Humoral Immune Response Induced by the BBIBP-CorV Vaccine (Sinopharm) in Healthcare Workers: A Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Seroconversion
3.2. Anti-S-RBD IgG by Elecsys® Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S
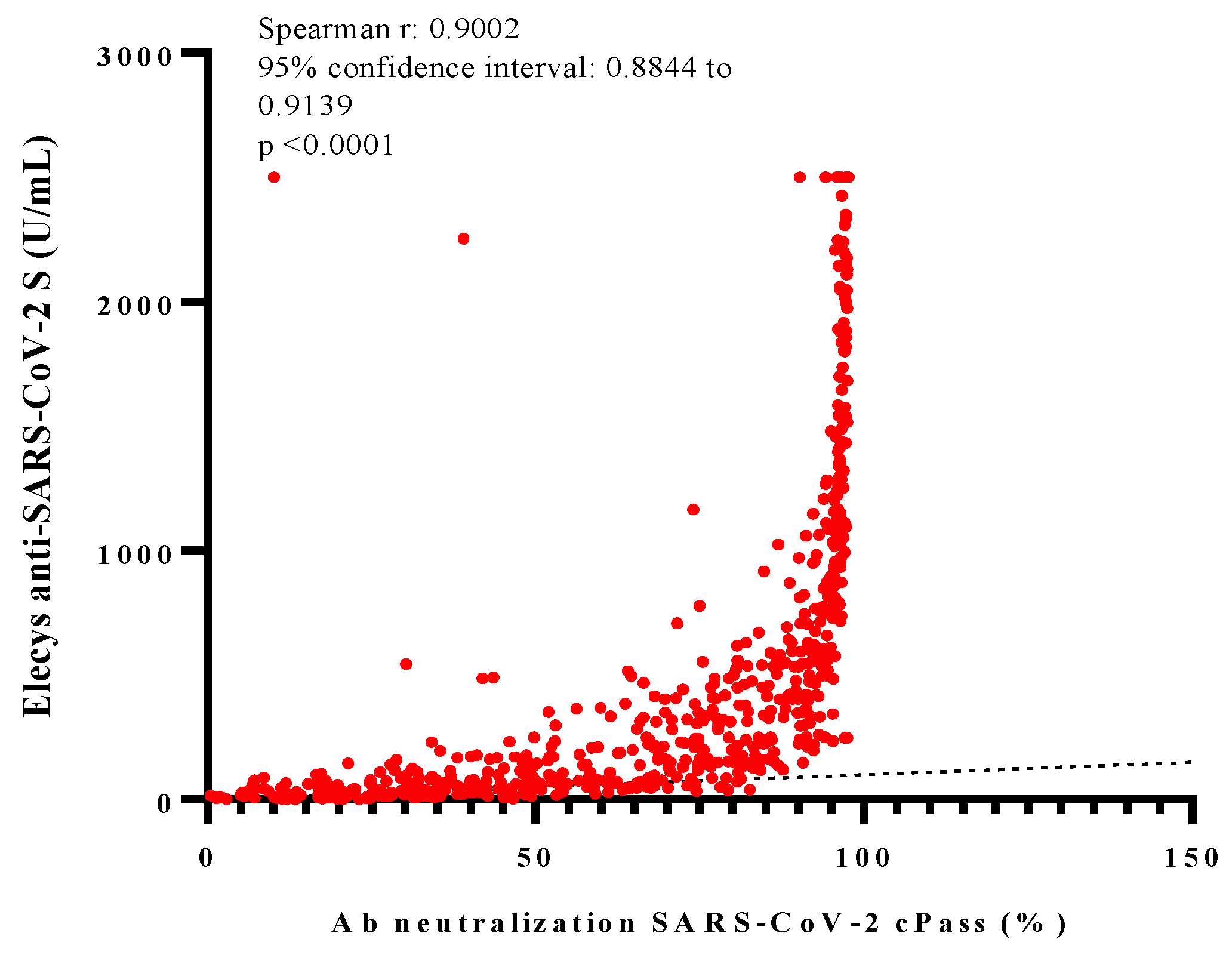
3.3. NAbs against SARS-CoV-2 by Ab Neutralization cPass™
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization WHO Issues Emergency Use Listing for Eighth COVID-19 Vaccine. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/03-11-2021-who-issues-emergency-use-listing-for-eighth-covid-19-vaccine (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Al Kaabi, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.; Yang, Y.; Al Qahtani, M.M.; Abdulrazzaq, N.; Al Nusair, M.; Hassany, M.; Jawad, J.S.; Abdalla, J.; et al. Effect of 2 Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines on Symptomatic COVID-19 Infection in Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvia Valencia, J.; Soto Becerra, P.; Escobar Agreda, S.; Fernández Navarro, M.; Moscoso Porras, M.; Solari, L.; Mayta Tristan, P. Efectividad de la Vacuna BBIBP-CorV Para Prevenir Infección y Muerte en Personal de Salud, Perú 2021; Repositorio INS; 2021. Available online: https://repositorio.ins.gob.pe/handle/INS/1318 (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- Lumley, S.F.; O’Donnell, D.; Stoesser, N.E.; Matthews, P.C.; Howarth, A.; Hatch, S.B.; Marsden, B.D.; Cox, S.; James, T.; Warren, F.; et al. Antibody Status and Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Health Care Workers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the MRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 MRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 Vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An Interim Analysis of Four Randomised Controlled Trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 2021, 397, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Antibody Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nature 2021, 593, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murin, C.D.; Wilson, I.A.; Ward, A.B. Antibody Responses to Viral Infections: A Structural Perspective across Three Different Enveloped Viruses. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, P.B.; Montefiori, D.C.; McDermott, A.; Fong, Y.; Benkeser, D.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Houchens, C.R.; Martins, K.; Jayashankar, L.; et al. Immune Correlates Analysis of the MRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Clinical Trial. Science 2021, 375, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing Antibody Levels Are Highly Predictive of Immune Protection from Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okba, N.M.A.; Müller, M.A.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Corman, V.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Sikkema, R.S.; Bruin, E.d.; Chandler, F.D.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2−Specific Antibody Responses in Coronavirus Disease Patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, B.; Reimerink, J.; Torriani, G.; Brouwer, F.; Godeke, G.-J.; Yerly, S.; Hoogerwerf, M.; Vuilleumier, N.; Kaiser, L.; Eckerle, I.; et al. Validation and Clinical Evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 Surrogate Virus Neutralisation Test (SVNT). Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2394–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trougakos, I.P.; Terpos, E.; Zirou, C.; Sklirou, A.D.; Apostolakou, F.; Gumeni, S.; Charitaki, I.; Papanagnou, E.-D.; Bagratuni, T.; Liacos, C.-I.; et al. Comparative Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Anti-Spike Protein RBD IgGs and Neutralizing Antibodies in Convalescent and Naïve Recipients of the BNT162b2 MRNA Vaccine versus COVID-19 Patients. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resman Rus, K.; Korva, M.; Knap, N.; Avšič Županc, T.; Poljak, M. Performance of the Rapid High-Throughput Automated Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay Targeting Total Antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Receptor Binding Domain in Comparison to the Neutralization Assay. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 139, 104820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riester, E.; Findeisen, P.; Hegel, J.K.; Kabesch, M.; Ambrosch, A.; Rank, C.M.; Pessl, F.; Laengin, T.; Niederhauser, C. Performance Evaluation of the Roche Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S Immunoassay. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 297, 114271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenburg, J.; Cheng, M.P.; Corsini, R.; Caya, C.; Mendoza, E.; Manguiat, K.; Lindsay, L.R.; Wood, H.; Drebot, M.A.; Dibernardo, A.; et al. Evaluation of a Commercial Culture-Free Neutralization Antibody Detection Kit for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus-2 and Comparison With an Antireceptor-Binding Domain Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, G.F.; Tan, W.; Wu, G.; Xu, M.; Lou, Z.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine, BBIBP-CorV: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 1/2 Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeewandara, C.; Aberathna, I.S.; Pushpakumara, P.D.; Kamaladasa, A.; Guruge, D.; Jayathilaka, D.; Gunasekara, B.; Tanussiya, S.; Kuruppu, H.; Ranasinghe, T.; et al. Antibody and T Cell Responses to Sinopharm/BBIBP-CorV in Naïve and Previously Infected Individuals in Sri Lanka. medRxiv 2021, 21260621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badano, M.N.; Sabbione, F.; Keitelman, I.; Pereson, M.; Aloisi, N.; Colado, A.; Ramos, M.V.; Wilczyñski, J.M.O.; Pozner, R.G.; Castillo, L.; et al. Humoral response to the BBIBP-CorV vaccine over time in healthcare workers with or without exposure to SARS-CoV-2. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 143, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vályi-Nagy, I.; Matula, Z.; Gönczi, M.; Tasnády, S.; Bekő, G.; Réti, M.; Ajzner, É.; Uher, F. Comparison of antibody and T cell responses elicited by BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 in healthy adult humans. GeroScience 2021, 43, 2321–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijeskić, O.; Klun, I.; Djaković, M.S.; Gligorić, N.; Štajner, T.; Srbljanović, J.; Djurković-Djaković, O. Prospective Cohort Study of the Kinetics of Specific Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and to Four SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Available in Serbia, and Vaccine Effectiveness: A 3-Month Interim Report. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebinger, J.E.; Fert-Bober, J.; Printsev, I.; Wu, M.; Sun, N.; Prostko, J.C.; Frias, E.C.; Stewart, J.L.; Van Eyk, J.E.; Braun, J.G.; et al. Antibody Responses to the BNT162b2 MRNA Vaccine in Individuals Previously Infected with SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.N.; Martin-Blais, R.; Tobin, N.H.; Wang, Y.; Brooker, S.L.; Li, F.; Gadoth, A.; Elliott, J.; Faure-Kumar, E.; Halbrook, M.; et al. Humoral Responses to SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccines: Role of Past Infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Deng, C.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Liu, D.; Liu, M.; Ruan, X.; Mei, J.; Mo, R.; et al. Robust Induction of B Cell and T Cell Responses by a Third Dose of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yin, S.; Tong, X.; Tao, Y.; Ni, J.; Pan, J.; Li, M.; Wan, Y.; Mao, M.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Dynamic SARS-CoV-2-Specific B-Cell and T-Cell Responses Following Immunization with an Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccine. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 28, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.G.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naaber, P.; Tserel, L.; Kangro, K.; Sepp, E.; Jürjenson, V.; Adamson, A.; Haljasmägi, L.; Rumm, A.P.; Maruste, R.; Kärner, J.; et al. Dynamics of Antibody Response to BNT162b2 Vaccine after Six Months: A Longitudinal Prospective Study. Lancet Reg. Health-Eur. 2021, 10, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria-Rose, N.; Suthar, M.S.; Makowski, M.; O’Connell, S.; McDermott, A.B.; Flach, B.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Mascola, J.R.; Graham, B.S.; Lin, B.C.; et al. Antibody Persistence through 6 Months after the Second Dose of MRNA-1273 Vaccine for Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barouch, D.H.; Stephenson, K.E.; Sadoff, J.; Yu, J.; Chang, A.; Gebre, M.; McMahan, K.; Liu, J.; Chandrashekar, A.; Patel, S.; et al. Durable Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses 8 Months after Ad26.COV2.S Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 951–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahla, R.E.; Tomas-Grau, R.H.; Cazorla, S.I.; Ploper, D.; Vera Pingitore, E.; López, M.A.; Aznar, P.; Alcorta, M.E.; Vélez, E.M.d.M.; Stagnetto, A.; et al. Long-Term Analysis of Antibodies Elicited by SPUTNIK V: A Prospective Cohort Study in Tucumán, Argentina. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2022, 6, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpos, E.; Karalis, V.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Gumeni, S.; Malandrakis, P.; Papanagnou, E.-D.; Kastritis, E.; Trougakos, I.P.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Robust Neutralizing Antibody Responses 6 Months Post Vaccination with BNT162b2: A Prospective Study in 308 Healthy Individuals. Life 2021, 11, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegu, A.; O’Connell, S.E.; Schmidt, S.D.; O’Dell, S.; Talana, C.A.; Lai, L.; Albert, J.; Anderson, E.; Bennett, H.; Corbett, K.S.; et al. Durability of MRNA-1273 Vaccine–Induced Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Science 2021, 373, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergwerk, M.; Gonen, T.; Lustig, Y.; Amit, S.; Lipsitch, M.; Cohen, C.; Mandelboim, M.; Levin, E.G.; Rubin, C.; Indenbaum, V.; et al. COVID-19 Breakthrough Infections in Vaccinated Health Care Workers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
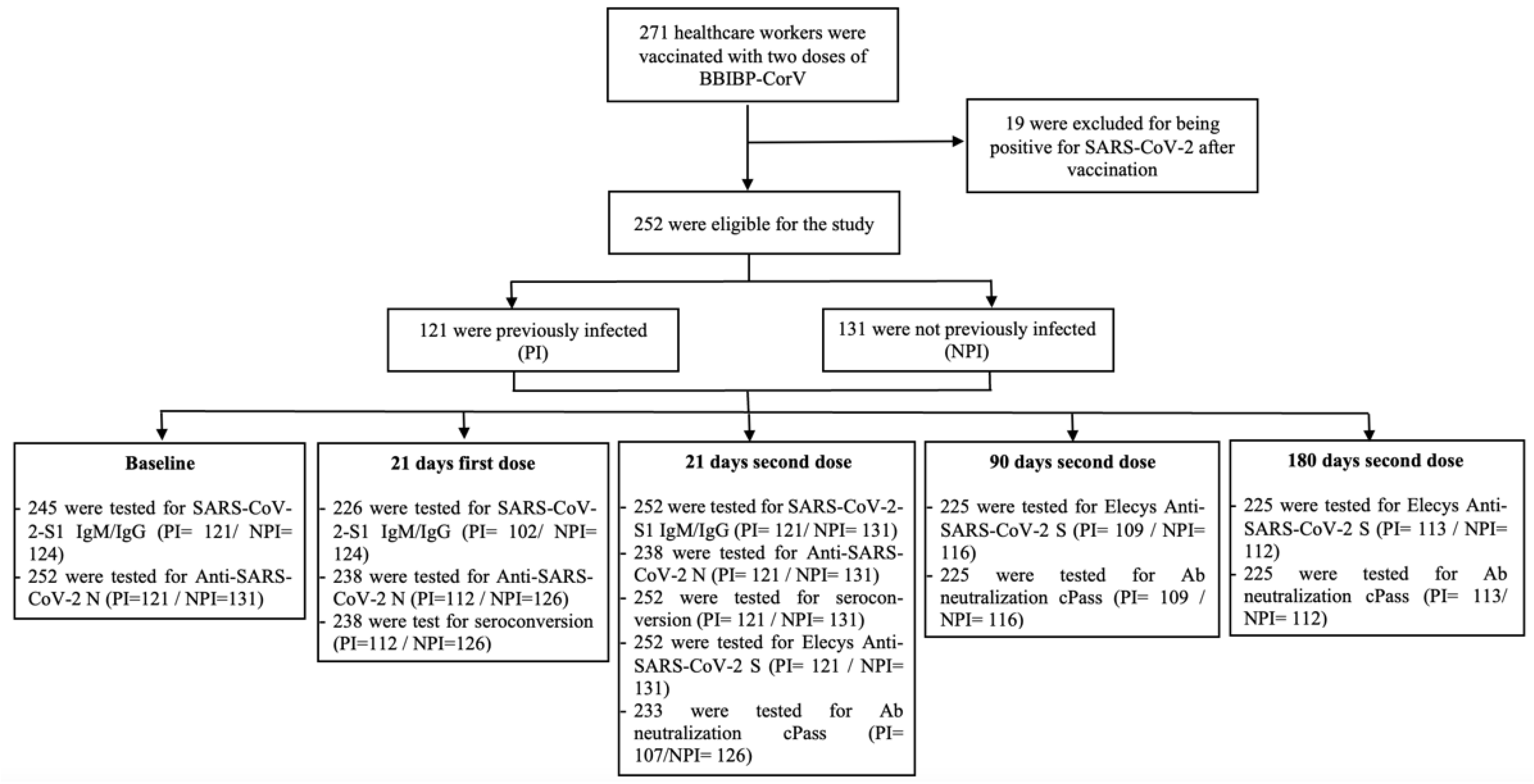

| Variable | Total (n = 252) | Previously Infected (n = 121) | Not Previously Infected (n = 131) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years * (IQR) | 35 (29–45) | 35 (29.5–45) | 35.5 (29–46) | 0.914 a |
| Sex (%) | 0.269 b | |||
| - Female | 203 (80.55) | 94 (46.31) | 109 (53.69) | |
| - Male | 49 (19.45) | 27 (55.10) | 22 (44.9) | |
| Laboral Area (%) | 0.203 b | |||
| - Phlebotomy | 78 (30.95) | 42 (53.85) | 36 (46.15) | |
| - Customer service | 52 (20.63) | 24 (46.15) | 28 (53.85) | |
| - Maintenance service | 28 (11.11) | 17 (60.71) | 11 (39.29) | |
| - Analytic Process | 35 (13.90) | 12 (34.29) | 23 (65.71) | |
| - Administrative | 59 (23.41) | 26 (44.07) | 33 (55.93) | |
| Working mode (%) | 0.911 b | |||
| - Remote | 35 (14.17) | 17 (48.57) | 18 (51.43) | |
| - Presence | 198 (78.35) | 96 (48.48) | 102 (51.52) | |
| - Both | 19 (7.54) | 9 (47.37) | 10 (52.63) | |
| Days since infection * (IQR) | 231.5 (173–277) | |||
| Humoral response rates ** | ||||
| 21 days after the first dose (%) | ||||
| - SARS-CoV-2 S1 IgM/IgG | 162 (71.68) | 97 (95.09) | 65 (52.41) | <0.001 b |
| - Anti-SARS-CoV-2-N | 117 (49.16) | 110 (98.21) | 7 (5.56) | <0.001 c |
| - Seroconversion | 176 (73.95) | 111 (99.10) | 65 (51.59) | <0.001 c |
| 21 days after the second dose (%) | ||||
| - SARS-CoV-2-S1 IgM/IgG | 241 (95.63) | 121 (100) | 120 (91.60) | <0.001 b |
| - Anti-SARS-CoV-2 N | 211 (88.66) | 121 (100) | 90 (68.70) | <0.001 c |
| - Elecsys® anti-SARS-CoV-2 S | 248 (98.41) | 121 (100) | 127 (96.94) | 0.071 c |
| - Ab neutralization cPass™ | 222 (95.28) | 106 (99.06) | 116 (92.06) | 0.013 c |
| - Seroconversion | 241 (95.63) | 121 (100) | 120 (91.60) | <0.001 c |
| 90 days after the second dose (%) | ||||
| - Elecsys® anti-SARS-CoV-2 S | 224 (99.56) | 109 (100) | 115 (99.14) | 0.516 c |
| - Ab neutralization cPass™ | 196 (87.11) | 109 (100) | 87 (75) | <0.001 c |
| 180 days after second dose (%) | ||||
| - Elecsys® anti-SARS-CoV-2 S | 224 (99.56) | 113 (100) | 111 (99.11) | 0.498 c |
| - Ab neutralization cPass™ | 164 (72.89) | 111 (98.23) | 53 (47.32) | <0.001 c |
| Variable | Total (n = 268) | Previously Infected (n = 121) | Not Previously Infected (n = 147) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgM/IgG SARS-CoV-2 S1 (UI/mL) * | ||||
| - Baseline | 3.3 (0.4–23.5) | 23.8 (10.3–85.3) | 0.95 (0.4–1.75) | <0.001 a |
| - 21 days after first dose | 21.7 (5.8–64.1) | 65.45 (44.6–102) | 8.4 (3.7–17.2) | <0.001 a |
| - 21 days after second dose | 66.1 (35.45–105.7) | 82.5 (57.9–110.9) | 49.5 (25.7–89.8) | <0.001 a |
| IgM/IgG/IgA anti-SARS-CoV-2 N (S/Co) *(IQR) | ||||
| - Baseline | 0.1 (0.1–24.65) | 25.9 (9.1–68.5) | 0.1 (0.1–0.1) | <0.001 a |
| - 21 days after first dose | 0.7 (0.1–128.1) | 135.6 (85.8–190.3) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | <0.001 a |
| - 21 days after second dose | 37.4 (2.75–155.35) | 159.7 (93.8–211.4) | 2.9 (0.5–7.8) | <0.001 a |
| Ab neutralization cPass™ (%) * (IQR) | ||||
| - 21 days after second dose | 88.1 (68–96.3) | 96.4 (92.4–97.1) | 73.5 (53.9–85.2) | <0.001 a |
| - 90 days after second dose | 72.4 (45.1–94.3) | 94.3 (82.9–96.1) | 45.6 (30.85–65.7) | <0.001 a |
| - 180 days after second dose | 63.6 (27.8–92.2) | 88.5 (72.4–95.8) | 28.15 (16.9–43.55) | <0.001 a |
| Elecsys® anti-SARS-CoV-2 S (UI/mL) * (IQR) | ||||
| - 21 days after second dose | 293.45 (92.75–1275) | 1288 (715.9–2334) | 117.4 (48.7–222.8) | <0.001 a |
| - 90 days after second dose | 187.1 (49–737.4) | 714.7 (414–1347) | 49.95 (28.05–101.25) | <0.001 a |
| - 180 days after second dose | 296.2 (63.9–782.1) | 558.2 (356.8–1135) | 64.2 (29.4–146.5) | <0.001 a |
| Variable | Crude Beta-Coefficient 95% | p-Value | Adjusted Beta-Coefficient 95% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ab Neutralization cPass | ||||
| Male sex | 17.076 (6.325–27.827) | 0.002 | 11.372 (−1.278–24.023) | 0.078 |
| Previously infected | 45.211 (39.964–51.457) | <0.001 | 44.692 (38.487–50.897) | <0.001 |
| Elecsys® Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S | ||||
| Male sex | 385.629 (134.249–637.008) | 0.003 | 334.735 (97.651–571.820) | 0.006 |
| Previously infected | 540.221 (351.556–728.886) | <0.001 | 519.961 (333.527–706.395) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez de la Torre, J.C.; Cáceres-DelAguila, J.A.; Muro-Rojo, C.; De La Cruz-Escurra, N.; Copaja-Corzo, C.; Hueda-Zavaleta, M.; Arenas Siles, D.; Benites-Zapata, V.A. Humoral Immune Response Induced by the BBIBP-CorV Vaccine (Sinopharm) in Healthcare Workers: A Cohort Study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7050066
Gómez de la Torre JC, Cáceres-DelAguila JA, Muro-Rojo C, De La Cruz-Escurra N, Copaja-Corzo C, Hueda-Zavaleta M, Arenas Siles D, Benites-Zapata VA. Humoral Immune Response Induced by the BBIBP-CorV Vaccine (Sinopharm) in Healthcare Workers: A Cohort Study. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(5):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7050066
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez de la Torre, Juan C., José Alonso Cáceres-DelAguila, Cecilia Muro-Rojo, Nathalia De La Cruz-Escurra, Cesar Copaja-Corzo, Miguel Hueda-Zavaleta, Daniella Arenas Siles, and Vicente A Benites-Zapata. 2022. "Humoral Immune Response Induced by the BBIBP-CorV Vaccine (Sinopharm) in Healthcare Workers: A Cohort Study" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 5: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7050066
APA StyleGómez de la Torre, J. C., Cáceres-DelAguila, J. A., Muro-Rojo, C., De La Cruz-Escurra, N., Copaja-Corzo, C., Hueda-Zavaleta, M., Arenas Siles, D., & Benites-Zapata, V. A. (2022). Humoral Immune Response Induced by the BBIBP-CorV Vaccine (Sinopharm) in Healthcare Workers: A Cohort Study. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(5), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7050066








