Recurrent Malaria with Plasmodium vivax: A Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Parasite factors: Strain variability in relapse frequency and timing plays a major role. The size of the hypnozoite reservoir, which is closely linked to the sporozoite inoculum, is a key determinant of this risk. This inoculum size varies depending on the number and intensity of infectious mosquito bites. A large reservoir increases the likelihood of relapse [11,12,13,14].
- Host factors: Age, acquired immunity, and treatment adherence are central to relapse risk. In addition, genetic polymorphisms can influence treatment outcomes. For example, CYP2D6 (cytochrome P450 2D6) variants may impair drug metabolism, and G6PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) deficiency can limit the use of hypnozoitocidal drugs due to the risk of hemolysis, leading to treatment failure. Coinfections and febrile illnesses may also act as external triggers for hypnozoite reactivation [1,4,12,14].
2. Case Report
2.1. Patient Background
2.2. Travel History
2.3. First Admission
2.4. Second Admission—First Relapse (25 Days Later)
2.5. Third Admission—Second Relapse (60 Days Later)
2.6. Follow-Up (After 25 Days)
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RT-PCR | Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| CYP2D6 | Cytochrome P450 2D6 |
| G6PD | Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| BMI | Body-mass index |
| RDTs | Rapid diagnostic tests |
| HBsAg | Hepatitis B surface antigen |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HAV | Hepatitis A virus |
| RBC | Red blood cell |
| ALT | Alanine transaminase |
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| CK | Creatine kinase |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| EGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| GGT | Gamma glutamyl transpherase |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| INR | International normalized ratio |
| CFU | Colony-forming units |
References
- White, N.J. Determinants of Relapse Periodicity in Plasmodium vivax Malaria. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandrala, D.; Gupta, N.; Lavu, A.; Nallapati, V.T.; Guddattu, V.; Saravu, K. Recurrence in Plasmodium vivax malaria: A prospective cohort study with long follow-up from a coastal region in South-West India. F1000Research 2022, 11, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatem, A.J.; Jia, P.; Ordanovich, D.; Falkner, M.; Huang, Z.; Howes, R.; Hay, S.I.; Gething, P.W.; Smith, D.L. The Geography of Imported Malaria to Non-Endemic Countries: A Meta-Analysis of Nationally Reported Statistics. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebstie, Y.A.; Abay, S.M.; Tadesse, W.T.; Ejigu, D.A. Tafenoquine and Its Potential in the Treatment and Relapse Prevention of Plasmodium vivax Malaria: The Evidence to Date. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 2387–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S. Plasmodium—A Brief Introduction to the Parasites Causing Human Malaria and Their Basic Biology. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2021, 40, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.T.; Shirreff, G.; Karl, S.; Ghani, A.C.; Mueller, I. Variation in Relapse Frequency and the Transmission Potential of Plasmodium vivax Malaria. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antinori, S.; Giacomelli, A.; Casalini, G.; Ridolfo, A.L. How to Manage Adult Patients with Malaria in the Non-Endemic Setting. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2024, 30, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusiyana, N.; Agustin, A.F. The Characteristic of Recurrent Malaria Episode: An Observational Study in Timika Papua. Acta Med. Indones. 2023, 55, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Hidalgo, M.F.; González, E.L.; Moles, S.I.; García, C.A.; Muñoz, J.M.R.; Ortega, R.L.; Navés, L.G.; Sánchez, A.B.; Jover-Sáenz, A. Diagnostic Challenges of Recurrent Malaria in Non-Endemic Areas. J. Travel Med. 2024, 31, taae041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wångdahl, A.; Sondén, K.; Wyss, K.; Stenström, C.; Björklund, D.; Zhang, J.; Hervius Askling, H.; Carlander, C.; Hellgren, U.; Färnert, A. Relapse of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale Malaria With and Without Primaquine Treatment in a Nonendemic Area. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battle, K.E.; Karhunen, M.S.; Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Howes, R.E.; Golding, N.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Messina, J.P.; Shanks, G.D.; Smith, D.L.; et al. Geographical Variation in Plasmodium vivax Relapse. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commons, R.J.; Simpson, J.A.; Watson, J.; White, N.J.; Price, R.N. Estimating the Proportion of Plasmodium vivax Recurrences Caused by Relapse: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, E.; Cromer, D.; Mehra, S.; Adekunle, A.I.; Flegg, J.A.; Anstey, N.M.; Watson, J.A.; Chu, C.S.; Mueller, I.; Robinson, L.J.; et al. Population Heterogeneity in Plasmodium vivax Relapse Risk. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishikesh, K.; Saravu, K. Primaquine Treatment and Relapse in Plasmodium vivax Malaria. Pathog. Glob. Health 2016, 110, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovici, J.; Friedrich, L.R.; Kim, S.; Bin, S.; Run, V.; Lek, D.; Cannon, M.V.; Menard, D.; Serre, D. Genomic Analyses Reveal the Common Occurrence and Complexity of Plasmodium vivax Relapses in Cambodia. mBio 2018, 9, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llanos-Cuentas, A.; Lacerda, M.V.G.; Hien, T.T.; Vélez, I.D.; Namaik-larp, C.; Chu, C.S.; Villegas, M.F.; Val, F.; Monteiro, W.M.; Brito, M.A.M.; et al. Tafenoquine Versus Primaquine to Prevent Relapse of Plasmodium vivax Malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, A.M.; González-Cerón, L.; Santillán-Valenzuela, F.; Parrales, M.E.; Montoya, A. Recurrent Plasmodium vivax Cases of Both Short and Long Latency Increased with Transmission Intensity and Were Distributed Year-Round in the Most Affected Municipalities of the RACCN, Nicaragua, 2013–2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.S.; Freedman, D.O. Tafenoquine and G6PD: A Primer for Clinicians. J. Travel Med. 2019, 26, taz023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, L.F.; Huber, J.H.; Rojas Salas, O.; Ramírez Rojas, M.; Romero, L.M.; Gutiérrez Alvarado, J.M.; Perkins, T.A.; Prado, M.; Rodríguez, R.M. Malaria Elimination in Costa Rica: Changes in Treatment and Mass Drug Administration. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Laboratory Test | Normal Range | First Admission | Second Admission | Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC (106/µL) | 4.0–5.5 | 4.48 | 4.33 | 6.64 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 40–54 | 40.2 | 39.7 | 42 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12–16 | 14.3 | 13.7 | 14.4 |
| Lymphocytes # (103/µL) | 0.8–4 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 1.82 |
| Lymphocytes % | 20–40 | 20.1 | 18.2 | 38.8 |
| Monocytes # (103/µL) | 0.12–1.2 | 0.51 | 0.4 | 0.33 |
| Monocytes % | 1–10 | 13 | 7.7 | 7 |
| Neutrophils # (103/µL) | 1.5–7 | 2.59 | 0.95 | 2.45 |
| Neutrophils % | 50–70 | 65.4 | 70.7 | 52.2 |
| Leucocytes (103/µL) | 4.0–10 | 3.95 | 5.23 | 4.69 |
| Platelets (103/µL) | 150–400 | 47 | 100 | 180 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 19–44 | 33 | 31 | 36 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.6–1.2 | 1.34 | 1.2 | 1.17 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | >90 | 65.18 | 74 | – |
| ALT (U/L) | 0–45 | 26 | 121 | 33 |
| AST (U/L) | 11–34 | 30 | 55 | 25 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.2–1.2 | 2.45 | 3.28 | 0.65 |
| Direct bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0–0.5 | 0.64 | 0.88 | – |
| GGT (U/L) | 0–55 | 22 | 26 | – |
| Serum glucose (mg/dL) | 70–105 | – | 110 | 86 |
| Amylase (U/L) | 28–100 | – | 45 | – |
| Total proteins (g/L) | 60–80 | – | 75.3 | – |
| Albumin (g/L) | 35–52 | – | 47.7 | – |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 0–150 | – | 193 | – |
| K (mmol/L) | 3.5–5.1 | 3.71 | 4.34 | – |
| Na (mmol/L) | 136–145 | 132 | 138 | – |
| Mg (mg/dL) | 1.6–2.6 | – | 1.97 | – |
| Fe (µg/dL) | 65–175 | – | 63 | – |
| CK (U/L) | 30–200 | 82 | 32 | 70 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 3.7–7.7 | – | 5.6 | – |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 50–118 | – | 124 | – |
| LDH (U/L) | 125–220 | – | 341 | 146 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | Negative | Positive (>6 mg/dL) | Positive (>6 mg/dL) | – |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 170–420 | 374.3 | 456.7 | – |
| ESR (mm/1 h) | 3–10 | 16 | 46 | 6 |
| INR | 0.8–1.2 | 0.94 | 1.01 | – |
| Procalcitonin | <0.5 | <0.5 | – | – |
| Blood culture | Negative | Negative | – | – |
| Urine culture | <1000 CFU | <1000 CFU | – | – |
| Test | First Admission | Second Admission | Third Admission |
|---|---|---|---|
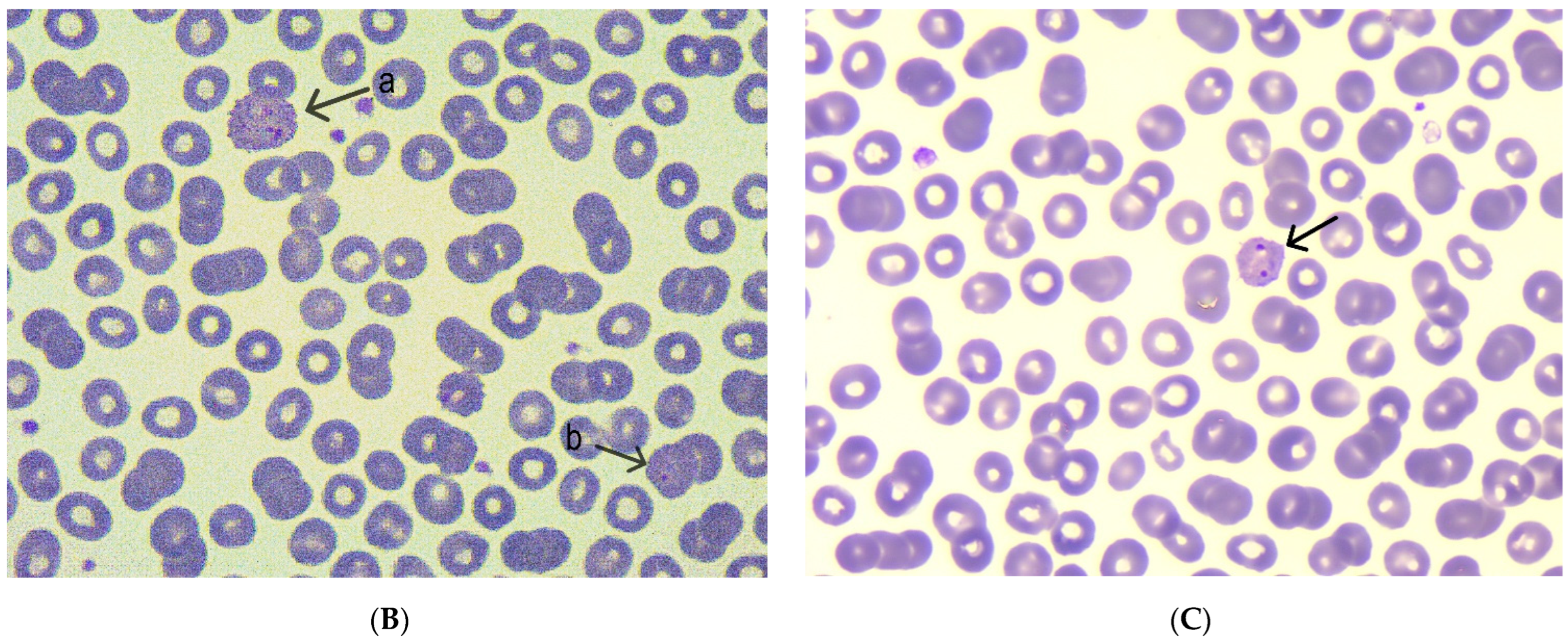
| Blood smear microscopy | Normochromic normocytic erythrocytes, discrete poikilocytosis | Normochromic normocytic erythrocytes | Normochromic normocytic erythrocytes |
| Presence of Plasmodium spp. | Presence of Plasmodium spp. with trophozoites and gametocytes | Presence of Plasmodium spp. | |
| Severe thrombocytopenia | Mild thrombocytopenia | Normal thrombocyte count | |
| Parasitemia (%) | – | 0.75% parasitemia | 0.3% parasitemia |
| RT-PCR | Plasmodium vivax detected | Plasmodium vivax detected | – |
| Malaria RDT | Positive | Negative | Negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrejkovits, Á.V.; Pop, A.V.; Fejér, M.; Gîrbovan, E.C.; Coșeriu, R.L.; Vintilă, C.; Văsieșiu, A.M. Recurrent Malaria with Plasmodium vivax: A Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090261
Andrejkovits ÁV, Pop AV, Fejér M, Gîrbovan EC, Coșeriu RL, Vintilă C, Văsieșiu AM. Recurrent Malaria with Plasmodium vivax: A Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(9):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090261
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrejkovits, Ákos Vince, Adrian Vlad Pop, Magdolna Fejér, Elena Cristina Gîrbovan, Răzvan Lucian Coșeriu, Camelia Vintilă, and Anca Meda Văsieșiu. 2025. "Recurrent Malaria with Plasmodium vivax: A Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 9: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090261
APA StyleAndrejkovits, Á. V., Pop, A. V., Fejér, M., Gîrbovan, E. C., Coșeriu, R. L., Vintilă, C., & Văsieșiu, A. M. (2025). Recurrent Malaria with Plasmodium vivax: A Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(9), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10090261







