History, Rats, Fleas, and Opossums: The Ascendency of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States, 1910–1944
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Presentation of Flea-Borne Typhus
3. The Vectors of Murine Typhus
4. The Reservoirs
5. The Epidemiology and Ecology of Flea-Borne Typhus is Deduced
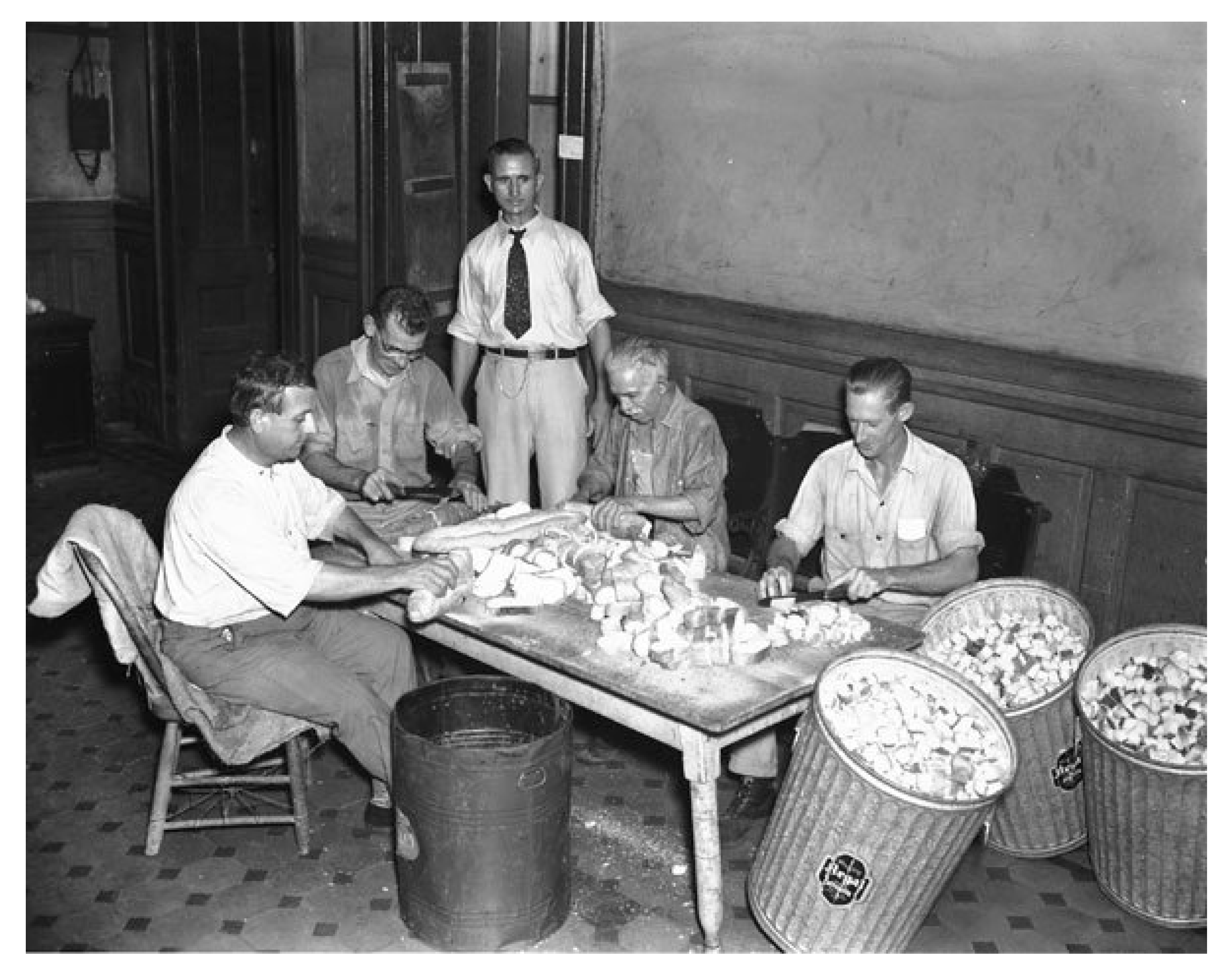
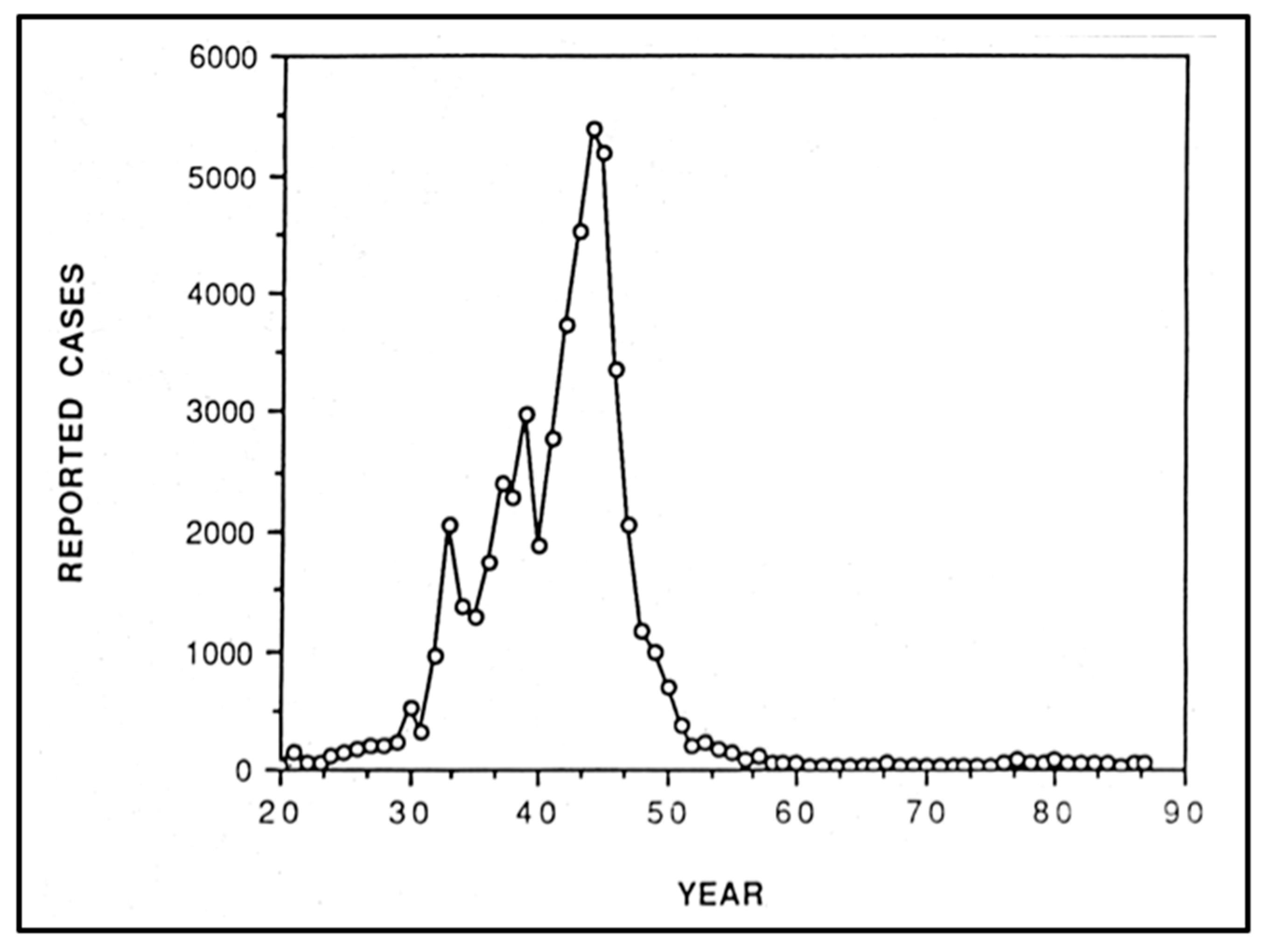
6. The Increasing Incidence of Flea-Borne Typhus and Initial Efforts at Control: 1930–1944
7. Factors in the Rise of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States 1913 to 1944
8. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Image Credits
References
- Azad, A.F. Epidemiology of murine typhus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1990, 35, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.D.; Banajee, K.H.; Foil, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Transmission mechanisms of an emerging insect-borne rickettsial pathogen. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.F.; Radulovic, S.; Higgins, J.A.; Noden, B.H.; Troyer, J.M. Flea-borne rickettsioses: Ecologic considerations. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civen, R.; Ngo, V. Murine typhus: An unrecognized suburban vector-borne disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smadel, J.E. Status of the rickettsioses in the United States. Ann. Intern. Med. 1959, 51, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DeBuono, B.A. Milestones in Public Health. Accomplishments in Public Health over the Last 100 Years; Pfizer Global Pharmaceuticals: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.W.; Warren, C. Silent Victories. The History and Practice of Public Health in Twentieth-Century America; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dumler, J.S.; Taylor, J.P.; Walker, D.H. Clinical and laboratory features of murine typhus in South Texas, 1980–1987. JAMA 1991, 266, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, K.O.; Evert, N.; Mayes, B.; Fonken, E.; Erickson, T.; Garcia, M.N.; Sidwa, T. Typhus group rickettsiosis, Texas, USA, 2003–2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Dept of Public Health, Human Flea-Borne Typhus Cases in California (2001–2019). Available online: https://www.10.CDPH.ca.gov/Programs/CID/DCDC/10.CDPH%20Document%20Library/Flea-borneTyphusCaseCounts.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2019).
- Zinsser, H. Rats, Lice, and History; Random House: New York, NY, USA, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, T.E. Murine typhus fever: Its clinical and biological similarity to epidemic typhus. In Biology of Rickettsial Diseases; Walker, D.H., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; pp. 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Reece, C.D. Typhus fever in Texas. Tex. State J. Med. 1934, 30, 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, T.E. Endemic (murine) typhus fever: Symptomatology. In Rickettsial Diseases of Man; Moulton, F.R., Ed.; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 1948; pp. 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Bernabeu-Wittel, M.; Villanueva-Marcos, J.L.; de Alarcón-González, A.; Pachón, J. Septic shock and multiorgan failure in murine typhus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1998, 17, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, M.S. Endemic typhus fever in Georgia. J. Med. Assoc. Ga. 1935, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Fergie, J. Murine typhus in South Texas children: An 18-year review. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsioutis, C.; Zafeiri, M.; Avramopoulos, A.; Prousali, E.; Miligkos, M.; Karageorgos, S.A. Clinical and laboratory characteristics, epidemiology, and outcomes of murine typhus: A systematic review. Acta Trop. 2017, 166, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjemian, J.; Parks, S.; McElroy, K.; Campbell, J.; Eremeeva, M.E.; Nicholson, W.L.; McQuiston, J.; Taylor, J. Murine typhus in Austin, Texas, USA, 2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, Z.; Kallumadanda, S.; Wang, F.; Hemmige, V.; Musher, D. Acute febrile illness and complications due to murine typhus, Texas, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteford, S.F.; Taylor, J.P.; Dumler, J.S. Clinical, laboratory, and epidemiologic features of murine typhus in 97 Texas children. Arch. Pediatrics Adolesc. Med. 2001, 155, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieracci, E.G.; Evert, N.; Drexler, N.A.; Mayes, B.; Vilcins, I.; Huang, P.; Campbell, J.; Behravesh, C.B.; Paddock, C.D. Fatal flea-borne typhus in Texas: A retrospective case series, 1985–2015. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chueng, T.A.; Koch, K.R.; Anstead, G.M.; Agarwal, A.N.; Dayton, C.L. Case report: Early doxycycline therapy for potential rickettsiosis in critically ill patients in flea-borne typhus-endemic areas. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binford, C.H.; Ecker, H.D. Endemic (murine) typhus; report of autopsy findings in three cases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1947, 17, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.H.; Parks, F.M.; Betz, T.G.; Taylor, J.P.; Muehlberger, J.W. Histopathology and immunohistologic demonstration of the distribution of Rickettsia typhi in fatal murine typhus. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1989, 91, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, B.E.; Thi, M.; Alkhateb, R.; Agarwal, A.; Sharkey, F.E.; Dayton, C.; Anstead, G.M. Case report: Fulminant murine typhus presenting with status epilepticus and multi-organ failure: An autopsy case and a review of the neurologic presentations of murine typhus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, R.J.; Gage, K.L. Transmission of flea-borne zoonotic agents. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2012, 57, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traub, R.; Wisseman, C.L.; Farhang-Azad, A. The ecology of murine typhus-a critical review. Trop. Dis. Bull. 1978, 75, 237–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, J.J.; Ammerman, N.C.; Beier-Sexton, M.; Sobral, B.S.; Azad, A.F. Louse- and flea-borne rickettsioses: Biologic and genomic analyses. Vet. Res. 2009, 40, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumreich, A.S.; Koepke, J.A. Epidemiological significance of seasonal variations in rodent-ectoparasite distribution. Public Health Rep. 1945, 60, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, E.L.; Ingraham, S.C., II. A study of murine typhus in Coffee County, Alabama. Public Health Rep. 1947, 62, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C. A limited rat flea survey of Savannah, Georgia. Public Health Rep. 1931, 46, 574–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasseltine, H.E. Rat-flea survey of the port of Norfolk, Va. Public Health Rep. 1929, 44, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.O. Entomological background of the distribution of murine typhus and murine plague in the United States. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1951, 31, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, H.D.; Wiseman, J.S. Fleas of Public Health Importance and Their Control; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1962. Available online: www.cdc_7681_DS1.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2018).
- Lang, J.D. Fleas. In Arthropods of Public Health Importance in California; Meyer, R.P., Madon, M.B., Eds.; Mosquito and Vector Control Association of California: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, A.F.; Traub, R. Transmission of murine typhus rickettsia by Leptopsylla segnis (Siphonaptera: Leptopsyllidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1987, 24, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.F. Relationship to vector biology and epidemiology of louse- and flea-borne rickettsioses. In Biology of Rickettsial Diseases; Walker, D.H., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; pp. 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, A.F.; Traub, R. Experimental transmission of murine typhus by Xenopsylla cheopis flea bites. Med. Vet. Entomol. 1989, 3, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, T.E. A historical account of the rickettsial diseases with a discussion of unsolved problems. J. Infect. Dis. 1973, 127, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rust, M.K.; Dryden, M.W. The biology, ecology, and management of the cat flea. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1997, 42, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, C.O.; Smith, W.W. Eradication of murine typhus fever in a rural area: Preliminary report. Bull. WHO 1957, 16, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Worth, C.B.; Rickard, E.R. Transmission of murine typhus in roof rats in the absence of ectoparasites. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1951, 31, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, N.J.; Seddon, J.M.; Šlapeta, J.; Wells, K. Parasite spread at the domestic animal-wildlife interface: Anthropogenic habitat use, phylogeny and body mass drive risk of cat and dog flea (Ctenocephalides spp.) infestation in wild mammals. Parasites Vectors 2018, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.E. Observations on rat ectoparasites and typhus fever in San Antonio, Texas. Public Health Rep. 1951, 66, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, F.M. Species of fleas collected in states west of 102D meridian and their relation the dissemination of plague. Public Health Rep. 1943, 58, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, R.E.; Workman, W.G.; Ceder, E.T.; Badger, L.F.; Rumreich, A. Typhus fever: The multiplication of the virus of endemic typhus in the rat flea Xenopsylla cheopis. Public Health Rep. 1932, 47, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedincamp, J., Jr.; Foil, L.D. Vertical transmission of Rickettsia felis in the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis Bouche). J. Vector Ecol. 2002, 27, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Parola, P. Rickettsia felis: From a rare disease in the USA to a common cause of fever in sub-Saharan Africa. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, R.E.; Ceder, E.T.; Workman, W.G.; Rumreich, A.; Badger, L.F. Typhus fever. Transmission of endemic typhus by rubbing either crushed infected fleas or infected flea feces into wounds. Public Health Rep. 1932, 47, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, E.A. What health officers can do to promote rat extermination. Am. J. Public Health 1921, 11, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Davis, W.B.; Schmidly, D.J. The Mammals of Texas; University of Texas Press: Austin, TX, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, J. The introduction and spread of house rats in the United States. J. Mammal. 1927, 8, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.E. Roof rats. In The Handbook: Prevention and Control of Wildlife Damage 6; Hygnstrom, S.E., Timm, R.M., Larson, G.E., Eds.; Internet Center for Wildlife Damage Management, University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point: Stevens Point, WI, USA, 1994; Available online: http://icwdm.org/handbook/rodents/RoofRats.asp (accessed on 6 June 2015).
- Ecke, D.H. An invasion of Norway rats in southwest Georgia. J. Mammal. 1954, 35, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boston, R.J. Public health engineering phases of murine typhus control. Am. J. Public Health 1940, 30, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckinger, D.L.; Dougherty, M.S. Endemic typhus fever in Georgia. J. Med. Assoc. Ga. 1935, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Morlan, H.B.; Utterback, B.C.; Dent, J.E. Domestic Rats in Relation to Murine Typhus Control, Public Health Monograph No. 5; Federal Security Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1953; pp. 3–20.
- Davis, D.E. The use of DDT to control murine typhus fever in San Antonio, TX. Public Health Rep. 1947, 62, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.E. Notes on commensal rats in Lavaca County, Texas. J. Mammal. 1947, 28, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, J.M. Rats in urban America. Public Health Rep. 1969, 84, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.G.; Sacci, J.B.; Schriefer, M.E.; Andersen, E.M.; Fujioka, K.K.; Sorvillo, F.J.; Barr, A.R.; Azad, A.F. Typhus and typhus-like rickettsiae associated with opossums and their fleas in Los Angeles County, California. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boostrom, A.; Beier, M.S.; Macaluso, J.A.; Macaluso, K.R.; Sprenger, D.; Hayes, J.; Radulovic, S.; Azad, A.F. Geographic association of Rickettsia felis-infected opossums with human murine typhus, Texas. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, W.H.; Emmons, R.W.; Brooks, J.E. The changing ecology of murine (endemic) typhus in Southern California. Am. J. Trop Med. Hyg. 1970, 19, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.W. The house mouse and murine typhus in Mississippi. Public Health Rep. 1954, 69, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, G.E.; Wilson, N.; Tomich, P.Q. Ectoparasites of the Hawaiian Islands. I. Siphonoptera. Contrib. Am. Entomol. Inst. (Ann. Arbor) 1972, 8, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard, W.W. On typhus fever, which occurred at Philadelphia in the spring and summer of 1836; illustrated by clinical observations at the Philadelphia Hospital; showing distinction between this form of disease and dothinenteritis, or the typhoid fever, with alteration of the follicles of the small intestine. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1836, 19, 289–322. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, R.E. Typhus fever. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1943, 27, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, C.; Comte, C.; Conseil, E. Experimental transmission of the exanthematic typhus through body lice. Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. 1909, 149, 486–489. [Google Scholar]
- Brill, N. An acute infectious disease of unknown origin: A clinical study based on 221 cases. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1910, 139, 482–502. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.F.; Goldberger, J. The relation of so-called Brill’s disease to typhus fever. Public Health Rep. 1912, 27, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinsser, H.; Castañeda, M.R. On the isolation from a case of Brill’s disease of a typhus strain resembling the European type. N. Engl. J. Med. 1933, 209, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, E. History of rickettsiology. In Biology of Rickettsial Diseases; Walker, D.H., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; pp. 16–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jellison, W.L. Fleas and disease. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1959, 4, 389–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.L.; Rao, K.N. Typhus fevers in Kashmir State. Part II. Murine typhus. Indian J. Med. Res. 1951, 39, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paullin, J.E. Typhus fever with a report of cases. South. Med. J. 1913, 6, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sellers, T.F. Recent developments in the knowledge of endemic typhus. J. Med. Assoc. Ga. 1935, 24, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, L.B.; Allan, W. Typhus fever: A report of four cases. South. Med. J. 1914, 7, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McNeil, H.L. Endemic typhus fever in South Texas. Tex. State J. Med. 1916, 12, 188–191. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, H.C. Typhus fever. Milit. Surg. 1916, 39, 474–491. [Google Scholar]
- White, P.C., Jr. A brief historical review of murine typhus in Virginia and the United States. Va. Med. Mon. 1970, 97, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, M.E.; Hurst, J.W. James Edgar Paullin: Internist to Franklin Delano Roosevelt, oslerian, and forgotten leader of American medicine. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, J. Notable Contributions to Medical Research by Public Health Service Scientists; U.S. Public Health Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1960. Available online: http://history.nih.gov/research/downloads/Notable_Cont_Med_Research.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2016).
- Phear, A.G. Medical experiences in Macedonia and the Caucasus. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1920, 13, 57–100. [Google Scholar]
- Neill, M.H. Experimental typhus fever in guinea pigs. A description of scrotal lesion in guinea pigs infected with Mexican typhus. Public Health Rep. 1917, 32, 1105–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooser, H. Experiments relating to pathology and etiology of Mexican typhus (tabardillo). I. Clinical course and pathologic anatomy of tabardillo in guinea pigs. J. Infect. Dis. 1928, 43, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahon, N. Selected Papers on the Pathogenic Rickettsiae; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Hone, F.S. A series of cases closely resembling typhus fever. Med. J. Aust. 1922, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.C. The United States Public Health Service 1798–1950; Commissioned Officers Association of the US Public Health Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, W.B., Jr.; Wood, M.L. Kenneth Fuller Maxcy, 1889–1966; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1971; Available online: www.nasonline.org/publications/biographical-memoirs/memoir-pdfs/maxcy-kenneth.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2015).
- Maxcy, K.F.; Havens, L.C. A series of cases giving a positive Weil-Felix reaction. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1923, 3, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxcy, K.F. Typhus fever in the United States. Public Health Rep. 1929, 44, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, C.G.; Maxcy, K.F. Mild typhus (Brill’s Disease) in the lower Rio Grande Valley. Public Health Rep. 1925, 40, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, F.; Brown, A.K. Typhus fever along the Rio Grande. Milit. Surg. 1926, 58, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Maxcy, K.F. An epidemiological study of endemic typhus (Brill’s disease) in the southeastern United States. Public Health Rep. 1926, 41, 2967–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxcy, K.F. Clinical observations on endemic typhus (Brill’s Disease) in Southern United States. Public Health Rep. 1926, 41, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilienfeld, A.M.; Lilienfeld, D.E. Foundations of Epidemiology, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.N.; McAlpine, J.G.; Gill, D.G. Endemic typhus in Alabama. Public Health Rep. 1935, 50, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.B.; Woodring, T.V.; Essick, H.C. An outbreak of typhus fever in Nashville, TN. Am. J. Public Health 1943, 31, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.N.; McAlpine, J.G.; Gill, D.G. Endemic typhus. Am. J. Public Health 1939, 24, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gersten, T. Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency. MedlinePlus. Available online: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000528.htm (accessed on 20 September 2015).
- Walker, D.H. The role of host factors in the severity of spotted fever and typhus rickettsioses. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 590, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitz, J.D. Men of medicine. Louse and flea farms. Postgrad. Med. 1951, 9, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, R.E.; Rumreich, A.; Badger, L.F. Typhus fever: A virus of the typhus type derived from fleas collected from wild rats. Public Health Rep. 1931, 46, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, R.E.; Rumreich, A.S.; Badger, L.F. The typhus-Rocky Mountain spotted fever group in the United States. JAMA 1931, 97, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumreich, A. The typhus and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever group: Developments in epidemiological and clinical considerations. JAMA 1933, 100, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooser, H.; Ruiz Casteñada, M.; Zinsser, H. Rats as carriers of Mexican typhus fever. JAMA 1931, 97, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, R.E.; Workman, W.G.; Rumreich, A.S. Endemic typhus fever virus recovered from wild rat trapped at typhus focus in the United States. Public Health Rep. 1932, 47, 2370–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, H.A. Endemic typhus fever. Rat flea as a possible vector. JAMA 1931, 97, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, R.E.; Workman, W.G.; Badger, L.F.; Rumreich, A. Typhus fever: The experimental transmission of endemic typhus fever of the United States by the rat flea Ceratophyllus fasciatus. Public Health Rep. 1932, 47, 931–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumreich, A.; Dyer, R.E.; Badger, L.F. The Typhus-Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever group: An epidemiological and clinical study in the eastern and southeastern states. Public Health Rep. 1931, 46, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, R.E.; Ceder, E.T.; Rumreich, A.; Badger, L.F. Experimental transmission of endemic typhus with rat fleas, Xenopsylla cheopsis. Public Health Rep. 1931, 46, 1869–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooser, H.; Ruiz Castañeda, M.; Zinsser, H. The transmission of the virus of Mexican typhus from rat to rat by Polyplax spinulosus. J. Exp. Med. 1931, 54, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, W.E.; Shelmire, B. Some observations on tropical rat mites and endemic typhus. J. Parasitol. 1932, 18, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, W.E.; Shelmire, B. Tropical rat mites, Liponyssus bacoti Hirst, vectors of endemic typhus. JAMA 1931, 97, 1506–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandtmann, R.W.; Eben, D.J. A survey of typhus in rats and rat ectoparasites in Galveston, Texas. Tex. Rep. Biol. Med. 1953, 11, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, K.H. Isolation of typhus rickettsiae from rat mites during an epidemic in an orphanage. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1941, 48, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.W. Populations of the most abundant ectoparasites as related to prevalence of typhus antibodies of farm rats in an endemic murine typhus region. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1957, 6, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceder, E.T.; Dyer, R.E.; Rumreich, A.; Badger, L.F. Typhus fever: Typhus virus in feces of infected fleas (Xenopsylla cheopis) and duration of infectivity of fleas. Public Health Rep. 1931, 46, 3103–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinsser, H. Varieties of typhus virus and the epidemiology of the American form of European typhus fever (Brill’s disease). Am. J. Hyg. 1934, 20, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, W.; Mooser, H. Ein weiterer Fall von Brill-Zinsserscher Krankheit in Zurich. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 1952, 82, 493–495. [Google Scholar]
- Mooser, H.; Ruiz Castañeda, M. The multiplication of the virus of Mexican typhus fever in fleas. J. Exp. Med. 1932, 55, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brigham, G.D. Susceptibility of animals to endemic typhus fever. Public Health Rep. 1937, 52, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, G.D.; Dyer, R.E. Endemic typhus fever in native rodents. JAMA 1938, 110, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlan, H.B.; Hill, E.L.; Schubert, J.H. Serological survey for murine typhus infection in southwest Georgia animals. Public Health Rep. 1950, 65, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigham, G.D. Two strains of typhus (endemic) virus isolated from naturally infected chicken fleas. Public Health Rep. 1941, 56, 1803–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, J.V.; Bohls, S.W.; Thurman, D.C., Jr.; McGregor, T. Probable role of the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis, in transmission of murine typhus. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1944, 24, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleney, H.E. Recent extension of endemic typhus fever in the southern United States. Am. J. Public Health 1941, 31, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, G.B. The emergence of the new South 1913–1945. In A History of the South; Stephenson, W.H., Coulter, E.M., Eds.; Louisiana State University Press: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1967; Volume X. [Google Scholar]
- Bohls, S.W. Typhus fever in Texas. South. Med. J. 1935, 28, 1162–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.T. America’s Struggle against Poverty 1900–1980; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- United States Department of Agriculture. Seven Million Rats Die in CWA Typhus-fever Campaign (4-Jun-1934). Available online: www.fws.gov/news/historic/1934/19340604 (accessed on 1 July 2015).
- Bradley, G.H.; Wiley, J.S. The control of murine typhus in the United States. In Rickettsial Diseases of Man; Moulton, F.R., Ed.; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 1948; pp. 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, J.; Chapman, A.A. Typhus-like fever contracted from o’possum fleas. Tex. State Med. J. 1935, 31, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Laurence, A.; Lee, J. Wharf Rats, the Plague, and Public Health. Available online: https://neworleanshistorical.org/items/show/131 (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- Anon. Typhus control combated century old malady. Tex. Health Bull. 1979, 32, 11-A. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, B.M.; Pullen, R.L. Endemic (murine) typhus fever: Clinical observation of 180 cases. Ann. Intern. Med. 1945, 23, 520–536. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, E.S.; Beeson, P.B. Murine typhus fever. Medicine 1946, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.W.; Schulze, W.H.; Ewing, C.L.; Schucker, G.W. Endemic typhus in Baltimore. South. Med. J. 1948, 41, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, C. Typhus fever in Charity Hospital. New Orleans Med. Surg. J. 1942, 95, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Badger, L.F. Endemic typhus in the United States. South. Med. J. 1933, 27, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowdoin, C.D.; Boston, R.J. A preliminary report on the practical epidemiology and control of endemic typhus in Georgia. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1940, 20, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.M.; Link, V.B. The murine typhus fever problem the United States. Pests Their Control 1947, 15, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Long, L.H. Inter-Regional Migration of the Poor: Some Recent Changes; Dept of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. Available online: http://catalog.hathitrust.org/Record/000692925 (accessed on 1 March 2015).
- United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization. Manual of Pest Control for Food Security Reserve Grain Stocks; UNFAO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Eskey, C.R. Murine typhus fever control. Public Health Rep. 1943, 58, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.N.; Brigham, G.D.; Dyer, R.E. Endemic typhus fever in native rodents. JAMA 1938, 110, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Phair, J.J.; Brigham, G.D.; Dyer, R.E. Endemic typhus fever in native rodents. JAMA 1938, 110, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Holsendorf, B.E.; Clark, P.W. The rat and ratproof construction of buildings. Public Health Rep. Suppl. 1937, 131, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Holsendorf, B.E. Rat surveys and rat proofing. Am. J. Public Health 1937, 27, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Texas Dept of Health Bureau of Epidemiology. Reported Morbidity and Mortality in Texas 1986; Texas Dept of Health: Austin, TX, USA, 1987.
- Anon. Typhus fever control unit of the United States Public Health Service. Public Health Rep. 1943, 58, 638–639. [Google Scholar]
- Love, G.J.; Smith, W.W. Murine typhus investigations in southwestern Georgia. Public Health Rep. 1960, 75, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, W.H.; Hines, V.D. Murine typhus fever in Southwest Georgia, January 1945-January 1953. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1954, 3, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banov, L. As I Recall. The Story of the Charleston County Health Department; R. L. Bryan Co.: Colombia, SC, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, E.S.; Schulze, W.H. The Practice of Sanitation, 2nd ed.; Williams and Wilkins Co.: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Bowens, C.V.; Hall, S.A. The organic insecticides. In Insects: The Yearbook in Agriculture; Stefferud, A., Ed.; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1952; pp. 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Symes, C.B.; Muirhead Thompson, R.C.; Busvine, J.R. Insect Control in Public Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Fukami, H.; Nakajima, M. Rotenone and the rotenoids. In Naturally Occurring Pesticides; Jacobson, M., Crosby, D.G., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 71–97. [Google Scholar]
- Schmeltz, I. Nicotine and other tobacco alkaloids. In Naturally Occurring Pesticides; Jacobson, M., Crosby, D.G., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 99–136. [Google Scholar]
- Matheson, R. Medical Entomology; Charles C. Thomas: Springfield, IL, USA, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, C.L. Fumigation deaths as compared with deaths from other poisonous gases. Public Health Rep. 1934, 49, 697–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, A.C. Introduction to Human Parasitology, 5th ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Creel, R.H. Fumigation by cyanide gas. Milit. Surg. 1916, 39, 282–287. [Google Scholar]
- Kinkela, D. DDT and the American Century; University of North Carolina Press: Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cushing, E.C. History of Entomology in World War II; Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, W.S. The role of DDT in controlling insect-borne diseases of man. JAMA 1946, 132, 507–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.B.; Elton, C.; Leslie, P.H.; Ranson, R.M.; Rzoska, J.; Thompson, H.V. Properties of the poisons used in rodent control. In Control of Rats and Mice; Chitty, D., Southern, H.N., Eds.; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1954; Volume 1, pp. 25–146. [Google Scholar]
- Link, V.B.; Mohr, C.O. Rodenticides in bubonic-plague control. Bull. WHO 1953, 9, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, A.G. Bubonic plague: The Black Death. In Plague, Pox, and Pestilence. Disease in History; Kiple, K.F., Ed.; Barnes and Noble Books: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Elton, C. Research on rodent control by the Bureau of Animal Population September 1939 to July 1947. In Control of Rats and Mice; Chitty, D., Ed.; Oxford at the Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1954; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, G.A. Zinc phosphide-a new look at an old rodenticide for field rodents. In Proceedings of the 5th Vertebrate Pest Conference, Fresno, CA, USA, 7–9 March 1972; Marsh, R.E., Ed.; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1972. Paper 16. Available online: http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/vpc5/16 (accessed on 6 March 2016).
- Williams, C.L. The control of murine typhus with DDT. Milit. Surg. 1949, 104, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.C. Rodent control with 1080, ANTU, and other war-developed toxic agents. Am. J. Public Health 1946, 36, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anon. Mobilizing the Home Front: The Role of Wildlife Services during World War II. Available online: www.aphis.usda.gov/wildlife_damage/nwrc/about/history/role_wwII.shtml (accessed on 13 June 2012).
- Ivanov, V.V.; Volgin, V.Y.; Krasnov, A.A.; Lizunov, N.V. Thallium; American Geological Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Radomski, J.L.; Woodard, G. A survey of the present status of red squill as a rodenticide. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 1946, 35, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.E. Relevant characteristics of zinc phosphide as a rodenticide. In Proceedings of the Great Plains Wildlife Damage Control Workshop Proceedings, Rapid City, South Dakota, 28–30 April 1987; Internet Center for Wildlife Damage Management. University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point: Stevens Point, WI, USA, 1987. Available online: http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/gpwdcwp/80/ (accessed on 26 August 2015).
- Dyer, R.E. The control of typhus fever. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1940, 21, 163–183. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, H.D. The changing picture of murine typhus in the United States. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1958, 70, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskey, C.R.; Hemphill, F.M. Relation of reported cases of typhus fever to location, temperature, and precipitation. Public Health Rep. 1948, 63, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, J.S. Recent developments in murine typhus fever control. Am. J. Public Health 1946, 36, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.O.; Good, N.E.; Schubert, J.H. Status of murine typhus infection in domestic rats in the United States, 1952, and relation to infestation by Oriental rat fleas. Am. J. Public Health 1953, 43, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.M. Clinical description and findings in 100 cases. In Typhus Fever in California, 1916–1948, Inclusive; Beck, D.M., van Allen, A., Eds.; California Dept of Public Health: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1950; pp. 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.E.; Pollard, M. Prevalence of typhus complement-fixing antibodies in human serums in San Antonio, Tex. Public Health Rep. 1946, 61, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, E.R.; Riley, E.G. A state-wide survey of typhus fever in Florida. Am. J. Public Health 1948, 38, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Quinby, G.E.; Schubert, J.H. Epidemiologic and serologic appraisal of murine typhus in the United States, 1948–1951. Am. J. Public Health 1953, 43, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, I.L.; Langmuir, A.D. Usefulness of communicable disease reports. Public Health Rep. 1952, 67, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynt, J.W. Dixie’s Forgotten People: The South’s Poor Whites; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, IN, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Mertz, P.E. New Deal Policy and the Southern Rural Poverty; Louisiana State University Press: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, O.E.; Taeuber, C. The Rural People. In The Yearbook of Agriculture; US Dept of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1940; pp. 827–847. [Google Scholar]
- Colean, M.L. American Housing. Problems and Prospects; Twentieth Century Fund: New York, NY, USA, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Leuchtenburg, W.E. Franklin D. Roosevelt and the New Deal, 1932–1940; Harper Collins: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Fite, G.C. Cotton Fields No More. Southern Agriculture 1865–1980; University of Kentucky Press: Lexington, KY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Pillsbury, R.; Orin, K. Atlas of American Agriculture; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Orloski, K.A.; Hayes, E.B.; Campbell, G.L.; Dennis, D.T. Surveillance for Lyme Disease–United States, 1992–1998. MMWR 2000, 49, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Conrad, D.E. The Forgotten Farmers. The Story of Sharecroppers in the New Deal; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, P. Standing at the Crossroads. Southern Life in the Twentieth Century; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, T.D. The Emerging South, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Roland, C.P. The Improbable Era. The South Since World War II; University of Kentucky Press: Lexington, KY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.H. Rodent control methods: Non-chemical and non-lethal chemical. In Rodent Pests and Their Control; Buckle, A.P., Smith, R.H., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1994; pp. 109–125. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfield, D.R. Cotton Fields and Skyscrapers. Southern City and Region, 1607–1980; Louisiana State University Press: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfield, D.R. Promised Land. The South Since 1945; Harlan Davidson: Arlington Heights, IL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, E.F. The southern metropolis 1940–1976. In The City in Southern History. The Growth of Urban Civilization in the South; Brownell, B.A., Goldfield, D.R., Eds.; Kennikat Press: Port Washington, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Passos, J. The people at war: III. Gold rush in the South. Harper’s Magazine, 1 May 1943; 599–606. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, A.E. Journey through Chaos; Harcourt, Brace, and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Anon. Medicine: Typhus time. Time, 9 October 1944; 43. [Google Scholar]
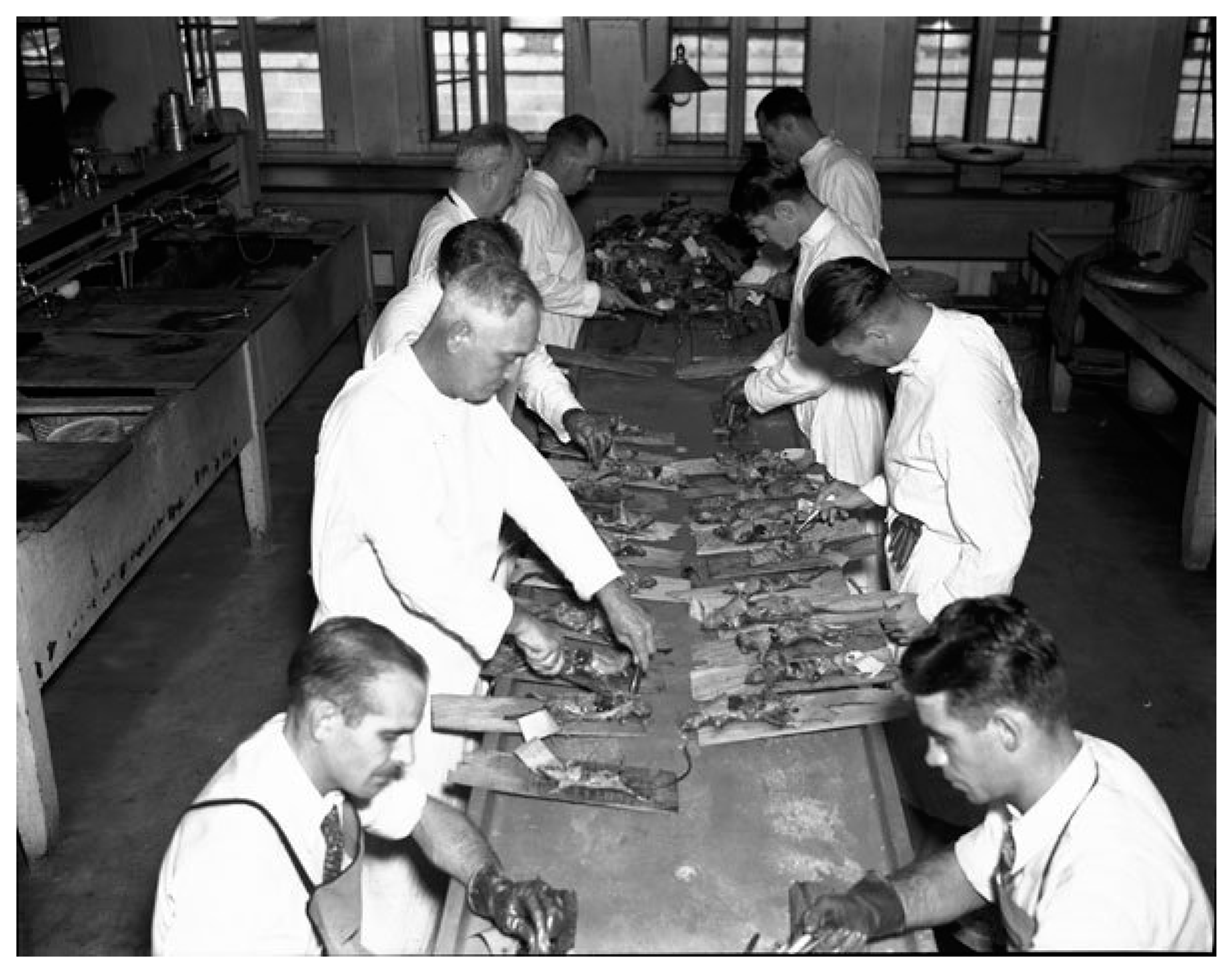
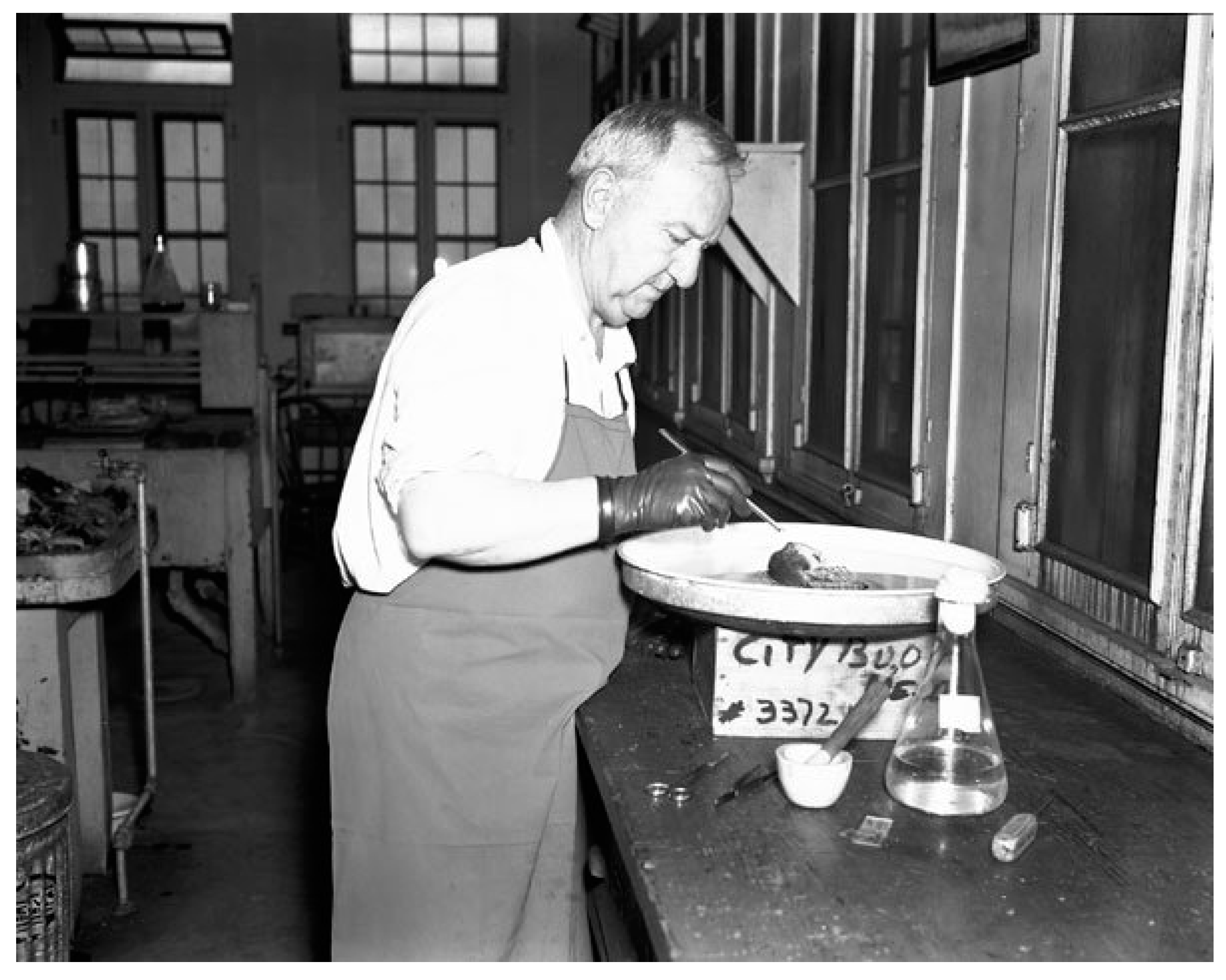










| Complications a |
|---|
| Neurologic: aseptic meningitis, hemiparesis, cerebellitis, facial nerve palsies, seizures, ataxia, altered mental status, transient hearing loss, abducens nerve palsy, neurocognitive deficits, cerebral infarction, encephalopathy, intracranial hemorrhage, brain abscess |
| Ocular: oculoglandular syndrome, retinitis, optic neuritis, uveitis, subconjunctival hemorrhage |
| Pulmonary: pneumonia, pulmonary edema, adult respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary embolism |
| Cardiac: endocarditis, pericarditis, myocarditis, coronary arteritis |
| Gastrointestinal: hepatitis, intestinal pseudo-obstruction, acalculous cholecystitis, pancreatitis |
| Hematologic: hemophagocytic syndrome, hemolysis, bone marrow granulomatosis, splenic infarction, splenic rupture, coagulopathy, venous thrombosis |
| Renal: renal failure |
| Other: parotitis, myositis, suppurative arthritis, leukocytoclastic vasculitis, septic shock, multi-organ failure, death |
| Rank d | State | Cumulative Number of Cases, 1922–1939 | Avg Annual Cases | Avg Pop c 1920, 1930, 1940 | Approx Cumulative Incidence; Cases/ 100,000 Avg Pop | Avg Annual Incidence/ 100,000 Avg Pop |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GA | 6225 | 345.8 | 2,976,020 | 209 | 11.6 |
| 2 | AL | 3751 | 208.4 | 2,609,128 | 144 | 8.0 |
| 3 | TX | 3277 | 182.1 | 5,634,256 | 58.1 | 3.2 |
| 4 | FL | 806 | 44.8 | 1,444,698 | 55.8 | 3.1 |
| 5 | SC | 707 | 39.3 | 1,774,098 | 39.9 | 2.2 |
| 6 | NC | 481 | 26.7 | 3,100,341 | 15.5 | 0.86 |
| 7 | LA | 244 | 13.6 | 2,087,994 | 11.7 | 0.65 |
| 8 | MD | 195 | 10.3 | 1,634,144 | 11.9 | 0.63 |
| 9 | VA | 181 | 10.1 | 2,531,172 | 7.51 | 0.42 |
| 10 | TN | 168 | 9.3 | 2,623,427 | 6.4 | 0.35 |
| 11 | MS | 158 | 8.8 | 1,994,745 | 7.9 | 0.44 |
| 12 | CA | 139 | 7.7 | 5,337,166 | 2.6 | 0.14 |
| Total | 16,332 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anstead, G.M. History, Rats, Fleas, and Opossums: The Ascendency of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States, 1910–1944. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5010037
Anstead GM. History, Rats, Fleas, and Opossums: The Ascendency of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States, 1910–1944. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2020; 5(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnstead, Gregory M. 2020. "History, Rats, Fleas, and Opossums: The Ascendency of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States, 1910–1944" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 5, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5010037
APA StyleAnstead, G. M. (2020). History, Rats, Fleas, and Opossums: The Ascendency of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States, 1910–1944. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 5(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5010037





