The Impact of Funding on Childhood TB Case Detection in Pakistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
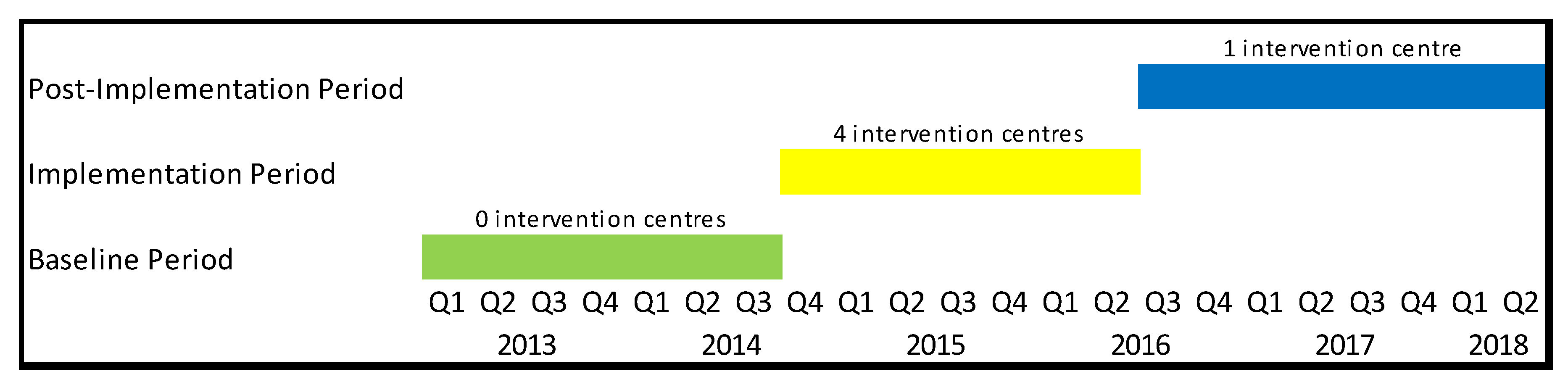
2.1. Setting and Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Analysis
2.4. Ethical Approval
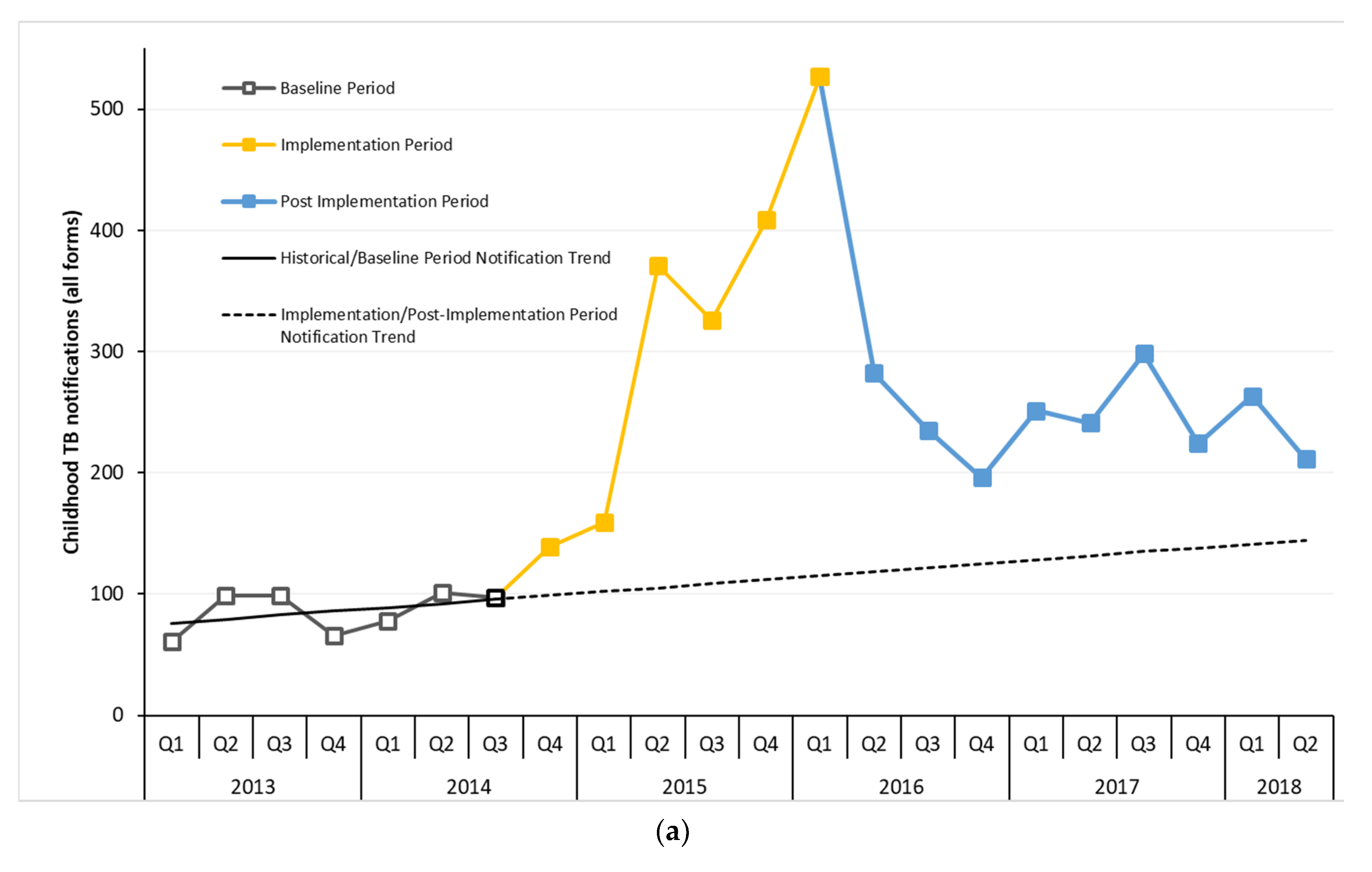
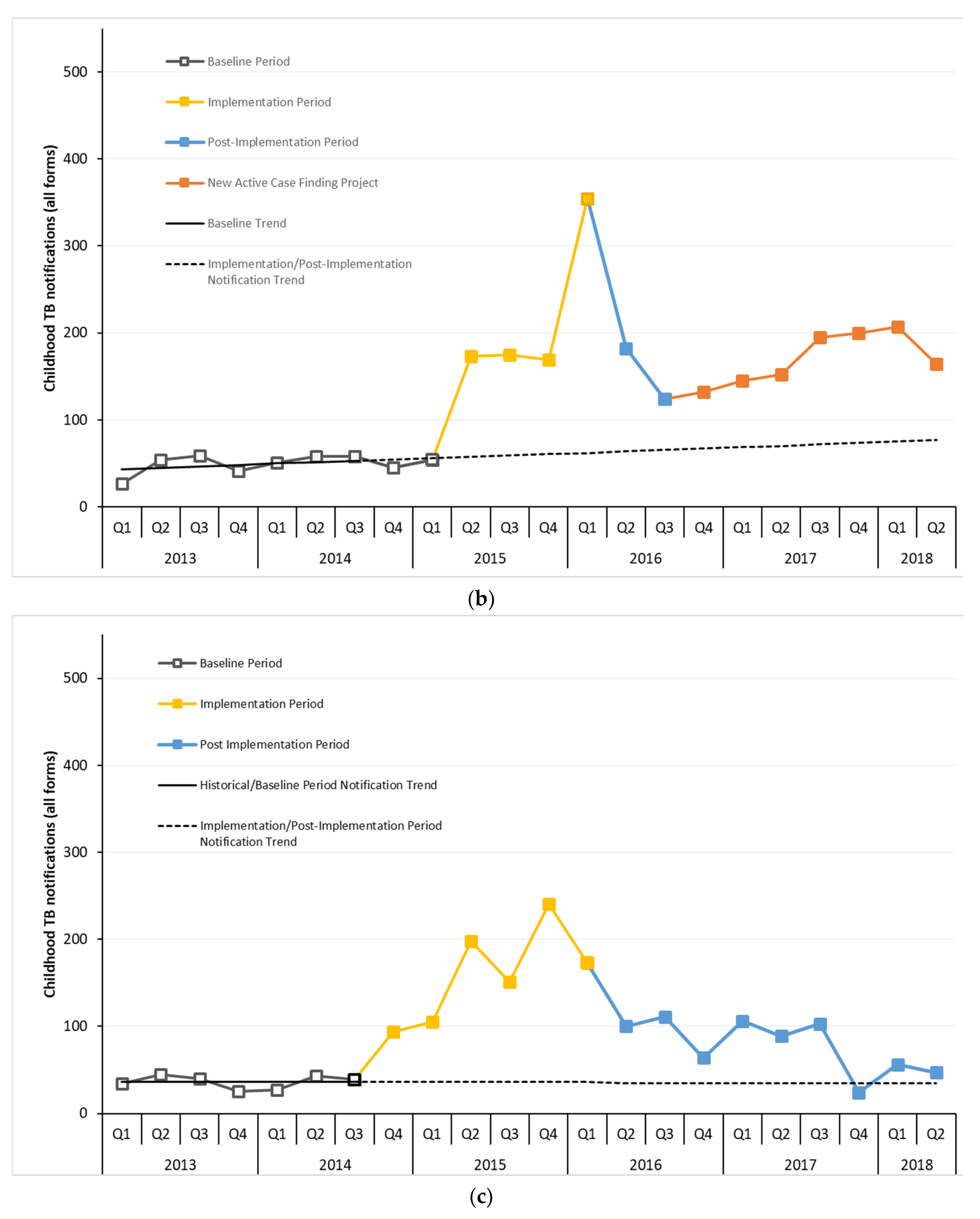
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2019; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Roadmap towards Ending TB in Children and Adolescents; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, P.J.; Yuen, C.M.; Sismanidis, C.; Seddon, J.A.; Jenkins, H.E. The global burden of tuberculosis mortality in children: A mathematical modelling study. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e898–e906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- André, E.; Lufungulo Bahati, Y.; Mulume Musafiri, E.; Bahati Rusumba, O.; Van der Linden, D.; Zech, F. Prediction of Under-Detection of Paediatric Tuberculosis in the Democratic Republic of Congo: Experience of Six Years in the South-Kivu Province. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerrum, S.; Rose, M.V.; Bygbjerg, I.C.; Mfinanga, S.G.; Tersboel, B.P.; Ravn, P. Primary health care staff’s perceptions of childhood tuberculosis: A qualitative study from Tanzania. BMC Health Serv. Res 2012, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hesseling, A.; Schaaf, H.; Gie, R.; Starke, J.; Beyers, N. A critical review of diagnostic approaches used in the diagnosis of childhood tuberculosis. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung. Dis. 2002, 6, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hatherill, M.; Hanslo, M.; Hawkridge, T.; Little, F.; Workman, L.; Mahomed, H.; Tameris, M.; Moyo, S.; Geldenhuys, H.; Hanekom, W. Structured approaches for the screening and diagnosis of childhood tuberculosis in a high prevalence region of South Africa. Bull. World Health Organ. 2010, 88, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.K.; Kumar, P.; Singh, A. Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of childhood tuberculosis. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2015, 6, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.J.; Khowaja, S.; Khan, F.S.; Qazi, F.; Lotia, I.; Habib, A.; Mohammed, S.; Khan, U.; Amanullah, F.; Hussain, H. Engaging the private sector to increase tuberculosis case detection: An impact evaluation study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A.; Amanullah, F.; Codlin, A.J.; Siddiqui, S.; Jaswal, M.; Ahmed, J.F.; Saleem, S.; Khurshid, A.; Hussain, H. Improving childhood tuberculosis detection and treatment through facility-based screening in rural Pakistan. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung. Dis. 2018, 22, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creswell, J.; Sahu, S.; Blok, L.; Bakker, M.I.; Stevens, R.; Ditiu, L. A Multi-Site Evaluation of Innovative Approaches to Increase Tuberculosis Case Notification: Summary Results. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stop TB Partnership. Un High-Level Meeting on Tb Key Targets & Commitments for 2022; Stop TB Partnership: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, B.; Chinnakali, P.; Shrestha, A.; Das, M.; Kumar, A.; Pant, R.; Lama, R.; Sarraf, R.; Dumre, S.; Harries, A. Impact of intensified case-finding strategies on childhood TB case registration in Nepal. Public Health Action. 2015, 5, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oshi, D.C.; Chukwu, J.N.; Nwafor, C.C.; Meka, A.O.; Madichie, N.O.; Ogbudebe, C.L.; Onyeonoro, U.U.; Ikebudu, J.N.; Ekeke, N.; Anyim, M.C. Does intensified case finding increase tuberculosis case notification among children in resource-poor settings? A report from Nigeria. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2016, 5, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pathak, R.R.; Mishra, B.K.; Moonan, P.K.; Nair, S.A.; Kumar, A.M.; Gandhi, M.P.; Mannan, S.; Ghosh, S. Can intensified tuberculosis case finding efforts at nutrition rehabilitation centers lead to pediatric case detection in Bihar, India? J. Tuberc. Res. 2016, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dolea, C. Increasing Access to Health Workers in Remote and Rural Areas through Improved Retention: Global Policy Recommendations; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Van Camp, J.; Chappy, S. The Effectiveness of Nurse Residency Programs on Retention: A Systematic Review. AORN J. 2017, 106, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.; Bloom, R.A.; Ted, C.; Christopher, D.; Hamish, F.; Gabriela, B.G.; Gwen, K.; Megan, M.; Edward, N.; Eric, R.; et al. Tuberculosis. In Major Infectious Diseases, 3rd ed.; King, K., Holmes, S.B., Barry, R.B., Prabhat, J., Eds.; The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Global Fund. Catalytic Investments. Available online: https://www.theglobalfund.org/en/funding-model/before-applying/catalytic-investments/ (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- James, R.; Khim, K.; Boudarene, L.; Yoong, J.; Phalla, C.; Saint, S.; Koeut, P.; Mao, T.E.; Coker, R.; Khan, M.S. Tuberculosis active case finding in Cambodia: A pragmatic, cost-effectiveness comparison of three implementation models. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ruan, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, F.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Das, M.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; et al. Comparing yield and relative costs of WHO TB screening algorithms in selected risk groups among people aged 65 years and over in China, 2013. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- United Nations General Assembly. Political Declaration of the High-Level Meeting of the General Assembly on the Fight Against Tuberculosis; United Nations General Assembly: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, K.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Pantoja, A.; Raviglione, M. Domestic and donor financing for tuberculosis care and control in low-income and middle-income countries: An analysis of trends, 2002–2011, and requirements to meet 2015 targets. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e105–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Specialized Chest Center (%) | General Centers (%) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | |||
| Number of children verbally screened | 10,534 | 94,804 | 105,338 |
| Children with presumptive TB | 3411 (32) | 2469 (3) | 5880 (6) |
| Children tested/investigated for TB | 2852 (84) | 2287 (93) | 5139 (87) |
| Children diagnosed with Bac + TB | 26 (1) | 16 (1) | 42 (1) |
| Children diagnosed with All Forms TB | 632 (22) | 785 (34) | 1417 (28) |
| Children with All Forms TB started on treatment | 626 (99) | 778 (99) | 1404 (99) |
| (b) | |||
| Number of child contacts screened | 1129 | 1885 | 3014 |
| Child contacts with presumptive TB | 802 (71) | 1034 (55) | 1836 (61) |
| Child contacts/investigated for TB | 707 (88) | 900 (87) | 1607 (88) |
| Child contacts diagnosed with Bac+ TB | 4 (1) | 1 (0.1) | 5 (0.3) |
| Child contacts diagnosed with All Forms TB | 188 (27) | 202 (22) | 390 (24) |
| Child contacts with All Forms TB started on treatment | 183 (97) | 202 (100) | 385 (99) |
| Cost Categories | Cost for May 2015 to March 2016 in USD (%) | Cost for October 2016 to June 2018 in USD (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Salaries for staff at center | 18,551 (70) | 6649 (35) |
| Diagnostic tests | 1344 (5) | 2810 (15) |
| Equipment (laptop and phones) | 987 (4) | 798 (4) |
| Clinical Decision Support System development (android based application) | 4658 (18) | 8424 (44) |
| Telephone and Internet cost | 572 (2) | 329 (2) |
| Stationery and Data Management | 154 (1) | 100 (1) |
| Training of staff | 142 (1) | 45 (0.2) |
| Total Cost | 26,409 | 19,155 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malik, A.A.; Hussain, H.; Creswell, J.; Siddiqui, S.; F. Ahmed, J.; Madhani, F.; Habib, A.; Khan, A.J.; Amanullah, F. The Impact of Funding on Childhood TB Case Detection in Pakistan. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040146
Malik AA, Hussain H, Creswell J, Siddiqui S, F. Ahmed J, Madhani F, Habib A, Khan AJ, Amanullah F. The Impact of Funding on Childhood TB Case Detection in Pakistan. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2019; 4(4):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040146
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalik, Amyn A., Hamidah Hussain, Jacob Creswell, Sara Siddiqui, Junaid F. Ahmed, Falak Madhani, Ali Habib, Aamir J. Khan, and Farhana Amanullah. 2019. "The Impact of Funding on Childhood TB Case Detection in Pakistan" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 4, no. 4: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040146
APA StyleMalik, A. A., Hussain, H., Creswell, J., Siddiqui, S., F. Ahmed, J., Madhani, F., Habib, A., Khan, A. J., & Amanullah, F. (2019). The Impact of Funding on Childhood TB Case Detection in Pakistan. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 4(4), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040146








