Zero Endemic Cases of Wildlife Rabies (Classical Rabies Virus, RABV) in the European Union by 2020: An Achievable Goal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Implementation of Oral Rabies Vaccination in Europe
3. Role of the EU
3.1. Rabies Eradication Policy
3.2. Funding
3.3. Technical Support
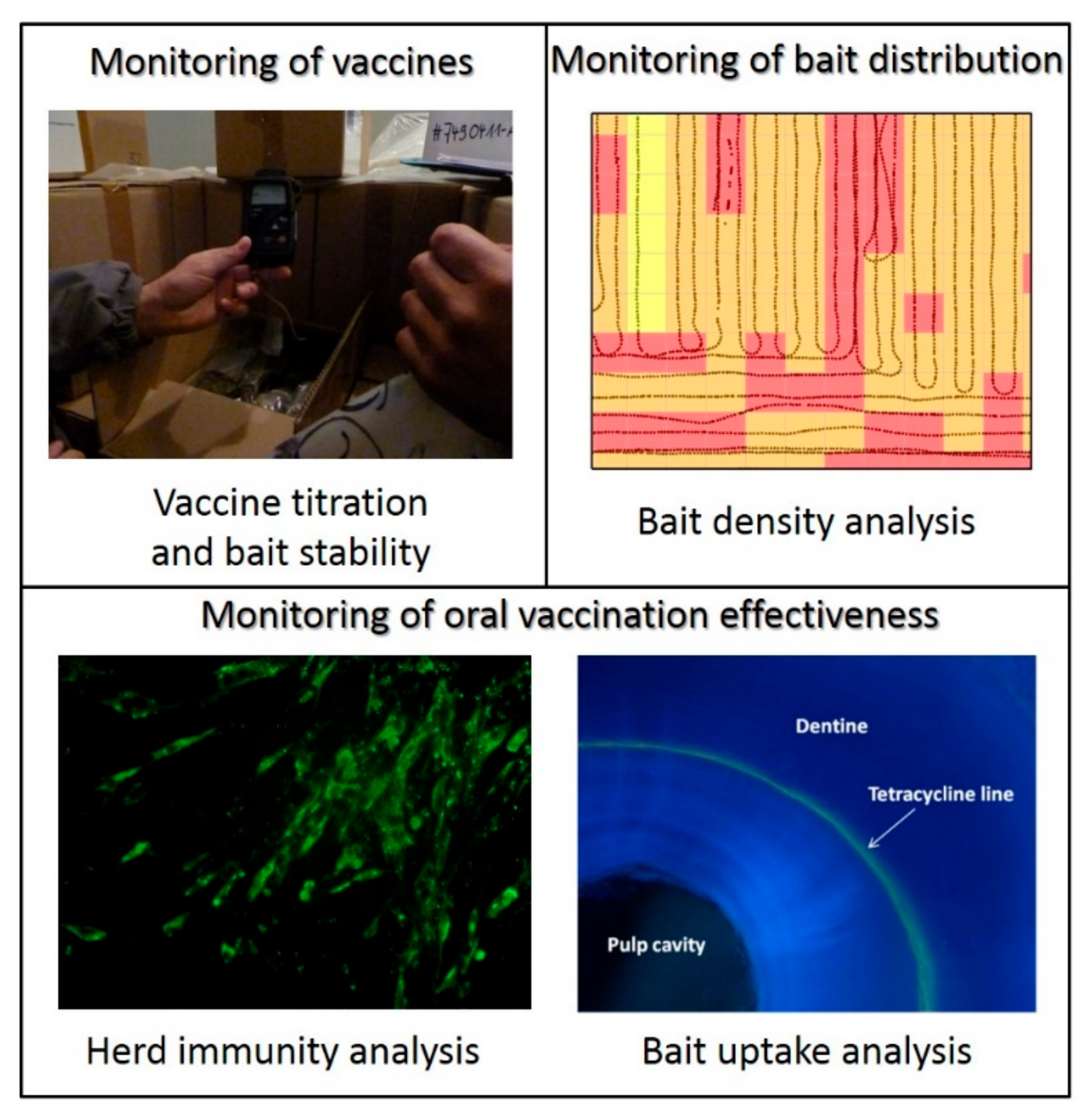
4. Key Control Parameters of Vaccines and Vaccination
5. Outcome of the EU Rabies Eradication Programs
6. Conclusions
- Finally, in the light of the EU experience, we would like to underline some key issues that are essential to eradicate the disease:
- Eradication programs should be conducted in large areas and maintained at least six years, and be stopped no earlier than two years after the last confirmed case;
- The vaccine to be used should be carefully selected and compliant with the legislation on veterinary medicines;
- The distribution of the vaccine should be mainly aerial and controlled on a regular basis to detect early areas where the bait density is not sufficient, in order to take immediate corrective actions;
- The surveillance and monitoring components of the program are critical to know whether rabies is being eradicated and whether the vaccination is being effective. Therefore, the collection of samples from an adequate number of animals is of foremost importance;
- Involvement of all stakeholders, including hunter associations and rural communities is necessary;
- International and cross-border cooperation in the planning and implementation of the eradication programs is needed to ensure a coordinated approach and the full vaccination of bordering areas.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayman, D.T.S.; Fooks, A.R.; Marston, D.A.; Garcia-R., J.C. The Global Phylogeography of Lyssaviruses—Challenging the ‘Out of Africa’ Hypothesis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théodoridès, J. Histoire de la Rage, Cave Canem; Fondation Singer-Polignac: Paris, France, 1986; p. 289. [Google Scholar]
- Pastoret, P.-P.; Kappeler, A.; Aubert, A. European rabies control and its history. In Historical Perspective of Rabies in Europe and the Mediterranean Basin; King, A.A., Fooks, A.R., Aubert, M., Wandeler, A.I., Eds.; OIE: Paris, France, 2004; pp. 337–350. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, D. Rabies: Epizootic aspects; diagnosis; vaccines; notes for guidance; official policy Epizootic aspects. Vet. Rec. 1976, 99, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliquet, F.; Aubert, M. Elimination of terrestrial rabies in Western European countries. In Control of Infectious Animal Diseases by Vaccination; Schudel, A., Lomard, M., Eds.; Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 119, pp. 185–204. [Google Scholar]
- Aubert, M.F.A.; Masson, E.; Artois, M.; Barrat, J. Oral wildlife rabies vaccination field trials in Europe, with recent emphasis on France. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1994, 187, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 195. [Google Scholar]
- Zero by 30: The Global Strategic Plan to End Human Deaths from Dog-Mediated Rabies by 2030; FAO: Rome, Italy; OIE: Paris, France; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland; GARC: Manhattan, KS, USA, 2018; p. 47.
- Rushton, S.P.; Shirley, M.D.F.; Macdonald, D.W.; Reynolds, J.C. Effects of culling fox populations at the landscape scale: A spatially explicit population modeling approach. J. Wildl. Manag. 2006, 70, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, M.F.A. Measures for controlling rabies by reducing the population of vectors. Consequences for animal population and for rabies epidemiology. Rev. Sci. Et Tech. (Int. Off. Epizoot.) 1989, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.G.; Lawson, K.F. Further studies of sylvatic rabies in the fox (Vulpes vulpes). Vaccination by the oral route. Can. Vet. J. La Rev. Vet. Can. 1973, 14, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Baer, G.M.; Abelseth, M.K.; Debbie, J.G. Oral vaccination of foxes against rabies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1971, 93, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandeler, A.I.; Capt, S.; Kappeler, A.; Hauser, R. Oral immunization of wildlife against rabies: concept and first field experiments. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10 (Suppl. 4), S649–S653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steck, F.; Wandeler, A.; Bichsel, P.; Capt, S.; Häfliger, U.; Schneider, L. Oral immunization of foxes against rabies laboratory and field studies. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Spec. Issue Anim. Rabies 1982, 5, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochier, B.; Kieny, M.P.; Costy, F.; Coppens, P.; Bauduin, B.; Lecoq, J.P.; Languet, B.; Chappuis, G.; Desmettre, P.; Afiademanyo, K.; et al. Large-scale eradication of rabies using recombinant vaccinia-rabies vaccine. Nature 1991, 354, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Bätza, H.J.; Freuling, C.; Kliemt, A.; Kliemt, J.; Heuser, R.; Schlüter, H.; Selhorst, T.; Vos, A.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Elimination of terrestrial rabies in Germany using oral vaccination of foxes. Berliner und Munchener Tierarztliche Wochenschrift 2012, 125, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.F.; Schröder, R.; Wysocki, P.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Freuling, C.M. Spatio-temporal use of oral rabies vaccines in fox rabies elimination programmes in Europe. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamand, A.; Coulon, P.; Lafay, F.; Kappeler, A.; Artois, M.; Aubert, M.; Blancou, J.; Wandeler, A.I. Eradication of rabies in Europe. Nature 1992, 360, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.T.; Freuling, C.M. Rabies control in Europe: An overview of past, current and future strategies. Rev. Sci. Et Tech. (Int. Off. Epizoot.) 2018, 37, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, C.E.; Hanlon, C.A.; Slate, D. Oral Vaccination of Wildlife against Rabies: Opportunities and Challenges in Prevention and Control. Dev. Biol. (Basel) 2004, 199, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Overview on Current EU Situation in Relation to EU Co-Funded Veterinary Programmes and Proposals as Regards Founding Priorities for 2018–2020; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Stohr, K.; Meslin, F.M. Progress and setbacks in the oral immunisation of foxes against rabies in Europe. Vet. Rec. 1996, 139, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Working Discussion Document Guidelines to Design an EU Co-Financed Programme on Eradication and Control of Rabies in Wildlife; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2015; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Overview Report—Rabies Eradication in the EU; European Commission: Luxembourg, 2017; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. National Veterinary Programmes. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/funding/animal-health/national-veterinary-programmes_en (accessed on 30 June 2019).
- Robardet, E.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Andrieu, S.; Servat, A.; Cliquet, F. International interlaboratory trials on rabies diagnosis: An overview of results and variation in reference diagnosis techniques (fluorescent antibody test, rabies tissue culture infection test, mouse inoculation test) and molecular biology techniques. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 177, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robardet, E.; Demerson, J.-M.; Andrieu, S.; Cliquet, F. First European interlaboratory comparison of tetracycline and age determination with red fox teeth following oral rabies vaccination programs. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasniewski, M.; Robardet, E.; Cliquet, F. Technical Report on the First Inter-Laboratory Study Based on the Rabies Antibody Detection in Wildlife Samples in Europe; Publisher: Anses Nancy, France, 2017; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Robardet, E.; Andrieu, S.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Dobrostana, M.; Horton, D.L.; Hostnik, P.; Jaceviciene, I.; Juhasz, T.; Muller, T.; Mutinelli, F.; et al. Comparative assay of fluorescent antibody test results among twelve European National Reference Laboratories using various anti-rabies conjugates. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 48, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servat, A.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Robardet, E.; Muzniece, Z.; Must, K.; Cliquet, F. Evaluation of a rapid immunochromatographic diagnostic test for the detection of rabies from brain material of European mammals. Biologicals 2012, 40, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard-Meyer, E.; Peytavin De Garam, C.; Schereffer, J.L.; Marchal, C.; Robardet, E.; Cliquet, F. Cross-platform evaluation of commercial real-time SYBR green RT-PCR kits for sensitive and rapid detection of european bat Lyssavirus type 1. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 839518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard-Meyer, E.; Peytavin de Garam, C.; Schereffer, J.L.; Robardet, E.; Cliquet, F. Evaluation of six TaqMan RT-rtPCR kits on two thermocyclers for the reliable detection of rabies virus RNA. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2019, 31, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EURL for Rabies. Training and Development. Available online: https://sitesv2.anses.fr/en/minisite/rabies/training-and-development (accessed on 30 June 2019).
- European Commission. The Oral Vaccination of Foxes against Rabies; Report of the Scientific Committee on Animal Health and Animal Welafare Adopted on 23 October 2002; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2002; pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Cliquet, F.; Freuling, C.; Smreczak, M.; van der Poel, W.H.M.; Horton, D.; Fooks, A.R.; Robardet, E.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Müller, T. Development of Harmonised Schemes for Monitoring and Reporting of Rabies in Animals in the European Union. EFSA J. 2010, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Animal Health and Welfare (AHAW). Update on oral vaccination of foxes and raccoon dogs against rabies. EFSA J. 2015, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIE. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, 7th ed.; OIE: Paris, France, 2018; p. 598. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Third WHO Consultation on Oral Immunization of Dogs against Rabies: Organized by WHO with the Participation of the Office International des Epizooties; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 22 July 1992; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Laboratory Techniques on Rabies; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; p. 150. [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopoeia. Rabies vaccine (live, oral) for foxes and raccoon dogs. In Monograph 0746, 8th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2014; Volume Monograph 01/2014: 0746. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, T.; Freuling, C.M.; Wysocki, P.; Roumiantzeff, M.; Freney, J.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Vos, A. Terrestrial rabies control in the European Union: Historical achievements and challenges ahead. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, R.; Krofel, M.; Giannatos, G.; Ćirović, D.; Mannil, P.; Volokh, A.M.; Lanszki, J.; Heltai, M.; Szabó, L.; Banea, O.C.; et al. A European concern? Genetic structure and expansion of golden jackals (canis aureus) in Europe and the caucasus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.M.; Jackson, H.C.; May, R.M.; Smith, A.M. Population dynamics of fox rabies in Europe. Nature 1981, 289, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.; Freuling, C.M.; Gschwendner, P.; Holzhofer, E.; Murke, H.; Rudiger, H.; Schuster, P.; Kloss, D.; Staubach, C.; Teske, K.; et al. SURVIS: A fully-automated aerial baiting system for the distribution of vaccine baits for wildlife. Berliner und Münchener Tierärztliche Wochenschrift 2012, 125, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, D.R.; Tinline, R.R.; Broekhoven, L.H. A Spatial Simulation Model for Rabies Control in Population Dynamics of Rabies in Wildlife. Acad. Press 1985, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Pastoret, P.P.; Brochier, B. Epidemiology and elimination of rabies in Western Europe. Vet. J. 1998, 156, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bedeković, T.; Lohman Janković, I.; Šimić, I.; Krešić, N.; Lojkić, I.; Sučec, I.; Robardet, E.; Cliquet, F. Control and elimination of rabies in Croatia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulatti, P.; Bonfanti, L.; Patregnani, T.; Lorenzetto, M.; Ferrè, N.; Gagliazzo, L.; Casarotto, C.; Ponti, A.M.; Ferri, G.; Marangon, S. 2008–2011 sylvatic rabies epidemic in Italy: Challenges and experiences. Pathog. Glob. Health 2013, 107, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Robardet, E.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Dobroštana, M.; Jaceviciene, I.; Mähar, K.; Muižniece, Z.; Pridotkas, G.; Masiulis, M.; Niin, E.; Olševskis, E.; et al. Rabies in the Baltic States: Decoding a Process of Control and Elimination. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freuling, C.M.; Hampson, K.; Selhorst, T.; Schröder, R.; Meslin, F.X.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Müller, T. The elimination of fox rabies from Europe: Determinants of success and lessons for the future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Animal Disease Notification System (ADNS). Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/animals/animal-diseases/not-system_en (accessed on 30 June 2019).
- Robardet, E.; Cliquet, F. Review of the Analysis Related to Rabies Diagnosis and Follow-Up of Oral Vaccination Performed in NRLs in 2018; European Union Reference Laboratory for Rabies: Nancy, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cliquet, F.; Wasniewski, M. Maintenance of rabies-free areas. Rev. Sci. Et Tech. (Int. Off. Epizoot.) 2018, 37, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Activities Indicators |
|---|
| Number of vaccine batches controlled before distribution |
| Number of oral vaccination campaigns performed within the year |
| Total number of baits distributed per campaign |
| Density per campaign (number of baits per square kilometer distributed) |
| Area covered with oral rabies vaccination per campaign |
| Number of monitoring tests for vaccination effectiveness on target species per campaign |
| Number of surveillance tests performed (passive surveillance) |
| Progress Indicators |
| Number of rabies cases (excluding bat cases) compared to the previous year |
| Number of rabies cases in previously (last year) case-free areas compared to previous year |
| Percentage of seroconversion in target species (juveniles /adults) compared to previous year |
| Percentage of vaccine uptake in target species (juveniles/adults separately) compared to the previous year. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robardet, E.; Bosnjak, D.; Englund, L.; Demetriou, P.; Rosado Martín, P.; Cliquet, F. Zero Endemic Cases of Wildlife Rabies (Classical Rabies Virus, RABV) in the European Union by 2020: An Achievable Goal. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040124
Robardet E, Bosnjak D, Englund L, Demetriou P, Rosado Martín P, Cliquet F. Zero Endemic Cases of Wildlife Rabies (Classical Rabies Virus, RABV) in the European Union by 2020: An Achievable Goal. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2019; 4(4):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040124
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobardet, Emmanuelle, Dean Bosnjak, Lena Englund, Panayiotis Demetriou, Pedro Rosado Martín, and Florence Cliquet. 2019. "Zero Endemic Cases of Wildlife Rabies (Classical Rabies Virus, RABV) in the European Union by 2020: An Achievable Goal" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 4, no. 4: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040124
APA StyleRobardet, E., Bosnjak, D., Englund, L., Demetriou, P., Rosado Martín, P., & Cliquet, F. (2019). Zero Endemic Cases of Wildlife Rabies (Classical Rabies Virus, RABV) in the European Union by 2020: An Achievable Goal. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 4(4), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed4040124





