosis in cattle and sheep. Practice 2002, 24, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G.; Berne, M.; Raffi, L. Influência da temperatura na longevidade de metacercárias de Fasciola hepatica. Rev. Bras. Agrociênc. 1999, 5, 164–165. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiki, A.; Uddin, M.; Hasan, M.; Hossain, M.; Rahman, M.; Das, B.; Sarker, M.; Hossain, M. Coproscopic and haematological approaches to determine the prevalence of helminthiasis and protozoan diseases of Red Chittagong Cattle (RCC) breed in Bangladesh. Pak. Vet. J. 2010, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, W.; Dai, R.; Tan, Y.; He, D.; Lin, R.; Zhu, X. Prevalence of helminths in water buffaloes in Hunan Province, China. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2009, 41, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, E.; Gonzaga, E.; Lumbao, L. Prevalence of infection with Fasciola gigantica and its relationship to carcase and liver weights, and fluke and egg counts in slaughter cattle and buffaloes in southern Mindanao, Philippines. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2005, 37, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spithill, T.W.; Smooker, P.M.; Copeman, D.B. Fasciola gigantica: Epidemiology, control, immunology and molecular biology. In Fasciolosis, 1st ed.; Dalton, J.P., Ed.; CABI Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 465–525. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B. Parasitic infection in farm animals in different climates: In climate in relation to livestock production and health. CAS Vet. Physiol. 2001, 4, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, Q.; Rashid, I.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Shahzad, K.; Ashraf, K.; Sargison, N.D.; Chaudhry, U. Population genetics of benzimidazole-resistant Haemonchus contortus and Haemonchus placei from buffalo and cattle: Implications for the emergence and spread of resistance mutations. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3575–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

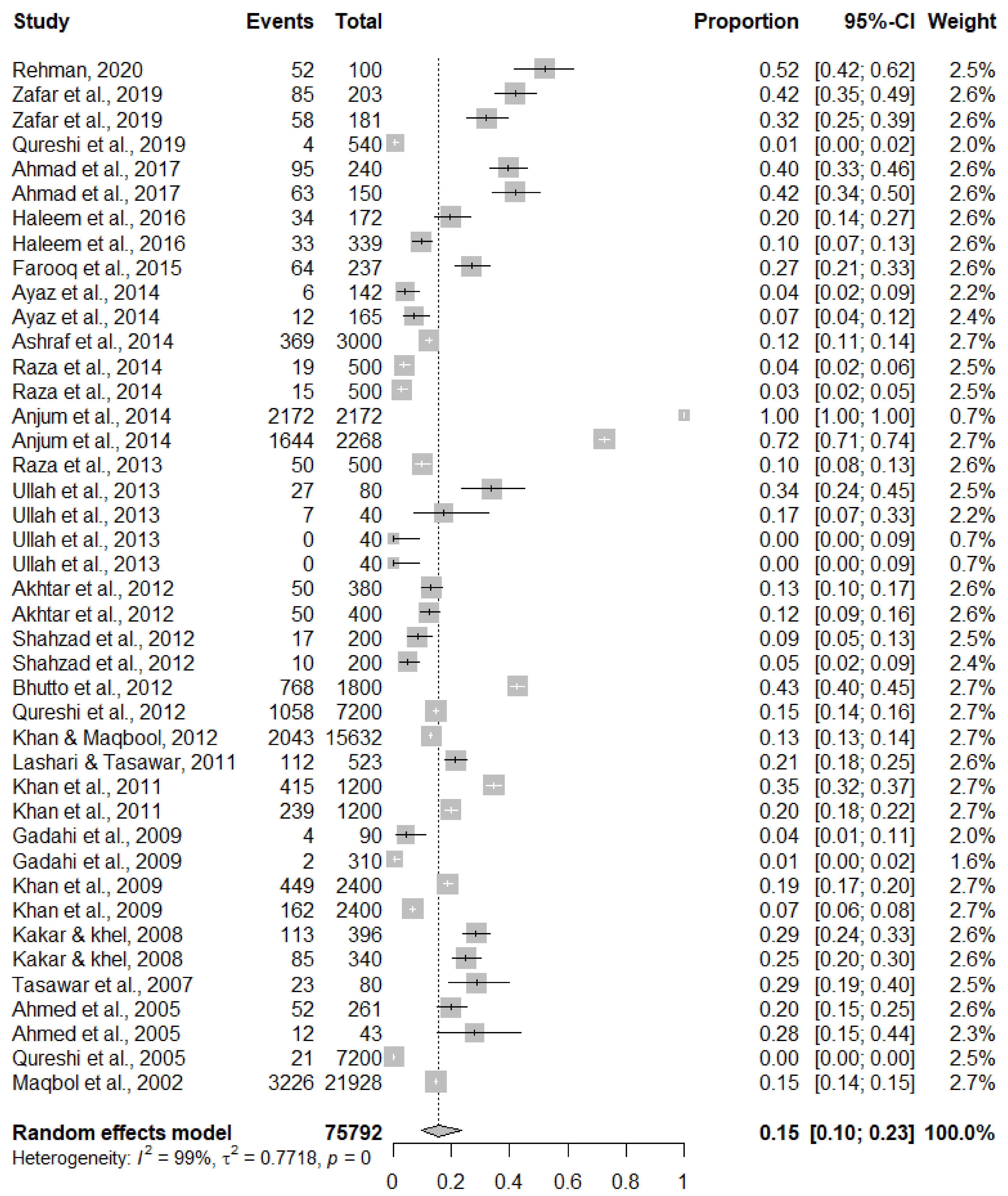
| Province | Species | Host | Detection Method | No. of Samples Examined | No. of Positive Samples | Proportion of Positive Samples | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KPK) | Fasciola spp. | Sheep | FM, Mic | 100 | 52 | 0.52 | [26] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Sheep | ELISA | 203 | 85 | 0.4187 | [27] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Goat | ELISA | 181 | 58 | 0.3204 | [27] |
| KPK | F. hepatica | Human | DS, Mic | 540 | 4 | 0.0074 | [28] |
| Punjab | Fasciola spp. | Goat | Sed, MT, Mic | 240 | 95 | 0.3958 | [29] |
| Punjab | Fasciola spp. | Sheep | Sed, MT, Mic | 150 | 63 | 0.42 | [29] |
| KPK | F. hepatica | Cow | DS, FF | 172 | 24 | 0.1395 | [30] |
| KPK | F. gigantica | Cow | DS, FF | 172 | 10 | 0.0581 | [30] |
| KPK | F. hepatica | Sheep | DS, FF | 339 | 20 | 0.059 | [30] |
| KPK | F. gigantica | Sheep | DS, FF | 339 | 13 | 0.0383 | [30] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Cattle | Sed, Mic | 237 | 39 | 0.1646 | [31] |
| Punjab | F. gigantica | Cattle | Sed, Mic | 237 | 20 | 0.0844 | [31] |
| KPK | F. hepatica | Cattle | PCR, Mic | 307 | 18 | 0.0586 | [32] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Buffalo | PCR, Mic | 3000 | 369 | 0.123 | [33] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Goat | Sed, FM | 500 | 16 | 0.032 | [34] |
| Punjab | F. gigantica | Goat | Sed, FM | 500 | 3 | 0.006 | [34] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Sheep | Sed, FM | 500 | 11 | 0.022 | [34] |
| Punjab | F. gigantica | Sheep | Sed, FM | 500 | 4 | 0.008 | [34] |
| Punjab | Fasciola spp. | Sheep | FF | 2172 | 1032 | 0.4751 | [35] |
| Punjab | Fasciola spp. | Sheep | FF | 2172 | 1140 | 0.5249 | [35] |
| Punjab | Fasciola spp. | Goat | FF | 2268 | 703 | 0.31 | [35] |
| Punjab | Fasciola spp. | Goat | FF | 2268 | 941 | 0.4149 | [35] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Cattle | Sed, Mic, FM | 500 | 45 | 0.09 | [35] |
| Punjab | F. gigantica | Cattle | Sed, Mic, FM | 500 | 5 | 0.01 | [35] |
| KPK | F. hepatica | Buffalo | PM | 80 | 11 | 0.1375 | [36] |
| KPK | F. hepatica | Cow | PM | 40 | 2 | 0.05 | [36] |
| KPK | F. hepatica | Sheep | PM | 40 | 0 | 0 | [36] |
| KPK | F. hepatica | Goat | PM | 40 | 0 | 0 | [36] |
| KPK | Fasciola spp. | Sheep | FS, EC, Sed | 380 | 50 | 0.1316 | [37] |
| KPK | Fasciola spp. | Goat | FS, EC, Sed | 400 | 50 | 0.125 | [37] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Sheep | PCR, Bile samples | 200 | 17 | 0.085 | [38] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Goat | PCR, Bile samples | 200 | 10 | 0.05 | [38] |
| Sindh | F. gigantica | Buffalo | DS, Sed | 1800 | 768 | 0.4267 | [39] |
| Punjab | Fasciola spp. | Buffalo | Mic | 7200 | 1058 | 0.1469 | [24] |
| Punjab | F. gigantica | Cattle | PM, DS, Sed, FM | 15,632 | 2043 | 0.1307 | [40] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Sheep | Sed, FM, Mic | 523 | 112 | 0.2141 | [41] |
| Punjab | Fasciola spp. | Buffalo | MT, EC | 1200 | 415 | 0.3458 | [42] |
| Punjab | Fasciola spp. | Cattle | MT, EC | 1200 | 239 | 0.1992 | [42] |
| ICT | Fasciola spp. | Sheep | Sed, FM, Mic | 90 | 4 | 0.0444 | [43] |
| ICT | Fasciola spp. | Goat | Sed, FM, Mic | 310 | 2 | 0.0065 | [43] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Buffalo | EE | 2400 | 16 | 0.0067 | [44] |
| Punjab | F. gigantica | Buffalo | EE | 2400 | 433 | 0.1804 | [44] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Cattle | EE | 2400 | 57 | 0.0238 | [44] |
| Punjab | F. gigantica | Cattle | EE | 2400 | 105 | 0.0437 | [44] |
| Baluchistan | F. hepatica | Cow | PM | 396 | 64 | 0.1616 | [45] |
| Baluchistan | F. gigantica | Cow | PM | 396 | 49 | 0.1237 | [45] |
| Baluchistan | F. hepatica | Buffalo | PM | 340 | 39 | 0.1147 | [45] |
| Baluchistan | F. gigantica | Buffalo | PM | 340 | 46 | 0.1353 | [45] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica | Goat | FM, Sed | 80 | 23 | 0.2875 | [46] |
| Baluchistan | F. hepatica | Sheep | PM | 261 | 20 | 0.0766 | [47] |
| Baluchistan | F. hepatica, F. gigantica | Sheep | PM | 261 | 32 | 0.1226 | [47] |
| Baluchistan | F. hepatica | Goat | PM | 43 | 3 | 0.0698 | [47] |
| Baluchistan | F. hepatica, F. gigantica | Goat | PM | 43 | 9 | 0.2093 | [47] |
| Punjab | F. hepatica, F. gigantica | Human | FF | 7200 | 21 | 0.0029 | [48] |
| Punjab | F. gigantica | Buffalo | FM, Sed | 21,928 | 3226 | 0.1471 | [49] |
| Type | Host/Province | No. of Studies | No. of Samples Examined | No. of Positive Samples | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Host | Human | 2 | 7740 | 25 | 0.3% |
| Sheep | 12 | 4958 | 2655 | 53.5% | |
| Goat | 10 | 4262 | 1913 | 44.9% | |
| Buffalo | 9 | 38,113 | 6409 | 16.8% | |
| Cattle | 6 | 20,276 | 2571 | 12.7% | |
| Cow | 4 | 750 | 160 | 21.3% | |
| Overall | 41 | 76,099 | 13,738 | 18.1% | |
| Region | Punjab | 15 | 70,114 | 12,409 | 17.7% |
| KPK | 6 | 2745 | 293 | 10.7% | |
| Baluchistan | 2 | 1040 | 262 | 25.2% | |
| Sindh | 1 | 1800 | 768 | 42.7% | |
| ICT | 1 | 400 | 6 | 1.5% | |
| Overall | 25 | 76,099 | 13,738 | 18.1% |
| Province | Host | No. of Studies | No. of Samples Examined | No. of Positive Samples | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Punjab | Human | 1 | 7200 | 21 | 0.3% |
| Sheep | 6 | 3748 | 2464 | 65.7% | |
| Goat | 6 | 3469 | 1849 | 53.3% | |
| Buffalo | 5 | 35,728 | 5517 | 15.4% | |
| Cattle | 5 | 19,969 | 2553 | 12.8% | |
| Total | - | 70,114 | 12,409 | 17.7% | |
| Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | Human | 1 | 540 | 4 | 0.7% |
| Sheep | 4 | 859 | 135 | 15.7% | |
| Goat | 2 | 440 | 50 | 11.4% | |
| Buffalo | 2 | 245 | 39 | 15.9% | |
| Cow | 3 | 354 | 47 | 13.3% | |
| Cattle | 1 | 307 | 18 | 5.9% | |
| Total | - | 2745 | 293 | 10.67% | |
| Baluchistan | Sheep | 1 | 261 | 52 | 19.9% |
| Goat | 1 | 43 | 12 | 27.9% | |
| Buffalo | 1 | 340 | 85 | 25.0% | |
| Cow | 1 | 396 | 113 | 28.5% | |
| Total | - | 1040 | 262 | 25.2% | |
| Sindh | Buffalo | 1 | 1800 | 768 | 42.7% |
| ICT | Sheep | 1 | 90 | 4 | 4.4% |
| Goat | 1 | 310 | 2 | 0.6% | |
| Overall | 43 | 76,099 | 13,738 | 18.1% |
| Characteristics | Host/Province | No. of Studies | Heterogeneity Factors | Heterogeneity | Publication Bias | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2 (%) | tau2 | Q | Egger’s Test Result | |||
| Human | Human | 2 | 65.8 | 0.288 | 2.93 n.s. | - |
| Animals | Sheep | 12 | 96.6 | 1.032 | 320.2 ** | −0.300 n.s. |
| Goat | 10 | 99.0 | 2.866 | 928.8 ** | −4.29 ** | |
| Buffalo | 9 | 99.4 | 0.336 | 1170 ** | 1.38 n.s. | |
| Cattle | 5 | 97.7 | 0.221 | 171.1 ** | 0.148 n.s. | |
| Cow | 4 | 89.8 | 0.451 | 29.3 ** | −2.45 n.s. | |
| Overall | 39 | 99.2 | 0.712 | 5036 ** | 0.752 n.s. | |
| Regions of Pakistan | Punjab | 15 | 99.8 | 1.213 | 7475 ** | 0.303 n.s. |
| KPK | 6 | 96.6 | 0.867 | 145.1 ** | −0.491 n.s. | |
| Baluchistan | 2 | 74.3 | 0.038 | 3.89 *** | - | |
| Sindh | 1 | - | - | - | - | |
| ICT | 1 | - | - | - | - | |
| Overall | 25 | 99.7 | 1.16 | 8316 ** | 0.161 n.s. | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizwan, M.; Khan, M.R.; Afzal, M.S.; Manahil, H.; Yasmeen, S.; Jabbar, M.; Irum, S.; Simsek, S.; Wasif, S.; Mahmood, T.; et al. Prevalence of Fascioliasis in Livestock and Humans in Pakistan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7070126
Rizwan M, Khan MR, Afzal MS, Manahil H, Yasmeen S, Jabbar M, Irum S, Simsek S, Wasif S, Mahmood T, et al. Prevalence of Fascioliasis in Livestock and Humans in Pakistan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(7):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7070126
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizwan, Muhammad, Mobushir Riaz Khan, Muhammad Sohail Afzal, Hajra Manahil, Sobia Yasmeen, Muhammad Jabbar, Shumaila Irum, Sami Simsek, Samia Wasif, Tahir Mahmood, and et al. 2022. "Prevalence of Fascioliasis in Livestock and Humans in Pakistan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 7: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7070126
APA StyleRizwan, M., Khan, M. R., Afzal, M. S., Manahil, H., Yasmeen, S., Jabbar, M., Irum, S., Simsek, S., Wasif, S., Mahmood, T., Ahmed, H., & Cao, J. (2022). Prevalence of Fascioliasis in Livestock and Humans in Pakistan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(7), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7070126








