Androgen receptors and Zinc finger (ZNF) Transcription Factors’ Interplay and Their miRNA Regulation in Prostate Cancer Prognosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. TCGA Database
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
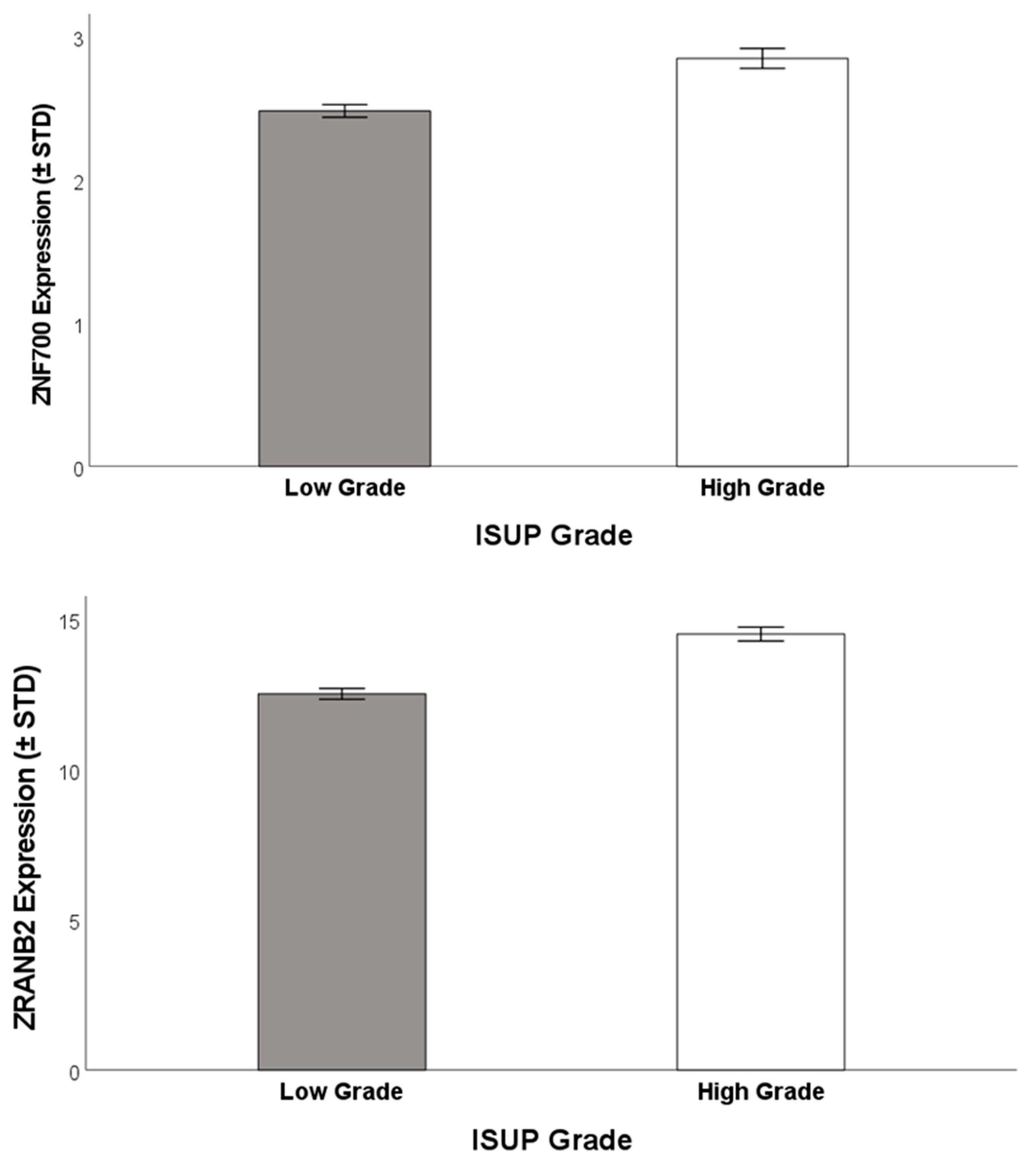
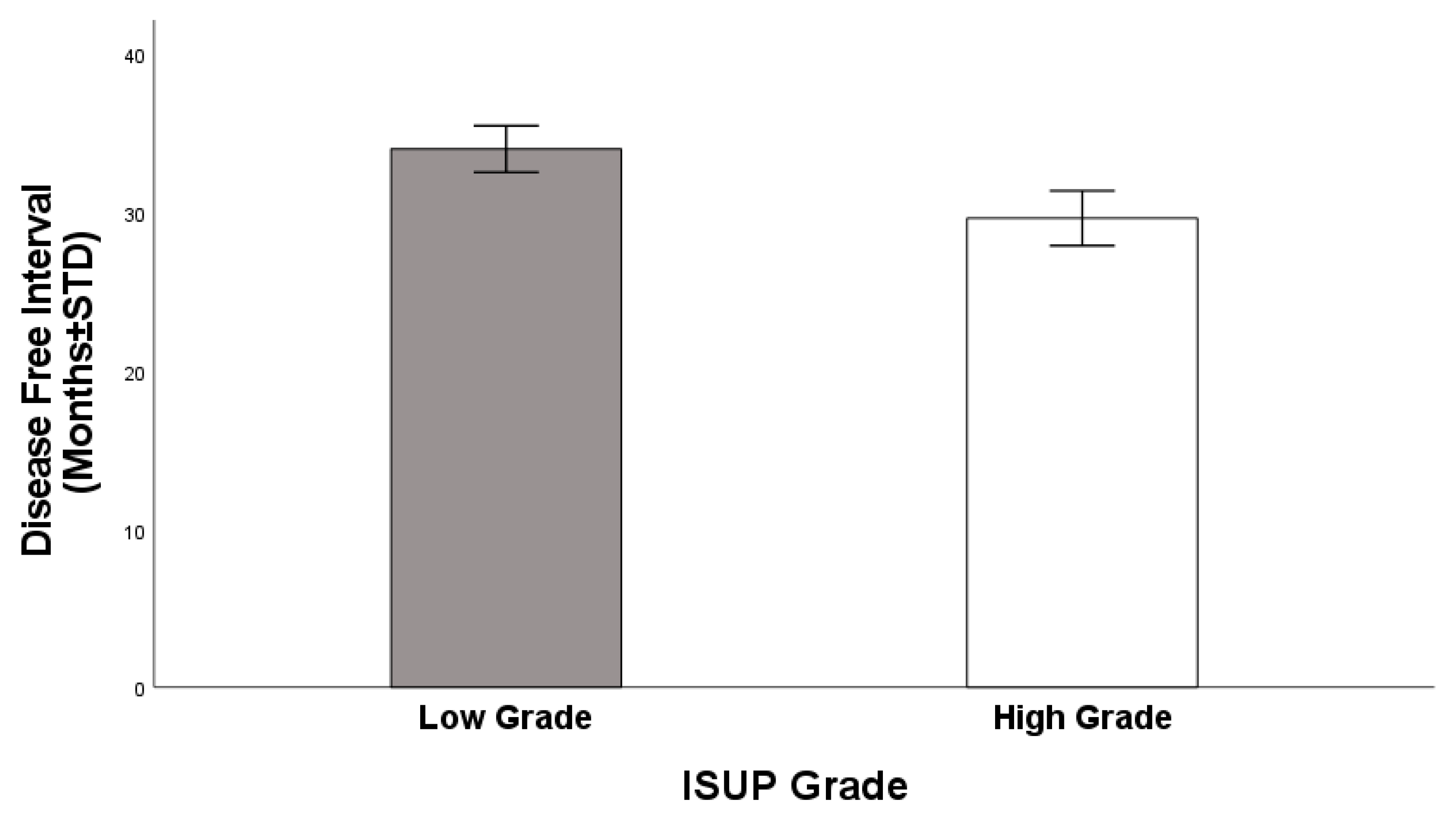
3.1. ISUP Grading Groups and Gene Expression
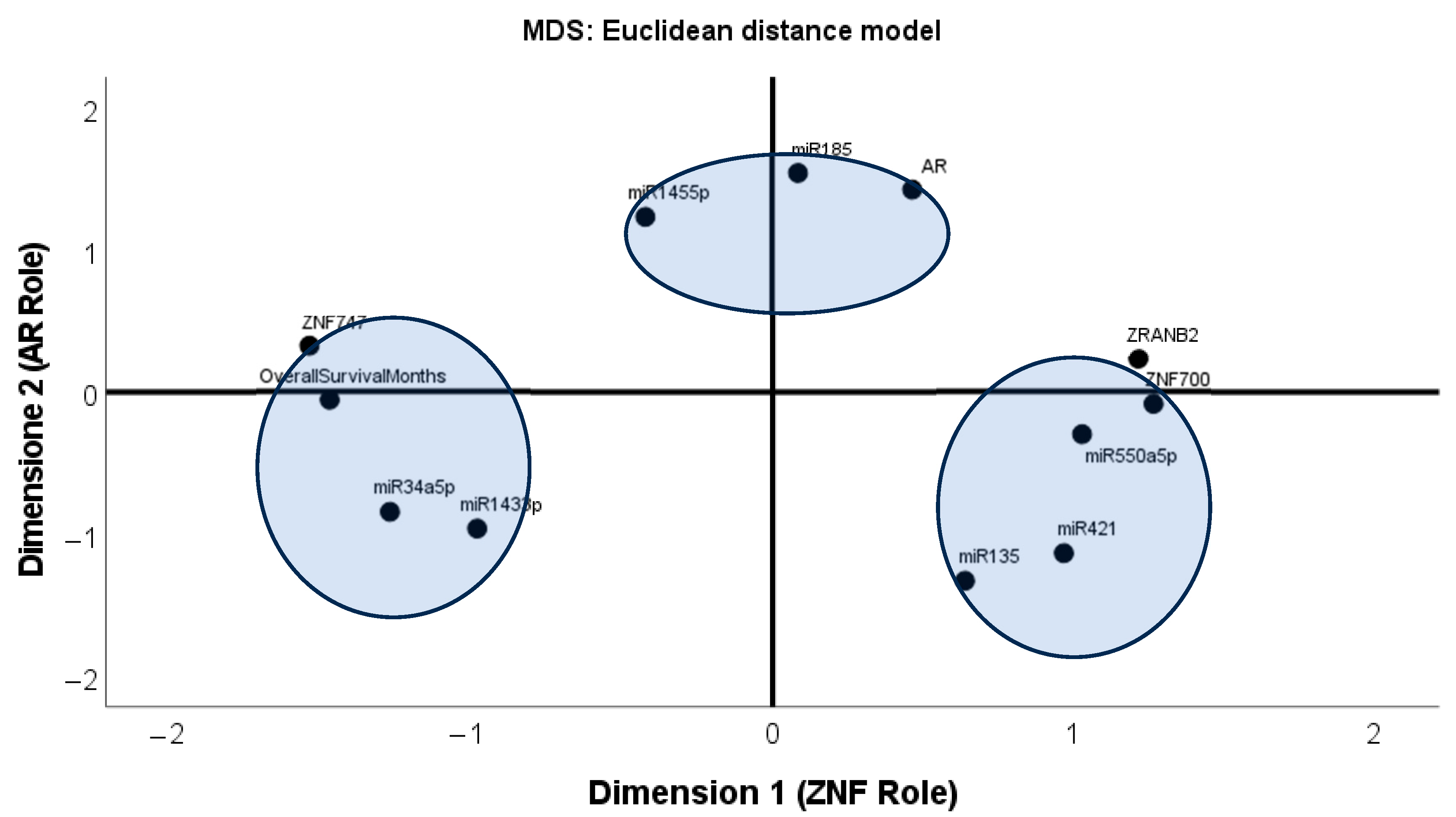
3.2. Association Among ZNFs/AR Gene Expressions and Associated miRNAs
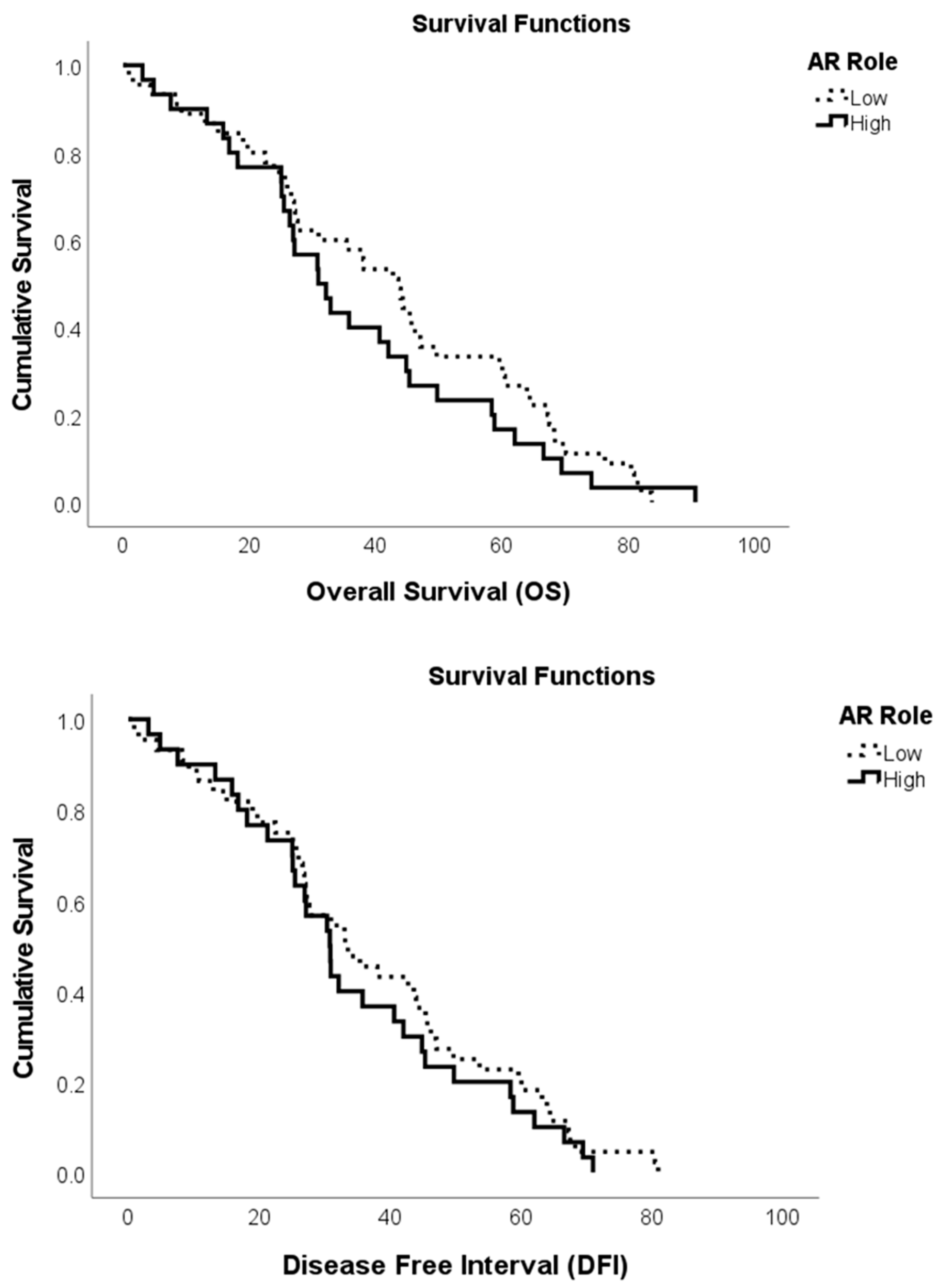
3.3. Survival Curves
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cancer TODAY|IARC. 2022. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Siegel, D.A. Prostate cancer incidence and survival, by stage and race/ethnicity—United States, 2001–2017. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolarz, B.; Durczyński, A.; Romanowicz, H.; Szyłło, K.; Hogendorf, P. miRNAs in cancer (review of literature). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozniak, T.; Shcharbin, D.; Bryszewska, M. Circulating microRNAs in medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Azmi, A.S.; Mohammad, R.M. Deregulated transcription factors and poor clinical outcomes in cancer patients. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, D.; Kumari, S.; Heemers, H.V. Androgen receptor co-regulation in prostate cancer. Asian J. Urol. 2020, 7, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemers, H.V.; Tindall, D.J. Androgen receptor (AR) coregulators: A diversity of functions converging on and regulating the AR transcriptional complex. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 778–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Senapati, D.; Heemers, H.V. Rationale for the development of alternative forms of androgen deprivation therapy. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, R275–R295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePriest, A.D.; Fiandalo, M.V.; Schlanger, S.; Heemers, F.; Mohler, J.L.; Liu, S.; Heemers, H.V. Regulators of Androgen Action Resource: A one-stop shop for the comprehensive study of androgen receptor action. Database 2016, 2016, bav125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, S.A.; Nekludova, L.; Pabo, C.O. DNA recognition by Cys2His2 zinc finger proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2000, 29, 183–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S. An overview of the basic helix-loop-helix proteins. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.P.; Tamkun, J.W.; Hartzell, G.W. The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 1989, 989, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, J.; Wang, Y.C. Zinc finger proteins in cancer progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Yang, Q.; Yin, H.; Wei, N.; Wang, W.; Yu, B. Comprehensive analysis of ZNF family genes in prognosis, immunity, and treatment of esophageal cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Tu, D.; Li, R.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Jin, W.; Li, T.; Zhu, H. The diagnostic significance of the ZNF gene family in pancreatic cancer: A bioinformatics and experimental study. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1089023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jing, Y.; Qin, Y.; Hunsucker, S.; Meng, H.; Sui, J.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, L.; An, G.; Yang, N.; et al. The zinc finger transcription factor ZKSCAN3 promotes prostate cancer cell migration. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Black, S.; Turner, O.; Daniel, J.M.; Dean-Colomb, W.; He, Q.P.; Davis, M.; Yates, C. Kaiso, a transcriptional repressor, promotes cell migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells through regulation of miR-31 expression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 5677–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafabadi, H.S.; Mnaimneh, S.; Schmitges, F.W.; Garton, M.; Lam, K.N.; Yang, A.; Albu, M.; Weirauch, M.T.; Radovani, E.; Kim, P.M.; et al. C2H2 zinc finger proteins greatly expand the human regulatory lexicon. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schitcu, V.H.; Raduly, L.; Nutu, A.; Zanoaga, O.; Ciocan, C.; Munteanu, V.C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. MicroRNA dysregulation in prostate cancer. Pharmacogenom. Pers. Med. 2022, 15, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Fehlmann, T.; Backes, C.; Kern, F.; Gislefoss, R.; Langseth, H.; Meese, E. Competitive learning suggests circulating miRNA profiles for cancers decades prior to diagnosis. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Zhang, J.; Sun, W.; Hua, H.; Sun, Y. Upregulation of miR-421 predicts poor prognosis and promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of papillary thyroid cancer cells. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, P.; Gong, J.; Ma, R. miR-550a-5p promotes the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting GNE via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Neoplasma 2022, 69, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.; Zhang, K. MicroRNA-144-3p inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in castration-resistant prostate cancer by targeting CEP55. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7660–7670. [Google Scholar]
- Iscaife, A.; Reis, S.; Morais, D.; Viana, N.; Silva, I.; Pimenta, R.; Bordini, A.; Dip, N.; Srougi, M.; Leite, K. Treating metastatic prostate cancer with microRNA-145. Apoptosis 2018, 23, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oto, J.; Herranz, R.; Plana, E.; Sánchez-González, J.V.; Pérez-Ardavín, J.; Hervás, D.; Fernández-Pardo, Á.; Cana, F.; Vera-Donoso, C.D.; Martínez-Sarmiento, M.; et al. Identification of miR-20a-5p as robust normalizer for urine microRNA studies in renal cell carcinoma and a profile of dysregulated microRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakula, A.; Leivonen, S.; Hintsanen, P.; Aittokallio, T.; Ceder, Y.; Børresen-Dale, A.; Perälä, M.; Östling, P.; Kallioniemi, O. MicroRNA-135b regulates ERα, AR and HIF1AN and affects breast and prostate cancer cell growth. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1287–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsunsky, I.; Millard, N.; Fan, J.; Slowikowski, K.; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Baglaenko, Y.; Brenner, M.; Loh, P.R.; Raychaudhuri, S. Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A.; Grading Committee. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma: Definition of grading patterns and proposal for a new grading system. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moch, H.; Humphrey, P.A.; Ulbright, T.M.; Reuter, V.E. (Eds.) WHO Classification of Tumors of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- van Leenders, G.J.L.H.; van der Kwast, T.H.; Grignon, D.J.; Evans, A.J.; Kristiansen, G.; Kweldam, C.F.; Litjens, G.; McKenney, J.K.; Melamed, J.; Mottet, N.; et al. ISUP Grading Workshop Panel Members (2020). The 2019 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, e87–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.L.; Meier, P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J. Am. Statist. Assoc. 1958, 53, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, J.B.; Wish, M. Multidimensional Scaling; Sage: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wen, D.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, H.; Di, X. The role of zinc finger proteins in malignant tumors. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2023, 37, e23157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, G.; Feng, L.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Bai, J.; He, L.; Gu, S.; Zhao, X. A bioinformatics analysis of zinc finger protein family reveals potential oncogenic biomarkers in breast cancer. Gene 2022, 828, 146471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobocińska, J.; Molenda, S.; Machnik, M.; Oleksiewicz, U. KRAB-ZFP Transcriptional Regulators Acting as Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Ju, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tian, C. The signaling pathways regulated by KRAB zinc-finger proteins in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, E.; Lupo, A.; Rapuano, R.; Pastore, A.; Grosso, M.; Costanzo, P. ZNF224 Protein: Multifaceted Functions Based on Its Molecular Partners. Molecules 2021, 26, 6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, R.O.; Thomas, J.H. Adaptive Evolution in Zinc Finger Transcription Factors. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Méndez, S.; Zentella-Dehesa, A.; Villegas-Ruíz, V.; Pérez-González, O.A.; Salcedo, M.; López-Romero, R.; Román-Basaure, E.; Lazos-Ochoa, M.; de Oca-Fuentes, V.E.M.; Vázquez-Ortiz, G.; et al. Splice variants of zinc finger protein 695 mRNA associated to ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2013, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Campos, J.; Iida, J. A gene regulatory program in human breast cancer. Genetics 2015, 201, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernova, O.B.; Hunyadi, A.; Malaj, E.; Pan, H.; Crooks, C.; Roe, B.; Cowell, J.K. A novel member of the WD-repeat gene family, WDR11, maps to the 10q26 region and is disrupted by a chromosome translocation in human glioblastoma cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5378–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesslinger, N.J.; Sahota, R.A.; Stone, B.; Johnson, K.; Chima, N.; King, C.; Rasmussen, D.; Bishop, D.; Rennie, P.S.; Gleave, M.; et al. Standard treatments induce antigen-specific immune responses in prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.A.; Fitzgerald, J.; Fitzgerald, S.; Kenny, D.; Kay, E.W.; O’Kennedy, R.; Kijanka, G.S. Diagnostic potential of zinc finger protein-specific autoantibodies and associated linear B-cell epitopes in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortesi, M.; Fridman, E.; Volkov, A.; Shilstein, S.; Chechik, R.; Breskin, A.; Vartsky, D.; Raviv, G.; Ramon, J. New prospective for non-invasive detection, grading, size evaluation, and tumor location of prostate cancer. Prostate 2010, 70, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.C.; Feng, P.; Milon, B.; Tan, M.; Franklin, R.B. Role of zinc in the pathogenesis and treatment of prostate cancer: Critical issues to resolve. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2004, 7, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Khan, M.; Sheikh, T.M.M.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Chohan, T.A.; Shamim, S.; Liu, Y. Zinc essentiality, toxicity, and its bacterial bioremediation: A comprehensive insight. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 900740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehm, S.M.; Tindall, D.J. Molecular regulation of androgen action in prostate cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 99, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.K.; Sadar, M.D. Non-genomic actions of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Coleman, I.; Morrissey, C.; Zhang, X.; True, L.D.; Gulati, R.; Etzioni, R.; Bolouri, H.; Montgomery, B.; White, T.; et al. Substantial interindividual and limited intraindividual genomic diversity among tumors from men with metastatic prostate cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Yang, Y.; He, H.; Xiong, Y.; Zhong, M.; Wang, S.; Xia, Q. Integrating multi-cohort machine learning and clinical sample validation to explore peripheral blood mRNA diagnostic biomarkers for prostate cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2025, 25, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C.; Jeon, S.S.; Seo, H.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.; Kang, M.; Kim, E.; Shin, K.; et al. Generation of prostate cancer assembloids modeling the patient-specific tumor microenvironment. PLoS Genet. 2025, 21, e1011652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, C. Application of Organoid Models in Prostate Cancer Research. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 736431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Wang, B.-D. Organoids: An Emerging Precision Medicine Model for Prostate Cancer Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranyutanon, S.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Dasgupta, S.; Pai, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.P. Cellular and Molecular Progression of Prostate Cancer: Models for Basic and Preclinical Research. Cancers 2020, 12, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gong, S.; Roy-Burman, P.; Lee, P.; Culig, Z. Current mouse and cell models in prostate cancer research. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, R155–R170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Classification | Primary GS | Secondary GS | N. of Cases | Percentage | Low/High Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 3 | 3 | 44 | 10% | L |
| Group 2 | 3 | 4 | 146 | 29% | L |
| Group 3 | 4 | 3 | 101 | 20% | L |
| Group 4 | 4 | 4 | 64 | 13% | H |
| Group 5 | 4, 5 | 4, 5 | 141 | 28% | H |
| OS | AR | ZNF747 | ZRANB2 | ZNF700 | miR421 | miR185 | miR135 | miR34a5p | miR1455p | miR1445p | miR550a5p | miR1433p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFI | 0.914 ** | −0.011 | 0.151 ** | −0.127 ** | −0.155 ** | −0.032 | 0.034 | −0.120 | 0.044 | 0.006 | 0.014 | −0.080 | 0.081 |
| OS | −0.036 | 0.139 ** | −0.084 | −0.131 ** | −0.057 | 0.047 | −0.128 * | 0.048 | −0.008 | 0.004 | −0.017 | 0.053 | |
| AR | −0.027 | 0.086 | 0.100 * | 0.124 | 0.176 ** | −0.201 ** | −0.080 | 0.229 ** | −0.026 | 0.046 | −0.087 | ||
| ZNF747 | −0.176 ** | −0.174 ** | −0.132 | −0.051 | −0.102 | −0.043 | −0.047 | −0.035 | −0.228 * | −0.079 | |||
| ZRANB2 | 0.527 ** | 0.098 | −0.018 | −0.014 | −0.030 | 0.104 | −0.038 | 0.206 * | 0.066 | ||||
| ZNF700 | 0.246 ** | 0.082 | 0.060 | −0.087 | 0.204 ** | −0.062 | 0.023 | −0.081 | |||||
| miR421 | 0.017 | 0.209 ** | −0.025 | 0.209 ** | −0.019 | 0.102 | −0.048 | ||||||
| miR185 | 0.008 | −0.086 | 0.089 | 0.014 | −0.123 | −0.086 | |||||||
| miR135 | 0.110 | −0.025 | −0.154 * | −0.137 | −0.037 | ||||||||
| miR34a5p | 0.031 | −0.036 | −0.088 | −0.027 | |||||||||
| miR1455p | −0.004 | −0.006 | −0.014 | ||||||||||
| miR1445p | 0.012 | 0.019 | |||||||||||
| miR550a5p | −0.078 |
| Model OS | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | |||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Adj. R2 | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 40.067 ± 3.36 | 1.678 | 23.876 | <0.001 | ||
| ZNF role | 17.958 ± 3.38 | 1.689 | 0.779 | 10.630 | <0.001 | 0.39 | |
| 2 | (Constant) | 40.067 ± 3.11 | 1.553 | 25.790 | <0.001 | ||
| ZNF role | 17.958 ± 3.13 | 1.564 | 0.779 | 11.482 | <0.001 | ||
| AR role | 5.677 ± 3.13 | 1.564 | 0.246 | 3.629 | <0.001 | 0.46 | |
| a. Dependent Variable: Overall Survival (OS) | |||||||
| Model DFI | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | |||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Adj. R2 | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 35.953 ± 3.77 | 1.884 | 19.082 | <0.001 | ||
| ZNF role | 12.427 ± 3.54 | 1.887 | 0.613 | 6.586 | <0.001 | 0.27 | |
| 2 | (Constant) | 35.963 ± 3.54 | 1.768 | 20.304 | <0.001 | ||
| ZNF role | 12.422 ± 3.54 | 1.771 | 0.613 | 7.015 | <0.001 | ||
| AR role | −5.801 ± 3.53 | 1.766 | −0.287 | −3.280 | <0.001 | 0.34 | |
| b. Dependent Variable: Disease-Free Interval (DFI) | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boldrini, L.; Watts, S.; Schneider, N.; Saravanan, R.; Bardi, M. Androgen receptors and Zinc finger (ZNF) Transcription Factors’ Interplay and Their miRNA Regulation in Prostate Cancer Prognosis. Sci 2025, 7, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7030111
Boldrini L, Watts S, Schneider N, Saravanan R, Bardi M. Androgen receptors and Zinc finger (ZNF) Transcription Factors’ Interplay and Their miRNA Regulation in Prostate Cancer Prognosis. Sci. 2025; 7(3):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7030111
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoldrini, Laura, Savana Watts, Noah Schneider, Rithanya Saravanan, and Massimo Bardi. 2025. "Androgen receptors and Zinc finger (ZNF) Transcription Factors’ Interplay and Their miRNA Regulation in Prostate Cancer Prognosis" Sci 7, no. 3: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7030111
APA StyleBoldrini, L., Watts, S., Schneider, N., Saravanan, R., & Bardi, M. (2025). Androgen receptors and Zinc finger (ZNF) Transcription Factors’ Interplay and Their miRNA Regulation in Prostate Cancer Prognosis. Sci, 7(3), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7030111






