Disseminated Human Subarachnoid Coenurosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
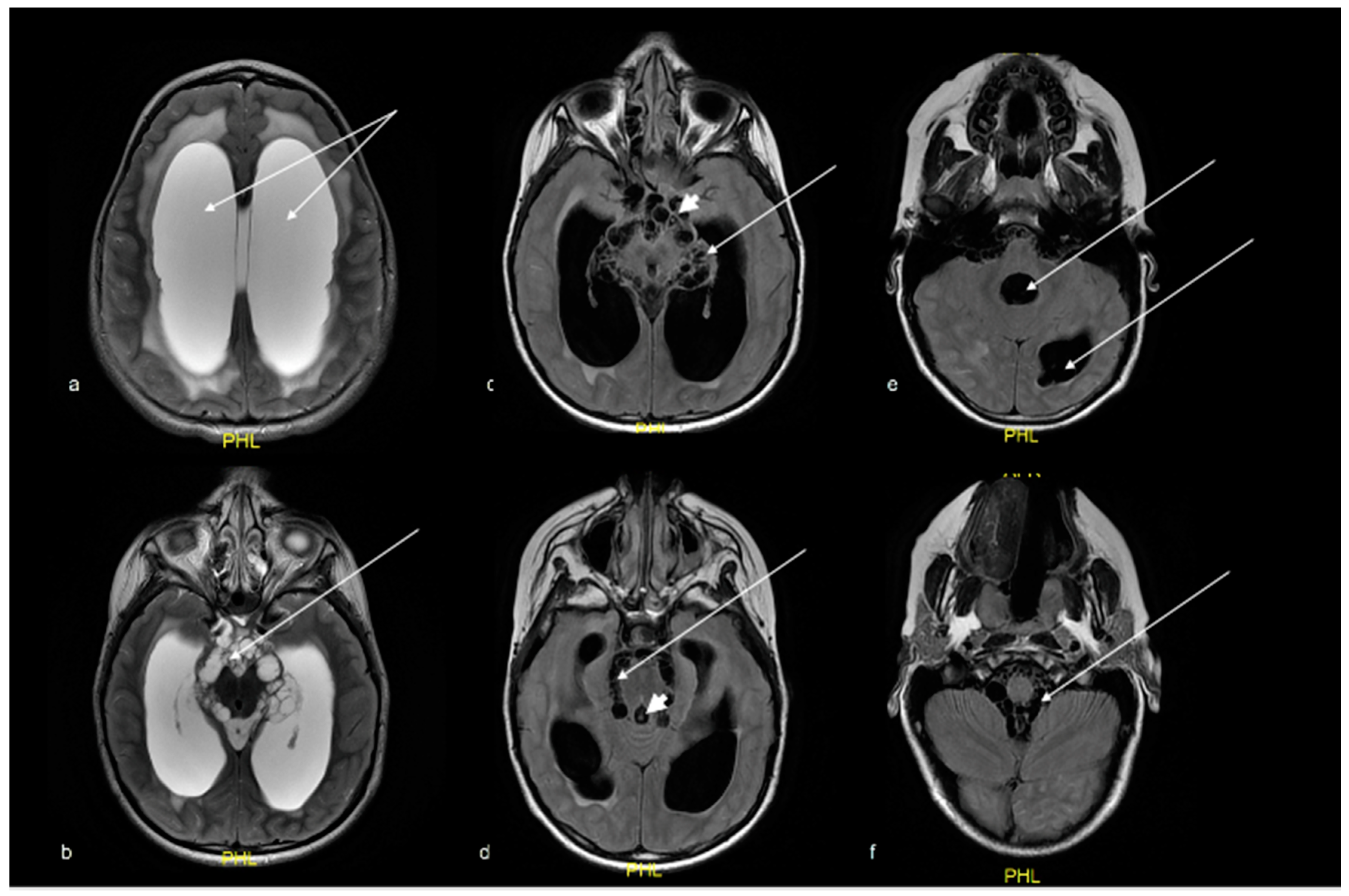
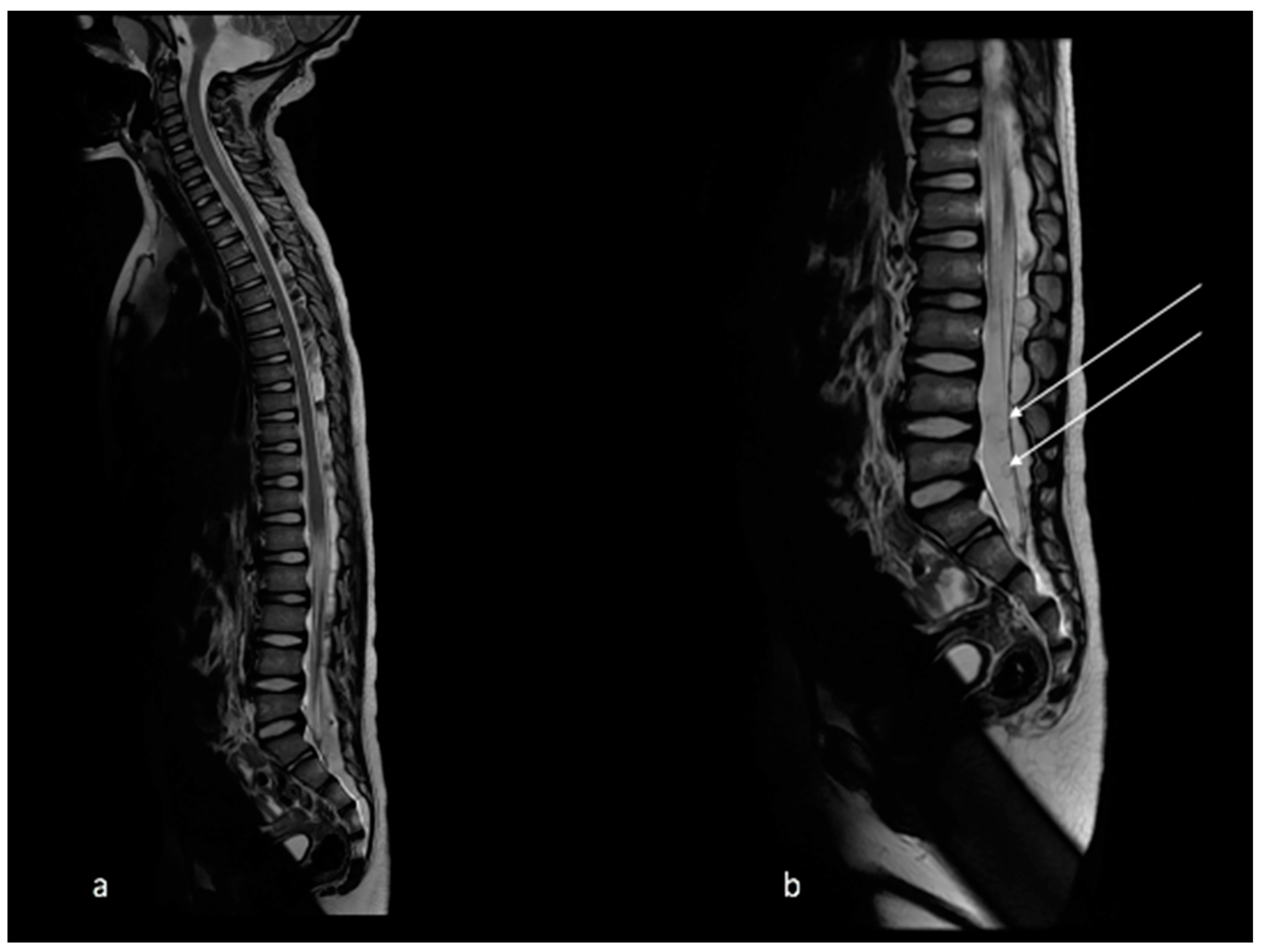
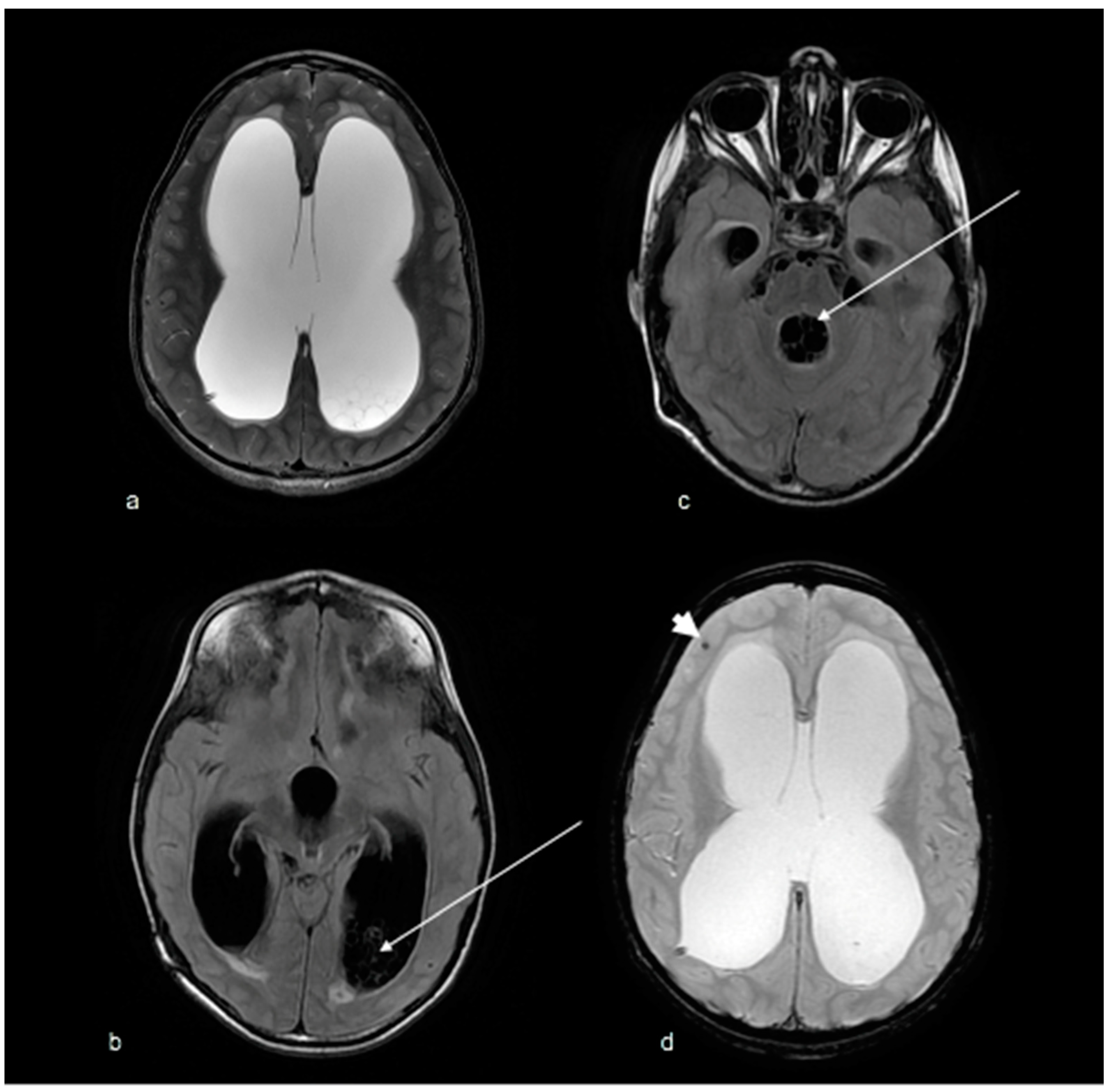
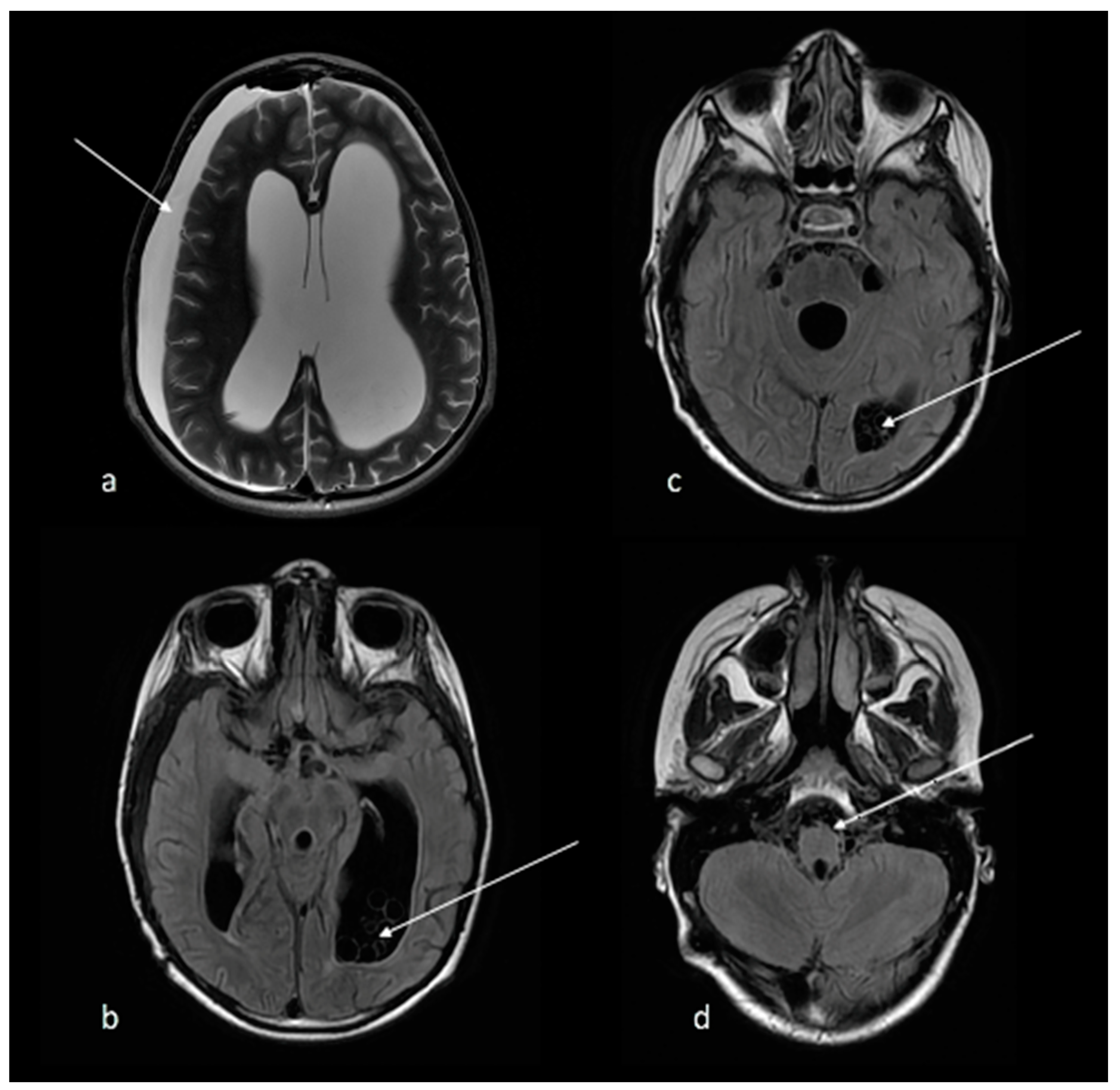
2. Case Report
3. Histopathological Diagnosis
4. Genetic Analysis
5. Discussion
| Author | Age/Gender | CNS Location | Geographical Region | Clinical Outcome | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brumpt, 1913 [38] | 40/M | Parenchymal and intraventricular | France | Died | T. multiceps |
| Spencer 1936 (no reference, described by Lescano [3]) | Age and gender unknown | Parenchymal | Africa | Unknown | Unknown |
| Cluver, 1940 [39] | Age and gender unknown | Parenchymal and intraventricular | South Africa | Died | T. multiceps |
| Clapham, 1941 [40] | 39/M | Parenchymal and intraventricular | England | Died | T. multiceps |
| Parkinson, 1942 (no reference, described by Lescano [3]) | Age and gender unknown | Parenchymal | England | Unknown | Unknown |
| Roger et al., 1942 [41] | 42/F | Parenchymal and cisternal | France | Died | T. multiceps |
| Landells et al., 1949 [42] | 14/F | Spinal cord | England | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| Johnstone et al., 1950 [43] | 2/M | Parenchymal | USA | Died | T. multiceps |
| Becker et al., 1951 [12] | 55/M | Intraventricular | South Africa | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| Becker et al., 1951 [12] | 34/M | Cisternal | South Africa | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| Becker et al., 1951 [12] | 33/M | Cisternal and intraventricular | South Africa | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| Becker et al., 1951 [44] | 28/M | Intraventricular | South Africa | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| Watson et al., 1955 [45] | 32/M | Parenchymal | South Africa | Died | T. multiceps |
| Watson et al., 1955 [45] | 33/M | Parenchymal | South Africa | Died | T. multiceps |
| Ranque et al., 1955 [46] | Age and gender unknown | Parenchymal | France | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| Bertrand et al., 1956 [47] | Age and gender unknown | Parenchymal | France | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| Correa et al., 1962 [48] | 42/F | Cisternal | Brazil | Died | T. multiceps |
| D’Andrea et al., 1964 [49] | Age and gender unknown | Parenchymal | Italy | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| Hermos et al., 1970 [50] | 2/M | Parenchymal and spinal cord | USA | Died | T. multiceps |
| Michal et al., 1977 [51] | 37/F | Parenchymal and cisternal | Switzerland | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| Jung et al., 1981 [52] | 48/M | Parenchymal | USA | Survived | Unknown |
| Schellhas et al., 1985 [11] | 3/F | Parenchymal, intraventricular and spinal cord | USA | Died | T. multiceps |
| Pau et al., 1987 [10] | 54/M | Parenchymal and cisternal | Italy | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Pau et al., 1990 [53] | 28/M | Parenchymal | Italy | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Pau et al., 1990 [53] | 51/F | Cisternal | Italy | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Pau et al., 1990 [53] | 32/M | Parenchymal | Italy | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Malomo et al., 1990 [54] | Age and gender unknown | Parenchymal | Nigeria | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| Sabattani et al., 2004 [55] | 46/F | Parenchymal | Italy | Unknown | T. multiceps |
| El-On et al., 2008 [4] | 4/F | Parenchymal | Israel | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Mahadevan et al., 2011 [56] | 55/M | Parenchymal | India | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Mahadevan et al., 2011 [56] | 36/M | Parenchymal | India | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Ali et al., 2019 [37] | 63/M | Base of skull with parenchymal extension | India | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Kulanthaiveluet al., 2020 [19] | 28/M | Parenchymal | India | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Kulanthaiveluet al., 2020 [19] | 55/M | Parenchymal | India | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Kulanthaiveluet al., 2020 [19] | 24/F | Intraventricular | India | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Kulanthaiveluet al., 2020 [19] | 56/F | Parenchymal | India | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Kulanthaiveluet al., 2020 [19] | 50/M | Parenchymal | India | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Kulanthaiveluet al., 2020 [19] | 34/M | Parenchymal | India | Survived | T. multiceps |
| Yamazawa et al., 2020 [6] | 38/M | Parenchymal | Japan | Survived | T. serialis |
| Nhlonzi et al., 2022 [9] | 46/F | Parenchymal | South Africa | Died | T. multiceps |
| Present case | 5/M | Cisternal and intraventricular | South Africa | Died | T. serialis |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krecek, R.C.; Mohammed, H.; Michael, L.M.; Schantz, P.M.; Ntanjana, L.; Morey, L.; Werre, S.R.; Willingham, A.L., 3rd. Risk factors of porcine cysticercosis in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelfsema, J.H.; Nozari, N.; Pinelli, E.; Kortbeek, L.M. Novel PCRs for differential diagnosis of cestodes. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 161, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescano, A.G.; Zunt, J. Other cestodes: Sparganosis, coenurosis and Taenia crassiceps cysticercosis. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 114, pp. 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-On, J.; Shelef, I.; Cagnano, E.; Benifla, M. Taenia multiceps: A rare human cestode infection in Israel. Vet. Ital. 2008, 44, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ing, M.B.; Schantz, P.M.; Turner, J.A. Human coenurosis in North America: Case reports and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazawa, E.; Ohno, M.; Satomi, K.; Yoshida, A.; Miyakita, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Satomi, N.; Asanome, T.; Maeshima, A.; Shiotsuka, M.; et al. First case of human neurocoenurosis caused by Taenia serialis: A case report. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 92, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachberg, S.; Thompson, R.C.; Lymbery, A.J. A contribution to the etiology of racemose cysticercosis. J. Parasitol. 1990, 76, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, A. Coenurus of Taenia brauni Setti parasitic in man and animals from the Belgian Congo and Ruanda-Urundi. Nature 1956, 178, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhlonzi, G.B.; Mwazha, A. Clinicopathological Review of Human Coenurosis in Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa: A Retrospective Single Center Study. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2022, 17, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, A.; Turtas, S.; Brambilla, M.; Leoni, A.; Rosa, M.; Viale, G.L. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral coenurosis. Surg. Neurol. 1987, 27, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellhas, K.P.; Norris, G.A. Disseminated human subarachnoid coenurosis: Computed tomographic appearance. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1985, 6, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, B.J.; Jacobson, S. Infestation of the human brain with Coenurus cerebralis; a report of three cases. Lancet 1951, 2, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danziger, J.; Bloch, S. Tapeworm cyst infestations of the brain. Clin. Radiol. 1975, 26, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, R.S.; Viana, D.C.; Colli, B.O.; Rajshekhar, V.; Salomão, J.F.M. Pediatric neurocysticercosis. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahale, R.R.; Mehta, A.; Rangasetty, S. Extraparenchymal (Racemose) Neurocysticercosis and Its Multitude Manifestations: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 11, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickerstaff, E.R.; Cloake, P.C.; Hughes, B.; Smith, W.T. The racemose form of cerebral cysticercosis. Brain 1952, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrego, M.A.; Verastegui, M.R.; Vasquez, C.M.; Koziol, U.; Laclette, J.P.; Garcia, H.H.; Nash, T.E. Cysticercosis Working Group in Peru. Identification and culture of proliferative cells in abnormal Taenia solium larvae: Role in the development of racemose neurocysticercosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.Y.; Kho, W.G.; Hwang, S.Y.; Je, E.Y.; Chung, Y.T.; Kim, T.S.; Eom, K.S.; Sohn, W.M.; Cho, S.Y.; Kong, Y. Molecular determination of the origin of acephalic cysticercus. Parasitology 2005, 130, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulanthaivelu, K.; Bhat, M.D.; Prasad, C.; Srinivas, D.; Mhatre, R.; Nandeesh, B.N. Brain MRI Findings in Coenurosis: A Helminth Infection. J. Neuroimaging 2020, 30, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haitchi, G.; Buchroithner, J.; Sonnberger, M.; Weis, S.; Fellner, F.A. AIRP best cases in radiologic-pathologic correlation: Human coenurosis (Taenia Larva). Radiographics 2012, 32, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poptani, H.; Gupta, R.K.; Roy, R.; Pandey, R.; Jain, V.K.; Chhabra, D.K. Characterization of intracranial mass lesions with in vivo proton MR spectroscopy. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1995, 16, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nash, T.E.; Garcia, H.H. Diagnosis and treatment of neurocysticercosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio, A.; Santillán, F.; León, P.; Flores, C.; Hauser, W.A. Is the course of neurocysticercosis modified by treatment with antihelminthic agents? Arch. Intern. Med. 1995, 155, 1982–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monk, E.J.M.; Abba, K.; Ranganathan, L.N. Anthelmintics for people with neurocysticercosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 6, CD000215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, H.H.; Evans, C.A.; Nash, T.E.; Takayanagui, O.M.; White, A.C.; Botero, D.; Rajshekhar, V.; Tsang, V.C.; Schantz, P.M.; Allan, J.C.; et al. Current consensus guidelines for treatment of neurocysticercosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.A., Jr.; Coyle, C.M.; Rajshekhar, V.; Singh, G.; Hauser, W.A.; Mohanty, A.; Garcia, H.H.; Nash, T.E. Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurocysticercosis: 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, e49–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, H.H.; Lescano, A.G.; Gonzales, I.; Bustos, J.A.; Pretell, E.J.; Horton, J.; Saavedra, H.; Gonzalez, A.E.; Gilman, R.H. Cysticercosis Working Group in Peru. Cysticidal Efficacy of Combined Treatment With Praziquantel and Albendazole for Parenchymal Brain Cysticercosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Brutto, O.H.; Roos, K.L.; Coffey, C.S.; García, H.H. Meta-analysis: Cysticidal drugs for neurocysticercosis: Albendazole and praziquantel. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, H.H.; Lescano, A.G.; Lanchote, V.L.; Pretell, E.J.; Gonzales, I.; Bustos, J.A.; Takayanagui, O.M.; Bonato, P.S.; Horton, J.; Saavedra, H.; et al. Cysticercosis Working Group in Peru. Pharmacokinetics of combined treatment with praziquantel and albendazole in neurocysticercosis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 72, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, H.H.; Gonzales, I.; Lescano, A.G.; Bustos, J.A.; Zimic, M.; Escalante, D.; Saavedra, H.; Gavidia, M.; Rodriguez, L.; Najar, E.; et al. Cysticercosis Working Group in Peru. Efficacy of combined antiparasitic therapy with praziquantel and albendazole for neurocysticercosis: A double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konar, S.; Kandregula, S.; Sashidhar, A.; Prabhuraj, A.R.; Saini, J.; Shukla, D.; Srinivas, D.; Indira Devi, B.; Somanna, S.; Arimappamagan, A. Endoscopic intervention for intraventricular neurocysticercal cyst: Challenges and outcome analysis from a single institute experience. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 198, 106179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Vazquez, O.H.; Nagore, N. Cisternal neurocysticercosis. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 22, 774–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colli, B.O.; Carlotti, C.G., Jr.; Assirati, J.A., Jr.; Machado, H.R.; Valença, M.; Amato, M.C. Surgical treatment of cerebral cysticercosis: Long-term results and prognostic factors. Neurosurg. Focus 2002, 12, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franko, L.R.; Pandian, B.; Gupta, A.; Savastano, L.E.; Chen, K.S.; Riddell, J.; Orringer, D.A. Posterior Fossa Craniotomy for Adherent Fourth Ventricle Neurocysticercosis. Oper. Neurosurg. 2019, 16, E154–E158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajshekhar, V. Surgical management of neurocysticercosis. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Rastogi, M.; Jha, D.K.; Husain, N.; Gupta, R.K. Endoscopic transaqueductal removal of fourth ventricular neurocysticercosis with an angiographic catheter. Neurosurgery 2007, 60, 249–253, discussion 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Reddy, P.S.; Venugopal, S.; Chhabra, M.; Mahadevan, A. Cerebral Coenurosis Masquerading as Malignancy: A Rare Case Report from India. J. Neurosci. Rural. Pract. 2019, 10, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumpt, E. Précis de Parasitology, 2nd ed.; Masson and Co.: Paris, France, 1913. [Google Scholar]
- Cluver, E.H.; Rep, S. Annual Report; South African Institute for Medical Research: Johannesburg, South Africa, 1940; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Clapham, P.A. An English case of Coenurus cerebralis in the human brain. J. Helminthol. 1941, 19, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, H.; Sautet, J.; Paillas, J.E. Un cas cénurose de la fosse cérébrale postérieure. Rev. Neurologie. 1942, 74, 319–321. [Google Scholar]
- Landells, J.W. Intra-medullary cyst of the spinal cord due to the cestode Multiceps multiceps in the coenurus stage; report of a case. J. Clin. Pathol. 1949, 2, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, H.G.; Jones, O.W., Jr. Cerebral coenurosis in an infant. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1950, 30, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B.J.; Jacobson, S. Infestation of the human brain with Coenurus cerebralis in human brain. Lancet 1951, 2, 1202–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, K.C.; Laurie, W. Cerebral coenuriasis in man. Lancet 1955, 269, 1321–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranque, J.; Nicoli, R.N. Parasitological aspects of cerebral coenurosis; a new case. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1955, 30, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bertrand, I.; Callot, J.; Terrasse, J.; Janny, P.; Perol, E. A new case of cerebral coenurosis. Presse Med. 1956, 64, 333–335. [Google Scholar]
- Correa, F.M.; Ferriolli Filho, F.; Forjaz, S.; Martelli, N. Cerebral coenurosis. Apropos of a human case. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1962, 4, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, F.; Morello, G. La cenurosi cerebrale. Acta Neurol. 1964, 19, 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Hermos, J.A.; Healy, G.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Barlow, J.; Church, W.G. Fatal human cerebral coenurosis. JAMA 1970, 213, 1461–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michal, A.; Regli, F.; Campiche, R.; Cavallo, J.; de Crousaz, G.; Oberson, R.; Rabinowicz, T. Cerebral coenurosis. Report of a case with arteritis. J. Neurol. 1977, 216, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, R.C.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Beaver, P.C.; Levy, R.W.; Schenthal, J.E. Racemose cysticercus in human brain. A case report. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, A.; Perria, C.; Turtas, S.; Brambilla, M.; Viale, G. Long-term follow-up of the surgical treatment of intracranial coenurosis. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1990, 4, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malomo, A.; Ogunniyi, J.; Ogunniyi, A.; Akang, E.; Shokunbi, M.T. Coenurosis of the central nervous system in a Nigerian. Trop. Geogr. Med. 1990, 42, 280–282. [Google Scholar]
- Sabattani, S.; Marliani, A.F.; Roncaroli, F.; Zucchelli, M.; Zini, A.; Calbucci, F.; Chiodo, F. Cerebral coenurosis. Case illustration. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, A.; Dwarakanath, S.; Pai, S.; Kovoor, J.; Radhesh, S.; Srinivas, H.; Chandramouli, B.; Shankar, S. Cerebral coenurosis mimicking hydatid disease-report of two cases from South India. Clin. Neuropathol. 2011, 30, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Labuschagne, J.; Frean, J.; Parbhoo, K.; Mutyaba, D.; Pillay, T.; Boughan, S.; Nkala, H. Disseminated Human Subarachnoid Coenurosis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7120405
Labuschagne J, Frean J, Parbhoo K, Mutyaba D, Pillay T, Boughan S, Nkala H. Disseminated Human Subarachnoid Coenurosis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(12):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7120405
Chicago/Turabian StyleLabuschagne, Jason, John Frean, Kaajal Parbhoo, Denis Mutyaba, Tanyia Pillay, Shareen Boughan, and Hlezikuhle Nkala. 2022. "Disseminated Human Subarachnoid Coenurosis" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 12: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7120405
APA StyleLabuschagne, J., Frean, J., Parbhoo, K., Mutyaba, D., Pillay, T., Boughan, S., & Nkala, H. (2022). Disseminated Human Subarachnoid Coenurosis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(12), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7120405








