Mapping and Assessment of Housing Informality Using Object-Based Image Analysis: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Origins and Characteristics of Informal Housing
3. Mapping and Monitoring Informal Settlements Using Remote Sensing Technologies
3.1. OBIA Processing Steps
3.2. Detection of Informal Settlements Using Object-Level Indicators
3.3. Detection of Informal Settlement Using Settlement-Level Indicators
3.4. Detection of Informal Settlement Using Environment-Level Indicators
3.5. Temporal Analysis of Informal Settlement Extent
3.6. Informal Settlement Mapping Using UAVs
3.7. Studying the Morphology of Informal Settlements Using Landscape Metrics
3.8. Mapping of Informal Settlement Land Use Features
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Satterthwaite, D. The Scale of Urban Change Worldwide 1950–2000 and Its Underpinnings; International Institute for Environment and Development: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Spence, M.; Clarke Annez, P.; Buckley, R.M. Urbanization and Growth; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Urbanization Prospects 2018 Highlights; United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Challenges; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kessides, C. The Urban Transition in Sub-Saharan Africa: Challenges and Opportunities. Environ. Plan. C Gov. Policy 2007, 25, 466–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Habitat. The Challenge of Slums: Global Report on Human Settlements 2003. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2004, 15, 337–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, S. Urbanization Revisited: Inner-City Slum of Hope and Squatter Settlement of Despair. World Dev. 1990, 18, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations: DESA. Guidelines on the Use of Electronic Data Collection Technologies in Population and Housing Censuses; United Nations: DESA: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Maluleke, R.; van Eeden, A. The Relationship between Settlement Type and Undercount in the South African Census of 2011. Town Reg. Plan. 2013, 62, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Okpala, D.D. Regional Overview of the Status of Urban Planning and Planning Practice in Anglophone Sub-Saharan. Afr. Ctries. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, M. A Historical Exposition of Spatial Injustice and Segregated Urban Settlement in South Africa. Fundamina 2019, 25, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenhoff, C.A. Elements of an Economic Model for Slums in a Developing Economy. Econ. Dev. Cult. Chang. 1967, 16, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics South Africa. GHS Series Volume VII, Housing from a Human Settlement Perspective. 2016. Available online: https://www.statssa.gov.za/publications/Report-03-18-06/Report-03-18-062014.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Pryce, G.; Wang, Y.P.; Chen, Y.; Shan, J.; Wei, H. (Eds.) Urban Inequality and Segregation in Europe and China; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R. Slums from Space-15 Years of Slum Mapping Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graesser, J.; Cheriyadat, A.; Vatsavai, R.; Chandola, V.; Long, J.; Bright, E. Image Based Characterisation of Formal and Informal Neighborhoods in an Urban Landscape. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 5, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, J.C.; Patino, J.E.; Betancourt, A. Exploring the Potential of Machine Learning for Automatic Slum Identification from VHR Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonita, G.; Kuffer, M.; Sliuzas, R.; Persello, C. Machine Learning-Based Slum Mapping in Support of Slum Upgrading Programs: The Case of Bandung City, Indonesia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadiraju, K.K.; Vatsavai, R.R.; Kaza, N.; Wibbels, E.; Krishna, A. Machine Learning Approaches for Slum Detection Using Very High Resolution Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Singapore, 17–20 November 2018; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mboga, N.; Persello, C.; Bergado, J.R.; Stein, A. Detection of Informal Settlements from VHR Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, P. Detecting Informal Settlements from IKONOS Image Data Using Methods of Object Oriented Image Analysis-an Example from Cape Town South Africa. Jürgens CEd Remote Sens. Urban AreasFernerkundung Urbanen Räum. 2001, 35, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Kohli, D.; Stein, A.; Sliuzas, R. Uncertainty Analysis for Image Interpretations of Urban Slums. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 60, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, G.; Hay, G.J. Image Objects and Geographic Objects. In Object-Based Image Analysis: Spatial Concepts for Knowledge-Driven Remote Sensing Applications; Blaschke, T., Lang, S., Hay, G.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-Pixel vs. Object-Based Classification of Urban Land Cover Extraction Using High Spatial Resolution Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kit, O.; Lüdeke, M.; Reckien, D. Texture-Based Identification of Urban Slums in Hyderabad, India Using Remote Sensing Data. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R.; Baud, I. Extraction of Slum Areas from VHR Imagery Using GLCM Variance. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, P.; Strobl, J.; Blaschke, T.; Kux, H. Detecting Informal Settlements from QuickBird Data in Rio de Janeiro Using an Object Based Approach. In Object-Based Image Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 531–553. [Google Scholar]
- Baatz, M. Multi Resolution Segmentation: An Optimum Approach for High Quality Multi Scale Image Segmentation. In Beutrage zum AGIT-Symposium; Salzburg: Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Esch, T.; Thiel, M.; Bock, M.; Roth, A.; Dech, S. Improvement of Image Segmentation Accuracy Based on Multiscale Optimization Procedure. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drǎguţ, L.; Tiede, D.; Levick, S.R. ESP: A Tool to Estimate Scale Parameter for Multiresolution Image Segmentation of Remotely Sensed Data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallatah, A.; Jones, S.; Mitchell, D. Object-Based Random Forest Classification for Informal Settlements Identification in the Middle East: Jeddah a Case Study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 4421–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naorem, V.; Kuffer, M.; Verplanke, J.; Kohli, D. Robustness of rule sets using VHR imagery to detect informal settlements-a case of Mumbai, India. In Proceedings of the GEOBIA 2016: Solutions and Synergies, Enschede, The Netherlands, 14–16 September 2016; University of Twente Faculty of Geo-Information and Earth Observation ITC: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallatah, A.; Jones, S.; Wallace, L.; Mitchell, D. Combining Object-Based Machine Learning with Long-Term Time-Series Analysis for Informal Settlement Identification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudau, N.; Mhangara, P. Investigation of Informal Settlement Indicators in a Densely Populated Area Using Very High Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallatah, A.; Jones, S.; Mitchell, D.; Kohli, D. Mapping Informal Settlement Indicators Using Object-Oriented Analysis in the Middle East. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 802–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratomo, J.; Kuffer, M.; Kohli, D.; Martinez, J. Application of the Trajectory Error Matrix for Assessing the Temporal Transferability of OBIA for Slum Detection. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarira, D.; Mutanga, O.; Naidu, M.; Vizzari, M. Object-Based Informal Settlement Mapping in Google Earth Engine Using the Integration of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope Satellite Data. Land 2022, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudau, N.; Mhangara, P. Towards Understanding Informal Settlement Growth Patterns: Contribution to SDG Reporting and Spatial Planning. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 27, 100801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ren, H.; Cui, C.; Huang, Y. A Partition-Based Detection of Urban Villages Using High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, D.; Sliuzas, R.; Kerle, N.; Stein, A. An Ontology of Slums for Image-Based Classification. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2012, 36, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, D. Identifying and Classifying Slum Areas Using Remote Sensing; University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, D.M.; Elsayed, H.G. From Informal Settlements to Sustainable Communities. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 2367–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliuzas, R. Report of the Expert Group Meeting on Slum Identification and Mapping Some of the Authors of This Publication Are Also Working on These Related Projects: Global Urban Mapping View Project Integrated Deprived Area Mapping System IDEAMAPS. View Project. 2008. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271074739 (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I.H. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, R.; Alagu Raja, R.A. Urban Slum Detection Approaches from High-Resolution Satellite Data Using Statistical and Spectral Based Approaches. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevalakshmi, D.; Reddy, S.N.; Manikiam, B. Land Cover Classification Based on NDVI Using LANDSAT8 Time Series: A Case Study Tirupati Region. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India, 6–8 April 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1332–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, K.K.; Wong, D.W. An Approach to Differentiate Informal Settlements Using Spectral, Texture, Geomorphology and Road Accessibility Metrics. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 38, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, Y.; Meir, Y.; Mandelbrot, B.B.; Aharony, A. Geometric Implementation of Hypercubic Lattices with Noninteger Dimensionality by Use of Low Lacunarity Fractal Lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, K. Settlement indicators of wellbeing and economic status-lacunarity and vegetation. In Pecora 18-Forty Years of Earth Observati; Understanding a Changing World: Herndon, Virginia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wasisa, K.P.; Santosa, S.H.M.B.; Hidayati, I.N. Slums detection on worldview-3 imagery based-on integration of image sharpening and lacunarity algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference of Indonesian Society for Remote Sensing, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 17–19 October 2016; Remote Sensing for a Better Governance: Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wurm, M.; Stark, T.; Zhu, X.X.; Weigand, M.; Taubenböck, H. Semantic Segmentation of Slums in Satellite Images Using Transfer Learning on Fully Convolutional Neural Networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmi, A.; Gevaert, C.M.; Kohli, D.; Kuffer, M.; Pratomo, J. Integrating Remote Sensing and Street View Imagery for Mapping Slums. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Tsurusaki, N.; Eissa, A.; Osman, T. Detection of Slums from Very High-Resolution Satellite Images Using Machine Learning Algorithms: A Case Study of Fustat Area in Cairo, Egypt. 2020, Volume 6, pp. 219–224. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2324/4102491 (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Norman, M.; Shahar, H.M.; Mohamad, Z.; Rahim, A.; Mohd, F.A.; Shafri, H.Z.M. Urban Building Detection Using Object-Based Image Analysis OBIA. and Machine Learning ML. Algorithms. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovey, K.; van Oostrum, M.; Chatterjee, I.; Shafique, T. Towards a Morphogenesis of Informal Settlements. Habitat Int. 2020, 104, 102240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, M.S.; Derebew, K.T.; Gemeda, D.O. Exploiting Temporal-Spatial Patterns of Informal Settlements Using GIS and Remote Sensing Technique: A Case Study of Jimma City, Southwestern Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2019, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githira, D.N. Growth and Eviction of Informal Settlements in Nairobi. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sirueri, F.O. Comparing Spatial Patterns of Informal Settlements between Nairobi and Dar es Salaam. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dubovyk, O.; Sliuzas, R.; Flacke, J. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Informal Settlements Development: A Case Study of Istanbul, Turkey; University of Twente Faculty of Geo-Information and Earth Observation ITC: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, S. Detecting Slums from Quick Bird Data in Pune Using an Object Oriented Approach. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2012, XXXIX-B8, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Kuffer, M.; Persello, C. The Temporal Dynamics of Slums Employing a CNN-Based Change Detection Approach. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kit, O.; Lüdeke, M. Automated Detection of Slum Area Change in Hyderabad, India Using Multitemporal Satellite Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 83, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiya, S.R.; Babu, S.C. Slum Segmentation and Change Detection: A Deep Learning Approach. arXiv 2018, arXiv:181107896. [Google Scholar]
- Gevaert, C.M.; Persello, C.; Sliuzas, R.; Vosselman, G. Monitoring Household Upgrading in Unplanned Settlements with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 90, 102117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, C.; Sliuzas, R.; Persello, C.; Vosselman, G. Opportunities for UAV Mapping to Support Unplanned Settlement Upgrading. Rwanda J. 2016, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nex, F.; Remondino, F. UAV for 3D Mapping Applications: A Review. Appl. Geomat. 2014, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, C.M.; Persello, C.; Sliuzas, R.; Vosselman, G. Informal Settlement Classification Using Point-Cloud and Image-Based Features from UAV Data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 125, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashilah, Q.P.; Rokhmatuloh; Hernina, R. Urban Slum Identification in Bogor Tengah Sub-District, Bogor City Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle UAV. Images and Object-Based Image Analysis. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; Agüera, F.; Carvajal, F. Low cost surveying using an unmanned aerial vehicle. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, XL-1/W2, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliuzas, R.; Kuffer, M.; Gevaert, C.; Persello, C.; Pfeffer, K. Slum Mapping From Space to Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Based Approaches. In Proceedings of the 2017 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 6–8 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, L.; Adeleke, A.; Hadden, R.; Rush, D. Spatial Metrics from LiDAR Roof Mapping for Fire Spread Risk Assessment of Informal Settlements in Cape Town, South Africa. Fire Saf. J. 2021, 120, 103053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawte, S.S.; Koeva, M.N.; Gevaert, C.M.; Oude Elberink, S.; Pedro, A.A. Digital twin creation for slums in Brazil based on UAV data. In International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences—ISPRS Archives; International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Grosvenor Ln, MD, USA, 2022; Volume 48, pp. 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, X.; Wen, D.; Li, J. The Use of Landscape Metrics and Transfer Learning to Explore Urban Villages in China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, S.; Garg, P.K.; Jat, M.K. Automated Extraction of Slum Built-up Areas from Multispectral Imageries. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 48, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayunga, S.D.; Coleman, D.J.; Zhang, Y. Semi-Automatic Building Extraction in Dense Urban Settlement Areas from High-Resolution Satellite Images. Surv. Rev. 2010, 42, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobrega, R.A.A.; O’hara, C.G.; Quintanilha, J.A. Detecting roads in informal settlements surrounding Sao Paulo city by using object-based classification. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Object-Based Image Analysis, Salzburg, Austria, 4–5 July 2006. [Google Scholar]

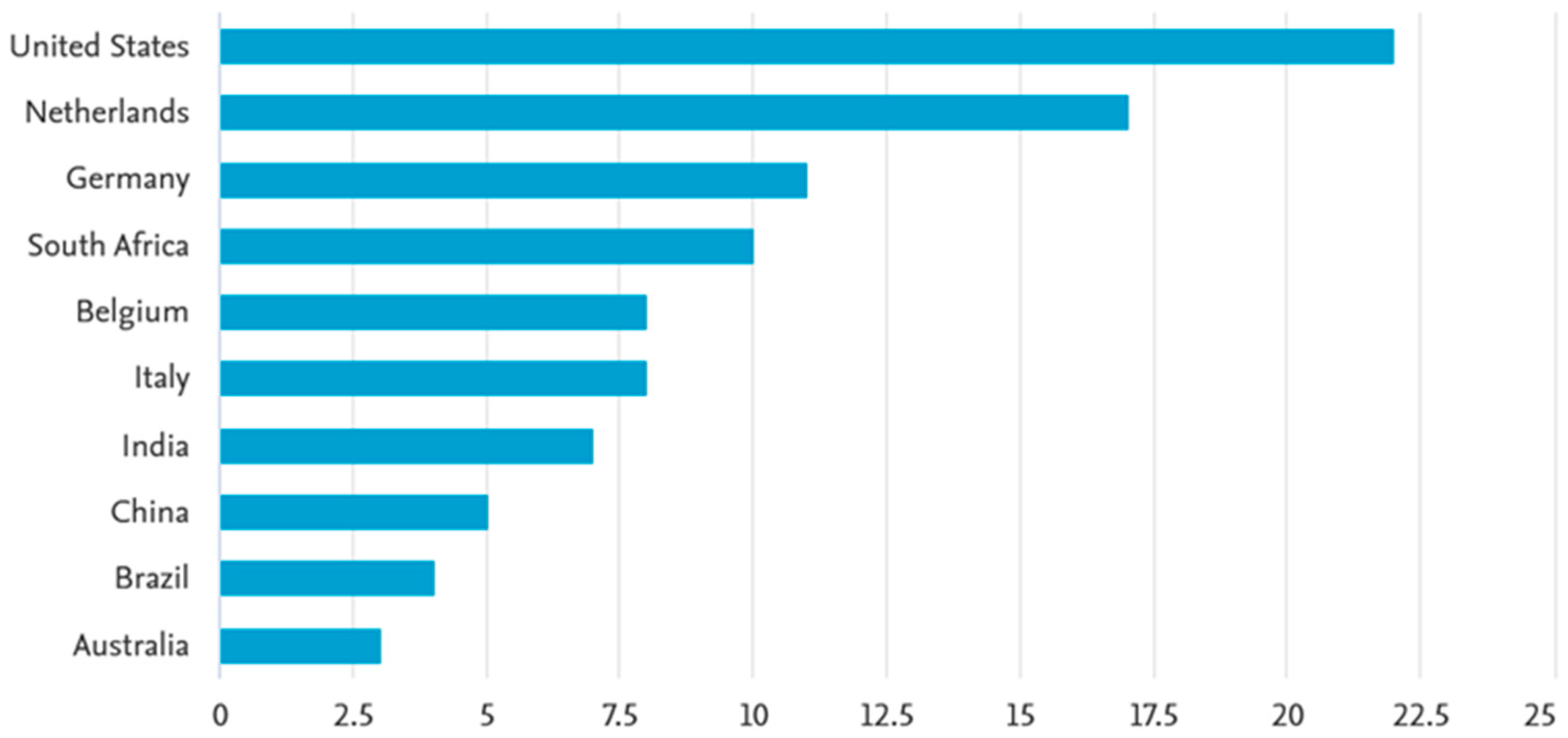
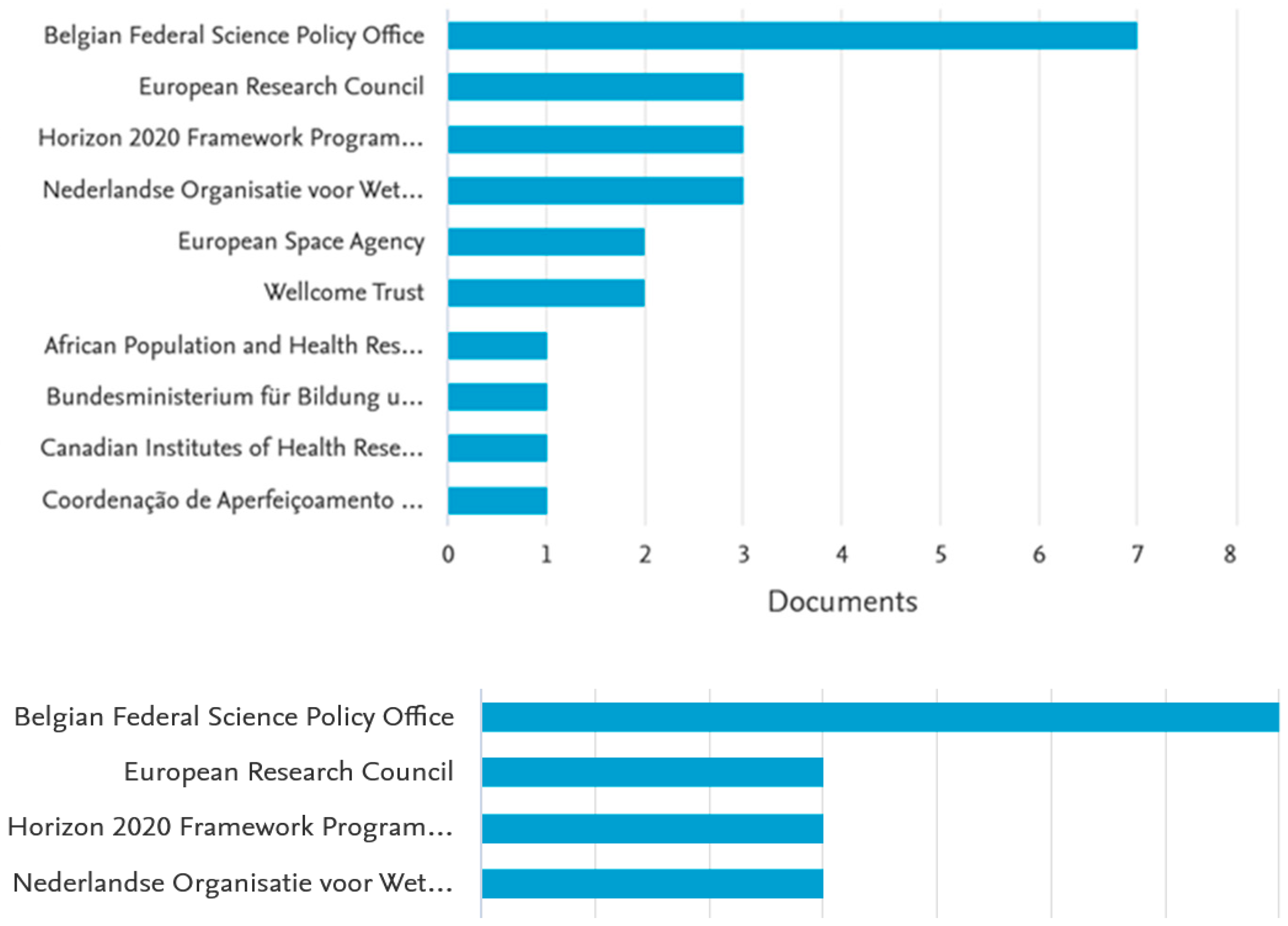
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Manual digitization | This method is time-consuming and resource-intensive; however, it yields more accurate results compared to other informal settlement detection methodologies [15]. |
| Pixel-based classification | This method results in high confusion between informal settlements and features with similar spectral signatures [24]. |
| Machine learning | This method can be used with other image classification techniques, such as OBIA, and texture [17,18]. |
| Texture-based classification | This methodology can easily be transferred to other areas with similar characteristics [25]. |
| OBIA | This methodology classifies image objects using contextual, spatial and spectral features [21]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mudau, N.; Mhangara, P. Mapping and Assessment of Housing Informality Using Object-Based Image Analysis: A Review. Urban Sci. 2023, 7, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci7030098
Mudau N, Mhangara P. Mapping and Assessment of Housing Informality Using Object-Based Image Analysis: A Review. Urban Science. 2023; 7(3):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci7030098
Chicago/Turabian StyleMudau, Naledzani, and Paidamwoyo Mhangara. 2023. "Mapping and Assessment of Housing Informality Using Object-Based Image Analysis: A Review" Urban Science 7, no. 3: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci7030098
APA StyleMudau, N., & Mhangara, P. (2023). Mapping and Assessment of Housing Informality Using Object-Based Image Analysis: A Review. Urban Science, 7(3), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci7030098







