Non-Linear Impacts of Social and Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services: A Threshold Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
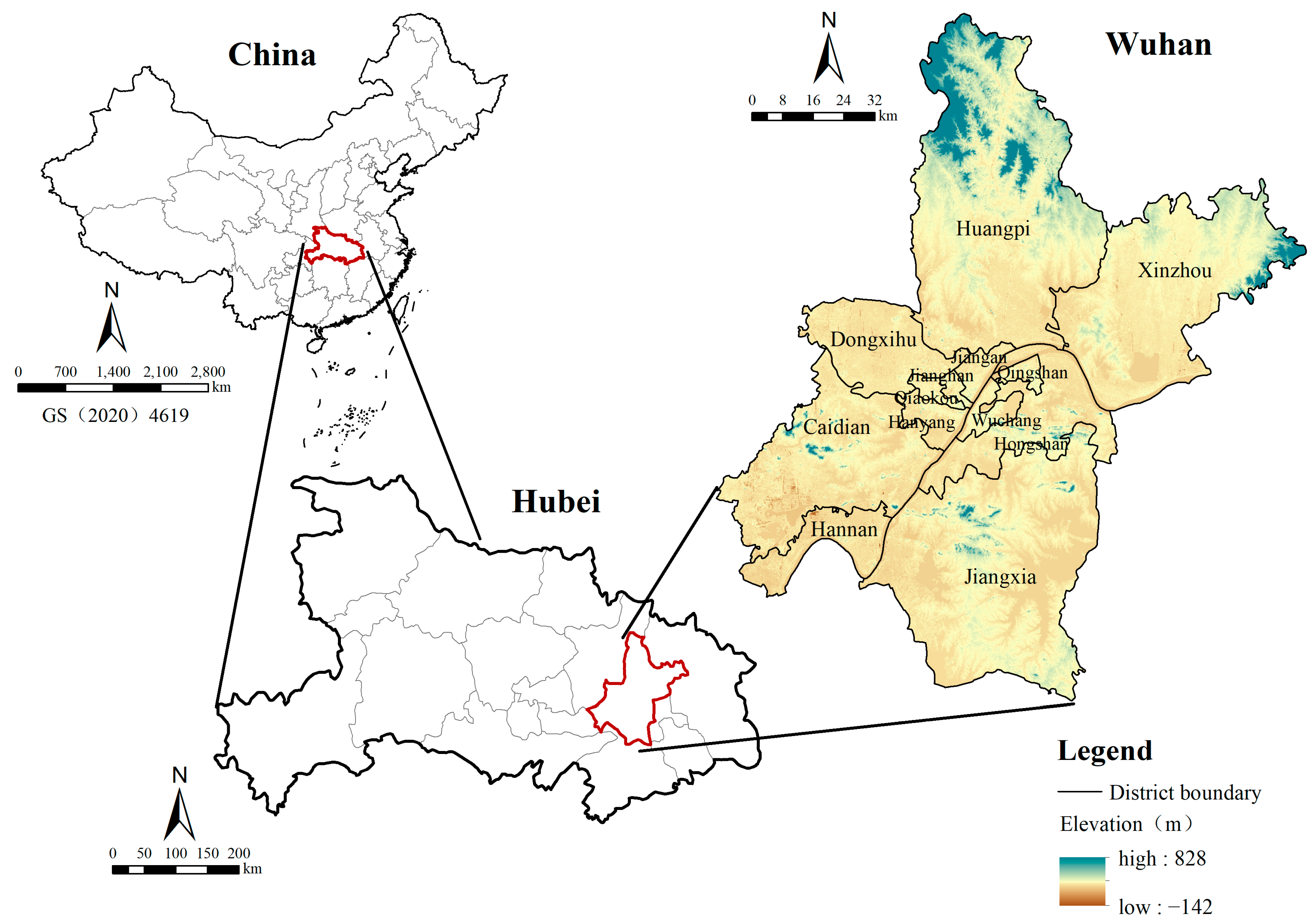
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Description
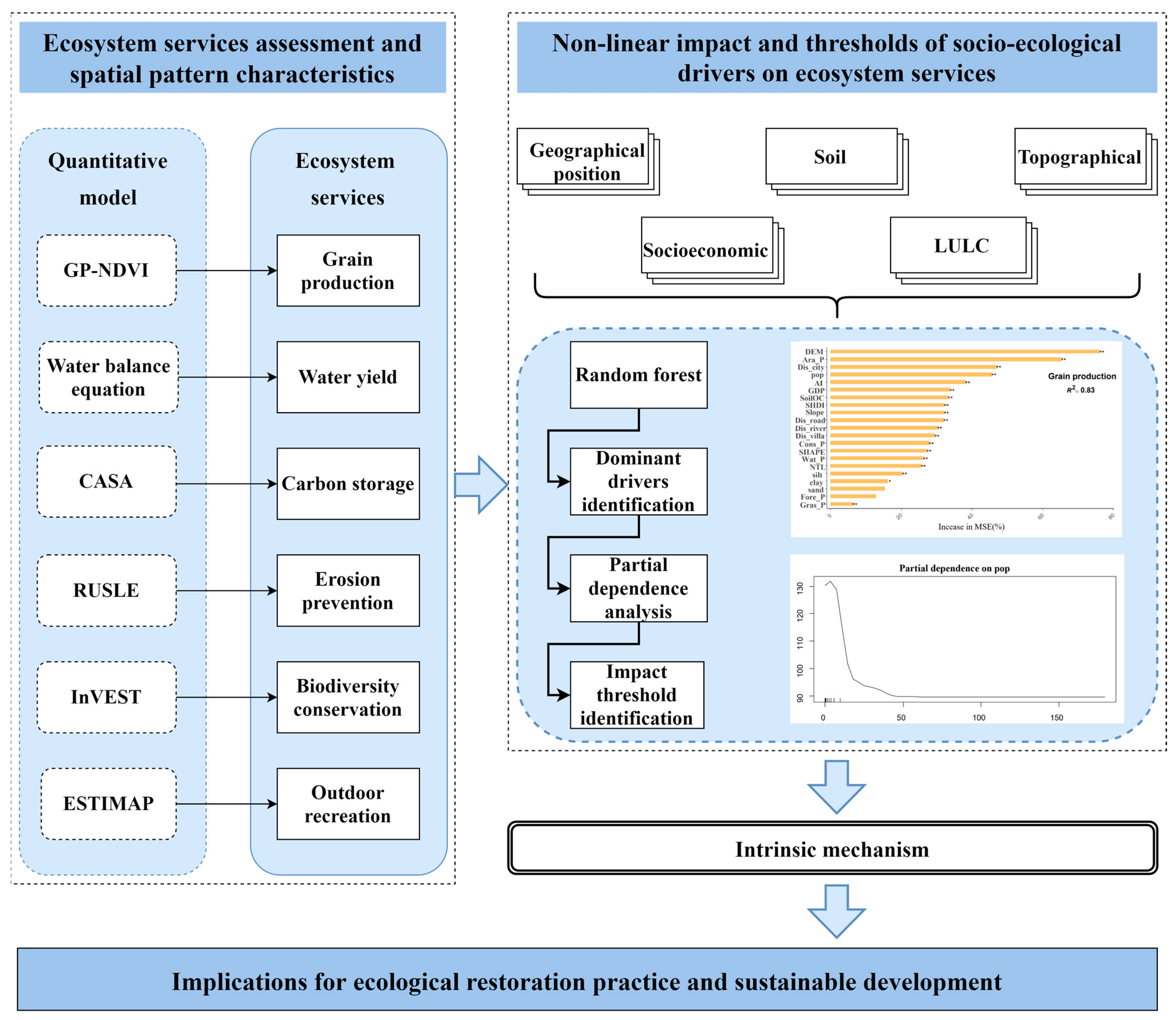
2.3. Method Framework
2.4. Selecting and Evaluating Ecosystem Services
2.5. Selecting Socio-Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services
2.6. Quantifying Impacts and Thresholds of Socio-Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services
2.6.1. Identifying Dominant Socio-Ecological Drivers on Ecological Services
2.6.2. Quantifying Non-Linear Impacts and Thresholds of Dominant Socio-Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distributions of Ecosystem Services
3.2. Dominant Socio-Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services
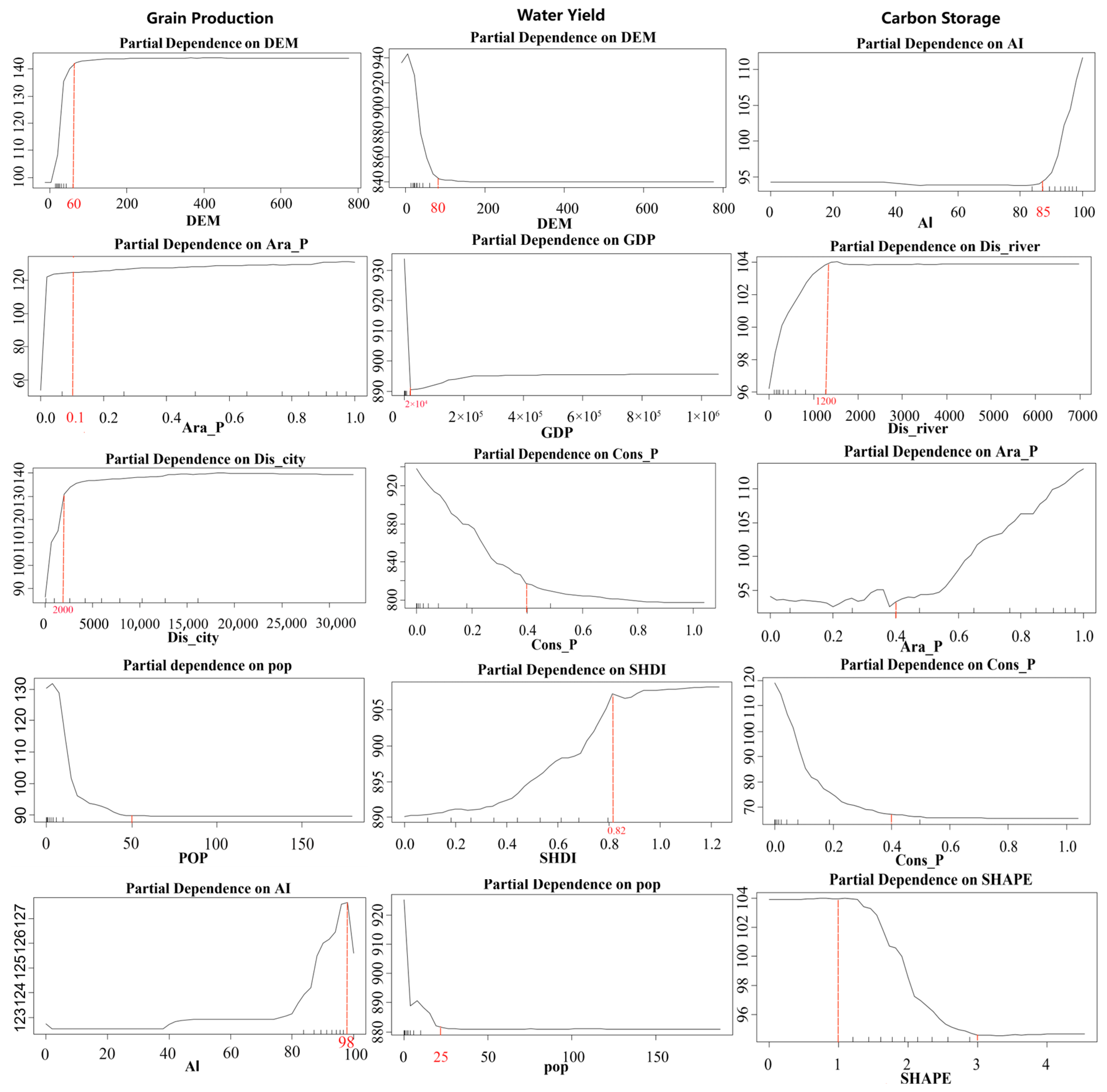
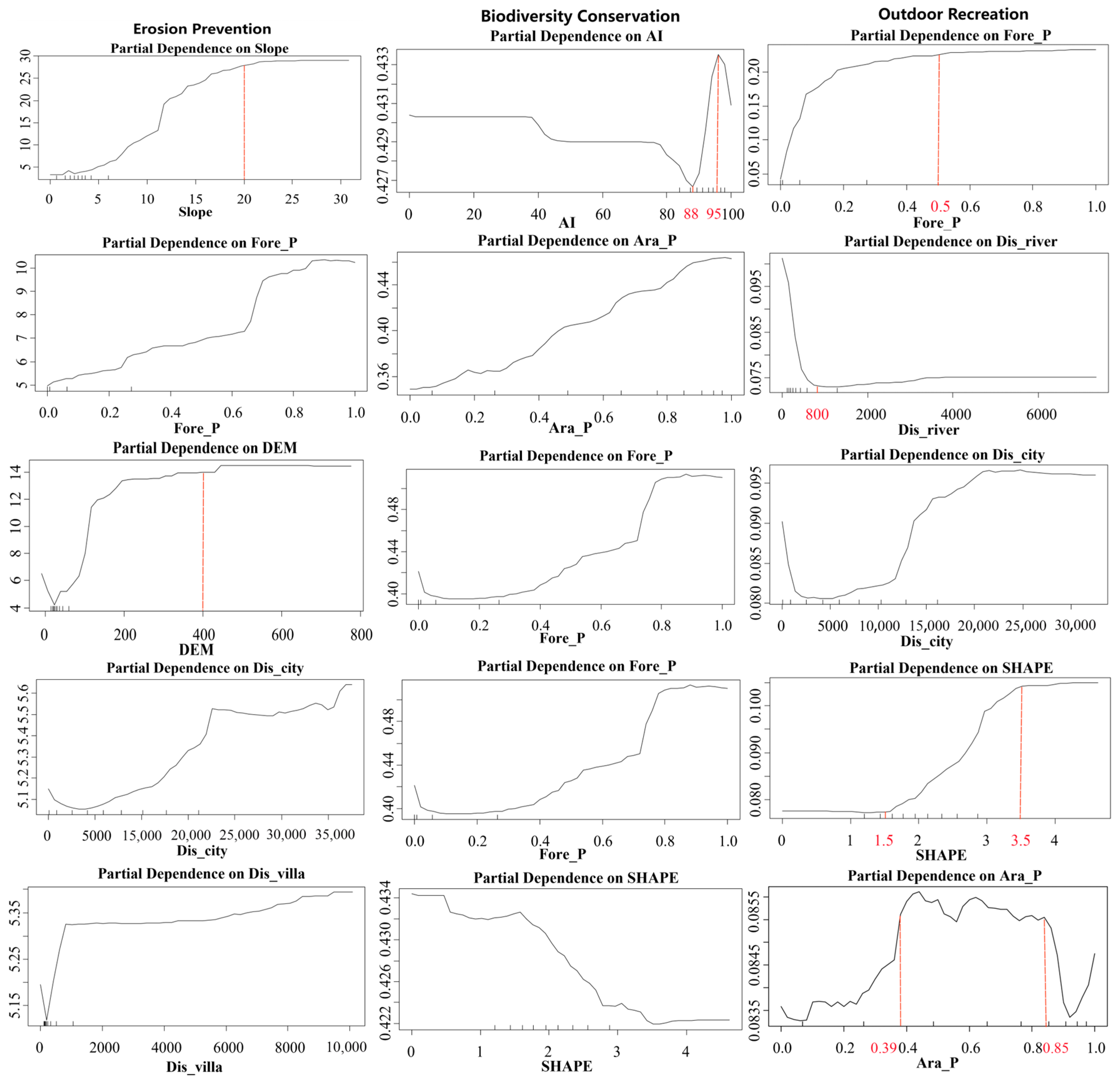
3.3. Non-Linear Impacts and Thresholds of Dominant Socio-Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services
4. Discussion
4.1. Understanding the Non-Linear Impacts of Socio-Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services from a Threshold Perspective
4.2. Policy Implications for Ecological Restoration
4.3. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; Groot, R.D.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Ecol. Econ. 1997, 25, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgewater, P.; Schmeller, D.S. The Ninth Plenary of the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES-9): Sustainable use, values, and business (as usual). Biodivers. Conserv. 2023, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhard, B.; Kandziora, M.; Hou, Y.; Müller, F. Ecosystem service potentials, flows and demands-concepts for spatial localisation, indication and quantification. Landsc. Online 2014, 34, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baró, F.; Palomo, I.; Zulian, G.; Vizcaino, P.; Haase, D.; Gómez-Baggethun, E. Mapping ecosystem service capacity, flow and demand for landscape and urban planning: A case study in the Barcelona metropolitan region. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qiao, W.; Gao, B.; Chen, Y. Unveiling spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem services and their drivers in varied landform types: Insights from the Sichuan-Yunnan ecological barrier area. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 442, 141158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifaw, E.; Sha, J.; Li, X.; Bao, Z.; Ji, J.; Ji, Z.; Kassaye, A.Y.; Lai, S.; Yang, Y. Ecosystem services dynamics and their influencing factors: Synergies/ tradeoffs interactions and implications, the case of upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 938, 173524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghaed, F.A.; Mohammadzadeh, M.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Mirkarimi, S.H. Decision scenarios using ecosystem services for land allocation optimization across Gharehsoo watershed in northern Iran. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Hu, Y.N.; Du, Y.Y.; Meersmans, J.; Qiu, S.J. Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.W.; Zhou, X.F.; Liao, Z.L. Ecological redline delineation based on the supply and demand of ecosystem services. Land Use Policy 2024, 140, 107109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Song, Y. Integrating ecosystem services and ecological connectivity to prioritize spatial conservation on Jeju Island, South Korea. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 239, 104865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissi, E.; Manea, E.; Mazaris, A.D.; Fraschetti, S.; Almpanidou, V.; Bevilacqua, S.; Coll, M.; Guarnieri, G.; Lloret-Lloret, E.; Pascual, M.; et al. A review of the combined effects of climate change and other local human stressors on the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helseth, E.V.; Vedeld, P.; Framstad, E.; Gómez-Baggethun, E. Forest ecosystem services in Norway: Trends, condition, and drivers of change (1950–2020). Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 58, 101491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.-J.; Lin, C. Impacts of future climate change and different management scenarios on water-related ecosystem services: A case study in the Jianghuai ecological economic Zone, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Yan, S. Zoning and Optimization Strategies of Land Spatial Ecological Restoration in Liangjiang New Area of Chongqing Based on the Supply–Demand Relationship of Ecosystem Services. Land 2023, 12, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngabire, M.; Wang, T.; Xue, X.; Liao, J.; Sahbeni, G.; Huang, C.; Duan, H.; Song, X. Soil salinization mapping across different sandy land-cover types in the Shiyang River Basin: A remote sensing and multiple linear regression approach. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 28, 100847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchet, M.A.; Paracchini, M.L.; Schulp, C.J.E.; Stürck, J.; Verkerk, P.J.; Verburg, P.H.; Lavorel, S. Bundles of ecosystem (dis)services and multifunctionality across European landscapes. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Kang, F.; Han, H.; Cheng, X.; Li, Z. Exploring drivers of ecosystem services variation from a geospatial perspective: Insights from China’s Shanxi Province. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Hu, Y. How do natural and human factors influence ecosystem services changing? A case study in two most developed regions of China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Yuan, M.; Xu, S.; Bai, T.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, D. Urban Expansion Was the Main Driving Force for the Decline in Ecosystem Services in Hainan Island during 1980–2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J. Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: Thresholds identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Tang, H.; Yang, P.; Hu, G.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal patterns and drivers of ecosystem service supply and demand across the conterminous United States: A multiscale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135005. [Google Scholar]
- Olaniyi, O.E.; Omowale, H.O. Evaluating the dynamics and eco-climatic predictors of forest conversion and restoration in Old Oyo National Park, Nigeria using geospatial and machine learning techniques. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 227–244. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Lee, D. Changes in land use or land cover and ecosystem service values in Wuhan city, China, from 1996 to 2018. J. Chin. Archit. Urban. 2023, 5, 0427. [Google Scholar]
- Han, P.; Hu, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Z. Integrating key ecosystem services to study the spatio-temporal dynamics and determinants of ecosystem health in Wuhan’s central urban área. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112352. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Ke, X.; Zhou, T.; He, L. Evaluation of ecological security of natural resources in Wuhan based on “contribution, vitality, organisational strength and resilience”. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 43, 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Fang, X.; Li, Y.; Tan, Y. Linking ecosystem services trade-offs, bundles and hotspot identification with cropland management in the coastal Hangzhou Bay area of China. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Fu, B.; Feng, X.; Hou, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. The tradeoff and synergy between ecosystem services in the Grain-for-Green areas in Northern Shaanxi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejani, R.; Rao, K.V.; Osman, M.; Rao, C.S.; Reddy, K.S.; Chary, G.R.; Pushpanjali; Samuel, J. Spatial and temporal estimation of soil loss for the sustainable management of a wet semi-arid watershed cluster. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallis, H.; Ricketts, T. InVEST 1.0 Beta User’s Guide: Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs; Woods Institute for the Environment, Stanford University: California, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Y. On the spatial relationship between ecosystem services and urbanization: A case study in Wuhan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 780–790. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Qiao, Y.-P.; Wang, L.-J.; Zhang, J.-C. Terrain gradient variations in ecosystem services of different vegetation types in mountainous regions: Vegetation resource conservation and sustainable development. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 482, 118856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici, N.; Cote-Navarro, F.; Escobedo, F.J.; Rubiano, K.; Villegas, J.C. Spatio-temporal and cumulative effects of land use-land cover and climate change on two ecosystem services in the Colombian Andes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, F.; Yan, H.; Zhang, F.; Wei, X. Impacts of urbanization-induced land-use changes on ecosystem services: A case study of the Pearl River Delta Metropolitan Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczynski, R.; Milne, E.; Banwart, S.A. Soil carbon, multiple benefits. J. Environ. Res. Dev. 2015, 13, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, W.; Mooney, H.; Cropper, A.; Capistrano, D.; Carpenter, S.; Chopra, K. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and human well-being. Synthesis 2005, 34, 534. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, T.; Wilson, J.D. Partial dependence through stratification. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2021, 6, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L. Dissecting ecosystem services distribution and inequality of typical cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Hu, T.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Pan, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, S.; Deng, S. Matching ecosystem services supply and demand in China’s urban agglomerations for multiple-scale management. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138351.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F.; Li, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Understanding the spatial relationships and drivers of ecosystem service supply-demand mismatches towards spatially-targeted management of social-ecological system. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 136882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Ren, H.; Xu, D.; Gao, Y. Spatial scale effects on the value of ecosystem services in China’s terrestrial area. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Cui, F. Exploring ecosystem services interactions in the dryland: Socio-ecological drivers and thresholds for better ecosystem management. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Huang, L. Integrating ecosystem services and ecological risks for urban ecological zoning: A case study of Wuhan City, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2023, 29, 1299–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sun, P.; Zhang, J.; Mo, J.; Wang, K. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of ecosystem services’ transformation in the Yellow River basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Théau, J. Spatiotemporal analysis of water-related ecosystem services under ecological restoration scenarios: A case study in northern Shaanxi, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, S.H.; Paulukonis, E.; Simmons, C.; Russell, M.; Fulford, R.; Harwell, L.; Smith, L. Projecting effects of land use change on human well-being through changes in ecosystem services. Ecol. Model. 2021, 440, 109358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Xie, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, B.; Wan, W. Exploring the interrelations and driving factors among typical ecosystem services in the Yangtze river economic Belt, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xie, Y.; Lei, F.; Cao, L.; Zeng, H. Analysis on spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of ecosystem service in the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 11, 1334458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Dai, S.; Cheng, J.; Liu, K. How urban sprawl affects local and nearby ecosystem services in China. Reg. Environ. Change 2023, 23, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe-Lucia, M.; Soliveres, S.; Penone, C.; Fischer, M.; Ammer, C.; Boch, S.; Boeddinghaus, R.S.; Bonkowski, M.; Buscot, F.; Fiore-Donno, A.M.; et al. Land-use intensity alters networks between biodiversity, ecosystem functions, and services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28140–28149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D. Spatiotemporal effects of urban sprawl on habitat quality in the Pearl River Delta from 1990 to 2018. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ouyang, B.; Yan, Z. Multiscale Analysis for Identifying the Impact of Human and Natural Factors on Water-Related Ecosystem Services. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Meadows, M.E. Ecological restoration for sustainable development in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Lin, W. Zoning strategies for ecological restoration in the karst region of Guangdong province, China: A perspective from the “socio-ecological system”. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1369635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Li, M.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xie, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, N. Identification of ecological restoration areas based on the ecological safety security assessment of wetland-hydrological ecological corridors: A case study of the Han River Basin in China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gu, T.; Xiang, J.; Luo, T.; Zeng, J.; Yuan, Y. Ecological restoration zoning of territorial space in China: An ecosystem health perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 364, 121371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Q.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, E. Threshold Effects between Ecosystem Services and Natural and Social Drivers in Karst Landscapes. Land 2024, 13, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Luan, X.; Zhang, Z. Wetland ecosystem service values in Beijing significantly increased from 1984 to 2020: Trend changes, type evolution, and driving factor. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.G. Delineation of ecosystem regions. Environ. Manag. 1983, 7, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, L.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Bai, W.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z. Dynamic characteristics and impacts of ecosystem service values under land use change: A case study on the Zoigê plateau, China. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 78, 102350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Di, Z.; Sun, P.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W. Spatiotemporal Differentiation and Its Attribution of the Ecosystem Service Trade-Off/Synergy in the Yellow River Basin. Land 2024, 13, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Luo, Y.; Pang, S.; Wang, G.; Ma, X. Factor analysis of hydrologic services in water-controlled grassland ecosystems by InVEST model and geodetector. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 20409–20433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, K.; Huang, A.; Yin, X.; Yang, J.; Deng, L.; Lin, Z. Investigating the Impact of Urbanization on Water Ecosystem Services in the Dongjiang River Basin: A Spatial Analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, R.; Yang, S.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Qu, W. Identification of bundles and driving factors of ecosystem services at multiple scales in the eastern China region. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal changes of ecosystem services value by incorporating planning policies: A case of the Pearl River Delta, China. Ecol. Model. 2021, 461, 109777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Category | Data | Datesource |
|---|---|---|
| Physical geographic data | Digital Elevation Model (DEM) | Geospatial Data Cloud GDEMV2 dataset (https://www.gscloud.cn/#page1/3, accessed on 28 January 2024) |
| Soil type | China soil map based harmonised world soil data base (HWSD) (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/, accessed on 30 January 2024) | |
| Precipitation | National Earth System Science Data Centre (http://www.geodata.cn/data/, accessed on 31 March 2024) | |
| Temperature | National Earth System Science Data Centre (http://www.geodata.cn/data/, accessed on 24 March 2024) | |
| Solar radiation | United States National Climatic Data Centre (https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/cdo-web/, accessed on 24 March 2024) | |
| Leaf area index | National Earth System Science Data Centre (http://www.geodata.cn/data/, accessed on 19 March 2024) | |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | Geospatial Data Cloud Landsat 8, Resource and Environment Science and Data Centre (https://www.resdc.cn/Default.aspx, accessed on 24 March 2024) | |
| Vegetation | Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform (https://www.resdc.cn/Default.aspx, accessed on 23 March 2024) | |
| Socio-economic data | Administrative subdivision | Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform (https://www.resdc.cn/Default.aspx, accessed on 24 January 2024) |
| Population density (POP) | National Earth System Science Data Centre (http://www.geodata.cn/data/, accessed on 27 March 2024) | |
| Gross domestic product (GDP) | Geographic remote sensing ecological network platform (http://gisrs.cn/, accessed on 29 January 2024) | |
| Night light data | National Earth System Science Data Centre (http://www.geodata.cn/data/, accessed on 24 March 2024) | |
| Land use/land cover | Resource and Environment Science and Data Centre (https://www.resdc.cn/Default.aspx, accessed on 26 January 2024) | |
| China Land Cover Dataset | National Cryosphere Desert Data Centre (https://www.ncdc.ac.cn/portal/?lang=en&clear_cache=1, accessed on 28 January 2024) | |
| Grain production | Wuhan Statistical Yearbook (https://tjj.wuhan.gov.cn/tjfw/tjnj/, accessed on 27 January 2024) |
| Objective | Criteria | Indicator | Encoding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator system for ESs impact factors | Topographical | Elevation | DEM |
| Slope | Slope | ||
| Soil | Clay content | Clay | |
| Silt content | Silt | ||
| Sand content | Sand | ||
| Soil organic carbon content | SoilOC | ||
| Geographical position | Distance from cities | Dis_city | |
| Distance from villages | Dis_villa | ||
| Distance from roads | Dis_road | ||
| Distance from rivers | Dis_river | ||
| Socio-economic | Population density | POP | |
| Gross domestic product | GDP | ||
| Nighttime Lighting Index | NTL | ||
| LULC | Proportion of arable land | Ara_P | |
| Proportion of forest land | Fore_P | ||
| Proportion of grassland | Gras_P | ||
| Proportion of construction land | Cons_P | ||
| Proportion of waters | Wat_P | ||
| Average shape index | SHAPE | ||
| Aggregation index | AI | ||
| Shannon diversity index | SHDI |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, P.; Liu, H.; Kong, F.; Jin, G.; Chen, Y. Non-Linear Impacts of Social and Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services: A Threshold Perspective. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9100390
Zhang Y, Liu S, Yu P, Liu H, Kong F, Jin G, Chen Y. Non-Linear Impacts of Social and Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services: A Threshold Perspective. Urban Science. 2025; 9(10):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9100390
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yan, Shuhan Liu, Peiheng Yu, Hongtao Liu, Fanjie Kong, Gui Jin, and Yiyun Chen. 2025. "Non-Linear Impacts of Social and Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services: A Threshold Perspective" Urban Science 9, no. 10: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9100390
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, S., Yu, P., Liu, H., Kong, F., Jin, G., & Chen, Y. (2025). Non-Linear Impacts of Social and Ecological Drivers on Ecosystem Services: A Threshold Perspective. Urban Science, 9(10), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci9100390








