The Impact of a Community Pharmacy-Led Deworming-Related Counselling Service: An Interventional Study in a Low-to-Middle Income Country
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Introduction to Parasitic Diseases
1.2. Parasites
1.3. Protozoa
1.4. Heliminths
1.5. Preventive Measures Against Parasitic Infections
1.6. Challenges of Parasitic Infections Management and Role of the Pharmacist
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Recruitment
2.3. Randomization
2.4. Intervention
- washing hands with soap and water after using the toilet;
- washing hands with soap and water before and after eating;
- trimming fingernails regularly;
- drinking clean, safe water (filtered/boiled/bottled);
- changing and washing bed sheets regularly;
- washing fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating;
- defecating in a sanitary toilet, not performing open defecation;
- educating my children/family members about handwashing and hygiene
2.5. Sample Size Calculation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bockarie, M.J.; Kelly-Hope, L.A.; Rebollo, M.; Molyneux, D.H. Preventive Chemotherapy as a Strategy for Elimination of Neglected Tropical Parasitic Diseases: Endgame Challenges. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bhargava, G. Editorial: Protozoal Infections: Treatment and Challenges. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1002602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guideline: Preventive Chemotherapy to Control Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in at-Risk Population Groups; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-155011-6. [Google Scholar]
- de Silva, N.R.; Brooker, S.; Hotez, P.J.; Montresor, A.; Engels, D.; Savioli, L. Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections: Updating the Global Picture. Trends Parasitol. 2003, 19, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamory, J.; Miguel, E.; Walker, M.; Kremer, M.; Baird, S. Twenty-Year Economic Impacts of Deworming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023185118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, J.; Garba, A.; Boubacar, K.; Yayé, Y.; Sebongou, H.; Barkire, A.; Fleming, F.M.; Mounkaila, I.; Adamou, S.; Jackou, M.L.B. Neglected Tropical Diseases: Comparison of the Costs of Integrated and Vertical Preventive Chemotherapy Treatment in Niger. Int. Health 2013, 5, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, L.S.; Latham, M.C.; Ottesen, E.A. Malnutrition and Parasitic Helminth Infections. Parasitology 2000, 121, S23–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-El-Naga, I.F. Towards Elimination of Schistosomiasis after 5000 Years of Endemicity in Egypt. Acta Trop. 2018, 181, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Dogs, Cats, Parasites, and Humans in Brazil: Opening the Black Box. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, B.; Keetile, M.; Ahinkorah, B.O.; Ameyaw, E.K.; Seidu, A.-A.; Yaya, S. Utilization of Deworming Medication and Its Associated Factors among Pregnant Married Women in 26 Sub-Saharan African Countries: A Multi-Country Analysis. Trop. Med. Health 2021, 49, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, F.; Gillam, S.J.; Ngondi, J.M. Improving Access to Medicines for Neglected Tropical Diseases in Developing Countries: Lessons from Three Emerging Economies. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.M.; Addiss, D.G. Sustainable Access to Deworming Drugs in a Changing Landscape. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e395–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooker, S.J.; Nikolay, B.; Balabanova, D.; Pullan, R.L. Global Feasibility Assessment of Interrupting the Transmission of Soil-Transmitted Helminths: A Statistical Modelling Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacorta Linaza, R.; Garner, T.; Genovezos, C. Building Supply Chain Capacity for Neglected Tropical Diseases: Experience from the Ascend West and Central Africa Programme. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 115, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capela, R.; Moreira, R.; Lopes, F. An Overview of Drug Resistance in Protozoal Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, T.G. Are New Anthelmintics Needed to Eliminate Human Helminthiases? Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotez, P.J. Global Deworming: Moving Past Albendazole and Mebendazole. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1101–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleman, S.; Zeleke, G.; Deti, H.; Mekonnen, Z.; Duchateau, L.; Levecke, B.; Vercruysse, J.; D’Hondt, M.; Wynendaele, E.; De Spiegeleer, B. Quality of Medicines Commonly Used in the Treatment of Soil Transmitted Helminths and Giardia in Ethiopia: A Nationwide Survey. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eassa, S.M.; Abd El-Wahab, E.W. Vector-Borne Diseases in Egypt: Present Status and Accelerating toward Elimination. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2022, 59, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Khurshid, M.; Arshad, M.I.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.; Yasmeen, N.; Shah, T.; Chaudhry, T.H.; Rasool, M.H.; Shahid, A.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance: One Health One World Outlook. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 771510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Taweel, H.A. Understanding Drug Resistance in Human Intestinal Protozoa. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 1647–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- One Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/one-health (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Moustafa, H.A.M.; Wen, M.M.; AbdElrahman, M.; Hamdan, A.M.E.; Alkhamali, A.; Kassem, A.B. Psychological Challenges Faced Community Pharmacists during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study. Pharm. Pr. 2025, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ending the Neglect to Attain the Sustainable Development Goals: A Rationale for Continued Investment in Tackling Neglected Tropical Diseases 2021–2030. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240052932 (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Jourdan, P.M.; Lamberton, P.H.L.; Fenwick, A.; Addiss, D.G. Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections. Lancet 2018, 391, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truscott, J.E.; Turner, H.C.; Anderson, R.M. What Impact Will the Achievement of the Current World Health Organisation Targets for Anthelmintic Treatment Coverage in Children Have on the Intensity of Soil Transmitted Helminth Infections? Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, B.; Bharti, S.; Khurana, S. Worm Infestation: Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention. Ind. J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, J.-F.; Milotic, M.; Filion, A.; Eriksson, A. Host Specificity and the Reproductive Strategies of Parasites. Parasitology 2022, 149, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theel, E.S.; Pritt, B.S.; Hayden, R.T.; Wolk, D.M.; Carroll, K.C.; Tang, Y.-W. Parasites. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 411–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennis, I.; De Brouwere, V.; Belrhiti, Z.; Sahibi, H.; Boelaert, M. Psychosocial Burden of Localised Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: A Scoping Review. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kc, B.; Alrasheedy, A.A.; Leggat, P.A.; Mohamed Ibrahim, M.I.; Christopher, C.M.; Sapkota, B.; Shrestha, S. Types and Outcomes of Pharmacist-Managed Travel Health Services: A Systematic Review. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 51, 102494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, S.M.; Stark, D.; Harkness, J.; Ellis, J. Enteric Protozoa in the Developed World: A Public Health Perspective. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanan, S.; Abd, H.; Bayoumi, M.; Saeed, A.; Sandström, G. Prevalence of Protozoa Species in Drinking and Environmental Water Sources in Sudan. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.D.O.; Resende, J.A.; Gil, F.F.; Santos, J.F.G.; Gomes, M.A. Prevalence of Entamoeba Histolytica and Other Enteral Parasitic Diseases in the Metropolitan Region of Belo Horizonte, Brazil. A Cross-Sectional Study. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2018, 136, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elswaifi, S.F.; Palmieri, J.R.; El-Tantawy, N.; El-Hussiny, M.; Besheer, T.; Abohashem, E. Comparison of Microscopic and Immunoassay Examination in the Diagnosis of Intestinal Protozoa of Humans in Mansoura, Egypt. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stanley, S.L., Jr. Amoebiasis. Lancet 2003, 361, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Faruque, A.S.; Hahn, P.; Lyerly, D.M.; Petri, W.A. Entamoeba Histolytica and Entamoeba Dispar Infection in Children in Bangladesh. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibeaux, R.; Weber, C.; Hon, C.-C.; Dillies, M.-A.; Avé, P.; Coppée, J.-Y.; Labruyère, E.; Guillén, N. Identification of the Virulence Landscape Essential for Entamoeba Histolytica Invasion of the Human Colon. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, D.M.; Guillen, N. Virulence and Virulence Factors in Entamoeba histolytica, the Agent of Human Amoebiasis. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, Y.; Sharma, M.; Izumiyama, S.; Singh, U. Exploring Virulence and Stress Response in Entamoeba histolytica: Insights from Clinical Strains. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0050625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, R.C.; Singh, U. Identification of an Entamoeba Histolytica Serine-, Threonine-, and Isoleucine-Rich Protein with Roles in Adhesion and Cytotoxicity. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Mollah, N.U.; Ali, I.K.; Alam, K.; Eubanks, A.; Lyerly, D.; Petri, W.A. Diagnosis of Amebic Liver Abscess and Intestinal Infection with the TechLab Entamoeba Histolytica II Antigen Detection and Antibody Tests. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3235–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Kabir, M.; Mondal, D.; Ali, I.K.M.; Petri, W.A.; Haque, R. Real-Time-PCR Assay for Diagnosis of Entamoeba Histolytica Infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, D.; Sehgal, R.; Chawla, Y.; Mahajan, R.C.; Malla, N. In Vitro Activity of Antiamoebic Drugs against Clinical Isolates of Entamoeba Histolytica and Entamoeba Dispar. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2004, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, T.; Nishise, S.; Ichihara, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Takeuchi, T. Difficulties in the Treatment of Intestinal Amoebiasis in Mentally Disabled Individuals at a Rehabilitation Institution for the Intellectually Impaired in Japan. Chemotherapy 2010, 56, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, L.R.; Singh, N.; Verma, A.K.; Paul, J. Differential Expression and Immunolocalization of Antioxidant Enzymes in Entamoeba histolytica Isolates during Metronidazole Stress. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzinelli-Guimaraes, P.H.; Nutman, T.B. Helminth Parasites and Immune Regulation. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboyá, M.I.; Catalá, L.; Nicholls, R.S.; Ault, S.K. Update on the Mapping of Prevalence and Intensity of Infection for Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Latin America and the Caribbean: A Call for Action. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strunz, E.C.; Addiss, D.G.; Stocks, M.E.; Ogden, S.; Utzinger, J.; Freeman, M.C. Water, Sanitation, Hygiene, and Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, K.; Dixon, R.; Khan, S.A.; Gunawardena, K.; Kihara, J.H.; Smith, J.L.; Drake, L.; Makkar, P.; Raman, S.; Singh, S.; et al. The Epidemiology of Soil-Transmitted Helminths in Bihar State, India. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moreno, O.; Domingo, L.; Teixidor, J.; Gracenea, M. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Intestinal Parasitisation: A Cross-Sectional Study among Outpatients with Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Catalonia, Spain. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J. Global Anthelmintic Chemotherapy Programs: Learning from History. Trends Parasitol. 2003, 19, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albonico, M.; Allen, H.; Chitsulo, L.; Engels, D.; Gabrielli, A.-F.; Savioli, L. Controlling Soil-Transmitted Helminthiasis in Pre-School-Age Children through Preventive Chemotherapy. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardim-Botelho, A.; Raff, S.; Rodrigues, R.D.; Hoffman, H.J.; Diemert, D.J.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Bethony, J.M.; Gazzinelli, M.F. Hookworm, Ascaris Lumbricoides Infection and Polyparasitism Associated with Poor Cognitive Performance in Brazilian Schoolchildren. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2008, 13, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, L.S.; Holland, C.V.; Cooper, E.S. The Public Health Significance of Trichuris Trichiura. Parasitology 2000, 121, S73–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotte, N.; Papaiakovou, M.; Grant, J.R.; Bierwert, L.A.; Llewellyn, S.; McCarthy, J.S.; Williams, S.A. Improved PCR-Based Detection of Soil Transmitted Helminth Infections Using a Next-Generation Sequencing Approach to Assay Design. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, J.D.; Hotez, P.J.; Amza, A.; Stoller, N.E.; Gaynor, B.D.; Porco, T.C.; Lietman, T.M. Elimination and Eradication of Neglected Tropical Diseases with Mass Drug Administrations: A Survey of Experts. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, A. Praziquantel: Do We Need Another Antischistosoma Treatment? Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J. Efficacy of Current Drugs against Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2008, 299, 1937–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaskou, M.; Duggan, C.; Joynes, R.; Rosado, H.R. Pharmacy’s Role in Antimicrobial Resistance and Stewardship. Available online: https://pharmaceutical-journal.com/article/research/pharmacys-role-in-antimicrobial-resistance-and-stewardship (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Balsom, C.; Pittman, N.; King, R.; Kelly, D. Impact of a Pharmacist-Administered Deprescribing Intervention on Nursing Home Residents: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pharm. Weekbl. 2020, 42, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, A.B.; Ghoneim, A.I.; Nounou, M.I.; El-Bassiouny, N.A. Community Pharmacists’ Needs, Education, and Readiness in Facing COVID-19: Actions & Recommendations in Egypt. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2021, 75, e14762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, H.A.M.; Hamid, A.E.; Hassoub, G.; Kassem, A.B. Assessing the Impact of Critical Care Training on Pharmacy Students in Egypt: A Pre-Post Study. BMC Med. Educ. 2024, 24, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.B.; Al Meslamani, A.Z.; Elmaghraby, D.H.; Magdy, Y.; AbdElrahman, M.; Hamdan, A.M.E.; Mohamed Moustafa, H.A. The Pharmacists’ Interventions after a Drug and Therapeutics Committee (DTC) Establishment during the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Pharm. Policy Pr. 2024, 17, 2372040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekenga, V.; Bailey-Wheeler, J.; Hart, T.; Sarpong, D.; Earls, M. Patients’ Perception of Community Pharmacists as Healthcare Providers and Willingness to Participate in Pharmacist Services: A Pilot Study. J. Pharm. Health Serv. Res. 2018, 9, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.B.; Abdelrahim, M.E.; Mousa, A.; Harun, A.; Al-husseini, H.; Khaled, S.; Elhadidy, M.; Ibrahim, O.M. The Screening of Diabetes, Obesity, and Hypertension Risks Associated with Hepatitis C Within the Egyptian Population in a Community Pharmacy Setting. J. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2022, 6, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thidrickson, D.; Goodyer, L. Pharmacy Travel Health Services in Canada: Experience of Early Adopters. Pharmacy 2019, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Qader, D.H.; Saadi Ismael, N.; Al Meslamani, A.Z.; Albassam, A.; El-Shara’, A.A.; Lewis, P.J.; Hamadi, S.; Al Mazrouei, N. The Role of Clinical Pharmacy in Preventing Prescribing Errors in the Emergency Department of a Governmental Hospital in Jordan: A Pre-Post Study. Hosp. Pharm. 2021, 56, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arredondo, E.; Udeani, G.; Horseman, M.; Hintze, T.D.; Surani, S. Role of Clinical Pharmacists in Intensive Care Units. Cureus 2021, 13, e17929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Meslamani, A.Z.; Kassem, A.B.; El-Bassiouny, N.A.; Ibrahim, O.M. An Emergency Plan for Management of COVID-19 Patients in Rural Areas. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2021, 75, e14563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S. The State of the World’s Pharmacy: A Portrait of the Pharmacy Profession. J. Interprof. Care 2002, 16, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineen-Griffin, S.; Garcia-Cardenas, V.; Rogers, K.; Vargas, C.; Williams, K.A.; Benrimoj, S.I. An Australian Minor Ailments Scheme: Evaluation of an Integrated Approach by Community Pharmacists and General Medical Practitioners; University of Technology Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Paudyal, V.; Watson, M.C.; Sach, T.; Porteous, T.; Bond, C.M.; Wright, D.J.; Cleland, J.; Barton, G.; Holland, R. Are Pharmacy-Based Minor Ailment Schemes a Substitute for Other Service Providers? A Systematic Review. Br. J. Gen. Pr. 2013, 63, e472–e481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steed, L.; Sohanpal, R.; Todd, A.; Madurasinghe, V.W.; Rivas, C.; Edwards, E.A.; Summerbell, C.D.; Taylor, S.J.; Walton, R.T. Community Pharmacy Interventions for Health Promotion: Effects on Professional Practice and Health Outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 12, CD011207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalaye, D.; De Bruijn, M.E.; De Jong, T.P. Prevalence of Schistosoma Haematobium Measured by a Mobile Health System in an Unexplored Endemic Region in the Subprefecture of Torrock, Chad. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2019, 5, e13359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, J.; Bassetti, M. Role of Pharmacists in Antimicrobial Stewardship Programmes. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2018, 40, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, I.Y.; Pratiwi, H.; Pitaloka, D.A.E. Role of Pharmacists in Antimicrobial Stewardship During COVID-19 Outbreak: A Scoping Review. J. Multidiscip. Health 2022, 15, 2605–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, H.A.M.; Kassem, A.B. COVID-19-Related Health Literacy and Preparedness to What May Come: A Cross-Sectional Study. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2023, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, D.M.; Morton, J. Role of the Pharmacist in Antimicrobial Stewardship. Med. Clin. North. Am. 2018, 102, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.J.; Dering-Anderson, A. Pharmacy-Based Travel Health Services: State Approaches to Prescriptive Authority. J. Pharm. Technol. 2018, 34, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raczkiewicz, D.; Sarecka-Hujar, B.; Pawełczak-Barszczowska, A.; Bojar, I. How Do Polish Pharmacy Staff Evaluate Own Qualifications, Competences, Relevance, Motivation, Effectiveness in Health Promotion? Health Promot. Int. 2022, 37, daab043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatewood, S.B.S.; Stanley, D.D.; Goode, J.-V.K.R. Implementation of a Comprehensive Pretravel Health Program in a Supermarket Chain Pharmacy. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2009, 49, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A. Role of the European Pharmacist in the Implementation of the Latest WHO Guidelines for Malaria. Pathogens 2023, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneux, D. Neglected Tropical Diseases. Community Eye Health 2013, 26, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Research Randomizer. Available online: https://randomizer.org/ (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- da Silva, J.V.L.; Fontes, G.; Dos Santos, C.D.; Dos Santos, R.V.; da Rocha, E.M.M. Factors Associated with Gastrointestinal Parasitic Infections among Young Population in Northeast Brazil. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 2016, 6239434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.F.; Busatti, H.G.N.O.; Cruz, V.L.; Santos, J.F.G.; Gomes, M.A. High Prevalence of Enteroparasitosis in Urban Slums of Belo Horizonte-Brazil. Presence of Enteroparasites as a Risk Factor in the Family Group. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2013, 107, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Japa, I.; Ancha, B.; Custodio, A.; Ohrenschall, R.; Cordero, R.; Deverlis, A.; Chapman, J.; Hickson, M.R.; Steenhoff, A.P.; Lowenthal, E.D. Effectiveness of Deworming with Single-Dose Albendazole for Preschool-Aged Children in the Dominican Republic. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2021, 8, 2333794X211002949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, A.J.; Njenga, S.M.; Steinbaum, L.; Swarthout, J.; Lin, A.; Arnold, B.F.; Stewart, C.P.; Dentz, H.N.; Mureithi, M.; Chieng, B.; et al. Effects of Single and Integrated Water, Sanitation, Handwashing, and Nutrition Interventions on Child Soil-Transmitted Helminth and Giardia Infections: A Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial in Rural Kenya. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belo, V.S.; de Oliveira, R.B.; Fernandes, P.C.; Nascimento, B.W.L.; Fernandes, F.V.; Castro, C.L.F.; dos Santos, W.B.; da Silva, E.S. Factors Associated with Intestinal Parasitosis in a Population of Children and Adolescents. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2012, 30, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, F.; Juncansen, C.; Ribeiro-Paes, J.T. Levantamento epidemiológico das parasitoses intestinais: Viés analítico decorrente do tratamento profilático. Cad. Saúde Pública 2008, 24, 2919–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayabina, D.V.; Clark, J.; Bayley, H.; Lamberton, P.H.L.; Toor, J.; Hollingsworth, T.D. Gender-Related Differences in Prevalence, Intensity and Associated Risk Factors of Schistosoma Infections in Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, S.; Mitchell, R.E.; El-Alim El-Dorey, A.; Smith, J.A.; Barocas, D.A. Successful Control of Schistosomiasis and the Changing Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer in Egypt. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, R.M.R. Epidemiology of Schistosomiasis in Egypt: Travel through Time: Review. J. Adv. Res. 2013, 4, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorkos, T.W.; Maheu-Giroux, M.; Blouin, B.; Saavedra, L.; Casapía, M. Efficacy of a single dose of Albendazole for soil-transmitted helminth infections in school children of a village in Iquitos, Perú. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Publica 2013, 30, 601–607. [Google Scholar]
- Pullan, R.L.; Halliday, K.E.; Oswald, W.E.; Mcharo, C.; Beaumont, E.; Kepha, S.; Witek-McManus, S.; Gichuki, P.M.; Allen, E.; Drake, T.; et al. Effects, Equity, and Cost of School-Based and Community-Wide Treatment Strategies for Soil-Transmitted Helminths in Kenya: A Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loker, E.S. This De-Wormed World? J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clarke, N.E.; Clements, A.C.A.; Doi, S.A.; Wang, D.; Campbell, S.J.; Gray, D.; Nery, S.V. Differential Effect of Mass Deworming and Targeted Deworming for Soil-Transmitted Helminth Control in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2017, 389, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawn McFarland, M.; Wallace, J.P.; Parra, J.; Baker, J. Evaluation of Patient Satisfaction with Diabetes Management Provided by Clinical Pharmacists in the Patient-Centered Medical Home. Patient 2014, 7, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrill, C.H.; Cavanaugh, J.; Shilliday, B.B. Patient Satisfaction with Medicare Annual Wellness Visits Administered by a Clinical Pharmacist Practitioner. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2017, 23, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliandani, Y.; Alfian, S.D.; Puspitasari, I.M. Patient Satisfaction with Clinical Pharmacy Services and the Affecting Factors: A Literature Review. Pharmacia 2022, 69, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaza, S.M. Treatment of Schistosomiasis: From Praziquantel to Development of New Drug Targets. PUJ 2013, 6, 127–148. [Google Scholar]
- Elmorshedy, H.; Bergquist, R.; El-Ela, N.E.A.; Eassa, S.M.; Elsakka, E.E.; Barakat, R. Can Human Schistosomiasis Mansoni Control Be Sustained in High-Risk Transmission Foci in Egypt? Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Gatewood, S.; Moczygemba, L.R.; Stanley, D.D.; Jean-Venable, R.G. Evaluating Health Outcomes Following a Pharmacist-Provided Comprehensive Pretravel Health Clinic in a Supermarket Pharmacy. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2015, 55, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hind, C.; Bond, C.; Lee, A.J.; van Teijlingen, E. Travel Medicine Services from Community Pharmacy: Evaluation of a Pilot Service. Available online: https://pharmaceutical-journal.com/article/research/travel-medicine-services-from-community-pharmacy-evaluation-of-a-pilot-service (accessed on 12 June 2024).
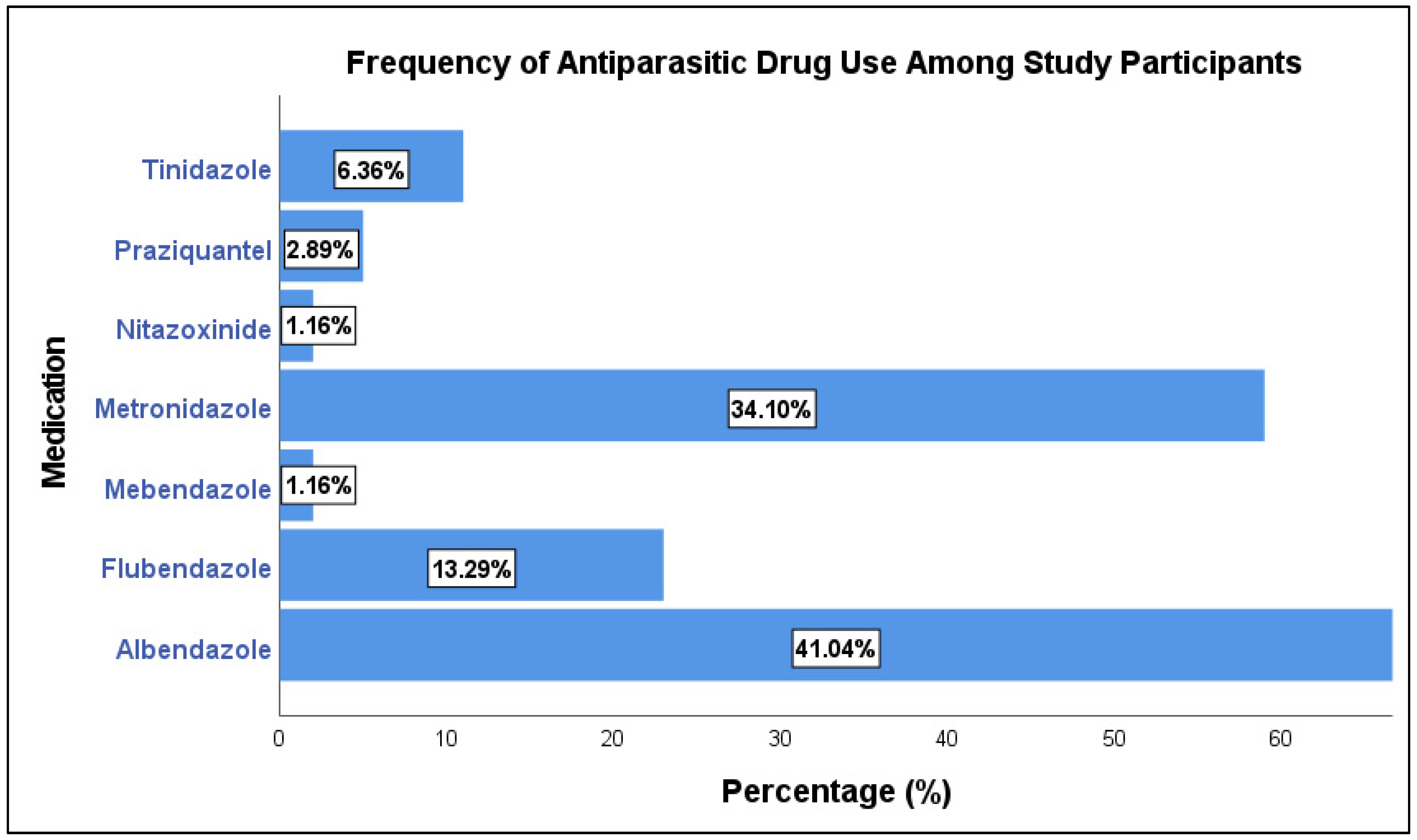
| Parameter | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Age, years | |
| 0–5 | 47 (27.2%) |
| 6–11 | 46 (26.6%) |
| 12–18 | 29 (16.8%) |
| >18 | 51 (29.5%) |
| Gender | |
| Female | 92 (53.2%) |
| Male | 81 (46.8%) |
| Type of infection | |
| Oxyuris | 77 (44.5%) |
| Entamoeba | 50 (28.9%) |
| Entamoeba Cyst | 15 (8.7%) |
| Ascaris | 15 (8.7%) |
| Schistosomiasis | 5 (2.9%) |
| Giardia | 8 (4.6%) |
| Pinworm | 3 (1.7%) |
| Personal hygiene | |
| Yes | 71 (41%) |
| No | 102 (59%) |
| Patient counseling | |
| Yes | 96 (55.5%) |
| No | 77 (44.5%) |
| Dose repeat | |
| Yes | 119 (68.8%) |
| No | 54 (31.2%) |
| Recurrence | |
| Yes | 101 (58.4%) |
| No | 72 (41.6%) |
| Parameter | Recurrence | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | ||
| Age, years | 0.002 * | ||
| 0–5 | 26 (55.3%) | 21 (44.7%) | |
| 6–11 | 35 (76.1%) | 11 (23.9%) | |
| 12–18 | 20 (69.0%) | 9 (31.0%) | |
| >18 | 20 (39.2%) | 31 (60.8%) | |
| Gender | 0.402 | ||
| Female | 51 (55.4%) | 41 (44.6%) | |
| Male | 50 (61.7%) | 31 (38.8%) | |
| Type of infection | 0.018 * | ||
| Oxyuris | 41 (53.2%) | 36 (46.8%) | |
| Entamoeba | 34 (68.0%) | 16 (32.0%) | |
| Entamoeba Cyst | 7 (46.7%) | 8 (53.3%) | |
| Ascaris | 7 (46.7%) | 8 (53.3%) | |
| Schistosomiasis | 1 (20.0%) | 4 (80.0%) | |
| Giardia | 8 (100%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Pinworm | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | |
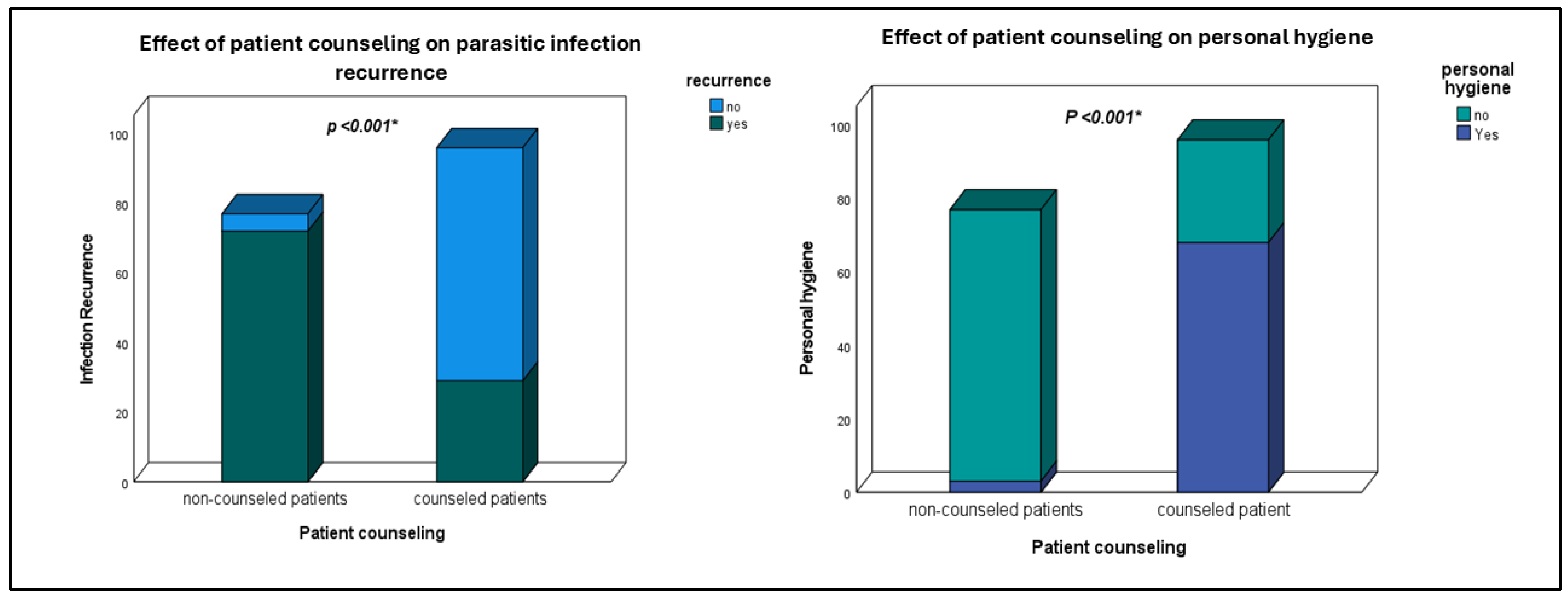
| Personal hygiene | <0.001 * | ||
| Yes | 16 (22.5%) | 55 (77.5%) | |
| No | 85 (83.3%) | 17 (16.7%) | |
| Patient counseling | <0.001 * | ||
| Yes | 29 (30.2%) | 67 (69.8%) | |
| No | 72 (93.5%) | 5 (6.5%) | |
| Dose repeat | 0.132 | ||
| Yes | 74 (62.2%) | 45 (37.8%) | |
| No | 27 (50.0%) | 27 (50.0%) | |
| Personal Hygiene | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Counseling | Yes | No | p Value |
| Yes | 68 (70.8%) | 28 (29.2%) | <0.001 * |
| No | 3 (3.9%) | 74 (96.1%) | |
| Variable | Coefficient | Odds Ratio | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| 6–11 (Ref) | 0.276 | ||
| 0–5 | −0.301 | 0.740 | 0.625 |
| 12–18 | −0.117 | 0.890 | 0.881 |
| >18 | −1.240 | 0.289 | 0.086 |
| Gender | 0.101 | 1.106 | 0.828 |
| Type of Infection | |||
| Schistosomiasis (Ref) | 0.979 | ||
| Oxyuris | 0.690 | 1.994 | 0.621 |
| Entamoeba | 1.165 | 3.207 | 0.402 |
| Entamoeba cyst | 1.092 | 2.980 | 0.451 |
| Ascaris | 0.846 | 2.331 | 0.573 |
| Giardia | 18.79 | 14,586 | 0.999 |
| Pinworm | 18.68 | 12,972 | 0.999 |
| Personal Hygiene | 1.516 | 4.554 | 0.004 * |
| Patient Counselling | 2.536 | 12.624 | <0.001 * |
| Dose Repeat | −0.724 | 0.485 | 0.238 |
| Constant | −1.521 | 0.218 | 0.313 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kassem, A.B.; Al Meslamani, A.Z.; AbdElrahman, M.; Al Mazrouei, N.; Okda, S.M.; El-Bassiouny, N.A.; Hamedo, A.A.-h.; Shaban, D.A.; Elsmadessy, D.F.; Binsaleh, A.Y.; et al. The Impact of a Community Pharmacy-Led Deworming-Related Counselling Service: An Interventional Study in a Low-to-Middle Income Country. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080215
Kassem AB, Al Meslamani AZ, AbdElrahman M, Al Mazrouei N, Okda SM, El-Bassiouny NA, Hamedo AA-h, Shaban DA, Elsmadessy DF, Binsaleh AY, et al. The Impact of a Community Pharmacy-Led Deworming-Related Counselling Service: An Interventional Study in a Low-to-Middle Income Country. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(8):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080215
Chicago/Turabian StyleKassem, Amira B., Ahmad Z. Al Meslamani, Mohamed AbdElrahman, Nadia Al Mazrouei, Sherouk M. Okda, Noha A. El-Bassiouny, Asmaa Abdel-hamed Hamedo, Doaa Abdelrazek Shaban, Dina Fathy Elsmadessy, Ammena Y. Binsaleh, and et al. 2025. "The Impact of a Community Pharmacy-Led Deworming-Related Counselling Service: An Interventional Study in a Low-to-Middle Income Country" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 8: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080215
APA StyleKassem, A. B., Al Meslamani, A. Z., AbdElrahman, M., Al Mazrouei, N., Okda, S. M., El-Bassiouny, N. A., Hamedo, A. A.-h., Shaban, D. A., Elsmadessy, D. F., Binsaleh, A. Y., Saleh, A., & Moustafa, H. A. M. (2025). The Impact of a Community Pharmacy-Led Deworming-Related Counselling Service: An Interventional Study in a Low-to-Middle Income Country. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(8), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10080215







