Impact of Health Education on Infectious Disease Knowledge in Indigenous Communities in Northwestern Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample
- Identified as Semai ethnicity;
- Aged 7 years and above;
- Able to provide informed consent.
- They did not complete both the pre- and post-surveys;
- Individuals who were unable to read and understand the survey independently.
2.2. Study Instrument
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Age Distribution
3.2. Pre-Test and Post-Test Scores Across Different Age Groups
3.3. Variations in Health Awareness Knowledge by Age Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Veiga, A.B.G.; Kaminski, V.L.; Valverde-Villegas, J.M.; Freitas, A.W.Q.; Chies, J.A.B. Control and prevention of infectious diseases from a One Health perspective. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), e20200256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.H.; Baharudin, U.M.; Md Isa, Z. Diseases among Orang Asli community in Malaysia: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, R.; Abdul Wahab, N.; Mustapha, R.; Goh, S.C.; Abdullah, R.; Md Sharif, M.P. Sustainability of Orang Asli indigenous knowledge and practices of green technology in medicine. J. Asian Vocat. Educ. Train. 2019, 12, 74–89. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.F.; Othman, A.; Jani, R.; Bartholomew, C.V.; Pesiu, E.; Abdullah, M.T. Traditional knowledge and the uses of natural resources by the resettlement of indigenous people in Malaysia. JATI-J. Southeast Asian Stud. 2020, 25, 168–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsudin, L.; Mohd Jaafar, M.F.; Kamarulzaman, M.K.A.; Mohd Nor, N.N.; Ahmad Shafei, S.; Mohamad Shukor, N.A.; Abdul Rahman, M.R.; Sangaran, K.; Wan Ismail, W.R.; Tam, J.Z.; et al. Knowledge, attitude and practice levels regarding malaria among the Semai sub-ethnic indigenous Orang Asli communities in Pahang, Peninsular Malaysia: A stepping stone towards the prevention of human malaria re-establishment. Malar. J. 2024, 23, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martell, R.; Reade, M.; Boesch, L.; Kaur, D.P.; Kumar, S.; McArthur, M.; Maar, M.A. The role of narratives in promoting vaccine confidence among Indigenous peoples in Canada, the United States, Australia, and New Zealand: A scoping review. Int. J. Equity Health 2025, 24, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, A.J.; Varcoe, C.; Lavoie, J.; Smye, V.; Wong, S.T.; Krause, M.; Tu, D.; Godwin, O.; Khan, K.; Fridkin, A. Enhancing health care equity with Indigenous populations: Evidence-based strategies from an ethnographic study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2016, 16, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.E.F.; Ulaganathan, V.; Kua, G.Y.L.; Adan, M.A.; Lim, S.Y. Nutritional Status of Orang Asli in Malaysia. Malays. J. Med. Sci. MJMS 2022, 29, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, I.J.; Lea, A.J.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Chow, S.K.W.; Sayed, I.B.M.; Ngui, R.; Shaffee, M.T.H.; Ng, K.S.; Nicholas, C.; Venkataraman, V.V.; et al. Orang Asli Health and Lifeways Project (OA HeLP): A cross-sectional cohort study protocol. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e058660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, J.J.-A.; Ting, R.S.-K.; Takeuchi, T.; Jobson, L.; Phipps, M.E. A qualitative study exploring the epistemology of suffering within a Malaysian Indigenous tribe. Transcult. Psychiatry 2024, 62, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.C.; Lim, X.J.; Low, L.L.; Lau, K.M.; Kari, M.; Shamsudin, U.K.; Rajan, P. The challenges in managing the growth of indigenous children in Perak State, Malaysia: A qualitative study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.A.; Romano, N.; Colin, N.; Chow, S.C.; Smith, H.V. Intestinal parasitic infections amongst Orang Asli (indigenous) in Malaysia: Has socioeconomic development alleviated the problem? Trop. Biomed. 2009, 26, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chew, C.C.; Ibrahim, H.A.; Balan, V.K.; Abd-Aziz, N.A.; Puah, H.M.; Hss, A.S. Growth management and prevalence of underweight of indigenous children (Orang Asli) in Peninsular Malaysia: A clinical audit. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.J. The role of traditional medicine practice in primary health care within Aboriginal Australia: A review of the literature. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2013, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampiao, F.; Chisaka, J.; Clements, C. Communication Between Traditional Medical Practitioners and Western Medical Professionals. Front. Sociol. 2019, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, T.; Wu, J.; Sun, C.; Han, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Qiao, C.; Tao, X. Exploring factors influencing awareness and knowledge of human papillomavirus in Chinese college students: A cross-sectional study. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2024, 20, 2388347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurc, J.; Laaksonen, C. Effectiveness of Health Promotion Interventions in Primary Schools-A Mixed Methods Literature Review. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancone, S.; Corrado, S.; Tosti, B.; Spica, G.; Diotaiuti, P. Integrating digital and interactive approaches in adolescent health literacy: A comprehensive review. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1387874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarthun, A.; Øymar, K.A.; Akerjordet, K. Parental involvement in decision-making about their child’s health care at the hospital. Nurs. Open 2018, 6, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Heinsch, M.; Betts, D.; Booth, D.; Kay-Lambkin, F. Barriers and facilitators to the use of e-health by older adults: A scoping review. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, R.M.; Benavente, J.Y.; Opsasnick, L.A.; Weiner-Light, S.; Curtis, L.M.; Wolf, M.S. Associations Between Cognitive Impairment Severity and Barriers to Healthcare Engagement Among Older Adults. J. Appl. Gerontol. 2023, 42, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, S.M.; Jan, S.S. Navigating the infodemic: Strategies and policies for promoting health literacy and effective communication. Front. Public Health 2024, 11, 1324330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garney, W.; Wilson, K.; Ajayi, K.V.; Panjwani, S.; Love, S.M.; Flores, S.; Garcia, K.; Esquivel, C. Social-Ecological Barriers to Access to Healthcare for Adolescents: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghupathi, V.; Raghupathi, W. The influence of education on health: An empirical assessment of OECD countries for the period 1995–2015. Arch. Public Health 2020, 78, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddock, A.; Ward, N.; Yu, R.; O’Dea, N. Positive Effects of Digital Technology Use by Adolescents: A Scoping Review of the Literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, M.; Hotez, E.; Roy, K.; Ledford, C.J.W.; Lewin, A.B.; Perez-Brena, N.; Childress, S.; Berge, J.M. Family Health Development: A Theoretical Framework. Pediatrics 2022, 149 (Suppl. S5), e2021053509I. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.Y.; Choi, B.Y.; Ryoo, S.W.; Son, S.Y.; Min, J.Y.; Min, K.B. Health Literacy and Health-Related Quality of Life in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2024, 25, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, P.J. Improving health literacy using the power of digital communications to achieve better health outcomes for patients and practitioners. Front. Digit. Health 2023, 5, 1264780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, W.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, P.C.; Hou, W.H. Investigating the effects of different game-based learning on the health care knowledge and emotions for middle-aged and older adults. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2024, 33, 2313–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.L.; Jensen, J.D.; Scherr, C.L.; Brown, N.R.; Christy, K.; Weaver, J. The Health Belief Model as an explanatory framework in communication research: Exploring parallel, serial, and moderated mediation. Health Commun. 2015, 30, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakshe, W.; Wickramasurendra, A.K.; Amarasinghe, R.R.; Kohilawatta Arachchige Wijerathne, S.L.M.; Wijesinghe, N.D.; Madhavika, N. Application of the Health Belief Model (HBM) to Explore the Quality of Sexual and Reproductive Health (SRH) Education in Sri Lanka. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandpierre, V.; Milloy, V.; Sikora, L.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Thomas, R.; Potter, B. Barriers and facilitators to cultural competence in rehabilitation services: A scoping review. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeoye, B.D.; Michael, T.O.; Agbana, R.D. Insights, beliefs, and myths surrounding tuberculosis among pulmonary patients with delayed healthcare access in a high-burden TB state in Nigeria—A qualitative inquiry. Front. Sociol. 2024, 9, 1378586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, S.; Luseka, E.; Bradley, D.; Brown, J.; Bhagwan, J.; Evans, B.; Freeman, M.C.; Howard, G.; Ray, I.; Ross, I.; et al. Water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH): The evolution of a global health and development sector. BMJ Glob. Health 2024, 9, e015367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, N.; Safwan, J.; Kerek, R.; Ghach, W. Hand hygiene during the spread of COVID-19: A cross-sectional study of awareness and practices among academic institutions in Lebanon. Front. Public Health 2024, 11, 1256433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çamdalı, S.; Teke, M.; Eren, M.T.; Yenidünya, E.; Akyol, E.; Değerli, S. Investigation of Head Lice and Intestinal Parasites in Primary and Secondary School in Sivas. Sivas’ta İlkokul ve Ortaokul Öğrencilerinde Baş Biti ve Bağırsak Parazitlerinin Araştırılması. Turk. Parazitolojii Derg. 2024, 48, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head lice infestations: A clinical update. Paediatr. Child Health 2004, 9, 647–657. [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.T.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Chong, C.W.; Teh, C.S.J.; Yap, I.K.S.; Lee, S.C.; Tee, M.Z.; Siow, V.W.Y.; Chua, K.H. Prevalence and risk factors of intestinal parasitism among two indigenous sub-ethnic groups in Peninsular Malaysia. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2016, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröder, J.; Okan, O.; Bauer, U.; Bruland, D.; Schlupp, S.; Bollweg, T.M.; Saboga-Nunes, L.; Bond, E.; Sørensen, K.; Bitzer, E.-M.; et al. Health literacy in childhood and youth: A systematic review of definitions and models. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syofyan, S.; Dachriyanus, D.; Masrul, M.; Rasyid, R. Children’s Perception and Belief about Medicines: Effectiveness and Its Autonomy. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 2556–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povey, J.; Plage, S.; Huang, Y.; Gramotnev, A.; Cook, S.; Austerberry, S.; Western, M. Adolescence a Period of Vulnerability and Risk for Adverse Outcomes across the Life Course: The Role of Parent Engagement in Learning. In Family Dynamics over the Life Course; Baxter, J., Lam, J., Povey, J., Lee, R., Zubrick, S.R., Eds.; Life Course Research and Social Policies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, L.M.; Font, S.A. The Role of the Family and Family-Centered Programs and Policies. Future Child. 2015, 25, 155–176. [Google Scholar]
- Chesser, A.K.; Keene Woods, N.; Smothers, K.; Rogers, N. Health Literacy and Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2016, 2, 2333721416630492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alon, N.; Perret, S.; Torous, J. Working towards a ready to implement digital literacy program. mHealth 2023, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, Z.A.; Anika, T.T.; Sachi, S.; Ferdous, J.; Sarker, Y.A.; Sabur, M.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Sikder, M.H. Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of garlic (Allium sativum) and ginger (Zingiber officinale) crude extract against multidrug-resistant (MDR) poultry pathogen. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2023, 10, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, P.; Prehn, R.; Rind, N.; Lin, I.; Choong, P.F.M.; Bessarab, D.; Coffin, J.; Mason, T.; Dowsey, M.M.; Bunzli, S. Laying the foundations of community engagement in Aboriginal health research: Establishing a community reference group and terms of reference in a novel research field. Res. Involv. Engagem. 2022, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, S.; Arora, A. Interventions to improve health literacy among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaborit, L.; Robinson, M.; Sutherland, S. Characterising health promotion in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander languages: A content analysis of COVID-19 and maternal health resources. Health Promot. J. Aust. 2022, 33 (Suppl. S1), 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reweti, A. Understanding how whānau-centred initiatives can improve Māori health in Aotearoa New Zealand. Health Promot. Int. 2023, 38, daad070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C. The Inconvenient Truth About Convenience and Purposive Samples. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2021, 43, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latkin, C.A.; Edwards, C.; Davey-Rothwell, M.A.; Tobin, K.E. The relationship between social desirability bias and self-reports of health, substance use, and social network factors among urban substance users in Baltimore, Maryland. Addict. Behav. 2017, 73, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela Dos Santos, O.; Melly, P.; Hilfiker, R.; Giacomino, K.; Perruchoud, E.; Verloo, H.; Pereira, F. Effectiveness of Educational Interventions to Increase Skills in Evidence-Based Practice among Nurses: The EDITcare Systematic Review. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamiri, M.; Esmaeili, A. Methods and Technologies for Supporting Knowledge Sharing within Learning Communities: A Systematic Literature Review. Adm. Sci. 2024, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulimeno, M.; Piscitelli, P.; Colazzo, S.; Colao, A.; Miani, A. School as ideal setting to promote health and wellbeing among young people. Health Promot. Perspect. 2020, 10, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
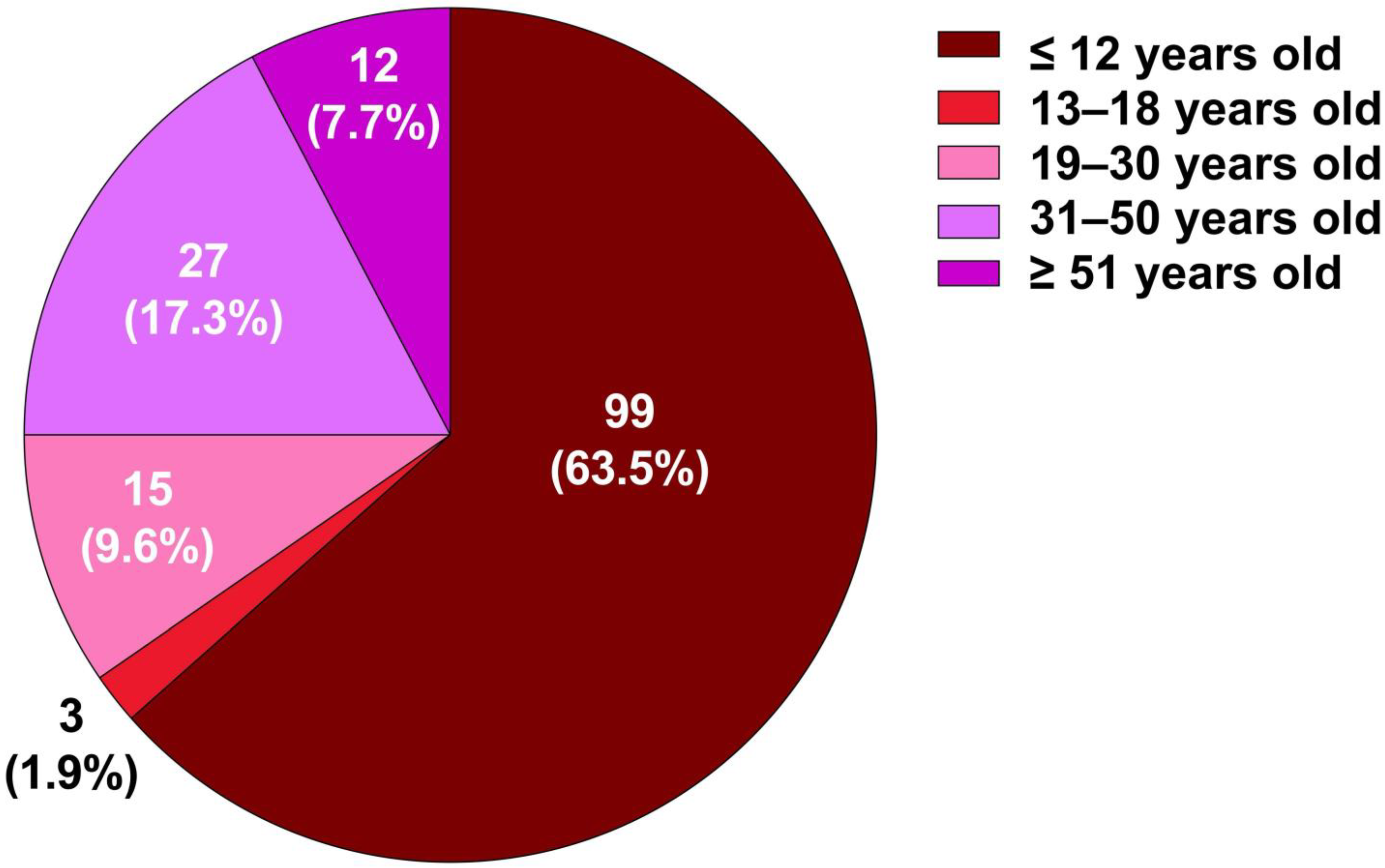

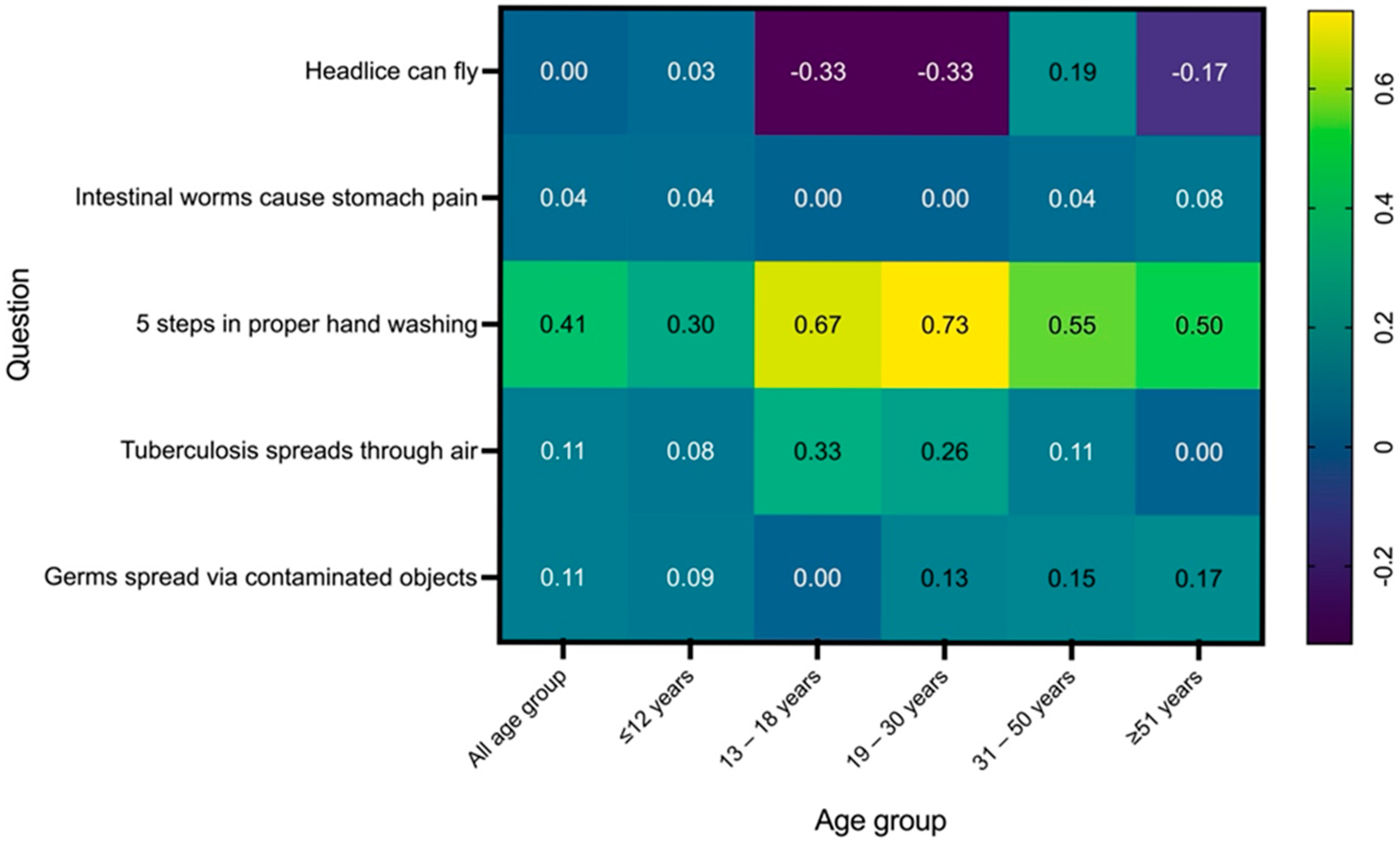
| Question | Age Group | Pre-Test Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Post-Test Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean Difference (Post–Pre) ± SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Question 1: Head lice can fly | All age group | 0.58 ± 0.50 | 0.50–0.66 | 0.58 ± 0.50 | 0.50–0.66 | 0.00 ± 0.60 | 1.0000 |
| ≤12 years | 0.63 ± 0.49 | 0.53–0.73 | 0.66 ± 0.48 | 0.56–0.76 | 0.03 ± 0.69 | 0.6015 | |
| 13–18 years | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.67 ± 0.58 | −0.77–2.11 | −0.33 ± 0.58 | 0.3173 | |
| 19–30 years | 0.60 ± 0.51 | 0.32–0.88 | 0.27 ± 0.46 | 0.02–0.52 | −0.33 ± 0.69 | 0.0588 | |
| 31–50 years | 0.37 ± 0.49 | 0.18–0.56 | 0.56 ± 0.51 | 0.36–0.76 | 0.19 ± 0.71 | 0.1655 | |
| ≥51 years | 0.50 ± 0.52 | 0.17–0.83 | 0.33 ± 0.49 | 0.02–0.64 | −0.17 ± 0.71 | 0.1573 | |
| Question 2: Intestinal worms cause stomach pain | All age group | 0.91 ± 0.29 | 0.86–0.95 | 0.95 ± 0.23 | 0.91–0.98 | 0.04 ± 0.31 | 0.1091 |
| ≤12 years | 0.88 ± 0.33 | 0.81–0.95 | 0.92 ± 0.27 | 0.87–0.97 | 0.04 ± 0.43 | 0.2482 | |
| 13–18 years | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.00 ± 0.00 | N/A | |
| 19–30 years | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.00 ± 0.00 | N/A | |
| 31–50 years | 0.96 ± 0.19 | 0.88–1.04 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.04 ± 0.19 | 0.3173 | |
| ≥51 years | 0.92 ± 0.29 | 0.74–1.10 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.08 ± 0.29 | 0.3173 | |
| Question 3: 5 steps in proper hand washing | All age group | 0.14 ± 0.35 | 0.09–0.20 | 0.55 ± 0.50 | 0.47–0.63 | 0.41 ± 0.55 | <0.0001 * |
| ≤12 years | 0.14 ± 0.35 | 0.07–0.21 | 0.44 ± 0.50 | 0.34–0.54 | 0.30 ± 0.61 | <0.0001 * | |
| 13–18 years | 0.33 ± 0.58 | −1.11–1.77 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.67 ± 0.58 | 0.1573 | |
| 19–30 years | 0.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.73 ± 0.46 | 0.48–0.98 | 0.73 ± 0.46 | 0.0009 * | |
| 31–50 years | 0.19 ± 0.40 | 0.03–0.35 | 0.74 ± 0.45 | 0.56–0.92 | 0.55 ± 0.60 | 0.00027 * | |
| ≥51 years | 0.17 ± 0.39 | −0.08–0.42 | 0.67 ± 0.49 | 0.36–0.98 | 0.50 ± 0.63 | 0.0143 * | |
| Question 4: Tuberculosis spreads through air | All age group | 0.75 ± 0.43 | 0.68–0.82 | 0.86 ± 0.35 | 0.80–0.91 | 0.11 ± 0.42 | 0.0022 * |
| ≤12 years | 0.71 ± 0.46 | 0.62–0.80 | 0.79 ± 0.41 | 0.71–0.87 | 0.08 ± 0.62 | 0.0881 | |
| 13–18 years | 0.67 ± 0.58 | −0.77–2.11 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.33 ± 0.58 | 0.4226 | |
| 19–30 years | 0.67 ± 0.49 | 0.40–0.94 | 0.93 ± 0.26 | 0.79–1.07 | 0.26 ± 0.55 | 0.0455 * | |
| 31–50 years | 0.85 ± 0.36 | 0.71–0.99 | 0.96 ± 0.19 | 0.88–1.04 | 0.11 ± 0.41 | 0.1797 | |
| ≥51 years | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.00 ± 0.00 | N/A | |
| Question 5: Germs spread via contaminated objects | All age group | 0.79 ± 0.41 | 0.72–0.86 | 0.90 ± 0.30 | 0.85–0.95 | 0.11 ± 0.41 | 0.0015 * |
| ≤12 years | 0.77 ± 0.42 | 0.69–0.85 | 0.86 ± 0.35 | 0.79–0.93 | 0.09 ± 0.55 | 0.0389 * | |
| 13–18 years | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.00 ± 0.00 | N/A | |
| 19–30 years | 0.80 ± 0.41 | 0.57–1.03 | 0.93 ± 0.26 | 0.79–1.07 | 0.13 ± 0.49 | 0.1573 | |
| 31–50 years | 0.85 ± 0.36 | 0.71–0.99 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.15 ± 0.36 | 0.0455 * | |
| ≥51 years | 0.83 ± 0.39 | 0.58–1.08 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | - | 0.17 ± 0.39 | 0.1573 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muttiah, B.; Wahid, W.; Hanafiah, A. Impact of Health Education on Infectious Disease Knowledge in Indigenous Communities in Northwestern Malaysia. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10070191
Muttiah B, Wahid W, Hanafiah A. Impact of Health Education on Infectious Disease Knowledge in Indigenous Communities in Northwestern Malaysia. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(7):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10070191
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuttiah, Barathan, Wathiqah Wahid, and Alfizah Hanafiah. 2025. "Impact of Health Education on Infectious Disease Knowledge in Indigenous Communities in Northwestern Malaysia" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 7: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10070191
APA StyleMuttiah, B., Wahid, W., & Hanafiah, A. (2025). Impact of Health Education on Infectious Disease Knowledge in Indigenous Communities in Northwestern Malaysia. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(7), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10070191







