Environmental Conditions and Mite Vectors Shape the Spatiotemporal Patterns of Scrub Typhus in Guangdong Province, Mainland China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Scrub Typhus Cases
2.1.2. Climate Data
2.1.3. Land Cover and Altitude Data
2.1.4. Habitat Suitability Index of Chigger Mites
2.1.5. Population
2.2. Spatiotemporal Modeling Approach
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Scrub Typhus
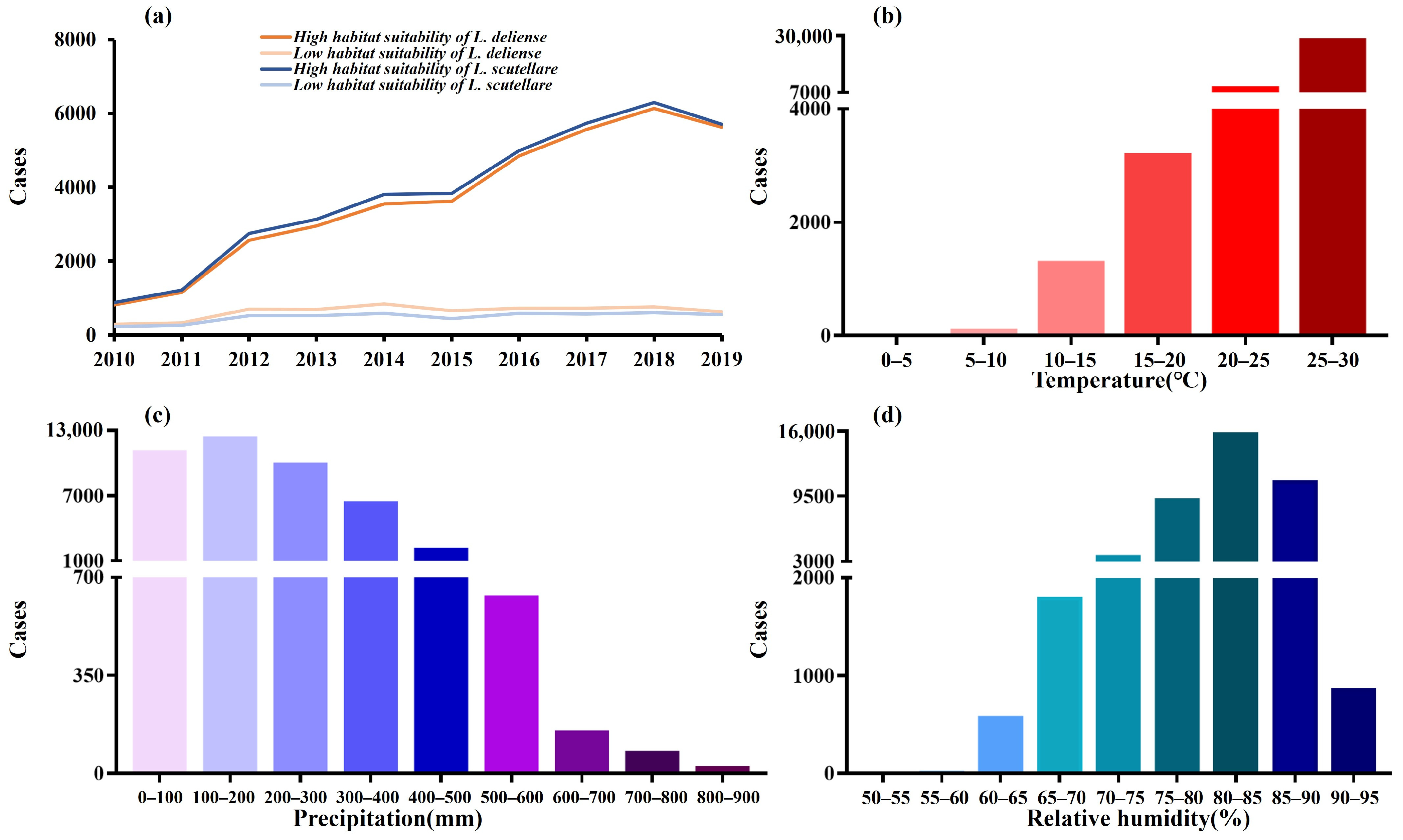
3.2. Distribution of Scrub Typhus Cases Under Different Environmental and Vector Conditions
3.3. The Spatiotemporal Modelling of Scrub Typhus
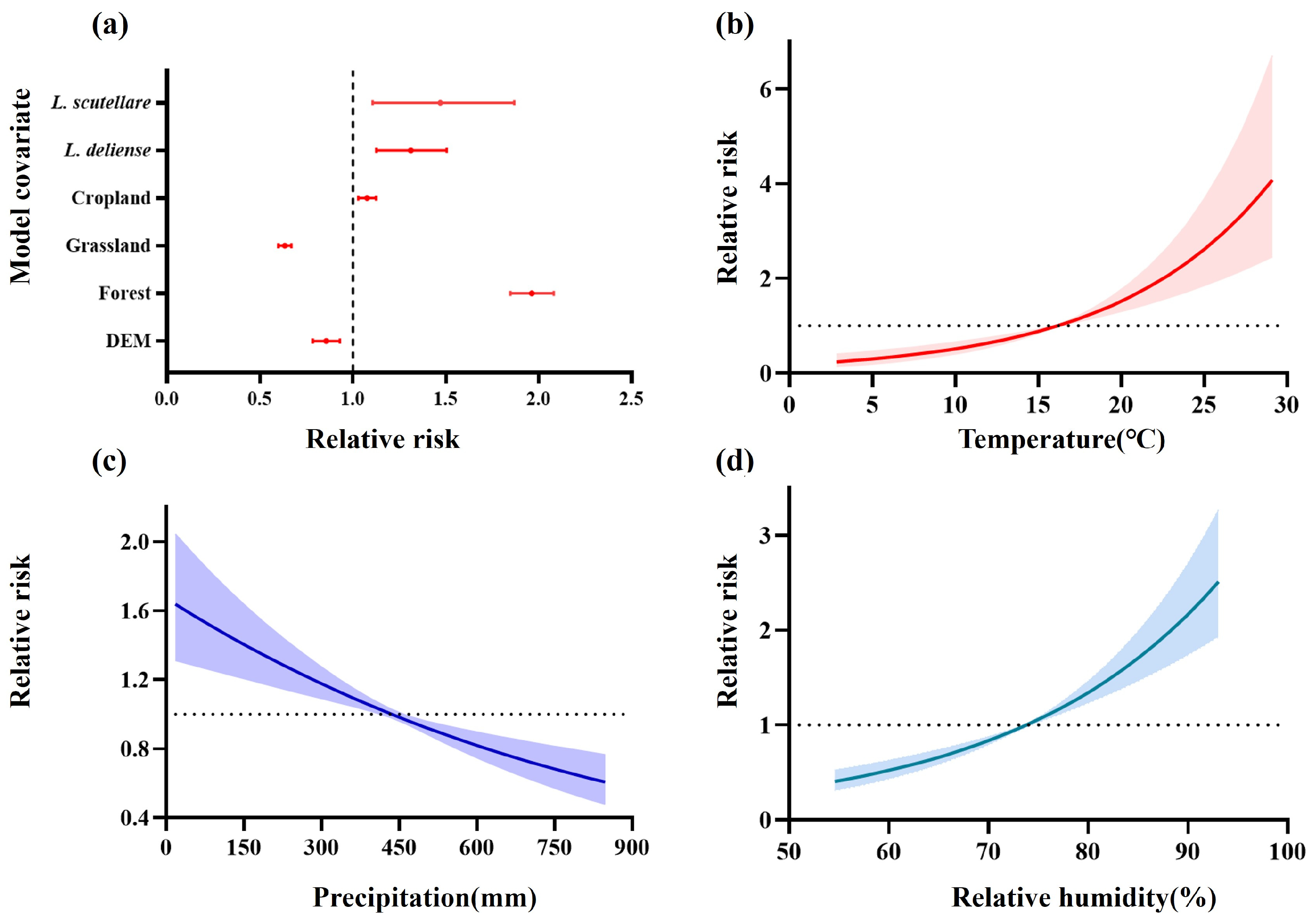
3.4. The Driving Factors on the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Scrub Typhus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rapmund, G.; Upham, R.W.; Kundin, W.D.; Manikumaran, C.; Chan, T.C. Transovarial development of scrub typhus rickettsiae in a colony of vector mites. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1969, 63, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J.; Fuerst, P.A.; Ching, W.-M.; Richards, A.L. Scrub typhus: The geographic distribution of phenotypic and genotypic variants of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, S.; Weeratunga, P.; Sivayoganathan, S.; Fernando, S.D. Clinical manifestations of scrub typhus. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 111, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, A.L.; Jiang, J. Scrub Typhus: Historic Perspective and Current Status of the Worldwide Presence of Orientia Species. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, K.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Angulo, J.; Jiang, J.; Farris, C.M.; Richards, A.L.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Weitzel, T. Molecular Description of a Novel Orientia Species Causing Scrub Typhus in Chile. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2148–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Ferrari, A.; Binazzi, R.; Beltrame, A.; Tacconi, D.; Moro, L.; Edouard, S.; Parola, P.; Buonfrate, D.; Gobbi, F. Imported scrub typhus in Europe: Report of three cases and a literature review. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 42, 102062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzard, L.; Fuller, A.; Blacksell, S.D.; Paris, D.H.; Richards, A.L.; Aukkanit, N.; Nguyen, C.; Jiang, J.; Fenwick, S.; Day, N.P.J.; et al. Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4404–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.H.; Mendell, N.L. A scrub typhus vaccine presents a challenging unmet need. npj Vaccines 2023, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, R. Drug-resistant scrub typhus: Paradigm and paradox. Parasitol. Today 1997, 13, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonell, A.; Lubell, Y.; Newton, P.N.; Crump, J.A.; Paris, D.H. Estimating the burden of scrub typhus: A systematic review. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.R. The distribution and general situation on epidemiology studies of tsutsugamushi disease in China. Chin. J. Dis. Control Prev. 2016, 20, 1176–1181. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Yue, D.; Bao, Z. Epidemiological research progress of srub typhus. Chin. Rural Health Serv. Adm. 2013, 33, 426–430. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, Z.T. Current epidemic status and issues on prevention and control of scrub typhus. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 4, 419–423. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Xu, L.; Ma, Q.Z.; Zhang, N.; Lu, L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Li, X.Z. Division of epidemic areas for summer- and autumn- type scrubtyphus in China. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2019, 30, 233–236. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.H.; Pan, Z.Q.; Li, W.Q.; Yang, Y.W.; Liu, M. Epidemiological characteristics trends and death related influencing factors of scrub typhus, Guangdong. Mod. Prev. Med. 2022, 49, 4259–4266. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.X.; Zeng, M.H.; Zhang, Y.M. Epidemic report of Tsutsugamushi disease in Guangzhou. Chin. J. Med. 1950, 36, 421–423. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Tao, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, Z. Climate variability, animal reservoir and transmission of scrub typhus in Southern China. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xie, B.; Long, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Fan, L.; Chen, S.; Chen, K.; Wei, Y. Prediction of risk factors for scrub typhus from 2006 to 2019 based on random forest model in Guangzhou, China. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2023, 28, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Guo, X.; Jin, D.; Song, W.; Peng, P.; Lin, H.; Fan, R.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, K.; et al. Infestation and seasonal fluctuation of chigger mites on the Southeast Asian house rat (Rattus brunneusculus) in southern Yunnan Province, China. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2021, 14, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global Consequences of Land Use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.K.; Chen, W.; Ren, Z.L.; Poudel, P.G.; Yang, Y.; Poudel, S.L.; Shah, L.P.; Cao, C.; Xu, Z.; Dhimal, M.; et al. Mapping Environmental Suitability of Scrub Typhus in Nepal Using MaxEnt and Random Forest Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Jing, Q.L.; Li, T.G.; Ren, H.Y. Spatiotemporal distribution of scrub typhus in Guangzhou, China from 2006 to 2015. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2017, 28, 336–339. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rocklöv, J.; Dubrow, R. Climate change: An enduring challenge for vector-borne disease prevention and control. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y. Impact of climate change on vector-borne diseases and related response strategies in China: Major research findings and recommendations for future research. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2021, 32, 1–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Morin, C.W.; Comrie, A.C.; Ernst, K. Climate and Dengue Transmission: Evidence and Implications. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audy, J.R. Epidemiology of scrub typhus in Assam and Burma. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1947, 40, 359. [Google Scholar]
- Sasa, M. Biology of Chiggers. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1961, 6, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubler, D.J.; Reiter, P.; Ebi, K.L.; Yap, W.; Nasci, R.; Patz, J.A. Climate variability and change in the United States: Potential impacts on vector- and rodent-borne diseases. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109 (Suppl. S2), 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, M.M.; Maude, R.J.; John Day, N.P.; Lai, S.; Chen, S.; Fang, L.; Ma, T.; Zheng, C.; et al. Climate drives the spatiotemporal dynamics of scrub typhus in China. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 6618–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Sun, Z.M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, S.; Qin, T.J. Impacts of meteorological factors on the risk of scrub typhus in China, from 2006 to 2020: A multicenter retrospective study. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1099576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangrangsimakul, T.; Elliott, I.; Nedsuwan, S.; Kumlert, R.; Hinjoy, S.; Chaisiri, K.; Day, N.P.; Morand, S. The estimated burden of scrub typhus in Thailand from national surveillance data (2003–2018). PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.J.; Jiang, D.; Ding, F.Y.; Fu, J.Y.; Hao, M.M. Spatiotemporal patterns and risk factors for scrub typhus from 2007 to 2017 in southern China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; Duan, C.; Jia, X.; Jia, R.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Spatiotemporal epidemiology and risk factors of scrub typhus in Hainan Province, China, 2011–2020. One Health 2023, 17, 100645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, T.H.; Ahmad, T.; Wana, M.N.; Li, W.; Musa, H.H.; Sharun, K.; Tiwari, R.; Dhama, K.; Chaicumpa, W.; Campbell, M.C.; et al. The epidemiology, diagnosis and management of scrub typhus disease in China. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 3795–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Hao, M.M.; Chen, S.; Ding, F.Y. The current and future risk of spread of Leptotrombidium deliense and Leptotrombidium scutellare in mainland China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.F.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.J.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, W.H.; Fan, Z.W.; Zhao, G.-P.; Jiang, B.G.; Shi, T.X.; Fang, L.Q.; et al. A dataset of distribution and diversity of blood-sucking mites in China. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisiri, K.; Gill, A.C.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Hinjoy, S.; McGarry, J.W.; Darby, A.C.; Morand, S.; Makepeace, B.L. Ecological and microbiological diversity of chigger mites, including vectors of scrub typhus, on small mammals across stratified habitats in Thailand. Anim. Microbiome 2019, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Research status and prospect of scrub typhus epidemiology in China. Chin. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 2, 69–71. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Xi, Z.; Ni, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C. Basic studies on trombicul id mites and vector chiggers mites in the transmission of tsutsugamushi disease for 45 years. Acad. J. Sums 2002, 23, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Ma, T.; Ding, F.Y.; Lim, A.; Takaya, S.; Saraswati, K.; Hao, M.M.; Jiang, D.; Fang, L.Q.; Sartorius, B.; et al. A systematic review of environmental covariates and methods for spatial or temporal scrub typhus distribution prediction. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, R.; Cazelles, B.; Paul, R.; Rodó, X. Quantifying the added value of climate information in a spatio-temporal dengue model. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besag, J.; York, J.; Mollié, A. Bayesian image restoration, with two applications in spatial statistics. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1991, 43, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S. Asymptotic Equivalence of Bayes Cross Validation and Widely Applicable Information Criterion in Singular Learning Theory. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 3571–3594. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.S.; Chu, C.; Han, D.Y. Spatial Distribution Analysis of Scrub Typhus in Korea. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2013, 4, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.A.; Huxley, P.; Elmes, J.; Murray, K.A. Agricultural land-uses consistently exacerbate infectious disease risks in Southeast Asia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C. Research Progress on Leptotrombidium deliense. Korean J. Parasitol. 2018, 56, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.N.; Day, N.P. Day, 68—Scrub Typhus. In Hunter’s Tropical Medicine and Emerging Infectious Diseases, 10th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z. Response of Soil Moisture to Four Rainfall Regimes and Tillage Measures under Natural Rainfall in Red Soil Region, Southern China. Water 2024, 16, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.B.; Epstein, P.R.; Lipp, E.K.; Sherman, B.H.; Bernard, S.M.; Patz, J.A. Climate variability and change in the United States: Potential impacts on water- and foodborne diseases caused by microbiologic agents. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.; Pervaiz, S.V.; Hussain, S.; Kang, S.H. Scrub Typhus Incidence Modeling with Meteorological Factors in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7254–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Qian, Q.; Soares Magalhaes, R.J.; Han, Z.; Hu, W.; Haque, U.; Weppelmann, T.A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, X.L.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Scrub Typhus Transmission in Mainland China, 2006–2014. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Base model | |
| ) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, P.; Ma, T.; Meng, Z.; Ding, F.; Chen, S.; Hao, M.; Li, J.; Zhuo, J.; Dong, J.; Xie, W.; et al. Environmental Conditions and Mite Vectors Shape the Spatiotemporal Patterns of Scrub Typhus in Guangdong Province, Mainland China. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10110326
Fan P, Ma T, Meng Z, Ding F, Chen S, Hao M, Li J, Zhuo J, Dong J, Xie W, et al. Environmental Conditions and Mite Vectors Shape the Spatiotemporal Patterns of Scrub Typhus in Guangdong Province, Mainland China. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(11):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10110326
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Peiwei, Tian Ma, Ze Meng, Fangyu Ding, Shuai Chen, Mengmeng Hao, Jiaqi Li, Jun Zhuo, Jiping Dong, Wenqi Xie, and et al. 2025. "Environmental Conditions and Mite Vectors Shape the Spatiotemporal Patterns of Scrub Typhus in Guangdong Province, Mainland China" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 11: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10110326
APA StyleFan, P., Ma, T., Meng, Z., Ding, F., Chen, S., Hao, M., Li, J., Zhuo, J., Dong, J., Xie, W., Wang, Q., Kang, T., Sun, K., Wu, G., Bai, Y., Zheng, C., & Jiang, D. (2025). Environmental Conditions and Mite Vectors Shape the Spatiotemporal Patterns of Scrub Typhus in Guangdong Province, Mainland China. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(11), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10110326







