Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Humans in West Africa, 1975–2024: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
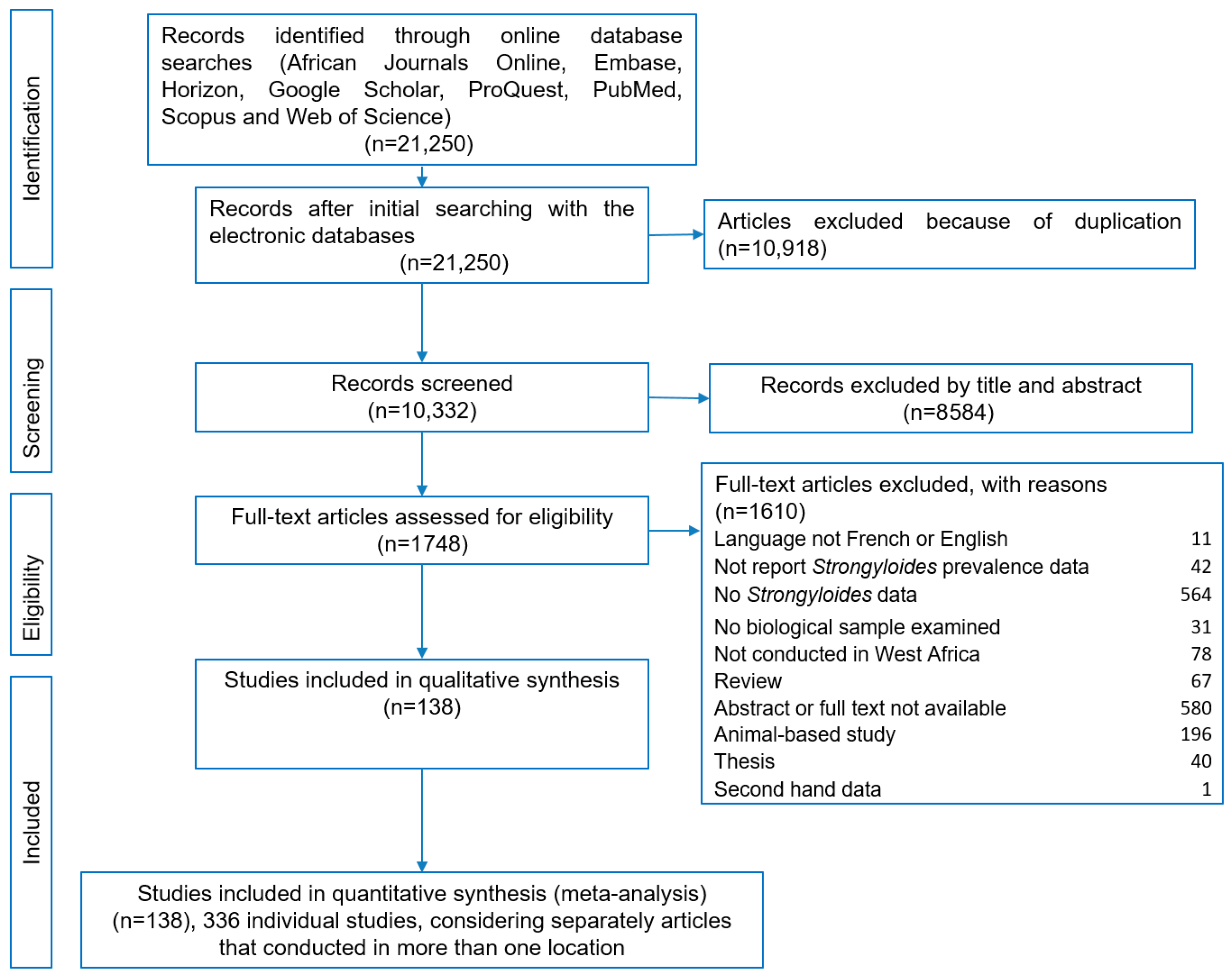
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.3. Quality of Studies
3.4. Publication Bias
3.5. Meta-Regression Analysis
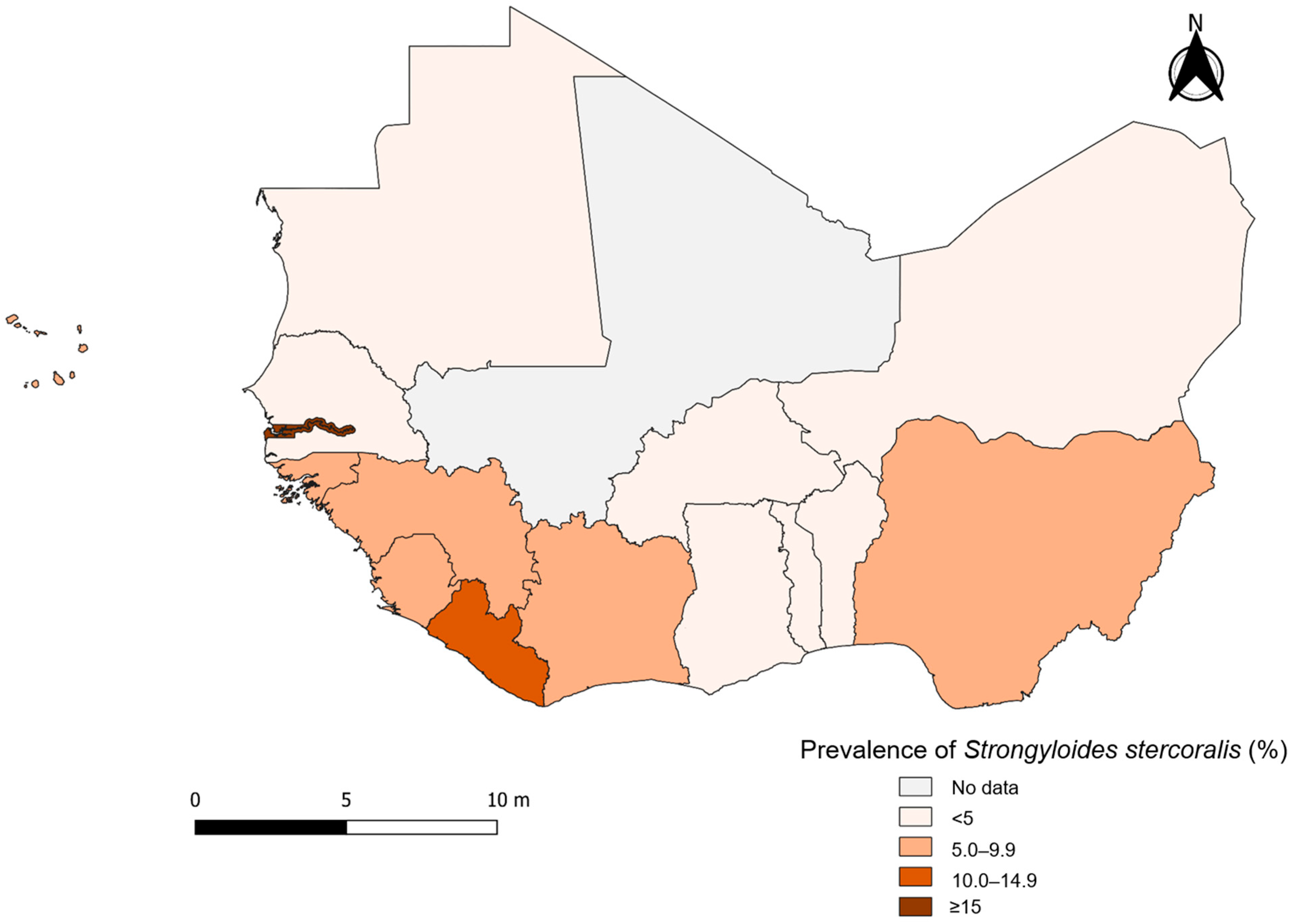
3.6. Strongyloidiasis in West Africa
3.7. Subgroup Analysis
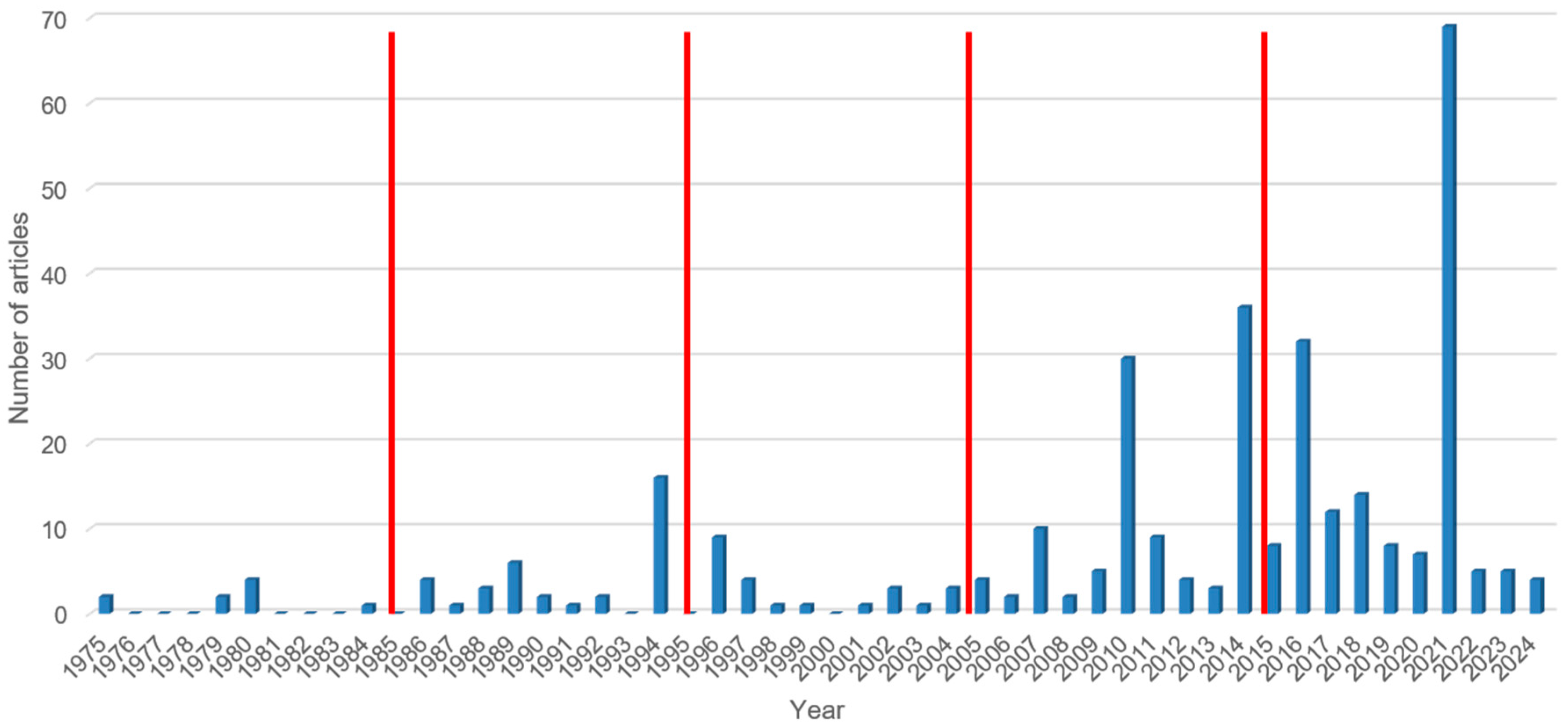
3.7.1. S. stercoralis Prevalence by Decade of Publication
3.7.2. Prevalence of S. stercoralis by Study Population (Age Group)
3.7.3. Prevalence of S. stercoralis by Setting
3.7.4. Prevalence of S. stercoralis by Sample Size
3.7.5. Prevalence of S. stercoralis by Gender
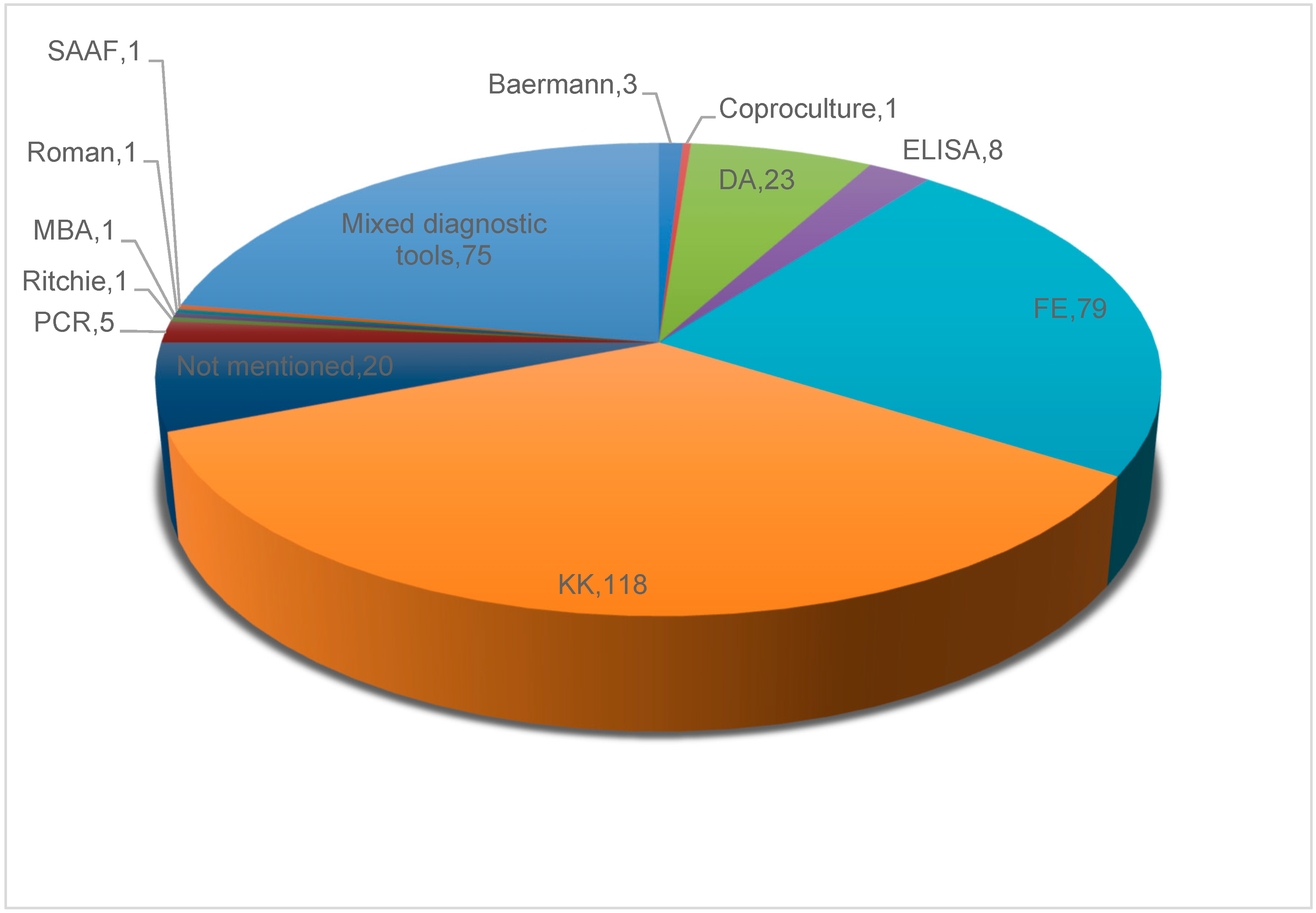
3.7.6. Approaches for Strongyloidiasis Diagnosis
3.8. Risk Factors for S. stercoralis Infection
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordon, C.A.; Utzinger, J.; Muhi, S.; Becker, S.L.; Keiser, J.; Khieu, V.; Gray, D.J. Strongyloidiasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonfrate, D.; Bisanzio, D.; Giorli, G.; Odermatt, P.; Fürst, T.; Greenaway, C.; French, M.; Reithinger, R.; Gobbi, F.; Montresor, A.; et al. The global prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Pathogens 2020, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schar, F.; Trostdorf, U.; Giardina, F.; Khieu, V.; Muth, S.; Marti, H.; Vounatsou, P.; Odermatt, P. Strongyloides stercoralis: Global distribution and risk factors. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scowden, E.B.; Schaffner, W.; Stone, W.J. Overwhelming strongyloidiasis: An unappreciated opportunistic infection. Medicine 1978, 57, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, S.L.; Verghese, A.; Alvarez, S.; Hall, K.; Smith, B. Clinical and epidemiologic features of strongyloidiasis. A prospective study in rural Tennessee. Arch. Intern. Med. 1987, 147, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.B.; Mojon, M. Improved diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis by seven consecutive stool specimens. Zentralbl Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. A 1987, 263, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.A.; Berk, S.L. Diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonfrate, D.; Formenti, F.; Perandin, F.; Bisoffi, Z. Novel approaches to the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslahi, A.V.; Badri, M.; Nahavandi, K.H.; Houshmand, E.; Dalvand, S.; Riahi, S.M.; Johkool, M.G.; Asadi, N.; Ahangari, S.A.H.; Taghipour, A.; et al. Prevalence of strongyloidiasis in the general population of the world: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pathog. Glob. Health 2021, 115, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, T.; Nibret, E.; Amor, A.; Munshea, A. Strongyloidiasis in Africa: Systematic review and meta-analysis on prevalence, diagnostic Methods, and Study Settings. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2868564. [Google Scholar]
- JBI. The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal Tools for Use in JBI Systematic Reviews: Checklist for Prevalence Studies. 2017. Available online: https://jbi.global/sites/default/files/2019-05/JBI_Critical_Appraisal-Checklist_for_Prevalence_Studies2017_0.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Kositz, C.; Drammeh, M.; Vasileva, H.; Houghton, J.; Ashall, J.; D’Alessandro, U.; Marks, M.; Bradley, J. Effects of ivermectin mass drug administration for malaria vector control on ectoparasites and soil-transmitted helminths: A cluster randomized trial. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 125, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyang, A.M.; Joof, E.; Sey, A.P.; Sambou, S.; Mohamed, Z.; Sanneh, B. Prevalence and risk factors of strongyloidiasis among schoolchildren in Sabach Sanjal and Upper Badibou districts in the North Bank East Region of The Gambia. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2021, 15, e00228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodeman, W.A., Jr. A longitudinal study of schistosome vector snail populations in Liberia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1979, 28, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbmacher, F.; Komlan, K.; Gantin, R.G.; Poutouli, W.P.; Padjoudoum, K.; Karabou, P.; Soboslay, P.T.; Kohler, C. Mansonella perstans, Onchocerca volvulus and Strongyloides stercoralis infections in rural populations in central and southern Togo. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2018, 3, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbadoe, A.D.; Koffi, K.S. Parasitoses intestinales chez les enfants de moins de cinq ans au Togo et recommandations de la PCIME. Arch. Pediatr. 2005, 12, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aplogan, A.; Schneider, D.; Dyck, J.L.; Berger, J. Parasitoses digestives chez le jeune enfant en milieu extra-hospitalier tropical. Ann. Pédiatr. 1990, 37, 677–681. [Google Scholar]
- Lapierre, J.; Tourte-Schaeffer, C.; Dupouy-Camet, J.; Heyer, F.; Faurant, C. Etude épidémiologique du foyer de bilharziose à Schistosoma mansoni de Kara (Nord Togo). Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1988, 81, 861–868. [Google Scholar]
- Farrant, O.; Marlais, T.; Houghton, J.; Goncalves, A.; Cassama, E.T.S.; Cabral, M.G.; Nakutum, J.; Manjuba, C.; Rodrigues, A.; Mabey, D.; et al. Prevalence, risk factors and health consequences of soil-transmitted helminth infection on the Bijagos Islands, Guinea Bissau: A community-wide cross-sectional study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Huth, S.; Kofoed, P.E.; Holmskov, U. Prevalence and potential risk factors for gastrointestinal parasitic infections in children in urban Bissau, Guinea-Bissau. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 113, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenhard, N.R.; Ornbjerg, N.; Molbak, K. Concurrent infections and socioeconomic determinants of geohelminth infection: A community study of schoolchildren in periurban Guinea-Bissau. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebbad, M.; Norrgren, H.; Naucler, A.; Dias, F.; Andersson, S.; Linder, E. Intestinal parasites in HIV-2 associated AIDS cases with chronic diarrhoea in Guinea-Bissau. Acta Trop. 2001, 80, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstensen, H.; Hansen, H.L.; Kristiansen, H.O.; Gomme, G. The epidemiology of cryptosporidiosis and other intestinal parasitoses in children in southern Guinea-Bissau. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1987, 81, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.S.; Thomas, R.; Green, A.D.; Bailey, J.W.; Beeching, N.J. Helminth infections in British troops following an operation in Sierra Leone. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 100, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbakima, A.A. Intestinal parasitic infections and swamp development in Sierra Leone. Afr. J. Health Sci. 1994, 1, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whitworth, J.A.G.; Morgan, D.; Maude, G.H.; McNicholas, A.M.; Taylor, D.W. A field study of the effect of ivermectin on intestinal helminths in man. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1991, 85, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colito, D.A.; Dorta-Guerra, R.; Da Costa Lima, H.S.; Pina, C.; Gonsalvez, D.; Valladares, B.; Foronda, P. Intestinal parasites among children with diarrhoea from Santiago (Cape Verde). Arch. Dis. Child. 2021, 106, 828–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavogui, A.H.; Cherif, M.S.; Camara, B.S.; Delamou, A.; Kolie, D.; Cisse, A.; Camara, D.; Sow, A.; Camara, G.; Yattara, M.; et al. Prevalence of parasitic infections in children of Boke, Guinea. J. Parasitol. 2021, 107, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glickman, L.T.; Camara, A.O.; Glickman, N.W.; McCabe, G.P. Nematode intestinal parasites of children in rural Guinea, Africa: Prevalence and relationship to geophagia. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 28, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorkos, T.W.; Camara, B.; Kokoskin, E.; Carabin, H.; Prouty, R. Enquête de prévalence parasitaire chez les enfants d’âge scolaire. Sante 1996, 6, 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, S.L.; Piraisoody, N.; Krammé, S.; Marti, H.; Silue, K.D.; Panning, M.; Nickel, B.; Kern, W.V.; Herrmann, M.; Hatz, C.F.; et al. Real-time PCR for detection of Strongyloides stercoralis in human stool samples from Côte d’Ivoire: Diagnostic accuracy, inter-laboratory comparison and patterns of hookworm co-infection. Acta Trop. 2015, 150, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.L.; Chatigre, J.K.; Gohou, J.-P.; Coulibaly, J.T.; Leuppi, R.; Polman, K.; Chappuis, F.; Mertens, P.; Herrmann, M.; N’Goran, E.K.; et al. Combined stool-based multiplex PCR and microscopy for enhanced pathogen detection in patients with persistent diarrhoea and asymptomatic controls from Côte d’Ivoire. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 591.e1–591.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adoubryn, K.D.; Kouadio-Yapo, C.G.; Ouhon, J.; Aka, N.A.; Bintto, F.; Assoumou, A. Parasitoses intestinales infantiles à Biankouma, région des 18 Montagnes (ouest de la Côte d’Ivoire): Étude de l’efficacité et de la tolérance du praziquantel et de l’albendazole. Med. Sante Trop. 2012, 22, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.L.; Sieto, B.; Silué, K.D.; Adjossan, L.; Koné, S.; Hatz, C.; Kern, W.V.; N’Goran, E.K.; Utzinger, J. Diagnosis, clinical features, and self-reported morbidity of Strongyloides stercoralis and hookworm infection in a co-endemic setting. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traore, S.G.; Odermatt, P.; Bonfoh, B.; Utzinger, J.; Aka, N.D.; Adoubryn, K.D.; Assoumou, A.; Dreyfuss, G.; Koussemon, M. No Paragonimus in high-risk groups in Côte d’Ivoire, but considerable prevalence of helminths and intestinal protozoon infections. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djohan, V.; Yavo, W.; Barro-Kiki, P.C.; Vanga, A.H.; Kassi, K.F.; Konate, A.; Ouattara, M.; Menan, E.I.; Kone, M. Epidémiologie de l’anguillulose chez les enfants scolarisés à l’école publique à Abidjan (Côte d’Ivoire). Med. Trop. 2010, 70, 305–306. [Google Scholar]
- Diakite, N.R.; Adja, A.M.; von Stamm, T.; Utzinger, J.; N’Goran, E.K. Situation épidémiologique avant la mise en eau du barrage hydroagricole de cinq villages de Bouaké, centre Côte-d’Ivoire. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2010, 103, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinz, D.; Silué, K.D.; Knopp, S.; Lohourignon, L.K.; Yao, K.P.; Steinmann, P.; Rinaldi, L.; Cringoli, G.; N’Goran, E.K.; Utzinger, J. Comparing diagnostic accuracy of Kato-Katz, Koga Agar plate, ether-concentration, and FLOTAC for Schistosoma mansoni and soil-transmitted helminths. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinz, D.; N’Guessan, N.A.; Utzinger, J.; N’Goran, E.K. High Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis among school children in rural Côte d’Ivoire. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menan, E.I.; Kassi, F.K.; Yavo, W.; Djohan, V.; Vanga, H.; Barro, P.C.; Oga, S.S.; Konate, A.; Gbocho, F.Y.; Adjetey, T.A.; et al. Helminthoses intestinales chez les enfants d’âge scolaire de la zone rurale et urbaine de Tiassalé (Côte d’Ivoire). Med. Trop. (Mars) 2008, 68, 658–659. [Google Scholar]
- Evi, J.B.; Yavo, W.; Barro-Kiki, P.C.; Menan, E.H.I.; Koné, M. Helminthoses intestinales en milieu scolaire dans six villes du sud-ouest de la Côte d’Ivoire. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2007, 100, 176–177. [Google Scholar]
- Yapi, Y.G.; Briet, O.J.; Vounatsou, P. Prevalence of geohelminths in savana and forest areas of Côte d’Ivoire. West. Afr. J. Med. 2006, 25, 124–125. [Google Scholar]
- Dancesco, P.; Abeu, J.; Akakpo, C.; Iamandi, I.; Kacou, E.; Quenou, F.; Keusse-Assi, J. Les parasitoses intestinales dans un village de Côte d’Ivoire. I: Essai de mise en place d’une stratégie de lutte et de prévention. Cahiers Santé 2005, 15, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Agbaya, S.S.; Yavo, W.; Menan, E.I.; Attey, M.A.; Kouadio, L.P.; Koné, M. Helminthiases intestinales chez les enfants d’âge scolaire: Résultats préliminaires d’une étude prospective à Agboville dans le sud de la Côte d’Ivoire. Sante 2004, 14, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Menan, E.I.H.; Nebavi, N.G.F.; Adjetey, T.A.K.; Assavo, N.N.; Kiki-Barro, P.C.; Koné, M. Profil des helminthiases intestinales chez les enfants d’âge scolaire dans la ville d’Abidjan. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1997, 90, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Menan, E.I.H.; Nebavi, N.G.F.; Adjetey, T.A.K.; Assavo, N.N.; Deddy, B.A.N.; Barro-Kiki, P.C.; Koné, M. Influence des conditions socio-économiques sur la survenue des helminthiases intestinales: Étude réalisée chez 1001 enfants d’âge scolaire à Abidjan (Côte d’Ivoire). Cahiers Santé 1997, 7, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Therizol-Ferly, P.; Tagliante-Saracino, M.J.; Koné, M.; Konan, A.; Ouhon, J.; Assoumou, A.; Aka, K.; Assalé, G. Diarrhées chroniques et paratitoses chez des adultes suspectés de SIDA en Côte d’Ivoire. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. Fil. 1989, 82, 690–693. [Google Scholar]
- Penali, K.L.; Koné, M.; Abrogoua, D.; Anick, S. Les helminthiases intestinales dans l’île d’ancien-Fresco (Côte-d’Ivoire). Bull. Soce Pathol. Exot. 1988, 81, 740–742. [Google Scholar]
- Haller, L.; Lauber, E. Santé de l’enfant d’âge scolaire en Cöte d’Ivoire. Acta Trop. 1980, 37 (Suppl. 11), 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Nozais, J.P.; Doucet, J.; Dunand, J.; Lebras, M. Enquête coprologique chez des enfants bilharziens de la région d’Adzopé (Côte d’Ivoire). Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1975, 68, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Gbonhinbor, J.; Abah, A.E.; Awi-Waadu, G. Geo-mapping of intestinal parasitic infection in a southern community in Nigeria. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2024, 34, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agabi, Y.A.; Emeka Ezeife, C.E.; Uneze, S.B.; Okojokwu, O.J.; Eya, B.S.; Jude, N.; Zakari, H.; Isaac, M.A.; Adoga, M.P.; Owuna, J.E.; et al. Prevalence of intestinal helminths among HIV patients accessing healthcare services at Faith Alive Foundation, Jos, Nigeria. Microbes Infect. Dis. 2023, 4, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alade, T.; Ta-Tang, T.H.; Nassar, S.A.; Akindele, A.A.; Capote-Morales, R.; Omobami, T.B.; Berzosa, P. Prevalence of Schistosoma haematobium and intestinal helminth infections among Nigerian school children. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imalele, E.E.; Braide, E.I.; Emanghe, U.E.; Effanga, E.O.; Usang, A.U. Soil-transmitted helminth infection among school-age children in Ogoja, Nigeria: Implication for control. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 122, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udeh, E.O.; Obiezue, R.N.; Ikele, C.B.; Otuu, C.A.; Okoye, I.C.; Eke, S.S.; Okafor, F.C.; Goselle, O.N.; Jwanle, P.; Iheanacho, N.S.; et al. Intestinal parasitic infections among HIV/AIDS Patients in relation to ART adherence in Nigeria. Niger. J. Parasitol. 2023, 441, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evbuomwan, I.O.; Edosomwan, E.U.; Idubor, V.; Bazuaye, C.; Abhulimhen-Iyoha, B.I.; Adeyemi, O.S.; Adeyemi, E.E. Survey of intestinal parasitism among schoolchildren in internally displaced persons camp, Benin City, Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2022, 17, e01373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inah, I.O.; Otu-Bassey, I.B.; Udefa, A.L. Intestinal parasitosis and CD4 levels among cancer patients in Calabar, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2022, 25, 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Nwankwo, A.; Onyebueke, A.C.; Irikannu, K.C.; Nzeukwu, C.I.; Onwuzulike, I.V.; Okafor, N.M. Soil-transmitted helminths infection and associated risk factors among primary school pupils in Omogho and Awa communities, Anambra State, Nigeria. Int. J. Trop. Dis. Health 2021, 42, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaro, C.A.; Kogi, E.; Luka, S.A.; Nassan, M.A.; Kabir, J.; Opara, K.N.; Hetta, H.F.; Batiha, G.E. Edaphic and climatic factors influence on the distribution of soil transmitted helminths in Kogi East, Nigeria. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnolim, C.; Adekeye, T.A.; Awobode, H.O. Intestinal helminth infection and malnutrition among public primary school children in Ibadan, Nigeria. Niger. J. Parasitol. 2020, 41, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, E.M.; Echeta, O.C.; Ombugadu, A.; Ajah, L.; Aimankhu, P.O.; Oluwole, A.S. Helminthiasis among school-age children and hygiene conditions of selected schools in Lafia, Nasarawa State, Nigeria. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, A.S.; Francis, E.O.; Francis, J.E.; Wamtas, F.I. Soil-transmitted helminths and associated risk factors among elementary school pupils in Dadin Kowa, Jos. Niger. Med. J. 2019, 60, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawaki, S.; Al-Mekhlafi, H.M.; Ithoi, I. The burden and epidemiology of polyparasitism among rural communities in Kano State, Nigeria. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 113, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udeh, E.O.; Obiezue, R.N.N.; Okafor, F.C.; Ikele, C.B.; Okoye, I.C.; Otuu, C.A. Gastrointestinal parasitic infections and immunological status of HIV/AIDS coinfected individuals in Nigeria. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayede, A.I.; Bello, F.A.; Kehinde, A.O. A community-based surveillance of gastrointestinal helminthiasis among pregnant women in Ibadan, South West Nigeria. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2018, 21, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Akinbo, F.; Akanbi, T. Enteric parasitic infections amongst cement masons in Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria. Niger. J. Health Sci. 2018, 16, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoo, J.K.; Akindele, A.A.; Amoo, A.O.J.; Efunshile, A.M.; Ojurongbe, T.A.; Fayemiwo, S.A.; Thomas, B.N.; Ojurongbe, O. Prevalence of enteric parasitic infections among people living with HIV in Abeokuta, Nigeria. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2018, 30, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbebi, Y.V.; Jafaaru, A.; Elkanah, O.S.; Chintem, D.G.W.; Njilmah, J.A.; Jonathan, J.; Tese, T. Prevalence of gastrointestinal helminths infections among school-aged children in Kurmi Local Government Area, Taraba State, Nigeria. Niger. J. Parasitol. 2018, 39, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojurongbe, O.; Okorie, P.N.; Opatokun, R.L.; Ojurongbe, T.A.; Mabayoje, V.O.; Olowe, O.A.; Adeyeba, O.A. Prevalence and associated factors of Plasmodium falciparum and soil transmitted helminth infections among pregnant women in Osun state, Nigeria. Afr. Health Sci. 2018, 18, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniran, A.A.; Mogaji, H.O.; Aladesida, A.A.; Olayiwola, I.O.; Oluwole, A.S.; Abe, E.M.; Olabinke, D.B.; Alabi, O.M.; Ekpo, U.F. Schistosomiasis, intestinal helminthiasis and nutritional status among preschool-aged children in sub-urban communities of Abeokuta, Southwest, Nigeria. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang-Etoh, P.C.; Agorye, A.H.; Okpokam, D.C.; Opara-Osuoha, U. Prevalence of malaria and intestinal parasites coinfections and their effects on haemoglobin levels among school aged children in Bebuatsuan clan, Obudu, cross River State, Nigeria. J. Med. Allied Sci. 2017, 7, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ivoke, N.; Ikpor, N.; Ivoke, O.; Ekeh, F.; Ezenwaji, N.; Odo, G.; Iyaji, F.; Onoja, U.; Eyo, J. Geophagy as risk behaviour for gastrointestinal nematode infections among pregnant women attending antenatal clinics in a humid tropical zone of Nigeria. Afr. Health Sci. 2017, 17, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muazu, I.; Abdullahi, Y.; Umar, Z. Prevalence of human intestinal parasitic nematode among out-patients attending wudil general hospital, kano state, Nigeria. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health 2017, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shitta, K.B.; Akogun, O.B. Intestinal helminth infections among the nomadic Fulanis in two localities of Adamawa State, North-East Nigeria. Niger. J. Parasitol. 2017, 38, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, O.T.; Sam-Wobo, S.O.; Idowu, O.A.; Talabi, A.O.; Taiwo, A.M. Comparative assessment of intestinal helminths prevalence in water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) intervention and non-intervention communities in Abeokuta, Nigeria. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, K.E.; Amadi, C.U. Soil transmitted helminth infection among farmers in Ukwa West Local Government Area, Abia State, south-east, Nigeria. Niger. J. Med. 2016, 25, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obateru, O.A.; Bojuwoye, B.J.; Olokoba, A.B.; Fadeyi, A.; Fowotade, A.; Olokoba, L.B. Prevalence of intestinal parasites in newly diagnosed HIV/AIDS patients in Ilorin, Nigeria. Alex. J. Med. 2016, in press. [CrossRef]
- Abah, A.E.; Arene, F.O.I. Status of intestinal parasitic infections among primary school children in rivers state, Nigeria. J. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 2015, 937096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, P.U.; Ogboi, J.S.; Akpoigbe, K.; Okeke, T.; Ezugwu, E. Impact of Plasmodium falciparum and hookworm infections on the frequency of anaemia in pregnant women of rural communities in Enugu, South East Nigeria. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2013, 14, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Ohaeri, C.C.; Orji, N.B. Intestinal parasites among undergraduate students of Michael Okpara university of agriculture, Umudike Abia state, Nigeria. World Appl. Sci. J. 2013, 25, 1171–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Abaver, D.T.; Nwobegahay, J.M.; Goon, D.T.; Iweriebor, B.C.; Khoza, L.B. Enteric parasitic infections in HIV-infected patients with low CD4 counts in Toto, Nigeria. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 28, 630–633. [Google Scholar]
- Akinbo, F.O.; Okaka, C.E.; Omoregie, R. Plasmodium falciparum and intestinal parasitic co-infections in HIV-infected patients in Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2012, 6, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguanya, F.C.; Okogun, G.R.A.; Akhile, A.O.; Eloka, C.C.V.; Okoro, C.J.; Okpe, A.C. Prevalence of soil-transmitted helminths infections among public primary school pupils in Ekpoma, Edo State, Nigeria. Int. J. Community Res. 2012, 1, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Abaver, D.T.; Nwobegahay, J.M.; Goon, D.T.; Iweriebor, B.C.; Anye, D.N. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections among HIV/AIDS patients from two health institutions in Abuja, Nigeria. Afr. Health Sci. 2011, 11 (Suppl. 1), 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Akinbo, F.O.; Okaka, C.E.; Omoregie, R. Seasonal variation of intestinal parasitic infections among HIV-positive patients in Benin City, Nigeria. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2011, 21, 191–194. [Google Scholar]
- Akinbo, F.O.; Okaka, C.E.; Omoregie, R. Prevalence of intestinal parasites in relation to CD4 counts and anaemia among HIV-infected patients in Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria. Tanzan. J. Health Res. 2011, 13, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinbo, F.O.; Omoregie, R. Intestinal parasitic infections in human immunodeficiency- virus-infected persons on highly active antiretroviral therapy in Benin City, Nigeria. Genom. Med. Biomarkers Health Sci. 2011, 3, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyaolu, A.O.; Oyibo, W.A.; Fagbenro-Beyioku, A.F.; Gbadegeshin, A.H.; Iriemenam, N.C. Comparative study of entero-parasitic infections among HIV sero-positive and sero-negative patients in Lagos, Nigeria. Acta Trop. 2011, 120, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, S.K.; Salami, A.K.; Fabiyi, J.P.; Agbede, O.O.; Desalu, O.O. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infestation in HIV seropositive and seronegative patients in Ilorin, Nigeria. Ann. Afr. Med. 2010, 9, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada-Adegbola, H.O.; Oluwatoba, O.A.; Bakaré, R.A. Strongyloidiasis: Prevalence, risk factors, clinical and laboratory features among diarrhea patients in Ibadan Nigeria. Afr. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2010, 39, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Damen, J.G.; Lar, P.; Mershak, P.; Mbaawuga, E.M.; Nyary, B.W. A Comparative study on the prevalence of intestinal helminthes in dewormed and non-dewormed students in a rural area of north-central Nigeria. Lab. Med. 2010, 41, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.A.; Bassey, S.E. Incidence of Strongyloides stercoralis infection in Ungogo, Nassarawa, Dala and Fagge local government areas of Kano State, Nigeria. Bayero J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2010, 3, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houmsou, R.S.; Amuta, E.; Olusi, T. Prevalence of intestinal parasites among primary school children in Makurdi, Benue State- Nigeria. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 8, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Morenikeji, O.A.; Azubike, N.C.; Ige, A.O. Prevalence of intestinal and vector-borne urinary parasites in communities in south-west Nigeria. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2009, 46, 164–167. [Google Scholar]
- Ibidapo, C.A.; Okwa, O. The prevalence and intensity of soil-transmitted helminths in a rural community, Lagos Suburb, southwest Nigeria. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2008, 10, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Adeoye, G.O.; Osayemi, C.O.; Oteniya, O.; Onyemekeihia, S.O. Epidemiological studies of intestinal helminthes and malaria among children in Lagos, Nigeria. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 2208–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agbolade, O.M.; Agu, N.C.; Adesanya, O.O.; Odejayi, A.O.; Adigun, A.A.; Adesanlu, E.B.; Ogunleye, F.G.; Sodimu, A.O.; Adeshina, S.A.; Bisiriyu, G.O.; et al. Intestinal helminthiases and schistosomiasis among school children in an urban center and some rural communities in southwest Nigeria. Korean J. Parasitol. 2007, 45, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeh, E.I.; Obadofin, M.O.; Brindeiro, B.; Baugherb, C.; Frost, F.; Vanderjagt, D.; Glew, R.H. Intestinal parasitism in Magama Gumau rural village and Jos township in north central Nigeria. Niger. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 14, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugbomoiko, U.S.; Ofoezie, I.E. Multiple infection diagnosis of intestinal helminthiasis in the assessment of health and environmental effect of development projects in Nigeria. J. Helminthol. 2007, 81, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagbatsoma, V.A.; Aisien, M.S. Helminthiasis in selected children seen at the University of Benin Teaching Hospital (UBTH), Benin City, Nigeria. Niger. Postgrad. Med. J. 2005, 12, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anosike, J.C.; Nwoke, B.E.; Onwuliri, C.O.; Obiukwu, C.E.; Duru, A.F.; Nwachukwu, M.I.; Ukaga, C.N.; Uwaezuoke, J.C.; Uduji, O.S.; Amajuoyi, O.U.; et al. Prevalence of parasitic diseases among nomadic Fulanis of south-eastern Nigeria. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2004, 11, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Dada-Adegbola, H.O.; Bakare, R.A. Strongyloidiasis in children five years and below. West. Afr. J. Med. 2004, 23, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyaeze, C.M. Reducing burden of hookworm disease in the management of upper abdominal pain in the tropics. Trop. Doct 2003, 33, 174–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoronkwo, M.O. Parasitic infections of dry season farmers in some parts of Plateau State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Clin. Exp. Microbiol. 2002, 3, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ozumba, U.C.; Ozumba, N. Patterns of helminth infection in the human gut at the University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu, Nigeria. J. Health Sci. 2002, 48, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokediuko, S.; Bababode, B.; Chinedu, O.U.; Ozoh, G. Peculiarities of chronic diarrhoea in Enugu, Southeastern Nigeria. J. Health Sci. 2002, 48, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nwaorgu, O.C.; Okeibunor, J.; Madu, E.; Amazigo, U.; Onyegegbu, N.; Evans, D. A school-based schistosomiasis and intestinal helminthiasis control programme in Nigeria: Acceptability to community members. Trop. Med. Int. Health 1998, 3, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodipo, J.O.; Padgett, D.; Warrie, E.; Olopoenia, L. Parasitic infections in sickle cell crisis: Nigerian experience. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 1997, 89, 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Udonsi, J.K.; Behnke, J.M.; Gilbert, F.S. Analysis of the prevalence of infection and associations between human gastrointestinal nematodes among different age classes living in the urban and suburban communities of Port Harcourt, Nigeria. J. Helminthol. 1996, 70, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Asaolu, S.O.; Holland, C.V.; Jegede, J.O.; Fraser, N.R.; Stoddard, R.C.; Crompton, D.W.T. The prevalence and intensity of soil-transmitted helminthiases in rural communities in southern Nigeria. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1992, 86, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akogun, O.B. Some social aspects of helminthiasis among the people of Gumau District, Bauchi State, Nigeria. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1989, 92, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, C.V.; Asaolu, S.O.; Crompton, D.W.; Stoddart, R.C.; Macdonald, R.; Torimiro, S.E. The epidemiology of Ascaris lumbricoides and other soil-transmitted helminths in primary school children from Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Parasitology 1989, 99 Pt 2, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arene, F.O. Preliminary parasitological survey of intestinal parasites among inhabitants of Okrika Island in the Niger Delta. J. Infect. 1984, 9, 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhaus, J.; Kann, S.; Hahn, A.; Weinreich, F.; Blohm, M.; Tanida, K.; Feldt, T.; Sarfo, F.S.; Di Cristanziano, V.; Loderstädt, U.; et al. Clustering of gastrointestinal microorganisms in human stool samples from Ghana. Pathogens 2024, 13, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deku, J.G.; Okyere, D.O.; Buabeng, S.; Edziah, F.S.; Bedzina, I.; Kinanyok, S.; Duedu, K.O.; Aninagyei, E. The burden and trend of intestinal parasitosis among women at Berekum, Ghana: A 9-year retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkoh, E.T.; Berkoh, D.; Fosu-Gyasi, S.; Boadu, W.I.O.; Raji, A.S.; Asamoah, S.; Otabil, K.B.; Otoo, J.E.; Yeboah, M.T.; Aganbire, B.A.; et al. Evidence of reduced academic performance among schoolchildren with helminth infection. Int. Health 2023, 15, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akenten, C.W.; Weinreich, F.; Paintsil, E.K.; Amuasi, J.; Fosu, D.; Loderstadt, U.; May, J.; Frickmann, H.; Dekker, D. Intestinal helminth infections in Ghanaian children from the Ashanti Region between 2007 and 2008-a retrospective cross-sectional real-time PCR-based assessment. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornace, K.M.; Senyonjo, L.; Martin, D.L.; Gwyn, S.; Schmidt, E.; Agyemang, D.; Marfo, B.; Addy, J.; Mensah, E.; Solomon, A.W.; et al. Characterising spatial patterns of neglected tropical disease transmission using integrated sero-surveillance in Northern Ghana. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aninagyei, E.; Yirenkyi, R.; Rufai, T.; Chandi, M.G. Enteroparasitism in hard-to-reach community dwellers: A cross-sectional study in Ga West municipality in Ghana. J. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 2020, 8890998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, L.J.; Campbell, S.J.; Armoo, S.; Koukounari, A.; Watson, V.; Selormey, P.; Stothard, J.R.; Idun, B.; Asiedu, M.; Ashong, Y.; et al. Assessing expanded community wide treatment for schistosomiasis: Baseline infection status and self-reported risk factors in three communities from the Greater Accra region, Ghana. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpene, G.E.; Lokpo, S.Y.; Deku, J.G.; Agboli, E.; Owiafe, P.K. Asymptomatic intestinal parasitic infestations among children under five years in selected communities in the Ho municipality, Ghana. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2020, 30, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Gyasi, D.; Asante, K.P.; Frempong, M.T.; Gyasi, D.K.; Iddrisu, L.F.; Ankrah, L.; Dosoo, D.; Adeniji, E.; Agyei, O.; Gyaase, S.; et al. Epidemiology of soil transmitted helminth infections in the middle-belt of Ghana, Africa. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2018, 3, e00071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, L.J.; Odoom, J.; Pratt, D.; Boatemaa, L.; Asante-Ntim, N.; Attiku, K.; Banahene, B.; Osei-Atweneboana, M.; Verweij, J.J.; Molyneux, D.; et al. Expanding molecular diagnostics of helminthiasis: Piloting use of the GPLN platform for surveillance of soil transmitted helminthiasis and schistosomiasis in Ghana. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forson, A.O.; Arthur, I.; Olu-Taiwo, M.; Glover, K.K.; Pappoe-Ashong, P.J.; Ayeh-Kumi, P.F. Intestinal parasitic infections and risk factors: A cross-sectional survey of some school children in a suburb in Accra, Ghana. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, S.C.K.; Nani, E.A.; Walana, W. Parasitic infections and maternal anaemia among expectant mothers in the Dangme east district of Ghana. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboli, E.; Tay, S.C.K.; Obirikorang, C.; Aidoo, E.Y. Malaria and intestinal parasites in pregnant and non-pregnant women: A comparative study at the University Hospital, Kumasi, Ghana. J. Med. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 4, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danikuu, F.M.; Azikala, O.; Baguo, F.M. Faeco-oral parasitic infection in street food vendors in Tamale, Ghana. J. Med. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 4, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duedu, K.O.; Karikari, Y.A.; Attah, S.K.; Ayeh-Kumi, P.F. Prevalence of intestinal parasites among patients of a Ghanaian psychiatry hospital. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, S.C.K.; Gbedema, S.Y.; Gyampomah, T.K. High prevalence of hookworm infection and apparent absence of Ascaris lumbricoides: A case study at the Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital in Ghana. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2011, 5, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Baidoo, S.E.; Tay, S.C.K.; Obiri-Danso, K.; Abruquah, H.H. Intestinal helminth infection and anaemia during pregnancy: A community based study in Ghana. J. Bacteriol. Res. 2010, 2, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yatich, N.J.; Jolly, P.E.; Funkhouser, E.; Agbenyega, T.; Rayner, J.C.; Ehiri, J.E.; Turpin, A.; Stiles, J.K.; Ellis, W.O.; Jiang, Y.; et al. The effect of malaria and intestinal helminth coinfection on birth outcomes in Kumasi, Ghana. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.J.; Canales, M.; Polman, K.; Ziem, J.; Brienen, E.A.; Polderman, A.M.; van Lieshout, L. Molecular diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis in faecal samples using real-time PCR. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatich, N.J.; Yi, J.; Agbenyega, T.; Turpin, A.; Rayner, J.C.; Stiles, J.K.; Ellis, W.O.; Funkhouser, E.; Ehiri, J.E.; Williams, J.H.; et al. Malaria and intestinal helminth co-infection among pregnant women in Ghana: Prevalence and risk factors. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelifari, L.; Bloch, P.; Magnussen, P.; van Lieshout, L.; Dery, G.; Anemana, S.; Agongo, E.; Polderman, A.M. Distribution of human Oesophagostomum bifurcum, hookworm and Strongyloides stercoralis infections in northern Ghana. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 99, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annan, A.; Crompton, D.W.; Walters, D.E.; Arnold, S.E. An investigation of the prevalence of intestinal parasites in pre-school children in Ghana. Parasitology 1986, 92, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boko, P.M.; Ibikounle, M.; Onzo-Aboki, A.; Tougoue, J.J.; Sissinto, Y.; Batcho, W.; Kinde-Gazard, D.; Kabore, A. Schistosomiasis and soil transmitted helminths distribution in Benin: A baseline prevalence survey in 30 districts. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibikounle, M.; Gbedjissi, L.G.; Ogouyemi-Hounto, A.; Batcho, W.; Kinde-Gazard, D.; Massougbodji, A. Schistosomose et géohelminthoses dans le nord-est du Bénin: Cas des écoliers des communes de Nikki et de Pèrèrè. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2014, 107, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chippaux, J.P.; Massougbodji, A.; Zomadi, A.; Kindafodji, B.M. Etude épidémiologique des schistosomes dans un complexe lacustre côtier de formation récente. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1990, 83, 498–508. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, O.; Sy, O.; Mbareck, A.M.; Issa, S.M.; Fofana, M.; Baba, W.S. Epidemiology of intestinal parasitosis in schoolchildren in the Moughatâa of Riyadh (Nouakchott). Tunis. Med. 2024, 102, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbani, C.; Touré, A.; Hamed, A.O.; Albonico, M.; Kane, I.; Cheikna, D.; Hamed, N.O.; Montresor, A.; Savioli, L. Parasitoses intestinales et schistosomiases dans la vallée du fleuve Sénégal en République Islamique de Mauritanie. Med. Trop. 1997, 57, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Intestinal parasitic infections and schistosomiasis. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 1995, 30, 217–218. [Google Scholar]
- Diongue, K.; Ndiaye, M.; Seck, M.C.; Diallo, M.A.; Ndiaye, Y.D.; Badiane, A.S.; Ndiaye, D. Distribution of parasites detected in stool samples of patients in Le Dantec University Hospital of Dakar, Senegal, from 2011 to 2015. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 2017, 8296313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, D.; Parola, P.; Sylla, K.; Ndiaye, M.; Delaunay, P.; Halfon, P.; Camiade, S.; Dieng, T.; Tine, R.C.K.; Faye, B.; et al. Performance of real-time polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of 20 gastrointestinal parasites in clinical samples from Senegal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, D.; Ndiaye, M.; Gueye, P.A.; Badiane, A.; Fall, I.D.; Ndiaye, Y.D.; Faye, B.; Ndiaye, J.L.; Tine, R.; Ndir, O. Prévalence des helminthoses digestives diagnostiquées à l’hôpital Le Dantec de Dakar, Sénégal. Med. Sante Trop. 2013, 23, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, G.; van de Velden, L.; Laloe, F.; Maire, B.; Ponton, A.; Traissac, P.; Prost, A. Parasitoses intestinales et environnement dans les villes sahélo-soudaniennes: l’exemple de Pikine (Sénégal). Rev. Epidemiol. Sante Publique 1994, 42, 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- Mouchet, F.; Develoux, M.; Balla Magassa, M.; Sellin, B. Etude epidémiologique du foyer à Schistosoma mansoni Bana (Niger). Med. Trop. 1988, 48, 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Sangaré, I.; Guiguemde, K.T.; Zida, A.; Sirima, C.; Sawadogo, P.M.; Cisse, M.; Assogba, S.B.; Guiguemde, T.R.; Bamba, S. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections among pregnant women in Bobo-Dioulasso (Burkina Faso). Ann. Parasitol. 2021, 67, 489–497. [Google Scholar]
- Sangaré, I.; Bamba, S.; Cissé, M.; Zida, A.; Bamogo, R.; Sirima, C.; Yameogo, B.K.; Sanou, R.; Drabo, F.; Dabire, R.K.; et al. Prevalence of intestinal opportunistic parasites infections in the University hospital of Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2015, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karou, S.D.; Sanou, D.; Ouermi, D.; Pignatelli, S.; Pietra, V.; Moret, R.; Nikiema, J.B.; Simpore, J. Enteric parasites prevalence at Saint Camille Medical Centre in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonfrate, D.; Bradbury, R.S.; Watts, M.R.; Bisoffi, Z. Human strongyloidiasis: Complexities and pathways forward. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 36, e0003323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, N.C.; Addiss, D.G.; Buonfrate, D.; Amor, A.; Anegagrie, M.; Bisoffi, Z.; Bradbury, R.S.; Keiser, J.; Kepha, S.; Khieu, V.; et al. Review of the WHO guideline on preventive chemotherapy for public health control of strongyloidiasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, e146–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, J.A.T.; Maure, T.; Carias, L.; Lew, D.; Goss, C.; Samuel, A.; Tavul, L.; Fischer, P.U.; Weil, G.J.; Laman, M.; et al. Impact of mass drug administration with ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine, and albendazole for lymphatic filariasis on hookworm and infections in Papua New Guinea. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2025, 19, e0012851. [Google Scholar]
- Tamarozzi, F.; Guevara, A.G.; Anselmi, M.; Vicuna, Y.; Prandi, R.; Marquez, M.; Vivero, S.; Robinzon Huerlo, F.; Racines, M.; Mazzi, C.; et al. Accuracy, acceptability, and feasibility of diagnostic tests for the screening of Strongyloides stercoralis in the field (ESTRELLA): A cross-sectional study in Ecuador. Lancet Glob. Health 2023, 11, e740–e748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaga, J.L.; Fernandez-Baca, M.V.; Castellanos-Gonzalez, A.; Tanabe, M.B.; Tift, C.; Morales, M.L.; Lopez, M.; Valdivia-Rodriguez, A.; Mamani-Licona, F.; Cabada, M.M. The recombinase polymerase amplification test for Strongyloides stercoralis is more sensitive than microscopy and real-time PCR in high-risk communities of Cusco, Peru. Pathogens 2024, 13, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chankongsin, S.; Wampfler, R.; Ruf, M.T.; Odermatt, P.; Marti, H.; Nickel, B.; Keoluangkhot, V.; Neumayr, A. Strongyloides stercoralis prevalence and diagnostics in Vientiane, Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailegebriel, T.; Petros, B.; Endeshaw, T. Evaluation of parasitological methods for the detection of Strongyloides Stercoralis among individuals in selected health institutions in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2017, 27, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alegria, M.; Colmenares, K.; Espasa, M.; Amor, A.; Lopez, I.; Nindia, A.; Kanjala, J.; Guilherme, D.; Sulleiro, E.; Barriga, B.; et al. Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis and other intestinal parasite infections in school children in a rural area of Angola: A cross-sectional study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, T.; Amor, A.; Nibret, E.; Munshea, A.; Anegagrie, M.; Flores-Chavez, M.D.; Tang, T.T.; Saugar, J.M.; Benito, A. Evaluation of five diagnostic methods for Strongyloides stercoralis infection in Amhara National Regional State, northwest Ethiopia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, A.; Rodriguez, E.; Saugar, J.M.; Arroyo, A.; Lopez-Quintana, B.; Abera, B.; Yimer, M.; Yizengaw, E.; Zewdie, D.; Ayehubizu, Z.; et al. High prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis in school-aged children in a rural highland of north-western Ethiopia: The role of intensive diagnostic work-up. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eamudomkarn, C.; Sithithaworn, P.; Kamamia, C.; Yakovleva, A.; Sithithaworn, J.; Kaewkes, S.; Techasen, A.; Loilome, W.; Yongvanit, P.; Wangboon, C.; et al. Diagnostic performance of urinary IgG antibody detection: A novel approach for population screening of strongyloidiasis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaisier, A.P.; Alley, E.S.; Boatin, B.A.; Van Oortmarssen, G.J.; Remme, H.; De Vias, S.J.; Bonneux, L.; Habbema, J.D.F. Irreversible effects of ivermectin on adult parasites in onchocerciasis patients in the onchocerciasis control programme in West Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawadogo, A.; Zoungrana, J.; Ouédraogo, A.G.; Diallo, I.; Tassembedo, M.; Kima, A.; Sermé, M.; Ouédraogo, B.; Tanon, A.K.; Eholié, S.P. Impact of mass drug administration of ivermectin and albendazole on transmission of Wuchereria bancrofti lymphatic filariasis from 2001 to 2017 in Burkina Faso. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2025, 30, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroma, A.S.; Conteh, S.G.; Bah, M.; Kamara, H.I.; Turay, M.; Kandeh, A.; Macauley, A.; Allieu, H.; Kargbo, A.A.; Sonnie, M.; et al. Routine vitamin A supplementation and other high impact interventions in Sierra Leone. Matern. Child. Nutr. 2020, 16, e13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Country | N Individual Studies | Study Setting | Study Population | References | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| School | Hospital | Community | All Age and Sex | PSAC | SAC | PSAC + SAC | Females | |||
| The Gambia | 19 | 18 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 | Kositz et al. (2022) [12], Sanyang et al. (2021) [13] |
| Liberia | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Sodeman (1979) [14] |
| Togo | 10 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Korbmacher et al. (2018) [15], Gbadoé et al. (2005) [16], Aplogan et al. (1990) [17], Lapierre et al. (1988) [18] |
| Guinea-Bissau | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | Farrant et al. (2020) [19], von Huth et al. (2019) [20], Steenhard et al. (2009) [21], Lebbad et al. (2001) [22], Carstensen et al. (1987) [23] |
| Sierra Leone | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Bailey et al. (2006) [24], Gbakima (1994) [25], Whitworth et al. (1991) [26] |
| Cape Verde | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Colito et al. (2021) [27] |
| Guinea | 10 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 2 | 0 | Beavogui et al. (2021) [28], Glickman et al. (1999) [29], Gyorkos et al. (1996) [30] |
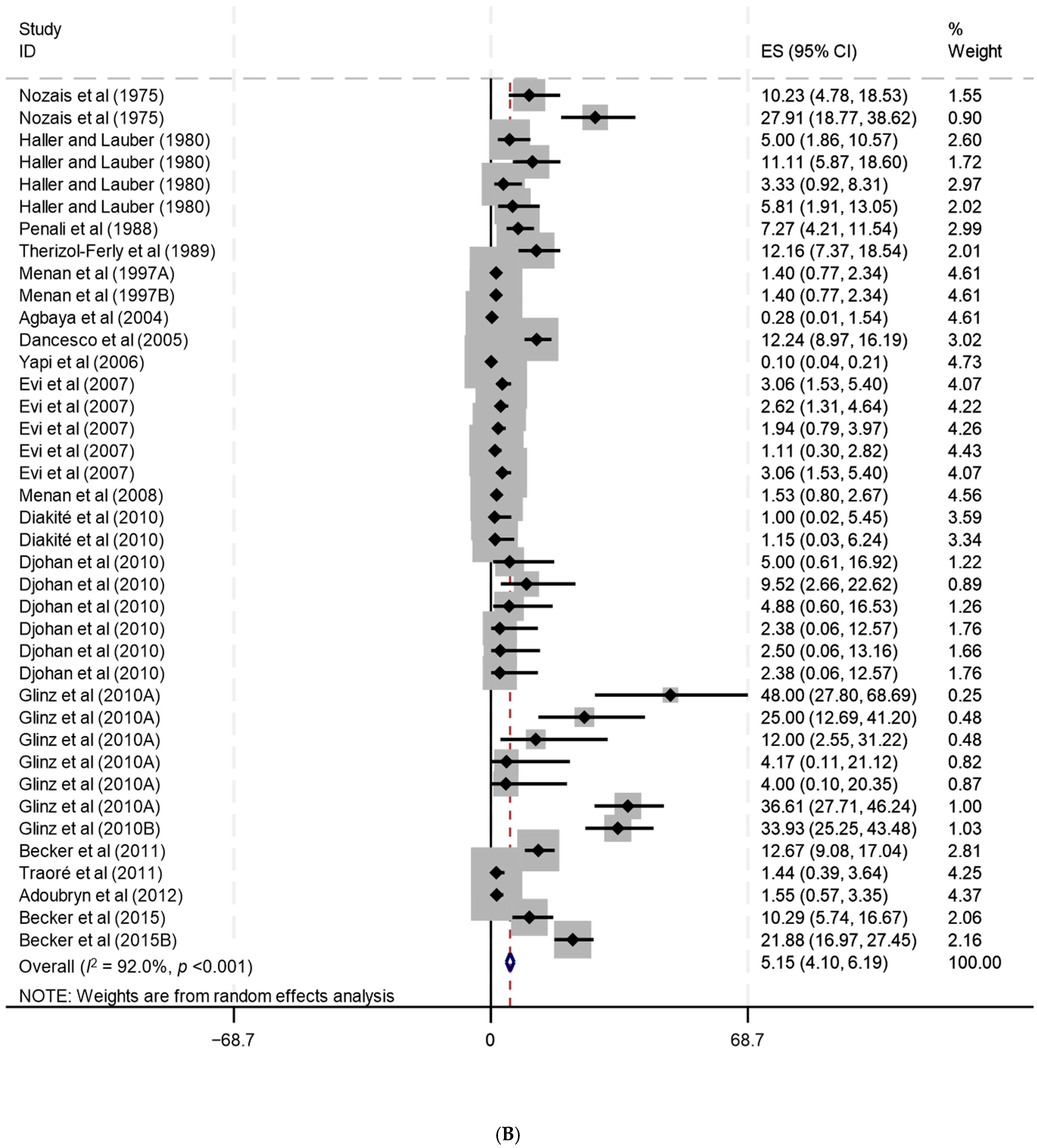
| Côte d’Ivoire | 46 | 36 | 1 | 9 | 5 | 1 | 25 | 15 | 0 | Becker et al. (2015b) [31], Becker et al. (2015a) [32], Adoubryn et al. (2012) [33], Becker et al. (2011) [34], Traoré et al. (2011) [35], Djohan et al. (2010) [36], Diakité et al. (2010) [37], Glinz et al. (2010b) [38], Glinz et al. (2010a) [39], Menan et al. (2008) [40], Evi et al. (2007) [41], Yapi et al. (2006) [42], Dancesco et al. (2005) [43], Agbaya et al. (2004) [44], Menan et al. (1997b) [45], Menan et al. (1997a) [46], Therizol-Ferly et al. (1989) [47], Penali et al. (1988) [48], Haller and Lauber (1980) [49], Nozais et al. (1975) [50] |
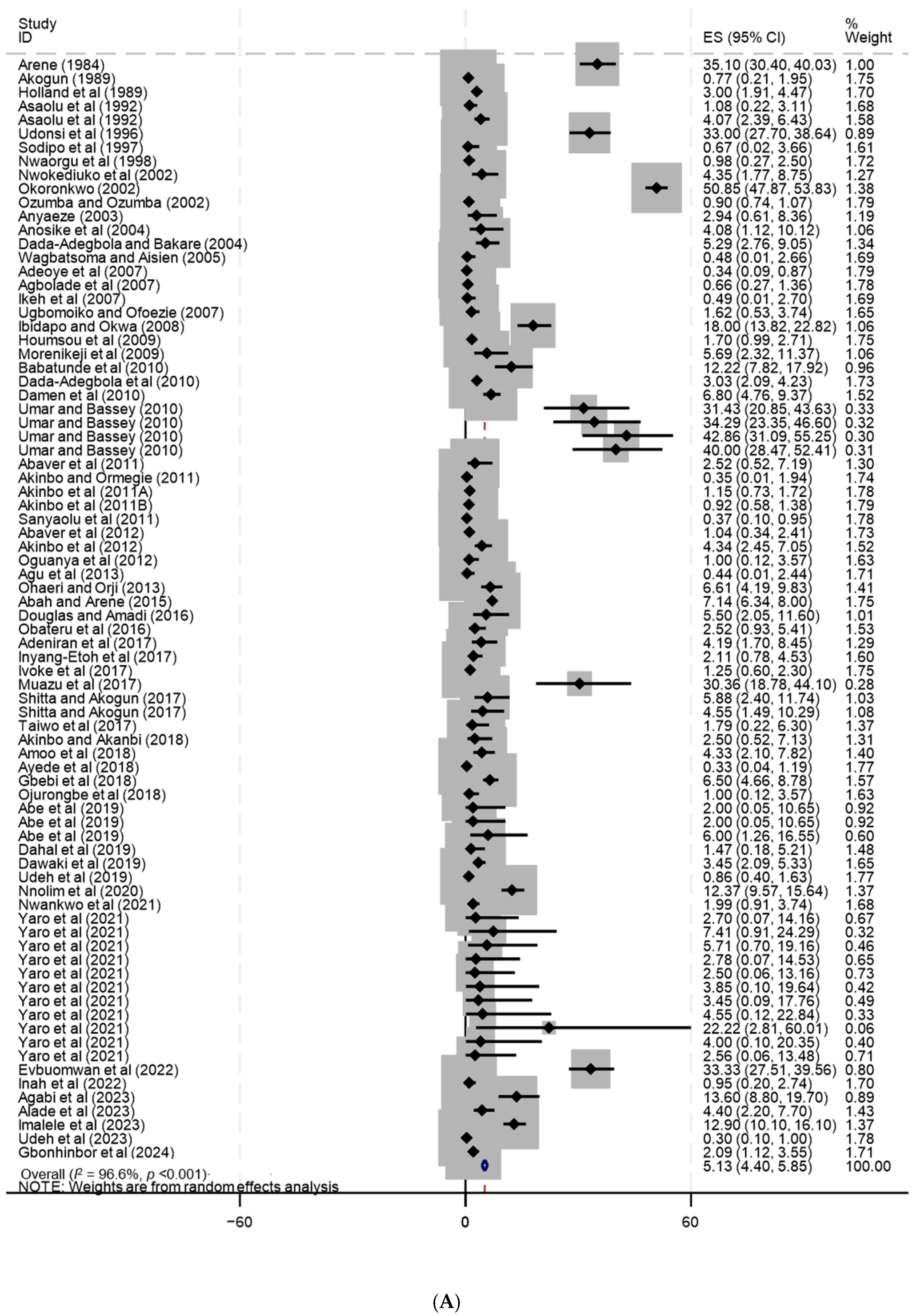
| Nigeria | 119 | 69 | 25 | 25 | 41 | 1 | 66 | 7 | 4 | Gbonhinbor et al. (2024) [51], Agabi et al. (2023) [52], Alade et al. (2023) [53], Imalele et al. (2023) [54], Udeh et al. (2023) [55], Evbuomwan et al. (2022) [56], Inah et al. (2022) [57], Nwankwo et al. (2021) [58], Yaro et al. (2021) [59], Nnolim et al. (2020) [60], Abe et al. (2019) [61], Dahal et al. (2019) [62], Dawaki et al. (2019) [63], Udeh et al. (2019) [64], Ayede et al. (2018) [65], Akinbo and Akanbi (2018) [66], Amoo et al. (2018) [67], Gbebi et al. (2018) [68], Ojurongbe et al. (2018) [69], Adeniran et al. (2017) [70], Inyang-Etoh et al. (2017) [71], Ivoke et al. (2017) [72], Muazu et al. (2017) [73], Shitta and Akogun (2017) [74], Taiwo et al. (2017) [75], Douglas and Amadi (2016) [76], Obateru et al. (2016) [77], Abah and Arene (2015) [78], Agu et al. (2013) [79], Ohaeri and Orji (2013) [80], Abaver et al. (2012) [81], Akinbo et al. (2012) [82], Oguanya et al. (2012) [83], Abaver et al. (2011) [84], Akinbo et al. (2011b) [85], Akinbo et al. (2011a) [86], Akinbo and Ormegie (2011) [87], Sanyaolu et al. (2011) [88], Babatunde et al. (2010) [89], Dada-Adegbola et al. (2010) [90], Damen et al. (2010) [91], Umar and Bassey (2010) [92], Houmsou et al. (2009) [93], Morenikeji et al. (2009) [94], Ibidapo and Okwa (2008) [95], Adeoye et al. (2007) [96], Agbolade et al. (2007) [97], Ikeh et al. (2007) [98], Ugbomoiko and Ofoezie (2007) [99], Wagbatsoma and Aisien (2005) [100], Anosike et al. (2004) [101], Dada-Adegbola and Bakare (2004) [102], Anyaeze (2003) [103], Okoronkwo (2002) [104], Ozumba and Ozumba (2002) [105], Nwokediuko et al. (2002) [106], Nwaorgu et al. (1998) [107], Sodipo et al. (1997) [108], Udonsi et al. (1996) [109], Asaolu et al. (1992) [110], Akogun (1989) [111], Holland et al. (1989) [112], Arene (1984) [113] |
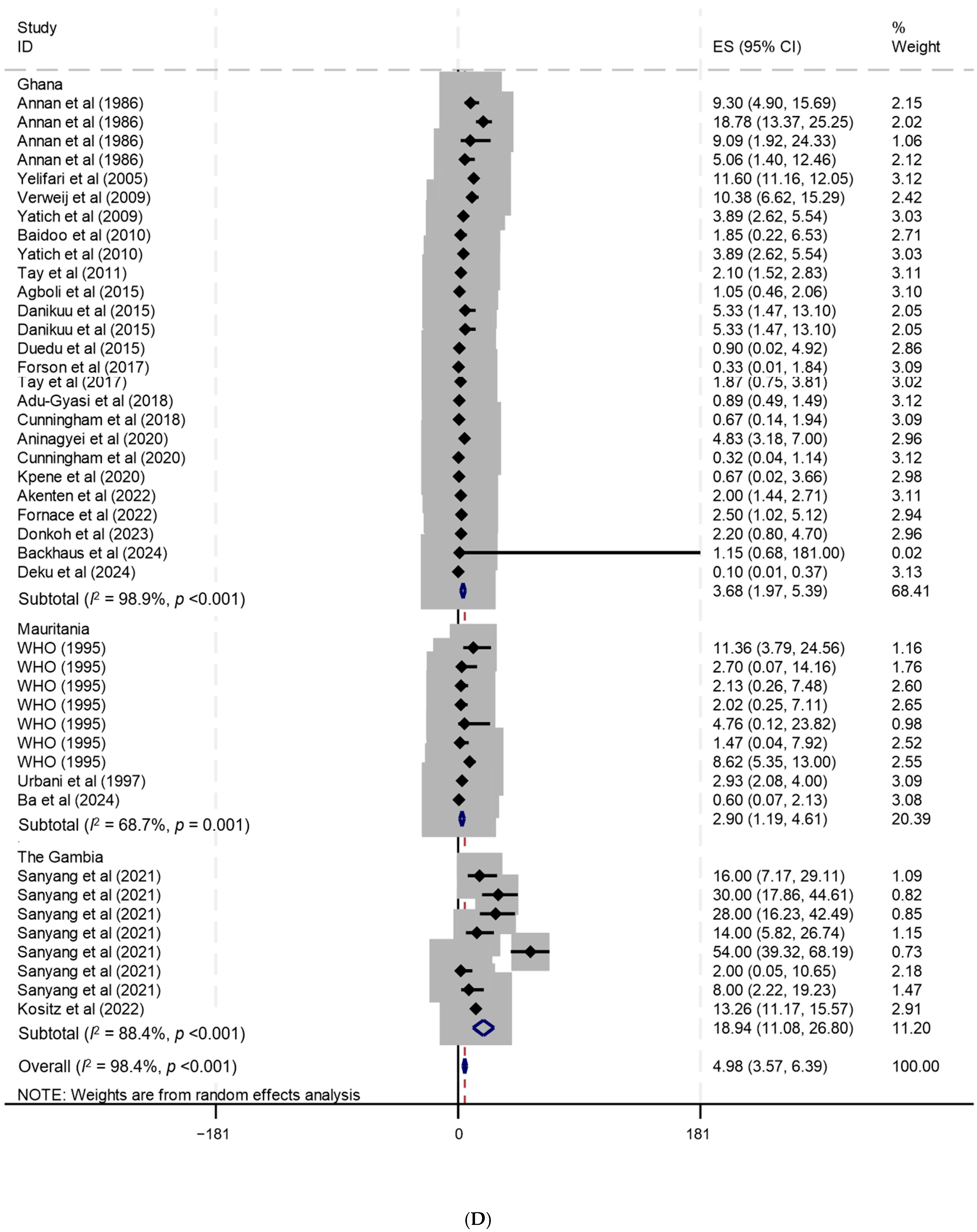
| Ghana | 28 | 2 | 5 | 21 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 6 | Backhaus et al. (2024) [114], Deku et al. (2024) [115], Donkoh et al. (2023) [116], Akenten et al. (2022) [117], Fornace et al. (2022) [118], Aninagyei et al. (2020) [119], Cunningham et al. (2020) [120], Kpene et al. (2020) [121], Adu-Gyasi et al. (2018) [122], Cunningham et al. (2018) [123], Forson et al. (2017) [124], Tay et al. (2017) [125], Agboli et al. (2015) [126], Danikuu et al. (2015) [127], Duedu et al. (2015) [128], Tay et al. (2011) [129], Baidoo et al. (2010) [130], Yatich et al. (2010) [131], Verweij et al. (2009) [132], Yatich et al. (2009) [133], Yelifari et al. (2005) [134], Annan et al. (1986) [135] |
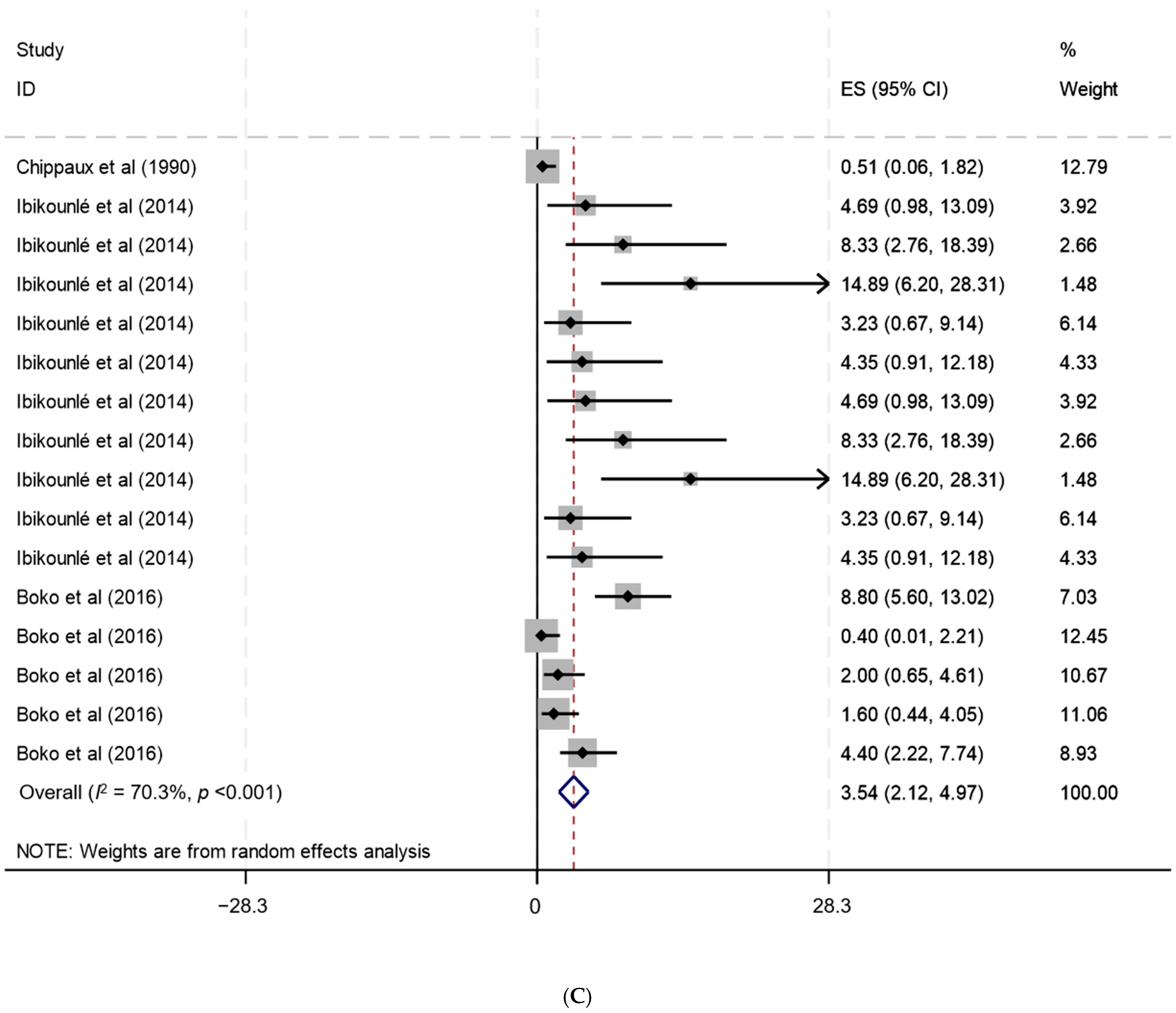
| Benin | 67 | 66 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | Boko et al. (2016) [136], Ibikounlé et al. (2014) [137], Chippaux et al. (1990) [138] |
| Mauritania | 16 | 1 | 0 | 15 | 14 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Ba et al. (2024) [139], Urbani et al. (1997) [140], WHO (1995) [141] |
| Senegal | 4 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Diongue et al. (2017) [142], Sow et al. (2017) [143], Ndiaye et al. (2013) [144], Salem et al. (1994) [145] |
| Niger | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Mouchet et al. (1988) [146] |
| Burkina Faso | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Sangaré et al. (2021) [147], Sangaré et al. (2015) [148], Karou et al. (2011) [149] |
| Mali | … | No data | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | |
| Total | 336 | 196 | 42 | 98 | 92 | 10 | 193 | 28 | 13 | |
| Variable | Sample Size | No Positive | Pooled Prevalence (%) | 95% CI | I2 (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | |||||||
| All age and sex | 85,082 | 4333 | 4.9 | 4.2–5.5 | 98.3 | <0.001 | |
| PSAC | 1927 | 127 | 6.3 | 3.7–8.9 | 83.0 | <0.001 | |
| SAC | 31,376 | 1469 | 7.1 | 6.1–8.1 | 90.6 | <0.001 | |
| PSAC + SAC | 19,955 | 324 | 2.0 | 1.4–2.5 | 90.3 | <0.001 | |
| Females | 4772 | 91 | 1.6 | 0.8–2.4 | 75.9 | <0.001 | |
| Study setting | |||||||
| School | 34,582 | 1325 | 5.5 | 4.7–6.3 | 91.5 | <0.001 | |
| Hospital | 49,266 | 629 | 1.5 | 1.2–1.8 | 91.0 | <0.001 | |
| Community | 59,264 | 4390 | 6.6 | 5.7–7.5 | 98.3 | <0.001 | |
| Sample size | |||||||
| <101 | 9111 | 544 | 9.1 | 7.4–10.7 | 80.5 | <0.001 | |
| 101–1000 | 45,977 | 1977 | 4.7 | 4.1–5.3 | 93.1 | <0.001 | |
| 1001–10,000 | 42,661 | 1335 | 3.1 | 2.4–3.8 | 98.7 | <0.001 | |
| >10,000 | 45,363 | 2488 | 4.2 | 0.7–7.7 | 99.9 | <0.001 | |
| Variable | β-Coefficient | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Publication decade | 0.90 | 0.77–1.04 | 0.141 |
| Study population | 0.95 | 0.82–1.10 | 0.478 |
| Study country | 1.01 | 0.95–1.05 | 0.812 |
| Study setting | 0.92 | 0.75–1.12 | 0.433 |
| Diagnostic method | 0.99 | 0.97–1.01 | 0.540 |
| Sample size | 0.42 | 0.34–0.53 | <0.001 |
| Country | N Individual Studies | N Participants | N Positive | S. stercoralis Prevalence | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | 95% CI | I2 | p-Value | |||||
| The Gambia | 19 | 1859 | 203 | 18.9 | 11.1–26.8 | 88.4 | <0.001 | Kositz et al. (2022) [12], Sanyang et al. (2021) [13] |
| Liberia | 2 | 549 | 84 | 14.9 | 9.8–19.9 | 62.3 | 0.103 | Sodeman (1979) [14] |
| Togo | 10 | 1749 | 149 | 10.7 | 6.9–14.6 | 92.3 | <0.001 | Korbmacher et al. (2018) [15], Gbadoé et al. (2005) [16], Aplogan et al. (1990) [17], Lapierre et al. (1988) [18] |
| Guinea-Bissau | 5 | 2631 | 126 | 7.8 | 2.4–13.2 | 96.4 | <0.001 | Farrant et al. (2020) [19], von Huth et al. (2019) [20], Steenhard et al. (2009) [21], Lebbad et al. (2001) [22], Carstensen et al. (1987) [23] |
| Sierra Leone | 3 | 2076 | 145 | 6.9 | 5.5–8.3 | 20.7 | 0.283 | Bailey et al. (2006) [24], Gbakima (1994) [25], Whitworth et al. (1991) [26] |
| Cape Verde | 1 | 105 | 7 | 6.8 | 2.7–13.2 | … | … | Colito et al. (2021) [27] |
| Guinea | 10 | 1478 | 84 | 5.5 | 2.8–8.1 | 80.8 | <0.001 | Beavogui et al. (2021) [28], Glickman et al. (1999) [29], Gyorkos et al. (1996) [30] |
| Côte d’Ivoire | 46 | 16,119 | 464 | 5.2 | 4.1–6.2 | 92 | <0.001 | Becker et al. (2015b) [31], Becker et al. (2015a) [32], Adoubryn et al. (2012) [33], Becker et al. (2011) [34], Traoré et al. (2011) [35], Djohan et al. (2010) [36], Diakité et al. (2010) [37], Glinz et al. (2010b) [38], Glinz et al. (2010a) [39], Menan et al. (2008) [40], Evi et al. (2007) [41], Yapi et al. (2006) [42], Dancesco et al. (2005) [43], Agbaya et al. (2004) [44], Menan et al. (1997b) [45], Menan et al. (1997a) [46], Therizol-Ferly et al. (1989) [47], Penali et al. (1988) [48], Haller and Lauber (1980) [49], Nozais et al. (1975) [50] |
| Nigeria | 119 | 47,705 | 2106 | 5.1 | 4.4–5.9 | 96.6 | <0.001 | Gbonhinbor et al. (2024) [51], Agabi et al. (2023) [52], Alade et al. (2023) [53], Imalele et al. (2023) [54], Udeh et al. (2023) [55], Evbuomwan et al. (2022) [56], Inah et al. (2022) [57], Nwankwo et al. (2021) [58], Yaro et al. (2021) [59], Nnolim et al. (2020) [60], Abe et al. (2019) [61], Dahal et al. (2019) [62], Dawaki et al. (2019) [63], Udeh et al. (2019) [64], Ayede et al. (2018) [65], Akinbo and Akanbi (2018) [66], Amoo et al. (2018) [67], Gbebi et al. (2018) [68], Ojurongbe et al. (2018) [69], Adeniran et al. (2017) [70], Inyang-Etoh et al. (2017) [71], Ivoke et al. (2017) [72], Muazu et al. (2017) [73], Shitta and Akogun (2017) [74], Taiwo et al. (2017) [75], Douglas and Amadi (2016) [76], Obateru et al. (2016) [77], Abah and Arene (2015) [78], Agu et al. (2013) [79], Ohaeri and Orji (2013) [80], Abaver et al. (2012) [81], Akinbo et al. (2012) [82], Oguanya et al. (2012) [83], Abaver et al. (2011) [84], Akinbo et al. (2011b) [85], Akinbo et al. (2011a) [86], Akinbo and Ormegie (2011) [87], Sanyaolu et al. (2011) [88], Babatunde et al. (2010) [89], Dada-Adegbola et al. (2010) [90], Damen et al. (2010) [91], Umar and Bassey (2010) [92], Houmsou et al. (2009) [93], Morenikeji et al. (2009) [94], Ibidapo and Okwa (2008) [95], Adeoye et al. (2007) [96], Agbolade et al. (2007) [97], Ikeh et al. (2007) [98], Ugbomoiko and Ofoezie (2007) [99], Wagbatsoma and Aisien (2005) [100], Anosike et al. (2004) [101], Dada-Adegbola and Bakare (2004) [102], Anyaeze (2003) [103], Okoronkwo (2002) [104], Ozumba and Ozumba (2002) [105], Nwokediuko et al. (2002) [106], Nwaorgu et al. (1998) [107], Sodipo et al. (1997) [108], Udonsi et al. (1996) [109], Asaolu et al. (1992) [110], Akogun (1989) [111], Holland et al. (1989) [112], Arene (1984) [113] |
| Ghana | 28 | 36,854 | 2671 | 3.7 | 2.0–5.4 | 98.9 | <0.001 | Backhaus et al. (2024) [114], Deku et al. (2024) [115], Donkoh et al. (2023) [116], Akenten et al. (2022) [117], Fornace et al. (2022) [118], Aninagyei et al. (2020) [119], Cunningham et al. (2020) [120], Kpene et al. (2020) [121], Adu-Gyasi et al. (2018) [122], Cunningham et al. (2018) [123], Forson et al. (2017) [124], Tay et al. (2017) [125], Agboli et al. (2015) [126], Danikuu et al. (2015) [127], Duedu et al. (2015) [128], Tay et al. (2011) [129], Baidoo et al. (2010) [130], Yatich et al. (2010) [131], Verweij et al. (2009) [132], Yatich et al. (2009) [133], Yelifari et al. (2005) [134], Annan et al. (1986) [135] |
| Benin | 67 | 10,583 | 87 | 3.5 | 2.1–5.0 | 70.3 | <0.001 | Boko et al. (2016) [136], Ibikounlé et al. (2014) [137], Chippaux et al. (1990) [138] |
| Mauritania | 16 | 2503 | 72 | 2.9 | 1.2–4.6 | 68.7 | 0.001 | Ba et al. (2024) [139], Urbani et al. (1997) [140], WHO (1995) [141] |
| Senegal | 4 | 4772 | 119 | 2.8 | 0.0–5.9 | 97.0 | <0.001 | Diongue et al. (2017) [142], Sow et al. (2017) [143], Ndiaye et al. (2013) [144], Salem et al. (1994) [145] |
| Niger | 1 | 1900 | 6 | 0.3 | 0.1–0.7 | … | … | Mouchet et al. (1988) [146] |
| Burkina Faso | 5 | 12,229 | 21 | 0.2 | 0.1–0.2 | 0 | 0.758 | Sangaré et al. (2021) [147], Sangaré et al. (2015) [148], Karou et al. (2011) [149] |
| Mali | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | |
| Total | 336 | 143,112 | 6344 | 4.4 | 4.1–4.8 | 96.8 | <0.001 | |
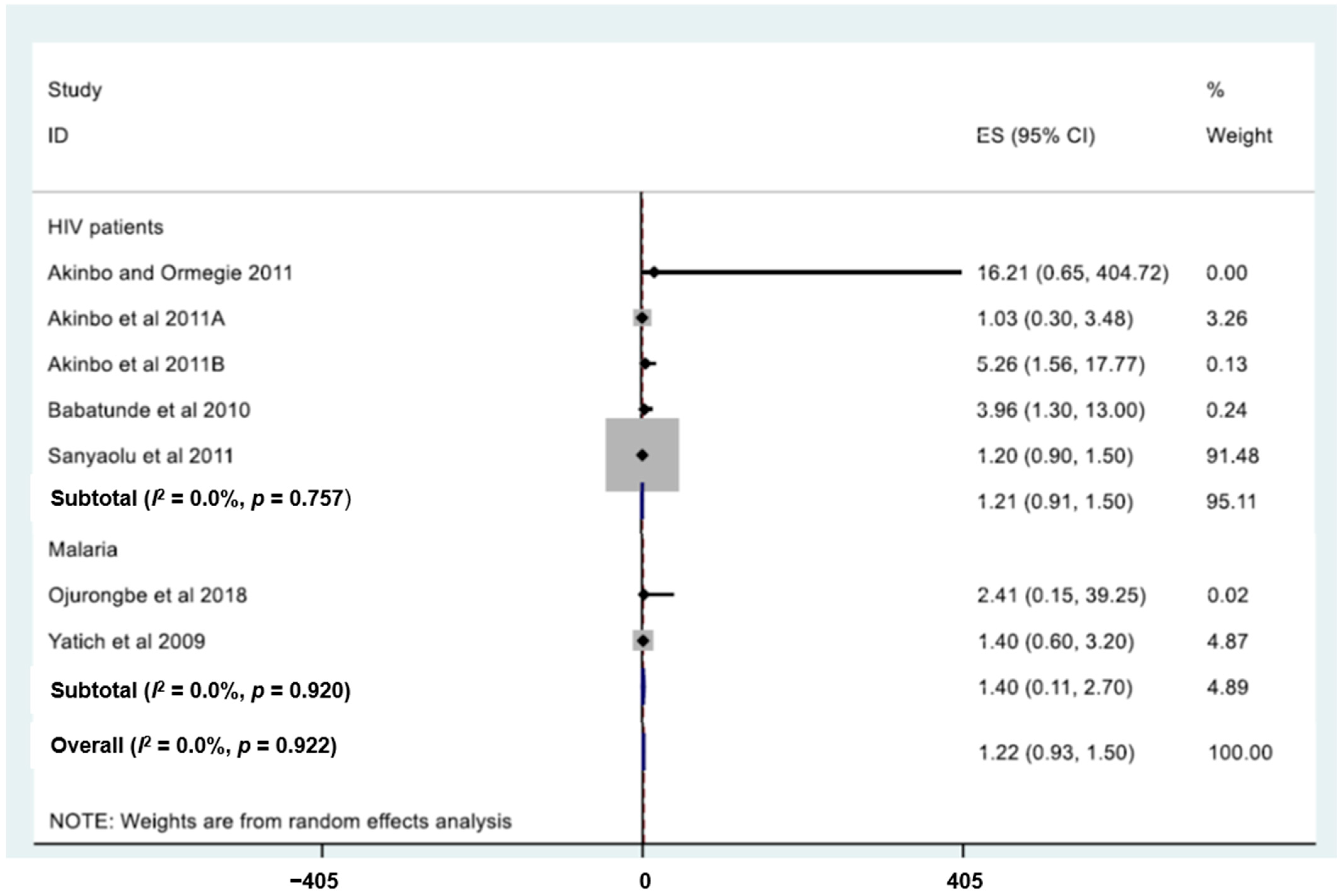
| Type of Predictor | Variable | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | HIV patients | 16.2 | 0.7–404.7 | 0.347 | [87] |
| HIV patients | 1.0 | 3.5 | 0.966 | [86] | |
| HIV patients | 5.3 | 1.6–17.8 | 0.006 | [85] | |
| HIV patients | 4.0 | 1.3–13.0 | 0.010 | [89] | |
| HIV patients | 1.2 | 0.9–1.5 | 0.067 | [88] | |
| Malaria | 2.4 | 0.2–39.3 | 0.500 | [69] | |
| Malaria | 1.4 | 0.6–3.2 | NA | [133] | |
| Symptoms | Anaemia | 3.4 | 0.2–56.8 | 0.383 | [86] |
| Anaemia | 1.7 | 0.130 | [19] | ||
| Stomach ache | 2.4 | 1.0–5.6 | 0.056 | [34] | |
| Nausea | 5.0 | 1.3–19.3 | NA | [32] | |
| WASH indicators | Use of community tap water | 6.2 | 1.4–28.2 | 0.019 | [34] |
| Water or tissue available sometime | 1.4 | 0.8–2.5 | 0.080 | [13] | |
| Water and soap available | 0.9 | 0.5–1.6 | 0.613 | [13] | |
| Demography | Pre-school-aged children | 0.3 | <0.010 | [19] | |
| 7–10 years | 3.3 | 1.8–5.8 | <0.001 | [13] | |
| Intervention | Females | 1.1 | 0.7–1.7 | 0.818 | [13] |
| MDA | 0.4 | 0.2–1.0 | 0.037 | [12] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assaré, R.K.; Ouattara, M.; Becker, S.L.; Bassa, F.K.; Diakité, N.R.; Utzinger, J.; N’Goran, E.K. Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Humans in West Africa, 1975–2024: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10110321
Assaré RK, Ouattara M, Becker SL, Bassa FK, Diakité NR, Utzinger J, N’Goran EK. Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Humans in West Africa, 1975–2024: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2025; 10(11):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10110321
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssaré, Rufin K., Mamadou Ouattara, Sören L. Becker, Fidèle K. Bassa, Nana R. Diakité, Jürg Utzinger, and Eliézer K. N’Goran. 2025. "Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Humans in West Africa, 1975–2024: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 10, no. 11: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10110321
APA StyleAssaré, R. K., Ouattara, M., Becker, S. L., Bassa, F. K., Diakité, N. R., Utzinger, J., & N’Goran, E. K. (2025). Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Humans in West Africa, 1975–2024: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 10(11), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed10110321









