Epidemiological Characteristics and Trends of Zoonotic Diseases in China from 2015 to 2022
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
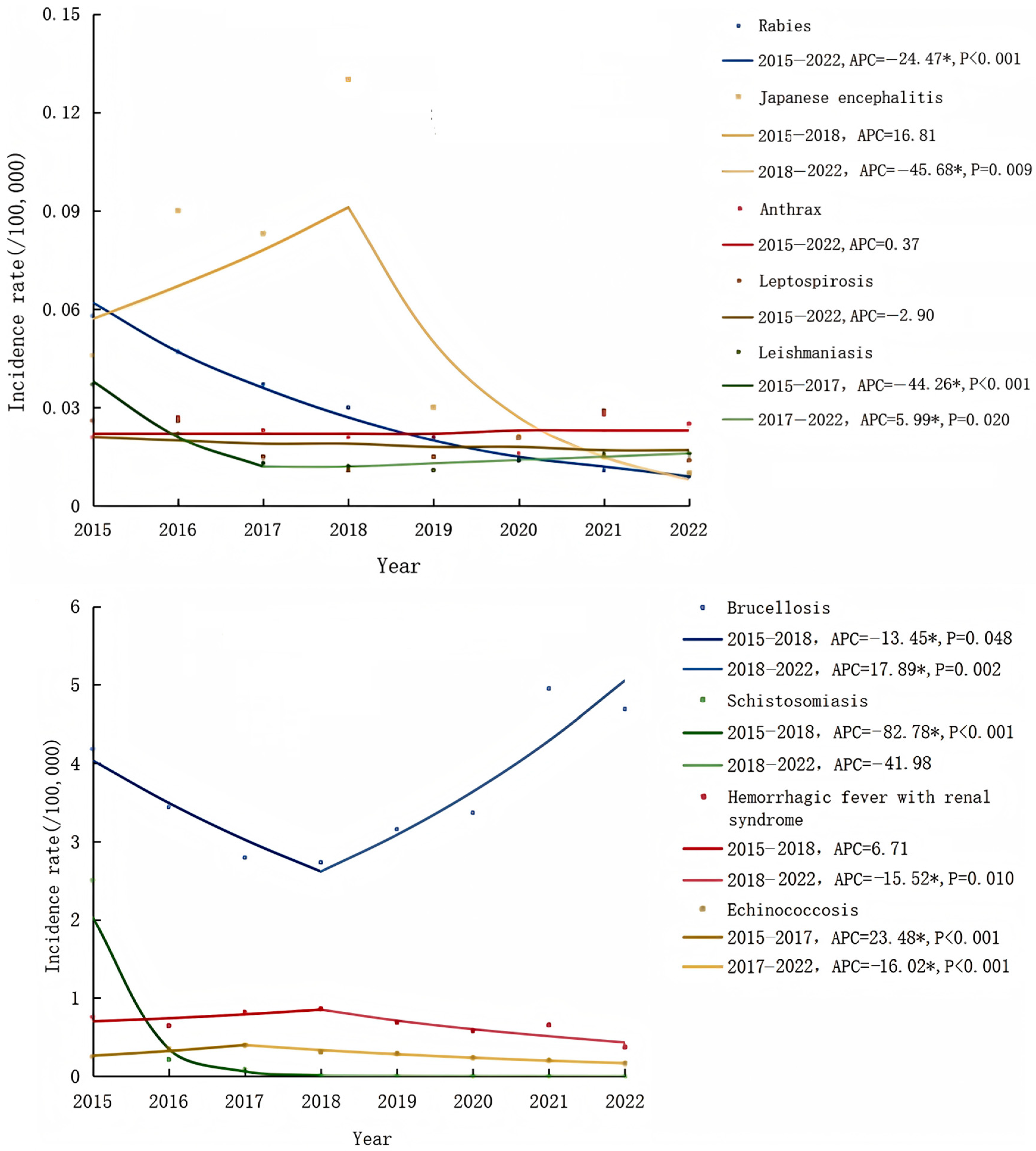
3.1. Incidence Trends
3.2. Population Distribution
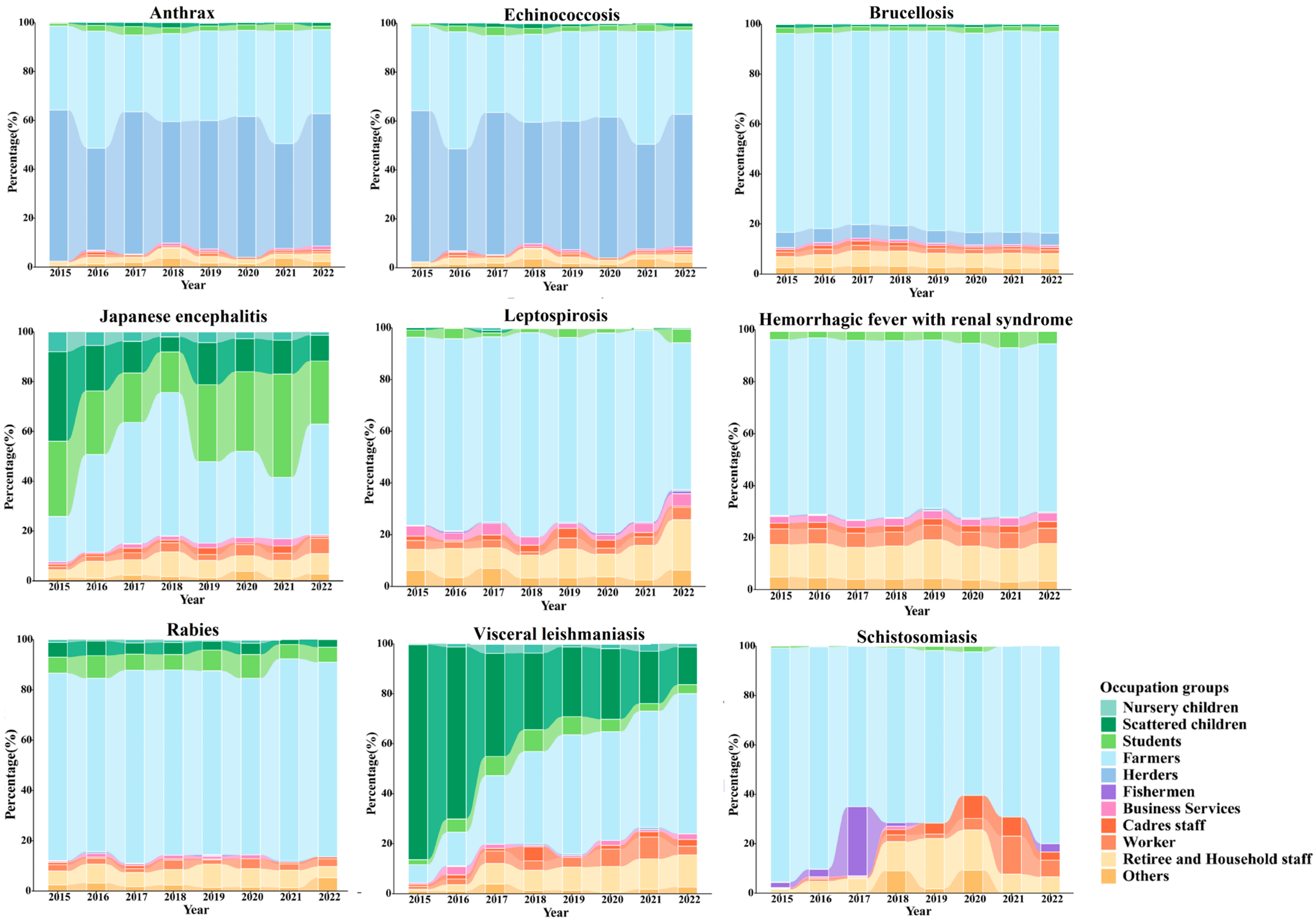
3.3. Occupational Distribution
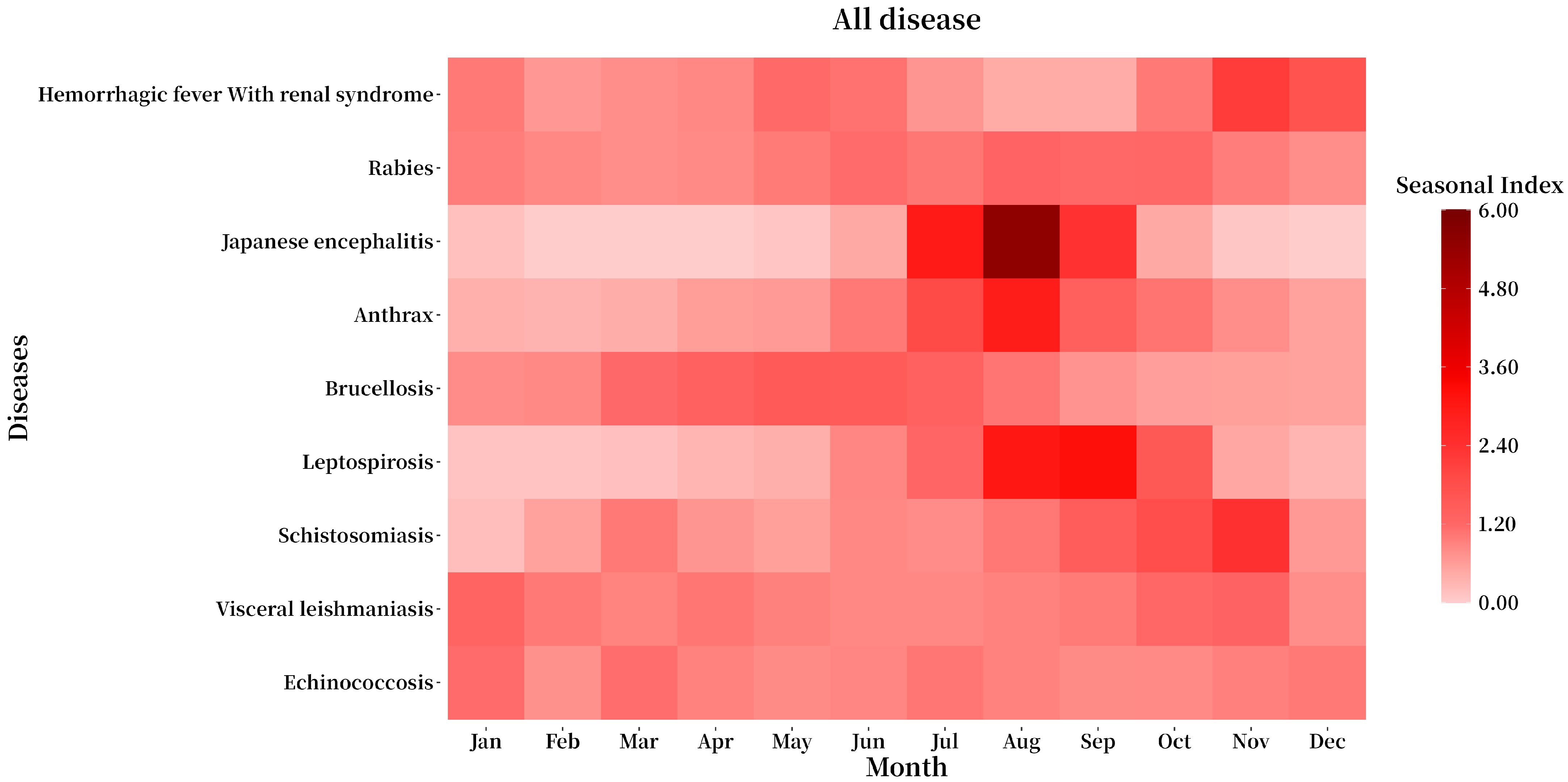
3.4. Seasonal Distribution
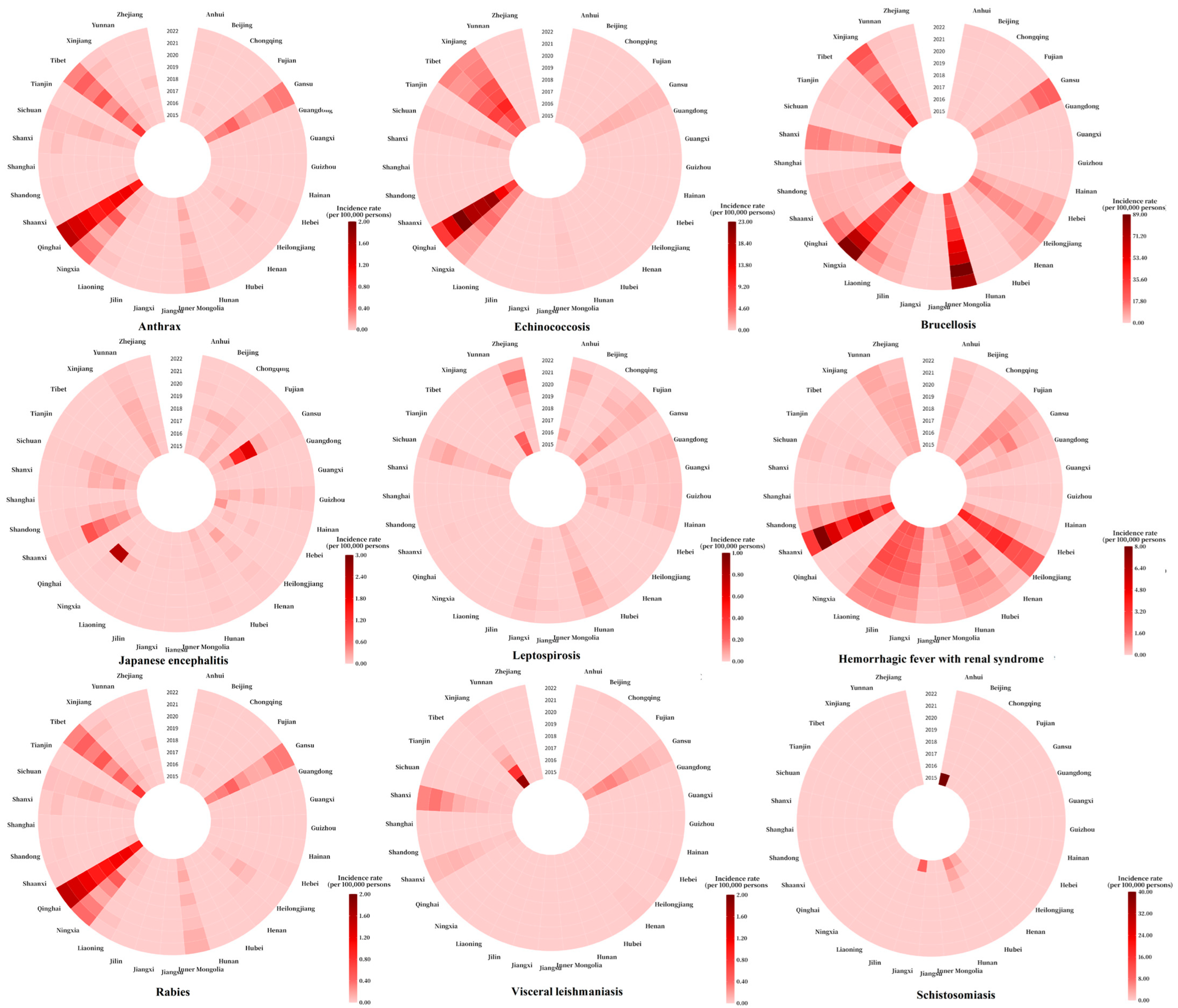
3.5. Regional Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HFRS | Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome |
| CISDCP | China Information System for Disease Control and Prevention |
| APC | Annual percent change |
| AAPC | Average annual percent change |
References
- World Health Organization. Zoonoses. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/zoonoses (accessed on 2 November 2024).
- Rahman, M.T.; Sobur, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Ievy, S.; Hossain, M.J.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Rahman, A.T.; Ashour, H.M. Zoonotic diseases: Etiology, impact, and control. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracey, J.F.; Collins, O.; Huey, R.J. Meat Hygiene, 10th ed.; Bailliere Tindall: London, UK, 1999; pp. 223–260. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, L.H.; Latham, S.M.; Woolhouse, M.E.J. Risk factors for human disease emergence. Philos. Trans. R Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 356, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daszak, P.; Cunningham, A.A.; Hyatt, A.D. Anthropogenic environmental change and the emergence of infectious diseases in wildlife. Acta Trop. 2001, 78, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (U.S.). Committee on Achieving Sustainable Global Capacity for Surveillance and Response to Emerging Diseases of Zoonotic Origin. Gerald. In Keusch, Sustaining Global Surveillance and Response to Emerging Zoonotic Diseases; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; Available online: http://site.ebrary.com/id/10367632 (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Welburn, S.C.; Beange, I.; Ducrotoy, M.J.; Okello, A.L. The neglected zoonoses—The case for integrated control and advocacy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bari, C.; Venkateswaran, N.; Fastl, C.; Gabriël, S.; Grace, D.; Havelaar, A.H.; Huntington, B.; Patterson, G.T.; Rushton, J.; Speybroeck, N.; et al. The global burden of neglected zoonotic diseases: Current state of evidence. One Health 2023, 17, 100595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. People, Pathogens and Our Plant, Vol 1: Towards a Once Health Approach for Controlling Zoonotic; Diseases Report 50833-GLB; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Ending the Neglect to Attain the Sustainable Development Goals: A Road Map for Reglected Tropical Diseases 2021–2030. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240010352 (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. National Development Plan for the Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Industry During the 14th Five-Year Plan Period. 2021. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/xmsyj/202112/t20211220_6385081.htm (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q. History of Human Schistosomiasis (bilharziasis) in China: From Discovery to Elimination. Acta Parasitol. 2021, 66, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.M. Collected Papers on the Research of Visceral Leishmaniasis (1950–1959); Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1959; pp. 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.L. Anthrax prevention and treatment achievement and research progress in China. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 20, 135–137. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Gao, X.; Ren, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liang, G. A spatial and temporal analysis of Japanese encephalitis in mainland China, 1963–1975: A period without Japanese encephalitis vaccination. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Xiao, D.L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.X.; Sun, L.; Tao, X.X.; Qu, Y.G. The epidemic characteristics and preventive measures of hemorrhagic fever with syndromes in China. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 25, 466–469. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Xue, C.; Yuan, M.; Li, Z.; Zheng, C. Epidemiological and Spatiotemporal Clustering Analysis of Human Brucellosis-China, 2019–2023. Chin. CDC Wkly. 2025, 7, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, Z.L.P.; Charypkhan, D.; Hartnack, S.; Torgerson, P.R.; Rüegg, S.R. The dual burden of animal and human zoonoses: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.; Murray, K.A.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.; Morse, S.S.; Rondinini, C.; Di Marco, M.; Breit, N.; Olival, K.J.; Daszak, P. Global hotspots and correlates of emerging zoonotic diseases. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.A.; Grace, D.; Kock, R.; Alonso, S.; Rushton, J.; Said, M.Y.; McKeever, D.; Mutua, F.; Young, J.; McDermott, J.; et al. Zoonosis emergence linked to agricultural intensification and environmental change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8399–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karesh, W.B.; Dobson, A.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; Lubroth, J.; Dixon, M.A.; Bennett, M.; Aldrich, S.; Harrington, T.; Formenty, P.; Loh, E.H.; et al. Ecology of zoonoses: Natural and unnatural histories. Lancet 2012, 380, 1936–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.Y. The cultural policies of schistosomiasis control in China: A historical analysis. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 122, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.P.; Dai, J.Y.; Hu, J.X.; Liu, T.; Gong, D.; Li, X.; Kang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Quan, Y.; et al. Co-benefits of nonpharmaceutical intervention against COVID-19 on infectious diseases in China: A large population-based observational study. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2021, 17, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Fay, M.P.; Feuer, E.J.; Midthune, D.N. Permutation tests for joinpoint regression with applications to cancer rates. Stat. Med. 2000, 19, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Du, L.B. Application of Joinpoint regression model in cancer epidemiological time trend analysis. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 54, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.K.; Wang, L.K.; Liu, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Q.; Jia, S.; Shen, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; et al. Epidemiological trends and characteristics of major respiratory infectious diseases in China from 2004 to 2018. Chin. J. Dis. Control Prev. 2022, 26, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; He, T.T.; Xie, J.Z.; Lv, S.; Li, Z.; Yuan, M.; Hu, F.; Lin, D. Trend of Human Schistosomiasis Japonica Prevalence in China from 1990 to 2019. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Hu, Y.; Guo, S.; Jin, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, C.; Hu, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, J. China’s prevention and control experience of echinococcosis: A 19-year retrospective. J. Helminthol. 2024, 98, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Tang, Q.; Wang, D.M.; Mo, Z.J.; Guo, S.H.; Li, H.; Tao, X.Y.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Feng, Z.J.; Liang, G.D. Epidemiological investigations of human rabies in China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.L.; Zhang, X.F.; Jin, H.; Cheng, X.Q.; Duan, C.X.; Wang, X.C.; Bao, C.J.; Zhou, M.H.; Ahmad, T. Post-exposure prophylaxis vaccination rate and risk factors of human rabies in mainland China: A meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 147, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.T.; Li, Q.F.; Ma, C.; Zhao, Z.X.; He, L.F.; Tang, T.T.; Yu, W.; Owiti, P. Reduction patterns of Japanese encephalitis incidence following vaccine introduction into long-term expanded program on immunization in Yunnan Province, China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.Z.; Lee, L.A.; Liu, Y.M.; Scherpbier, R.W.; Wen, N.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, X.; Ning, G.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; et al. Vaccine-preventable disease control in the People’s Republic of China:1949–2016. Vaccine 2018, 36, 8131–8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.Z.; Lv, H.; Yan, H.C.; Zhu, C.; Ai, L.; Li, W.; Yi, J.; Zhang, L.; Tan, W. Meteorological change and hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome epidemic in China, 2004–2018. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Xiao, X.; Yin, W.; He, J.; Ren, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, M.; Tong, S.; Guo, Y.; et al. Climate and socio-economic factors drive the spatio-temporal dynamics of HFRS in Northeastern China. One Health 2022, 15, 100466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Lai, S.J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, X.L.; Yao, H.W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.P.; Mu, D.; et al. Mapping the Distribution of Anthrax in Mainland China, 2005–2013. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Geng, M.; Zhou, S.; Chen, X.; Sun, J.; Tian, X.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, C. Epidemiological characteristics of leptospirosis in China from 2010 to 2022. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2024, 36, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Z.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, S. Epidemiological features and spatial-temporal clustering of visceral leishmaniasis in mainland China from 2019 to 2021. Front. Microbial. 2022, 13, 959901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.J.; Wang, L.P.; Li, N.; Zhou, X.N. Visceral leishmaniasis in northwest China from 2004 to 2018: A spatio-temporal analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.D.; Zheng, H.Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, X.M. Spatiotemporal distribution and ecological factors of brucellosis among children from 2016 to 2020 in Inner Mongolia, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, X.R.; Bu, Q.Q.; Tan, B.; Yang, T.; Qing, L.; Wang, Y.; Deng, D. Spatiotemporal dynamics and influencing factors of human brucellosis in Mainland China from 2005–2021. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, B.J.; Wall, P.G.; Fanning, S.; Fahey, A.G. Targets to increase food production: One Health implications. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 27708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okello, A.; Welburn, S.; Smith, J. Crossing institutional boundaries: Mapping the policy process for improved control of endemic and neglected zoonoses in sub-Saharan Africa. Health Policy Plan. 2015, 30, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meslin, F.X.; Stohr KHeyman, D. Public health implication of emerging zoonoses. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2000, 19, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salyer, S.J.; Silver, R.; Simone, K.; Barton Behravesh, C. Prioritizing Zoonoses for Global Health Capacity Building-Themes from One Health Zoonotic Disease Workshops in 7 Countries, 2014–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, S55–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; UNEP United Nations Environment Programme; World Organisation for Animal Health. One Health Joint Plan of Action (2022–2026); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/363518 (accessed on 22 May 2025).



| Diseases | Relative Reduction (%) (2015–2019 vs. 2020) | Relative Reduction (%) (2015–2019 vs. 2021) | Relative Reduction (%) (2015–2019 vs. 2022) | Relative Reduction (%) (2015–2019 vs. 2020–2022) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabies | 62.21 | 70.63 | 75.12 | 69.32 |
| Anthrax | 30.56 | −21.51 | −8.18 | 0.29 |
| Japanese encephalitis | 72.43 | 80.19 | 86.03 | 79.55 |
| Brucellosis | −5.15 | −55.27 | −47.19 | −35.87 |
| Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome | 21.90 | 11.65 | 49.82 | 27.79 |
| Leptospirosis | −15.93 | −57.30 | 25.84 | −15.79 |
| Leishmaniasis | 22.61 | 11.88 | 13.41 | 15.96 |
| Schistosomiasis | 99.44 | 99.83 | 99.61 | 99.63 |
| Echinococcosis | 24.42 | 36.42 | 46.82 | 35.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Geng, M.; Shi, Y.; Jin, B.; Xiong, Q.; Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; Kan, B.; Zhou, M.; Qin, T.; et al. Epidemiological Characteristics and Trends of Zoonotic Diseases in China from 2015 to 2022. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10060159
Zhang Y, Geng M, Shi Y, Jin B, Xiong Q, Zhou S, Liu J, Kan B, Zhou M, Qin T, et al. Epidemiological Characteristics and Trends of Zoonotic Diseases in China from 2015 to 2022. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(6):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10060159
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yunfei, Mengjie Geng, Yue Shi, Baijun Jin, Qian Xiong, Sheng Zhou, Jiangmei Liu, Biao Kan, Maigeng Zhou, Tian Qin, and et al. 2025. "Epidemiological Characteristics and Trends of Zoonotic Diseases in China from 2015 to 2022" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 6: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10060159
APA StyleZhang, Y., Geng, M., Shi, Y., Jin, B., Xiong, Q., Zhou, S., Liu, J., Kan, B., Zhou, M., Qin, T., & Zheng, C. (2025). Epidemiological Characteristics and Trends of Zoonotic Diseases in China from 2015 to 2022. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(6), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10060159






