Identification of Mosquito Bloodmeals Collected in Diverse Habitats in Malaysian Borneo Using COI Barcoding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
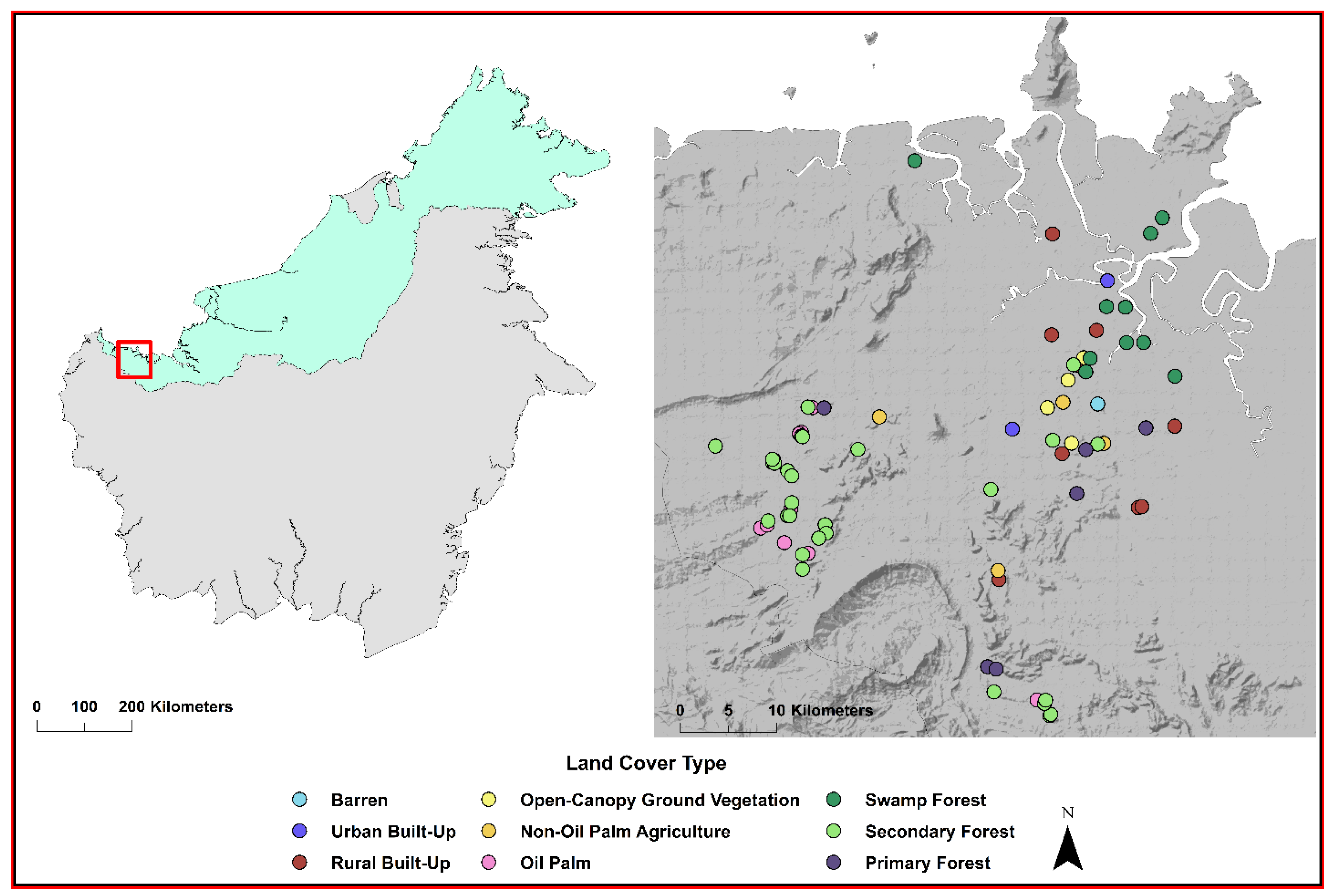
2.1. Study Site and Design
2.2. Mosquito Collection and Identification of Bloodfed Females
2.3. Bloodmeal DNA Extraction and COI Amplification
2.4. Sequence Analysis and Host Identification
2.5. Molecular Confirmation of Bloodfed Mosquito Species
2.6. COI Cloning and Molecular Identification of Mosquitos from Bloodmeal DNA
2.7. Descriptions of Host and Vector Networks
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Mosquito Bloodmeal Sources
3.2. Identification of Mosquitoes Collected
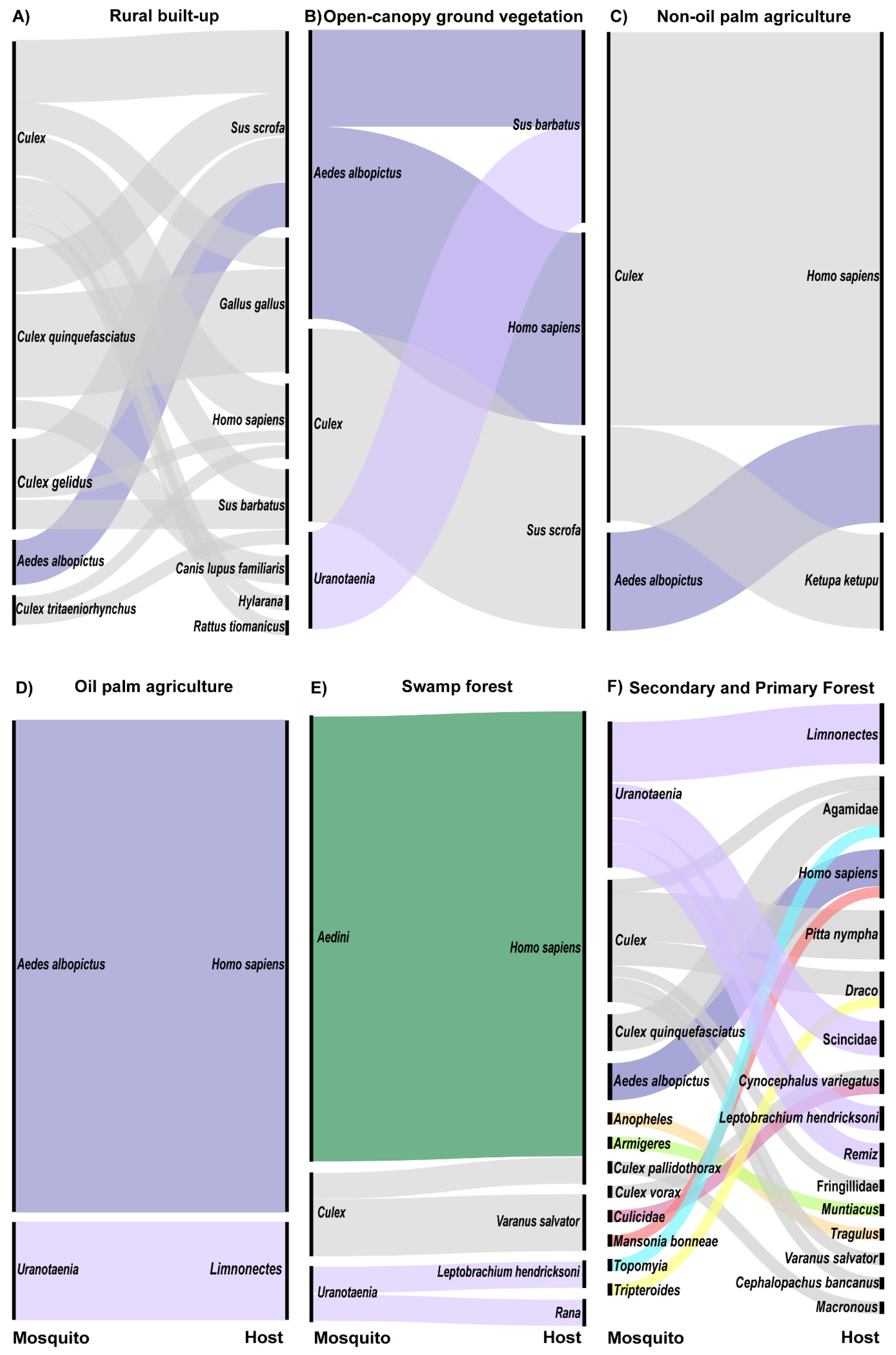
3.3. Mosquito–Host Networks by Land Cover Type
3.4. Site Level Networks Between Mosquitoes and Hosts
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weaver, S.C.; Charlier, C.; Vasilakis, N.; Lecuit, M. Zika, Chikungunya, and other emerging vector-borne viral diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2018, 69, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, S.V.; Tesh, R.B.; Vasilakis, N. The emergence of arthropod-borne viral diseases: A global prospective on dengue, chikungunya and zika fevers. Acta Trop. 2017, 166, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilakis, N.; Weaver, S.C. Flavivirus transmission focusing on Zika. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 22, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, S.C.; Barrett, A.D.T. Transmission cycles, host range, evolution and emergence of arboviral disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, L.L.; Forrester, N.; Tsetsarkin, K.; Vasilakis, N.; Weaver, S.C. Factors shaping the adaptive landscape for arboviruses: Implications for the emergence of disease. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, S.C.; Reisen, W.K. Present and future arboviral threats. Antivir. Res. 2010, 85, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakis, N.; Cardosa, J.; Hanley, K.A.; Holmes, E.C.; Weaver, S.C. Fever from the forest: Prospects for the continued emergence of sylvatic dengue virus and its impact on public health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.C.; Learoyd, T.P.; Langendorf, B.J.; Logan, J.G. Japanese encephalitis: The vectors, ecology and potential for expansion. J. Travel Med. 2018, 25, S16–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, R.J. Molecular methods for arthropod bloodmeal identification and applications to ecological and vector-borne disease studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.E.; Taylor, L.H.; Haydon, D.T. Population biology of multihost pathogens. Science 2001, 292, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borremans, B.; Faust, C.; Manlove, K.R.; Sokolow, S.H.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O. Cross-species pathogen spillover across ecosystem boundaries: Mechanisms and theory. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takken, W.; Verhulst, N.O. Host preferences of blood-feeding mosquitoes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, J.E.; Shearman, P.L.; Asner, G.P.; Knapp, D.E.; Aoro, G.; Lokes, B. Extreme differences in forest degradation in Borneo: Comparing practices in Sarawak, Sabah, and Brunei. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, L.P.; Miettinen, J.; Liew, S.C.; Ghazoul, J. Remotely sensed evidence of tropical peatland conversion to oil palm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5127–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaveau, D.L.A.; Sheil, D.; Salim, M.A.; Arjasakusuma, S.; Ancrenaz, M.; Pacheco, P.; Meijaard, E. Rapid conversions and avoided deforestation: Examining four decades of industrial plantation expansion in Borneo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaveau, D.L.A.; Sloan, S.; Molidena, E.; Yaen, H.; Sheil, D.; Abram, N.K.; Ancrenaz, M.; Nasi, R.; Quinones, M.; Wielaard, N.; et al. Four decades of forest persistence, clearance and logging on Borneo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, J.; Shi, C.; Liew, S.C. Land cover distribution in the peatlands of Peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra and Borneo in 2015 with changes since 1990. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 6, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, J.A.; Olson, S.H.; Uejio, C.K.; Gibbs, H.K. Disease emergence from global climate and land use change. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 92, 1473–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Tran, A.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Linard, C.; Soti, V. Pathogenic landscapes: Interactions between land, people, disease vectors, and their animal hosts. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2010, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, M.A.; Gowler, C.D.; Shaw, C.L.; Hufbauer, R.A.; Duffy, M.A. Human drivers of ecological and evolutionary dynamics in emerging and disappearing infectious disease systems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2017, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, C.L.; McCallum, H.I.; Bloomfield, L.S.P.; Gottdenker, N.L.; Gillespie, T.R.; Torney, C.J.; Dobson, A.P.; Plowright, R.K. Pathogen spillover during land conversion. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, G.; Way, H.; Bowen, E.; Simpson, D.; Hill, M. Arbovirus infections in Sarawak, October 1968–February 1970 Tembusu and Sindbis virus isolations from mosquitoes. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1975, 69, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- How Ooi, M.; Lewthwaite, P.; Foo Lai, B.; Mohan, A.; Clear, D.; Lim, L.; Krishnan, S.; Preston, T.; Hee Chieng, C.; Hooi Tio, P.; et al. The epidemiology, clinical features, and long-term prognosis of Japanese encephalitis in Central Sarawak, Malaysia, 1997–2005. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simpson, D.I.H.; Smith, C.E.G.; Bowen, E.T.W.; Platt, G.S.; Way, H.; McMahon, D.; Bright, W.F.; Hill, M.N.; Mahadevan, S.; Macdonald, W.W. Arbovirus infections in Sarawak: Virus isolations from mosquitoes. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1970, 64, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, C.H.; Bujang, M.A.; Tg Abu Bakar Sidik, T.M.I.; Ngui, R.; Lim, Y.A.-L. Over two decades of Plasmodium knowlesi infections in Sarawak: Trend and forecast. Acta Trop. 2017, 176, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, S.B.; Cox-Singh, J. Human infections with Plasmodium knowlesi—Zoonotic malaria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Pickering, P.; Duchêne, S.; Holmes, E.C.; Aaskov, J.G. Highly divergent dengue virus type 2 in traveler returning from Borneo to Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2146–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, A.T.; Moore, P.R.; Taylor, C.T.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Cameron, J.N.; Hewitson, G.R.; Pukallus, D.S.; Huang, B.; Warrilow, D.; Van den Hurk, A.F. Highly divergent dengue virus type 1 genotype sets a new distance record. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardosa, J.; Ooi, M.H.; Tio, P.H.; Perera, D.; Holmes, E.C.; Bibi, K.; Manap, Z.A. Dengue virus serotype 2 from a sylvatic lineage isolated from a patient with dengue hemorrhagic fever. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, B.-T.; Sam, S.-S.; Abd-Jamil, J.; AbuBakar, S. Isolation of ancestral sylvatic dengue virus type 1, Malaysia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the köppen-geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.I.; Mundis, S.; Widen, S.G.; Wood, T.G.; Tesh, R.B.; Cardosa, J.; Vasilakis, N.; Perera, D.; Hanley, K.A. Abundance and distribution of sylvatic dengue virus vectors in three different land cover types in Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, R.; Schlapfer, D. Atmostpheric/Topographic Correction for Satellite Imagery (ATCOR-2/3 User Guide, Version 9.3.0, April 2019). Available online: https://www.rese-apps.com/pdf/atcor3_manual.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Richter, R. ATCOR 2 and ATCOR 3 for Satellite Systems; ReSe Applications Schläpfer: Wil, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- USGS Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, 1 Arc Second Digital Elevation Model; Earth Resources Observation and Science Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2000.
- Rodriguez, E.; Morris, C.S.; Belz, J.E.; Chapin, E.; Martin, J.; Daffer, W.; Hensley, S. An Assessment of the SRTM Topographic Products. Available online: https://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/srtm/SRTM_D31639.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Obenauer, P.J.; Abdel-Dayem, M.S.; Stoops, C.A.; Villinski, J.T.; Tageldin, R.; Fahmy, N.T.; Diclaro, J.W.; Bolay, F. Field responses of Anopheles gambiae complex (Diptera: Culicidae) in Liberia using yeast-generated carbon dioxide and synthetic lure-baited light traps. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Reuben, R.; Tewari, S.C.; Hiriyan, J.; Akiyama, J. Illustrated keys to species of Culex (Culex) associated with Japanese encephalitis in Southeast Asia (Diptera: Culicidae). Mosq. Syst. 1994, 26, 75–96. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-M.; Rueda, L.M. Description of a paralectotype female of Aedes (Finlaya) niveus (Ludlow)(Diptera: Culicidae). Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 1998, 100, 824–827. [Google Scholar]
- Rueda, L.M. Pictorial keys for the identification of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) associated with dengue virus transmission. Zootaxa 2004, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit PACOM Arthropod Identification Keys. Available online: http://www.wrbu.org/aors/pacom_Keys.html (accessed on 10 March 2016).
- Thiemann, T.C.; Brault, A.C.; Ernest, H.B.; Reisen, W.K. Development of a high-throughput microsphere-based molecular assay to identify 15 common bloodmeal hosts of Culex mosquitoes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townzen, J.S.; Brower, A.V.Z.; Judd, D.D. Identification of mosquito bloodmeals using mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I and cytochrome b gene sequences. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2008, 22, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; De Waard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Ratnasingham, S.; De Waard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizard, J.; Patel, S.; Waugh, J.; Tavares, E.; Bergmann, T.; Gill, B.; Norman, J.; Christidis, L.; Scofield, P.; Haddrath, O.; et al. DNA barcoding a unique avifauna: An important tool for evolution, systematics and conservation. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- RAWGraphs Team. How to Make An Alluvial Diagram. Available online: https://rawgraphs.io/learning/how-to-make-an-alluvial-diagram/ (accessed on 16 September 2019).
- Gyawali, N.; Taylor-Robinson, A.W.; Bradbury, R.S.; Huggins, D.W.; Hugo, L.E.; Lowry, K.; Aaskov, J.G. Identification of the source of blood meals in mosquitoes collected from north-eastern Australia. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, T.; Aihara, N.; Maeda, K.; Shinzato, C.; Koyanagi, R.; Kobayashi, H.; Yamahira, K. Bloodmeal host identification with inferences to feeding habits of a fish-fed mosquito, Aedes baisasi. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Hing, C.T.; Fornace, K.; Ferguson, H.M. Evaluation of resting traps to examine the behaviour and ecology of mosquito vectors in an area of rapidly changing land use in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, T.; Miyagi, I.; Tamashiro, M. Blood meal identification and feeding habits of Uranotaenia species collected in the Ryukyu archipelago. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2014, 30, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchgatter, K.; Tubaki, R.M.; Dos Malafronte, R.S.; Alves, I.C.; De Lima, G.F.M.C.; De Guimarães, L.O.; De Zampaulo, R.A.; Wunderlich, G. Anopheles (Kerteszia) cruzii (Diptera: Culicidae) em área peridomiciliar durante transmissão de malária assintomática na Mata Atlântica: Identificação molecular das fontes de repasto sanguíneo indica humanos como hospedeiros intermediários primários. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2014, 56, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abella-Medrano, C.A.; Ibáñez-Bernal, S.; Carbó-Ramírez, P.; Santiago-Alarcon, D. Blood-meal preferences and avian malaria detection in mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) captured at different land use types within a neotropical montane cloud forest matrix. Parasitol. Int. 2018, 67, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonschot, P.F.M.; Besse-Lototskaya, A.A. Flight distance of mosquitoes (Culicidae): A metadata analysis to support the management of barrier zones around rewetted and newly constructed wetlands. Limnologica 2014, 45, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luskin, M.S.; Ke, A. Bearded pig Sus barbatus (Müller, 1838). In Ecology, Conservation and Management of Wild Pigs and Peccaries; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Keuling, O.; Podgórski, T.; Monaco, A.; Melletti, M.; Merta, D.; Albrycht, M.; Genov, P.V.; Gethöffer, F.; Vetter, S.G.; Jori, F.; et al. Eurasian wild boar Sus scrofa (Linnaeus, 1758). In Ecology, Conservation and Management of Wild Pigs and Peccaries; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 202–233. [Google Scholar]
- Philip Samuel, P.; Arunachalam, N.; Hiriyan, J.; Tyagi, B.K. Host feeding pattern of Japanese encephalitis virus vector mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) from Kuttanadu, Kerala, India. J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, A.; Egizi, A.; Fonseca, D.M.; Unlu, I.; Crepeau, T.; Healy, S.P.; Gaugler, R. Comparative host feeding patterns of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus, in urban and suburban Northeastern USA and implications for disease transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, L.E.; Holderman, C.J.; Blosser, E.M.; Gillett-Kaufman, J.L.; Kawahara, A.Y.; Kaufman, P.E.; Burkett-Cadena, N.D. Identification of uranotaenia sapphirina as a specialist of annelids broadens known mosquito host use patterns. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blosser, E.M.; Lord, C.C.; Stenn, T.; Acevedo, C.; Hassan, H.K.; Reeves, L.E.; Unnasch, T.R.; Burkett-Cadena, N.D. Environmental drivers of seasonal patterns of host utilization by Culiseta melanura (Diptera: Culicidae) in Florida. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshaghi, M.A.; Chavshin, A.R.; Vatandoost, H.; Yaaghoobi, F.; Mohtarami, F.; Noorjah, N. Effects of post-ingestion and physical conditions on PCR amplification of host blood meal DNA in mosquitoes. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 112, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, L.E.; Holderman, C.J.; Gillett-Kaufman, J.L.; Kawahara, A.Y.; Kaufman, P.E. Maintenance of host DNA integrity in field-preserved mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) blood meals for identification by DNA barcoding. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Ruiz, S.; Soriguer, R.; Figuerola, J. Effect of blood meal digestion and DNA extraction protocol on the success of blood meal source determination in the malaria vector Anopheles atroparvus. Malar. J. 2013, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukabana, W.R.; Takken, W.; Seda, P.; Killeen, G.F.; Hawley, W.A.; Knols, B.G.J. Extent of digestion affects the success of amplifying human DNA from blood meals of Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2002, 92, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Sinka, M.E.; Duda, K.A.; Mylne, A.Q.N.; Shearer, F.M.; Barker, C.M.; Moore, C.G.; Carvalho, R.G.; Coelho, G.E.; Van Bortel, W.; et al. The global distribution of the arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus. Elife 2015, 4, e08347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonizzoni, M.; Gasperi, G.; Chen, X.; James, A.A. The invasive mosquito species Aedes albopictus: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Trends Parasitol. 2013, 29, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kek, R.; Hapuarachchi, H.C.; Chung, C.-Y.; Humaidi, M.B.; Razak, M.A.B.A.; Chiang, S.; Lee, C.; Tan, C.-H.; Yap, G.; Chong, C.-S.; et al. Feeding host range of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) demonstrates its opportunistic host-seeking behavior in rural Singapore. J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponlawat, A.; Harrington, L.C. Blood feeding patterns of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in Thailand. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, A.; Shriram, A.N.; Sunish, I.P.; Vidhya, P.T. Host-feeding pattern of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) in heterogeneous landscapes of South Andaman, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 3539–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaklang, S.; Kittayapong, P. Species composition and blood meal analysis of mosquitoes collected from a tourist island, Koh Chang, Thailand. J. Vector Ecol. 2014, 39, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucharit, S.; Surathin, K.; Shrestha, S.R. Vectors of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV): Species complexes of the vectors. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1989, 20, 611–621. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Hurk, A.F.; Ritchie, S.A.; Mackenzie, J.S. Ecology and geographical expansion of Japanese encephalitis virus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2009, 54, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendell, P.J.E. Japanese encephalitis in Sarawak: Studies on mosquito behaviour in a land Dayak village. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1970, 64, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancey, C.; Grinev, A.; Volkova, E.; Rios, M. The global ecology and epidemiology of west nile virus. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 376230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajollahi, A.; Fonseca, D.M.; Kramer, L.D.; Marm Kilpatrick, A. “Bird biting” mosquitoes and human disease: A review of the role of Culex pipiens complex mosquitoes in epidemiology. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hurk, A.F.; Nisbet, D.J.; Johansen, C.A.; Foley, P.N.; Ritchie, S.A.; Mackenzie, J.S. Japanese encephalitis on Badu Island, Australia: The first isojation of Japanese encephalitis virus from Culex gelidus in the Australasian region and the role of mosquito host-feeding patterns in virus transmission cycles. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 95, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatov, S. Little pigeons can carry great messages: Potential distribution and ecology of Uranotaenia (Pseudoficalbia) unguiculata Edwards, 1913 (Diptera: Culicidae), a lesser-known mosquito species from the Western Palaearctic. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinert, J.F.; Harbach, R.E.; Kitching, I.J. Phylogeny and classification of Aedini (Diptera: Culicidae), based on morphological characters of all life stages. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2004, 142, 289–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, T.N.S.T.; Kassim, N.F.A.; Rahman, A.A.; Yahya, K.; Webb, C.E. Day biting habits of mosquitoes associated with mangrove forests in Kedah, Malaysia. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbach, R.E. Mosquito Taxonomic Inventory, Culcidae Classification, Verrallina. Available online: http://mosquito-taxonomic-inventory.info/simpletaxonomy/term/6158 (accessed on 3 October 2019).
- Rajavel, A.R.; Natarajan, R.; Munirathinam, A.; Vaidyanathan, K. The larval habitat of Verrallina (Verrallina) lugubris and chaetotaxy of field-collected larvae. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2005, 21, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, J.A.L.; Kay, B.H.; Ryan, P.A. Role of Verrallina funerea (Diptera: Culicidae) in transmission of Barmah forest virus and Ross River virus in coastal areas of Eastern Australia. J. Med. Entomol. 2006, 43, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.E.; Doggett, S.L.; Ritchie, S.A.; Russell, R.C. Vector competence of three Australian mosquitoes, Verrallina carmenti, Verraullina lineata, and Mansonia septempunctata (Diptera: Culicidae), for Ross River virus. J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 737–740. [Google Scholar]
- Harbach, R.E. Mosquito Taxonomic Inventory. Available online: http://mosquito-taxonomic-inventory.info/ (accessed on 15 September 2019).
- International Union for Conservation of Nature the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: http://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Tessler, M.; Weiskopf, S.R.; Berniker, L.; Hersch, R.; Mccarthy, K.P.; Yu, D.W.; Siddall, M.E. Bloodlines: Mammals, leeches, and conservation in southern Asia. Syst. Biodivers. 2018, 16, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, A.; De Thoisy, B.; Catzeflis, F.; Valière, S.; Bañuls, A.L.; Murienne, J. iDNA screening: Disease vectors as vertebrate samplers. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6478–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egizi, A.; Martinsen, E.S.; Vuong, H.; Zimmerman, K.I.; Faraji, A.; Fonseca, D.M. Using bloodmeal analysis to assess disease risk to wildlife at the new northern limit of a mosquito species. Ecohealth 2018, 15, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriven, S.A.; Gillespie, G.R.; Laimun, S.; Goossens, B. Edge effects of oil palm plantations on tropical anuran communities in Borneo. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 220, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twining, J.P.; Bernard, H.; Ewers, R.M. Increasing land-use intensity reverses the relative occupancy of two quadrupedal scavengers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheyne, S.M.; Sastramidjaja, W.J.; Rayadin, Y.; Macdonald, D.W. Mammalian communities as indicators of disturbance across Indonesian Borneo. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 7, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, F.M.; Manin, B.O.; Cooper, A.; Daim, S.; Homathevi, R.; Jelip, J.; Husin, T.; Chua, T.H. Vector compositions change across forested to deforested ecotones in emerging areas of zoonotic malaria transmission in Malaysia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Host | Common Name | Aedes | Anopheles | Armigeres | Culex | Culicidae | Mansonia | Topomyia | Tripteroides | Uranotaenia | Aedini |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphibian | 1% | 63% | |||||||||
| Hylarana spp. | Golden-backed frog | 1 | |||||||||
| Leptobrachium hendricksoni | Spotted litter frog | 3 | |||||||||
| Limnonectes spp. | Forked-tongued frog | 6 | |||||||||
| Rana spp. | Brown frog | 1 | |||||||||
| Avian | 32% | 13% | |||||||||
| Ketupa ketupu | Buffy fish owl | 1 | |||||||||
| Fringillidae | Finches | 1 | |||||||||
| Gallus gallus | Red jungle fowl | 12 | |||||||||
| Macronous spp. | Pin-stripedtit-babbler | 1 | |||||||||
| Pitta nympha | Fairy pitta | 4 | |||||||||
| Remiz spp. | Eurasian pendulines | 2 | |||||||||
| Streptopelia chinensis | Spotted dove | 1 | |||||||||
| Mammal | 100% | 100% | 100% | 52% | 100% | 100% | 5% | 100% | |||
| Canis lupus familiaris | Domestic dog | 2 | |||||||||
| Cephalopachus bancanus | Horsfields tarsier | 1 | |||||||||
| Cynocephalus variegatus | Malayan colugo | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Homo sapiens | Human | 12 | 10 | 1 | 16 | ||||||
| Muntiacus muntjak | Barking deer | 1 | |||||||||
| Rattus tiomanicus | Malaysian field rat | 1 | |||||||||
| Sus barbatus | Bornean bearded pig | 1 | 5 | 1 | |||||||
| Sus scrofa | Wild boar | 3 | 12 | ||||||||
| Tragulus spp | Mouse deer | 1 | |||||||||
| Reptile | 15% | 100% | 100% | 19% | |||||||
| Agamidae | Dragon lizard | 4 | 1 | ||||||||
| Draco spp. | Flying lizard | 2 | 1 | ||||||||
| Scincidae | Skink | 3 | |||||||||
| Varanus salvator | Water monitor | 3 | |||||||||
| TOTALS | 16 | 1 | 1 | 62 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 16 |
| Site ID | Mosquito Taxa | Host Taxa | Number Bloodmeals Identified |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Built-Up | |||
| U_009 | Culex quinquefasciatus | Gallus gallus | 1 |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | Streptopelia chinensis | 1 | |
| Rural Built-Up | |||
| R_015 | Culex gelidus | Homo sapiens | 1 |
| Culex gelidus | Sus barbatus | 2 | |
| Culex gelidus | Sus scrofa | 3 | |
| Culex tritaeniorhynchus | Homo sapiens | 1 | |
| Culex tritaeniorhynchus | Sus barbatus | 1 | |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | Sus scrofa | 1 | |
| Culex species | Gallus gallus | 2 | |
| Culex species | Homo sapiens | 3 | |
| Culex species | Hylarana species | 1 | |
| Culex species | Rattus tiomanicus | 1 | |
| Culex species | Sus barbatus | 2 | |
| Culex species | Sus scrofa | 4 | |
| R_001 | Culex quinquefasciatus | Gallus gallus | 5 |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | Sus scrofa | 1 | |
| R_013 | Aedes albopictus | Sus scrofa | 2 |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | Sus scrofa | 1 | |
| Durian Farm | |||
| Ag_017 | Culex species | Ketupa ketupu | 1 |
| Culex species | Homo sapiens | 1 | |
| Secondary Forest | |||
| SF_017 | Culex species | Draco species | 1 |
| Culex species | Pitta nympha | 2 | |
| F_123 | Uranotaenia species | Leptobrachium hendricksoni | 1 |
| Uranotaenia species | Scincidae family | 1 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Young, K.I.; Medwid, J.T.; Azar, S.R.; Huff, R.M.; Drumm, H.; Coffey, L.L.; Pitts, R.J.; Buenemann, M.; Vasilakis, N.; Perera, D.; et al. Identification of Mosquito Bloodmeals Collected in Diverse Habitats in Malaysian Borneo Using COI Barcoding. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020051
Young KI, Medwid JT, Azar SR, Huff RM, Drumm H, Coffey LL, Pitts RJ, Buenemann M, Vasilakis N, Perera D, et al. Identification of Mosquito Bloodmeals Collected in Diverse Habitats in Malaysian Borneo Using COI Barcoding. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2020; 5(2):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020051
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoung, Katherine I., Joseph T. Medwid, Sasha R. Azar, Robert M. Huff, Hannah Drumm, Lark L. Coffey, R. Jason Pitts, Michaela Buenemann, Nikos Vasilakis, David Perera, and et al. 2020. "Identification of Mosquito Bloodmeals Collected in Diverse Habitats in Malaysian Borneo Using COI Barcoding" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 5, no. 2: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020051
APA StyleYoung, K. I., Medwid, J. T., Azar, S. R., Huff, R. M., Drumm, H., Coffey, L. L., Pitts, R. J., Buenemann, M., Vasilakis, N., Perera, D., & Hanley, K. A. (2020). Identification of Mosquito Bloodmeals Collected in Diverse Habitats in Malaysian Borneo Using COI Barcoding. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 5(2), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020051






