Advances in Diagnostic Techniques for Influenza Virus Infection: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
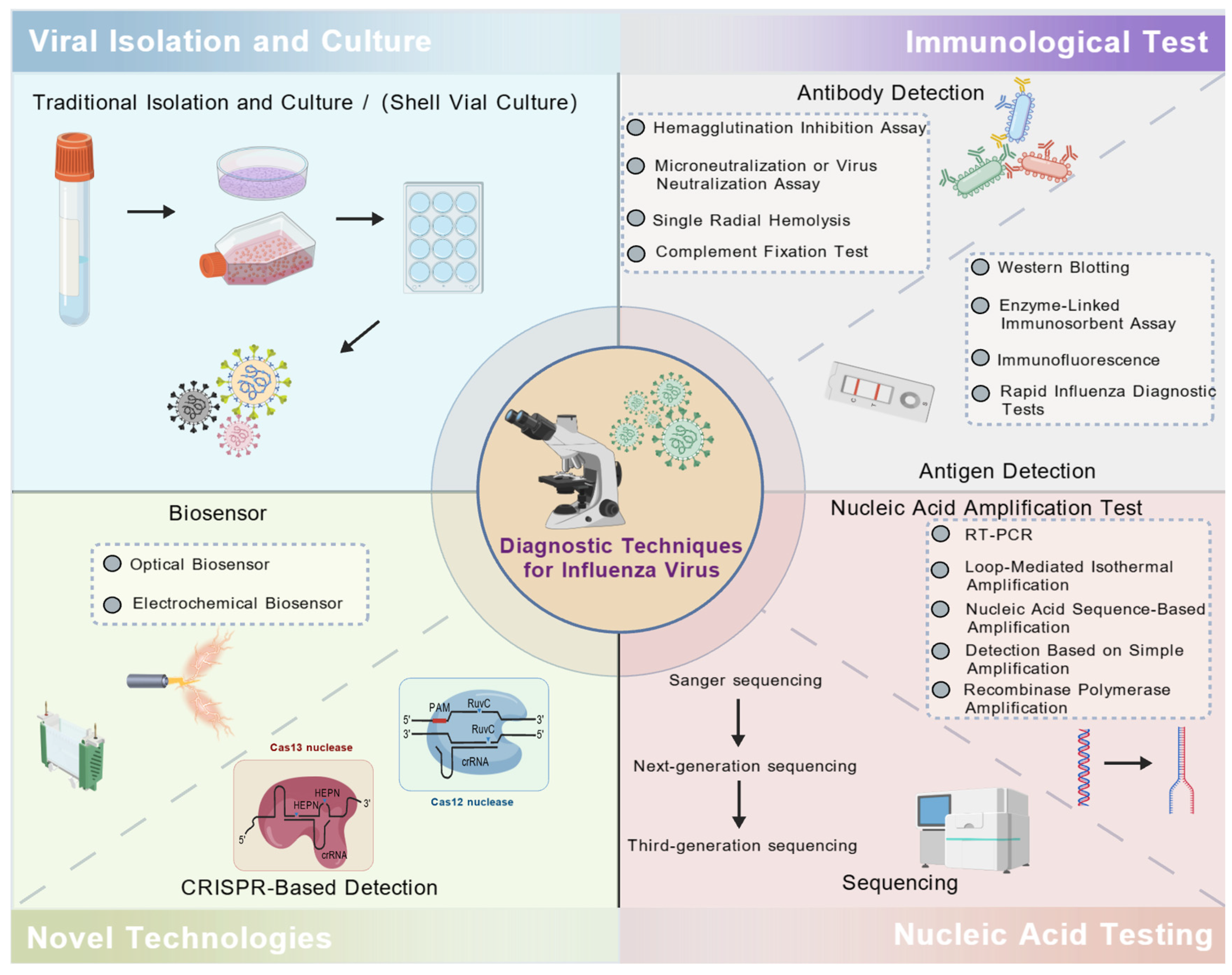
1. Introduction
2. Viral Isolation and Culture
3. Immunological Test
3.1. Hemagglutination Inhibition Assay (HAI)
3.2. Microneutralization or Virus Neutralization Assay (VN)
3.3. Single Radial Hemolysis (SRH)
3.4. Complement Fixation Test (CFT)
3.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
3.6. Western Blotting (WB)
3.7. Immunofluorescence (IF)
3.8. Rapid Influenza Diagnostic Tests (RIDTs) Method
4. Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT)
4.1. Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.2. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)
4.3. Nucleic Acid Sequence-Based Amplification (NASBA)
4.4. Detection Based on Simple Amplification (SAMBA)
4.5. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA)
4.6. Sequencing
5. Novel Technologies
5.1. CRISPR-Based Detection
5.2. Biosensor
5.2.1. Optical Biosensor
5.2.2. Electrochemical Biosensor
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krammer, F.; Smith, G.J.D.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Peiris, M.; Kedzierska, K.; Doherty, P.C.; Palese, P.; Shaw, M.L.; Treanor, J.; Webster, R.G.; et al. Influenza. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machała, M.K.; Brydak, L.B. Various sides of influenza, part I--structure, replication, changeability of influenza viruses, clinical course of the disease, immunological response and laboratory diagnostics. Pol. Merkur. Lekarski 2006, 21, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.H.; Mahmood, T.A. Influenza A H1N1 2009 (Swine Flu) and Pregnancy. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. India 2011, 61, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuliano, A.D.; Roguski, K.M.; Chang, H.H.; Muscatello, D.J.; Palekar, R.; Tempia, S.; Cohen, C.; Gran, J.M.; Schanzer, D.; Cowling, B.J.; et al. Estimates of global seasonal influenza-associated respiratory mortality: A modelling study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanian, M.; Barary, M.; Ghebrehewet, S.; Koppolu, V.; Vasigala, V.; Ebrahimpour, S. A brief review of influenza virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 4638–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyeki, T.M.; Hui, D.S.; Zambon, M.; Wentworth, D.E.; Monto, A.S. Influenza. Lancet 2022, 400, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.; Gurley, S.A.; Overman, R.G.; Sharak, A.; Mudrak, S.V.; Oguin, T., 3rd; Sempowski, G.D.; Sarzotti-Kelsoe, M.; Walter, E.B.; Xie, H.; et al. H3N2 influenza hemagglutination inhibition method qualification with data driven statistical methods for human clinical trials. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1155880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziąbowska, K.; Czaczyk, E.; Nidzworski, D. Detection Methods of Human and Animal Influenza Virus-Current Trends. Biosensors 2018, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemula, S.V.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Biswas, S.; Hewlett, I. Current Approaches for Diagnosis of Influenza Virus Infections in Humans. Viruses 2016, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Poudel, B. Tools to detect influenza virus. Yonsei Med. J. 2013, 54, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Comparative Analysis of Three Influenza Virus Detection Methods. Henan J. Prev. Med. 2019, 30, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhirnov, O.P.; Ikizler, M.R.; Wright, P.F. Cleavage of influenza a virus hemagglutinin in human respiratory epithelium is cell associated and sensitive to exogenous antiproteases. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8682–8689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steed, L.L.; Salmon, V.C.; Overall, J.C., Jr. Identification of influenza A virus by shell vial culture and two commercially available antigen detection methods. Clin. Diagn. Virol. 1994, 2, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, W.C. Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McAdam, A.J.; Riley, A.M. Developments in tissue culture detection of respiratory viruses. Clin. Lab. Med. 2009, 29, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, A.; Brewster, L.; Clark, J.; Simoes, E. Evaluation of R-Mix shell vials for the diagnosis of viral respiratory tract infections. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 30, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, J.J.; Woolstenhulme, R.D.; Langer, J.; Carroll, K.C. Sensitivity of respiratory virus culture when screening with R-mix fresh cells. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthey, S.; Nicholson, D.; Ruhs, S.; Alden, B.; Knock, M.; Schultz, K.; Schmuecker, A. Rapid detection of respiratory viruses by shell vial culture and direct staining by using pooled and individual monoclonal antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Wu, S.; Meng, S.; Zheng, G.; Chen, D.; LI, J.; Chen, C. Rapid culture and identification of human parainfluenza viruses. J. Med. Postgra. 2016, 29, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydak, L.B.; Wozniak-Kosek, A.; Nitsch-Osuch, A. Influenza diagnosis and vaccination in Poland. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 187, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Influenza Signs and Symptoms and the Role of Laboratory Diagnostics; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- McClelland, L.; Hare, R. The adsorption of influenza virus by red cells and a new in vitro method of measuring antibodies for influenza virus. Can. Public Health J. 1941, 32, 530–538. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.N.; Weber, K.M.; Limmer, R.A.; Horne, B.J.; Stevens, J.; Schwerzmann, J.; Wrammert, J.; McCausland, M.; Phipps, A.J.; Hancock, K.; et al. Evaluation of multiplex assay platforms for detection of influenza hemagglutinin subtype specific antibody responses. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 243, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killian, M.L. Hemagglutination Assay for Influenza Virus. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2123, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, L.; Syedbasha, M.; Vogt, D.; Hollenstein, Y.; Hartmann, J.; Linnik, J.E.; Egli, A. An Optimized Hemagglutination Inhibition (HI) Assay to Quantify Influenza-specific Antibody Titers. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 130, e55833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivitskaya, V.; Kuznecova, E.; Majorova, V.; Kadyrova, R.; Lvov, N.; Go, A.; Sominina, A. Microneutralization reaction compared to hemagglutination inhibition assay to evaluate immunogenicity of influenza vaccines and influenza diagnostics. Russ. J. Infect. Immun. 2019, 9, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, I.; Heath, A.; Major, D.; Newman, R.W.; Hoschler, K.; Junzi, W.; Katz, J.M.; Weir, J.P.; Zambon, M.C.; Wood, J.M. Reproducibility of serologic assays for influenza virus A (H5N1). Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.; McCahon, D.; Beare, A. A single radial haemolysis technique for the measurement of influenza antibody. J. Gen. Virol. 1975, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Russell, M.L.; Brewer, A.; Newton, J.; Singh, P.; Ward, B.J.; Loeb, M. Single radial haemolysis compared to haemagglutinin inhibition and microneutralization as a correlate of protection against influenza A H3N2 in children and adolescents. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2017, 11, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, C.M.; Remarque, E.J.; Mortier, D.; Montomoli, E. Comparison of hemagglutination inhibition, single radial hemolysis, virus neutralization assays, and ELISA to detect antibody levels against seasonal influenza viruses. Influenza Other Respir. viruses 2018, 12, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaheim, R. Single-radial-complement-fixation: A new immunodiffusion technique. 2. Assay of the antibody response to the internal antigens (MP and NP) of influenza A virus in human sera after vaccination and infection. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1977, 39, 481–484. [Google Scholar]
- West, E.E.; Woodruff, T.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Kemper, C. Complement in human disease: Approved and up-and-coming therapeutics. Lancet 2024, 403, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, D.C.; Gomes, A.S.; Tessler, D.K.; Chiebao, D.P.; Fava, C.D.; Romaldini, A.; Araujo, M.C.; Pompei, J.; Marques, G.F.; Harakava, R.; et al. Systematic monitoring of glanders-infected horses by complement fixation test, bacterial isolation, and PCR. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2020, 10, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, T., Jr. Differentiation of Influenza A and Influenza B by the Complement-Fixation Reaction. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1940, 45, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, V.; Braun, K.M.P.; Willrich, M.A.V. Challenges for complement functional assays in the clinical laboratory: From test validation to clinical interpretation. J. Immunol. Methods 2025, 537, 113824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Qamar, A.; Liu, H. The complement system testing in clinical laboratory. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 541, 117238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaei, M.S.; Ahmed, M. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2508, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhajj, M.; Zubair, M.; Farhana, A. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. In StatPearls; 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555922/ (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Hayrapetyan, H.; Tran, T.; Tellez-Corrales, E.; Madiraju, C. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay: Types and Applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2612, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishai, F.; Galli, R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to influenza A and B and parainfluenza type 1 in sera of patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1978, 8, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steininger, C.; Kundi, M.; Aberle, S.W.; Aberle, J.H.; Popow-Kraupp, T. Effectiveness of reverse transcription-PCR, virus isolation, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of influenza A virus infection in different age groups. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2051–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule, R.; Rivera, G.; Gomes, A.V. Western blotting (immunoblotting): History, theory, uses, protocol and problems. Biotechniques 2023, 75, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, T.; Abernathy, R.A.; Hu-Primmer, J.; Thompson, W.W.; Lu, X.; Lim, W.; Fukuda, K.; Cox, N.J.; Katz, J.M. Detection of antibody to avian influenza A (H5N1) virus in human serum by using a combination of serologic assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurien, B.T.; Scofield, R.H. Western blotting. Methods 2006, 38, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odell, I.D.; Cook, D. Immunofluorescence techniques. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzoli, R.; Antico, A.; Porcelli, B.; Bassetti, D. Automation in indirect immunofluorescence testing: A new step in the evolution of the autoimmunology laboratory. Autoimmun. Highlights 2012, 3, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piña, R.; Santos-Díaz, A.I.; Orta-Salazar, E.; Aguilar-Vazquez, A.R.; Mantellero, C.A.; Acosta-Galeana, I.; Estrada-Mondragon, A.; Prior-Gonzalez, M.; Martinez-Cruz, J.I.; Rosas-Arellano, A. Ten approaches that improve immunostaining: A review of the latest advances for the optimization of immunofluorescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, N.R.; Duong, S.; Cheng, A.; Han, L.L.; Smole, S.; Kirby, J.E. Ruling out novel H1N1 influenza virus infection with direct fluorescent antigen testing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, e66–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Rapid Diagnostic Testing for Influenza: Information for Clinical Laboratory Directors; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/professionals/diagnosis/rapidlab.htm (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Landry, M.L. Diagnostic tests for influenza infection. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2011, 23, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyola, D.E.; Clark, B.; O’Donnell, F.T.; Atmar, R.L.; Greer, J.; Demmler, G.J. Comparison of a new neuraminidase detection assay with an enzyme immunoassay, immunofluorescence, and culture for rapid detection of influenza A and B viruses in nasal wash specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, S.E. The role of rapid antigen testing for influenza in the era of molecular diagnostics. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2010, 14, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morehouse, Z.P.; Chance, N.; Ryan, G.L.; Proctor, C.M.; Nash, R.J. A narrative review of nine commercial point of care influenza tests: An overview of methods, benefits, and drawbacks to rapid influenza diagnostic testing. J. Osteopath. Med. 2022, 123, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, R.R.; Klepser, M.E. A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for influenza: Considerations for the community pharmacist. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2017, 57, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Evaluation of rapid influenza diagnostic tests for detection of novel influenza A (H1N1) Virus--United States, 2009. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2009, 58, 826. [Google Scholar]
- Gavin, P.J.; Thomson, R.B., Jr. Review of rapid diagnostic tests for influenza. Clin. Appl. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 4, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravina; Manjeet; Mohan, H.; Narang, J.; Pundir, S.; Pundir, C.S. A changing trend in diagnostic methods of Influenza A (H3N2) virus in human: A review. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angione, S.L.; Inde, Z.; Beck, C.M.; Artenstein, A.W.; Opal, S.M.; Tripathi, A. Microdroplet sandwich real-time RT-PCR for detection of pandemic and seasonal influenza subtypes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.L.; Hu, P.; Shafer, D.A. Seven novel probe systems for real-time PCR provide absolute single-base discrimination, higher signaling, and generic components. J. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 16, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Osborn, A.M. Advantages and limitations of quantitative PCR (Q-PCR)-based approaches in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z. Design, Synthesis, Purification, and Characterization of Molecular Beacons. In Molecular Beacons; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Yan, A.; Ding, G.; Chen, Y.; Xie, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Hao, P. Detection of human novel influenza A (H1N1) viruses using multi-fluorescent real-time RT-PCR. Virus Res. 2010, 147, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrberg, C.D.; Lee, J.M.; Chung, B.G. Microwell array-based digital PCR for influenza virus detection. BioChip J. 2019, 13, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becherer, L.; Borst, N.; Bakheit, M.; Frischmann, S.; Zengerle, R.; von Stetten, F. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)–review and classification of methods for sequence-specific detection. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 717–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullen, A.R.; Anderson, N.W.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; for the Education Committee of the Academy of Clinical Laboratory Physicians and Scientists. Pathology consultation on influenza diagnostics. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 145, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, N.C.; Watts, D.M.; Frolov, I.; Weaver, S.C. Experimental infection of Aedes sollicitans and Aedes taeniorhynchus with two chimeric Sindbis/Eastern equine encephalitis virus vaccine candidates. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, L.L.; Leung, C.S.; Chan, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yuen, K.Y.; Guan, Y.; Peiris, J.S. Detection of human influenza A viruses by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahony, J.; Chong, S.; Bulir, D.; Ruyter, A.; Mwawasi, K.; Waltho, D. Multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification (M-LAMP) assay for the detection of influenza A/H1, A/H3 and influenza B can provide a specimen-to-result diagnosis in 40 min with single genome copy sensitivity. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Segawa, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Yotoriyama, T.; Kai, S.; Yasuda, A.; Shimizu, N.; Tojo, N. Point-of-care testing system enabling 30 min detection of influenza genes. Lab A Chip 2011, 11, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, A.; Shibasaki, F. Updated values for molecular diagnosis for highly pathogenic avian influenza virus. Viruses 2012, 4, 1235–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, S.J.; Stromberg, Z.R.; Kubicek-Sutherland, J.Z. Nucleic acid-based sensing techniques for diagnostics and surveillance of influenza. Biosensors 2021, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.; Hibbitts, S.; Owen, N.; Corden, S.A.; Harrison, G.; Fox, J.; Gelder, C.; Westmoreland, D. Development and evaluation of a real-time nucleic acid sequence based amplification assay for rapid detection of influenza A. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 74, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Cui, L.; Qi, X.; Shan, J.; Shan, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wu, B.; Wang, H.; Shi, Z. Detection of novel swine origin influenza A virus (H1N1) by real-time nucleic acid sequence-based amplification. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 163, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, K.; Wiske, C.; Tripathi, A. Engineering insights for multiplexed real-time nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA): Implications for design of point-of-care diagnostics. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2013, 17, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, J. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification. Nature 1991, 350, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, F. Application of molecular diagnostic techniques for viral testing. Open Virol. J. 2012, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.T.; Curran, M.; Ellis, J.; Parmar, S.; Ritchie, A.V.; Sharma, P.I.; Allain, J.P.; Jalal, H.; Zambon, M.; Lee, H.H. Nucleic acid dipstick test for molecular diagnosis of pandemic H1N1. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3608–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.-T.; Thomas, I.; Curran, M.D.; Ellis, J.S.; Parmar, S.; Goel, N.; Sharma, P.I.; Allain, J.-P.; Lee, H.H. Duplex molecular assay intended for point-of-care diagnosis of influenza A/B virus infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3031–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boora, S.; Kumari, S.; Garg, D.; Lath, A.; Kaushik, S.; Chand, K.; Kaushik, S. Influenza Diagnostic Approaches: Different Roads to the Same Destination. Indian J. Health Sci. Care 2024, 11, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Daher, R.K.; Stewart, G.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Recombinase polymerase amplification for diagnostic applications. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Macdonald, J.; von Stetten, F. Correction: Review: A comprehensive summary of a decade development of the recombinase polymerase amplification. Analyst 2020, 145, 1950–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Liao, C.; Liang, L.; Yi, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wei, G. Recent advances in recombinase polymerase amplification: Principle, advantages, disadvantages and applications. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1019071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.G.; Zhu, M.j.; He, R.; Shi, D.R.; Luo, R.; Ji, J.; Cheng, L.F.; Lu, X.Y.; Lu, W.; Liu, F.M. Development of a multi-recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid identification of COVID-19, influenza A and B. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustin, T.; Ling, G.; Sharabi, S.; Ram, D.; Friedman, N.; Zuckerman, N. A method to identify respiratory virus infections in clinical samples using next-generation sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behjati, S.; Tarpey, P.S. What is next generation sequencing? Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. 2013, 98, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilt, E.E.; Ferrieri, P. Next generation and other sequencing technologies in diagnostic microbiology and infectious diseases. Genes 2022, 13, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, F.E.; Grove, M.E.; Pan, C.; Goldstein, B.A.; Bernstein, J.A.; Chaib, H.; Merker, J.D.; Goldfeder, R.L.; Enns, G.M.; David, S.P. Clinical interpretation and implications of whole-genome sequencing. JAMA 2014, 311, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, K.N.; Street, T.L.; Sanderson, N.D.; Eyre, D.W. Metagenomic sequencing as a pathogen-agnostic clinical diagnostic tool for infectious diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 10.1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamanova, L.; Coffey, A.J.; Scott, C.E.; Kozarewa, I.; Turner, E.H.; Kumar, A.; Howard, E.; Shendure, J.; Turner, D.J. Target-enrichment strategies for next-generation sequencing. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Stelzer-Braid, S.; Scotch, M.; Rawlinson, W.D. Detection of respiratory viruses directly from clinical samples using next-generation sequencing: A literature review of recent advances and potential for routine clinical use. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H. Complete genome sequencing of influenza A viruses using next-generation sequencing. Anim. Influenza Virus Methods Protoc. 2020, 2123, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Van Poelvoorde, L.A.; Saelens, X.; Thomas, I.; Roosens, N.H. Next-generation sequencing: An eye-opener for the surveillance of antiviral resistance in influenza. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quer, J.; Colomer-Castell, S.; Campos, C.; Andrés, C.; Piñana, M.; Cortese, M.F.; González-Sánchez, A.; Garcia-Cehic, D.; Ibáñez, M.; Pumarola, T. Next-generation sequencing for confronting virus pandemics. Viruses 2022, 14, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Man, S.; Ye, S.; Liu, G.; Ma, L. CRISPR-Cas based virus detection: Recent advances and perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhrvold, C.; Freije, C.A.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Metsky, H.C.; Durbin, A.F.; Kellner, M.J.; Tan, A.L.; Paul, L.M.; Parham, L.A. Field-deployable viral diagnostics using CRISPR-Cas13. Science 2018, 360, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, D.; Dai, W.; Gong, J.; Li, G.; Liu, N.; Wu, W.; Pan, J.; Chen, C.; Jiao, Y.; Deng, H. Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 with CRISPR-Cas12a. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Park, M.S.; Lee, J.M.; Song, Y.J. Specific detection of influenza A and B viruses by CRISPR-Cas12a-based assay. Biosensors 2021, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayuramart, O.; Nimsamer, P.; Rattanaburi, S.; Chantaravisoot, N.; Khongnomnan, K.; Chansaenroj, J.; Puenpa, J.; Suntronwong, N.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Poovorawan, Y. Detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and influenza viruses based on CRISPR-Cas12a. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ren, L. Recent progress on the diagnosis of 2019 Novel Coronavirus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A review on biosensors and recent development of nanostructured materials-enabled biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Cui, D.; Huang, J.; Fan, W.; Miao, Y.; Pu, K. Near-infrared afterglow semiconducting nano-polycomplexes for the multiplex differentiation of cancer exosomes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4983–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damborský, P.; Švitel, J.; Katrlík, J. Optical biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłos-Witkowska, A. The phenomenon of fluorescence in immunosensors. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ren, Z.H.; Zhao, W.M.; Wang, L.; Yan, X.; Zhu, A.S.; Qiu, F.M.; Zhang, K.K. Research advances on surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 564–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.L.; Chua, M.; Mittman, H.; Choo, L.X.; Lim, H.Q.; Olivo, M. A phase-intensity surface plasmon resonance biosensor for avian influenza A (H5N1) detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Charconnet, M.; Jiang, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lawrie, C.H. Optical biosensor based on the dual-functional gold nanoparticles for rapid and accurate multiplex detection of influenza A and B viruses. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2024, 46, 100689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Mittal, S.; Das, M.; Saharia, A.; Tiwari, M. Optical biosensors: A decade in review. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 67, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.H.; Hasan, M.R.; Hossain, S.I.; Ahommed, M.S.; Daizy, M. Ultrasensitive detection of pathogenic viruses with electrochemical biosensor: State of the art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamikawa, T.L.; Mikolajczyk, M.G.; Kennedy, M.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Scott, D.E.; Alocilja, E.C. Nanoparticle-based biosensor for the detection of emerging pandemic influenza strains. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Yu, K. Sensitive and rapid detection of influenza A virus for disease surveillance using dual-probe electrochemical biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 153, 108497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, Q.; Ma, B.; Zhang, B.; Sun, K.; Yu, X.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, M. Advances in Detection Techniques for the H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, Q.; Fan, G.; Yang, W.; Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, W. Advances in Diagnostic Techniques for Influenza Virus Infection: A Comprehensive Review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10060152
Qian Q, Fan G, Yang W, Shen C, Yang Y, Liu Y, Xiao W. Advances in Diagnostic Techniques for Influenza Virus Infection: A Comprehensive Review. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(6):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10060152
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Qi, Guohao Fan, Wei Yang, Chenguang Shen, Yang Yang, Yingxia Liu, and Weiwei Xiao. 2025. "Advances in Diagnostic Techniques for Influenza Virus Infection: A Comprehensive Review" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 6: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10060152
APA StyleQian, Q., Fan, G., Yang, W., Shen, C., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., & Xiao, W. (2025). Advances in Diagnostic Techniques for Influenza Virus Infection: A Comprehensive Review. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(6), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10060152





