Integrated Surveillance for Human and Animal Brucellosis in Kenya: A Predictive Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
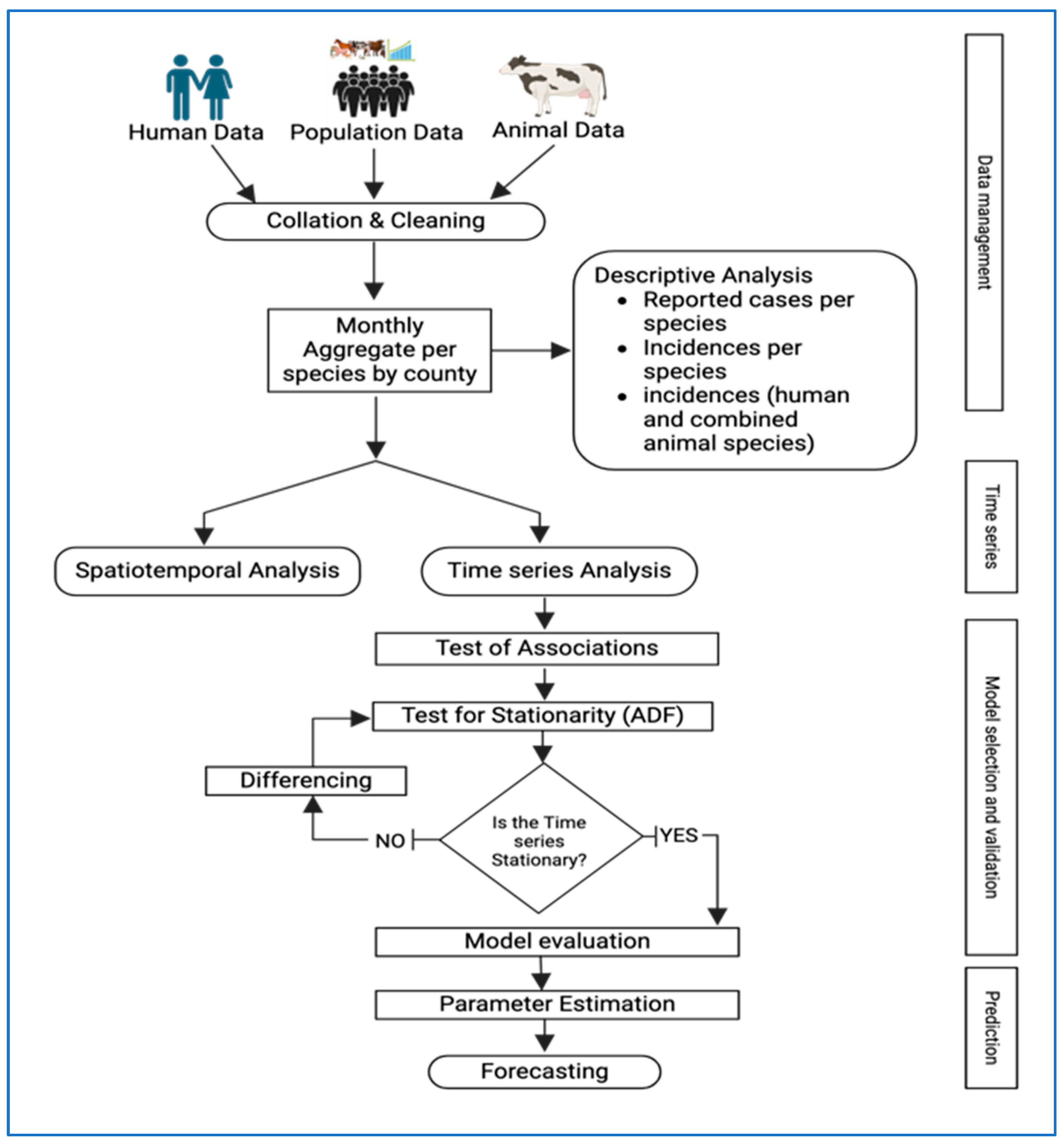
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Estimating Incidence
2.2.2. Test of Association Between Animal and Human Brucellosis Cases
2.2.3. Forecasting of Human Brucellosis Cases
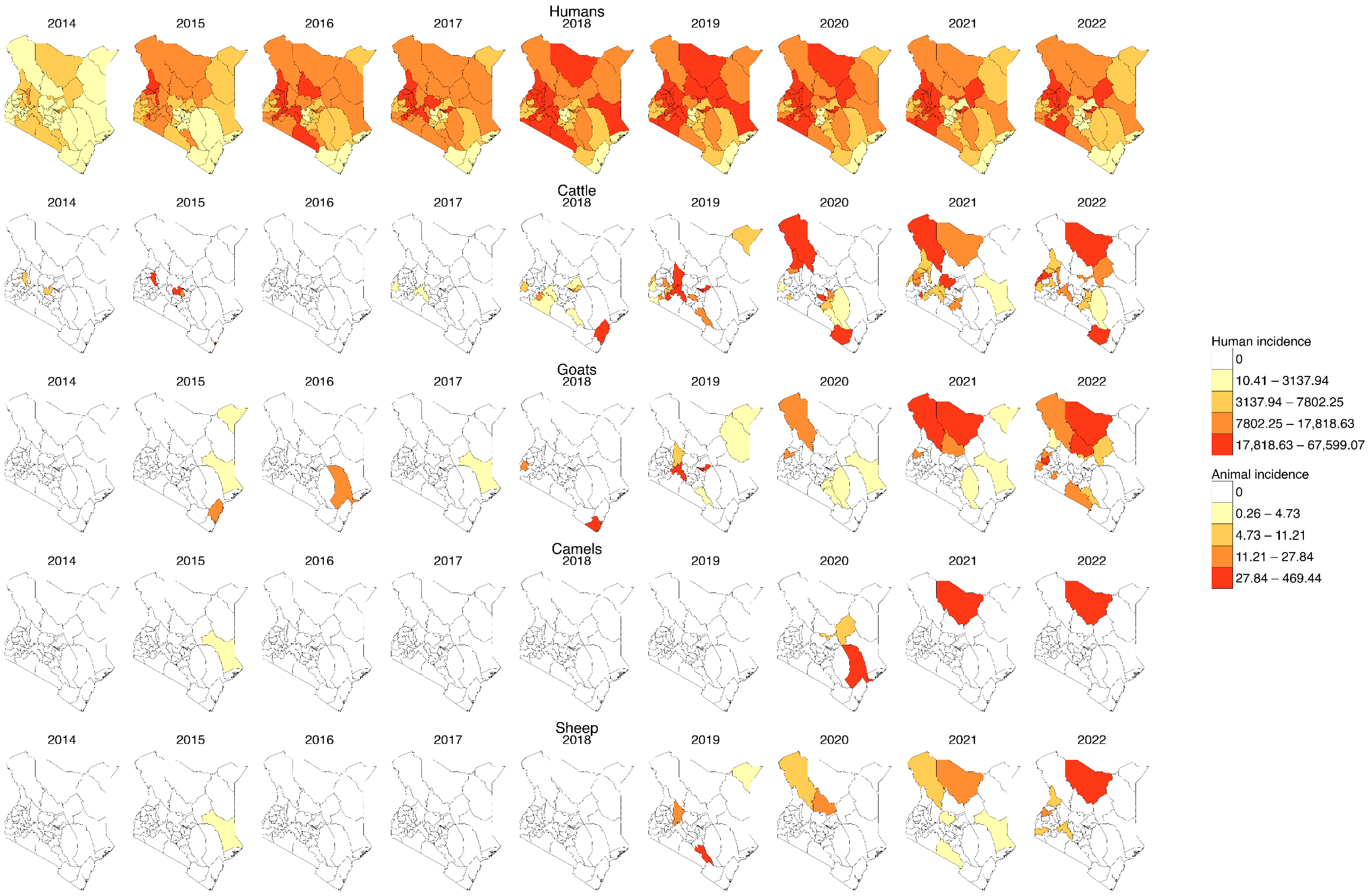
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SARIMA | Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average |
| KHIS | Kenya Health Information System |
| KABS | Kenya Animal Bio-surveillance System |
| KNBS | Kenya National Bureau of Statistics |
| TSLM | Time Series Linear Model |
| ADF | Augmented Dickey–Fuller |
Appendix A
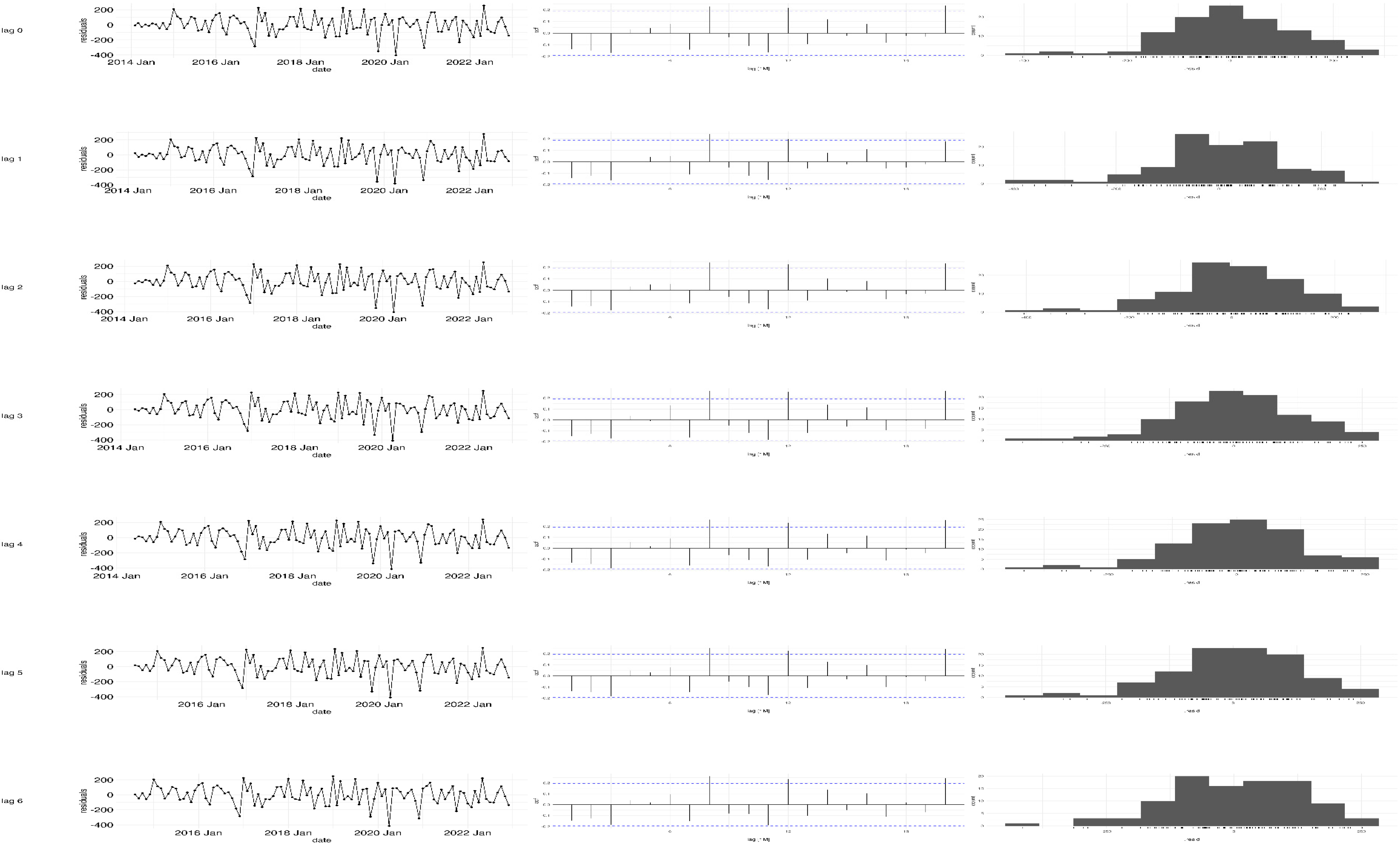
Appendix B
| Lag | MAE | RMSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lag 0 | 107.340785 | 121.775861 | 11.412123 |
| Lag 1 | 110.164144 | 127.631526 | 11.9027991 |
| Lag 2 | 110.096513 | 124.752796 | 11.7661673 |
| Lag 3 | 106.71078 | 121.684391 | 11.3373693 |
| Lag 4 | 110.259697 | 122.84345 | 11.4226258 |
| Lag 5 | 113.204553 | 131.292121 | 12.2466865 |
| Lag 6 | 99.0380344 | 118.30954 | 10.2856198 |
References
- Laine, C.G.; Johnson, V.E.; Scott, H.M.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Global Estimate of Human Brucellosis Incidence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, J.; Grace, D.; Zinsstag, J. Economics of brucellosis impact and control in low-income countries. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2013, 32, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasinyama, G.; Ssekawojwa, E.; Opuda, J.; Grimaud, P.; Etter, E.; Bellinguez, A. Brucella sero-prevalence and modifiable risk factors among predisposed cattle keepers and consumers of un-pasteurized milk in Mbarara and Kampala districts, Uganda. Afr. Health Sci. 2014, 14, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, R.B.; Krecek, R.C.; Khalaf, O.H.; Hailat, N.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Brucellosis in the middle east: Current situation and a pathway forward. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008071. [Google Scholar]
- Njeru, J.; Wareth, G.; Melzer, F.; Henning, K.; Pletz, M.W.; Heller, R.; Neubauer, H. Systematic review of brucellosis in Kenya: Disease frequency in humans and animals and risk factors for human infection. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, K.A.; Parvez, A.; Fahmy, N.A.; Abdel Hady, B.H.; Kumar, S.; Ganguly, A.; Atiya, A.; Elhassan, G.O.; Alfadly, S.O.; Parkkila, S.; et al. Brucellosis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment—A comprehensive review. Ann. Med. 2024, 55, 2295398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Munyua, P.; Osoro, E.; Hunsperger, E.; Ngere, I.; Muturi, M.; Mwatondo, A.; Marwanga, D.; Ngere, P.; Tiller, R.; Onyango, C.O.; et al. High incidence of human brucellosis in a rural pastoralist community in Kenya, 2015. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenya Zoonotic Disease Unit. Kenya Brucellosis Control Strategy; Government of Kenya: Nairobi, Kenya, 2022.
- Osoro, E.M.; Munyua, P.; Omulo, S.; Ogola, E.; Ade, F.; Mbatha, P.; Mbabu, M.; Ng’ang’a, Z.; Kairu, S.; Maritim, M.; et al. Strong association between human and animal brucella seropositivity in a linked study in Kenya, 2012–2013. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muema, J.; Oboge, H.; Mutono, N.; Makori, A.; Oyugi, J.; Bukania, Z.; Njuguna, J.; Jost, C.; Ogoti, B.; Omulo, S.; et al. Sero—Epidemiology of brucellosis in people and their livestock: A linked human—Animal cross-sectional study in a pastoralist community in Kenya. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1031639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoko, J.M.; Mwatondo, A.; Muturi, M.; Wambua, L.; Abkallo, H.M.; Nyamota, R.; Bosire, C.; Oloo, S.; Limbaso, K.S.; Gakuya, F.; et al. Mapping brucellosis risk in Kenya and its implications for control strategies in sub-Saharan Africa. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokamar, P.N.; Kutwah, M.A.; Munde, E.O.; Oloo, D.; Atieli, H.; Gumo, S.; Akoko, J.M.; Ouma, C. Prevalence of brucellosis in livestock keepers and domestic ruminants in Baringo County, Kenya. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2022, 2, e0000682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwatondo, A.; Muturi, M.; Akoko, J.; Nyamota, R.; Nthiwa, D.; Maina, J.; Omolo, J.; Gichuhi, S.; Mureithi, M.W.; Bett, B. Seroprevalence and related risk factors of Brucella spp. in livestock and humans in Garbatula subcounty, Isiolo county, Kenya. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoko, J.M.; Pelle, R.; Lukambagire, A.H.S.; Machuka, E.M.; Nthiwa, D.; Mathew, C.; Fèvre, E.M.; Bett, B.; Cook, E.A.J.; Othero, D.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Brucella species in mixed livestock-human ecosystems in Kenya. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoko, J.; Pelle, R.; Kivali, V.; Schelling, E.; Shirima, G.; MacHuka, E.M.; Mathew, C.; Fèvre, E.M.; Kyallo, V.; Falzon, L.C.; et al. Serological and molecular evidence of Brucella species in the rapidly growing pig sector in Kenya. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemunto, N.; Mogoa, E.; Osoro, E.; Bitek, A.; Kariuki Njenga, M.; Thumbi, S.M. Zoonotic disease research in East Africa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Surveillance in Emergencies. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/surveillance (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- One Health High-Level Expert Panel (OHHLEP); Hayman, D.T.S.; Adisasmito, W.B.; Almuhairi, S.; Behravesh, C.B.; Bilivogui, P.; Bukachi, S.A.; Casas, N.; Becerra, N.C.; Charron, D.F.; et al. Developing One Health surveillance systems. One Health 2023, 17, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsubuga, P.; White, M.E.; Thacker, S.B.; Anderson, M.A.; Blount, S.B.; Broome, C.V.; Chiller, T.M.; Espitia, V.; Imtiaz, R.; Dan Sosin, D.; et al. Public Health Surveillance: A Tool for Targeting and Monitoring Interventions. In Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries; The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK11770/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Huppert, A.; Katriel, G. Mathematical modelling and prediction in infectious disease epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahariri, S.; Thumbi, S.M.; Bett, B.; Mureithi, M.W.; Nyaga, N.; Ogendo, A.; Muturi, M.; Thomas, L.F. The evolution of Kenya’s animal health surveillance system and its potential for efficient detection of zoonoses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1379907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, C.; Miriam, C. IST-Africa 2012 Conference Proceedings and Exhibition 9–12 May 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania; IIMC: Dublin, Ireland, 2012.
- Njenga, K.; Kemunto, N.; Kahariri, S.; Holmstrom, L.; Oyas, H.; Biggers, K.; Riddle, A.; Gachohi, J.; Muturi, M.; Mwatondo, A.; et al. High Real-time Reporting of Domestic and Wild Animal Diseases Following Rollout of Mobile Phone Reporting System in Kenya. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KNBS. 2019 Kenya Population and Housing Census; KNBS: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019.
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016; Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1574231874043578752 (accessed on 27 May 2023).
- Dean, A.S.; Crump, L.; Greter, H.; Schelling, E.; Zinsstag, J. Global Burden of Human Brucellosis: A Systematic Review of Disease Frequency. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbel, M. Brucellosis: An Overview. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, N.C.; Schumaker, B.A. Comparisons of brucellosis between human and veterinary medicine. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2018, 8, 1500846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Glanville, W.A.; Conde-Álvarez, R.; Moriyón, I.; Njeru, J.; Díaz, R.; Cook, E.A.J.; Morin, M.; Bronsvoort, B.M.C.; Thomas, L.F.; Kariuki, S.; et al. Poor performance of the rapid test for human brucellosis in health facilities in Kenya. PLoS. Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, G.; Akritidis, N.; Bosilkovski, M.; Tsianos, E. Brucellosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyimo, B.; Hugho, E.; Mathew, C.; Mayenga, C.; Lukambagire, A.H.; Lyimo, S.; Munuo, L.; Byukusenge, M.; Withall, J.; Ashford, R.T.; et al. Seroprevalence and risk factors for brucellosis amongst livestock and humans in a multi-herd ranch system in Kagera, Tanzania. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1478494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagupsky, P.; Morat, P.; Colmenero, J.D. Laboratory diagnosis of human brucellosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00073-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Wu, B.; Pan, H.; Paudyal, N.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Yue, M. ONE Health Approach to Address Zoonotic Brucellosis: A Spatiotemporal Associations Study Between Animals and Humans. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Massis, F.; Di Girolamo, A.; Petrini, A.; Pizzigallo, E.; Giovannini, A. Correlation between animal and human brucellosis in Italy during the period 1997–2002. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njeru, J.; Nthiwa, D.; Akoko, J.; Oyas, H.; Bett, B. Incidence of Brucella infection in various livestock species raised under the pastoral production system in Isiolo County, Kenya. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, G.; Birkhead, G.S.; Horan, J.M.; Herrera, G.; Lee, L.M.; Milstein, R.L.; Pertowski, C.A.; Waller, M.N. Updated Guidelines for Evaluating Public Health Surveillance Systems Recommendations from the Guidelines Working Group; The Following CDC Staff Members Prepared this Report; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2001.
- Chow, A.; Leo, Y.S. Surveillance of Disease: Overview. In International Encyclopedia of Public Health, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Reif, J.S. Animal sentinels for environmental and public health. Public Health Rep. 2011, 126, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, N.; Douwes, J. Research at the interface between human and veterinary health. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 111, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allport, R.; Mosha, R.; Bahari, M.; Swai, E.; Catley, A. The use of community-based animal health workers to strengthen disease surveillance systems in Tanzania. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2005, 24, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, J.; Daborn, C.; Auty, H.; Mtema, Z.; Lembo, T.; Bronsvoort, B.M.; Handel, I.; Knobel, D.; Hampson, K.; Cleaveland, S. Bringing together emerging and endemic zoonoses surveillance: Shared challenges and a common solution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 2872–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.; Sawford, K.; Daniel, S.L.A.; Nelson, T.A.; Stephen, C. Mobile phone-based infectious disease surveillance system, Sri Lanka. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omondi, M.; Ngere, I.; Ndeta, C. Report on the Evaluation of Surveillance Systems Relevant to Zoonotic Diseases in Kenya-2015: A Basis for Design of an Integrated Human Livestock Surveillance System Evaluation Report. 2016. Available online: https://cgspace.cgiar.org/items/47ea8b86-57aa-4b45-9b5e-47684b6dfa77 (accessed on 4 December 2025).
- Don Bamunusinghage Nihal, P.; Dangolla, A.; Hettiarachchi, R.; Abeynayake, P.; Stephen, C. Challenges and opportunities for wildlife disease surveillance in Sri Lanka. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, I.; Hansen, A.; Bi, P. The challenges of implementing an integrated One Health surveillance system in Australia. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, e229–e236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worsley-Tonks, K.E.L.; Bender, J.B.; Deem, S.L.; Ferguson, A.W.; Fèvre, E.M.; Martins, D.J.; Muloi, D.M.; Murray, S.; Mutinda, M.; Ogada, D.; et al. Strengthening global health security by improving disease surveillance in remote rural areas of low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e579–e584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisa Were, A.M.; Otieno, J.A.; Nyanchoka, M.; Karanja, P.W.; Omia, D.; Ngere, P.; Osoro, E.; Njenga, M.K.; Mulaku, M.; Ngere, I. Advance Warning and Response Systems in Kenya: A Scoping Review. medRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Guo, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Predictive analysis of the number of human brucellosis cases in Xinjiang, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
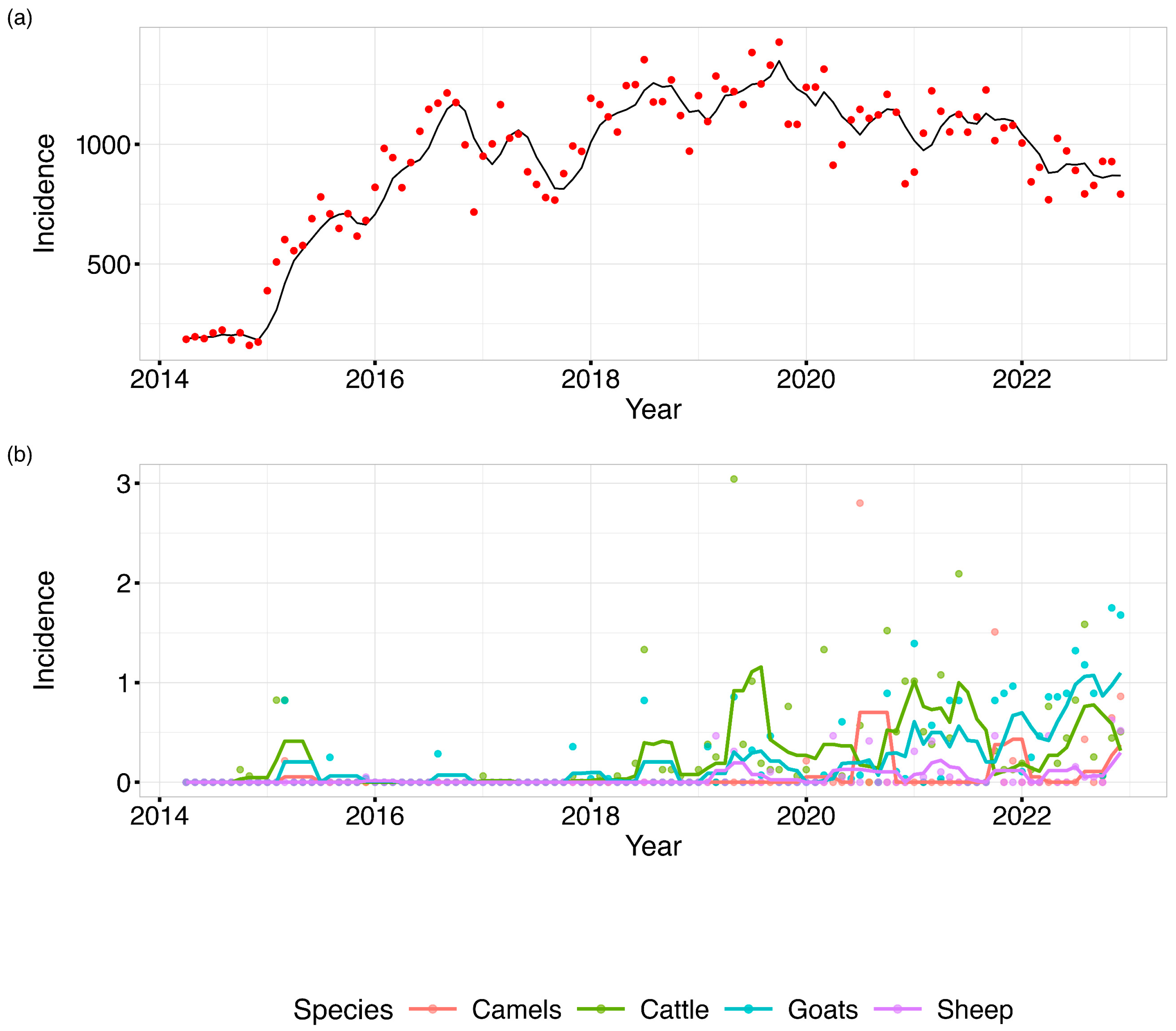
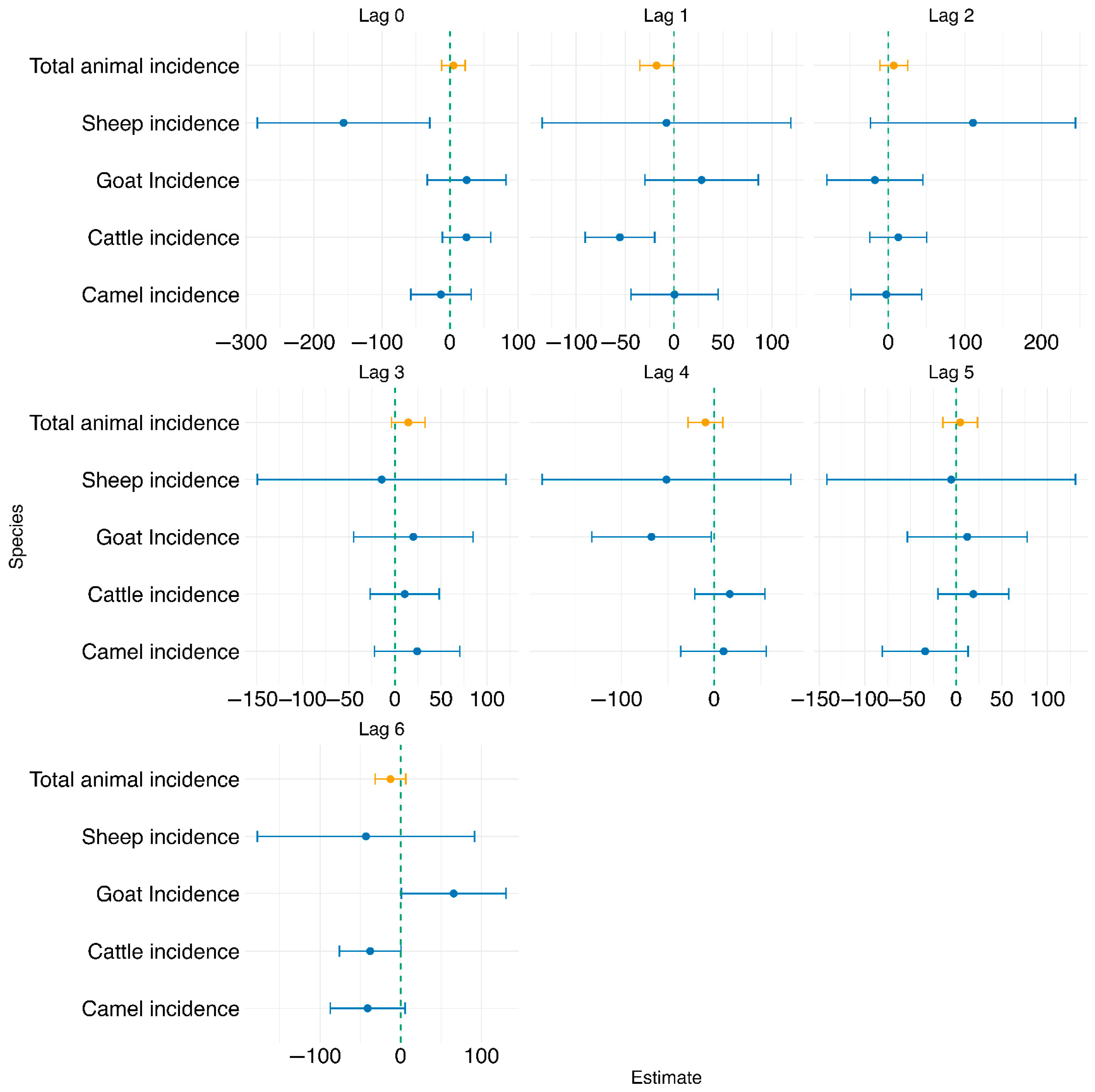
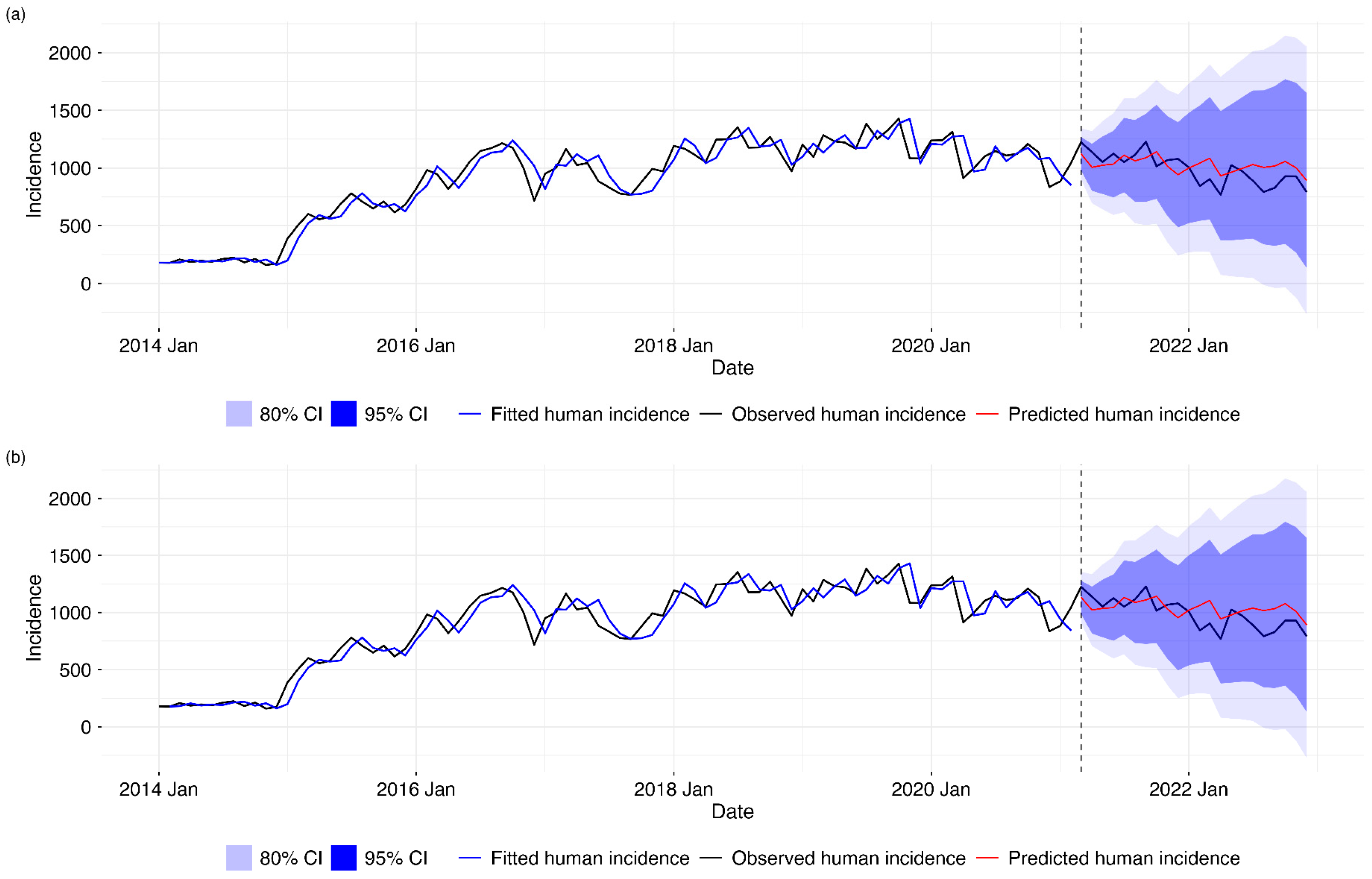
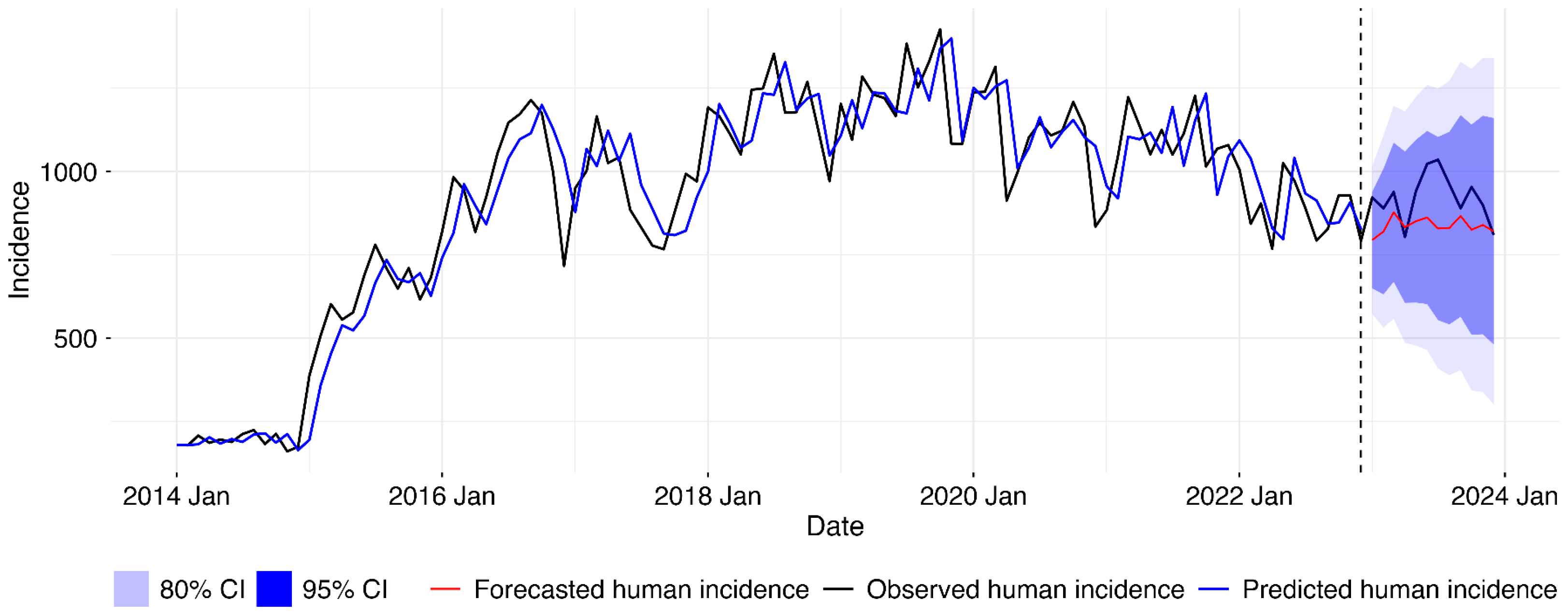
| Species | Total Cases | Average Annual Cases | Clinically Confirmed | Lab-Confirmed | Postmortem | Mean Incidence Rate | Minimum Incidence Rate | Median Incidence Rate | Maximum Incidence Rate | SD of Incidence Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | 4,688,787 | 520,976.3 | 1,058,236 (22.57%) | 3,630,551 (77.43%) | 0 (0%) | 10,992.68 | 2292.39 | 11,968.15 | 14,764.17 | 3918.56 |
| Cattle | 427 | 47.4 | 270 (63.23%) | 140 (32.79%) | 17 (3.98%) | 3.01 | 0 | 1.97 | 6.47 | 2.74 |
| Camel | 32 | 3.6 | 30 (93.75%) | 2 (6.25%) | 0 (0%) | 0.77 | 0 | 0 | 3.02 | 1.15 |
| Goat | 656 | 72.9 | 514 (78.35%) | 142 (21.65%) | 0 (0%) | 2.6 | 0 | 1.11 | 10.32 | 3.47 |
| Sheep | 99 | 11 | 82 (82.83%) | 17 (17.17%) | 0 (0%) | 0.57 | 0 | 0.05 | 1.86 | 0.72 |
| Model | MAE | RMSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model with no exogenous variable | 108.88 | 123.44 | 11.63 |
| Model with exogenous variable | 110.16 | 127.63 | 11.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kahariri, S.; Thomas, L.F.; Bett, B.; Mureithi, M.W.; Makori, A.; Njuguna, B.; Kadivane, S.; Makau, D.N.; Mutono, N.; Thumbi, S.M. Integrated Surveillance for Human and Animal Brucellosis in Kenya: A Predictive Analysis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10120344
Kahariri S, Thomas LF, Bett B, Mureithi MW, Makori A, Njuguna B, Kadivane S, Makau DN, Mutono N, Thumbi SM. Integrated Surveillance for Human and Animal Brucellosis in Kenya: A Predictive Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(12):344. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10120344
Chicago/Turabian StyleKahariri, Samuel, Lian F. Thomas, Bernard Bett, Marianne W. Mureithi, Anita Makori, Brian Njuguna, Samuel Kadivane, Dennis N. Makau, Nyamai Mutono, and S. M. Thumbi. 2025. "Integrated Surveillance for Human and Animal Brucellosis in Kenya: A Predictive Analysis" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 12: 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10120344
APA StyleKahariri, S., Thomas, L. F., Bett, B., Mureithi, M. W., Makori, A., Njuguna, B., Kadivane, S., Makau, D. N., Mutono, N., & Thumbi, S. M. (2025). Integrated Surveillance for Human and Animal Brucellosis in Kenya: A Predictive Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(12), 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10120344







