Brucella, Coxiella, and Theileria Species DNA in Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis Ticks Collected from Goats and Sheep in Qinghai Province, Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.2. Molecular Identification of Brucella spp., Coxiella sp., and Theileria/Babesia
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Collection of Tick Samples
3.2. Detection and Analysis of the Brucella spp.
3.3. Detection and Analysis of the Coxiella
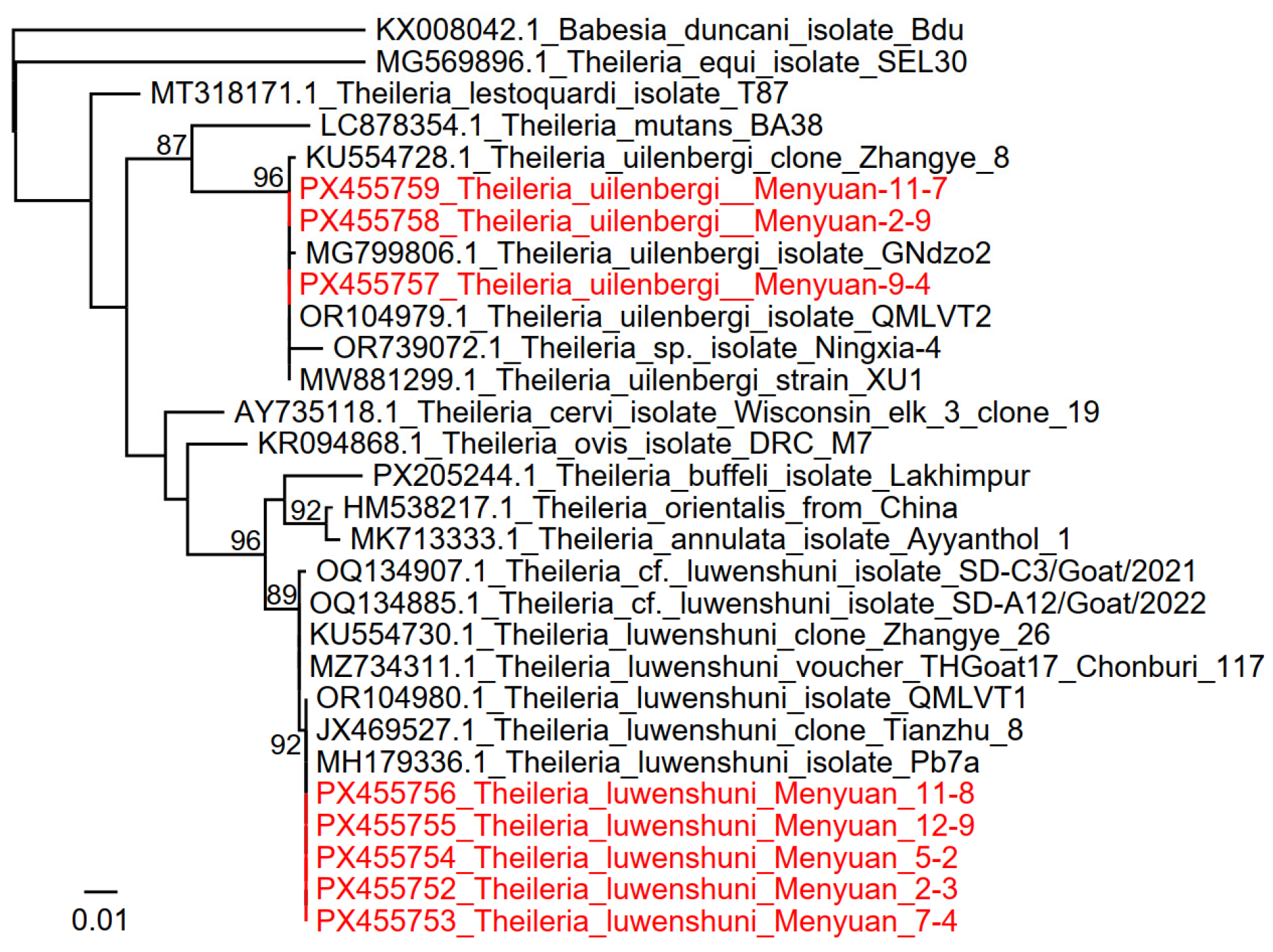
3.4. Detection and Analysis of the Theileria/Babesia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Robbins, R.G.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Petney, T.N.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Horak, I.G. Comments on controversial tick (Acari: Ixodida) species names and species described or resurrected from 2003 to 2008. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2009, 48, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.; Kahl, O.; Zintl, A. Pathogens transmitted by Ixodes ricinus. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2024, 15, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Estrada-Pena, A.; Venzal, J.M.; Kocan, K.M.; Sonenshine, D.E. Overview: Ticks as vectors of pathogens that cause disease in humans and animals. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 6938–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Galon, E.M.; Lao, Y.; Kang, M.; Xuan, X.; Li, J.; Sun, Y. De novo assembled transcriptomics assisted label-free quantitative proteomics analysis reveals sex-specific proteins in the intestinal tissue of Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2023, 109, 105409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Tian, J.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, H.; Qin, X.; Wang, W.; Li, K. Molecular survey of vector-borne pathogens in ticks, sheep keds, and domestic animals from Ngawa, Southwest China. Pathogens 2022, 11, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tian, Z.; Liu, Z.; Niu, Q.; Han, R.; Li, Y.; Guan, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, G.; Luo, J.; et al. Novel spotted fever group rickettsiae in Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis ticks from Gansu, Northwest China. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Guan, G.; Ma, M.; Luo, J.; Yin, H. Investigations into the natural infection rate of Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis with piroplasma using a nested PCR. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2008, 44, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Guan, G.; Ma, M.; Luo, J.; Lu, B.; Yuan, G.; Bai, Q.; Lu, C.; Yuan, Z.; Preston, P. Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis ticks transmit at least two different Theileria species: One is infective to yaks, one is infective to sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 107, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Du, C.H.; Zhao, Y.L.; Luo, Z.; Li, M.; Zeng, D.N.; Wang, F.; Du, C.B.; Sun, Y.; Chang, Q.C.; et al. Theileria luwenshuni and Novel Babesia spp. Infections in Humans, Yunnan Province, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2025, 31, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Shen, J. Classific Atlas of Parasites for Livestock and Poultry in China; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Leray, M.; Yang, J.Y.; Meyer, C.P.; Mills, S.C.; Agudelo, N.; Ranwez, V.; Boehm, J.T.; Machida, R.J. A new versatile primer set targeting a short fragment of the mitochondrial COI region for metabarcoding metazoan diversity: Application for characterizing coral reef fish gut contents. Front. Zool. 2013, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamian, S.; Esmaelizad, M.; Zahraei, T.; Etemadi, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Afshar, D.; Ghaderi, S. A Novel PCR Assay for detecting Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2017, 8, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Cheng, D.; Xing, Z.; Fan, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Piao, D.; Jiang, H. A family cluster of Brucella abortus infections possibly due to contact with a sika deer in Northeast China. Future Microbiol. 2025, 20, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Cheng, D.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, W.; Tursun, B.; Jiang, H. The clinical manifestations and laboratory test results of Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus in acute brucellosis patients. J. Infect. Public Health 2025, 19, 103031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.G.; Lee, S.H.; VanBik, D.; Ouh, I.O.; Yun, S.H.; Choi, E.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, J.W.; Cho, G.J.; et al. Detection and genotyping of Coxiella burnetii and Coxiella-like bacteria in horses in South Korea. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Klempner, M.S. Babesiosis in patients with AIDS: A chronic infection presenting as fever of unknown origin. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duron, O.; Noël, V.; McCoy, K.D.; Bonazzi, M.; Sidi-Boumedine, K.; Morel, O.; Vavre, F.; Zenner, L.; Jourdain, E.; Durand, P.; et al. The recent evolution of a maternally-inherited endosymbiont of ticks led to the emergence of the Q fever pathogen, Coxiella burnetii. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, N.; Gao, C.; Liu, M.; Jie, R.; Lu, M.; Ma, Y.; Meng, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Investigation of Babesia spp. and Theileria spp. in ticks from Western China and identification of a novel genotype of Babesia caballi. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Delsuc, F.; Dufayard, J.F.; Gascuel, O. Estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies with PhyML. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 537, 113–137. [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl-Rajala, E.; Hoffman, T.; Fretin, D.; Godfroid, J.; Sattorov, N.; Boqvist, S.; Lundkvist, Å.; Magnusson, U. Detection and characterization of Brucella spp. in bovine milk in small-scale urban and peri-urban farming in Tajikistan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundle, D.R.; McGiven, J. Brucellosis: Improved diagnostics and vaccine insights from synthetic glycans. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2958–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, C.G.; Johnson, V.E.; Scott, H.M.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Global estimate of human brucellosis incidence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Bracho, C.; Salgado-Jiménez, B.; Beltrán-Parra, L.G.; Hernández-Monroy, I.; Vargas-Pino, F.; Rodríguez, D.; López-Martínez, I.; Pastén-Sánchez, S.; González-Roldán, J.F.; Membrillo-Hernández, J.; et al. Evaluation of serological diagnostic tests of human brucellosis for prevention and control in Mexico. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Wureli, H.; Xie, S.; Chen, C.; Wei, Q.; Cui, B.; Tu, C.; Wang, Y. Brucella melitensis and B. abortus in eggs, larvae and engorged females of Dermacentor marginatus. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, R.; Qiu, Y. Investigation of the presence of Ochrobactrum spp. and Brucella spp. in Haemaphysalis longicornis. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wen, X.; Li, M.; Moumouni, P.F.A.; Galon, E.M.; Guo, Q.; Rizk, M.A.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Ji, S.; et al. Molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens harbored by ticks collected from livestock in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chahan, B.; Zhang, W. Molecular analysis of Anaplasma ovis, Theileria ovis and Brucella abortus in adult Ornithodoros lahorensis soft ticks (Acari: Ixodida: Argasidae) isolated from the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 68, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.F.; Xu, L.Q.; Hu, G.Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, H.Y.; Piao, D.R.; Qin, Y.M.; et al. MLVA and MLST typing of Brucella from Qinghai, China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2016, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Maharana, B.R.; Thakre, B.; Brahmbhatt, N.N.; Joseph, J.P. 18S rRNA Gene-Based Piroplasmid PCR: An Assay for Rapid and Precise Molecular Screening of Theileria and Babesia Species in Animals. Acta Parasitol. 2022, 67, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, Y.; Hu, J.; Dan, X.; Zhao, H. Epidemiological and Molecular Characteristics of Piroplasmids and Anaplasma spp. in Tan Sheep, Ningxia, Northwest China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 2529855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Wu, X.; Tang, L.; Yang, M.; Hornok, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Y. Molecular-phylogenetic analyses of Babesia and Theileria species from small mammals and their ticks in northern China suggest new reservoirs of bovine and equine piroplasms. Vet. Parasitol. 2024, 332, 110304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, M.; Prior, S.; Brüning-Richardson, A. Human babesiosis: The past, present and future. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2025, 27, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primer Name | Targeted Gene | Round | Sequence | Annealing Temperature | Amplicon Length | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BruRbin5-Forward | rpoB | 1, 2 | 5-CGAGTTCGATTCCAAGGACATCG-3 | 55 °C | 450 bp | [15] |
| BruRbex3-Reverse | rpoB | 1 | 5-ATATTGACATGGTCGATATCGAGAAC-3 | 55 °C | ||
| BruRbin3-Reverse | rpoB | 2 | 5-AACCTTTTCATCGATTTCGTCACC-3 | 55 °C | ||
| Osong-F234-Forward | A unique repeat sequence | 1, 2 | 5-ACTGCATGGCATTTTTCGCCC-3 | 53 °C | 320–340 bp | [16] |
| Osong-R609-Reverse | A unique repeat sequence | 1 | 5-GGGAAGAGCGTTACAGGCGT-3 | 53 °C | ||
| Osong-inR-Reverse | A unique repeat sequence | 2 | 5-CGCAAAGTGACGCCACAGAG -3 | 53 °C | ||
| Bcspex5-Forward | Bcsp31 | 1 | 5-ATGACCTGGCATTCTTCACATC-3 | 53 °C | 800 bp | [15] |
| Bcspin5-Forward | Bcsp31 | 2 | 5-CTGCGTTTTTAATCGTTTCAGTC-3 | 53 °C | ||
| Bcsp3-Reverse | Bcsp31 | 1, 2 | 5-AGATCGGAACGAGCGAAATA-3 | 53 °C |
| Species | Goat Ticks | Sheep Ticks | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coxiella | Coxiella endosymbiont of H. qinghaiensis | 88/90 (97.78%) | 44/46 (95.65%) | 132/136 (97.06%) |
| Brucella | Brucella melitensis | 5/90 (5.56%) | 1/46 (2.17%) | 6/136 (4.41%) |
| Brucellaabortus | 3/90 (3.33%) | 2/46 (4.35%) | 5/136 (3.68%) | |
| Theileria | Theileria luwenshuni | 79/90 (87.78%) | 23/46 (50.00%) | 102/136 (75.00%) |
| Theileria uilenbergi | 6/90 (6.67%) | 16/46 (34.78%) | 22/136 (16.18%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, X.; Cai, S.; Wu, L.; An, G.; Zhao, H.; Piao, D.; et al. Brucella, Coxiella, and Theileria Species DNA in Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis Ticks Collected from Goats and Sheep in Qinghai Province, Northwest China. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2026, 11, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed11010017
Li K, Yang X, Wang J, Li S, Zhao X, Cai S, Wu L, An G, Zhao H, Piao D, et al. Brucella, Coxiella, and Theileria Species DNA in Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis Ticks Collected from Goats and Sheep in Qinghai Province, Northwest China. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2026; 11(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed11010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kun, Xuxin Yang, Jianling Wang, Shengyu Li, Xu Zhao, Shengjun Cai, Leyu Wu, Guoqiang An, Hongyan Zhao, Dongri Piao, and et al. 2026. "Brucella, Coxiella, and Theileria Species DNA in Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis Ticks Collected from Goats and Sheep in Qinghai Province, Northwest China" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 11, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed11010017
APA StyleLi, K., Yang, X., Wang, J., Li, S., Zhao, X., Cai, S., Wu, L., An, G., Zhao, H., Piao, D., Xu, Q., Fan, Y., Li, J., & Jiang, H. (2026). Brucella, Coxiella, and Theileria Species DNA in Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis Ticks Collected from Goats and Sheep in Qinghai Province, Northwest China. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 11(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed11010017




