Epibionts and Epiphytes in Seagrass Habitats: A Global Analysis of Their Ecological Roles
Abstract
1. Introduction
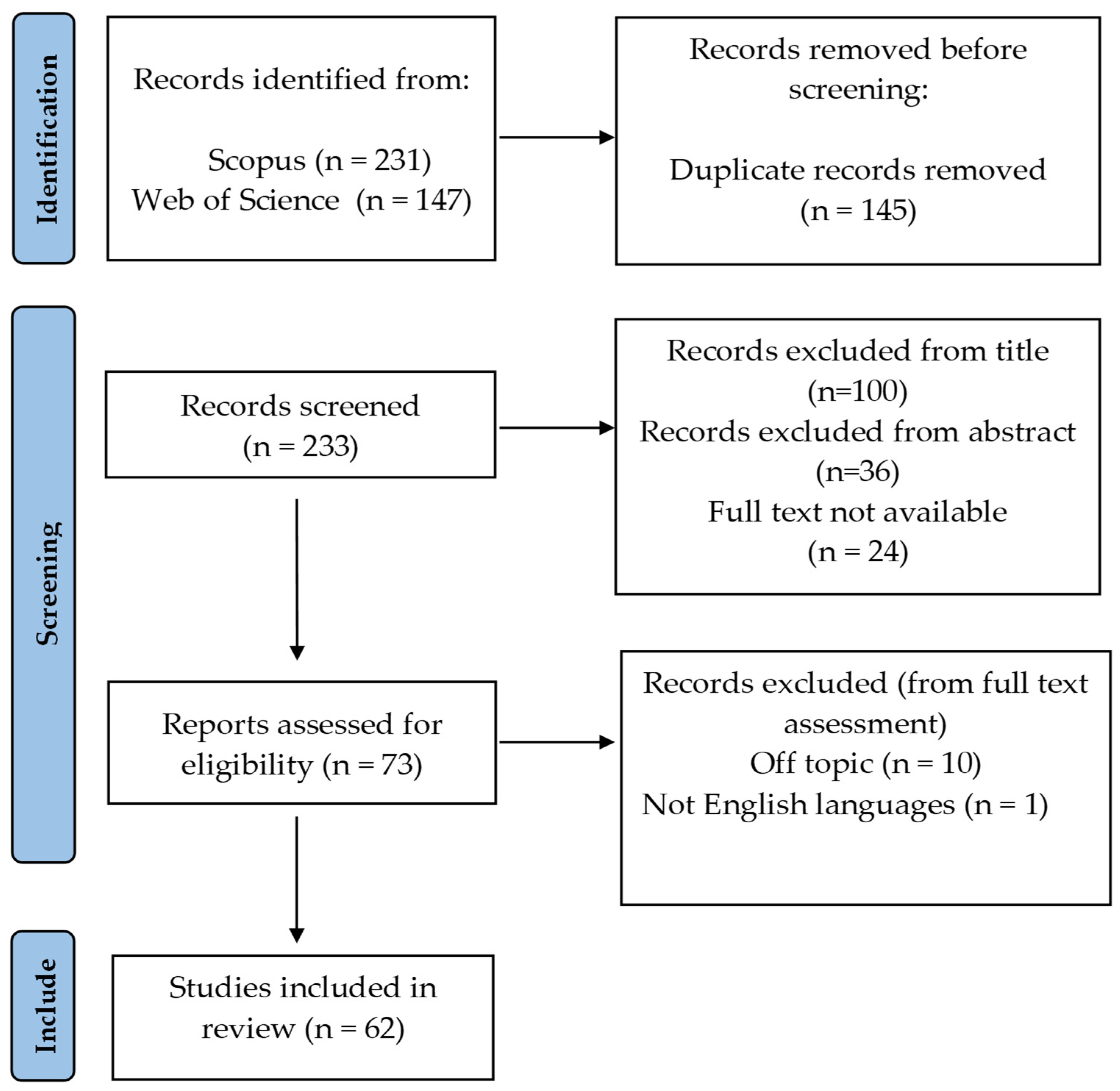
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
- (1)
- The biotic interactions between seagrasses and epibionts, mobile fauna, and epiphytes;
- (2)
- The effects of these biotic interactions on the host.
- (1)
- Off-topic studies;
- (2)
- Non-English-language publications;
- (3)
- Incomplete book chapters.
2.3. Data Extraction
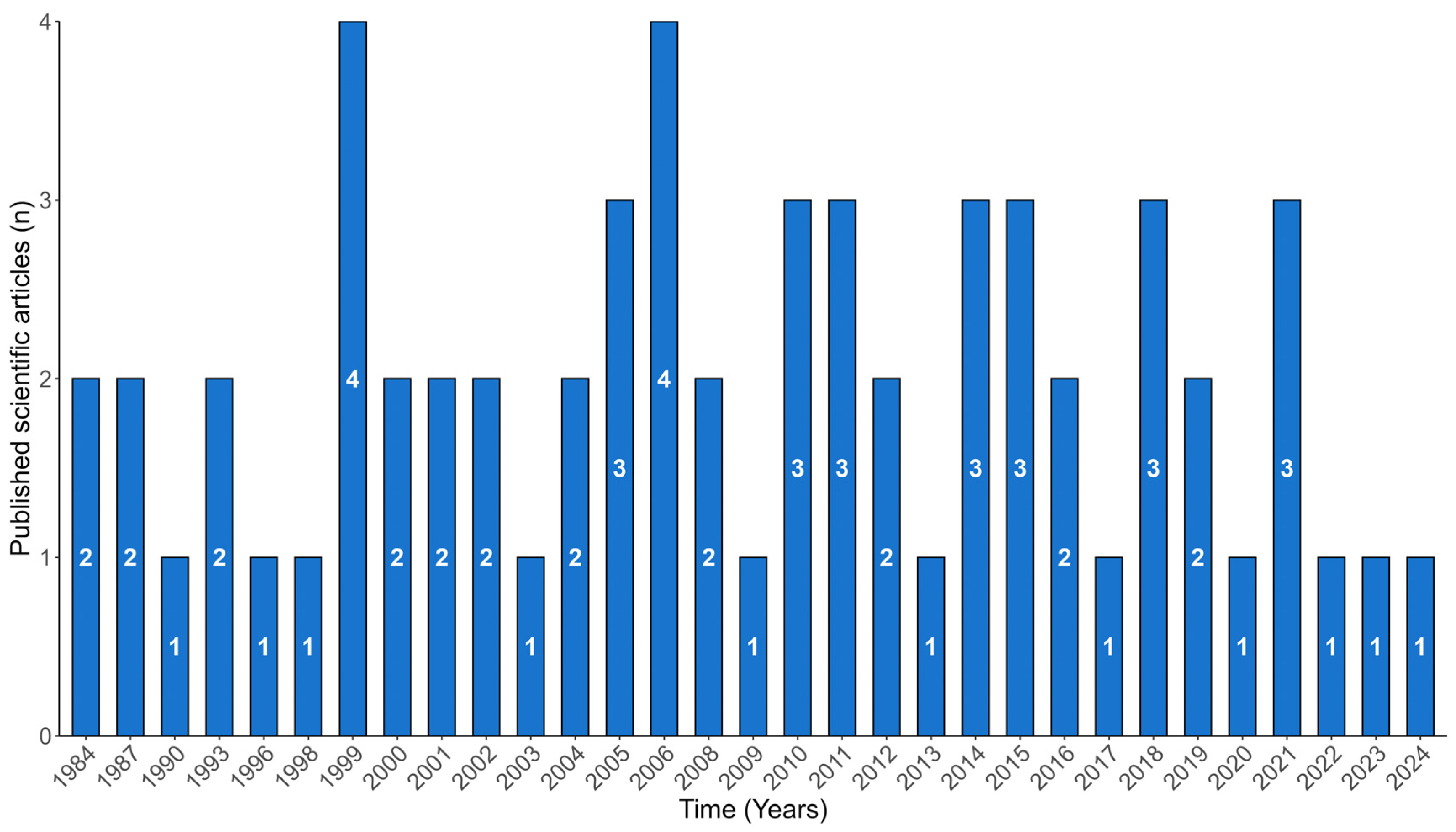
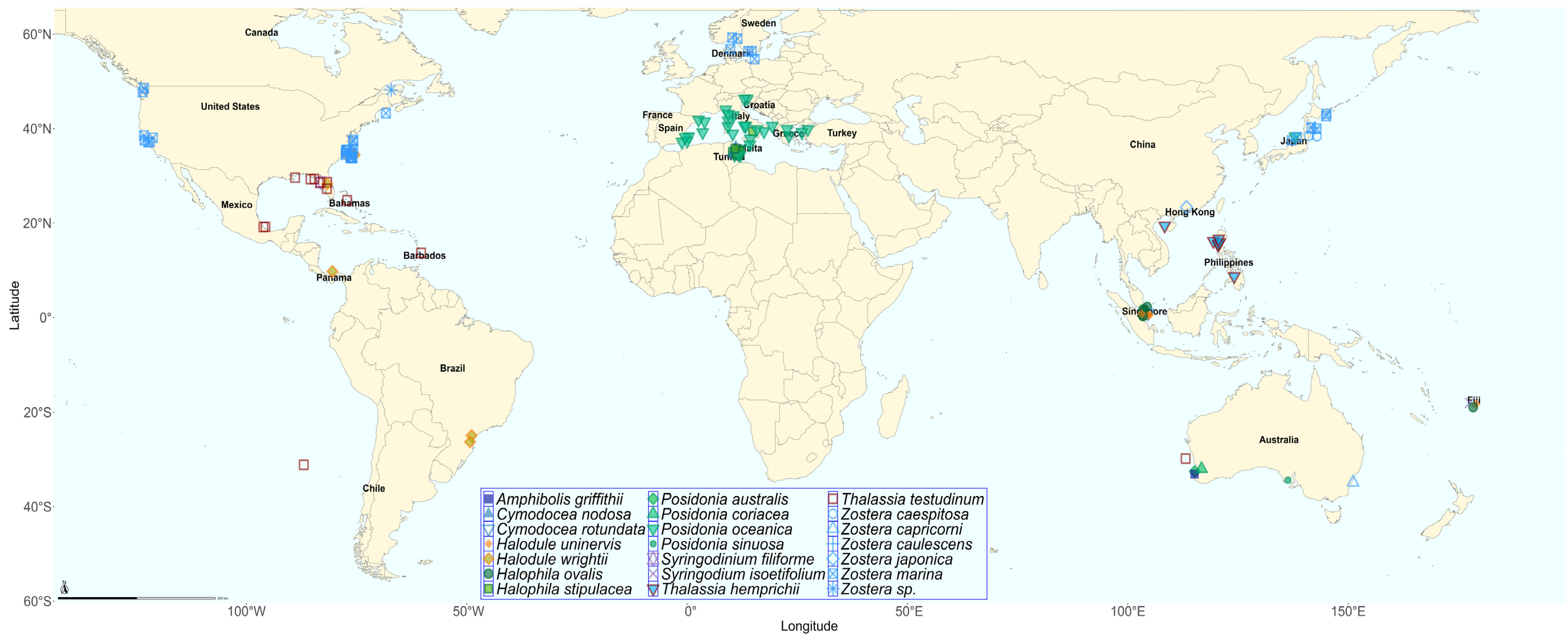
3. Results
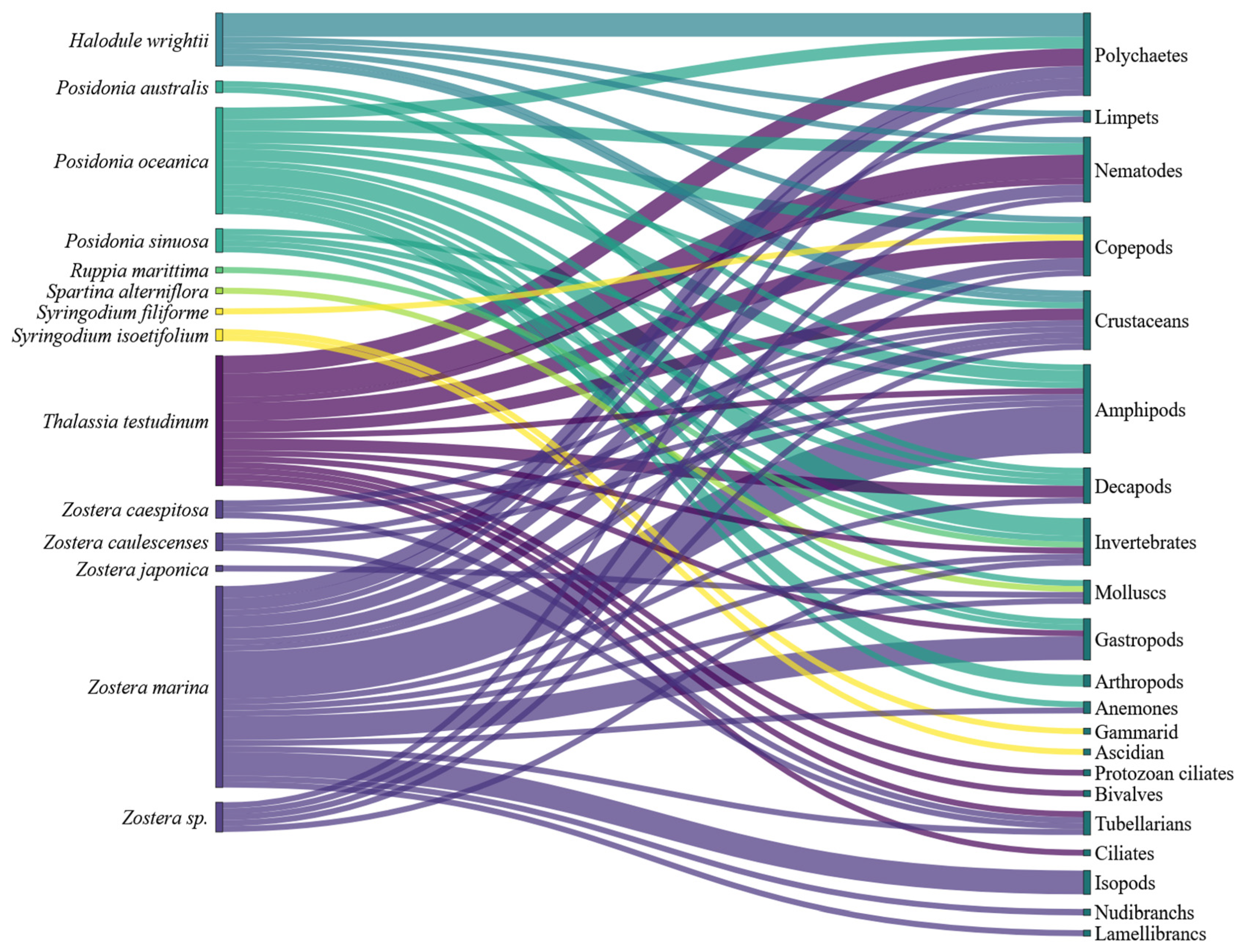
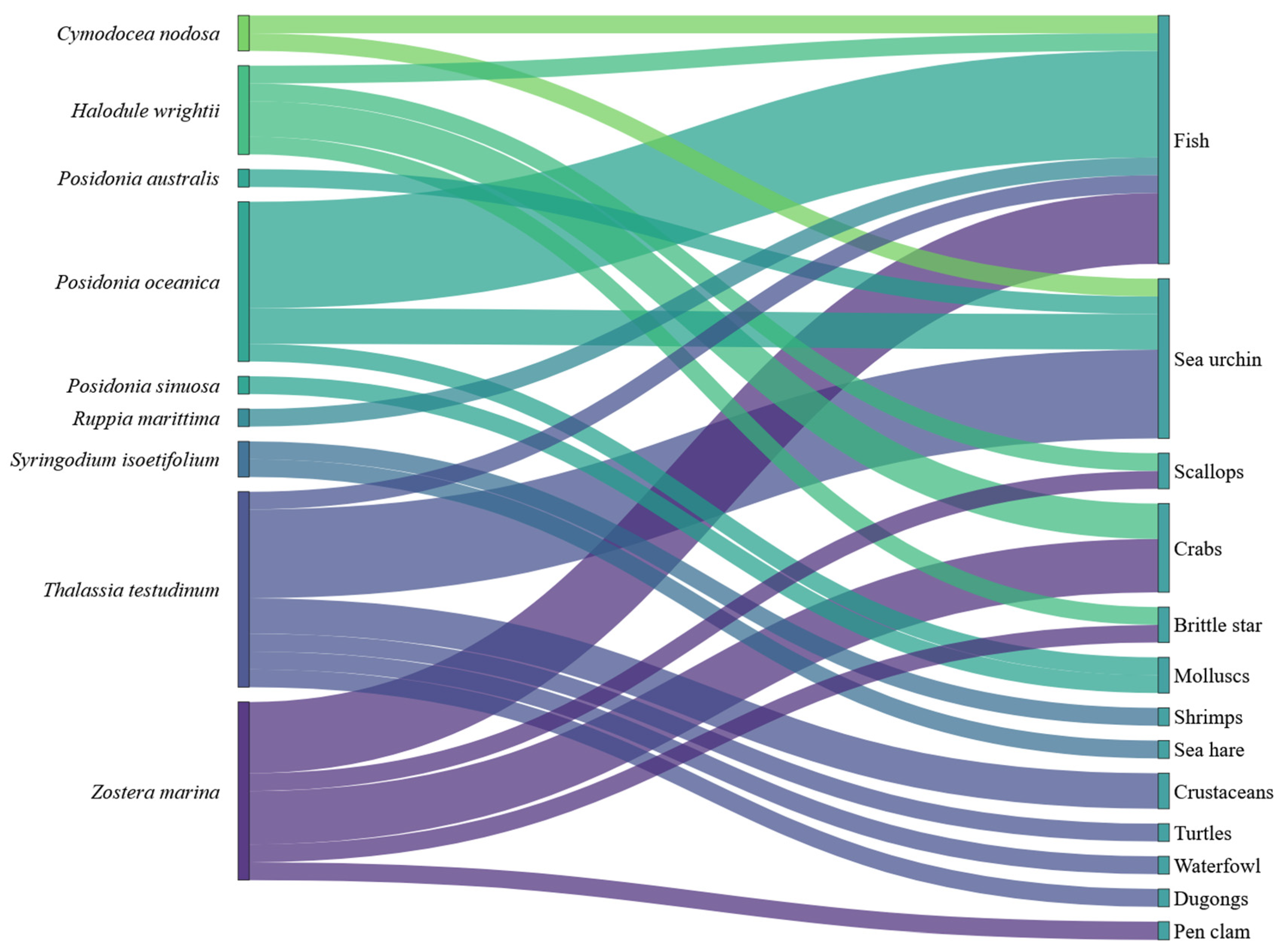
3.1. Seagrasses and Epiphytes–Epibionts Communities
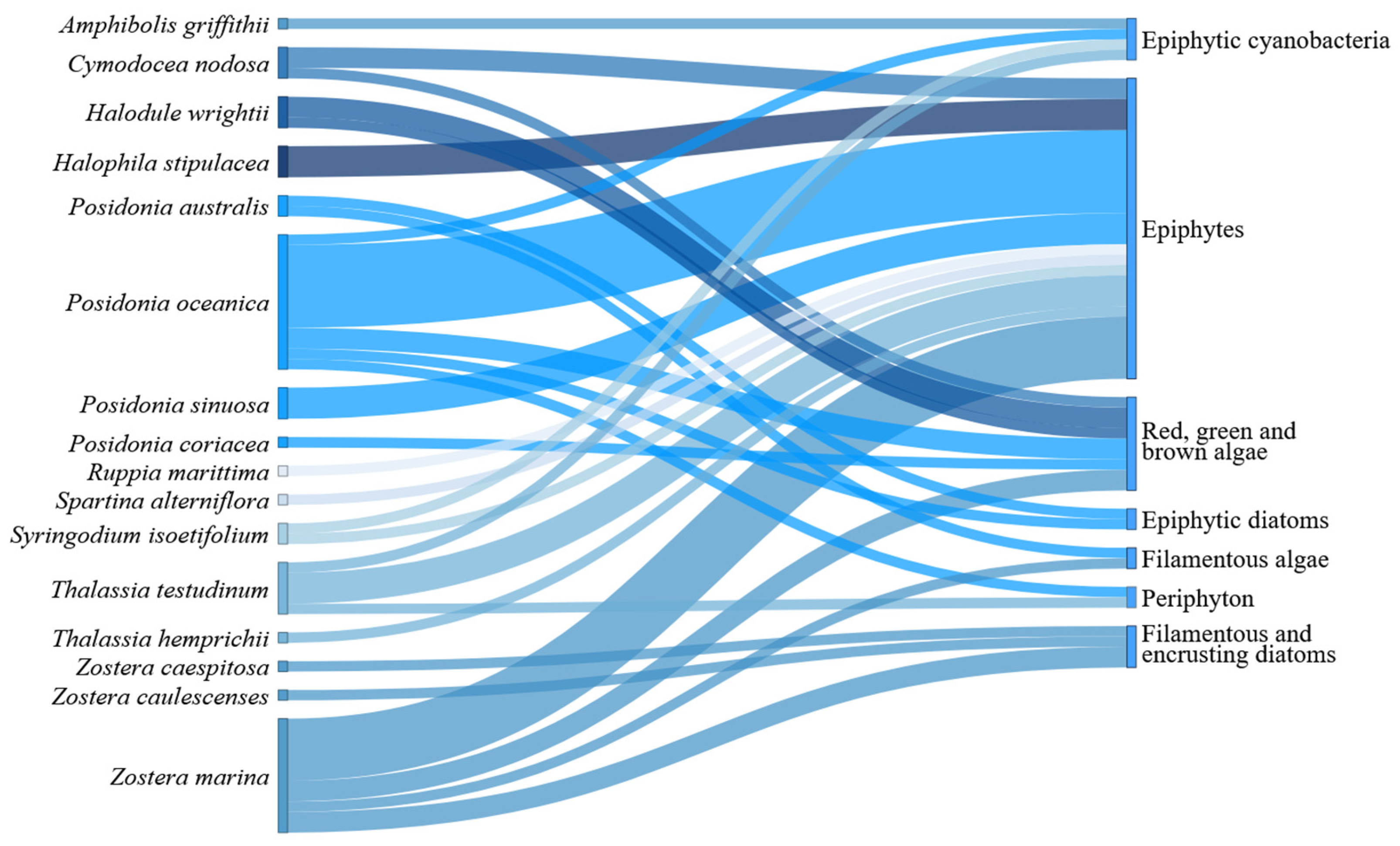
3.2. Detected Interactions
4. Discussion
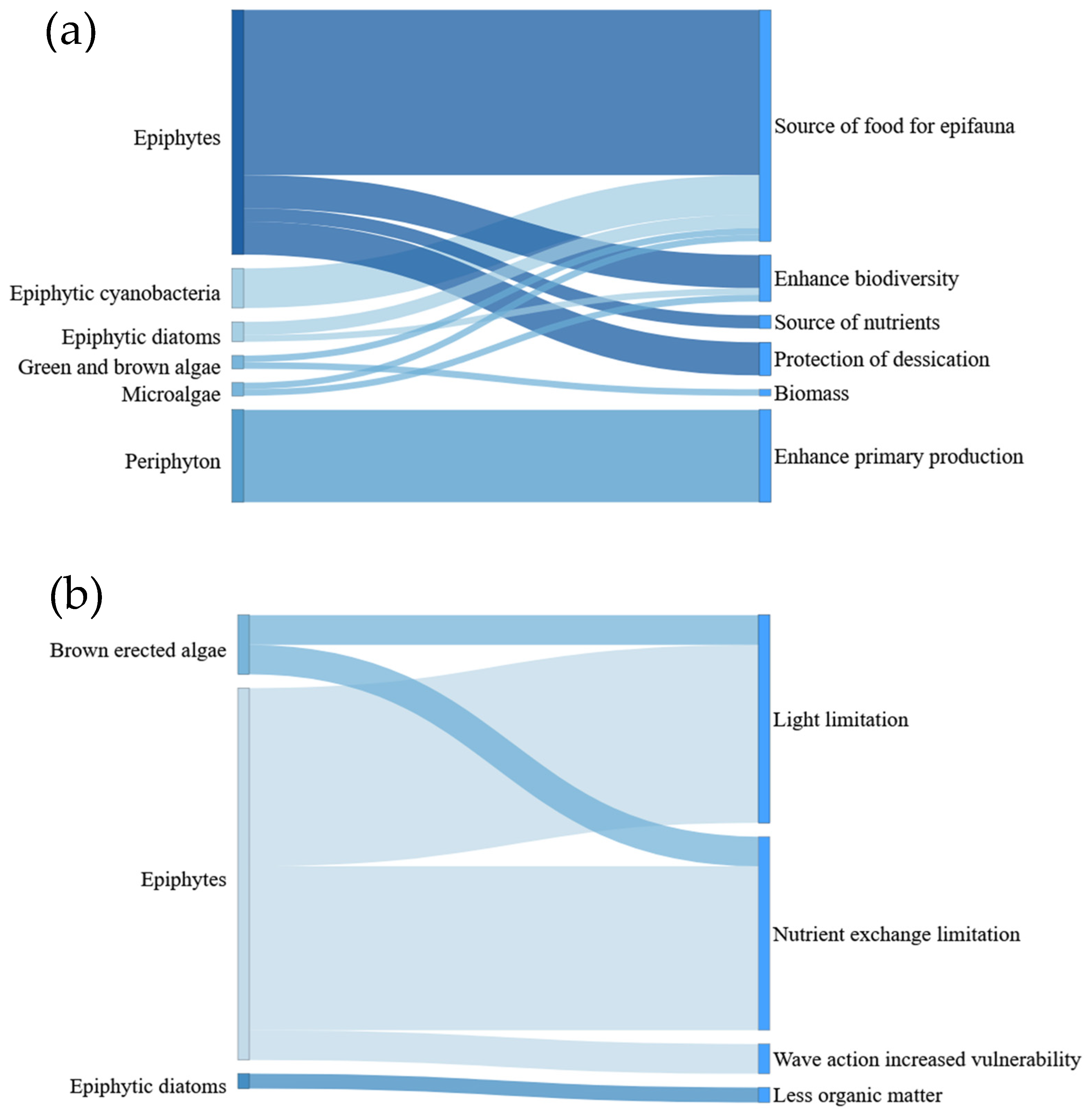
4.1. Seagrass-Epiphytes Interactions
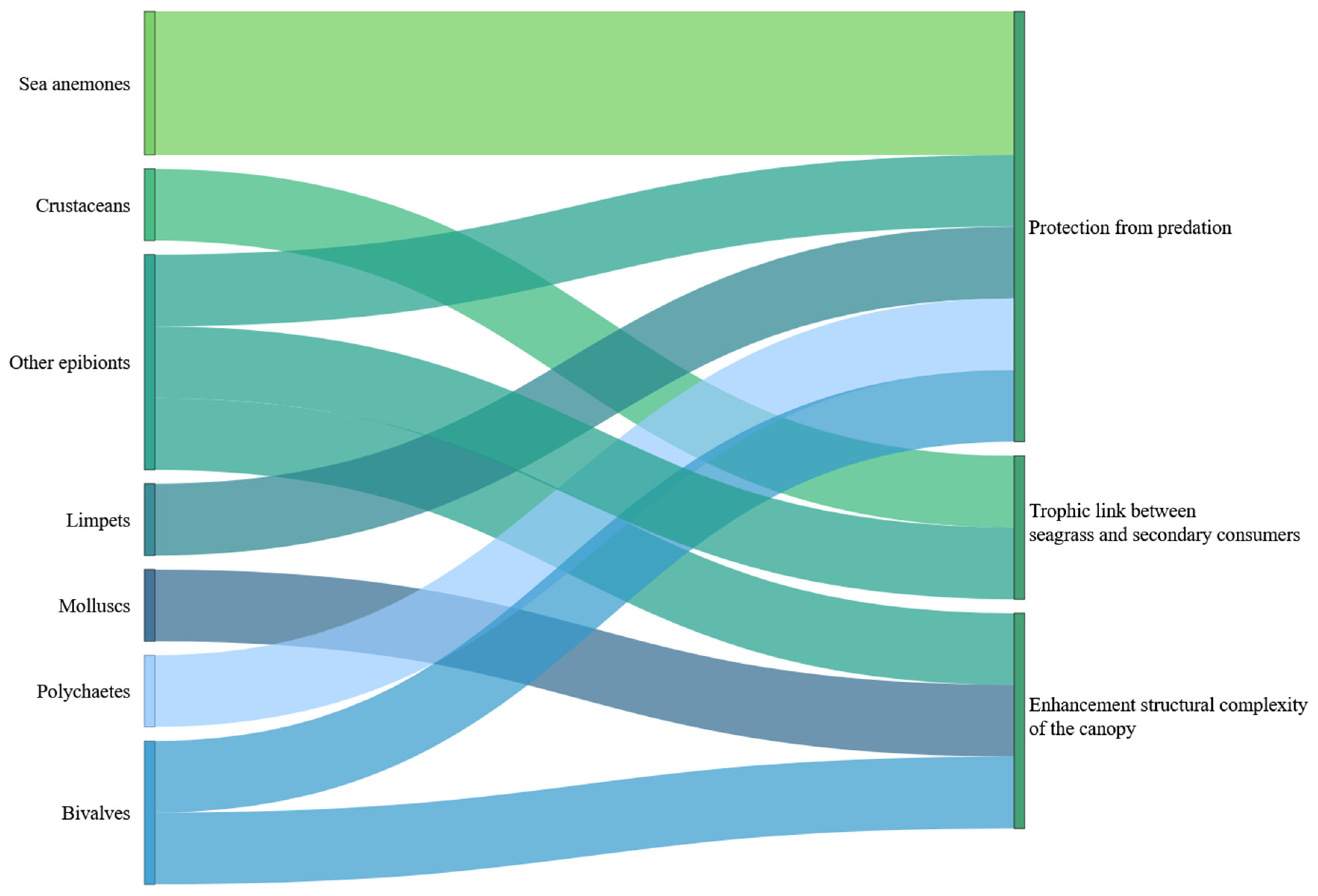
4.2. Seagrass–Epibionts Interactions
5. Gaps in Knowledge and Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M. Organisms as Ecosystem Engineers. Oikos 1994, 69, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelling-Wood, T.P.; Poore, A.G.B.; Hughes, A.R.; Everett, J.D.; Gribben, P.E. Habitat Traits and Predation Interact to Drive Abundance and Body Size Patterns in Associated Fauna. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teagle, H.; Hawkins, S.J.; Moore, P.J.; Smale, D.A. The Role of Kelp Species as Biogenic Habitat Formers in Coastal Marine Ecosystems. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2017, 492, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertness, M.D.; Gaines, S.D.; Hay, M.E.; Stachowicz, J.J.; Grosholz, E. Marine Community Ecology. In Marine Community Ecology; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001; Volume 47, p. 332. ISBN 10.2307/3069148. [Google Scholar]
- Klecka, J.; Boukal, D.S. The Effect of Habitat Structure on Prey Mortality Depends on Predator and Prey Microhabitat Use. Oecologia 2014, 176, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, G.Q.; Gonçalves-Souza, T.; Vieira, C.; Koricheva, J. Ecosystem Engineering Effects on Species Diversity across Ecosystems: A Meta-Analysis. Biol. Rev. 2015, 90, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.T.; Gribben, P.E. Disturbance-Mediated Facilitation by an Intertidal Ecosystem Engineer. Ecology 2017, 98, 2425–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, L.; Bourget, E. Influence of Substratum Heterogeneity Scales and Complexity on a Temperate Epibenthic Marine Community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 189, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J.F.; Boyer, K.E.; Duffy, J.E.; Lee, S.C.; Kertesz, J.S. Effects of Macroalgal Species Identity and Richness on Primary Production in Benthic Marine Communities. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Ramos, R.; Brun, F.G.; Vergara, J.J.; Hernández, I.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L.; Egea, L.G. Nutrient Enrichment and Herbivory Alter Carbon Balance in Temperate Seagrass Communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, T.M.; Borum, J.; Pedersen, O. Meristematic Oxygen Variability in Eelgrass (Zostera marina). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, A.M.; Ward, M.; Hill, T.M.; Sanford, E.; Kroeker, K.J.; Takeshita, Y.; Merolla, S.; Shukla, P.; Ninokawa, A.T.; Elsmore, K.; et al. Coast-Wide Evidence of Low PH Amelioration by Seagrass Ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2580–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodersen, K.E.; Kühl, M. Effects of Epiphytes on the Seagrass Phyllosphere. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 821614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Middelburg, J.J.; Caraco, N. Major Role of Marine Vegetation on the Oceanic Carbon Cycle. Biogeosciences 2005, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Duarte, C.M.; Kennedy, H.; Marbà, N.; Holmer, M.; Mateo, M.A.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Kendrick, G.A.; Krause-Jensen, D.; McGlathery, K.J.; et al. Seagrass Ecosystems as a Globally Significant Carbon Stock. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutar, L.; Espinosa, F.; Bazairi, H. Reconstruction of Cymodocea Nodosa’s Dynamivs as Tool to Examine the Conservation Status of a Mediterranean Declared Marine Proteced Area. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2021, 23, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, S.; Nakajima, K.; Hamasaki, K.; Shishidou, H.; Waples, R.S.; Kishino, H. Rigorous Monitoring of a Large-Scale Marine Stock Enhancement Program Demonstrates the Need for Comprehensive Management of Fisheries and Nursery Habitat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, M.E.; Woods, C.L. A Case for Studying Biotic Interactions in Epiphyte Ecology and Evolution. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2022, 54, 125658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Montfrans, J.; Wetzel, R.; Orth, R.J. Epiphytes-Grazer Relationships in Seagrass Meadows: Consequences for Seagrass Growth and Production. Estuaries 1984, 7, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.K.; Edgar, G.J.; Hutchings, P.A. Faunal Assemblages of Seagrasses Beds. In Biology of Seagrasses: A Treatise on the Biology of Seagrasses with Special Reference to the Australian Region; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 536–564. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, A.I.; Mann, K.H. Population Dynamics and Life History Adaptations of Littorina Neglecta Bean in an Eelgrass Meadow (Zostera marina L.) in Nova Scotia. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1982, 63, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, A.V.; Falkenberg, L.J. Seasonal Effects and Trophic Pressure Shape the Responses of Species Interactions in a Tropical Seagrass Meadow to Marine Heatwaves. Oikos 2024, 2024, e10382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Van Montfrans, J. Epiphyte—Segrass Relationships with an Emphasis on the Role of Micrograzing: A Review. Aquat. Bot. 1984, 18, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Dennison, W.C.; Duarte, C.M.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L.; Hughes, A.R.; Kendrick, G.A.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Olyarnik, S.; et al. A Global Crisis for Seagrass Ecosystems. Bioscience 2006, 56, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waycott, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Olyarnik, S.; Calladine, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L.; Hughes, A.R.; et al. Accelerating Loss of Seagrasses across the Globe Threatens Coastal Ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12377–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Edgar, G.J.; Fox, R.J. The Nature and Ecological Significance of Epifaunal Communities within Marine Ecosystems. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2021, 59, 585–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M. Seagrass Depth Limits. Aquat. Bot. 1991, 40, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, J.A.; Peterson, C.H. Marine Ecological Research in Seashore and Seafloor Systems: Accomplishments and Future Directions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 195, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Open Med. 2009, 3, e123–e130. [Google Scholar]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA Extension Statement for Reporting of Systematic Reviews Incorporating Network Meta-Analyses of Health Care Interventions: Checklist and Explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernakoff, P.; Brearley, A.; Nielsen, J. Factors Affecting Grazer-Epiphyte Interactions in Temperate Seagrass Meadows. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1996, 34, 109–162. [Google Scholar]
- Pinckney, J.L.; Micheli, F. Microalgae on Seagrass Mimics: Does Epiphyte Community Structure Differ from Live Seagrasses? J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1998, 221, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jephson, T.; Nyström, P.; Moksnes, P.O.; Baden, S.P. Trophic Interactions in Zostera marina Beds along the Swedish Coast. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 369, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarelli, K.; Chakrabarti, S.; Laas, P.; Stingl, U. The Seagrass Holobiont and Its Microbiome. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabrouk, L.; Ben Brahim, M.; Hamza, A.; Mahfoudhi, M.; Bradai, M.N. A Comparison of Abundance and Diversity of Epiphytic Microalgal Assemblages on the Leaves of the Seagrasses Posidonia oceanica (L.) and Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Asch in Eastern Tunisia. J. Mar. Biol. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, S.M.J. Similarity of Epiphyte Biomass Distribution on Posidonia and Artificial Seagrass Leaves. Aquat. Bot. 1987, 27, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpp, D.W.; Salita-Espinosa, J.T.; Fortes, M.D. Feeding Ecology and Trophic Role of Sea Urchins in a Tropical Seagrass Community. Aquat. Bot. 1993, 45, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael Martin-Smith, K. Abundance of Mobile Epifauna: The Role of Habitat Complexity and Predation by Fishes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1993, 174, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, L.; Ben Brahim, M.; Jebara, A.; Jribi, I. Comparison of Epiphyte Algal Assemblages on the Leaves of Marine Seagrasses Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile, Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Asch, and the Lessepsian Halophila stipulacea (Forssk.) Asch in Chebba (East of Tunisia). Mar. Ecol. 2021, 42, e12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, T.; Shin, H.W.; Spafford, D.; Michael, T.S.; Hanna, R.; Spafford, D.C. A Review of Epiphyte Community Development: Surface Interactions and Settlement on Seagrass. J. Environ. Biol. 2008, 29, 629–638. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamuro, M. Importance of Epiphytic Cyanobacteria as Food Sources for Heterotrophs in a Tropical Seagrass Bed. Coral Reefs 1999, 18, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaoka, M.; Toyohara, T.; Matsumasa, M. Seasonal and Between-Substrate Variation in Mobile Epifaunal Community in a Multispecific Seagrass Bed of Otsuchi Bay, Japan. Mar. Ecol. 2001, 22, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooker, R.M.; Feeney, W.E.; Sih, T.L.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; Chivers, D.P. Comparative Diversity of Anemone-Associated Fishes and Decapod Crustaceans in a Belizean Coral Reef and Seagrass System. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 2609–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Heck, K.L. Positive Interactions between Suspension-Feeding Bivalves and Seagrass—A Facultative Mutualism. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 213, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Gladstone, S.; Ng, W.-K.; Zhang, J.; Shao, Q. Effects of Isoenergetic Diets with Varying Protein and Lipid Levels on the Growth, Feed Utilization, Metabolic Enzymes Activities, Antioxidative Status and Serum Biochemical Parameters of Black Sea Bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii). Aquaculture 2019, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.L.; Valentine, J.F. Plant-Herbivore Interactions in Seagrass Meadows. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 330, 420–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, A.M.; Micheli, C. Ecological Function of Phenolic Compounds from Mediterranean Fucoid Algae and Seagrasses: An Overview on the Genus Cystoseira Sensu Lato and Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, J.E.; Attrill, M.J.; Shaw, S.M.; Rowden, A.A. Spatial Variability in the Epiphytic Algal Assemblages of Zostera marina Seagrass Beds. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 249, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.P.; Edwards, M.; Bunker, F.; Maggs, C.A. Algal Epiphytes of Zostera marina: Variation in Assemblage Structure from Individual Leaves to Regional Scale. Aquat. Bot. 2005, 82, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderklift, M.A.; Lavery, P.S. Patchiness in Assemblages of Epiphytic Macroalgae on Posidonia Coriacea at a Hierarchy of Spatial Scales. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 192, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, L.A.; Dobbs, F.C.; Zimmerman, R.C. Effects of Epiphyte Load on Optical Properties and Photosynthetic Potential of the Seagrasses Thalassia testudinum Banks Ex König and Zostera marina L. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Armitage, A.R.; Fourqurean, J.W. Nutrient Impacts on Epifaunal Density and Species Composition in a Subtropical Seagrass Bed. Hydrobiologia 2006, 569, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, P.; Alcoverro, T.; Martínez-Crego, B.; Vergés, A.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J. Macrograzers Strongly Influence Patterns of Epiphytic Assemblages in Seagrass Meadows. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 350, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, P.S.; Reid, T.; Hyndes, G.A.; Elven, B.R.V. Effect of Leaf Movement on Epiphytic Algal biomass of Seagrass Leaves. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 338, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, G.A.; Burt, J.S. Seasonal Changes in Epiphytic Macro-Algae Assemblages Between Offshore Exposed and Inshore Protected Posidonia sinuosa Cambridge et Kuo Seagrass Meadows, Western Australia. Bot. Mar. 1997, 40, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrián, J.; Enríquez, S.; Fortes, M.; Agawin, N.; Vermaat, J.E.; Duarte, C.M. Epiphyte Accrual on Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile Leaves: Implications for Light Absorption. Bot. Mar. 1999, 42, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, J.M.; Lai, S.; Yaakub, S.M.; Ow, Y.X.; Todd, P.A. The Diet and Feeding Rates of Gastropod Grazers in Singapore’s Seagrass Meadows. Bot. Mar. 2018, 61, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindi, F.; Maltagliati, F.; Rossi, F.; Acunto, S.; Cinelli, F. Algal Flora Associated with a Halophila stipulacea (Forssksl) Ascherson (Hydrocharitaceae, Helobiae) Stand in the Western Mediterranean. Oceanol. Acta 1999, 22, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.R.; Paula, C.A.; Leite, F.P.P.; Costa, T.M.; Machado, G.B.O. The Role of Food Value on Host Use by the Herbivorous Amphipod Sunamphitoe Pelagica. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2024, 574, 152007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchette, B.W.; Burkholder, J.M. Review of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Metabolism in Seagrasses. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 250, 133–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Obando, S.E.; Heck, K.L.; Spitzer, P.M. Effects of Simultaneous Changes in Light, Nutrients, and Herbivory Levels, on the Structure and Function of a Subtropical Turtlegrass Meadow. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 301, 193–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, F.D. Ecology of Ruppia maritima, L. in New Hampshire (U.S.A.) Tidal Marshes. Rhodora 1980, 82, 403–439. [Google Scholar]
- Penhale, P.A.; Smith, J.R. Excretion of Dissolved Organic Carbon by Eelgrass (Zostera) and Its Epiphytes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trocine, R.P.; Rice, J.D.; Wells, G.N. Inhibition of Seagrass Photosynthesis by Ultraviolet B. Plant Physiol. 1981, 68, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, M.; Goecke, F.; Labes, A.; Dobretsov, S.; Weinberger, F. The Second Skin: Ecological Role of Epibiotic Biofilms on Marine Organisms. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.L. Seagrass Ecosystems: A Careerlong Quest to Understand Their Inner Workings. Gulf Caribb. Res. 2019, 30, II. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovel, K.A.; Warneke, A.M.; Virtue-Hilborn, S.P.; Sanchez, A.E. Mesopredator Foraging Success in Eelgrass (Zostera marina L.): Relative Effects of Epiphytes, Shoot Density, and Prey Abundance. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 474, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.W.; Lee, Y.; Wu, R.S.S. The Effects of Epiphytic Algae and Their Grazers on the Intertidal Seagrass Zostera japonica. Aquat. Bot. 2000, 67, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, S.R.; Zhang, Y.S.; van der Heide, T.; Vanderklift, M.A.; Tarquinio, F.; Orth, R.J.; Silliman, B.R. Positive Ecological Interactions and the Success of Seagrass Restoration. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitzka, M.A.; Lavery, P.S.; Van Keulen, M. Epiphytes of Seagrasses. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 441–461. ISBN 140202942X. [Google Scholar]
- Borum, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Greve, T.M. European Seagrasses: An Introduction to Monitoring and Management; Monitoring and Managing of European Seagrasses [EU Project]; The M&M Project: Cumbria, UK, 2004; ISBN 8789143213. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo, E.; Lozano, P.; Blasco, J.; Moreno-Garrido, I. Epiphyte Toxicity Bioassay for Ecotoxicological and Coastal Monitoring. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 4647–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.B.; Hollingworth, C.E. Leaf Epifauna of the Seagrass Thalassia testudinum. Mar. Biol. 1982, 71, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coull, B.C.; Bell, S.S. Perspectives of Marine Meiofaunal Ecology. In Ecological Processes in Coastal and Marine Systems; Livingston, R.J., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1979; Volume 10, pp. 189–216. [Google Scholar]
- Guilini, K.; Weber, M.; De Beer, D.; Schneider, M.; Molari, M.; Lott, C.; Bodnar, W.; Mascart, T.; De Troch, M.; Vanreusel, A. Response of Posidonia Oceanica Seagrass and Its Epibiont Communities to Ocean Acidification. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombara, A.M.; Quinn, D.; Chadwick, N.E. Habitat Segregation and Population Structure of Caribbean Sea Anemones and Associated Crustaceans on Coral Reefs at Akumal Bay, Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2017, 93, 1025–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.K.; McVay, M.J.; Chadwick, N.E. Demographic Modelling of Giant Sea Anemones: Population and Effects of Mutualistic Anemonefish in the Jordanian Red Sea. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 68, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titus, B.M.; Daly, M.; Macrander, J.; Del Rio, A.; Santos, S.R.; Chadwick, N.E. Contrasting abundance and Contribution of Clonal Proliferation to the Population Structure of the Corkscrew Sea Anemone Bartholomea annulata in the Tropical Western Atlantic. Invertebr. Biol. 2017, 136, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, N.E.; Ďuriš, Z.; Horkà, I. Biodiversity and Behavior of Shrimps and Fishes Symbiotic with sea Anemones in the Gulf of Aqaba, Northern Red Sea. In The Improbable Gulf: History, Biodiversity, and Protection of the Gulf of Aqaba (Eilat); Magnes Press: Jerusalem, Israel, 2008; pp. 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Briones-Fourzán, P.; Pérez-Ortiz, M.; Negrete-Soto, F.; Barradas-Ortiz, C.; Lozano-Álvarez, E. Ecological Traits of Caribbean Sea Anemones and Symbiotic Crustaceans. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 470, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, W.E.; Brooker, R.M.; Johnston, L.N.; Gilbert, J.D.J.; Besson, M.; Lecchini, D.; Dixson, D.L.; Cowman, P.F.; Manica, A. Predation Drives Recurrent Convergence of an Interspecies Mutualism. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dame, R.F.; Wolaver, T.G.; Libes, S.M. The Summer Uptake and Release of Nitrogen by an Intertidal Oyster Reef. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1985, 19, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, E.; Montefalcone, M.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N.; Albertelli, G. Early Warning Response of Posidonia oceanica Epiphyte Community to Environmental Alterations (Ligurian Sea, NW Mediterranean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Balata, D.; Ceccherelli, G. Epiphyte Assemblages of the Mediterranean Seagrass Posidonia Oceanica: An Overview. Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marsiglia, N.; Bosch-Belmar, M.; Mancuso, F.P.; Sarà, G. Epibionts and Epiphytes in Seagrass Habitats: A Global Analysis of Their Ecological Roles. Sci 2025, 7, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7020062
Marsiglia N, Bosch-Belmar M, Mancuso FP, Sarà G. Epibionts and Epiphytes in Seagrass Habitats: A Global Analysis of Their Ecological Roles. Sci. 2025; 7(2):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7020062
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarsiglia, Nicoletta, Mar Bosch-Belmar, Francesco Paolo Mancuso, and Gianluca Sarà. 2025. "Epibionts and Epiphytes in Seagrass Habitats: A Global Analysis of Their Ecological Roles" Sci 7, no. 2: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7020062
APA StyleMarsiglia, N., Bosch-Belmar, M., Mancuso, F. P., & Sarà, G. (2025). Epibionts and Epiphytes in Seagrass Habitats: A Global Analysis of Their Ecological Roles. Sci, 7(2), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci7020062







