A Review of Pneumatic Actuators Used for the Design of Medical Simulators and Medical Tools
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Control of Compliant Pneumatic Actuators
2.1. Compliant Actuators
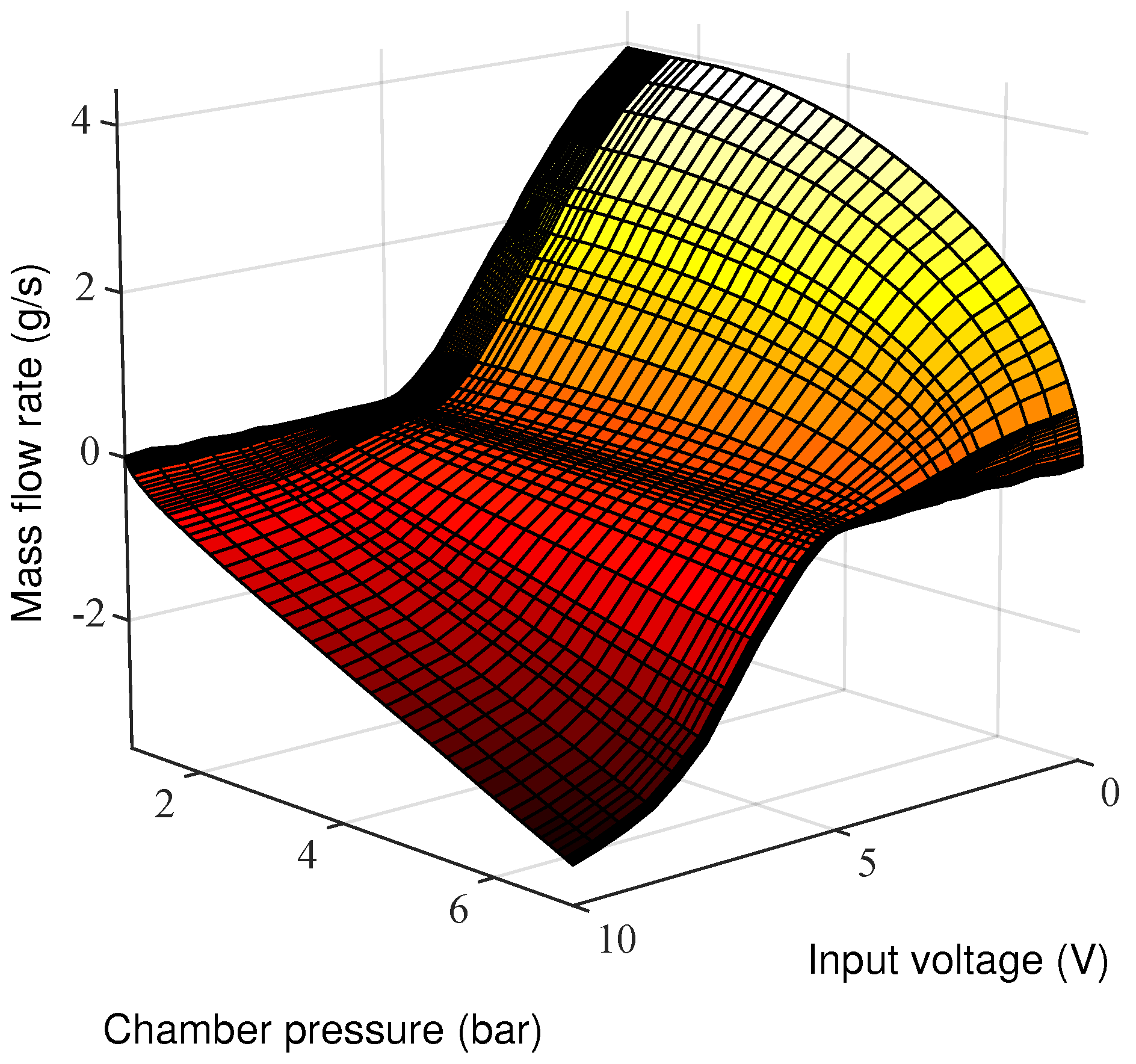
2.2. Pneumatic Control Chain
- air is a perfect gas and its kinetic energy is negligible in the chamber,
- the pressure and the temperature are homogeneous in each chamber,
- the evolution of the gas in each chamber is polytropic and is characterized by coefficient k,
- the temperature variation in chambers is negligible with respect to the supply temperature,
- the temperature in each chamber can be considered equal to the supply temperature,
- the mass flow rate leakages are negligible,
- the supply and exhaust pressures are constant.
2.3. Use in Medical Systems
2.4. Control
3. Applications
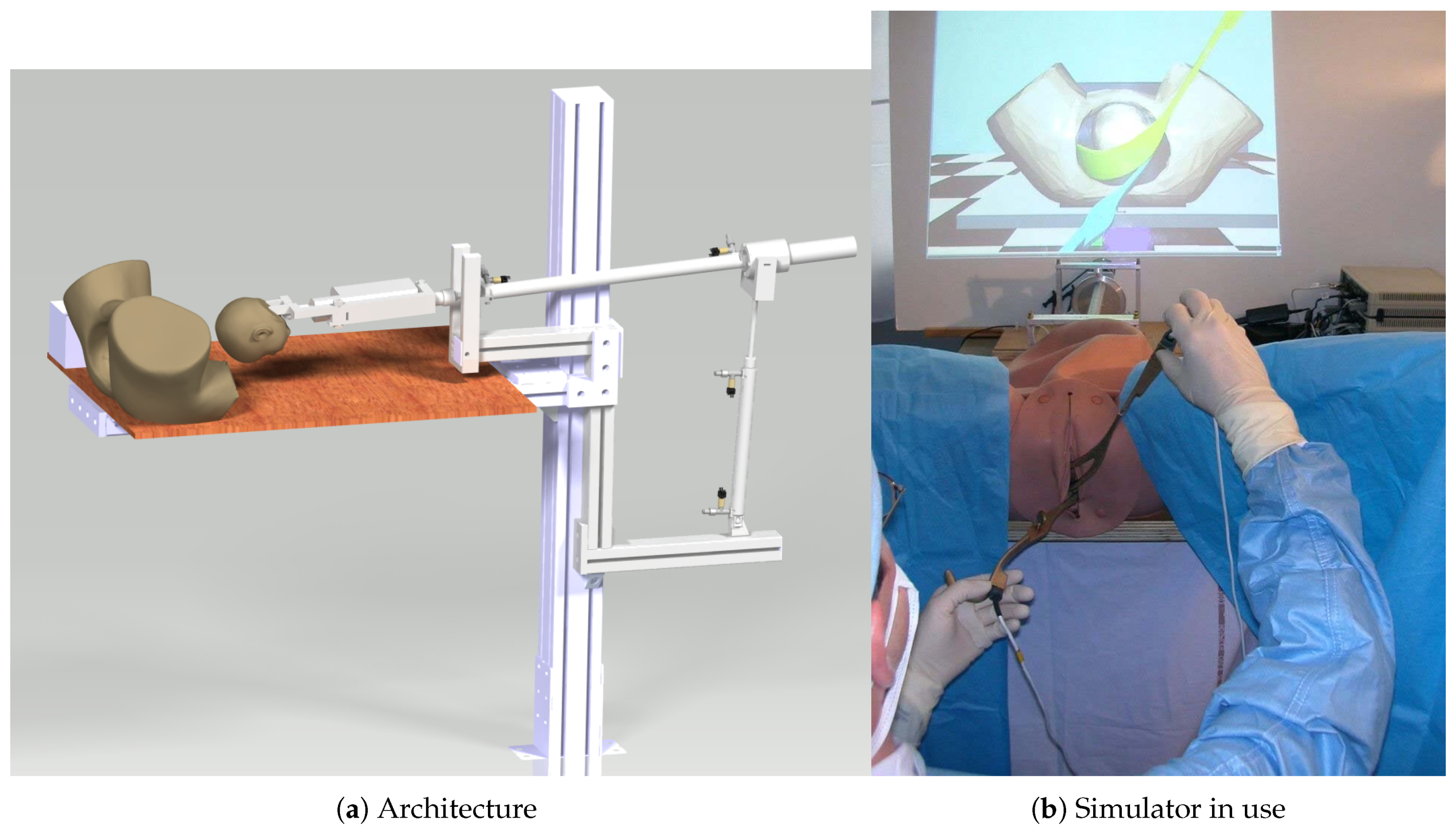
3.1. Birthsim: A Simulator to Train on Difficult Childbirths
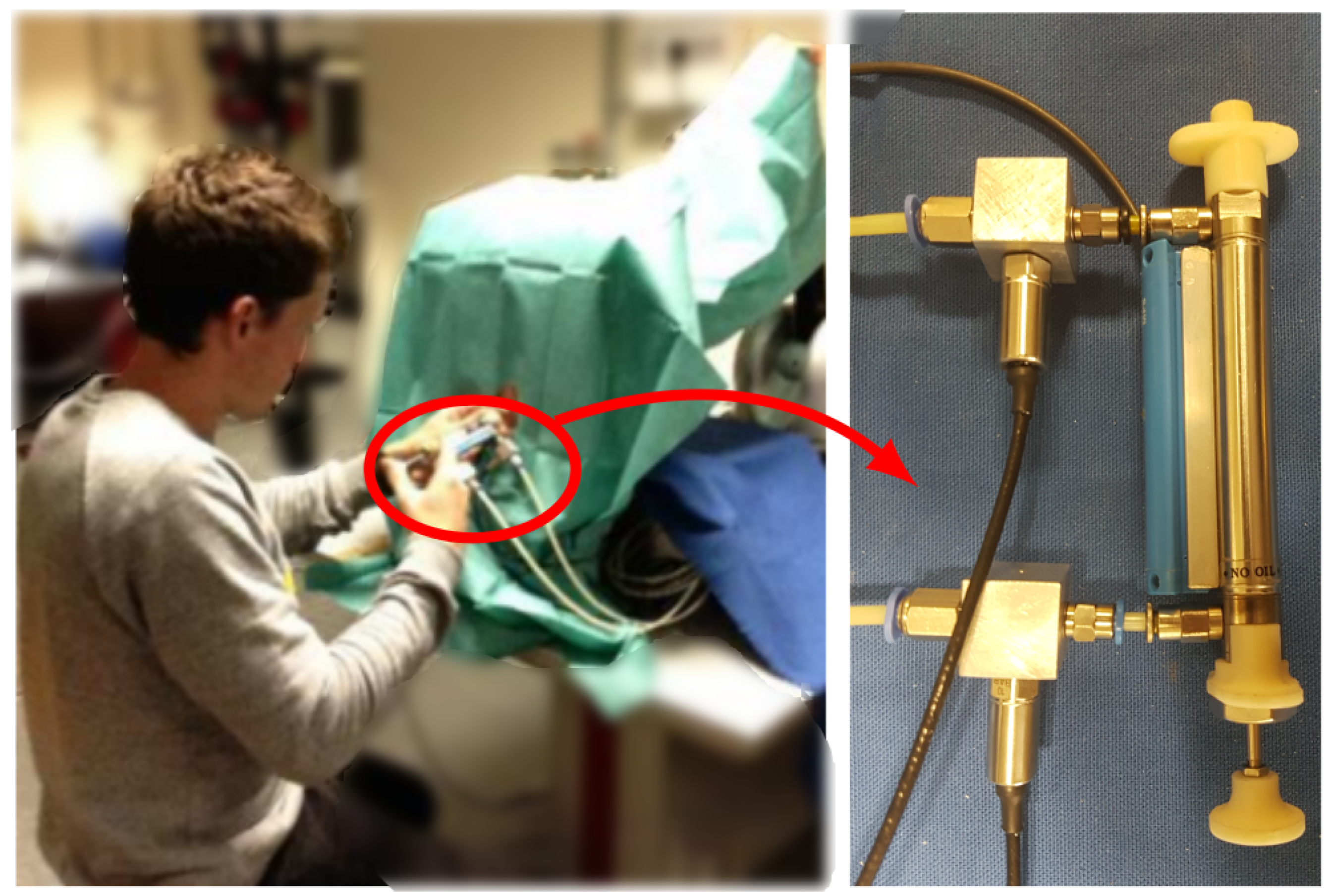
3.2. Perisim: Epidural Needle Insertion Simulator
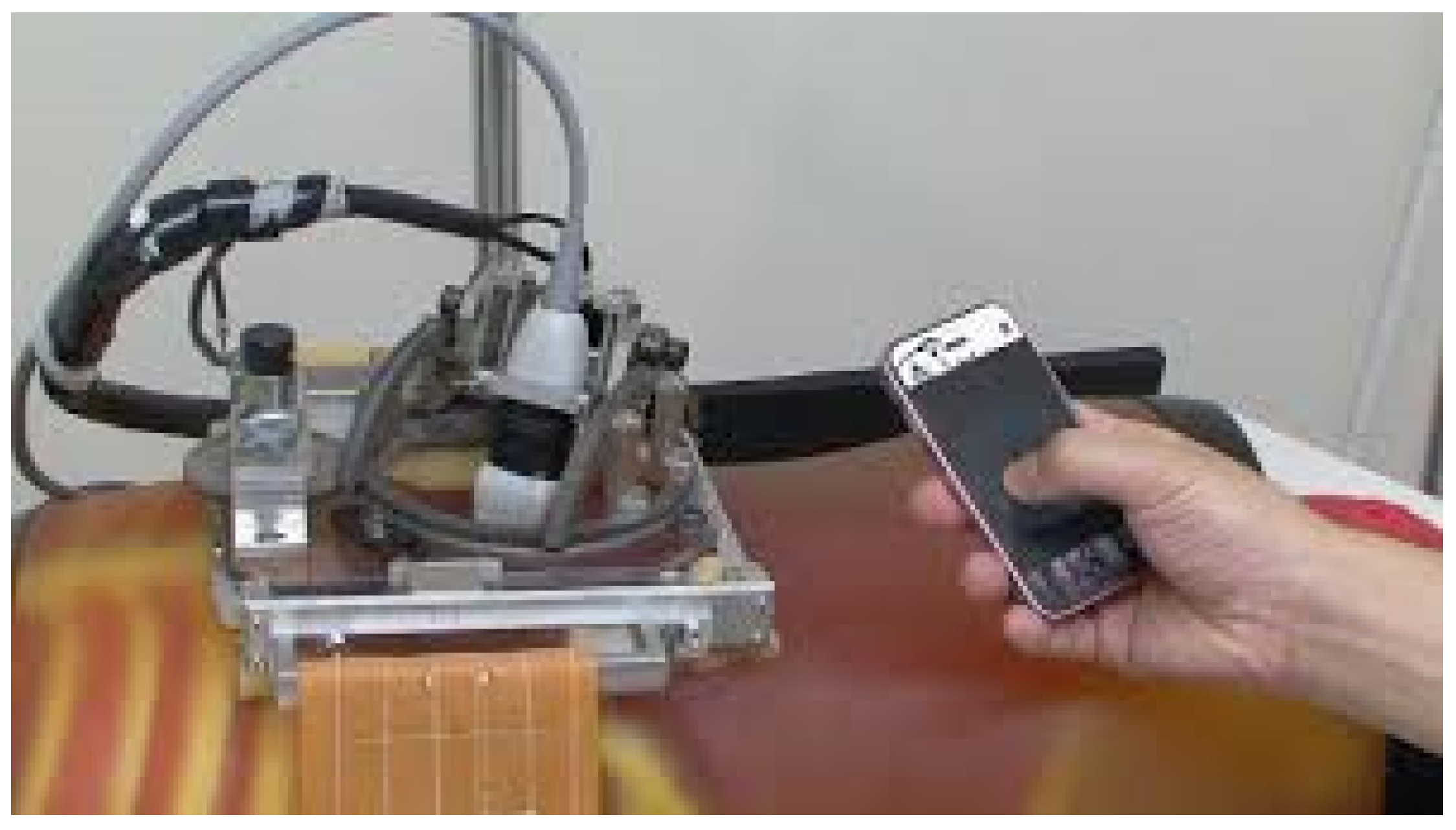
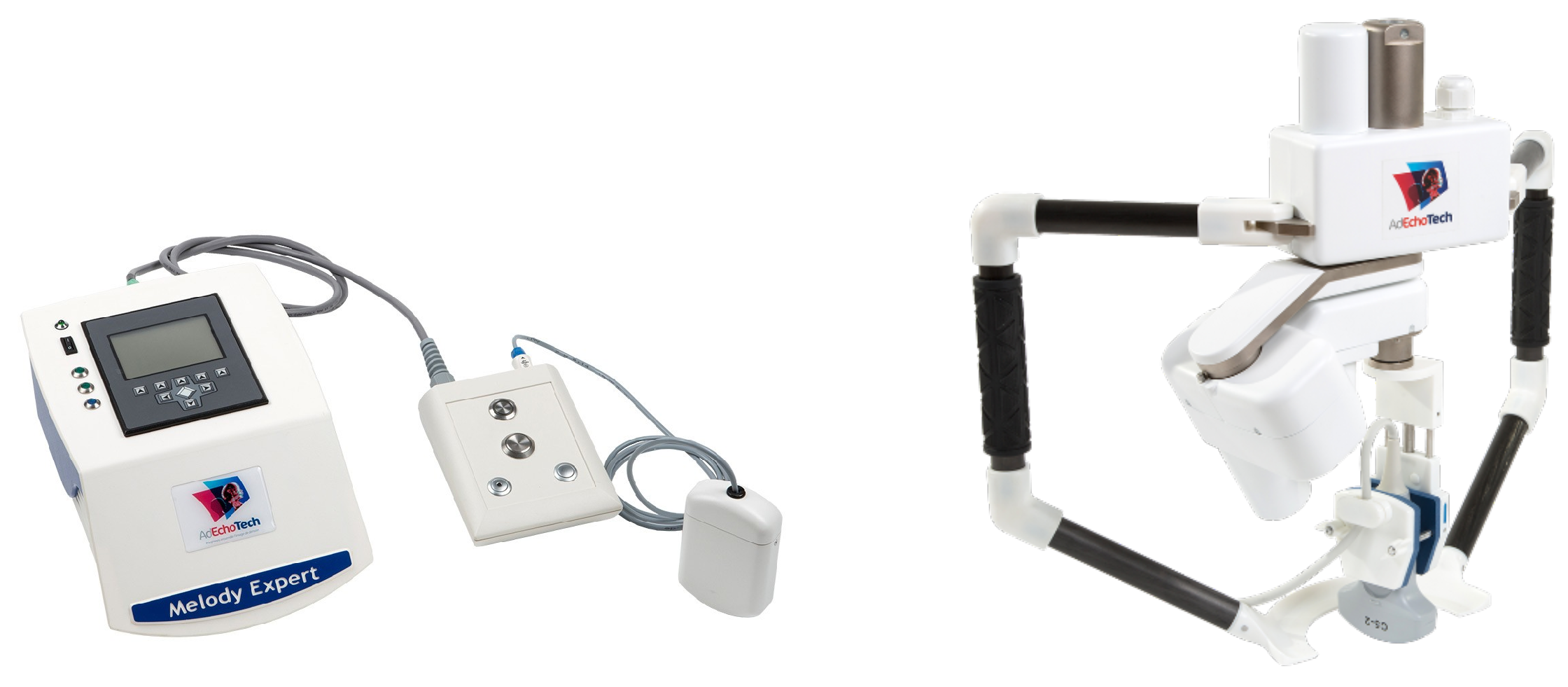
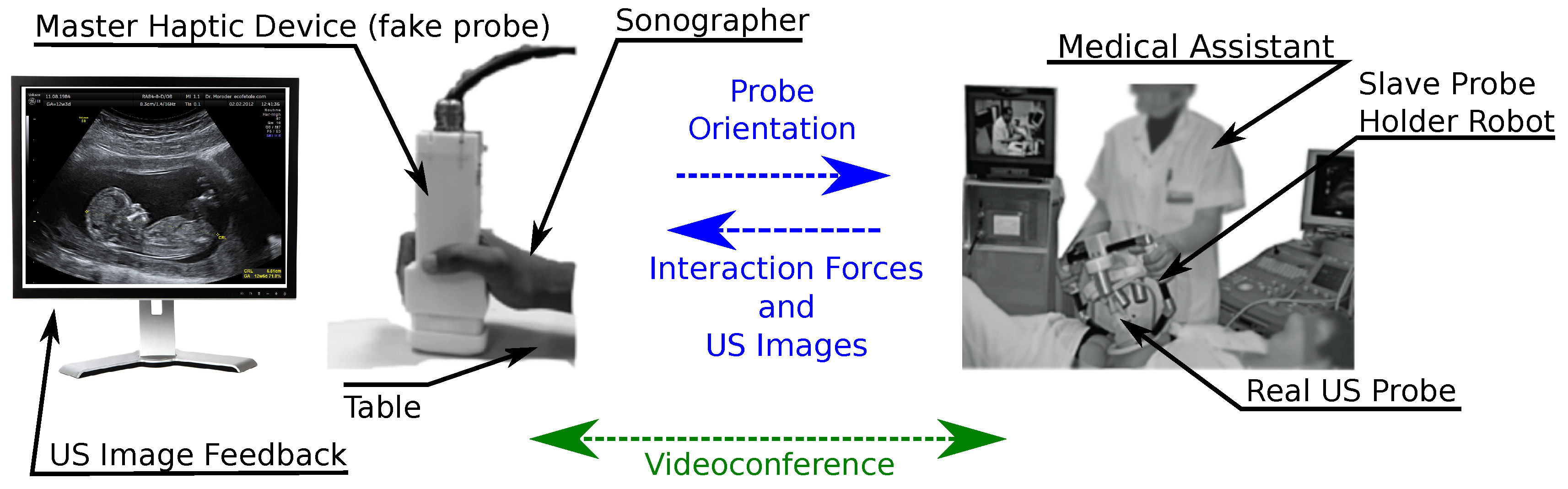
3.3. Remote Ultrasonography Haptic Master
- on the patient side, a slave robot holding the ultrasound probe;
- on the medical expert side, a hand-free probe replica;
- a TCP/IP connection links the two parts.
- a reversible mechanism with small dimensions (12 cm long, 6.5 cm wide and 3.5 cm thick at most),
- a continuous force feedback level of about 15 N and a maximum force of about 25 N, in the z-direction normal to the patient’s skin,
- a maximum stroke distance of 50 mm with a maximum velocity of 200 mm/s,
- an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensor record the prototype master probe displacements.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOF | Degrees Of Freedom |
| FL | Fuzzy Logic |
| GPC | Generalized Predictive Controller |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| LMI | Linear Matrix Inequality |
| LOR | Loss Of Resistance |
| LVDT | Linear Variable Differential Transformer |
| MIS | Minimal Invasive Surgery |
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| PAM | Pneumatic Artificial Muscle |
| PID | Proportional Integral Derivative |
| SISO | Single-Input-Single-Output |
| VIA | Variable Impedance Actuator |
| VSA | Variable Stiffness Actuator |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
References
- Reznick, R.K.; MacRae, H. Teaching Surgical Skills—Changes in the Wind. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2664–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spruit, E.N.; Band, G.P.; Hamming, J.F.; Ridderinkhof, K.R. Optimal training design for procedural motor skills: A review and application to laparoscopic surgery. Psychol. Res. 2014, 78, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danzer, E.; Dumon, K.; Kolb, G.; Pray, L.; Selvan, B.; Resnick, A.S.; Morris, J.B.; Williams, N.N. What is the cost associated with the implementation and maintenance of an ACS/APDS-based surgical skills curriculum? J. Surg. Educ. 2011, 68, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granry, J.C.; Moll, M.C. état de l’art (national et international) en matière de pratiques de simulation dans le domaine de la santé; Technical Report; Haute Autorité de la Santé (HAS): Saint-Denis La Plaine, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, C.; Hashtrudi-Zaad, K.; Sellens, R.; Abolmaesumi, P.; Mousavi, P. An Augmented Reality Haptic Training Simulator for Spinal Needle Procedures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 3009–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panait, L.; Akkary, E.; Bell, R.L.; Roberts, K.E.; Dudrick, S.J.; Duffy, A.J. The Role of Haptic Feedback in Laparoscopic Simulation Training. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 156, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, J.; de Almeida, F. Using two servovalves to improve pneumatic force control in industrial cylinders. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 66, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, D.L.; Meyer, J.; Lee, E.S.; Pevec, W.C. Training with simulation improves residents’ endovascular procedure skills. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 45, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overtoom, E.M.; Horeman, T.; Jansen, F.W.; Dankelman, J.; Schreuder, H.W.R. Haptic Feedback, Force Feedback, and Force-Sensing in Simulation Training for Laparoscopy: A Systematic Overview. J. Surg. Educ. 2019, 76, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cestari, M.; Sanz-Merodio, D.; Arevalo, J.; Garcia, E. ARES, a variable stiffness actuator with embedded force sensor for the ATLAS exoskeleton. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2014, 41, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groothuis, S.; Rusticelli, G.; Zucchelli, A.; Stramigioli, S.; Carloni, R. The Variable Stiffness Actuator vsaUT-II: Mechanical Design, Modeling, and Identification. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Tsagarakis, N.; Sardellitti, I.; Caldwell, D. A New Actuator With Adjustable Stiffness Based on a Variable Ratio Lever Mechanism. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaiwa, M.; Noritsugu, T. Development of pneumatic human interface and its application for compliance display. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2000), Nagoya, Japan, 22–28 October 2000; Volume 2, pp. 806–811. [Google Scholar]
- Semini, C.; Tsagarakis, N.; Guglielmino, E.; Focchi, M.; Cannella, F.; Caldwell, D. Design of HyQ—A hydraulically and electrically actuated quadruped robot. Syst. Control Eng. 2011, 225, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, N.; Kiyoshi, O.; Yokokura, Y.; Miyazaki, T. Force sensorless force control using notch-type friction free disturbance observer. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control (AMC), Tokyo, Japan, 9–11 March 2018; pp. 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindlbeck, C.; Haddadin, S. Unified passivity-based Cartesian force/impedance control for rigid and flexible joint robots via task-energy tanks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, N.; Neto, P.; Loureiro, A.; Moreira, A.P. Machines and control systems for friction stir welding: A review. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanca, A.; Muradore, R.; Fiorini, P. A Review of Algorithms for Compliant Control of Stiff and Fixed-Compliance Robots. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Culha, U.; Giardina, F.; Guenther, F.; Rosendo, A.; Iida, F. Soft Manipulators and Grippers: A Review. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasota, P.A.; Fong, T.; Shah, J.A. A Survey of Methods for Safe Human-Robot Interaction. Found. Trends® Robot. 2017, 5, 261–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, C.G.; Nunes, F.L.; Ranzini, E.; Nakamura, R.; Tori, R. Haptic interaction for needle insertion training in medical applications: The state-of-the-art. Med. Eng. Phys. 2019, 63, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupa, A.; Folio, D.; Novales, C.; Vieyres, P.; Li, T. Robotized Tele-Echography: An Assisting Visibility Tool to Support Expert Diagnostic. IEEE Syst. J. 2016, 10, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.I. The contribution of force feedback to human performance in the teleoperation of multiple unmanned aerial vehicles. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheddar, A.; Devine, C.; Brunel, M.; Duriez, C.; Sibony, O. Preliminary design of a childbirth simulator haptic feedback. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Robots and Systems Conference, Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004; Volume 4, pp. 3270–3275. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ham, R.; Sugar, T.; Vanderborght, B.; Hollander, K.; Lefeber, D. Compliant actuator designs. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2009, 16, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Vanderborght, B.; Van Ham, R.; Wang, Q.; Van Damme, M.; Xie, G.; Lefeber, D. Step Length and Velocity Control of a Dynamic Bipedal Walking Robot With Adaptable Compliant Joints. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, J. Active stiffness control of a manipulator in cartesian coordinates. In Proceedings of the 1980 19th IEEE Conference onDecision and Control including the Symposium on Adaptive Processes, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 10–12 December 1980; pp. 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, N. Stable execution of contact tasks using impedance control. In Proceedings of the 1987 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Raleigh, NC, USA, 31 March–3 April 1987; Volume 4, pp. 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, S. Hybrid position/Force control of multi-arm cooperating robots. In Proceedings of the 1986 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–10 April 1986; Volume 3, pp. 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, D.; Mohan, B.; Muthuramalingam, T. A review on recent research trends in servo pneumatic positioning systems. Precis. Eng. 2017, 49, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dov, D.; Salcudean, S. A force-controlled pneumatic actuator for use in teleoperation masters. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA’93), Atlanta, GA, USA, 2–6 May 1993; pp. 938–943. [Google Scholar]
- Le, M.; Pham, M.; Tavakoli, M.; Moreau, R.; Simon, J.; Redarce, T. Bilateral Control of a Nonlinear Pneumatic Teleoperation System with Solenoid Valves. Trans. Control Syst. Technol. (TCST) 2013, 21, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognon, C.; Wu, A.R.; Mintchev, S.; Ijspeert, A.; Floreano, D. Haptic Guidance with a Soft Exoskeleton Reduces Error in Drone Teleoperation. In Haptics: Science, Technology, and Applications; Prattichizzo, D., Shinoda, H., Tan, H.Z., Ruffaldi, E., Frisoli, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkseven, M.; Ueda, J. Model-Based Force Control of Pneumatic Actuators with Long Transmission Lines. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Lim, J.H.; Nasrallah, F.; Goh, J.C.H.; Yeow, R.C.H. A soft exoskeleton for hand assistive and rehabilitation application using pneumatic actuators with variable stiffness. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 25–30 May 2015; pp. 4967–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, C.M.; Gillespie, M.T.; Hyatt, P.; Rupert, L.; Sherrod, V.; Killpack, M.D. A New Soft Robot Control Method: Using Model Predictive Control for a Pneumatically Actuated Humanoid. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2016, 23, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, G.S.; Iordachita, I.; Csoma, C.; Tokuda, J.; DiMaio, S.P.; Tempany, C.M.; Hata, N.; Fichtinger, G. MRI-Compatible Pneumatic Robot for Transperineal Prostate Needle Placement. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2008, 13, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugurlu, B.; Forni, P.; Doppmann, C.; Morimoto, J. Torque and variable stiffness control for antagonistically driven pneumatic muscle actuators via a stable force feedback controller. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiziani, L.O.; Cahoon, T.W.; Hammond, F.L. Sensorized pneumatic muscle for force and stiffness control. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 5545–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okui, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakamura, T. Delta-type four-DOF force-feedback device composed of pneumatic artificial muscles and magnetorheological clutch and its application to lid opening. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 064003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, B. The Analysis and Design of Pneumatic Systems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson, S.; Tavakoli, M.; Lelevé, A.; Pham, M.T. High-fidelity sliding mode control of a pneumatic haptic teleoperation system. Adv. Robot. 2014, 28, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrow, J.; McDonell, B. Modeling, identification, and control of a pneumatically actuated, force controllable robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1998, 14, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herzig, N.; Moreau, R.; Redarce, T.; Abry, F.; Brun, X. Nonlinear position and stiffness Backstepping controller for a two Degrees of Freedom pneumatic robot. Control Eng. Pract. 2018, 73, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.; Guldner, J.; Shi, J. Sliding Mode Control in Electro-Mechanical Systems; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.K. Nonlinear Systems I; Prentice Hal: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toedtheide, A.; Lilge, T.; Haddadin, S. Antagonistic Impedance Control for Pneumatically Actuated Robot Joints. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 1, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhan, A.; Jeon, S. Pneumatic Actuation in Haptic-Enabled Medical Simulators: A Review. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3184–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Gu, Y.; Lee, D.Y. A pneumatic haptic module for simulation of catheters used in gastrointestinal endoscopy. In Proceedings of the 2016 16th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Gyeongju, Korea, 16–19 October 2016; pp. 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, E.; Rea, M.; Gedroyc, W.; Ristic, M. Control of a Master-Slave Pneumatic System for Teleoperated Needle Insertion in MRI. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 2595–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, R.; Kanno, T.; Endo, G.; Kawashima, K. Pneumatically driven handheld forceps with force display operated by motion sensor. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, T.; Akagi, T.; Dohta, S.; Matsui, Y. Development of Flexible Displacement Sensor Using Ultrasonic Sensor for Flexible Pneumatic Robot Arm. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 76, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fras, J.; Althoefer, K. Soft Pneumatic Prosthetic Hand. In Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems; Giuliani, M., Assaf, T., Giannaccini, M.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Gopura, R.; Bandara, D.; Kiguchi, K.; Mann, G. Developments in hardware systems of active upper-limb exoskeleton robots: A review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ferguson, P.W.; Ma, J.; Rosen, J. Chapter 4—Upper Limb Wearable Exoskeleton System for Rehabilitation: State of the Art Review and a Case Study of the EXO-UL8—Dual-Arm Exoskeleton System. In Wearable Technology in Medicine and Health Care; Tong, R.K.Y., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsotti, M.; Stroppa, F.; Mastronicola, N.; Marcheschi, S.; Frisoli, A. Teleoperated Bilateral-Arm Rehabilitation with ALEx Rehab Station. In Converging Clinical and Engineering Research on Neurorehabilitation III; Masia, L., Micera, S., Akay, M., Pons, J.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veale, A.J.; Xie, S.Q. Towards compliant and wearable robotic orthoses: A review of current and emerging actuator technologies. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polygerinos, P.; Correll, N.; Morin, S.A.; Mosadegh, B.; Onal, C.D.; Petersen, K.; Cianchetti, M.; Tolley, M.T.; Shepherd, R.F. Soft Robotics: Review of Fluid-Driven Intrinsically Soft Devices; Manufacturing, Sensing, Control, and Applications in Human-Robot Interaction. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchetti, M.; Laschi, C.; Menciassi, A.; Dario, P. Biomedical applications of soft robotics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Pham, M.T.; Redarce, T. Sensor-based guidance control of a continuum robot for a semi-autonomous colonoscopy. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2009, 57, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, A.A.; Okamura, A.M. Controllable Surface Haptics via Particle Jamming and Pneumatics. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2015, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Kappers, A.M.L.; Fujiwara, M.; Sano, A. A Pneumatic Tactile Ring for Instantaneous Sensory Feedback in Laparoscopic Tumor Localization. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2018, 11, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talhan, A.; Kim, H.; Kumar, S.; Raza, A.; Jeon, S. Pneumatic Actuated Haptic Glove to Interact with the Virtual Human. In Haptic Interaction; Kajimoto, H., Lee, D., Kim, S.Y., Konyo, M., Kyung, K.U., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 213–215. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudeni, C.; Meli, L.; Prattichizzo, D. A Novel Pneumatic Force Sensor for Robot-Assisted Surgery. In Haptics: Science, Technology, and Applications; Prattichizzo, D., Shinoda, H., Tan, H.Z., Ruffaldi, E., Frisoli, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 587–599. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, W.; Su, H.; Li, G.; Fischer, G.S. Teleoperation system with hybrid pneumatic-piezoelectric actuation for MRI-guided needle insertion with haptic feedback. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 4092–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinq-Mars, M.; Gurocak, H. Pneumatic cylinder with magnetorheological brake using serpentine and helix flux guide as a linear hybrid actuator for haptics. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2017, 28, 1303–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, K.; Miyazaki, R.; Kanno, T.; Endo, G.; Kawashima, K. Pneumatically Driven Multi-DOF Surgical Forceps Manipulator with a Bending Joint Mechanism Using Elastic Bodies. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2016, 28, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.A.; He, L.; Sepehri, N. Design and experimental study of a dynamical adaptive backstepping-sliding mode control scheme for position tracking and regulating of a low-cost pneumatic cylinder. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2016, 26, 853–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, J. Study of pneumatic processes in the continuous control of motion with compressed air: Part I and II. Trans. ASME 1956, 78, 233–249. [Google Scholar]
- Wikander, J. Adaptive Control of Pneumatic Cylinders. Ph.D. Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology, Department of Machine Elements, Stockholm, Sweden, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Chikh, L.; Poignet, P.; Pierrot, F.; Michelin, M. A Generalized Predictive Force Controller for electropneumatic cylinders. In Proceedings of the 8th IFAC Symposium on Nonlinear Control Systems (NOLCOS’2010), Bologna, Italy, 1–3 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chikh, L.; Poignet, P.; Pierrot, F.; Baradat, C. A mixed GPC-H infinity robust cascade position-pressure control strategy for electropneumatic cylinders. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA’10), Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Wang, X.; Fan, J.; Kaynak, O. Adaptive Backstepping Control of a Pneumatic System With Unknown Model Parameters and Control Direction. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 64471–64482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmsiri, N.; Sun, Y.; Yang, C.; Sepehri, N. Bilateral teleoperation of a pneumatic actuator: Experiment and stability analysis. Int. J. Fluid Power 2015, 16, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Ayadi, A.; Smaoui, M.; Maatoug, T.; Farza, M.; M’saad, M. Position Control of Pneumatic System Using High Gain and Backstepping Controllers. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2019, 141, 081001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abry, F.; Brun, X.; Sesmat, S.; Bideaux, E. Nonlinear position control of a pneumatic actuator with closed-loop stiffness and damping tuning. In Proceedings of the European Control Conference 2013, Zurich, Switzerland, 17–19 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abry, F.; Brun, X.; Sesmat, S.; Bideaux, E.; Ducat, C. Electropneumatic Cylinder Backstepping Position Controller Design With Real-Time Closed-Loop Stiffness and Damping Tuning. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2016, 24, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hirzinger, G. Joint torque based Cartesian impedance control for the DLR hand. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME Intl. Conf. on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Atlanta, GA, USA, 19–23 September 1999; pp. 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sénac, T.; Lelevé, A.; Moreau, R.; Krahenbuhl, L.; Sigwalt, F.; Bauer, C.; Rouby, Q. Designing an accurate and customizable epidural anesthesia haptic simulator. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lapeer, R.; Chen, M.; Villagrana, J. Simulating Obstetric Forceps Delivery in an Augmented Environment. In Proceedings of the AMI/ARCS sattelite workshop of MICCAI 2004, Copenhagen, Denmark, 30 September 2004; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sielhorst, T.; Blum, T.; Navab, N. Synchronizing 3D Movements for Quantitative Comparison and Simultaneous Visualization of Actions. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR’05), Washington, DC, USA, 5 December 2005; pp. 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, A.F.; Acampora, G.; Loia, V.; Ricciardi, S.; Vasilakos, A.V. A Pervasive Visual-Haptic Framework for Virtual Delivery Training. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deering, S.; Brown, J.; Hodor, J.; Satin, A.J. Simulation training and resident performance of singleton vaginal breech delivery. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 107, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, R.; Pham, M.T.; Redarce, T.; Betemps, M.; Dupuis, O. A new mechanical birth simulator: BirthSIM. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37566), Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, R.; Pham, M.T.; Silveira, R.; Redarce, T.; Brun, X.; Dupuis, O. Design of a New Instrumented Forceps: Application to Safe Obstetrical Forceps Blade Placement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konrad, C.; Schupfer, G.; Wietlisbach, M.; Gerber, H. Learning Manual Skills in Anesthesiology: Is There a Recommended Number of Cases for Anesthetic Procedures? Anesth. Analg. 1998, 86, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, N.; Dubey, N.; Venketesh, M.Y.; Wee, K.; Isaacs, R. A review of epidural simulators: Where are we today? Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 1235–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, V.; van Gerwen, D.; van den Dobbelsteen, J.J.; Dankelman, J. Design and validation of an epidural needle insertion simulator with haptic feedback for training resident anaesthesiologists. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Haptics Symposium (HAPTICS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 March 2012; pp. 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Magill, J.C.; Byl, M.F.; Hinds, M.F.; Agassounon, W.; Pratt, S.D.; Hess, P.E. A Novel Actuator for Simulation of Epidural Anesthesia and Other Needle Insertion Procedures. Simul. Heal. J. Soc. Simul. Healthc. 2010, 5, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubey, V.; Vaughan, N.; Wee, M.Y.K.; Isaacs, R. Biomedical Engineering in Epidural Anaesthesia Research. In Practical Applications in Biomedical Engineering; Andrade, A., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, T.; Annaswamy, T.M.; Srinivasan, M.A. Development and Evaluation of an Epidural Injection Simulator with Force Feedback for Medical Training. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2001, 81, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senac, T.; Lelevé, A.; Moreau, R. Control laws for pneumatic cylinder in order to emulate the Loss of Resistance principle. In Proceedings of the IFAC 2017—20th World Congress of the International Federation of Automatic Control, Toulouse, France, 9–14 July 2017; IIFAC: Toulouse, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gourdon, A.; Poignet, P.; Poisson, G.; Vieyres, P.; Marche, P. A new robotic mechanism for medical application. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM 1999), Atlanta, GA, USA, 19–23 September 1999; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courreges, F.; Smith-Guerin, N.; Poisson, G.; Vieyres, P.; Gourdon, A.; Szpieg, M.; Merigeaux, O. Real-time exhibition of a simulated space tele-echography using an ultra-light robot. In Proceedings of the ISAIRAS Conference, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–22 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vilchis Gonzales, A.; Cinquin, P.; Troccaz, J.; Guerraz, A.; Hennion, B.; Pellissier, F.; Thorel, P.; Courreges, F.; Gourdon, A.; Poisson, G.; et al. TER: A System for Robotic Tele-echography. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2001); Niessen, W., Viergever, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Volume 2208, pp. 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, K.; Kimura, E.; Tateishi, N.; Ishihara, K. Three dimensional motion mechanism of ultrasound probe and its application for tele-echography system. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Maui, HI, USA, 29 October–3 November 2001; Volume 2, pp. 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, F.; Sepehri, N. A novel hand-controller for remote ultrasound imaging. Mechatronics 2008, 18, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouaille, L.; Vieyres, P.; Poisson, G. Process of optimisation for a 4 DOF tele-echography robot. Robotica 2012, 30, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Sugano, S.; Iwata, H. Portable and Attachable TeleEchography Robot System: FASTele. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 487–490. [Google Scholar]
- Mathiassen, K.; Fjellin, J.E.; Glette, K.; Hol, P.K.; Elle, O.J. An Ultrasound Robotic System Using the Commercial Robot UR5. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.; Park, J.; Khatib, O. Interface Design and Control Strategies for a Robot Assisted Ultrasonic Examination System. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Experimental Robotics, Marrakech and Essaouira, Morocco, 15–18 June 2014; Khatib, O., Kumar, V., Sukhatme, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arent, K.; Cholewiński, M.; Chojnacki, L.; Domski, W.; Drwięga, M.; Jakubiak, J.; Janiak, M.; Kreczmer, B.; Kurnicki, A.; Stańczyk, B.; et al. Selected topics in design and application of a robot for remote medical examination with the use of ultrasonography and ascultation from the perspective of the REMEDI project. J. Autom. Mob. Robot. Intell. Syst. 2017, 11, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courreges, F.; Novales, C.; Poisson, G.; Vieyres, P. Modelisation, commande geometrique et utilisation d’un robot portable de tele-echographie: Teresa. J. Eur. Des Syst. Autom. (JESA) 2009, 43, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieyres, P.; Novales, C.; Rivas, R.; Vilcahuaman, L.; Sandoval, J.; Clark, T.; DeStigter, K.; Josserand, L.; Morrison, Z.; Robertson, A.; et al. The next challenge for WOrld wide Robotized Tele-Echography eXperiment (WORTEX 2012): From engineering success to healthcare delivery. In Proceedings of the TUMI II, Congreso Peruano de Ingeniera Biomedical Bioingeniera, Biotecnologica y Fisica Medica, Lima, Peru, 29–31 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mourioux, G.; Novales, C.; Smith-Guerin, N.; Vieyres, P.; Poisson, G. A free haptic device for tele-echography. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Research and Education in Mechatronics (REM’2005), Annecy, France, 30 June–1 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Charron, G.; Morette, N.; Essomba, T.; Vieyres, P.; Canou, J.; Fraisse, P.; Zeghloul, S.; Krupa, A.; Arbeille, P. Robotic Platform for an Interactive Tele-echographic System: The PROSIT ANR-2008 project. In Proceedings of the Hamlyn Symposium on Medical Robotics, London, UK, 25 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vieyres, P.; Sandoval, J.; Josserand, L.; Novales, C.; Chiccoli, M.; Morette, N.; Fonte, A.; Avgousti, S.; Voskarides, S.; Kasparis, T. An Anticipative Control Approach and Interactive GUI to Enhance the Rendering of the Distal Robot Interaction with Its Environment During Robotized Tele-Echography: Interactive Platform for Robotized Tele-Echography. Int. J. Monit. Surveill. Technol. Res. 2013, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieyres, P.; Poisson, G.; Courreges, F.; Smith-Guerin, N.; Novales, C.; Arbeille, P. A Tele-Operated Robotic System for Mobile Tele-Echography: The Otelo Project. In M-Health; Istepanian Robert, S., Laxminarayan, S., Pattichis, C.S., Eds.; Topics in Biomedical Engineering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
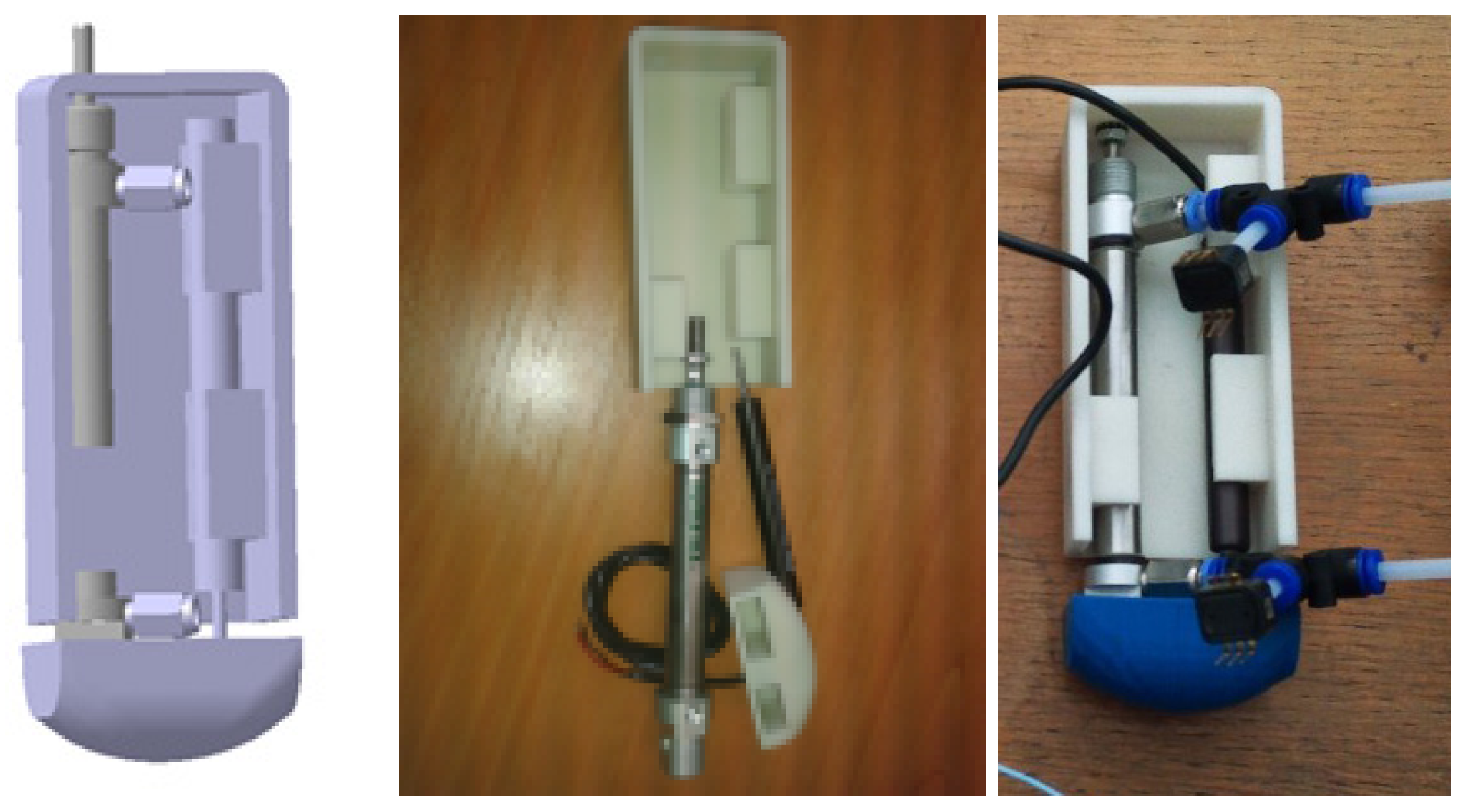
- Abdallah, I.; Gatwaza, F.; Morette, N.; Lelevé, A.; Novales, C.; Nouaille, L.; Brun, X.; Vieyres, P. A Pneumatic Haptic Probe Replica for Tele-Robotized Ultrasonography. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Multimedia (ICSM-2018), Toulon, France, 24–26 August 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Chapter Smart Multimedia (ICSM 2018). Basu, A., Berretti, S., Eds.; Springer: Toulon, France, 2018; Volume 11010. [Google Scholar]
- Alamilla D., M.d.l.A.; Moreau, R.; Redarce, T. A new method to render virtual walls for haptic systems: “Tracking wall”. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Conference on Mechatronics and Control Engineering (ICMCE 2018), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 27–29 November 2018. [Google Scholar]




| Symbol | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| y | Piston position | m |
| l | Stroke of the rod | m |
| Piston velocity | m/s | |
| M | load mass | kg |
| Chamber P section area | m | |
| Chamber N section area | m | |
| Pressure inside chamber P | Pa | |
| Pressure inside chamber N | Pa | |
| b | Viscous friction coefficient | N·s/m |
| Stiction force | N | |
| Force applied by the atmospheric pressure on the cylinder piston 1 | N | |
| r | Perfect gas constant | J/(kg·K) |
| Temperature of the supply air | K | |
| Chamber P volume at position y | ||
| Chamber N volume at position y | ||
| Mass flow rate entering the chamber P | kg/s | |
| Mass flow rate entering the chamber N | kg/s | |
| Chamber-P-servovalve input voltage | V | |
| Chamber-N-servovalve input voltage | V |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sénac, T.; Lelevé, A.; Moreau, R.; Novales, C.; Nouaille, L.; Pham, M.T.; Vieyres, P. A Review of Pneumatic Actuators Used for the Design of Medical Simulators and Medical Tools. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2019, 3, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3030047
Sénac T, Lelevé A, Moreau R, Novales C, Nouaille L, Pham MT, Vieyres P. A Review of Pneumatic Actuators Used for the Design of Medical Simulators and Medical Tools. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction. 2019; 3(3):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3030047
Chicago/Turabian StyleSénac, Thibault, Arnaud Lelevé, Richard Moreau, Cyril Novales, Laurence Nouaille, Minh Tu Pham, and Pierre Vieyres. 2019. "A Review of Pneumatic Actuators Used for the Design of Medical Simulators and Medical Tools" Multimodal Technologies and Interaction 3, no. 3: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3030047
APA StyleSénac, T., Lelevé, A., Moreau, R., Novales, C., Nouaille, L., Pham, M. T., & Vieyres, P. (2019). A Review of Pneumatic Actuators Used for the Design of Medical Simulators and Medical Tools. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 3(3), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti3030047






