Portable XRF Quick-Scan Mapping for Potential Toxic Elements Pollutants in Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems: A Methodological Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Portable XRF (pXRF)
2.2. Instrument Description
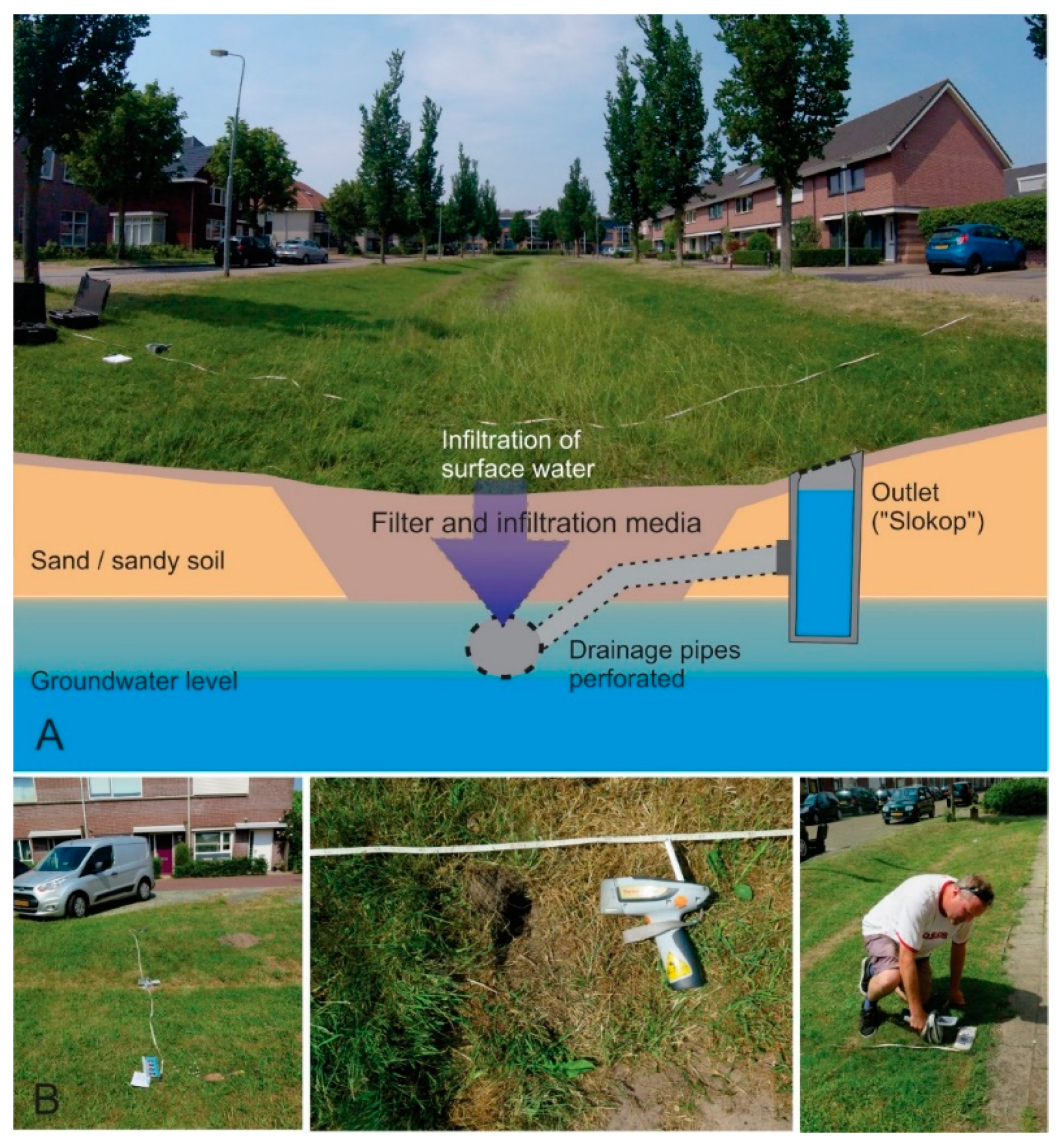
2.3. In Situ Measurements with Portable XRF
2.4. Soil Sampling for Quality Control
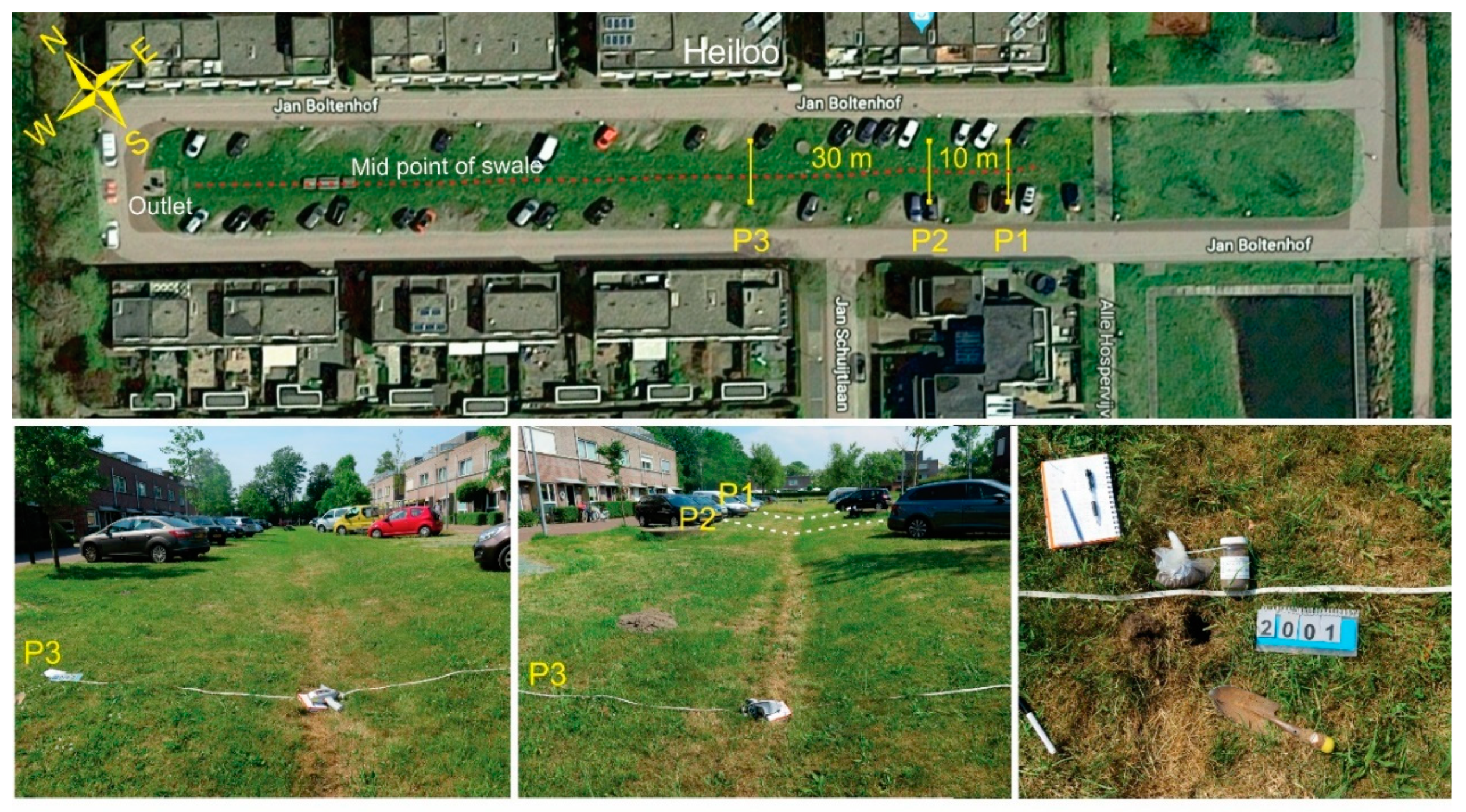
2.5. Data Collection at Locations
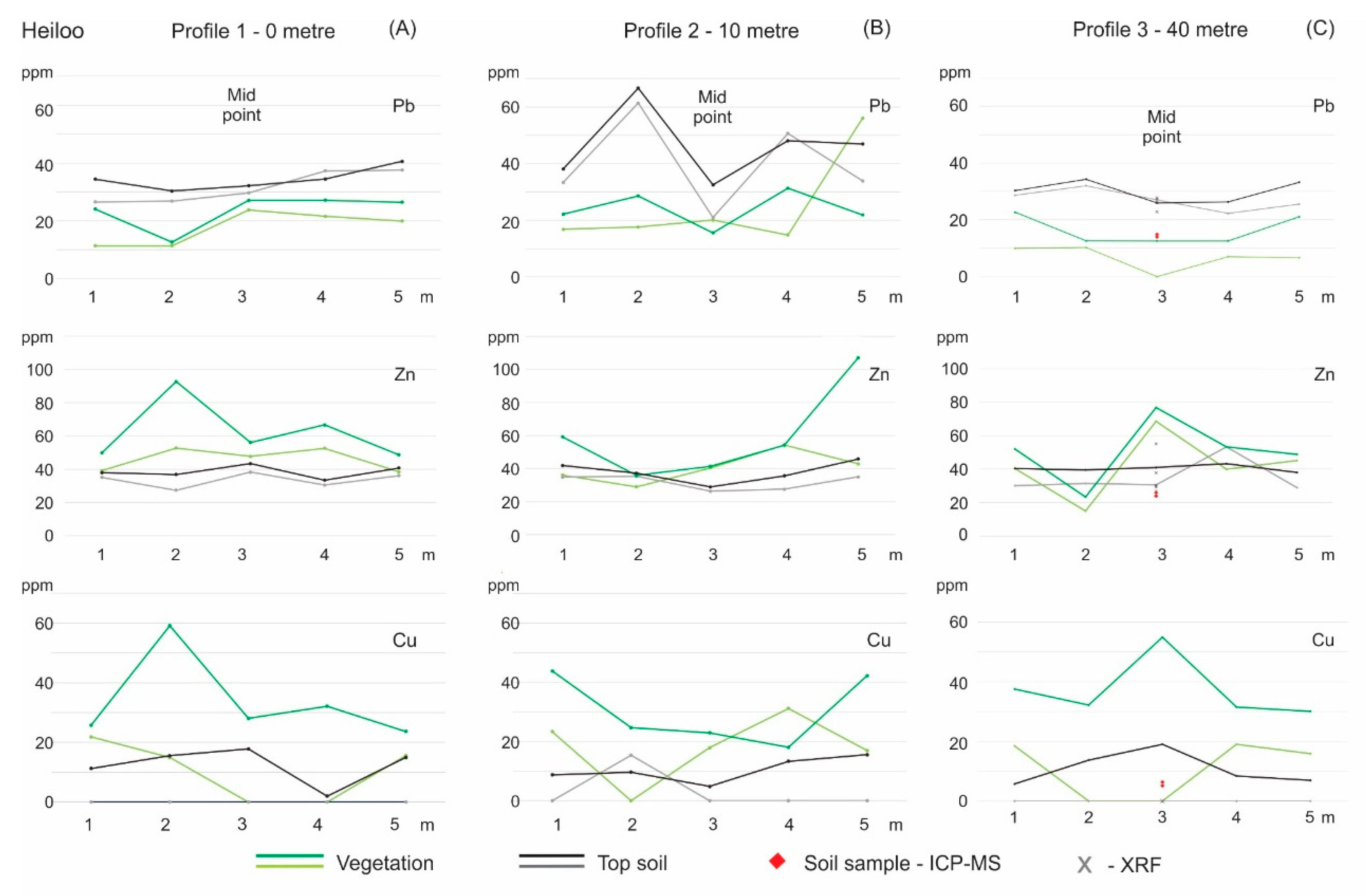
2.5.1. Heiloo
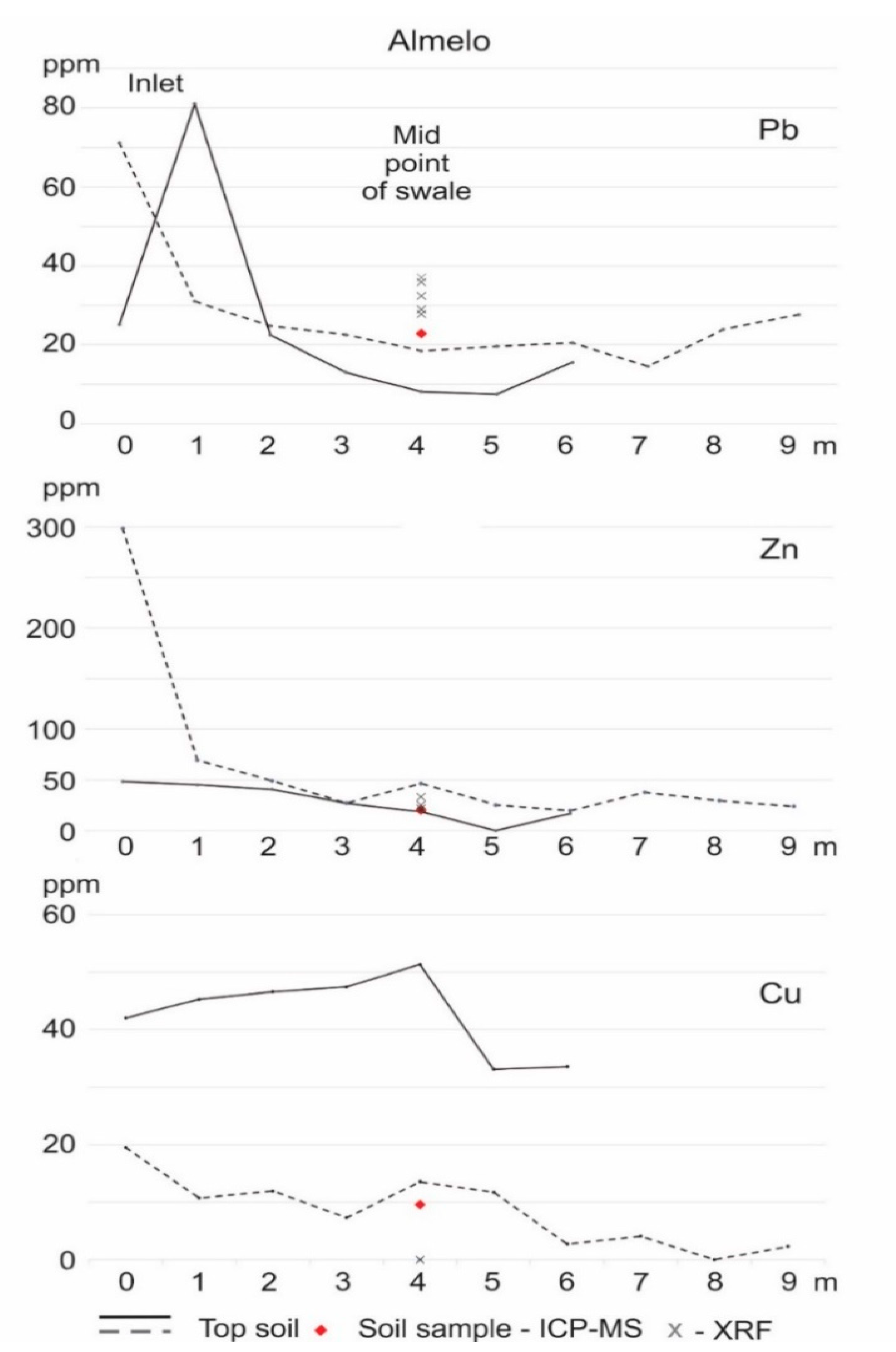
2.5.2. Almelo
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results Heiloo
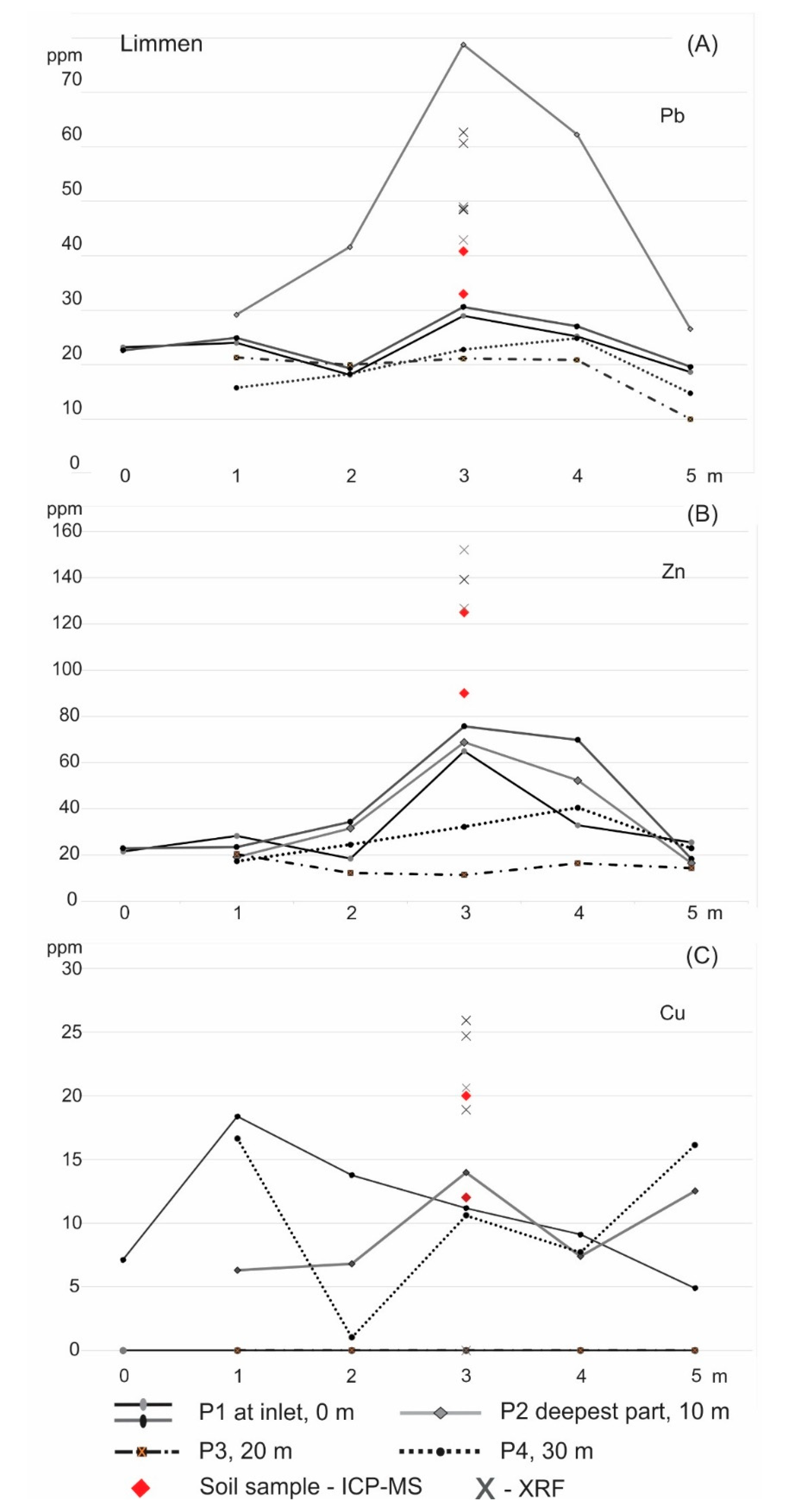
3.2. Results Limmen
3.3. Results Almelo
3.4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tu, M.-C.; Smith, P. Modelling pollutant buildup and washoff parameters for SWMM based on land use in a semiarid urban watershed. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods Ballard, B.; Wilson, S.; Udale-Clarke, H.; Illman, S.; Scott, T.; Ashely, R.; Kellagher, R. CIRIA—The SuDS Manual; CIRIA Research Project (RP); Department for Environment Food & Rural Affairs; Construction Industry Research and Information Association (CIRIA), Griffin Court: London, UK, 2015; p. 992. ISBN 978–0-86017–760–9. Available online: https://www.ciria.org/Memberships/The_SuDs_Manual_C753_Chapters.aspx (accessed on 15 April 2018).
- Fletcher, T.D.; Shuster, W.; Hunt, W.F.; Ashley, R.; Butler, D.; Arthur, S.; Trowsdale, S.; Barraud, S.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; et al. SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and more—The evolution and application of terminology surrounding urban drainage. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Andrieu, H.; Hamel, P. Understanding, management and modelling of urban hydrology and its consequences for receiving waters: A state of the art. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogaard, F.C.; van de Ven, F.; Langeveld, J.; van de Giesen, N. Stormwater Quality Characteristics in (Dutch) Urban Areas and Performance of Settlement Basins. Challenges 2014, 5, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Field, C.B., Barros, V.R., Dokken, D.J., Mach, K.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Bilir, T.E., Chatterjee, M., Ebi, K.L., Estrada, Y.O., Genova, R.C., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Haughton, G.; Hunter, C. Sustainable Cities; Jessica Kingsley Publishers Ltd.: London, UK, 1994; pp. 1–357. [Google Scholar]
- Tedoldi, D.; Ghassan, C.; Pierlot, D.; Kovacs, Y.; Gromarie, M.-C. Impact of runoff infiltration on contaminat accumulation and transport in the soil/filter media of Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems: A literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 904–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedoldi, D.; Ghassan, C.; Pierlot, D.; Branchu, P.; Kovacs, Y.; Gromarie, M.-C. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in the surface soil of source-control stormwater infiltration devices—Inter-site comparison. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.S.; Davis, A.P. Spatial accumulation and strength of affiliation of heavy metals in bioretention media. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnicky, D.J.; Singhvi, R. Field portable XRF analysis of environmental samples. J. Hazard Mater. 2001, 83, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, K.; Deatrick, J.; Johnson, H. Field X-ray Fluorescence Measuring. SESD Operating Procedure SESDPROC-107-R3; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015.
- Adams, G.; Keefer, D.; Turner, N.; Hill, F.E. Superfund X-Ray Fluoresence Field Operation Guide. SFDGUID-001-R0; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017.
- Lemière, B. A Review of pXRF (Field Portable X-ray Fluorescence) Applications for Applied Geochemistry. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 188, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, M.H.; Boon, K.A. Can in situ geochemical measurements be more fit-for-purpose than those made ex situ? Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Soro, L.; Le Guern, C.; Bechet, B.; Lebeau, T.; Ringeard, M.F. Origin of trace elements in an urban garden in Nantes, France. J. Soils Sediments 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogaard, F.C.; Venvik, G. National mapping of long-term pollution in Dutch swales using a new XRF quick scan method. unpublished; manuscript in preparation.
- Boogaard, F.C. Research on Long Term Soil Continanation in Swales (in Dutch: Bodemvervuiling in Wadis Onderzocht Met Nieuwe Methode). H20 Magazine, 14. May 2019. Available online: https://www.h2owaternetwerk.nl/vakartikelen/bodemvervuiling-in-wadi-s-onderzocht-met-nieuwe-methode (accessed on 20 May 2019).
- Boogaard, F.C.; Olsson, J.; Muthanna, T.M.; Heikoop, R.; Venvik, G. International knowledge exchange on climate adaptation with the Climatescan platform (8857). In Proceedings of the 4th European Climate Change Adaptation conference ECCA, Lisbon, Portugal, 28–31 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- NMHSPE 2000 Circular on Target Values and Intervention Values for Soil Remediation. The Netherlands Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and the Environment, Amsterdam. 2000. Available online: https://www.esdat.net/Environmental%20Standards/Dutch/annexS_I2000Dutch%20Environmental%20Standards.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2018).
- Goldschmidt, V.M. The principles of distribution of chemical elements in minerals and rocks. J. Chem. Soc. 1937, 655–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, S.; Nagarkar, V.; Squillante, M.R. Quantitative Measurement of Lead in Paint by XRF analysis Without Manual Substrate Correction. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1997, 48, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernick, M.B.; Kalnicky, D.J.; Prince, G.; Singhvi, R. Results of field-portable X-ray flourescence analysis of metal contaminations in soil and sediments. J. Hazard Mater. 1995, 43, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernick, M.B.; Getty, D.; Prince, G.; Sprenger, M. Statistical evaluation of field-portable X-ray flourescence soil preparation methods. J. Hazard Mater. 1995, 43, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallard, M.O.; Apriz, S.E.; Dooley, C.A. X-Ray Flourescence Spectromerty for Field Analysis of Metals in Marine Sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, T.; Diamond, D. Comparison of soil pollution concentrations determined using AAS and portable XRF techniques. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 171, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincheval, M.; Cohen, D.R.; Hemmings, F.A. Biogeochemical mapping of metal contamination from mine tailing using field-portable XRF. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Poon, H.; Taylor, A.; Brown, M.T. In situ determination of trace elements in Fucus spp. By field-portable-XRF. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593–594, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ThermoFisher. Available online: https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/CAD/posters/CAD-Niton-Periodictable-fxl.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2018).
- ThermoFisher. Available online: www.thermofisher.com (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Mineral Laboratories, Bureau Veritas Commodities Canada Ltd. Available online: https://www.bureauveritas.com/um (accessed on 7 March 2018).
- AGROLABS Group. AL-West B.V. Available online: https://www.agrolab.com/nl (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Demetriades, A.; Birke, M. Urban Topsoil Geochemical in situ Mapping Manual (URGEII). EuroGeoSurveys, Brussels, 2015, pp. 1–52. Available online: http://www.eurogeosurveys.org/wp-content/upload/2015/06/FGS_Uran_Topsoil_Geochemical_Mapping_Manual_URGE_II_HR_version.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2018).
- Flem, B.; Eggen, O.A.; Torgersen, E.; Kongsvik, M.K.; Ottesen, R.T. Urban geochemistry in Kristiansand, Norway. JGE 2018, 187, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimdahl, R.L. Entry and Movement in Vegetation of Lead Derived from Air and Soil Sources. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 2012, 26, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingvertsen, S.T.; Cederkvist, K.; Régent, Y.; Sommer, H.; Magid, J.; Jensen, M.B. Assessment of exsisting Roadside Swales with Engineered Filter Soil: 1. Characterization and Lifetime Expectancy. JEQ 2011, 41, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, A.; Brown, M.; Turner, A. Novel use of field-portable-XRF for the direct analysis of trace elements in marine macroalgae. Environ. Poll. 2017, 220, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.; Solman, K.R. Analysis of the elemental composition of marine litter by field-protable-XRF. Talanta 2016, 159, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Chan, C.C.; Brown, M.T. Application of field-portable-XRF for the determination of trace elements in deciduous leaves from a mine-impacted region. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemière, B.; Laperche, V.; Haouche, L.; Auger, P. Portable XRF and wet materials: Application to dredged contaminated sediments from waterways. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2014, 14, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC). Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/water/water-framework/index_en.html (accessed on 10 May 2018).
- Boogaard, F.C.; Blanksby, J.; de Jong, J.; van de Ven, F.H.M. Optimizing SUDS by transnational knowledge exchange—Guidelines for the design & construction and operation. In Proceedings of the Conference proceeding NOVATECH 2010 - 7th International Conference on Sustainable Techniques and Strategies for Urban Water Management, Lyon, France, 28 June–1 July 2010. [Google Scholar]



| Metals | National Background Concentration ppm (mg/kg) | Target Value ppm (mg/kg) | Intervention Value ppm (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead (Pb) | 85 | 85 | 530 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 140 | 140 | 720 |
| Copper (Cu) | 36 | 36 | 190 |
| Metals | Portable XRF ppm (mg/kg) (ThermoFisher) | ICP-MS ppm (mg/kg) (Mineral Laboratories) | ICP-MS ppm (mg/kg) (Mineral Laboratories) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead (Pb) | 1 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Copper (Cu) | 5 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Location (Municipality/Street) | Heiloo Jan Boltenhof | Limmen Zonnendauw | Almelo Ter Kleef |
|---|---|---|---|
| Areal use | Residential | Residential | Residential |
| Year of construction | 1999 | Approximately 2000 | 2002 |
| Estimated storage [volume m3/connected area m2] | 20 mm | 15 mm | 10 mm |
| Type of infiltration test | Observation * | Observation * | Long term monitoring (loggers) |
| Infiltration rate (m/day) | >0.3 m/day * | >0.3 m/day * | 0.15–0.49 m/day |
| Soil type | Sandy soil | Clay/organic soil | Sandy soil |
| More information | https://climatescan.org/projects/135/detail | https://climatescan.org/projects/3/detail | https://climatescan.org/projects/941/detail |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venvik, G.; Boogaard, F.C. Portable XRF Quick-Scan Mapping for Potential Toxic Elements Pollutants in Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems: A Methodological Approach. Sci 2020, 2, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci2030064
Venvik G, Boogaard FC. Portable XRF Quick-Scan Mapping for Potential Toxic Elements Pollutants in Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems: A Methodological Approach. Sci. 2020; 2(3):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci2030064
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenvik, Guri, and Floris C. Boogaard. 2020. "Portable XRF Quick-Scan Mapping for Potential Toxic Elements Pollutants in Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems: A Methodological Approach" Sci 2, no. 3: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci2030064
APA StyleVenvik, G., & Boogaard, F. C. (2020). Portable XRF Quick-Scan Mapping for Potential Toxic Elements Pollutants in Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems: A Methodological Approach. Sci, 2(3), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci2030064






