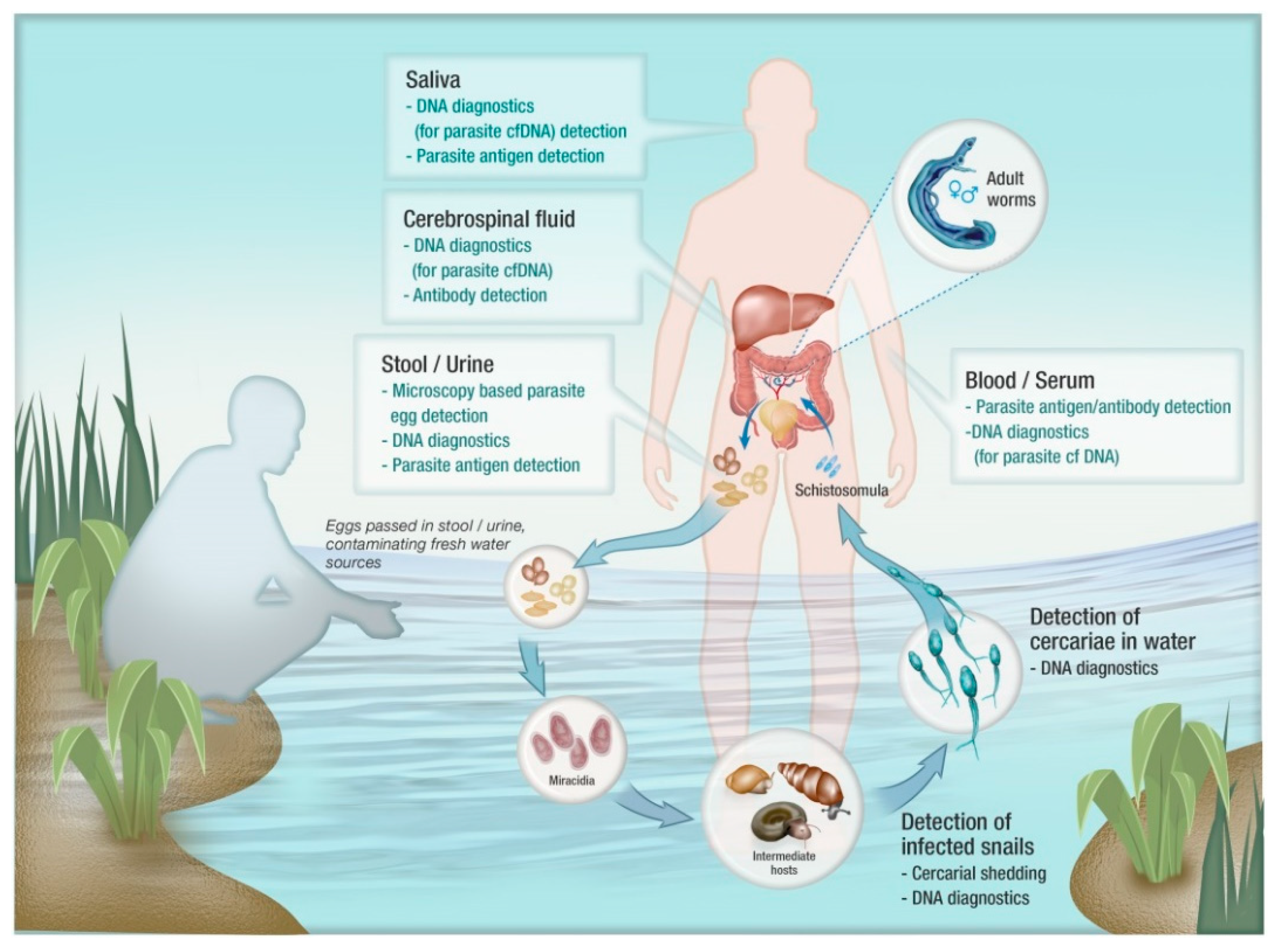
DNA Diagnostics for Schistosomiasis Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A General Overview of Diagnostics for Schistosomiasis
3. DNA-Based Diagnostics for Schistosomiasis
3.1. Sample Preservation and DNA Isolation for DNA Amplification Assays
3.2. Conventional and Quantitative Real Time PCR
3.3. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)
3.4. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA)
3.5. Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR)
3.6. Direct PCR
3.7. Parasite cfDNA Detection in Clinical Samples
4. Applications of DNA Diagnostics for Schistosomiasis
4.1. Individual Case Detection
4.2. Diagnosis of Zoonotic Schistosomiasis in Animal Reservoirs
4.3. Detection of Infected Snail Hosts
4.4. Surveillance of Environmental Sources
4.5. Assessment of Progress of Control Measures
5. Challenges and the Way Forward
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cfDNA | Cell-free DNA |
| CAA | Circulating anodic antigen |
| CCA | Circulating cathodic antigen |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| cPCR | Conventional PCR |
| ddPCR | Droplet digital PCR |
| KK | Kato-Katz fecal smear |
| LAMP | Loop-mediated isothermal amplification |
| MDA | Mass drug administration |
| nPCR | Nested PCR |
| PCR-RFLP | Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR products |
| POC | Point of care |
| qPCR | Real time quantitative PCR |
| RPA | Recombinase polymerase amplification |
| STH | Soil transmitted helminths |
| WASH | Water, sanitation and hygiene |
References
- Hotez, P.J.; Alvarado, M.; Basáñez, M.G.; Bolliger, I.; Bourne, R.; Boussinesq, M.; Brooker, S.J.; Brown, A.S.; Buckle, G.; Budke, C.M.; et al. The global burden of disease study 2010: Interpretation and implications for the neglected tropical diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Prevention and Control of Schistosomiasis and Soil-Transmitted Helminthiasis: WHO Technical Report Series (912); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Schistosomiasis: Progress Report 2001–2011 and Strategic Plan 2012–2020; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, A.G.P.; Olveda, R.M.; Acosta, L.; Harn, D.A.; Chy, D.; Li, Y.; Gray, D.J.; Gordon, C.A.; McManus, D.P.; Williams, G.M. Road to the elimination of schistosomiasis from Asia: The journey is far from over. Microbes Infect. 2013, 15, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boatin, B.A.; Basáñez, M.G.; Prichard, R.K.; Awadzi, K.; Barakat, R.M.; García, H.H.; Gazzinelli, A.; Grant, W.N.; McCarthy, J.S.; N’Goran, E.K.; et al. A research agenda for helminth diseases of humans: Towards control and elimination. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.P.; Wang, W.; Hong, Q.B.; Li, S.Z.; Liang, Y.S.; Yang, H.T.; Zhou, X.N. Approaches being used in the national schistosomiasis elimination programme in China: A review. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.; Lai, H. Mao Zedong’s fight against schistosomiasis. Perspect. Biol. Med. 2008, 51, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- WHO. Accelerating Work to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Roadmap for Implementation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Integrating Neglected Tropical Diseases into Global Health and Development: Fourth WHO Report on Neglected Tropical Diseases; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bergquist, R.; Zhou, X.N.; Rollinson, D.; Reinhard-Rupp, J.; Klohe, K. Elimination of schistosomiasis: The tools required. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiff, C. Accurate diagnostics for schistosomiasis: A new role for PCR? Rep. Parasitol. 2015, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Expert Consultation to Accelerate Elimination of Asian Schistosomiasis; WHO: Shanghai, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Gordon, C.A.; Williams, G.M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Gray, D.J.; Ross, A.G.; Harn, D.; McManus, D.P. Real-time PCR diagnosis of Schistosoma japonicum in low transmission areas of China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, R.C.; Seto, E.Y.W.; Carlton, E.J.; Liang, S.; Remais, J.V.; Zhong, B.; Qiu, D. The challenge of effective surveillance in moving from low transmission to elimination of schistosomiasis in China. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongs, A.; Marks, G.; Verlé, P.; Van der Stuyft, P. The unreliability of the Kato-Katz technique limits its usefulness for evaluating S. mansoni infections. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2001, 6, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerakoon, K.G.A.D.; Gobert, G.N.; Cai, P.; McManus, D.P. Advances in the diagnosis of human schistosomiasis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 939–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Gordon, C.A.; Hu, W.; McManus, D.P.; Chen, H.G.; Gray, D.J.; Ju, C.; Zeng, X.J.; Gobert, G.N.; Ge, J.; et al. A novel procedure for precise quantification of Schistosoma japonicum eggs in bovine feces. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legesse, M.; Erko, B. Field-based evaluation of a reagent strip test for diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni by detecting circulating cathodic antigen in urine before and after chemotherapy. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 101, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stothard, J.R.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Tukahebwa, E.M.; Kazibwe, F.; Rollinson, D.; Mathieson, W.; Webster, J.P.; Fenwick, A. Use of circulating cathodic antigen (CCA) dipsticks for detection of intestinal and urinary schistosomiasis. Acta Trop. 2006, 97, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochodo, E.A.; Gopalakrishna, G.; Spek, B.; Reitsma, J.B.; van Lieshout, L.; Polman, K.; Lamberton, P.; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; Leeflang, M.M.G. Circulating antigen tests and urine reagent strips for diagnosis of active schistosomiasis in endemic areas. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 11, CD009579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Grootveld, R.; van Dam, G.J.; de Dood, C.; de Vries, J.J.C.; Visser, L.G.; Corstjens, P.L.A.M.; van Lieshout, L. Improved diagnosis of active Schistosoma infection in travellers and migrants using the ultra-sensitive in-house lateral flow test for detection of circulating anodic antigen (CAA) in serum. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, S.; Corstjens, P.L.A.M.; Koukounari, A.; Cercamondi, C.I.; Ame, S.M.; Ali, S.M.; de Dood, C.J.; Mohammed, K.A.; Utzinger, J.; Rollinson, D.; et al. Sensitivity and specificity of a urine circulating anodic antigen test for the diagnosis of Schistosoma haematobium in low endemic settings. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Lu, G.; Zheng, H.; Brindley, P.J.; McManus, D.P.; Blair, D.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhong, Y.; et al. Schistosoma japonicum genome sequencing and functional analysis consortium the Schistosoma japonicum genome reveals features of host-parasite interplay. Nature 2009, 460, 345–351. [Google Scholar]
- Young, N.D.; Jex, A.R.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Xiong, Z.; Li, Y.; Cantacessi, C.; Hall, R.S.; Xu, X.; et al. Whole-genome sequence of Schistosoma haematobium. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.H.; Blair, D.; Agatsuma, T.; Humair, P.F.; Campbell, N.J.; Iwagami, M.; Littlewood, D.T.; Peacock, B.; Johnston, D.A.; Bartley, J.; et al. Phylogenies inferred from mitochondrial gene orders—A cautionary tale from the parasitic flatworms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lier, T.; Simonsen, G.S.; Wang, T.; Lu, D.; Haukland, H.H.; Vennervald, B.J.; Hegstad, J.; Johansen, M.V. Real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection of low-intensity Schistosoma japonicum infections in China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 81, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ten Hove, R.J.; Verweij, J.J.; Vereecken, K.; Polman, K.; Dieye, L.; van Lieshout, L. Multiplex real-time PCR for the detection and quantification of Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium infection in stool samples collected in northern Senegal. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeng, B.B.; Aryeetey, Y.A.; Amoah, A.S.; Larbi, I.A.; Deelder, A.M.; Yazdanbakhsh, M.; Hartgers, F.C.; Boakye, D.A.; Verweij, J.J.; van Dam, G.J.; et al. Application of a circulating-cathodic-antigen (CCA) strip test and real-time PCR, in comparison with microscopy, for the detection of Schistosoma haematobium in urine samples from Ghana. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2008, 102, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnops, L.; Soentjens, P.; Clerinx, J.; Van Esbroeck, M. A Schistosoma haematobium-specific real-time PCR for diagnosis of urogenital schistosomiasis in serum samples of international travelers and migrants. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Song, L.G.; Xie, H.; Liang, J.Y.; Yuan, D.Y.; Wu, Z.D.; Lv, Z.Y. Nucleic acid detection in the diagnosis and prevention of schistosomiasis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2016, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lier, T.; Johansen, M.V.; Hjelmevoll, S.O.; Vennervald, B.J.; Simonsen, G.S. Real-time PCR for detection of low intensity Schistosoma japonicum infections in a pig model. Acta Trop. 2008, 105, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobert, G.N.; Chai, M.; Duke, M.; McManus, D.P. Copro-PCR based detection of Schistosoma eggs using mitochondrial DNA markers. Mol. Cell. Probes 2005, 19, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, L.A.; Dias-Neto, E.; Rabello, A. Detection by polymerase chain reaction of Schistosoma mansoni DNA in human serum and feces. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 66, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laha, T.; Brindley, P.J.; Smout, M.J.; Verity, C.K.; McManus, D.P.; Loukas, A. Reverse transcriptase activity and untranslated region sharing of a new RTE-like, non-long terminal repeat retrotransposon from the human blood fluke, Schistosoma japonicum. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerakoon, K.G.; Gordon, C.A.; Cai, P.; Gobert, G.N.; Duke, M.; Williams, G.M.; McManus, D.P. A novel duplex ddPCR assay for the diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonica: Proof of concept in an experimental mouse model. Parasitology 2017, 144, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, D.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.M.; Hu, F.; Qing, X.; Xia, C.; Pan, W. Serodiagnosis of Schistosoma japonicum infection: Genome-wide identification of a protein marker, and assessment of its diagnostic validity in a field study in China. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lier, T.; Simonsen, G.S.; Haaheim, H.; Hjelmevoll, S.O.; Vennervald, B.J.; Johansen, M.V. Novel real-time PCR for detection of Schistosoma japonicum in stool. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2006, 37, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.; Acosta, L.P.; Gobert, G.N.; Olveda, R.M.; Ross, A.G.; Williams, G.M.; Gray, D.J.; Harn, D.; Li, Y.; McManus, D.P. Real-time PCR demonstrates high prevalence of Schistosoma japonicum in the Philippines: Implications for surveillance and control. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espírito-Santo, M.; Alvarado-Mora, M.; Dias-Neto, E.; Botelho-Lima, L.; Moreira, J.; Amorim, M.; Pinto, P.; Heath, A.R.; Castilho, V.; Gonçalves, E.; et al. Evaluation of real-time PCR assay to detect Schistosoma mansoni infections in a low endemic setting. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, S.; Shinkafi, S.H.; Hudu, S.A.; Neela, V.; Suresh, K.; Nordin, S.A.; Malina, O. Prevalence and molecular characterisation of Schistosoma haematobium among primary school children in Kebbi State, Nigeria. Ann. Parasitol. 2017, 63, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lodh, N.; Naples, J.M.; Bosompem, K.M.; Quartey, J.; Shiff, C.J. Detection of parasite-specific DNA in urine sediment obtained by filtration differentiates between single and mixed infections of Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium from endemic areas in Ghana. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.A.; Acosta, L.P.; Gray, D.J.; Olveda, R.M.; Jarilla, B.; Gobert, G.N.; Ross, A.G.; McManus, D.P. High prevalence of Schistosoma japonicum infection in Carabao from Samar Province, the Philippines: Implications for transmission and control. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, L.A.; Oliveira, M.C.; Katz, N.; Dias-Neto, E.; Rabello, A. Comparison of a polymerase chain reaction and the Kato-Katz technique for diagnosing infection with Schistosoma mansoni. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 68, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ibironke, O.A.; Phillips, A.E.; Garba, A.; Lamine, S.M.; Shiff, C. Diagnosis of Schistosoma haematobium by detection of specific DNA fragments from filtered urine samples. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; He, C.C.; Liu, J.M.; Li, H.; Lu, K.; Fu, Z.Q.; Zhu, C.G.; Liu, Y.P.; Tong, L.B.; Zhou, D.-B.; et al. Nested-PCR assay for detection of Schistosoma japonicum infection in domestic animals. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruscky, I.S.; de Melo, F.L.; de Medeiros, Z.M.; Albuquerque, F.F.; Wanderley, L.B.; da Cunha-Correia, C. Nested polymerase chain reaction in cerebrospinal fluid for diagnosing spinal cord schistosomiasis: A promising method. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 366, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwangi, I.N.; Agola, E.L.; Mugambi, R.M.; Shiraho, E.A.; Mkoji, G.M. Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni infection in faecal samples. J. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1267826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandasegui, J.; Fernández-Soto, P.; Muro, A.; Simões Barbosa, C.; Lopes de Melo, F.; Loyo, R.; de Souza Gomes, E.C. A field survey using LAMP assay for detection of Schistosoma mansoni in a low-transmission area of schistosomiasis in Umbuzeiro, Brazil: Assessment in human and snail samples. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulton, K.; Webster, B. Development of a lateral flow recombinase polymerase assay for the diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni infections. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 546, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Yu, X.; Feng, J.; Sun, K.; Fu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zou, M.; Xia, W.; Luo, Z.; He, H.; et al. Field evaluation of a recombinase polymerase amplification assay for the diagnosis of Schistosoma japonicum infection in Hunan province of China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosser, A.; Rollinson, D.; Forrest, M.; Webster, B.L. Isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) of Schistosoma haematobium DNA and oligochromatographic lateral flow detection. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerakoon, K.G.; Gordon, C.A.; Gobert, G.N.; Cai, P.; McManus, D.P. Optimisation of a droplet digital PCR assay for the diagnosis of Schistosoma japonicum infection: A duplex approach with DNA binding dye chemistry. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 125, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerakoon, K.G.; Gordon, C.A.; Williams, G.M.; Cai, P.; Gobert, G.N.; Olveda, R.M.; Ross, A.G.; Olveda, D.U.; McManus, D.P. Droplet digital PCR diagnosis of human schistosomiasis: Parasite cell-free DNA detection in diverse clinical samples. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eraky, M.; Aly, N.M. Assessment of diagnostic performance of a commercial direct blood PCR kit for the detection of Schistosoma mansoni infection in mice compared with the pre-extracted PCR assay. Parasitol. United J. 2016, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.A.L.D.; Medeiros, Z.; Soares, C.R.P.; Silva, E.D.D.; Miranda-Filho, D.B.; Melo, F.L. De. A comparison of four DNA extraction protocols for the analysis of urine from patients with visceral leishmaniasis. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2014, 47, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Broeck, F.; Geldof, S.; Polman, K.; Volckaert, F.A.M.; Huyse, T. Optimal sample storage and extraction procotols for reliable multilocus genotyping of the human parasite Schistosoma mansoni. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Messaoudi, S.; Rolet, F.; Mouliere, F.; Thierry, A.R. Circulating cell free DNA: Preanalytical considerations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 424, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaiakovou, M.; Pilotte, N.; Baumer, B.; Grant, J.; Asbjornsdottir, K.; Schaer, F.; Hu, Y.; Aroian, R.; Walson, J.; Williams, S.A. A comparative analysis of preservation techniques for the optimal molecular detection of hookworm DNA in a human fecal specimen. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-López, R.; Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Gangoso, L.; Soriguer, R.C.; Figuerola, J. Comparison of manual and semi-automatic DNA extraction protocols for the barcoding characterization of hematophagous louse flies (Diptera: Hippoboscidae). J. Vector Ecol. 2015, 40, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warton, K.; Graham, L.J.; Yuwono, N.; Samimi, G. Comparison of 4 commercial kits for the extraction of circulating DNA from plasma. Cancer Genet. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathay, C.; Hamot, G.; Henry, E.; Mommaerts, K.; Thorlaksdottir, A.; Trouet, J.; Betsou, F. Method validation for extraction of nucleic acids from peripheral whole blood. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2016, 14, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Lee, E.H.; Park, G.; Jang, S.J.; Moon, D.S. Comparison of MagNA Pure 96, Chemagic MSM1, and QIAamp MinElute for hepatitis B virus nucleic acid extraction. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2012, 42, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.; Choi, J.R.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, H.S. Comparisons of three automated systems for genomic DNA extraction in a clinical diagnostic laboratory. Yonsei Med. J. 2010, 51, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schunk, M.; Kebede Mekonnen, S.; Wondafrash, B.; Mengele, C.; Fleischmann, E.; Herbinger, K.H.; Verweij, J.J.; Geldmacher, C.; Bretzel, G.; Löscher, T.; et al. Use of occult blood detection cards for real-time PCR-based diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodh, N.; Mikita, K.; Bosompem, K.M.; Anyan, W.K.; Quartey, J.K.; Otchere, J.; Shiff, C.J. Point of care diagnosis of multiple schistosome parasites: Species-specific DNA detection in urine by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Acta Trop. 2017, 173, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainabadi, K.; Adams, M.; Han, Z.Y.; Lwin, H.W.; Han, K.T.; Ouattara, A.; Thura, S.; Plowe, C.V.; Nyunt, M.M. A novel method for extracting nucleic acids from dried blood spots for ultrasensitive detection of low-density Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax infections. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, M.S.; Xiao, N.; Wang, S.; Carlton, E.J. Field evaluation of a PCR test for Schistosoma japonicum egg detection in low-prevalence regions of China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, O.C.; Verly, T.; Finamore-Araujo, P.; Gomes, S.A.O.; Lopes, C.M.; de Sousa, D.M.; Azevedo, L.R.; da Mota, F.F.; D’Avila-Levy, C.M.; Santos-Mallet, J.R.; et al. Development of conventional and real-time multiplex PCR-based assays for estimation of natural infection rates and Trypanosoma cruzi load in triatomine vectors. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, N.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Pérez-Arellano, J.L.; Carranza, C.; Puente, S.; López-Abán, J.; Muro, A. A new PCR-based approach for the specific amplification of DNA from different Schistosoma species applicable to human urine samples. Parasitology 2006, 133, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, L.M.A.; Santos, H.L.C.; Gonçalves, M.M.L.; Barreto, M.G.M.; Peralta, J.M. Evaluation of polymerase chain reaction as an additional tool for the diagnosis of low-intensity Schistosoma mansoni infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 68, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, L.I.; Dos Santos Marques, L.H.; Enk, M.J.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Coelho, P.M.Z.; Rabello, A. Development and evaluation of a sensitive PCR-ELISA system for detection of Schistosoma infection in feces. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, E.; Bøgh, H.O.; Johansen, M.V.; McManus, D.P. PCR-based identification of individuals of Schistosoma japonicum representing different subpopulations using a genetic marker in mitochondrial DNA. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaeili, F.; Mathis, A.; Deplazes, P.; Mirhendi, H.; Barazesh, A.; Ebrahimi, S.; Kia, E.B. Differentiation of Toxocara canis and Toxocara cati based on PCR-RFLP analyses of rDNA-ITS and mitochondrial cox1 and nad1 regions. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, L.M.; Montero, E.; Morakote, N.; Puente, S.; Díaz De Tuesta, J.L.; Serra, T.; López-Velez, R.; McManus, D.P.; Harrison, L.J.S.; Parkhouse, R.M.E.; et al. Differential diagnosis of Taenia saginata and Taenia saginata asiatica taeniasis through PCR. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2004, 49, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldeira, R.L.; Teodoro, T.M.; Jannotti-Passos, L.K.; Lira-Moreira, P.M.; Goveia, C.D.O.; Carvalho, O.D.S. Characterization of South American snails of the genus Biomphalaria (Basommatophora: Planorbidae) and Schistosoma mansoni (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda) in molluscs by PCR-RFLP. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1045391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, D.J.; Ross, A.G.; Li, Y.S.; McManus, D.P. Diagnosis and management of schistosomiasis. BMJ 2011, 342, d2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.L.D.V.; Melo, F.L.; Werkhauser, R.P.; Abath, F.G.C. Development of a real time polymerase chain reaction for quantitation of Schistosoma mansoni DNA. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2006, 101 (Suppl. 1), 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, P.; Taylor, M.; Zulu, S.G.; Gundersen, S.G.; Verweij, J.J.; Hoekstra, P.; Brienen, E.A.T.; Kleppa, E.; Kjetland, E.F.; van Lieshout, L. Real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection of Schistosoma DNA in small-volume urine samples reflects focal distribution of urogenital schistosomiasis in primary school girls in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easton, A.V.; Oliveira, R.G.; O’Connell, E.M.; Kepha, S.; Mwandawiro, C.S.; Njenga, S.M.; Kihara, J.H.; Mwatele, C.; Odiere, M.R.; Brooker, S.J.; et al. Multi-parallel qPCR provides increased sensitivity and diagnostic breadth for gastrointestinal parasites of humans: Field-based inferences on the impact of mass deworming. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejia, R.; Vicuña, Y.; Broncano, N.; Sandoval, C.; Vaca, M.; Chico, M.; Cooper, P.J.; Nutman, T.B. A novel, multi-parallel, real-time polymerase chain reaction approach for eight gastrointestinal parasites provides improved diagnostic capabilities to resource-limited at-risk populations. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimino, R.O.; Jeun, R.; Juarez, M.; Cajal, P.S.; Vargas, P.; Echazú, A.; Bryan, P.E.; Nasser, J.; Krolewiecki, A.; Mejia, R. Identification of human intestinal parasites affecting an asymptomatic peri-urban Argentinian population using multi-parallel quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotte, N.; Papaiakovou, M.; Grant, J.R.; Bierwert, L.A.; Llewellyn, S.; McCarthy, J.S.; Williams, S.A. Improved PCR-based detection of soil transmitted helminth infections using a next-generation sequencing approach to assay design. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sady, H.; Al-Mekhlafi, H.M.; Ngui, R.; Atroosh, W.M.; Al-Delaimy, A.K.; Nasr, N.A.; Dawaki, S.; Abdulsalam, A.M.; Ithoi, I.; Lim, Y.A.L.; et al. Detection of Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma haematobium by real-time PCR with high resolution melting analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16085–16103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, N.; Mori, Y.; Kanda, H.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) of gene sequences and simple visual detection of products. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 3, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Rong, R.; Zhang, H.Q.; Shi, C.J.; Zhu, X.Q.; Xia, C.M. Sensitive and rapid detection of Schistosoma japonicum DNA by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, K.; Mage, P.L.; Csordas, A.T.; Eisenstein, M.; Soh, H.T. Simultaneous elimination of carryover contamination and detection of DNA with uracil-DNA-glycosylase-supplemented loop-mediated isothermal amplification (UDG-LAMP). Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2014, 50, 3747–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Jing, H.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C. A novel method to control carryover contamination in isothermal nucleic acid amplification. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2017, 53, 10696–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Soto, P.; Gandasegui Arahuetes, J.; Sánchez Hernández, A.; López Abán, J.; Vicente Santiago, B.; Muro, A. A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for early detection of Schistosoma mansoni in stool samples: A diagnostic approach in a murine model. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyan, D.C.; Swinson, K.L. A novel multiplex isothermal amplification method for rapid detection and identification of viruses. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zou, D.; Dong, D.; Yang, Z.; Ao, D.; Liu, W.; Huang, L. Development of a multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella spp. and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, S.; Inpankaew, T.; Nery, S.V.; Gray, D.J.; Verweij, J.J.; Clements, A.C.A.; Gomes, S.J.; Traub, R.; McCarthy, J.S. Application of a multiplex quantitative PCR to assess prevalence and intensity of intestinal parasite infections in a controlled clinical trial. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.A.; McManus, D.P.; Acosta, L.P.; Olveda, R.M.; Williams, G.M.; Ross, A.G.; Gray, D.J.; Gobert, G.N. Multiplex real-time PCR monitoring of intestinal helminths in humans reveals widespread polyparasitism in Northern Samar, the Philippines. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, R.; Roy, S.; Siddique, A.; Mondal, U.; Rahman, S.M.M.; Mondal, D.; Houpt, E.; Petri, W.A. Multiplex real-time PCR assay for detection of Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia intestinalis, and Cryptosporidium spp. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piepenburg, O.; Williams, C.H.; Stemple, D.L.; Armes, N.A. DNA detection using recombination proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoli, L.M.; Spoto, G. Isothermal amplification methods for the detection of nucleic acids in microfluidic devices. Biosensors 2013, 3, 18–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Paparini, A.; Monis, P.; Ryan, U. Comparison of next-generation droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) with quantitative PCR (qPCR) for enumeration of Cryptosporidium oocysts in faecal samples. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sze, M.A.; Abbasi, M.; Hogg, J.C.; Sin, D.D. A Comparison between droplet digital and quantitative PCR in the analysis of bacterial 16S load in lung tissue samples from control and COPD GOLD 2. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindson, C.M.; Chevillet, J.R.; Briggs, H.A.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ruf, I.K.; Hindson, B.J.; Vessella, R.L.; Tewari, M. Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manokhina, I.; Singh, T.K.; Peñaherrera, M.S.; Robinson, W.P. Quantification of cell-free DNA in normal and complicated pregnancies: Overcoming biological and technical issues. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlak, R.H.; Cook, L.; Cheng, A.; Magaret, A.; Jerome, K.R. Clinical utility of droplet digital PCR for human cytomegalovirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2844–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmedillas-López, S.; García-Arranz, M.; García-Olmo, D. Current and emerging applications of droplet digital PCR in Oncology. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 21, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudecova, I. Digital PCR analysis of circulating nucleic acids. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall Sedlak, R.; Jerome, K.R. The potential advantages of digital PCR for clinical virology diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongthawin, J.; Intapan, P.M.; Lulitanond, V.; Sanpool, O.; Thanchomnang, T.; Sadaow, L.; Maleewong, W. Detection and quantification of Wuchereria bancrofti and Brugia malayi DNA in blood samples and mosquitoes using duplex droplet digital polymerase chain reaction. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2967–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisutham, S.; Saralamba, N.; Malleret, B.; Rénia, L.; Dondorp, A.M.; Imwong, M. Four human Plasmodium species quantification using droplet digital PCR. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, D.E.; Roy, R. An evaluation of direct PCR amplification. Croat. Med. J. 2014, 55, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, W.H.; Sun, Y.; Høgberg, J.; Quyen, T.L.; Engelsmann, P.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. Direct PCR—A rapid method for multiplexed detection of different serotypes of Salmonella in enriched pork meat samples. Mol. Cell. Probes 2017, 32, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silbermayr, K.; Eigner, B.; Duscher, G.G.; Joachim, A.; Fuehrer, H.-P. The detection of different Dirofilaria species using direct PCR technique. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverry, D.F.; Deason, N.A.; Davidson, J.; Makuru, V.; Xiao, H.; Niedbalski, J.; Kern, M.; Russell, T.L.; Burkot, T.R.; Collins, F.H.; et al. Human malaria diagnosis using a single-step direct-PCR based on the Plasmodium cytochrome oxidase III gene. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichmann, D.; Poppert, S.; Von Thien, H.; Clerinx, J.; Dieckmann, S.; Jensenius, M.; Parola, P.; Richter, J.; Schunk, M.; Stich, A.; et al. Prospective European-wide multicentre study on a blood based real-time PCR for the diagnosis of acute schistosomiasis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichmann, D.; Panning, M.; Quack, T.; Kramme, S.; Burchard, G.-D.; Grevelding, C.; Drosten, C. Diagnosing schistosomiasis by detection of cell-free parasite DNA in human plasma. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, A.; Guo, J.; Wang, B.; Qiu, S.J.; Sun, H.; Guan, W.; Zhu, X.Q.; Xia, C.M.; Wu, Z.D. The sources and metabolic dynamics of Schistosoma japonicum DNA in serum of the host. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerakoon, K.G.; McManus, D.P. Cell-Free DNA as a diagnostic tool for human parasitic infections. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Osada, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Hamada, A.; Okuzawa, E.; Kanazawa, T. Early detection of Schistosoma mansoni infection by touchdown PCR in a mouse model. Parasitol. Int. 2006, 55, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.-M.; Rong, R.; Lu, Z.-X.; Shi, C.-J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Gong, W.; Luo, W. Schistosoma japonicum: A PCR assay for the early detection and evaluation of treatment in a rabbit model. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 121, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato-Hayashi, N.; Kirinoki, M.; Iwamura, Y.; Kanazawa, T.; Kitikoon, V.; Matsuda, H.; Chigusa, Y. Identification and differentiation of human schistosomes by polymerase chain reaction. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 124, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato-Hayashi, N.; Yasuda, M.; Yuasa, J.; Isaka, S.; Haruki, K.; Ohmae, H.; Osada, Y.; Kanazawa, T.; Chigusa, Y. Use of cell-free circulating schistosome DNA in serum, urine, semen, and saliva to monitor a case of refractory imported schistosomiasis hematobia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3435–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato-Hayashi, N.; Leonardo, L.R.; Arevalo, N.L.; Tagum, M.N.B.; Apin, J.; Agsolid, L.M.; Chua, J.C.; Villacorte, E.A.; Kirinoki, M.; Kikuchi, M.; et al. Detection of active schistosome infection by cell-free circulating DNA of Schistosoma japonicum in highly endemic areas in Sorsogon Province, the Philippines. Acta Trop. 2015, 141, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Härter, G.; Frickmann, H.; Zenk, S.; Wichmann, D.; Ammann, B.; Kern, P.; Fleischer, B.; Tannich, E.; Poppert, S. Diagnosis of neuroschistosomiasis by antibody specificity index and semi-quantitative real-time PCR from cerebrospinal fluid and serum. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kincaid-Smith, J.; Rey, O.; Toulza, E.; Berry, A.; Boissier, J. Emerging schistosomiasis in Europe: A need to quantify the risks. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblanc, C.; Pham, L.L.; Mariani, P.; Titomanlio, L.; El Ghoneimi, A.; Paris, L.; Escoda, S.; Lottmann, H.; Toubiana, J.; Paugam, A.; et al. Imported schistosomiasis in children: Clinical, diagnostic aspects and outcome in 5 tertiary hospitals in France. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, e349–e351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olveda, D.U.; Li, Y.; Olveda, R.M.; Lam, A.K.; McManus, D.P.; Chau, T.N.P.; Harn, D.A.; Williams, G.M.; Gray, D.J.; Ross, A.G.P. Bilharzia in the Philippines: Past, present, and future. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 18, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.G.; Zhao, Y.E.; Lee Willingham, A.; Wang, T.P. Towards the elimination of schistosomiasis japonica through control of the disease in domestic animals in the People’s Republic of China: A tale of over 60 years. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 92, 269–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.W.; Qin, Y.F.; Chu, K.; Meng, R.; Liu, Y.; McGarvey, S.T.; Olveda, R.; Acosta, L.; Ji, M.-J.; Fernandez, T.; et al. High prevalence of Schistosoma japonicum infection in water buffaloes in the Philippines assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamburger, J.; Hoffman, O.; Kariuki, H.C.; Muchiri, E.M.; Ouma, J.H.; Koech, D.K.; Sturrock, R.F.; King, C.H. Large-scale, polymerase chain reaction-based surveillance of Schistosoma haematobium DNA in snails from transmission sites in coastal Kenya: A new tool for studying the dynamics of snail infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 71, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- King, C.H.; Sturrock, R.F.; Kariuki, H.C.; Hamburger, J. Transmission control for schistosomiasis—Why it matters now. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarir, F.; Sebti, F.; Abbasi, I.; Sadak, A.; Fellah, H.; Nhammi, H.; Ameur, B.; El Idrissi, A.L.; Rhajaoui, M. Schistosoma haematobium detection in snails by DraI PCR and Sh110/Sm-Sl PCR: Further evidence of the interruption of schistosomiasis transmission in Morocco. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Tsuji, M. From discovery to eradication of schistosomiasis in Japan: 1847–1996. Int. J. Parasitol. 1997, 27, 1465–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, I.; King, C.H.; Muchiri, E.M.; Hamburger, J. Detection of Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma haematobium DNA by loop-mediated isothermal amplification: Identification of infected snails from early prepatency. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abath, F.G.C.; Gomes, A.L.D.V.; Melo, F.L.; Barbosa, C.S.; Werkhauser, R.P. Molecular approaches for the detection of Schistosoma mansoni: Possible applications in the detection of snail infection, monitoring of transmission sites, and diagnosis of human infection. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2006, 101 (Suppl. 1), 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, F.L.; Gomes, A.L.D.V.; Barbosa, C.S.; Werkhauser, R.P.; Abath, F.G.C. Development of molecular approaches for the identification of transmission sites of schistosomiasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldeira, R.L.; Jannotti-Passos, L.K.; Dos Santos Carvalho, O. Use of molecular methods for the rapid mass detection of Schistosoma mansoni (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda) in Biomphalaria spp. (Gastropoda: Planorbidae). J. Trop. Med. 2017, 2017, 8628971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandasegui, J.; Fernández-Soto, P.; Hernández-Goenaga, J.; López-Abán, J.; Vicente, B.; Muro, A. Biompha-LAMP: A new rapid loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detecting Schistosoma mansoni in Biomphalaria glabrata snail host. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Q.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.-J.; Kumagai, T.; Furushima-Shimogawara, R.; Lou, D.; Yang, K.; Wen, L.; Lu, S.; et al. A new surveillance and response tool: Risk map of infected Oncomelania hupensis detected by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) from pooled samples. Acta Trop. 2015, 141, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannotti-Passos, L.K.; Magalhães, K.G.; Carvalho, O.S.; Vidigal, T.H.D.A. Multiplex PCR for both identification of Brazilian Biomphalaria species (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) and diagnosis of infection by Schistosoma mansoni (Trematoda: Schistosomatidae). J. Parasitol. 2006, 92, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhoho, N.D.; Katsumata, T.; Kimura, E.; Migwi, D.K.; Mutua, W.R.; Kiliku, F.M.; Habe, S.; Aoki, Y. Cercarial density in the river of an endemic area of schistosomiasis haematobia in Kenya. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 57, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, Y.; Sato, K.; Muhoho, N.D.; Noda, S.; Kimura, E. Cercariometry for detection of transmission sites for schistosomiasis. Parasitol. Int. 2003, 52, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, J.; Kedves, K.; Hassan, A.H.M.; Haberl, B.; Haas, W. Detection of Schistosoma mansoni cercariae in plankton samples by PCR. Acta Trop. 2004, 91, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worrell, C.; Xiao, N.; Vidal, J.E.; Chen, L.; Zhong, B.; Remais, J. Field detection of Schistosoma japonicum cercariae in environmental water samples by quantitative PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2192–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.W.; Remais, J. Quantitative detection of Schistosoma japonicum cercariae in water by real-time PCR. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzinger, J.; Becker, S.L.; van Lieshout, L.; van Dam, G.J.; Knopp, S. New diagnostic tools in schistosomiasis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, K.R.; Cantera, J.L.; Storey, H.L.; Leader, B.T.; de Los Santos, T. Diagnostic tests to support late-stage control programs for schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmeier, H.; Poggensee, G. Diagnostic techniques in schistosomiasis control. A review. Acta Trop. 1993, 52, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TchuemTchuenté, L.A. Control of soil-transmitted helminths in sub-Saharan Africa: Diagnosis, drug efficacy concerns and challenges. Acta Trop. 2011, 120 (Suppl 1), S4–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stothard, J.R.; Stanton, M.C.; Bustinduy, A.L.; Sousa-Figueiredo, J.C.; Van Dam, G.J.; Betson, M.; Waterhouse, D.; Ward, S.; Allan, F.; Hassan, A.A.; et al. Diagnostics for schistosomiasis in Africa and Arabia: A review of present options in control and future needs for elimination. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1947–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Assay Type | Advantages | Limitations | Relative Cost * | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cPCR |
|
| $$ | [42,43,44] |
| nPCR |
|
| $$ | [45,46] |
| qPCR |
|
| $$$ | [13,29,38] |
| LAMP |
|
| $ | [47,48] |
| RPA |
|
| $ | [49,50,51] |
| ddPCR |
|
| $$$ | [35,52,53] |
| Direct PCR |
|
| $ | [54] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weerakoon, K.G.; Gordon, C.A.; McManus, D.P. DNA Diagnostics for Schistosomiasis Control. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3030081
Weerakoon KG, Gordon CA, McManus DP. DNA Diagnostics for Schistosomiasis Control. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2018; 3(3):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3030081
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeerakoon, Kosala G., Catherine A. Gordon, and Donald P. McManus. 2018. "DNA Diagnostics for Schistosomiasis Control" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 3, no. 3: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3030081
APA StyleWeerakoon, K. G., Gordon, C. A., & McManus, D. P. (2018). DNA Diagnostics for Schistosomiasis Control. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 3(3), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed3030081






